Impact of Environmental and Pharmacologic Changes on the Upper Gastrointestinal Microbiome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Esophagus
3.1.1. Differences in Microbiome for Various Esophageal Diseases
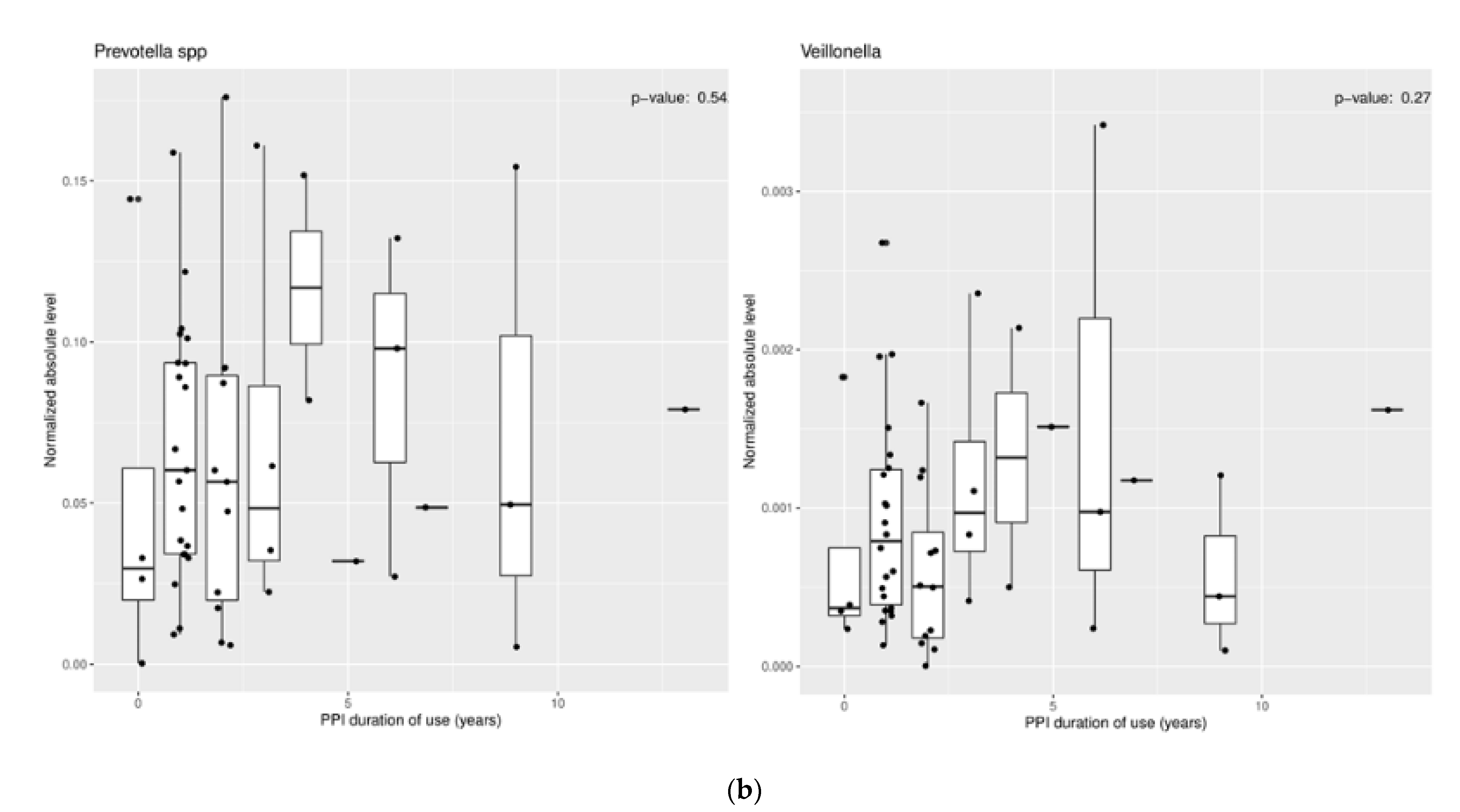
3.1.2. Effect of Proton Pump Inhibitors
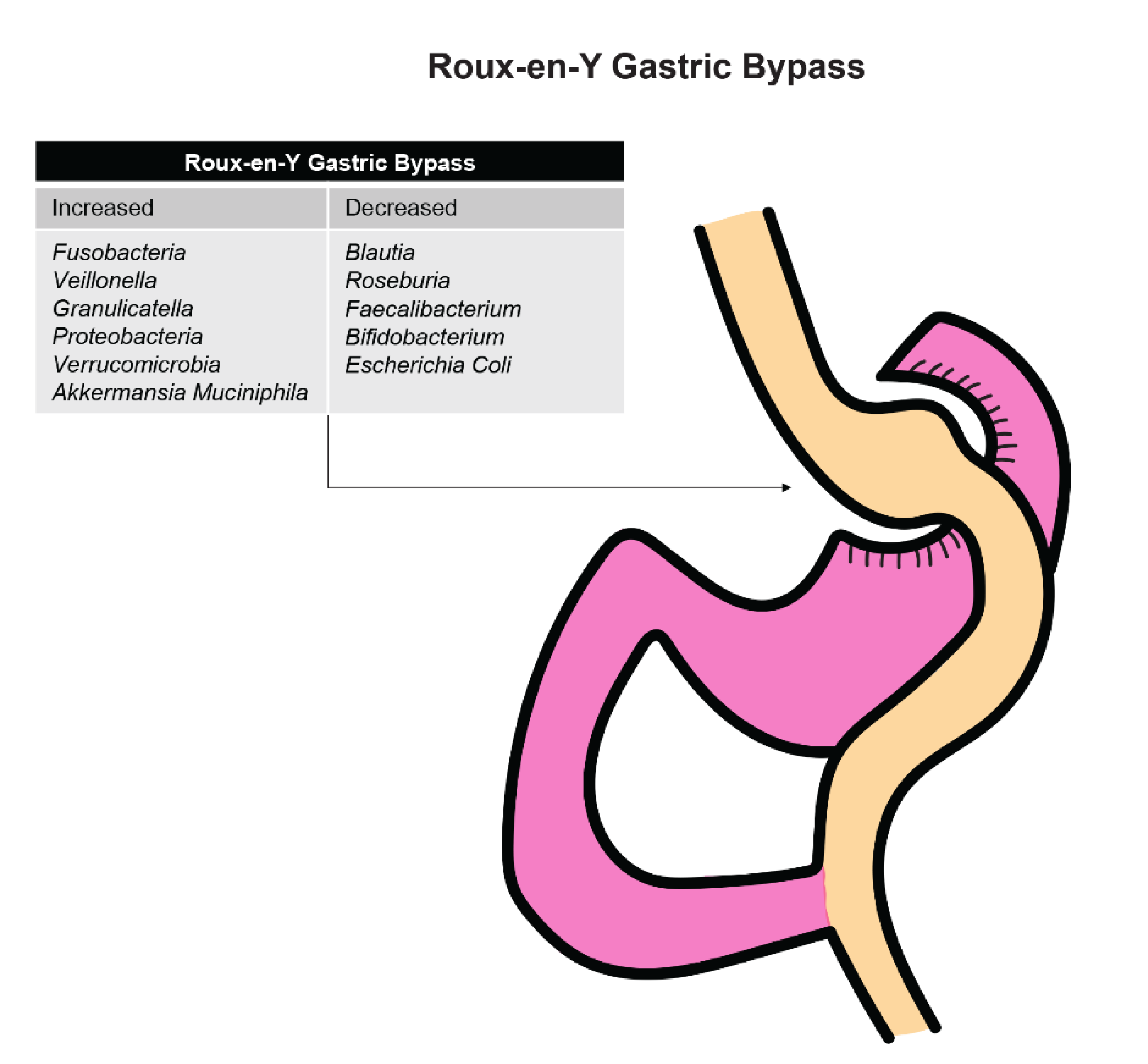
3.1.3. Effect of Bariatric Surgery
3.1.4. Effect of Antibiotics
3.1.5. Impact of Environmental Differences (i.e., Rural vs. Urban)
3.2. Stomach
3.2.1. Differences in Microbiome for Various Diseases of the Stomach
3.2.2. Effect of Proton Pump Inhibitors
3.2.3. Effect of Bariatric Surgery
3.3. Duodenum
3.3.1. Differences in Microbiome with Duodenal Ulcer Disease
3.3.2. Effect of Proton Pump Inhibitors
3.4. Future Directions
3.5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ursell, L.K.; Metcalf, J.L.; Parfrey, L.W.; Knight, R. Defining the human microbiome. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okereke, I.; Hamilton, C.; Wenholz, A.; Jala, V.; Giang, T.; Reynolds, S.; Miller, A.; Pyles, R. Associations of the microbiome and esophageal disease. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 1588–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazmanian, S.K.; Round, J.L.; Kasper, D.L. A Microbial Symbiosis Factor Prevents Intestinal Inflammatory Disease. Nature 2008, 453, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MacFarlane, S.; Furrie, E.; MacFarlane, G.T.; Dillon, G.T. Microbial Colonization of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract in Patients with Barrett’s Esophagus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okereke, I.; Hamilton, C.; Reep, G.; Krill, T.; Booth, A.; Ghouri, Y.; Jala, V.; Andersen, C.; Pyles, R. Microflora composition in the gastrointestinal tract in patients with Barrett’s esophagus. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 1581–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, E.J.; Compres, G.; Freedberg, D.E.; Khiabanian, H.; Nobel, Y.R.; Stump, S.; Uhlemann, A.; Lightdale, C.J.; Abrams, J.A. Alterations to the Esophageal Microbiome Associated with Progression from Barrett’s Esophagus to Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 1687–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Lu, X.; Nossa, C.W.; Francois, F.; Peek, R.M.; Pei, Z. Inflammation and intestinal metaplasia of the distal esophagus are associated with alterations in the microbiome. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clarrett, D.M.; Hachem, C. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD). Mo. Med. 2018, 115, 214–218. [Google Scholar]
- Mennini, M.; Tambucci, R.; Riccardi, C.; Rea, F.; DeAngelis, P.; Fiocchi, A.; Assa’ad, A. Eosinophilic esophagitis and microbiota: State of the art. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 595762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pan, Z. Influence of microbiota on immunity and immunotherapy for gastric and esophageal cancers. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2020, 8, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chaudhary, N.; Baghdadi, J.; Pei, Z. Microbiome in reflux disorders and esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer J. 2014, 20, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, J.; Guo, L.; Liu, J.J.; Zhao, H.P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.H. Alteration of the esophageal microbiota in Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 2149–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, D.R.F.; Walker, A.W.; O’Donovan, M.; Parkhill, J.; Fitzgerald, R.C. A non-endoscopic device to sample the oesophageal microbiota: A case-control study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, B.A.; Wu, J.; Pei, Z.; Yang, L.; Purdue, M.P.; Freedman, N.D.; Jacobs, E.J.; Gapstur, S.M.; Hayes, R.B.; Ahn, J. Oral Microbiome Composition Reflects Prospective Risk for Esophageal Cancers. