Characterization of Direct Perturbations on Voltage-Gated Sodium Current by Esaxerenone, a Nonsteroidal Mineralocorticoid Receptor Blocker
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Drugs, and Solutions Used in This Study
2.2. Cell Preparations
2.3. Electrophysiological Measurements
2.4. Potential and Current Recordings
2.5. Data Analyses
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
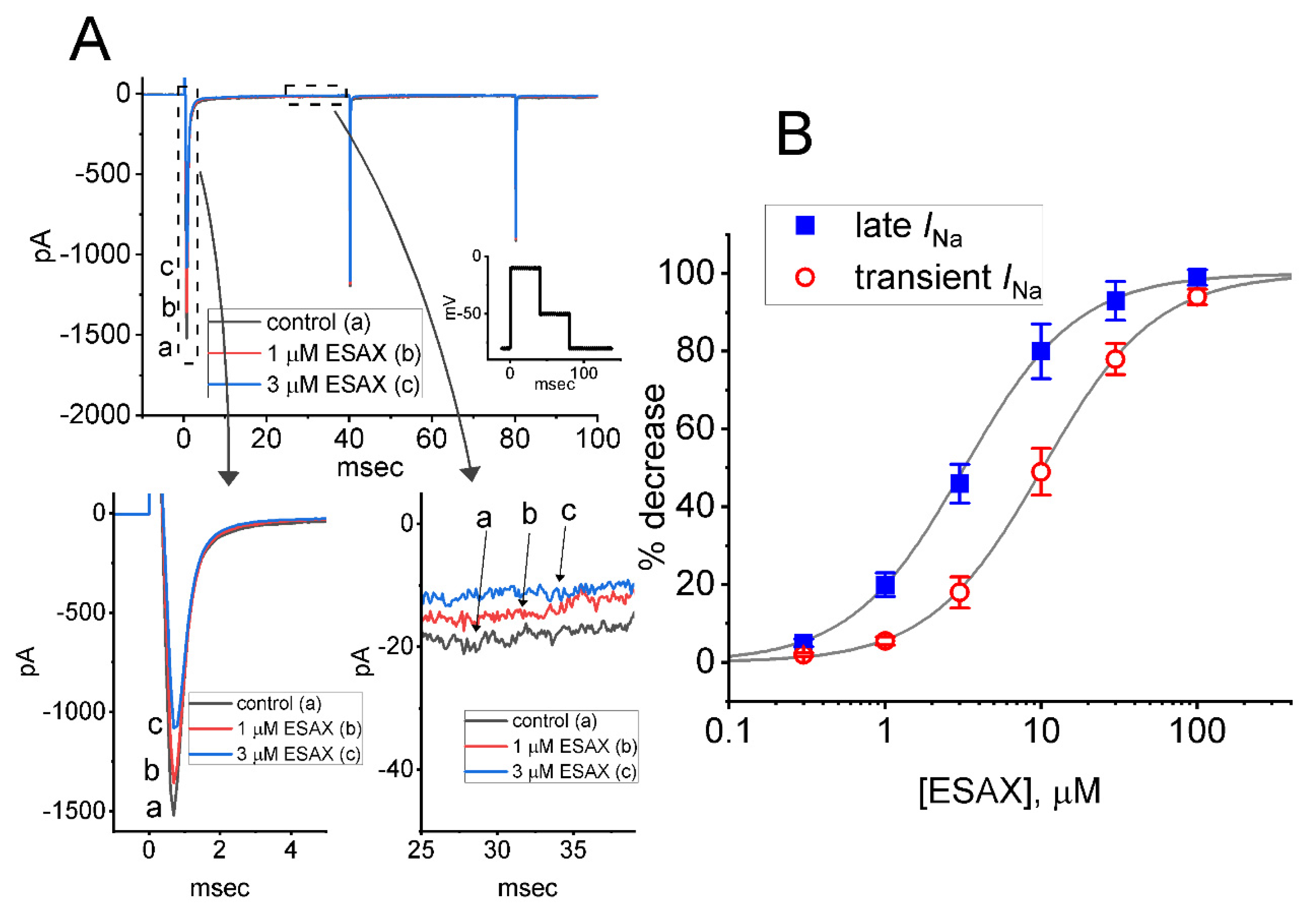
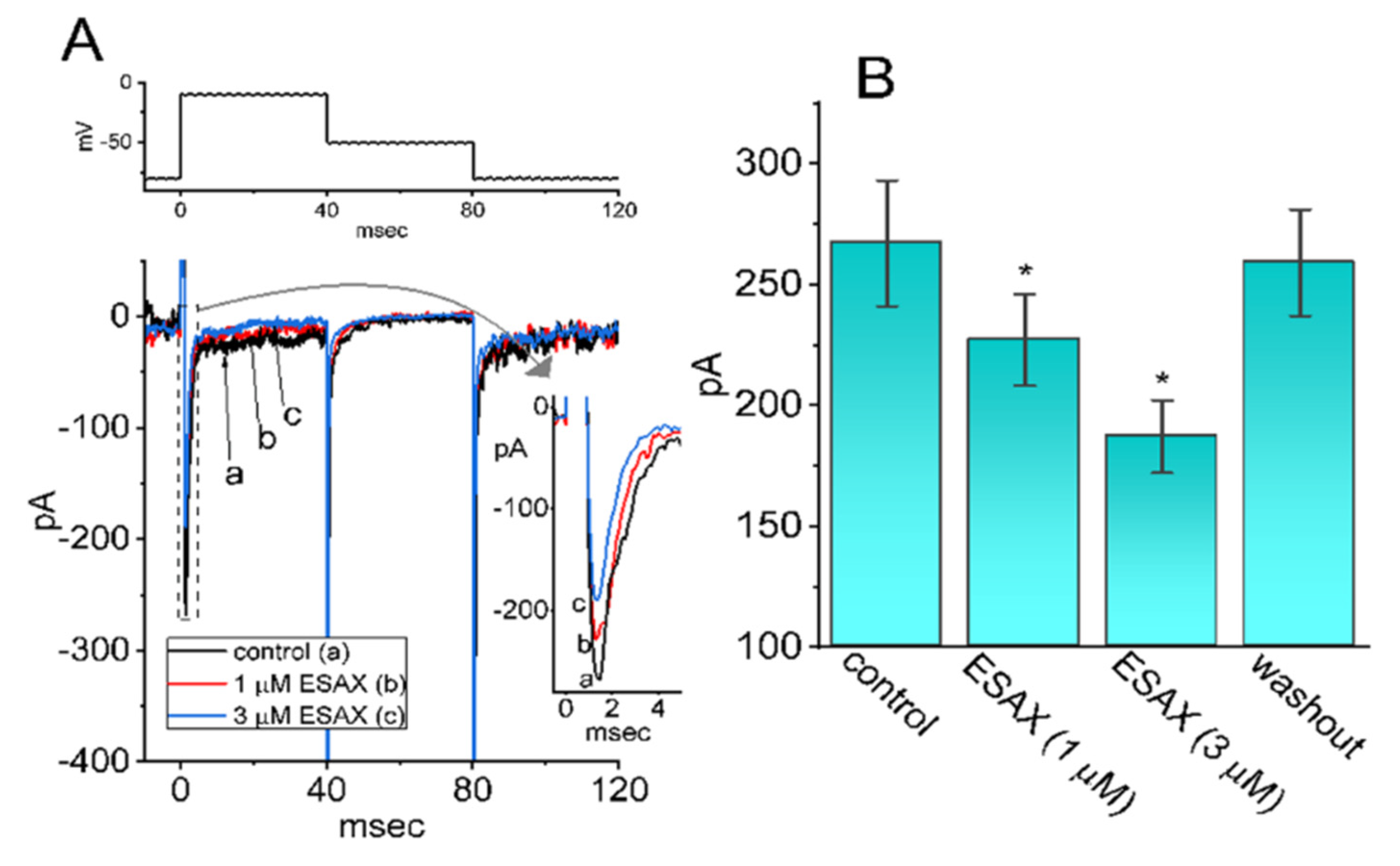
3.1. Effect of Esaxerenone (ESAX) on Voltage-Gated Na+ Current (INa) Measured from GH3 Cells
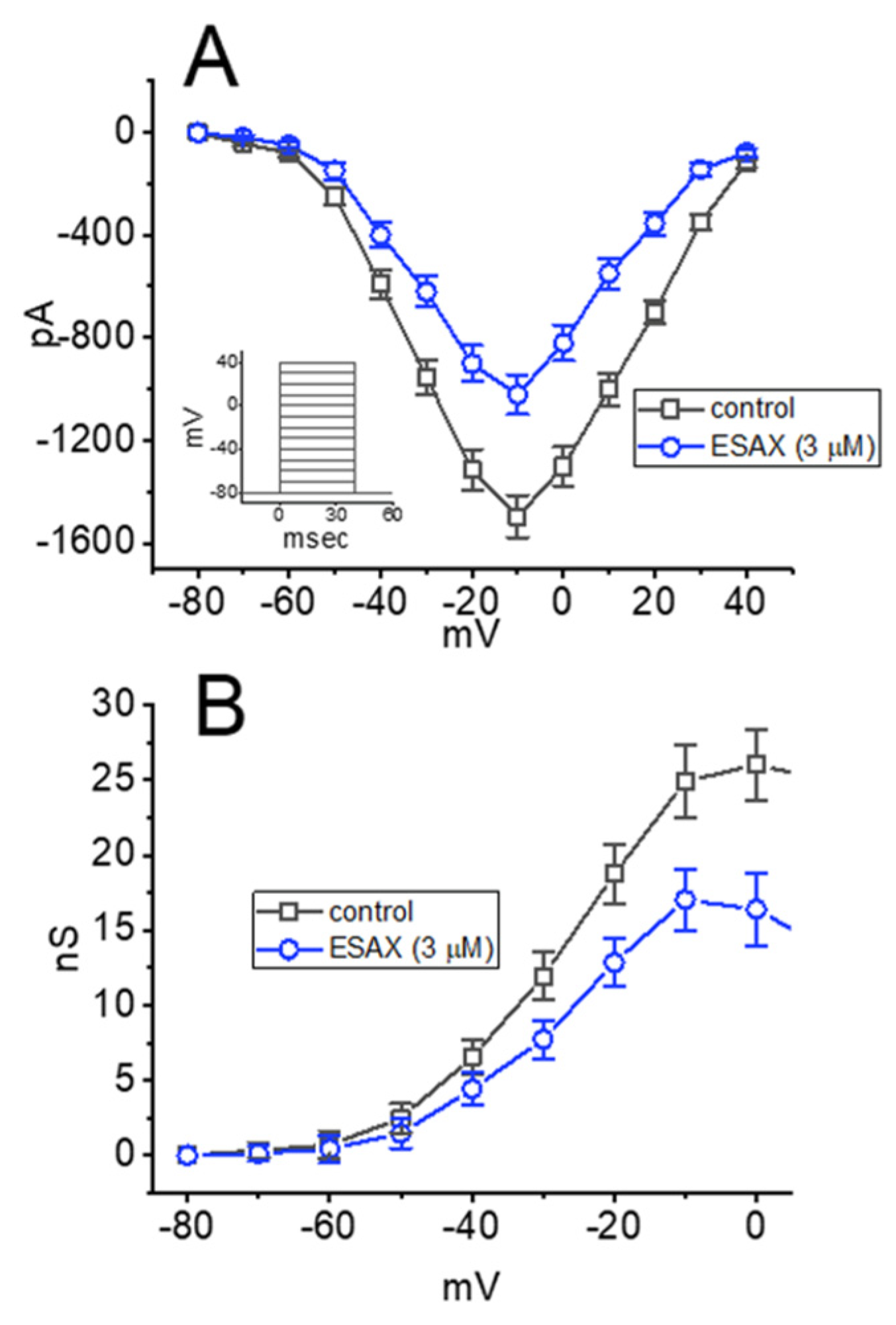
3.2. Effect of ESAX on the Steady-State Current-Voltage (I–V) or Conductance-Voltage Relationship of Peak INa
3.3. Effect of ESAX on the Recovery of I(Na) Block Recorded from GH3 Cells
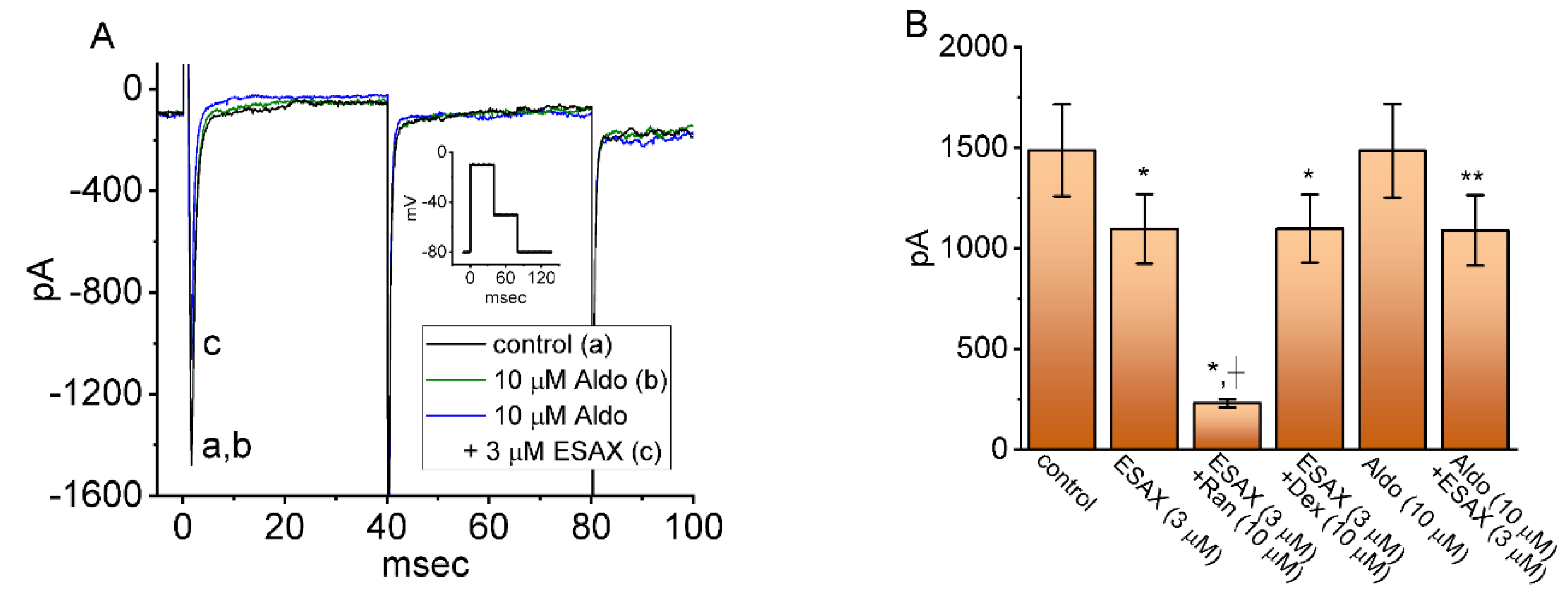
3.4. Comparisons among Effect of ESAX, ESAX plus Ranolazine (Ran), ESAX plus Dexamethasone (Dex), Aldosterone (Aldo), and Aldosterone plus ESAX on Peak INa Recorded from GH3 Cells
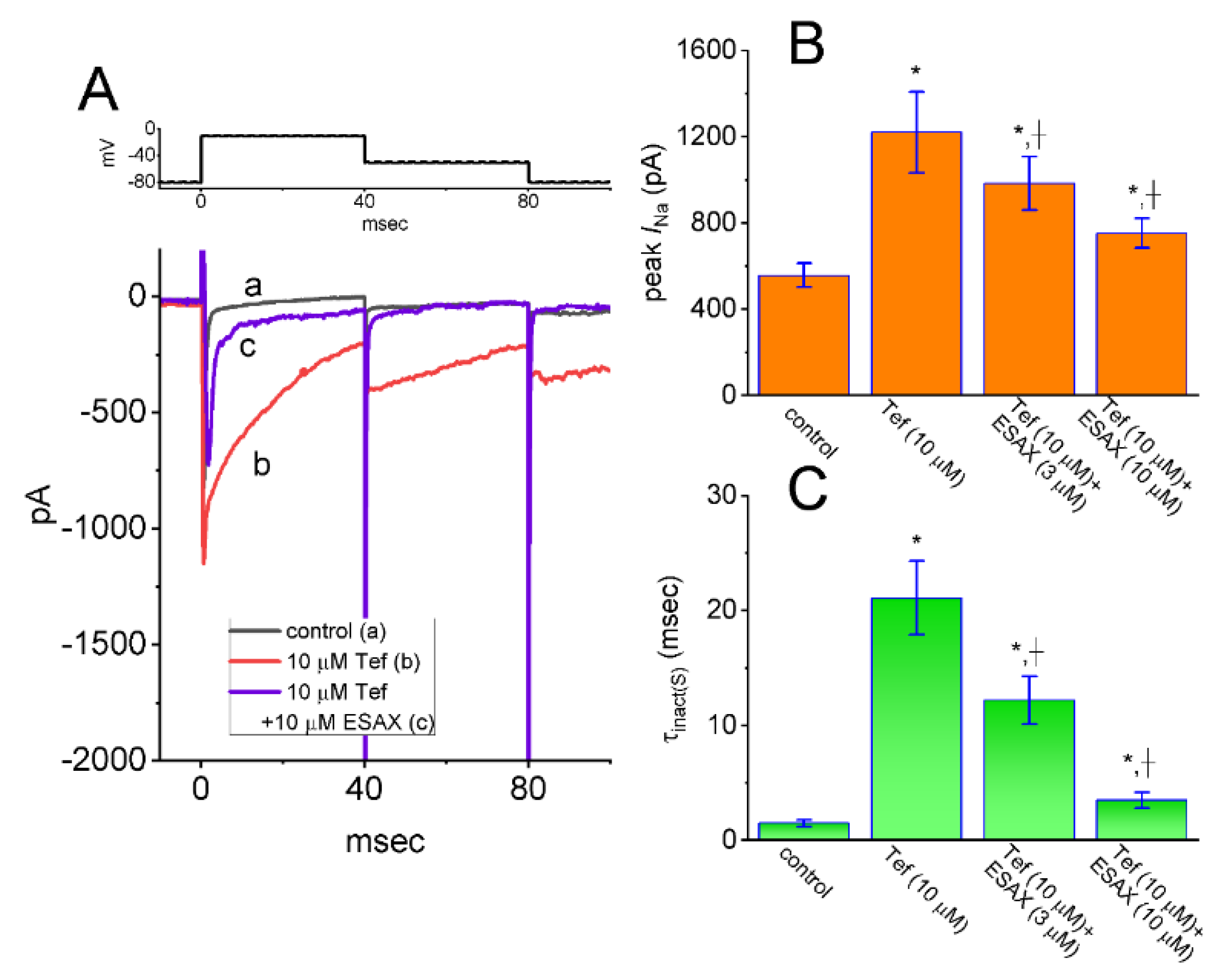
3.5. Enhanced Amplitude by Tef of INa Attenuated by ESAX
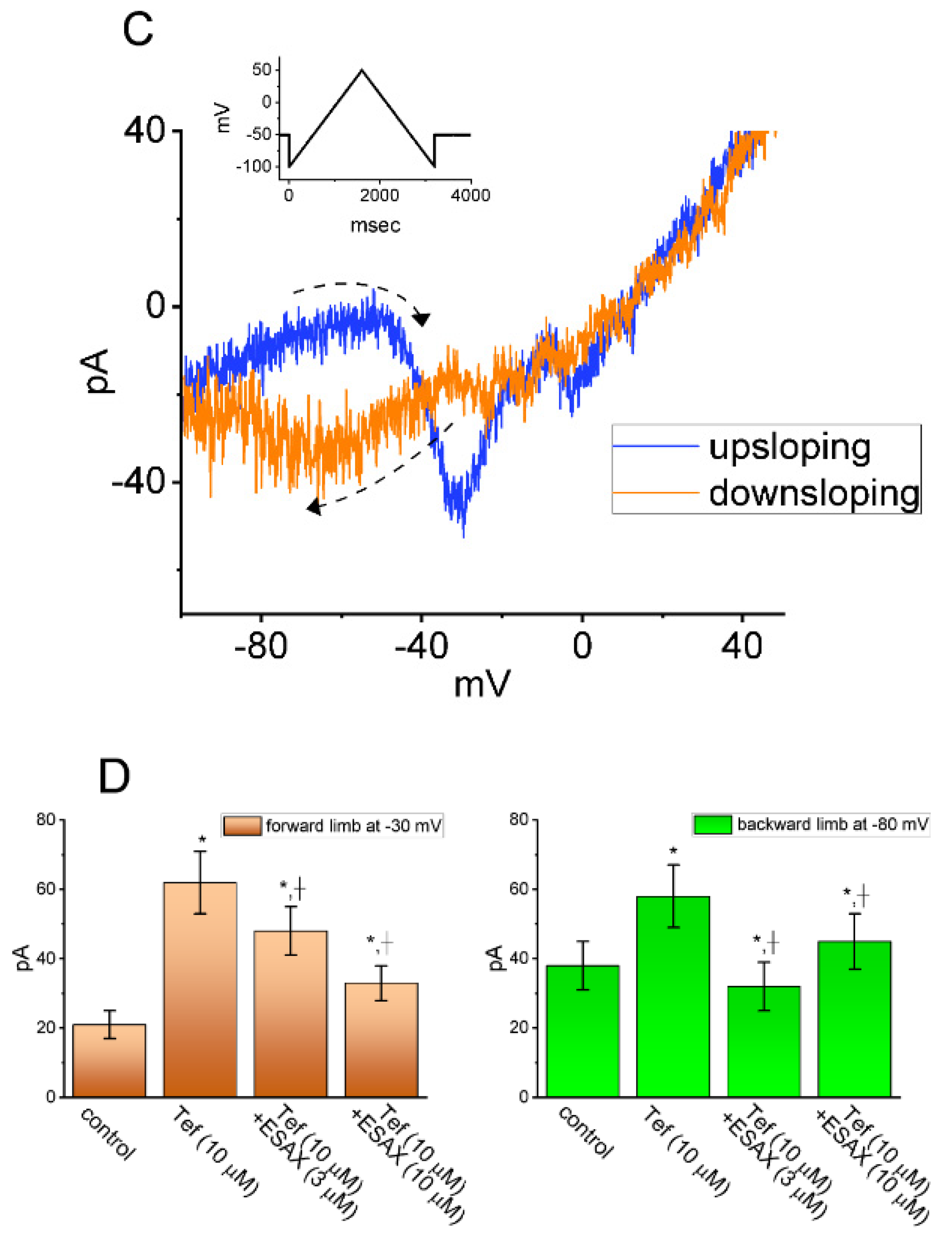
3.6. Augmented Amplitude and Hysteresis by Tef of Persistent Na+ Current (INa(P)) Attenuated by ESAX
3.7. Effect of ESAX on INa Identified in Pituitary MMQ Cells
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Arai, K.; Tsuruoka, H.; Homma, T. CS-3150, a novel non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, prevents hypertension and cardiorenal injury in Dahl salt-sensitive hypertensive rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 769, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duggan, S. Esaxerenone: First Global Approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakugi, H.; Ito, S.; Itoh, H.; Okuda, Y.; Yamakawa, S. Long-term phase 3 study of esaxerenone as mono or combination therapy with other antihypertensive drugs in patients with essential hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2019, 