Heme-Mediated Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Axis Attenuates Calcification of Valve Interstitial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Induction of Osteogenesis
2.3. Cell Treatments
2.4. Alizarin Red (AR) Staining and Quantification
2.5. Quantification of Ca Deposition
2.6. Quantification of OCN
2.7. Determination of Cell Viability
2.8. Quantitative RT-PCR
2.9. Western Blot
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
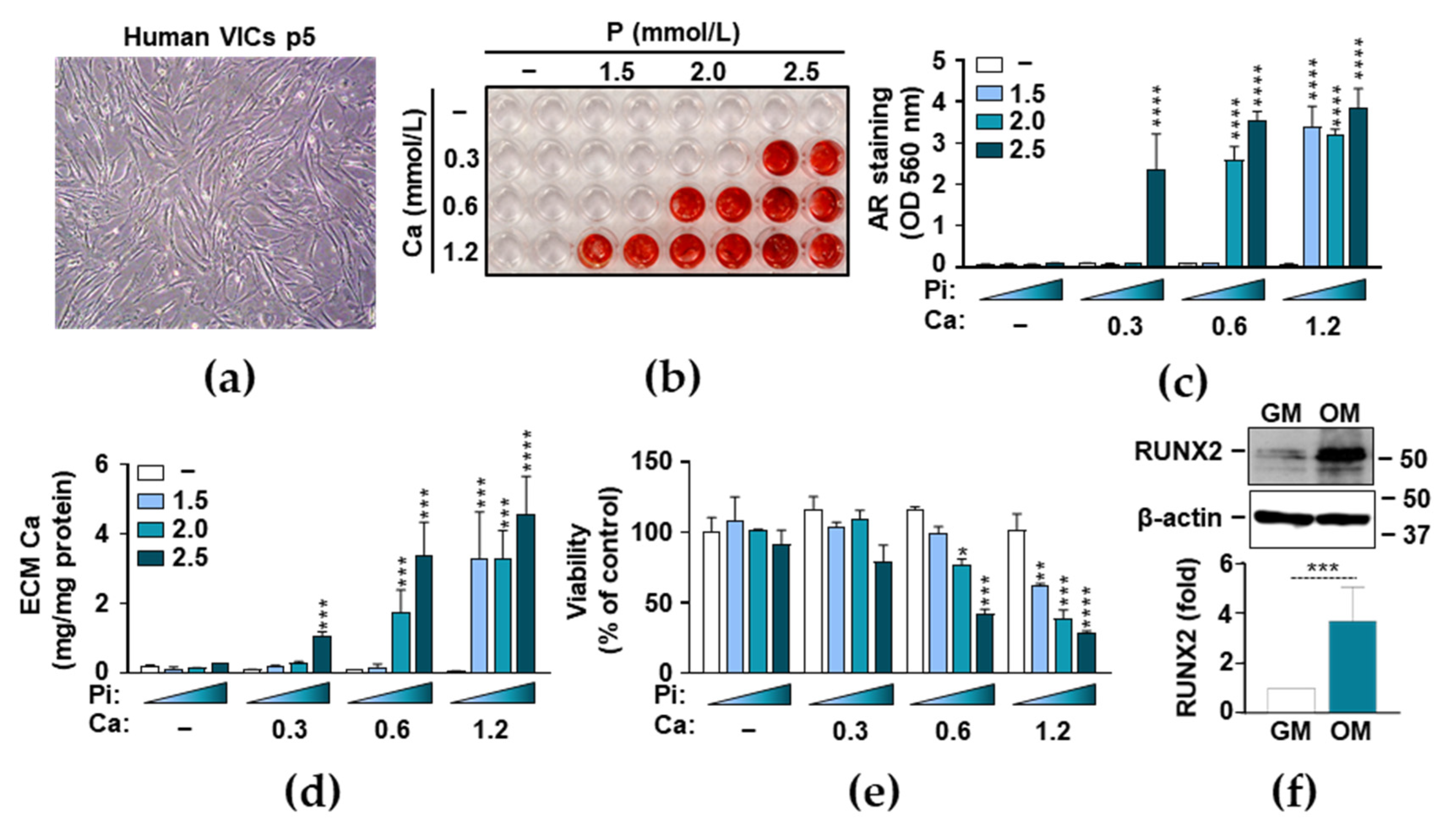
3.1. Phosphate and Ca Synergistically Induce ECM Mineralization and Cell Death in VICs
3.2. Heme Inhibits P- and Ca-Induced ECM Calcification and Osteogenic Transdifferentiation of VICs
3.3. Induction of the Nrf2/HO-1 Axis by Heme in VICs
3.4. Anti-Calcification Effect of Heme Requires Integrity of the Nrf2/HO-1 Axis
3.5. Heme Degradation Products Possess Anti-Calcification Activities
3.6. Ferritin Mimics the Inhibitory Effect of Heme on VIC Calcification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| AR | Alizarin red |
| BMP2 | Bone morphogenetic protein 2 |
| BR | Bilirubin |
| BVR | Biliverdin reductase |
| CAVS | Calcific aortic valve stenosis |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CO | Carbon monoxide |
| CORM2 | CO releasing molecule 2 |
| DPBS | Dulbecco’s Phosphate Buffered Saline |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium |
| DMSO | Dimethyl-sulfoxide |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| EDTA | Ethylenediamine-tetraacetic acid |
| FT, FTH, FTL | Ferritin, ferritin heavy chain, ferritin light chain |
| GM | Growth medium |
| HBSS | Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution |
| HPRT | Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase-1 |
| Keap1 | Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 |
| MSCs | Mesenchymal stem cells |
| MTT | 3-[4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| NLRP3 | Nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat-containing family and pyrin domain containing 3 |
| OCN | Osteocalcin |
| OD | Optical density |
| OPN | Osteopontin |
| OM | Osteogenic medium |
| P | Phosphate |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RUNX2 | Runt-related transcription factor 2 |
| SnPP | Tin protoporphyrin IX |
| SOX9 | Sry-related HMG box-9 |
| VSMCs | Vascular smooth muscle cells |
| VICs | Valvular Interstitial Cells |
| ZnPP | Zinc protoporphyrin IX |
References
- Lindman, B.R.; Clavel, M.A.; Mathieu, P.; Iung, B.; Lancellotti, P.; Otto, C.M.; Pibarot, P. Calcific aortic stenosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, J.D.; Weiss, R.M.; Heistad, D.D. Calcific aortic valve stenosis: Methods, models, and mechanisms. Circ. Res. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goody, P.R.; Hosen, M.R.; Christmann, D.; Niepmann, S.T.; Zietzer, A.; Adam, M.; Bönner, F.; Zimmer, S.; Nickenig, G.; Jansen, F. Aortic valve stenosis: From basic mechanisms to novel therapeutic targets. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, L.; Yacoub, M.H.; Latif, N.; Amrani, M.; Chester, A.H. Role of human valve interstitial cells in valve calcification and their response to atorvastatin. Circulation 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.J.; Kao, Y.H.; Chung, C.C.; Chen, W.Y.; Cheng, W.L.; Chen, Y.J. Activated p300 acetyltransferase activity modulates aortic valvular calcification with osteogenic transdifferentiation and downregulation of Klotho. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 232, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirrig, E.E.; Hinton, R.B.; Yutzey, K.E. Differential expression of cartilage and bone-related proteins in pediatric and adult diseased aortic valves. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2011, 50, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kooman, J.P.; Kotanko, P.; Schols, A.M.W.J.; Shiels, P.G.; Stenvinkel, P. Chronic kidney disease and premature ageing. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanahan, C.M. Mechanisms of vascular calcification in CKD—Evidence for premature ageing? Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2013, 9, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikee, R.; Honda, K.; Ishioka, K.; Oka, M.; Maesato, K.; Moriya, H.; Hidaka, S.; Ohtake, T.; Kobayashi, S. Differences in associated factors between aortic and mitral valve calcification in hemodialysis. Hypertens. Res. 2010, 33, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guerraty, M.A.; Chai, B.; Hsu, J.Y.; Ojo, A.O.; Gao, Y.; Yang, W.; Keane, M.G.; Budoff, M.J.; Mohler, E.R. Relation of aortic valve calcium to chronic kidney disease (from the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 115, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Webster, A.C.; Nagler, E.V.; Morton, R.L.; Masson, P. Chronic Kidney Disease. Lancet 2017, 389, 1238–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, M.; Wiebe, N.; Culleton, B.; House, A.; Rabbat, C.; Fok, M.; McAlister, F.; Garg, A.X. Chronic kidney disease and mortality risk: A systematic review. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2037–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schoppet, M.; Shroff, R.C.; Hofbauer, L.C.; Shanahan, C.M. Exploring the biology of vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease: What’s circulating? Kidney Int. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jono, S.; McKee, M.D.; Murry, C.E.; Shioi, A.; Nishizawa, Y.; Mori, K.; Morii, H.; Giachelli, C.M. Phosphate regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell calcification. Circ. Res. 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giachelli, C.M. The emerging role of phosphate in vascular calcification. Kidney Int. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adeney, K.L.; Siscovick, D.S.; Ix, J.H.; Seliger, S.L.; Shlipak, M.G.; Jenny, N.S.; Kestenbaum, B.R. Association of serum phosphate with vascular and valvular calcification in moderate CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tóth, A.; Balogh, E.; Jeney, V. Regulation of vascular calcification by reactive oxygen species. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberman, M.; Bassi, E.; Martinatti, M.K.; Lario, F.C.; Wosniak, J.; Pomerantzeff, P.M.A.; Laurindo, F.R.M. Oxidant generation predominates around calcifying foci and enhances progression of aortic valve calcification. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Q. Role of Nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, R.; Sun, H.; Peng, J.; Ma, X.; Bao, L.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Luo, C.; Gao, C.; Jin, Y.; et al. Rosmarinic acid exerts an antagonistic effect on vascular calcification by regulating the Nrf2 signalling pathway. Free Radic. Res. 2019, 53, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefin, S.; Buchanan, S.; Hobson, S.; Steinmetz, J.; Alsalhi, S.; Shiels, P.G.; Kublickiene, K.; Stenvinkel, P. Nrf2 in early vascular ageing: Calcification, senescence and therapy. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 505, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Enaka, M.; Muragaki, Y. Activation of KEAP1/NRF2/P62 signaling alleviates high phosphate-induced calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells by suppressing reactive oxygen species production. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gozzelino, R.; Jeney, V.; Soares, M.P. Mechanisms of cell protection by heme Oxygenase-1. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 50, 323–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeney, V.; Balla, J.; Yachie, A.; Varga, Z.; Vercellotti, G.M.; Eaton, J.W.; Balla, G. Pro-oxidant and cytotoxic effects of circulating heme. Blood 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soares, M.P.; Bozza, M.T. Red alert: Labile heme is an alarmin. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2016, 38, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bozza, M.T.; Jeney, V. Pro-inflammatory Actions of Heme and Other Hemoglobin-Derived DAMPs. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenhunen, R.; Marver, H.S.; Schmid, R. The enzymatic conversion of heme to bilirubin by microsomal heme oxygenase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alam, J.; Stewart, D.; Touchard, C.; Boinapally, S.; Choi, A.M.K.; Cook, J.L. Nrf2, a Cap’n’Collar transcription factor, regulates induction of the heme oxygenase-1 gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pamplona, A.; Ferreira, A.; Balla, J.; Jeney, V.; Balla, G.; Epiphanio, S.; Chora, Â.; Rodrigues, C.D.; Gregoire, I.P.; Cunha-Rodrigues, M.; et al. Heme oxygenase-1 and carbon monoxide suppress the pathogenesis of experimental cerebral malaria. Nat. Med. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, A.; Marguti, I.; Bechmann, I.; Jeney, V.; Chora, Â.; Palha, N.R.; Rebelo, S.; Henri, A.; Beuzard, Y.; Soares, M.P. Sickle hemoglobin confers tolerance to plasmodium infection. Cell 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larsen, R.; Gozzelino, R.; Jeney, V.; Tokaji, L.; Bozza, F.A.; Japiassú, A.M.; Bonaparte, D.; Cavalcante, M.M.; Chora, Â.; Ferreira, A.; et al. A central role for free heme in the pathogenesis of severe sepsis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olkowicz, M.; Jablonska, P.; Rogowski, J.; Smolenski, R.T. Simultaneous accurate quantification of HO-1, CD39, and CD73 in human calcified aortic valves using multiple enzyme digestion—filter aided sample pretreatment (MED-FASP) method and targeted proteomics. Talanta 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeone, A.; Brunetti, G.; Oranger, A.; Greco, G.; Di Benedetto, A.; Mori, G.; Colucci, S.; Zallone, A.; Paparella, D.; Grano, M. Aortic valvular interstitial cells apoptosis and calcification are mediated by TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 169, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.M.U.; Luo, L.; Namani, A.; Wang, X.J.; Tang, X. Nrf2 signaling pathway: Pivotal roles in inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arosio, P.; Elia, L.; Poli, M. Ferritin, cellular iron storage and regulation. IUBMB Life 2017, 69, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro1, S.; Ramos1, A.; Brandão2, A.; Reis Rebelo2, J.; Guerra1, A. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation Cardiac valve calcification in haemodialysis patients: Role of calcium-phosphate metabolism. Neprhrol. Dial. Transplant. 1998, 13, 2037–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lerman, D.A.; Prasad, S.; Alotti, N. Using Na3PO4 to Enhance In vitro Animal Models of Aortic Valve Calcification. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balla, J.; Vercellotti, G.M.; Jeney, V.; Yachie, A.; Varga, Z.; Eaton, J.W.; Balla, G. Heme, heme oxygenase and ferritin in vascular endothelial cell injury. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2005, 49, 1030–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcher, J.D.; Chen, C.; Nguyen, J.; Milbauer, L.; Abdulla, F.; Alayash, A.I.; Smith, A.; Nath, K.A.; Hebbel, R.P.; Vercellotti, G.M. Heme triggers TLR4 signaling leading to endothelial cell activation and vaso-occlusion in murine sickle cell disease. Blood 2014, 123, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merle, N.S.; Paule, R.; Leon, J.; Daugan, M.; Robe-Rybkine, T.; Poillerat, V.; Torset, C.; Frémeaux-Bacchi, V.; Dimitrov, J.D.; Roumenina, L.T. P-selectin drives complement attack on endothelium during intravascular hemolysis in TLR-4/hemedependent manner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 6280–6285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wagener, F.A.D.T.G.; Feldman, E.; de Witte, T.; Abraham, N.G. Heme Induces the Expression of Adhesion Molecules ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and E Selectin in Vascular Endothelial Cells. Exp. Biol. Med. 1997, 216, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdei, J.; Tóth, A.; Balogh, E.; Nyakundi, B.B.; Bányai, E.; Ryffel, B.; Paragh, G.; Cordero, M.D.; Jeney, V. Induction of NLRP3 inflammasome activation by heme in human endothelial cells. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 4310816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Minol, J.P.; Reinsch, I.; Luik, M.; Leferink, A.; Barth, M.; Assmann, A.; Lichtenberg, A.; Akhyari, P. Focal induction of ROS-release to trigger local vascular degeneration. PLoS ONE 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balogh, E.; Tóth, A.; Méhes, G.; Trencsényi, G.; Paragh, G.; Jeney, V. Hypoxia Triggers Osteochondrogenic Differentiation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in an HIF-1 (Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1)-Dependent and Reactive Oxygen Species-Dependent Manner. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 1088–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raines, E.W.; Garton, K.J.; Ferri, N. Beyond the Endothelium: NF-κB Regulation of Smooth Muscle Function. Circ. Res. 2004, 94, 706–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, M.M.; Xu, M.J.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, G.; Guan, Y.; Kong, W.; Tang, C.; Wang, X. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species promote p65 nuclear translocation mediating high-phosphate-induced vascular calcification in vitro and in vivo. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voelkl, J.; Lang, F.; Eckardt, K.U.; Amann, K.; Kuro-o, M.; Pasch, A.; Pieske, B.; Alesutan, I. Signaling pathways involved in vascular smooth muscle cell calcification during hyperphosphatemia. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 2077–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zarjou, A.; Jeney, V.; Arosio, P.; Poli, M.; Antal-Szalma, P.; Agarwal, A.; Balla, G.; Balla, J. Ferritin prevents calcification and osteoblastic differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aghagolzadeh, P.; Radpour, R.; Bachtler, M.; van Goor, H.; Smith, E.R.; Lister, A.; Odermatt, A.; Feelisch, M.; Pasch, A. Hydrogen sulfide attenuates calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells via KEAP1/NRF2/NQO1 activation. Atherosclerosis 2017, 265, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ha, C.M.; Park, S.; Choi, Y.K.; Jeong, J.Y.; Oh, C.J.; Bae, K.H.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Park, K.G.; Jun, D.Y.; et al. Activation of Nrf2 by dimethyl fumarate improves vascular calcification. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2014, 63, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, Y.; Du, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, L.; Zhou, F. Resveratrol Ameliorated Vascular Calcification by Regulating Sirt-1 and Nrf2. Transplant. Proc. 2016, 48, 3378–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, C.T.; Yeh, H.Y.; Tsai, Y.T.; Chuang, P.H.; Yuan, T.H.; Huang, J.W.; Chen, H.W. Natural and non-natural antioxidative compounds: Potential candidates for treatment of vascular calcification. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Wang, J.; Tian, B.Y.; Xu, T.H.; Sheng, Z.T. Activation of the Nrf2-ARE Signaling Pathway Prevents Hyperphosphatemia-Induced Vascular Calcification by Inducing Autophagy in Renal Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 4708–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Zhou, Q.; Zheng, X.; Sun, B.; Zhao, S. Mitoquinone attenuates vascular calcification by suppressing oxidative stress and reducing apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells via the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 161, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.H.; Tang, C.H.; Hung, S.Y.; Lui, S.H.; Lin, Y.M.; Fu, W.M.; Yang, R. Sen Upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 inhibits the maturation and mineralization of osteoblasts. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 222, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boczkowski, J.; Poderoso, J.J.; Motterlini, R. CO-metal interaction: Vital signaling from a lethal gas. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2006, 31, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motterlini, R.; Mann, B.E.; Foresti, R. Therapeutic applications of carbon monoxide-releasing molecules. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2005, 14, 1305–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozzelino, R.; Soares, M.P. Coupling heme and iron metabolism via ferritin H chain. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 1754–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boon, A.C.; Bulmer, A.C.; Coombes, J.S.; Fassett, R.G. Circulating bilirubin and defense against kidney disease and cardiovascular mortality: Mechanisms contributing to protection in clinical investigations. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2014, 307, F123–F136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bulmer, A.C.; Bakrania, B.; Du Toit, E.F.; Boon, A.C.; Clark, P.J.; Powell, L.W.; Wagner, K.H.; Headrick, J.P. Bilirubin acts as a multipotent guardian of cardiovascular integrity: More than just a radical idea. Am. J. Physiol. Hear. Circ. Physiol. 2018, 315, H429–H447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunutsor, S.K.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Chowdhury, R.; Dullaart, R.P.F. Circulating Total Bilirubin and Risk of Incident Cardiovascular Disease in the General Population. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrison, P.M.; Arosio, P. The ferritins: Molecular properties, iron storage function and cellular regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 1996, 1275, 161–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, D.S.; Choi, Y.; Lee, J.W. Cellular localization of NRF2 determines the self-renewal and osteogenic differentiation potential of human MSCs via the P53-SIRT1 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanella, L.; Kim, D.H.; Asprinio, D.; Peterson, S.J.; Barbagallo, I.; Vanella, A.; Goldstein, D.; Ikehara, S.; Kappas, A.; Abraham, N.G. HO-1 expression increases mesenchymal stem cell-derived osteoblasts but decreases adipocyte lineage. Bone 2010, 46, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balogh, E.; Tolnai, E.; Nagy, B.; Nagy, B.; Balla, G.; Balla, J.; Jeney, V. Iron overload inhibits osteogenic commitment and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via the induction of ferritin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2016, 1862, 1640–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zarjou, A.; Jeney, V.; Arosio, P.; Poli, M.; Zavaczki, E.; Balla, G.; Balla, J. Ferritin ferroxidase activity: A potent inhibitor of osteogenesis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2010, 25, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, M.; Oeser, C.; Kainz, F.; Shabanian, S.; Aref, T.; Bilban, M.; Messner, B.; Heidtmann, J.; Laufer, G.; Kocher, A.; et al. Intravenous heme arginate induces HO-1 (heme oxygenase-1) in the human heart. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 2755–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balogh, E.; Chowdhury, A.; Ababneh, H.; Csiki, D.M.; Tóth, A.; Jeney, V. Heme-Mediated Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Axis Attenuates Calcification of Valve Interstitial Cells. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040427
Balogh E, Chowdhury A, Ababneh H, Csiki DM, Tóth A, Jeney V. Heme-Mediated Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Axis Attenuates Calcification of Valve Interstitial Cells. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(4):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040427
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalogh, Enikő, Arpan Chowdhury, Haneen Ababneh, Dávid Máté Csiki, Andrea Tóth, and Viktória Jeney. 2021. "Heme-Mediated Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Axis Attenuates Calcification of Valve Interstitial Cells" Biomedicines 9, no. 4: 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040427
APA StyleBalogh, E., Chowdhury, A., Ababneh, H., Csiki, D. M., Tóth, A., & Jeney, V. (2021). Heme-Mediated Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Axis Attenuates Calcification of Valve Interstitial Cells. Biomedicines, 9(4), 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040427