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 6777–6787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Czesnikiewicz-Guzik, M.; Loster, B.; Bielanski, W.; Guzki, T.J.; Konturek, P.C.; Zapala, J.; Konturek, S.J. Implications of Oral Helicobacter Pylori for the Outcome of Its Gastric Eradication Therapy. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 41, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Francois, F.; Pei, Z. Molecular pathways: Pathogenesis and clinical implications of microbiome alteration in esophagitis and Barrett esophagus. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 2138–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baba, Y.; Iwatsuki, M.; Yoshida, N.; Watanabe, M.; Baba, H. Review of the gut microbiome and esophageal cancer: Pathogenesis and potential clinical implications. Ann. Gastroenterol. Surg. 2017, 1, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, D.M.; Narasimhan, S.; Michaylira, C.Z.; Wang, M.L. TLR3-mediated NF-KB signaling in human esophageal epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 297, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klump, B.; Hsieh, C.J.; Holzmann, K.; Borchard, F.; Gaco, V.; Greschniok, A.; Eckardt, V.F.; Bettendorf, U.; Gregor, M.; Porschen, R. Diagnostic Significance of Nuclear p53 Expression in the Surveillance of Barrett’s Esophagus—A Longitudinal Study. Z. Gastroenterol. 1999, 37, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Parenti, A.; Leo, G.; Porzionato, A.; Zaninotto, G.; Rosato, A.; Ninfo, V. Expression of Survivin, p53 and caspase 3 in Barrett’s Esophagus Carcinogenesis. Hum. Pathol. 2006, 37, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwalt, D.M.; Duong, C.; Smyth, G.K.; Ciavarella, M.L.; Thompson, N.J.; Tiang, T.; Murray, W.K.; Thomas, R.J.; Phillips, W.A. Gene Expression Profiling of Esophageal Cancer: Comparative Analysis of Barrett’s Esophagus, Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer. 2007, 120, 1914–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cass, S.; Hamilton, C.; Miller, A.; Jupiter, D.; Khanipov, K.; Booth, A.; Pyles, R.; Krill, T.; Reep, G.; Okereke, I.C. Novel ex-vivo model to examine the mechanism and relationship of esophageal microbiota and disease. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackett, K.L.; Siddhi, S.S.; Cleary, S.; Steed, H.; Miller, M.H.; Macfarlane, S.; Macfarlane, G.T.; Dillon, J.F. Oesophageal bacterial biofilm changes in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease, Barrett’s and oesophageal carcinoma: Association or causality? Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 37, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, J.M.; Pandit, S. Eosinophilic Esophagitis; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, J.K.; Fang, R.; Wagner, B.D.; Choe, H.N.; Kelly, C.J.; Schroeder, S.; Moore, W.; Stevens, M.J.; Yeckes, A.; Amsden, K. Esophageal microbiome in eosinophilic esophagitis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, A.J.; Hoffmann, C.; Muir, A.B.; Dods, K.K.; Spergel, J.M.; Bushman, F.D.; Wang, M. Inflammation-associated microbiota in pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. Microbiome 2015, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guajardo, J.R.; Zegarra-Bustamante, M.A.; Brooks, E.G. Does Aeroallergen Sensitization Cause or Contribute to Eosinophilic Esophagitis? Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 55, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-González, D.; Franco, J.; Navarro-Ortega, D.; Muñoz, C.; Martí-Obiol, R.; Borrás-Salvador, R. Achalasia and mycobacterium goodii pulmonary infection. Pediatric Infect. Dis. J. 2011, 30, 447–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.J.; Tu, L.X.; Yu, C.; Zheng, X.L.; Hong, J.B.; Lu, N.H. Achalasia secondary to cardial tuberculosis caused by AIDS. J. Dig. Dis. 2015, 16, 752–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Clarke, J.O. Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPI); StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, M.A.; Goodrich, J.K.; Maxan, M.E.; Freedberg, D.E.; Abrams, J.A.; Poole, A.C.; Sutter, J.L.; Welter, D.; Ley, R.E.; Bell, J.T.; et al. Proton pump inhibitors alter the composition of the gut microbiota. Gut 2016, 65, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosen, R.; Amirault, J.; Liu, H.; Mitchell, P.; Hu, L.; Khatwa, U.; Onderdonk, A. Changes in gastric and lung microflora with acid suppression: Acid suppression and bacterial growth. JAMA Pediatr. 2014, 168, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amir, I.; Konikoff, F.M.; Oppenheim, M.; Gophna, U.; Half, E.E. Gastric microbiota is altered in oesophagitis and Barrett’s oesophagus and further modified by proton pump inhibitors. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2905–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasnim, S.; Miller, A.L.; Jupiter, D.C.; Hamilton, C.F.; Reep, G.L.; Krill, T.S.; Pyles, R.B.; Okereke, I.C. Effects of proton pump inhibitor use on the esophageal microbial community. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020, 20, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagoonee, S.; Pellicano, R. Helicobacter pylori: Molecular basis for colonization and survival in gastric environment and resistance to antibiotics. A short review. Infect. Dis. 2019, 51, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alba, C.; Blanco, A.; Alarcon, T. Antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 30, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonezawa, H.; Osaki, T.; Kamiya, S. Structural aspects of Helicobacter pylori antibiotic resistance. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1149, 227–241. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Surathu, A.; Raplee, I.; Chockalingam, A.; Stewart, S.; Walker, L.; Sacks, L.; Patel, V.; Li, Z.; Rouse, R. The effect of antibiotics on the gut microbiome: A metagenomics analysis of microbial shift and gut antibiotic resistance in antibiotic treated mice. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, D.C. Facing a new challenge: The adverse effects of antibiotics on gut microbiota and host immunity. Chin. Med. J. 2019, 132, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weersma, R.K.; Zhernakova, A.; Fu, J. Interaction between drugs and the gut microbiome. Gut 2020, 69, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Yang, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, R.; Jiang, Y. Lower esophageal microbiota species are affected by the eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection using antibiotics. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snider, E.J.; Freedberg, D.E.; Abrams, J.A. Potential Role of the Microbiome in Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 2217–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Filippo, C.; Cavalieri, D.; Di Paola, M.; Ramazzotti, M.; Poullet, J.B.; Massart, S.; Collini, S.; Pieraccini, G.; Lionetti, P. Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14691–14696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munch, N.; Fang, H.; Ingermann, J.; Maurer, H.C.; Anand, A.; Kellner, V.; Sahm, V.; Wiethaler, M.; Baumeister, T.; Wein, F.; et al. High-fat diet accelerates carcinogenesis in a mouse model of Barrett’s esophagus via interleukin 8 and alterations to the gut microbiome. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nesteruk, K.; Spaander, M.; Leeuwenburgh, I.