42, 1932–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capelli, I.; Gasperoni, L.; Ruggeri, M.; Donati, G.; Baraldi, O.; Sorrenti, G.; Caletti, M.T.; Aiello, V.; Cianciolo, G.; La Manna, G. New mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists: Update on their use in chronic kidney disease and heart failure. J. Nephrol. 2020, 33, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Itoh, H.; Rakugi, H.; Okuda, Y.; Iijima, S. Antihypertensive effects and safety of esaxerenone in patients with moderate kidney dysfunction. Hypertens. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Itoh, H.; Rakugi, H.; Okuda, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Yamakawa, S. Double-Blind Randomized Phase 3 Study Comparing Esaxerenone (CS-3150) and Eplerenone in Patients With Essential Hypertension (ESAX-HTN Study). Hypertension 2020, 75, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naruke, T.; Maemura, K.; Oki, T.; Yazaki, M.; Fujita, T.; Ikeda, Y.; Nabeta, T.; Ishii, S.; Minami, Y.; Fukaya, H.; et al. Efficacy and safety of esaxerenone in patients with hypertension and concomitant heart failure. Hypertens. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Sawano, T.; Sen, A.; Hossain, A.; Jahan, N.; Kobara, H.; Masaki, T.; Kosaka, S.; Kitada, K.; Nakano, D.; et al. Cardioprotective Effects of a Nonsteroidal Mineralocorticoid Receptor Blocker, Esaxerenone, in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Hypertensive Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, F.; Ito, S.; Itoh, H.; Rakugi, H.; Shibata, H.; Ichihara, A.; Omura, M.; Takahashi, K.; Okuda, Y.; Iijima, S. Efficacy and safety of esaxerenone (CS-3150), a newly available nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor blocker, in hypertensive patients with primary aldosteronism. Hypertens. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, N.; Rahman, A.; Nishiyama, A. Esaxerenone, a novel nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor blocker (MRB) in hypertension and chronic kidney disease. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2021, 35, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, P.M.; Whorwood, C.B. 11 beta-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity and corticosteroid hormone action. Steroids 1994, 59, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castren, M.; Patchev, V.K.; Almeida, O.F.; Holsboer, F.; Trapp, T.; Castren, E. Regulation of rat mineralocorticoid receptor expression in neurons by progesterone. Endocrinology 1995, 136, 3800–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez Sanchez, E.P. Central mineralocorticoid receptors and cardiovascular disease. Neuroendocrinology 2009, 90, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Sanchez, E.P. Brain mineralocorticoid receptors in cognition and cardiovascular homeostasis. Steroids 2014, 91, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Gomez-Sanchez, C.E.; Penman, A.; May, P.J.; Gomez-Sanchez, E. Expression of mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptors in preautonomic neurons of the rat paraventricular nucleus. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2014, 306, R328–R340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, M.; Wilson, R.; Sharma, K.; Mills, N.J.; Teruyama, R. Localisation of 11beta-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 2 in Mineralocorticoid Receptor Expressing Magnocellular Neurosecretory Neurones of the Rat Supraoptic and Paraventricular Nuclei. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2015, 27, 835–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, N.G.; Webster, N.A.; Cruz-Topete, D. Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis Modulation of Glucocorticoids in the Cardiovascular System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, P.T.; McNally, M.; Funder, J.W. Nuclear localization of type 1 aldosterone binding sites in steroid-unexposed GH3 cells. