The Integrated Effects of Brivaracetam, a Selective Analog of Levetiracetam, on Ionic Currents and Neuronal Excitability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Drugs, and Solutions Used in This Study
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Electrophysiological Measurements
2.4. Data Recordings
2.5. Data Analyses
2.6. Single-Channel Analyses
2.7. Simulation Modeling
2.8. Animal Experiments
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
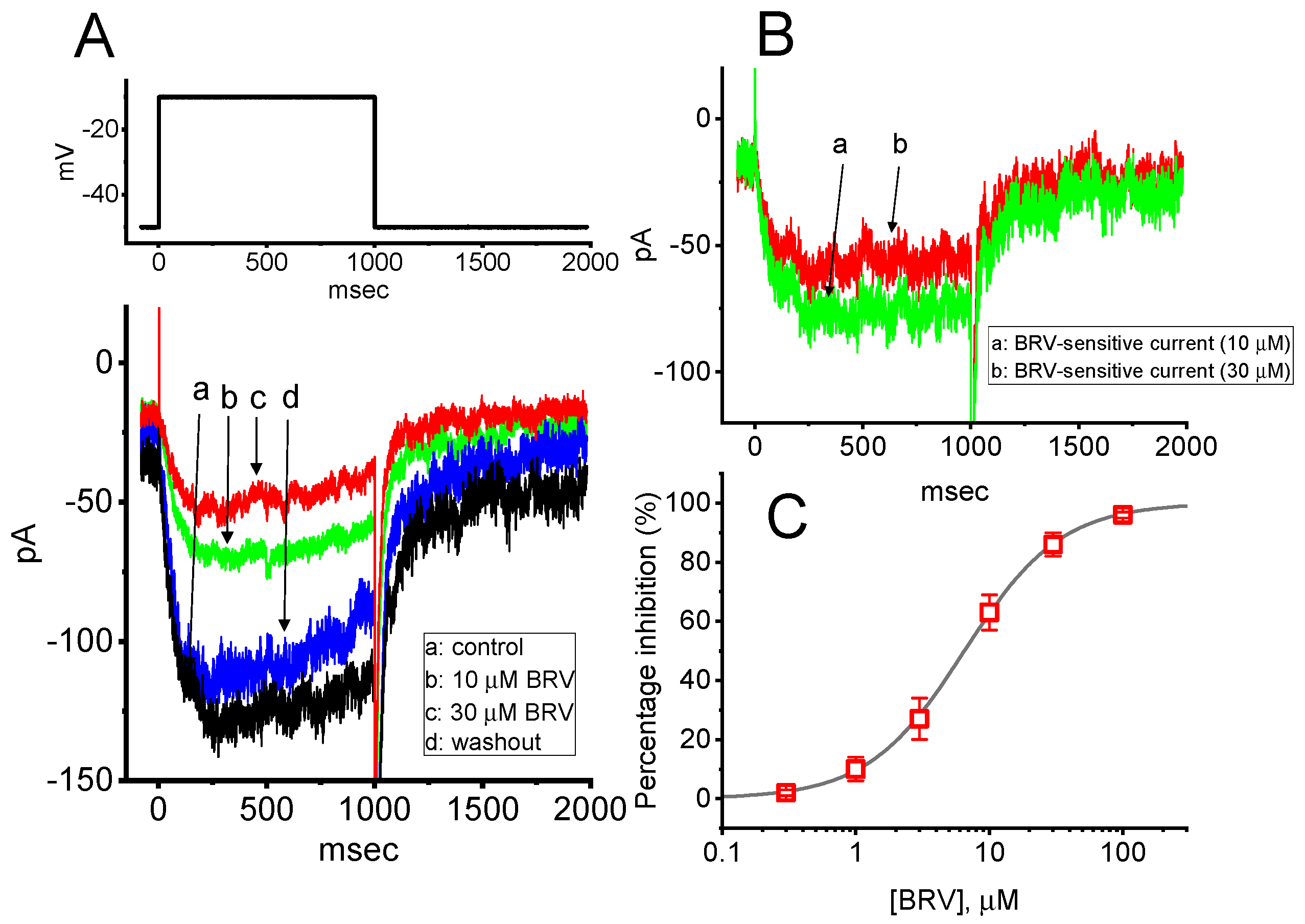
3.1. Inhibitory Effect of BRV on the Amplitude of M-Type K+ Current (IK(M))
3.2. Mild Inhibition of BRV on Delayed-Rectifier K+ Current (IK(DR))
3.3. Mild Inhibitory Effect on Hyperpolarization-Activated Cation Current (Ih) Caused by BRV
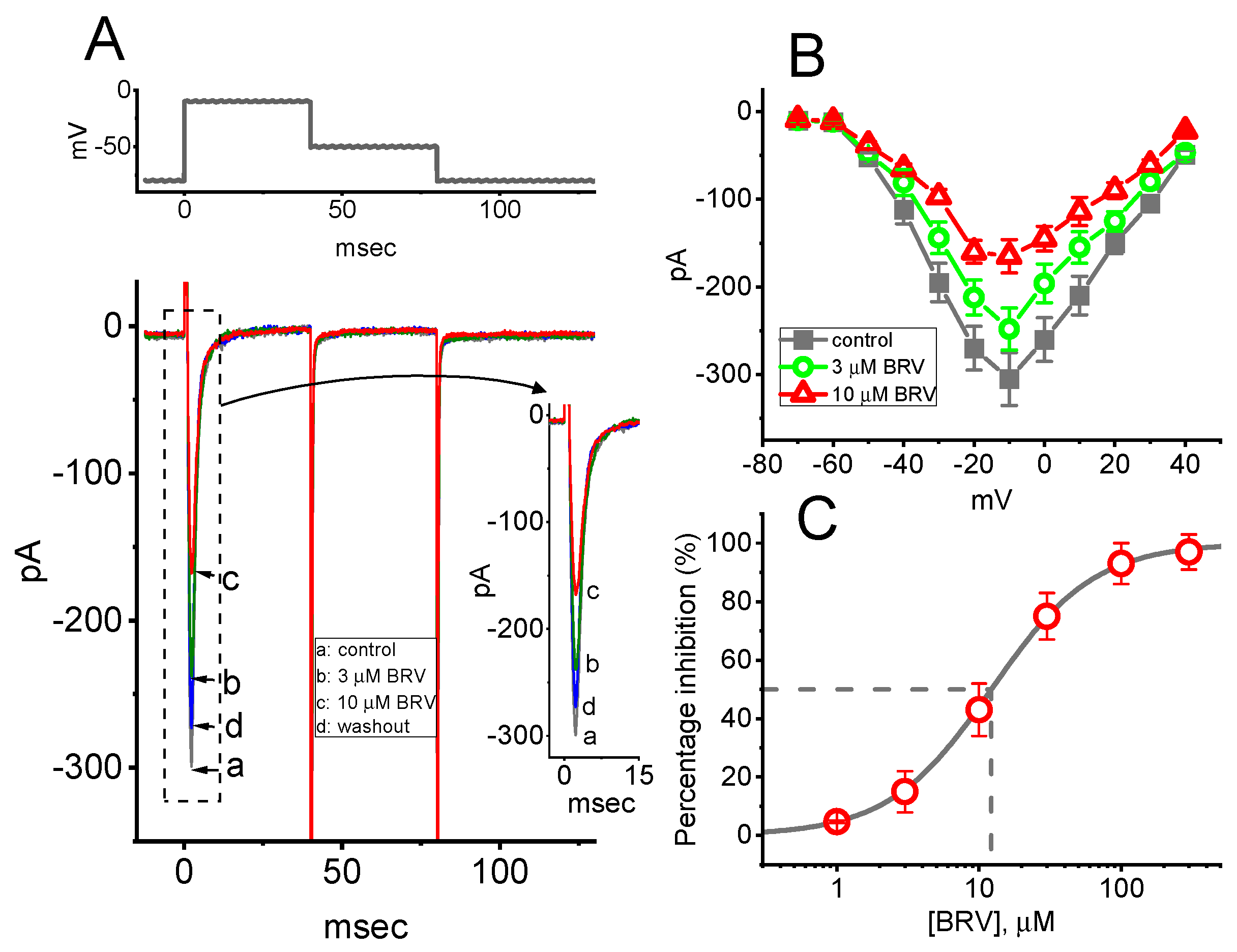
3.4. Effect of BRV on Voltage-Gated Na+ Current (INa)
3.5. Steady-State Inactivation Curve of Peak INa Taken with or without Addition of BRV
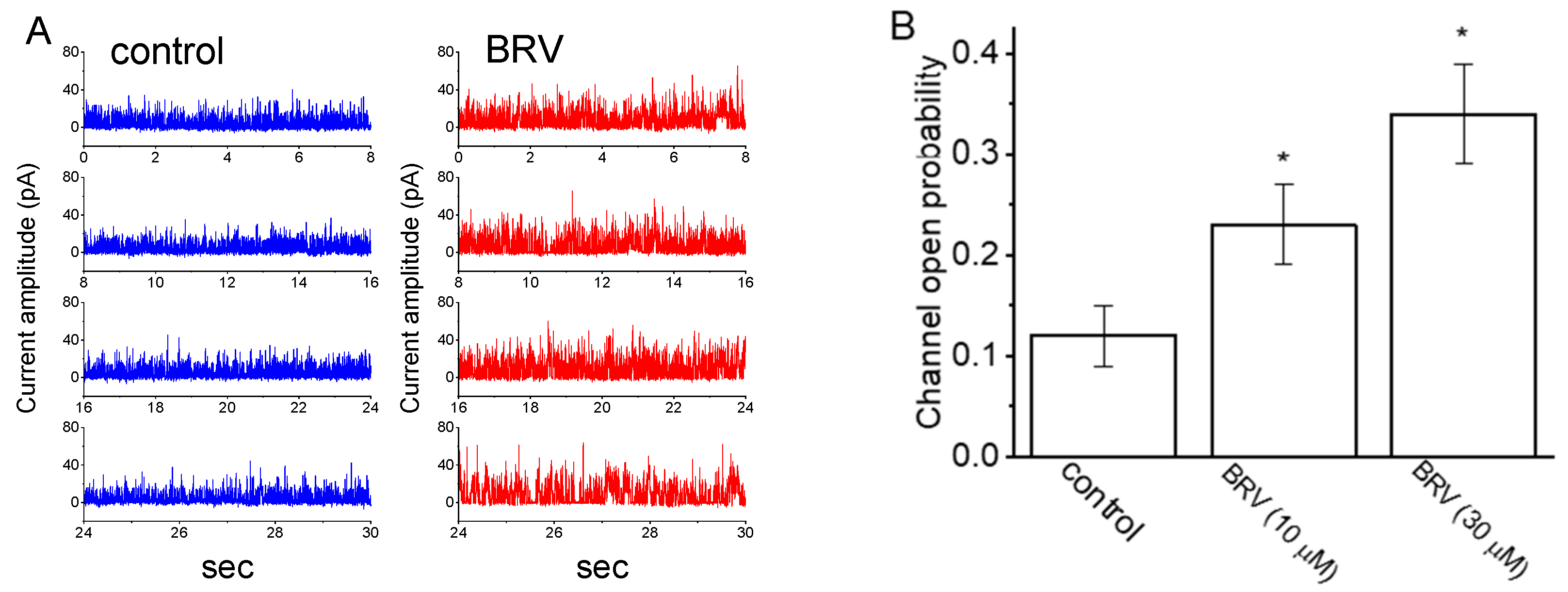
3.6. Stimulatory Effect of BRV on the Activity of Large-Conductance Ca2+-Activated K+ (BKCa) Channels
3.7. Inhibitory Effect of BRV on INa in Hippocampal Neurons
3.8. Effect of BRV on BKCa-Channel Activity Recorded from mHippoE-14 Hippocampal Neurons
3.9. Simulated Firing of Action Potentials (APs) in Modeled Neurons Used to Mimic the Effect of BRV
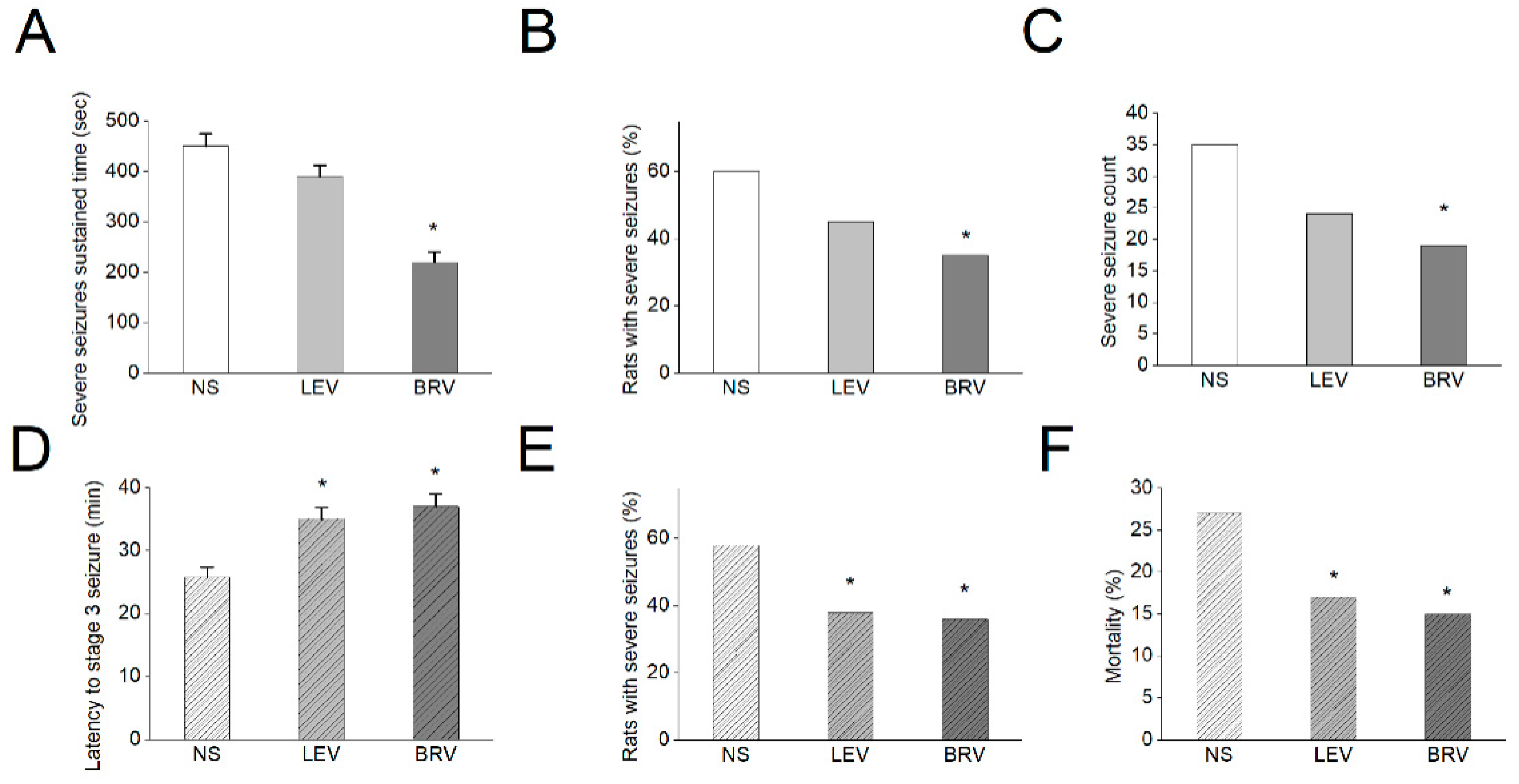
3.10. Effects of BRV versus LEV on Acute Seizures in Different Animal Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malawska, B.; Kulig, K. Brivaracetam UCB. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2005, 6, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malawska, B.; Kulig, K. Brivaracetam: A new drug in development for epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2008, 17, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, P.; Schiemann, J.; Sperling, M.R.; Whitesides, J.; Liang, W.; Stalvey, T.; Brandt, C.; Kwan, P. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, parallel-group study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of adjunctive brivaracetam in adult patients with uncontrolled partial-onset seizures. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1890–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, P.; Tyrlikova, I.; Brazdil, M.; Rektor, I. Brivaracetam for the treatment of epilepsy. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2016, 17, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, P.; Diaz, A.; Gasalla, T.; Whitesides, J. A review of the pharmacology and clinical efficacy of brivaracetam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 10, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brigo, F.