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Fuhler, G.M. Achalasia and associated esophageal cancer risk: What lessons can we learn from the molecular analysis of Barrett’s-associated adenocarcinoma? Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2019, 1872, 188291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.H.; Song, Y.; Wu, W.; Yu, K.; Zhang, G. The gut microbiota, environmental factors, and links to the development of food allergy. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2020, 18, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wu, S.; Zeng, Z.; Fu, Z. Effects of environmental pollutants on gut microbiota. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 222, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.L. Gut reaction: Environmental effects on the human microbiota. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J. Effect of Diet and Gut Environment on the Gastrointestinal Formation of N-nitroso Compounds: A Review. Nitric Oxide 2018, 73, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X.; Ling, Z.; Ji, F. Role of the Gastric Microbiome in Gastric Cancer: From Carcinogenesis to Treatment. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 641322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnareddy, S. The Microbiome in Celiac Disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 48, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chey, W.D.; Kurlander, J.; Eswaran, S. Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Clinical Review. JAMA 2015, 313, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoshima, O.; Nishizawa, T.; Sakitani, K.; Yamakawa, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Yamamichi, N.; Hata, K.; Seto, Y.; Koike, K.; Watanabe, H.; et al. Serum Anti-Helicobacter Pylori Antibody Titer and Its Association with Gastric Nodularity, Atrophy, and Age: A Cross-Sectional Study. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 4061–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardone, G.; Compare, D. The human gastric microbiota: Is it time to rethink the pathogenesis of stomach diseases? United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2015, 3, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.X.; Wong, G.L.; To, K.F.; Wong, V.W.; Lai, L.H.; Chow, D.K.; Lau, J.Y.; Sung, J.L.; Ding, C. Bacterial microbiota profiling in gastritis without Helicobacter pylori infection or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbey, G.; Sproston, E.; Hanafiah, A. Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gastric Microbiota. Euroasian J. Hepatogastroenterol. 2020, 10, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engstrand, L.; Lindberg, M. Helicobacter pylori and the gastric microbiota. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 27, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, L. Detection of gastritis-associated pathogens by culturing of gastric juice and mucosa. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 2214–2220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; He, L.H.; Xiao, D.; Liu, G.; Gu, Y.; Tao, X.; Zhang, J. Bacterial flora concurrent with Helicobacter pylori in the stomach of patients with upper gastrointestinal diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coker, O.O.; Dai, Z.; Nie, Y.; Zhao, G.; Cao, L.; Nakatsu, G.; Wu, W.K.; Wong, S.H.; Chen, Z.; Sung, J.J.; et al. Mucosal microbiome dysbiosis in gastric carcinogenesis. Gut 2018, 67, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eun, C.S.; Kim, B.K.; Han, D.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, K.M.; Choi, B.Y.; Song, K.