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1986, 13, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, W.A.; Goldin, A.L.; Waxman, S.G. International Union of Pharmacology. XLVII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated sodium channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojilkovic, S.S.; Tabak, J.; Bertram, R. Ion channels and signaling in the pituitary gland. Endocr. Rev. 2010, 31, 845–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Lo, Y.C.; Peng, H.; Hsu, T.I.; Wu, S.N. Effects of ranolazine, a novel anti-anginal drug, on ion currents and membrane potential in pituitary tumor GH(3) cells and NG108-15 neuronal cells. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 110, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, Y.C.; Tseng, Y.T.; Liu, C.M.; Wu, B.N.; Wu, S.N. Actions of KMUP-1, a xanthine and piperazine derivative, on voltage-gated Na(+) and Ca(2+) -activated K(+) currents in GH3 pituitary tumour cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 5110–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.N.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, B.S.; Lo, Y.C.; Liu, Y.C. Underlying mechanism of actions of tefluthrin, a pyrethroid insecticide, on voltage-gated ion currents and on action currents in pituitary tumor (GH3) cells and GnRH-secreting (GT1-7) neurons. Toxicology 2009, 258, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.T.; Wu, S.N. Activation of voltage-gated sodium current and inhibition of erg-mediated potassium current caused by telmisartan, an antagonist of angiotensin II type-1 receptor, in HL-1 atrial cardiomyocytes. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2018, 45, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, E.C.; Wu, S.N.; Lo, Y.C.; Su, K. Differential regulation of tefluthrin and telmisartan on the gating charges of INa activation and inactivation as well as on resurgent and persistent INa in a pituitary cell line (GH3). Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 285, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, M.C.; Wu, S.N.; Huang, C.W. Telmisartan, an Antagonist of Angiotensin II Receptors, Accentuates Voltage-Gated Na(+) Currents and Hippocampal Neuronal Excitability. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Yu, C.; Yue, S.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhao, M. Enantioselectivity in endocrine disrupting effects of four cypermethrin enantiomers based on in vitro models. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, C.M.; Bezanilla, F. Currents related to movement of the gating particles of the sodium channels. Nature 1973, 242, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheets, M.F.; Fozzard, H.A.; Hanck, D.A. Important Role of Asparagines in Coupling the Pore and Votage-Sensor Domain in Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. Biophys. J. 2015, 109, 2277–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Villalba-Galea, C.A. Hysteresis in voltage-gated channels. Channels Austin 2017, 11, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalba-Galea, C.A.; Chiem, A.T. Hysteretic Behavior in Voltage-Gated Channels. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 579596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.T.; Liu, P.Y.; Gao, Z.H.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, W.K.; Wu, S.N. Evidence for the effectiveness of remdesivir (GS-5734), a nucleoside-analog antiviral drug in the inhibition of IKM or IK(DR) and in the stimulation of IMEP. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, L.; Zhang, Y. Effects of an estrogen receptor antagonist on proliferation, prolactin secretion and growth factor expression in the MMQ pituitary prolactinoma cell line. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 18, 1694–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.H.; So, E.C.; Liu, Y.C.; Wu, S.N. Glucocorticoids stimulate the activity of large-conductance Ca2+ -activated K+ channels in pituitary GH3 and AtT-20 cells via a non-genomic mechanism. Steroids 2006, 71, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, T.; Jo, T.; Meguro, K.; Oonuma, H.; Ma, J.; Kubota, N.; Imuta, H.; Takano, H.; Iida, H.; Nagase, T.; et al. Effect of dexamethasone on voltage-gated Na+ channel in cultured human bronchial smooth muscle cells. Life Sci. 2008, 82, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Sanchez, E.; Gomez-Sanchez, C.E. The multifaceted mineralocorticoid receptor. Compr. Physiol. 2014, 4, 965–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmer, C.; Spencer, K.A. Modifications of glucocorticoid receptors mRNA expression in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in response to early-life stress in female Japanese quail. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2014, 26, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.T.; Wu, S.N. Effectiveness of columbianadin, a bioactive coumarin derivative, in perturbing transient and persistent INa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Furuie, H.; Shimizu, T.; Miyazaki, A.; Kobayashi, F.; Ishizuka, H. Single- and multiple-dose escalation study to assess pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of oral esaxerenone in healthy Japanese subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 1821–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankaranarayanan, S.; Simasko, S.M. A role for a background sodium current in spontaneous action potentials and secretion from rat lactotrophs. Am. J. Physiol. 1996, 271, C1927–C1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, K.; Matsushima, M.; Yamamoto, F.; Takamiya, Y.; Okuda, T.; Shirai, K.; Okamura, K.; Urata, H. A Patient with Bilateral Primary Aldosteronism Refractory to Oral Eplerenone Who Responded to Esaxerenone with Increased Renin Activity. Am. J. Case Rep. 2020, 21, e920615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghatage, T.; Goyal, S.G.; Dhar, A.; Bhat, A. Novel therapeutics for the treatment of hypertension and its associated complications: Peptide- and nonpeptide-based strategies. Hypertens. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, S.; Yeung, S.Y.; Prestwich, S.; Pucovsky, V.; Greenwood, I. Electrophysiological and molecular identification of voltage-gated sodium channels in murine vascular myocytes. J. Physiol. 2005, 568, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meguro, K.; Iida, H.; Takano, H.; Morita, T.; Sata, M.; Nagai, R.; Nakajima, T. Function and role of voltage-gated sodium channel NaV1.7 expressed in aortic smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2009, 296, H211–H219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berra-Romani, R.; Blaustein, M.P.; Matteson, D.R. TTX-sensitive voltage-gated Na+ channels are expressed in mesenteric artery smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol 2005, 289, H137–H145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Forfia, P.; Vaidya, A.; Mazurek, J.A.; Park, M.H.; Ramani, G.; Chan, S.Y.; Waxman, A.B. Ranolazine Improves Right Ventricular Function in Patients With Precapillary Pulmonary Hypertension: Results From a Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Card. Fail. 2021, 27, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega, A.V.; Espinosa, J.L.; Lopez-Dominguez, A.M.; Lopez-Santiago, L.F.; Navarrete, A.; Cota, G. L-type calcium channel activation up-regulates the mRNAs for two different sodium channel alpha subunits (Nav1.2 and Nav1.3) in rat pituitary GH3 cells. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2003, 116, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amazit, L.; Le Billan, F.; Kolkhof, P.; Lamribet, K.; Viengchareun, S.; Fay, M.R.; Khan, J.A.; Hillisch, A.; Lombes, M.; Rafestin-Oblin, M.E.; et al. Finerenone Impedes Aldosterone-dependent Nuclear Import of the Mineralocorticoid Receptor and Prevents Genomic Recruitment of Steroid Receptor Coactivator-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 21876–21889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, H.; Ito, S.; Rakugi, H.; Okuda, Y.; Nishioka, S. Efficacy