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Nardone, R.; Trinka, E. Efficacy and tolerability of brivaracetam compared to lacosamide, eslicarbazepine acetate, and perampanel as adjunctive treatments in uncontrolled focal epilepsy: Results of an indirect comparison meta-analysis of RCTs. Seizure 2016, 42, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoy, S.M. Brivaracetam: A review in partial-onset (focal) seizures in patients with epilepsy. CNS Drugs 2016, 30, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, A. Brivaracetam: First global approval. Drugs 2016, 76, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelczyk, A.; Klein, K.M.; Willems, L.M.; Rosenow, F.; Bauer, S. Brivaracetam in the treatment of focal and idiopathic epilepsies and of status epilepticus. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 9, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelczyk, A.; Kay, L.; Bauer, S.; Immisch, I.; Klein, K.M.; Knake, S.; Kowski, A.; Kunz, R.; Kurlemann, G.; Langenbruch, L.; et al. Use of brivaracetam in genetic generalized epilepsies and for acute, intravenous treatment of absence status epilepticus. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaccara, G. Brivaracetam: New compound approved for the treatment of epilepsy. Drugs Today 2016, 52, 219–227. [Google Scholar]
- Coppola, G.; Iapadre, G.; Operto, F.F.; Verrotti, A. New developments in the management of partial-onset epilepsy: Role of brivaracetam. Drug. Des. Devel. Ther. 2017, 11, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kappes, J.A.; Hayes, W.J.; Strain, J.D.; Farver, D.K. Brivaracetam: An adjunctive treatment for partial-onset seizures. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 57, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milovanović, J.R.; Janković, S.M.; Pejčić, A.; Milosavljević, M.; Opančina, V.; Radonjić, V.; Protrka, Z.; Kostić, M. Evaluation of brivaracetam: A new drug to treat epilepsy. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2017, 18, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoemaker, R.; Wade, J.R.; D’Souza, J.; Stockis, A. Evaluation of brivaracetam efficacy as monotherapy in adult patients with focal seizures. Epilepsy Res. 2017, 137, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, L.J.; Brodie, M.J. Brivaracetam: A novel antiepileptic drug for focal-onset seizures. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2017, 11, 1756285617742081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalss, G.; Rohracher, A.; Leitinger, M.; Pilz, G.; Novak, H.; Neuray, C.; Kreidenhuber, R.; Höfler, J.; Kuchukhidze, G.; Trinka, E. Intravenous brivaracetam in status epilepticus: A retrospective single-center study. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert-Bast, S.; Willems, L.M.; Kurlemann, G.; Knake, S.; Müller-Schlüter, K.; Rosenow, F.; Strzelczyk, A. Postmarketing experience with brivaracetam in the treatment of focal epilepsy in children and adolescents. Epilepsy Behav. 2018, 89, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresnahan, R.; Panebianco, M.; Marson, A.G. Brivaracetam add-on therapy for drug-resistance epilepsy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 3, CD011501. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feyissa, A.M. Brivaracetam in the treatment of epilepsy: A review of clinical trial data. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2019, 15, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hellerslia, V.; Asistido, J.M.; Iyamu, A. Brivaracetam for epilepsy. JAAPA 2019, 32, 21–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, E.; Dilley, D.; McDonough, B.; Stockis, A.; Daniels, T. Safety and tolerability of adjunctive brivaracetam in pediatric patients <16 years with epilepsy: An open-label trial. Paediatric Drugs 2019, 21, 291–301. [Google Scholar]
- Makke, Y.; Abou-Khalil, B. Brivaracetam efficacy and safety in focal epilepsy. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2019, 19, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissenkorn, A.; Tzadok, M.; Bar-Yosef, O.; Ben-Zeev, B. Treatment with brivaracetam in children—The experience of a pediatric epilepsy center. Epilepsy Behav. 2019, 101, 106541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhoff, B.J.; Staack, A.M. Levetiracetam and brivaracetam: A review of evidence from clinical trials and clinical experience. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2019, 12, 1756286419873518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Theochari, E.; Cock, H.; Lozsadi, D.; Galtrey, C.; Arevalo, J.; Mula, M. Brivaracetam in adults with drug-resistant epilepsy and psychiatric comorbidities. Epilepsy Behav. 2019, 90, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, M.; Abraira, L.; Mazuela, G.; Quintana, M.; Cazorla, S.; Santamarina, E. Effect of brivaracetam on the anger levels of epilepsy patients. a prospective open-labelled controlled study. Seizure 2019, 69, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, V.; López-González, F.J.; Mauri, J.A.; Rodriguez-Uranga, J.; Olivé-Gadea, M.; Montoya, J.; Ruiz-Giménez, J.; Zurita, J.; BRIVA-LIFE study group. BRIVA-LIFE-A multicenter retrospective study of the long-term use of brivaracetam in clinical practice. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2019, 139, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, F.M.; Coveñas, R. Neural networks in generalized epilepsy and novel antiepileptic drugs. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, L.M.; Bauer, S.; Rosenow, F.; Strzelczyk, A. Recent advances in the pharmacotherapy of epilepsy: Brivaracetam and perampanel as broad-spectrum antiseizure drugs for the treatment of epilepsies and status epilepticus. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2019, 20, 1755–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, E.; Guzmán, L.; Quintana, M.; Abraira, L.; Santamarina, E.; Salas-Puig, X.; Toledo, M. Efficacy, retention, and safety of brivaracetam in adult patients with genetic generalized epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2019, 102, 106657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, S.; Silva, G.; Lai, D.; Khurana, D.S.; Legido, A.; Hasbani, D.; Carvalho, K.S.; Melvin, J.; Valencia, I. Safety and efficacy of brivaracetam in pediatric refractory epilepsy: A single-center clinical experience. J. Child Neurol. 2020, 35, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Väätäinen, S.; Soini, E.; Peltola, J.; Charokopou, M.; Taiha, M.; Kälviäinen, R. Economic value of adjunctive brivaracetam treatment strategy for focal onset seizures in Finland. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 477–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aicua-Rapun, I.; André, P.; Rossetti, A.O.; Decosterd, L.A.; Buclin, T.; Novy, J. Intravenous brivaracetam in status epilepticus: Correlation between loading dose, plasma levels and clinical response. Epilepsy Res. 2019, 149, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amengual-Gual, M.; Sánchez Fernández, I.; Wainwright, M.S. Novel drugs and early polypharmacology in status epilepticus. Seizure 2019, 68, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigo, F.; Lattanzi, S.; Nardone, R.; Trinka, E. Intravenous brivaracetam in the treatment of status epilepticus: A systematic review. CNS Drugs 2019, 33, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrokh, S.; Bon, J.; Erdman, M.; Tesoro, E. Use of newer anticonvulsants for the treatment of status epilepticus. Pharmacotherapy 2019, 39, 297–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moalong, K.M.C.; Espiritu, A.I.; Fernandez, M.L.L. Efficacy and tolerability of intravenous brivaracetam for status epilepticus: A systemic review. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 413, 116799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsymbalyuk, S.; Smith, M.; Gore, C.; Tsymbalyuk, O.; Ivanova, S.; Sansur, C.; Gerzanich, V.; Simard, J.M. Biravaracetam attenuates pain behaviors in a murine model of neuropathic pain. Mol. Pain 2019, 15, 1744806919886503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A.; Donzelli, S.; Girgenti, V.; Sacconi, A.; Vasco, C.; Salmaggi, A.; Blandino, G.; Maschio, M.; Ciusani, E. In vitro antineoplastic effects of brivaracetam and lacosamide on human glioma cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portela-Gomes, G.M.; Lukinius, A.; Grimelius, L. Synaptic vesicle protein 2, a new neuroendocrine cell marker. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogawski, M.A.; Bazil, C.W. New molecular targets for antiepileptic drugs: α2δ, SV2A, and Kv7/KCNQ/M potassium channels. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2008, 8, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Bognar, J., Jr.; He, T.; Mohammed, M.; Niespodziany, I.; Wolff, C.; Esguerra, M.; Rothman, S.M.; Dubinsky, J.M. Brivaracetam augments short-term depression and slows vesicle recycling. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1899–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, J.M.; Hannestad, J.; Holden, D.; Kervyn, S.; Nabulsi, N.; Tytgat, D.; Huang, Y.; Chanteux, H.; Staelens, L.; Matagne, A.; et al. Brivaracetam, a selective high-affinity synaptic vesicle protein 2A (SV2A) ligand with preclinical evidence of high brain permeability and fast onset of action. Epilepsia 2016, 57, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rogawski, M.A. A new SV2A ligand for epilepsy. Cell 2016, 167, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matagne, A.; Margineanu, D.G.; Kenda, B.; Michel, P.; Klitgaard, H. Anti-convulsive and anti-epileptic properties of brivaracetam (ucb 34714), a high-affinity ligand for the synaptic vesicle protein, SV2A. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niespodziany, I.; André, V.M.; Leclère, N.; Hanon, E.; Ghisdal, P.; Wolff, C. Brivaracetam diferentially affects voltage-gated sodium currents without impairing sustained repetitive firing in neurons. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2015, 21, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adewusi, J.; Burness, C.; Ellawela, S.; Emsley, H.; Hughes, R.; Lawthom, C.; Maguire, M.; McLean, B.; Mohanraj, R.; Oto, M.; et al. efficacy and tolerability in clinical practice: A UK-based retrospective multicenter service evaluation. Epilepsy Behav. 2020, 106, 106967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.C.; Wang, Y.J.; Wu, P.Y.; Wu, S.N. Tramadol-induced block of hyperpolarization-activated cation current in rat pituitary lactotrophs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg Arch. Pharmacol. 2009, 379, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingerich, S.; Kim, G.L.; Chalmers, J.A.; Koletar, M.M.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Belsham, D.D. Estrogen receptor α and G-protein coupled receptor 30 mediate the neuroprotective effects of 17β-estradiol in novel murine hippocampal cell models. Neuroscience 2010, 170, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.C.; Wu, S.N.; Huang, C.W. Telmisartan, an antagonist of angiotensin II receptors, accentuates voltage-gated Na+ currents and hippocampal neuronal excitability. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milton, R.L.; Caldwell, J.H. How do patch clamp seals form? A lipid bleb model. Pflugers Arch. 1990, 416, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golomb, D.; Yue, C.; Yaari, Y. Contribution of persistent Na+ current and M-type K+ current to somatic bursting in CA1 pyramidal cells: Combined experimental and modeling study. J. Neurophysiol. 2006, 96, 1912–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeldenrust, F.; Chameau, P.J.; Wadman, W.J. Reliability of spike and burst firing in thalamocortical relay cells. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2013, 35, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, M.C.; Wu, S.N.; Huang, C.W. The Specific Effects of OD-1, a Peptide Activator, on Voltage-Gated Sodium Current and Seizure Susceptibility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.Y.; Chu, F.L.; Wu, D.; Wu, S.N.; Huang, C.W. The Protective Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-Gamma in Seizure and Neuronal Excitotoxicity. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 5497–5506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.C.; Lin, K.M.; Yeh, P.S.; Wu, S.N.; Huang, C.W. The Novel Effect of Immunomodulator-Glatiramer Acetate on Epileptogenesis and Epileptic Seizures. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 50, 150–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, L.E.; Cavalheiro, E.A.; Tan, A.M.; Kupfer, W.R.; Pretorius, J.K.; Babb, T.L.; Finch, D.M. Circuit mechanisms of seizures in the pilocarpine model of chronic epilepsy: Cell loss and mossy fiber sprouting. Epilepsia 1993, 34, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, S.; Simasko, S.M. Characterization of an M-like current modulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone in normal rat lactotrophs. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 1668–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selyanko, A.A.; Hadley, J.K.; Wood, I.C.; Abogadie, F.C.; Delmas, P.; Buckley, N.J.; London, B.; Brown, D.A. Two types of K+ channel subunit Erg1 and KCNQ2/3, contribute to the M-like current in a mammalian neuronal cell. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 7742–7756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, W.T.; Liu, P.Y.; Gao, Z.H.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, W.K.; Wu, S.N. Evidence for the effectiveness of remdesivir (GS-5734), a nucleoside-analog antiviral drug in the inhibition of IK(M) and IK(DR) and in the stimulation of IMEP. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.W.; Tsai, J.J.; Huang, C.C.; Wu, S.N. Experimental and simulation studies on the mechanisms of levetiracetam-mediated inhibition of delayed-rectifier potassium current (Kv3.1): Contribution to the firing of action potentials. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2009, 60, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simasko, S.M.; Sankaranarayanan, S. Characterization of a hyperpolarization-activated cation current in rat pituitary cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 272, E405–E414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.L.; Gao, Z.H.; Li, S.W.; Wu, S.N. High efficacy by GAL-021: A known intravenous peripheral chemoreceptor modulator that suppresses BKCa-channel activity and inhibits IK(M) or Ih. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, T.L.; Lu, T.J.; Wu, S.N. Inhibitory effective perturbations of cilobradine (DK-AH269), a blocker of HCN channels, on the amplitude and gating of both hyperpolarization-activated cation and delayed-rectifier potassium currents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, P.C.; Ruan, J.S.; Wu, S.N. Evidence of decreased activity in intermediate-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels during retinoic acid-induced differentiation in motor neuron-like NSC-34 cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 2374–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, E.C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.Q.; So, K.H.; Lo, Y.C.; Wu, S.N. Multiple regulatory actions of 2-guanidine-4-methylquinazoline (GMQ), an agonist of acid-sensing ion channel type 3, on ionic currents in pituitary GH3 cells and in olfactory sensory (Rolf B1.T) neurons. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 151, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Lin, K.M.; Hung, T.Y.; Chuang, Y.C.; Wu, S.N. Multiple actions of rotenone, an inhibitor of mitochondrial respiratory chain, on ionic currents and miniature end-plate potential in mouse hippocampal (mHippoE-14) neurons. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.N.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, B.S.; Lo, Y.C.; Liu, Y.C. Underlying mechanism of actions of tefluthrin, a pyrethroid insecticide, on voltage-gated ion currents and on action currents in pituitary tumor (GH3) cells and GnRH-secreting (GT1-7) neurons. Toxicology 2009, 258, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.N.; Chen, B.S.; Hsu, T.I.; Peng, H.; Wu, Y.H.; Lo, Y.C. Analytical studies of rapidly inactivation and noninactivating sodium currents in differentiated NG108-15 neuronal cells. J. Theor. Biol. 2009, 259, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoemaker, R.; Wade, J.R.; Stockis, A. Brivaracetam population pharmacokinetics in children with epilepsy aged 1 month and 16 years. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 73, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klotz, K.A.; Hirsch, M.; Heers, M.; Schulze-Bonhage, A.; Jacobs, J. Effects of cannabidiol on brivaracetam plasma levels. Epilepsia 2019, 60, e74–e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.C.; Tzeng, R.C.; Huang, C.W.; Wu, S.N. The novel direct modulatory effects of perampanel, an antagonist of AMPA receptors, on voltage-gated sodium and M-type potassium currents. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niespodziany, I.; Rigo, J.M.; Moonen, G.; Matagne, A.; Klitgaard, H.; Wolff, C. Brivaracetam does not modulate ionotropic channels activated by glutamate, γ-aminobutyric acid, and glycine in hippocampal neurons. Epilepsia 2017, 58, e157–e161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Contreras-García, I.J.; Pichardo-Macías, L.A.; Santana-Gómez, C.E.; Sánchez-Huerta, K.; Ramírez-Hernández, R.; Gómez-González, B.; Rocha, L.; Mendoza Torreblanca, J.G. Differential expression of synaptic vesicle protein 2A after status epilepticus and during epilepsy in a lithium-pilocarpine model. Epilepsy Behav. 