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, J.F. Differences in gastric mucosal microbiota profiling in patients with chronic gastritis, intestinal metaplasia, and gastric cancer using pyrosequencing methods. Helicobacter 2014, 19, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gerhard, M.; Gao, J.J.; Mejias-Luque, R.; Zhang, L.; Vieth, M.; Ma, J.L.; Bajbouj, M.; Suchanek, S.; et al. Effect of Helicobacter pylori on gastrointestinal microbiota: A population-based study in Linqu, a high-risk area of gastric cancer. Gut 2020, 69, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rastogi, Y.R.; Saini, A.K.; Thakur, V.K.; Saini, R.V. New Insights into Molecular Links Between Microbiota and Gastrointestinal Cancers: A Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorkiewicz, G.; Moschen, A. Gut microbiome: A new player in gastrointestinal disease. Virchows Arch. 2018, 472, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brawner, K.M.; Morrow, C.D.; Smith, P.D. Gastric microbiome and gastric cancer. Cancer J. 2014, 20, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castaño-Rodríguez, N.; Goh, K.L.; Fock, K.M.; Mitchell, H.M.; Kaakoush, N.O. Dysbiosis of the microbiome in gastric carcinogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, R.M.; Pereira-Marques, J.; Pinto-Ribeiro, I.; Costa, J.L.; Carneiro, F.; Carneiro, F.; Machado, J.C.; Figueiredo, C. Gastric microbial community profiling reveals a dysbiotic cancer-associated microbiota. Gut 2018, 67, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saxena, A.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Nandi, S.P. Helicobacter pylori: Perturbation and restoration of gut microbiome. J. Biosci. 2020, 45, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, G.; Rocco, G.; Zaccari, P.; Porowska, B.; Mascellino, M.T.; Severi, C. Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gastric Dysbiosis: Can Probiotics Administration Be Useful to Treat This Condition? Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 2018, 6237239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vergara, D.; Simeone, P.; Damato, M.; Maffia, M.; Lanuti, P.; Trerotola, M. The Cancer Microbiota: EMT and Inflammation as Shared Molecular Mechanisms Associated with Plasticity and Progression. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 1253727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dicksved, J.; Lindberg, M.; Rosenquist, M.; Enroth, H.; Jansson, J.K.; Engstrand, L. Molecular characterization of the stomach microbiota in patients with gastric cancer and in controls. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Gao, X.; Wu, L.; Yan, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Peng, L.; Yu, J.; Sun, G.; Yang, Y. Salivary microbiota for gastric cancer prediction: An exploratory study. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 640309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudmann, D.; Albretsen, J.; Doolan, C.; Gregson, M.; Dray, B.; Sargeant, A.; O’Shea, D.; Kuklyte, J.; Power, A.; Fitzgerald, J. Using deep learning artificial intelligence algorithms to verify N-nitroso-N-methylurea and urethane positive control proliferative changes in Tg-RasH2 mouse carcinogenicity studies. Toxicol. Pathol. 2020, 192623320973986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, F.; Lam, K.; Lau, C.; Ho, K.H.; Kan, Y.H.; Poon, M.Y.; El-Nezami, H.; Sze, E.T. Reduction in biogenic amines in douche fermented by probiotic bacteria. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinasco, K.; Mitchell, H.; Kaakoush, N.; Castano-Rodriguez, N. Microbial carcinogenesis: Lactic acid bacteria in gastric cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2019, 1872, 188309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, M.; Chiu, Y.; Wei, P.; Chiang, C.; Fang, H.; Wei, S. Microbiota and gastrointestinal cancer. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2019, 118, S32–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Yu, X.J.; Zhan, S.H.; Jia, S.; Tian, Z.; Dong, Q. Participation of Microbiota in the Development of Gastric Cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 4948–4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keku, T.; McCoy, A.; Azcarate-Peril, A. Fusobacterium spp. and colorectal cancer: Cause or consequence? Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 506–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhai, J.; Shen, J.; Xie, G.; Wu, J.; He, M.; Gao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, X.; Shen, L. Cancer-associated fibroblasts-derived IL-8 mediates resistance to cisplatin in human gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019, 454, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Xia, J.; Zhu, F.; Xi, Z.; Pan, C.; Gu, L.; Tian, Y. LPS promotes the expression of PD-L1 in gastric cancer cells through NF-kappaB activation. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 9997–10004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aviles-Jimenez, F.; Vazquez-Jimenez, F.; Medrano-Guzman, R.; Mantilla, A.; Torres, J. Stomach microbiota composition varies between patients with non-atrophic gastritis and patients with intestinal type of gastric cancer. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajilic-Stojanovic, M.; Figueiredo, C.; Smet, A.; Hansen, R.; Kupcinskas, J.; Rokkas, T.; Andersen, L.; C Machado, J.; Ianiro, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. Systematic review: Gastric microbiota in health and disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 582–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusselaers, N.; Wahlin, K.; Engstrand, L.; Lagergren, J. Maintenance therapy with proton pump inhibitors and risk of gastric cancer: A nationwide population-based cohort study in Sweden. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e017739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waldum, H.; Sordal, O.; Fossmark, R. Proton pump inhibitors may cause gastric cancer—Clinical consequences. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Tian, B.; Guo, X. Repositioning of proton pump inhibitors in cancer therapy. Cancer ChemoTher. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havu, N.; Mattsson, H.; Ekman, L.; Carlsson, E. Enterochromaffin-like cell carcinoids in the rat gastric mucosa following long-term administration of ranitidine. Digestion 1990, 45, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Dangler, C.; Chen, D.; Goldenring, J.R.; Koh, T.; Raychowdhury, R.; Coffey, R.J.; Ito, S.; Varro, A.; Dockray, G.J.; et al. Synergistic interaction between hypergastrinemia and Helicobacter infection in a mouse model of gastric cancer. Gastroenterology 2000, 118, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, T.; Mukaisho, K.; Nakayama, T.; Hattori, T.; Sugihara, H. Proton pump inhibitors and Helicobacter pylori-associated pathogenesis. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bruno, G.; Zaccari, P.; Rocco, G.; Scalese, G.; Panetta, C.; Porowska, B.; Pontone, S.; Severi, C. Proton pump inhibitors and dysbiosis: Current knowledge and aspects to be clarified. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 2706–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vich-Vila, A.; Collij, V.; Sanna, S.; Sinha, T.; Imhann, F.; Bourgonje, A.R.; Mujagic, Z.; Jonkers, D.M.; Masclee, A.A.; Fu, J.; et al. Impact of commonly used drugs on the composition and metabolic function of the gut microbiota. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.; Griffin, B.T.; Clarke, G.; Hyland, N.P. Drug-gut microbiota interactions: Implications for neuropharmacology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 4415–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Floch, N. The Influence of Microbiota on Mechanisms of Bariatric Surgery; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.C.; Cai, S.T.; Tian, Y.P.