Influence of Serotonin 5-HT4 Receptors on Responses to Cardiac Stressors in Transgenic Mouse Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Transgenic Mice
2.2. Contraction Studies of the Atrium
2.3. Contraction Studies of the Ventricle (Langendorff Procedure)
2.4. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
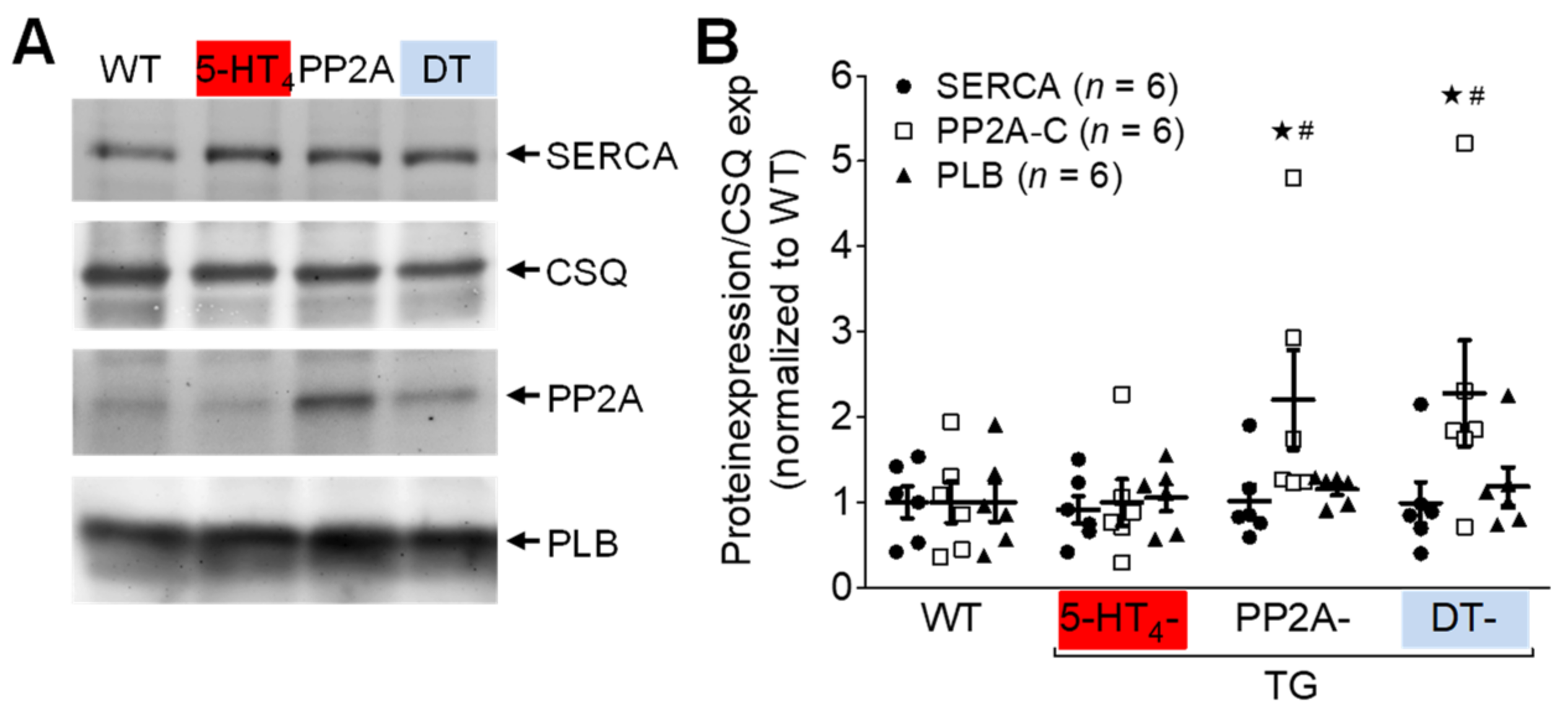
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Echocardiography
2.7. Lipopolysaccharide Treatment
2.8. Data Analysis
2.9. Drugs and Materials
3. Results
3.1. Cardiac Response to LPS-induced Sepsis
3.2. Atrial Response to Hypoxia in Vitro
3.3. Ventricular Response to Ischemia In Vitro
3.4. Influence of 5-HT4 Receptors on a Genetically Induced Hypertrophy
4. Discussion
4.1. Lipopolysaccharide-Simulated Sepsis
4.2. Ischemia and Hypoxia
4.3. PP2A-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy
4.4. Conclusions, Potential Relevance in Clinical Pharmacology and Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rapport, M.M.; Green, A.A.; Page, I.H. Serum vasoconstrictor, serotonin; chemical inactivation. J. Biol. Chem. 1948, 176, 1237–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baganz, N.L.; Blakely, R.D. A dialogue between the immune system and brain, spoken in the language of serotonin. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2013, 4, 48–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Erspamer, V.; Ottolenghi, A. Antidiuretic action of enteramine. Experientia 1950, 6, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shajib, M.S.; Khan, W.I. The role of serotonin and its receptors in activation of immune responses and inflammation. Acta Physiol. 2015, 213, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muma, N.A.; Mi, Z. Serotonylation and Transamidation of Other Monoamines. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, S. Role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in platelet thrombus formation and mechanisms of inhibition of thrombus formation by 5-hydroxytryptamine2A antagonists in rabbits. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 1995, 330, 297–308. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, J.; Hofmann, B.; Gergs, U. Production and Function of Serotonin in Cardiac Cells. In Serotonin—A Chemical Messenger between All Types of Living Cells; Shad, K.F., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pönicke, K.; Gergs, U.; Buchwalow, I.B.; Hauptmann, S.; Neumann, J. On the presence of serotonin in mammalian cardiomyocytes. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 365, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, S.W. Oh, The places you’ll go! My many colored serotonin (apologies to Dr. Seuss). Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2016, 311, H1225–H1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, S.W.; Morrison, S.F.; Davis, R.P.; Barman, S.M. Serotonin and blood pressure regulation. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 359–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brattelid, T.; Qvigstad, E.; Lynham, J.A.; Molenaar, P.; Aass, H.; Geiran, O.; Skomedal, T.; Osnes, J.-B.; Levy, F.O.; Kaumann, A.J. Functional serotonin 5-HT4 receptors in porcine and human ventricular myocardium with increased 5-HT4 mRNA in heart failure. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2004, 370, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, L.; Kaumann, A.J. A 5-HT4-like receptor in human left atrium. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1992, 345, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, L.; Lynham, J.A.; Bond, B.; del Monte, F.; Harding, S.E.; Kaumann, A.J. Sensitization of human atrial 5-HT4 receptors by chronic beta-blocker treatment. Circulation 1995, 92, 2526–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, R.; Cerbai, E.; Calamai, G.; Alajmo, F.; Borgioli, A.; Braconi, L.; Cassai, M.; Montesi, G.F.; Mugelli, A. Effect of 5-HT4 receptor stimulation on the pacemaker current If in human isolated atrial myocytes. Cardiovasc. Res. 1998, 40, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Workman, A.J.; Rankin, A.C. Serotonin, I(f) and human atrial arrhythmia. Cardiovasc. Res. 1998, 40, 436–437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaumann, A.J. Piglet sinoatrial 5-HT receptors resemble human atrial 5-HT4-like receptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1990, 342, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, D.; Clarke, D.E.; Fozard, J.R.; Hartig, P.R.; Martin, G.R.; Mylecharane, E.J.; Saxena, P.R.; Humphrey, P.P. International Union of Pharmacology classification of receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (Serotonin). Pharmacol. Rev. 1994, 46, 157–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaumann, A.J. Do human atrial 5-HT4 receptors mediate arrhythmias? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1994, 15, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergs, U.; Neumann, J.; Simm, A.; Silber, R.-E.; Remmers, F.O.; Läer, S. Phosphorylation of phospholamban and troponin I through 5-HT4 receptors in the isolated human atrium. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2009, 379, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergs, U.; Baumann, M.; Böckler, A.; Buchwalow, I.B.; Ebelt, H.; Fabritz, L.; Hauptmann, S.; Keller, N.; Kirchhof, P.; Klöckner, U.; et al. Cardiac overexpression of the human 5-HT4 receptor in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2010, 299, H788–H798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gergs, U.; Böckler, A.; Ebelt, H.; Hauptmann, S.; Keller, N.; Otto, V.; Pönicke, K.; Schmitz, W.; Neumann, J. Human 5-HT₄receptor stimulation in atria of transgenic mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2013, 386, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gergs, U.; Fritsche, J.; Fabian, S.; Christ, J.; Neumann, J. Desensitization of the human 5-HT4 receptor in isolated atria of transgenic mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2017, 390, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, N.; Dhein, S.; Neumann, J.; Gergs, U. Cardiovascular effects of cisapride and prucalopride on human 5-HT4 receptors in transgenic mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2018, 391, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gergs, U.; Gerigk, T.; Wache, H.; Neumann, J. β-Adrenergic Function is Attenuated in Double Transgenic Mice Overexpressing 5-HT4 Receptors and PP2A in the Heart. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 1069-6. [Google Scholar]
- Gerigk, T.; Gergs, U.; Neumann, J. In 5-HT4-receptor overexpressing mice, diastolic function is partially preserved in a model of sepsis. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2016, 389, S27–S28. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, J.; Gerigk, T.; Gergs, U.; Wache, H. Potentially beneficial effects of coexpression of 5HT4 receptors and PP2A in the mammalian heart. Eur. Phosphatases Cell Fates Decis. 2017, 144, P60. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, J.; Gerigk, T.; Mahnkopf, M.; Edler, H.; Gergs, U. Physiological and biochemical alterations of experimental systolic heart failure in mice overexpressing a serotonin receptor in the heart. Acta Physiol. 2017, 221, 114. [Google Scholar]