2018, 88, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.X.; Lin, Y.Y.; Bi, Q.Q.; Chen, Y.J. Brivaracetam Prevents the Over-expression of Synaptic Vesicle Protein 2A and Rescues the Deficits of Hippocampal Long-term Potentiation In Vivo in Chronic Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Rats. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2020, 17, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, R.C.; Rosenfeld, W.E.; Lippmann, S.M.; Eijkemans, R.M.J.C.; Kasteleijn-Nolst Trenité, D.G.A. Rapidity of CNS Effect on Photoparoxysmal Response for Brivaracetam vs. Levetiracetam: A Randomized, Double-blind, Crossover Trial in Photosensitive Epilepsy Patients. CNS Drugs 2020, 34, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klitgaard, H.; Matagne, A.; Nicolas, J.M.; Gillard, M.; Lamberty, Y.; De Ryck, M.; Kaminski, R.M.; Leclercq, K.; Niespodziany, I.; Wolff, C.; et al. Brivaracetam: Rationale for discovery and preclinical profile of a selective SV2A ligand for epilepsy treatment. Epilepsia 2016, 57, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Symbol | Description | Value (in Control) | Value (in the Presence of 10 µM BRV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cm | Membrane capacitance (pF) | 1 | 1 |
| gNa | Na+ current conductance (mS/cm2) | 35 | 17.5 |
| gCa | Ca2+ current conductance (mS/cm2) | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| gKDR | Delayed-rectifier K+ current conductance (mS/cm2) | 6.0 | 5.4 |
| gA | A-type K+ current conductance (mS/cm2) | 1.4 | 1.4 |
| gM | M-type K+ current conductance (mS/cm2) | 1 | 0.7 |
| gKCa | Ca2+-activated K+ current conductance (mS/cm2) | 10 | 20 |
| gh | Hyperpolarization-activated cation current conductance (mS/cm2) | 0.4 | 0.36 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hung, T.-Y.; Wu, S.-N.; Huang, C.-W. The Integrated Effects of Brivaracetam, a Selective Analog of Levetiracetam, on Ionic Currents and Neuronal Excitability. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040369
Hung T-Y, Wu S-N, Huang C-W. The Integrated Effects of Brivaracetam, a Selective Analog of Levetiracetam, on Ionic Currents and Neuronal Excitability. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(4):369. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040369
Chicago/Turabian StyleHung, Te-Yu, Sheng-Nan Wu, and Chin-Wei Huang. 2021. "The Integrated Effects of Brivaracetam, a Selective Analog of Levetiracetam, on Ionic Currents and Neuronal Excitability" Biomedicines 9, no. 4: 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040369
APA StyleHung, T.-Y., Wu, S.-N., & Huang, C.-W. (2021). The Integrated Effects of Brivaracetam, a Selective Analog of Levetiracetam, on Ionic Currents and Neuronal Excitability. Biomedicines, 9(4), 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040369