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Ren, R.; Luo, X.; Peng, L.; Sun, G.; et al. Effects of Proton Pump Inhibitors on the Gastrointestinal Microbiota in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2019, 17, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinert, R.E.; Rehman, A.; Souto Lima, E.J.; Agamennone, V.; Schuren, F.H.; Gero, D.; Schreiner, P.; Vonlanthen, R.; Ismaeil, A.; Tzafos, S.; et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery changes fungal and bacterial microbiota in morbidly obese patients-A pilot study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Kong, Y.; Shi, T.; Xiao, H.; Cao, S.; Zhu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y. Alterations of Serum Uric Acid Level and Gut Microbiota After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Sleeve Gastrectomy in a Hyperuricemic Rat Model. Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 1799–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Damms-Machado, A.; Mitra, S.; Schollenberger, A.E.; Kramer, K.M.; Meile, T.; Konigsrainer, A.; Huson, D.H.; Bischoff, S.C. Effects of surgical and dietary weight loss therapy for obesity on gut microbiota composition and nutrient absorption. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 806248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanmiguel, C.P.; Jacobs, J.; Gupta, A.; Ju, T.; Stains, J.; Coveleskie, K.; Lagishetty, V.; Balioukova, A.; Chen, Y.; Dutson, E.; et al. Surgically Induced Changes in Gut Microbiome and Hedonic Eating as Related to Weight Loss: Preliminary Findings in Obese Women Undergoing Bariatric Surgery. Psychosom. Med. 2017, 79, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, G.A.; Encarnacion, B.; Downey, J.R.; Peraza, J.; Chong, K.; Hernandez-Boussard, T.; Morton, J.M. Probiotics Improve Outcomes After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery: A Prospective Randomized Trial. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2009, 13, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherf-Dagan, S.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Zilberman-Schapira, G.; Webb, M.; Buch, A.; Keidar, A.; Raziel, A.; Sakran, N.; Goitein, D.; Goldenberg, N.; et al. Probiotics Administration Following Sleeve Gastrectomy Surgery: A Randomized Double-Blind Trial. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrone, V.; Vajana, E.; Minuti, A.; Callegari, M.L.; Federico, A.; Loguercio, C.; Dallio, M.; Tolone, S.; Docimo, L.; Morelli, L. Postoperative Changes in Fecal Bacterial Communities and Fermentation Products in Obese Patients Undergoing Bilio-Intestinal Bypass. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leite, G.; Morales, W.; Weitsman, S.; Celly, S.; Parodi, G.; Mathur, R.; Barlow, G.M.; Sedighi, R.; Villanueva-Millan, M.J.; Rezaie, A.; et al. The duodenal microbiome is altered in small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Argenio, V.; Casaburi, G.; Precone, V.; Pagliuca, C.; Colicchio, R.; Sarnataro, D.; Discepolo, V.; Kim, S.M.; Russo, I.; Blanco, G.D. Metagenomics Reveals Dysbiosis and a Potentially Pathogenic N. flavescens Strain in Duodenum of Adult Celiac Patients. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, L.B.S.; Roager, H.M.; Sondertoft, N.B.; Gobel, R.J.; Kristensen, M.; Valles-Colomer, M.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Ibrugger, S.; Lind, M.V.; Maerkedahl, R.B. A Low-Gluten Diet Induces Changes in the Intestinal Microbiome of Healthy Danish Adults. Nat. Commun. 