- Röttger, C.; Gergs, U.; Schmidbaur, C.T.; Neumann, J. Altered signaling and gene expression after ischemia/reperfusion in 5-HT4 receptor overexpressing mouse hearts. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2019, 392, S42. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidbaur, C.T.; Mißlinger, N.; Gergs, U.; Neumann, J. Ischemia and reperfusion in the mouse heart overexpressing the 5-HT4 receptor. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2019, 392, S41. [Google Scholar]
- Wittschier, J.; Gergs, U.; Neumann, J. Influence of 5-HT4-receptors on the impact of hypoxia in the mouse heart. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2019, 392, S42. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council; Division on Earth and Life Studies; Institute for Laboratory Animal Research; Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gergs, U.; Boknik, P.; Buchwalow, I.; Fabritz, L.; Matus, M.; Justus, I.; Hanske, G.; Schmitz, W.; Neumann, J. Overexpression of the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 2A impairs cardiac function. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 40827–40834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gergs, U.; Bernhardt, G.; Buchwalow, I.B.; Edler, H.; Fröba, J.; Keller, M.; Kirchhefer, U.; Köhler, F.; Mißlinger, N.; Wache, H.; et al. Initial Characterization of Transgenic Mice Overexpressing Human Histamine H2 Receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 369, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neumann, J.; Boknik, P.; DePaoli-Roach, A.A.; Field, L.J.; Rockman, H.A.; Kobayashi, Y.M.; Kelley, J.S.; Jones, L.R. Targeted overexpression of phospholamban to mouse atrium depresses Ca2+ transport and contractility. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1998, 30, 1991–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boknik, P.; Drzewiecki, K.; Eskandar, J.; Gergs, U.; Hofmann, B.; Treede, H.; Grote-Wessels, S.; Fabritz, L.; Kirchhof, P.; Fortmüller, L.; et al. Evidence for Arrhythmogenic Effects of A2A-Adenosine Receptors. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhefer, U.; Hammer, E.; Heinick, A.; Herpertz, T.; Isensee, G.; Müller, F.U.; Neumann, J.; Schulte, K.; Seidl, M.D.; Boknik, P.; et al. Chronic β-adrenergic stimulation reverses depressed Ca handling in mice overexpressing inhibitor-2 of protein phosphatase 1. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2018, 125, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergs, U.; Jahn, T.; Werner, F.; Köhler, C.; Köpp, F.; Großmann, C.; Neumann, J. Overexpression of protein phosphatase 5 in the mouse heart: Reduced contractility but increased stress tolerance—Two sides of the same coin? PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergs, U.; Rothkirch, D.; Hofmann, B.; Treede, H.; Robaye, B.; Simm, A.; Müller, C.E.; Neumann, J. Mechanism underlying the contractile activity of UTP in the mammalian heart. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 830, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gergs, U.; Fahrion, C.M.; Bock, P.; Fischer, M.; Wache, H.; Hauptmann, S.; Schmitz, W.; Neumann, J. Evidence for a functional role of calsequestrin 2 in mouse atrium. Acta Physiol. 2017, 219, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhefer, U.; Baba, H.A.; Kobayashi, Y.M.; Jones, L.R.; Schmitz, W.; Neumann, J. Altered function in atrium of transgenic mice overexpressing triadin 1. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2002, 283, H1334–H1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asatryan, B.; Yee, L.; Ben-Haim, Y.; Dobner, S.; Servatius, H.; Roten, L.; Tanner, H.; Crotti, L.; Skinner, J.R.; Remme, C.A.; et al. Sex-Related Differences in Cardiac Channelopathies: Implications for Clinical Practice. Circulation 2021, 143, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connelly, P.J.; Azizi, Z.; Alipour, P.; Delles, C.; Pilote, L.; Raparelli, V. The importance of Gender to Understand Sex Differences in Cardiovascular Disease. Can. J. Cardiol. 2021, 37, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, K.M.; Moon, R.J. Quantitative analysis of serotonin biosynthesis in endotoxemia. Infect. Immun. 1974, 10, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alvarez, S.; Vico, T.; Vanasco, V. Cardiac dysfunction, mitochondrial architecture, energy production, and inflammatory pathways: Interrelated aspects in endotoxemia and sepsis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 81, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.-J.; Liu, H.; Wu, C.; Xue, K. Effect of sepsis on the action potential and cardiac serotonin response in rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 2207–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Wu, C.; Liu, H. Tropisetron inhibits sepsis by repressing hyper-inflammation and regulating the cardiac action potential in rat models. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bi, J.; Liu, S.; Pang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Wang, S.; Liu, C. 5-HT Drives Mortality in Sepsis Induced by Cecal Ligation and Puncture in Mice. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 6374283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mauler, M.; Herr, N.; Schoenichen, C.; Witsch, T.; Marchini, T.; Härdtner, C.; Koentges, C.; Kienle, K.; Ollivier, V.; Schell, M.; et al. Platelet Serotonin Aggravates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via Neutrophil Degranulation. Circulation 2019, 139, 918–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, C.-K.; Zhan, D.-Y.; Akiyama, T.; Inagaki, T.; Shishido, T.; Shirai, M.; Pearson, J.T. Myocardial interstitial levels of serotonin and its major metabolite 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid during ischemia-reperfusion. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2017, 312, H60–H67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shimizu, Y.; Minatoguchi, S.; Hashimoto, K.; Uno, Y.; Arai, M.; Wang, N.; Chen, X.; Lu, C.; Takemura, G.; Shimomura, M.; et al. The role of serotonin in ischemic cellular damage and the infarct size-reducing effect of sarpogrelate, a 5-hydroxytryptamine-2 receptor blocker, in rabbit hearts. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 40, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandra, M.; Gupta, V.; Johri, A.K.; Misra, R.; Kumar, A.; Gujrati, V.; Shanker, K. Serotonergic mechanisms in heart failure. Indian Heart J. 1994, 46, 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, A.C.; Brazin, J.A.; Morrey, C.; Silver, R.B.; Levi, R. Targeting cardiac mast cells: Pharmacological modulation of the local renin-angiotensin system. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 3744–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, E.K.; Schmitz, J.M.; Benedict, C.R.; Malloy, C.R.; Willerson, J.T.; Dehmer, G.J. Transcardiac serotonin concentration is increased in selected patients with limiting angina and complex coronary lesion morphology. Circulation 1989, 79, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meissner, A.; Lüss, I.; Rolf, N.; Boknik, P.; Kirchhefer, U.; Kehm, V.; Knapp, J.; Linck, B.; Lüss, H.; Müller, F.U.; et al. The early response genes c-jun and HSP-70 are induced in regional cardiac stunning in conscious mammals. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2000, 119, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lüss, H.; Meissner, A.; Rolf, N.; van Aken, H.; Bokník, P.; Kirchhefer, U.; Knapp, J.; Läer, S.; Linck, B.; Lüss, I.; et al. Biochemical mechanism(s) of stunning in conscious dogs. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 279, H176–H184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergeeva, I.A.; Hooijkaas, I.B.; van der Made, I.; Jong, W.M.C.; Creemers, E.E.; Christoffels, V.M. A transgenic mouse model for the simultaneous monitoring of ANF and BNP gene activity during heart development and disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 101, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gergs, U.; Kirchhefer, U.; Bergmann, F.; Künstler, B.; Mißlinger, N.; Au, B.; Mahnkopf, M.; Wache, H.; Neumann, J. Characterization of Stressed Transgenic Mice Overexpressing H2-Histamine Receptors in the Heart. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2020, 374, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Ma, C.-T.; Gu, H.-L.; Shi, L.; Tian, X.-T.; Xu, W.-Q. Sitagliptin improves cardiac function after myocardial infarction through activation of autophagy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 8973–8983. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keppner, L.; Heinrichs, M.; Rieckmann, M.; Demengeot, J.; Frantz, S.; Hofmann, U.; Ramos, G. Antibodies aggravate the development of ischemic heart failure. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 315, H1358–H1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Möllmann, H.; Nef, H.M.; Kostin, S.; Dragu, A.; Maack, C.; Weber, M.; Troidl, C.; Rolf, A.; Elsässer, A.; Böhm, M.; et al. Ischemia triggers BNP expression in the human myocardium independent from mechanical stress. Int. J. Cardiol. 2010, 143, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerniway, R.J.; Morrison, R.R.; Byford, A.M.; Lankford, A.R.; Headrick, J.P.; van Wylen, D.G.L.; Matherne, G.P. A1 adenosine receptor overexpression decreases stunning from anoxia-reoxygenation: Role of the mitochondrial K(ATP) channel. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2002, 97, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerkowski, H.R.; Broede, A.; Kunde, K.; Hillemann, S.; Schäfer, E.; Vogelsang, M.; Michel, M.C.; Brodde, O.E. Comparison of the positive inotropic effects of serotonin, histamine, angiotensin II, endothelin and isoprenaline in the isolated human right atrium. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1993, 347, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouadid, H.; Albat, B.; Nargeot, J. Calcium currents in diseased human cardiac cells. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1995, 25, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brattelid, T.; Kvingedal, A.M.; Krobert, K.A.; Andressen, K.W.; Bach, T.; Hystad, M.E.; Kaumann, A.J.; Levy, F.O. Cloning, pharmacological characterisation and tissue distribution of a novel 5-HT4 receptor splice variant, 5-HT4(i). Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2004, 369, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Läer, S.; Remmers, F.; Scholz, H.; Stein, B.; Müller, F.U.; Neumann, J. Receptor mechanisms involved in the 5-HT-induced inotropic action in the rat isolated atrium. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 123, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qvigstad, E.; Brattelid, T.; Sjaastad, I.; Andressen, K.W.; Krobert, K.A.; Birkeland, J.A.; Sejersted, O.M.; Kaumann, A.J.; Skomedal, T.; Osnes, J.