and safety of dosage-escalation of low-dosage esaxerenone added to a RAS inhibitor in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes and albuminuria: A single-arm, open-label study. Hypertens. Res. 2019, 42, 1572–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamoto, K.; Ando, K.; Fujita, T.; Hasebe, N.; Higaki, J.; Horiuchi, M.; Imai, Y.; Imaizumi, T.; Ishimitsu, T.; Ito, M.; et al. The Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension (JSH 2014). Hypertens. Res. 2014, 37, 253–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, A.S.; Rafiq, K.; Kobara, H.; Masaki, T.; Nakano, D.; Nishiyama, A. Effect of a novel nonsteroidal selective mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, esaxerenone (CS-3150), on blood pressure and renal injury in high salt-treated type 2 diabetic mice. Hypertens. Res. 2019, 42, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, W.-T.; Wu, S.-N. Characterization of Direct Perturbations on Voltage-Gated Sodium Current by Esaxerenone, a Nonsteroidal Mineralocorticoid Receptor Blocker. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9050549
Chang W-T, Wu S-N. Characterization of Direct Perturbations on Voltage-Gated Sodium Current by Esaxerenone, a Nonsteroidal Mineralocorticoid Receptor Blocker. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(5):549. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9050549
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Wei-Ting, and Sheng-Nan Wu. 2021. "Characterization of Direct Perturbations on Voltage-Gated Sodium Current by Esaxerenone, a Nonsteroidal Mineralocorticoid Receptor Blocker" Biomedicines 9, no. 5: 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9050549
APA StyleChang, W.-T., & Wu, S.-N. (2021). Characterization of Direct Perturbations on Voltage-Gated Sodium Current by Esaxerenone, a Nonsteroidal Mineralocorticoid Receptor Blocker. Biomedicines, 9(5), 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9050549