2018, 13, 4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.; Kalliomäki, M.; Heilig, H.G.; Palva, A.; Lahteenoja, H.; de Vos, W.M.; Salojarvi, J.; Satokari, R. Duodenal microbiota composition and mucosal homeostasis in pediatric celiac disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, I.; Ullah, N.; Zha, L.; Bai, Y.; Khan, A.; Zhao, T.; Che, T.; Zhang, C. Alteration of Gut Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Cause or Consequence? IBD Treatment Targeting the Gut Microbiome. Pathogens 2019, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zuo, T.; Ng, S.C. The Gut Microbiota in the Pathogenesis and Therapeutics of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrei, M.; Nicolaie, T.; Stoicescu, A.; Teiușanu, A.; Gologan, Ș.; Diculescu, M. Intestinal Microbiome, Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases—What are the Connections? Curr. Health Sci. J. 2015, 41, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöberg, F.; Barkman, C.; Nookaew, I.; Ostman, S.; Adlerberth, I.; Saalman, R.; Wold, A.E. Low-complexity microbiota in the duodenum of children with newly diagnosed ulcerative colitis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, K. Characterization of the Duodenal Microbiome in Children with and without Crohn’s disease. Research Days 3 2020. Available online: https://scholarlyexchange.childrensmercy.org/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1148&context=researchdays (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- Saffouri, G.B.; Shields-Cutler, R.R.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Lekatz, H.R.; Hale, V.L.; Cho, J.M.; Battaglioli, E.J.; Bhattarai, Y.; Thompson, K.J.; et al. Small intestinal microbial dysbiosis underlies symptoms associated with functional gastrointestinal disorders. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishima, Y.; Ishihara, S. Molecular Mechanisms of Microbiota-Mediated Pathology in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, S.; Scher, J.U.; Djukovic, A.; Jiménez, N.; Littman, D.R.; Abramson, S.B.; Pamer, E.G.; Ubeda, C. Short and long-term effects of oral vancomycin on the human intestinal microbiota. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitsman, S.; Celly, S.; Leite, G.; Mathur, R.; Sedighi, R.; Barlow, G.M.; Morales, W.; Sanchez, M.; Parodi, G.; Villanueva-Millan, M.J. Effects of Proton Pump Inhibitors on the Small Bowel and Stool Microbiomes. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleemans, J.M.; Chleilat, F.; Reimer, R.A.; Henning, J.; Baydoun, M.; Piedalue, K.; McLennan, A.; Carlson, L.E. The Chemo-Gut Study: Investigating the Long-Term Effects of Chemotherapy on Gut Microbiota, Metabolic, Immune, Psychological and Cognitive Parameters in Young Adult Cancer Survivors; Study Protocol. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eberl, C.; Ring, D.; Munch, P.; Beutler, M.; Basic, M.; Slack, E.C.; Schwarzer, M.; Srutkova, D.; Lange, A.; Frick, J.S.; et al. Reproducible Colonization of Germ-Free Mice with the Oligo-Mouse-Microbiota in Different Animal Facilities. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bilello, J.; Okereke, I. Impact of Environmental and Pharmacologic Changes on the Upper Gastrointestinal Microbiome. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9060617
Bilello J, Okereke I. Impact of Environmental and Pharmacologic Changes on the Upper Gastrointestinal Microbiome. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(6):617. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9060617
Chicago/Turabian StyleBilello, Joshua, and Ikenna Okereke. 2021. "Impact of Environmental and Pharmacologic Changes on the Upper Gastrointestinal Microbiome" Biomedicines 9, no. 6: 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9060617
APA StyleBilello, J., & Okereke, I. (2021). Impact of Environmental and Pharmacologic Changes on the Upper Gastrointestinal Microbiome. Biomedicines, 9(6), 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9060617