-B.; et al. Appearance of a ventricular 5-HT4 receptor-mediated inotropic response to serotonin in heart failure. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 65, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kjekshus, J.K.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Gullestad, L.; Køber, L.; Edvardsen, T.; Olsen, I.C.; Sjaastad, I.; Qvigstad, E.; Skomedal, T.; Osnes, J.-B.; et al. Effect of piboserod, a 5-HT4 serotonin receptor antagonist, on left ventricular function in patients with symptomatic heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2009, 11, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, S.; Stein, B.; Eschenhagen, T.; Mende, U.; Neumann, J.; Schmitz, W.; Krause, E.G.; Karczewski, P.; Scholz, H. Protein phosphorylation in isolated trabeculae from nonfailing and failing human hearts. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1996, 157, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, J.; Eschenhagen, T.; Jones, L.R.; Linck, B.; Schmitz, W.; Scholz, H.; Zimmermann, N. Increased expression of cardiac phosphatases in patients with end-stage heart failure. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1997, 29, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, A.R. Ryanodine receptors/calcium release channels in heart failure and sudden cardiac death. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2001, 33, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebigil, C.G.; Hickel, P.; Messaddeq, N.; Vonesch, J.L.; Douchet, M.P.; Monassier, L.; György, K.; Matz, R.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Manivet, P.; et al. Ablation of serotonin 5-HT(2B) receptors in mice leads to abnormal cardiac structure and function. Circulation 2001, 103, 2973–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaffré, F.; Callebert, J.; Sarre, A.; Etienne, N.; Nebigil, C.G.; Launay, J.-M.; Maroteaux, L.; Monassier, L. Involvement of the serotonin 5-HT2B receptor in cardiac hypertrophy linked to sympathetic stimulation: Control of interleukin-6, interleukin-1beta, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha cytokine production by ventricular fibroblasts. Circulation 2004, 110, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]











Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gergs, U.; Gerigk, T.; Wittschier, J.; Schmidbaur, C.T.; Röttger, C.; Mahnkopf, M.; Edler, H.; Wache, H.; Neumann, J. Influence of Serotonin 5-HT4 Receptors on Responses to Cardiac Stressors in Transgenic Mouse Models. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9050569
Gergs U, Gerigk T, Wittschier J, Schmidbaur CT, Röttger C, Mahnkopf M, Edler H, Wache H, Neumann J. Influence of Serotonin 5-HT4 Receptors on Responses to Cardiac Stressors in Transgenic Mouse Models. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(5):569. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9050569
Chicago/Turabian StyleGergs, Ulrich, Timo Gerigk, Jonas Wittschier, Constanze T. Schmidbaur, Clara Röttger, Mareen Mahnkopf, Hanna Edler, Hartmut Wache, and Joachim Neumann. 2021. "Influence of Serotonin 5-HT4 Receptors on Responses to Cardiac Stressors in Transgenic Mouse Models" Biomedicines 9, no. 5: 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9050569
APA StyleGergs, U., Gerigk, T., Wittschier, J., Schmidbaur, C. T., Röttger, C., Mahnkopf, M., Edler, H., Wache, H., & Neumann, J. (2021). Influence of Serotonin 5-HT4 Receptors on Responses to Cardiac Stressors in Transgenic Mouse Models. Biomedicines, 9(5), 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9050569





