PI3K and MAPK Pathways as Targets for Combination with the Pan-HER Irreversible Inhibitor Neratinib in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer and TNBC by Kinome RNAi Screening
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Reagents
2.2. In vitro Cell Proliferation Assay
2.3. High-Throughput RNAi Screening:
2.4. Anchorage-Independent Colony Formation (Soft Agar Assay)
2.5. RPPA
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Caspase 3/7 Activity Assay
2.8. Animal Studies
2.9. IHC Staining
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
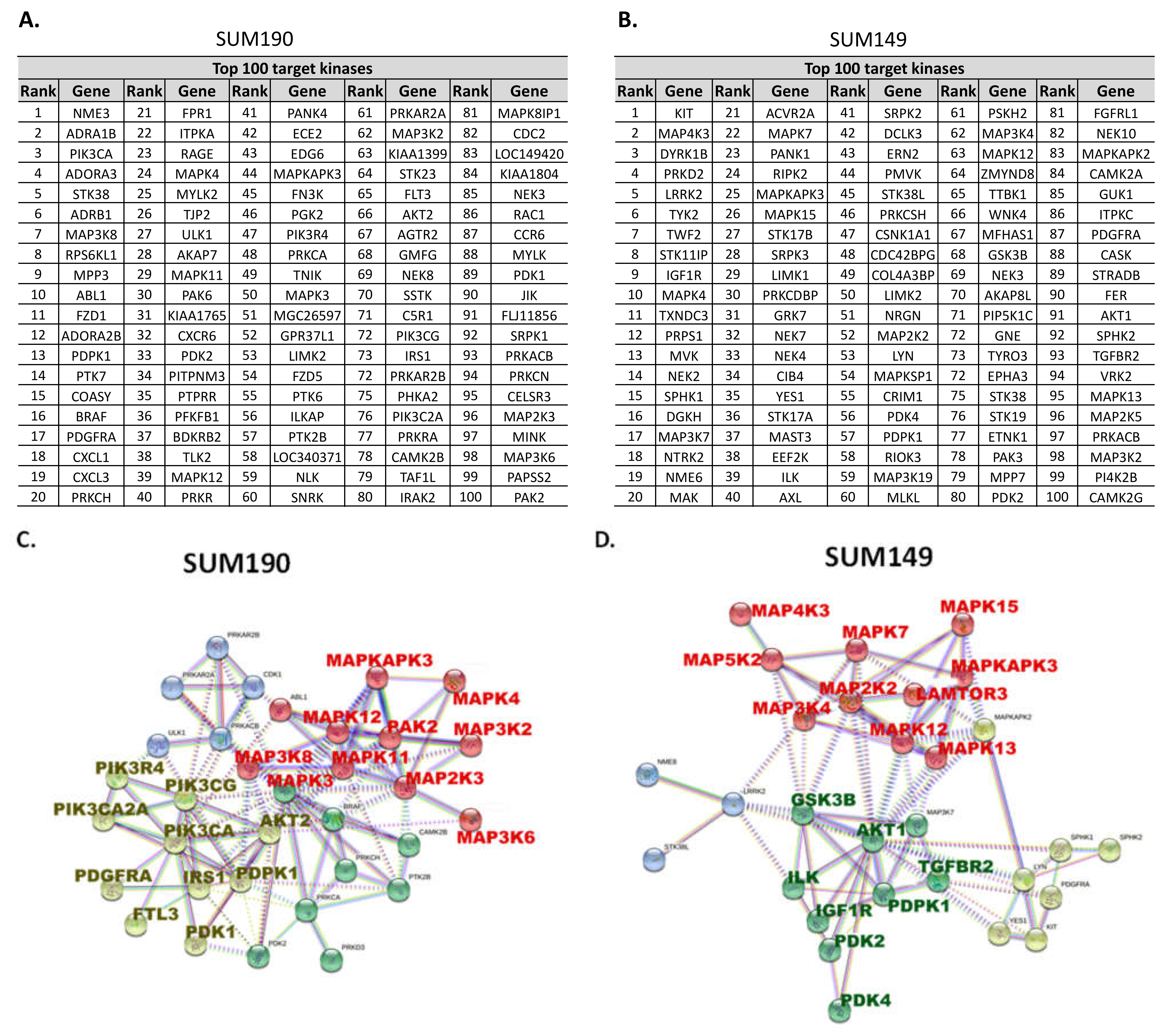
3.1. Kinome RNAi Screening Revealed That PI3K and MAPK Pathways Are Potential Targets for Combination with Neratinib
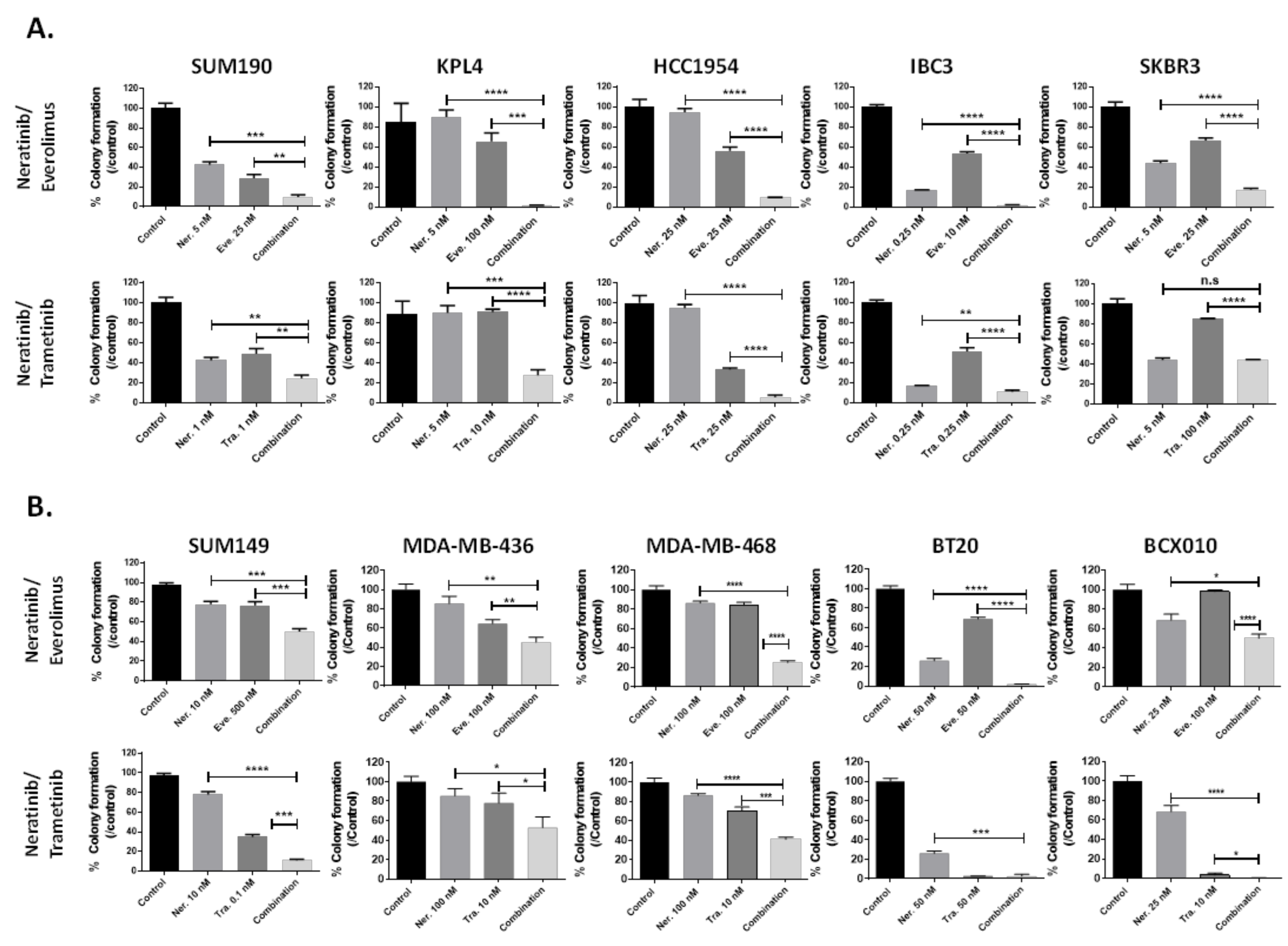
3.2. Everolimus (mTOR Inhibitor) and Trametinib (MEK Inhibitor) Enhance the Efficacy of Neratinib in Both TNBC and HER2+ Breast Cancer Cell Lines
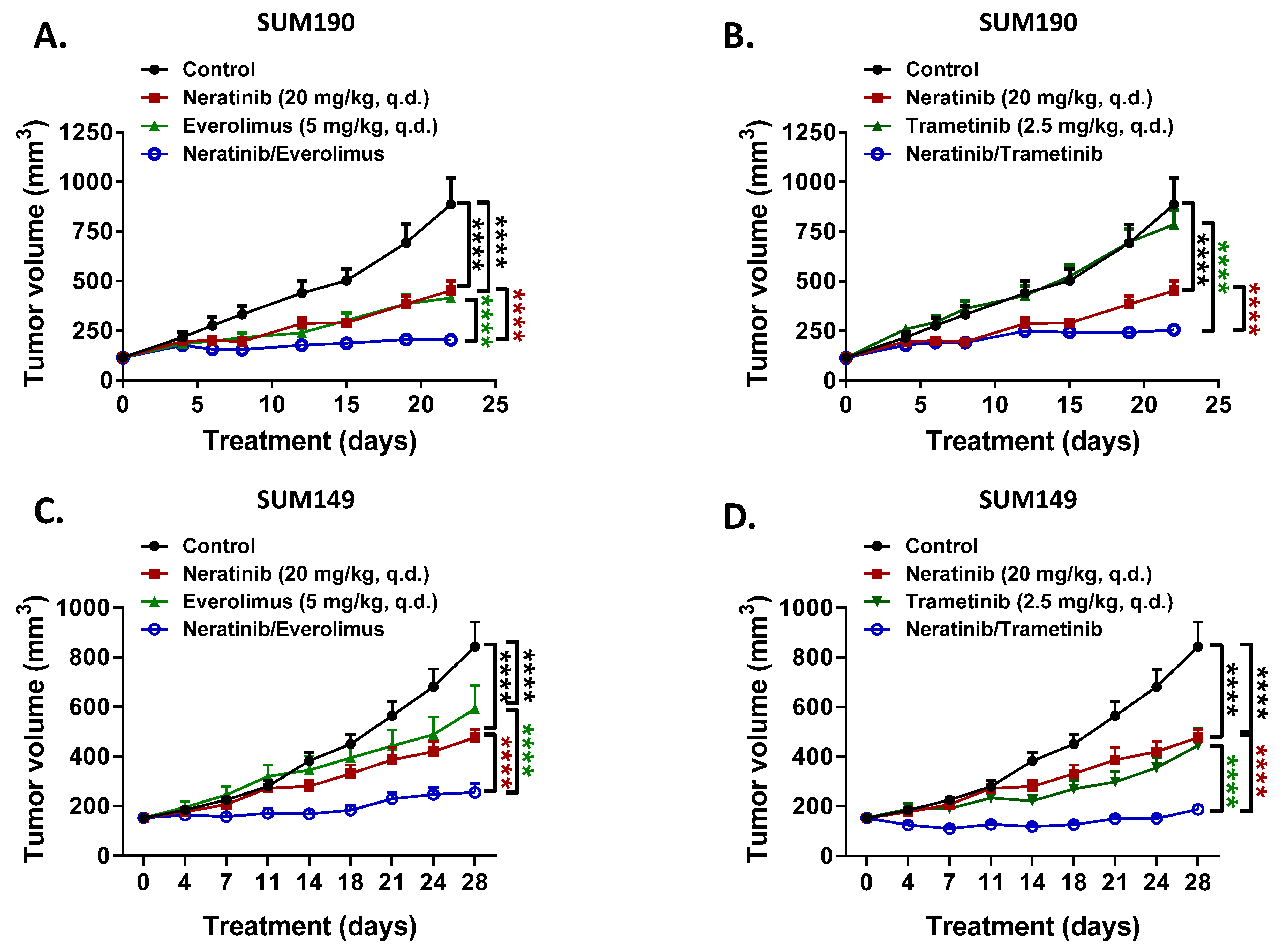
3.3. Everolimus and Trametinib Enhance the Anti-Tumor Activity of Neratinib in Xenograft Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nakai, K.; Hung, M.C.; Yamaguchi, H. A perspective on anti-EGFR therapies targeting triple-negative breast cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 1609–1623. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rimawi, M.F.; Shetty, P.B.; Weiss, H.L.; Schiff, R.; Osborne, C.K.; Chamness, G.C.; Elledge, R.M. Epidermal growth factor receptor expression in breast cancer association with biologic phenotype and clinical outcomes. Cancer 2010, 116, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, C.; Wyckoff, J.; Liang, F.; Sidani, M.; Violini, S.; Tsai, K.L.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Sahai, E.; Condeelis, J.; Segall, J.E. Epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression results in increased tumor cell motility in vivo coordinately with enhanced intravasation and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dickler, M.N.; Cobleigh, M.A.; Miller, K.D.; Klein, P.M.; Winer, E.P. Efficacy and safety of erlotinib in patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat 2009, 115, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Wendt, M.K. The paradoxical functions of EGFR during breast cancer progression. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, J.; Gomez, P.; Greil, R.; Braga, S.; Climent, M.A.; Wardley, A.M.; Kaufman, B.; Stemmer, S.M.; Pego, A.; Chan, A.; et al. Randomized phase II study of the anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody cetuximab with cisplatin versus cisplatin alone in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 2586–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, N.; Wang, X.; Lim, B.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Alvarez, R.H.; Willey, J.S.; Parker, C.A.; Song, J.; Shen, Y.; Hu, J.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Panitumumab Plus Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients With Primary HER2-Negative Inflammatory Breast Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga, C.L.; Sliwkowski, M.X.; Osborne, C.K.; Perez, E.A.; Puglisi, F.; Gianni, L. Treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer: Current status and future perspectives. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 9, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhtala, S.; Staff, S.; Kallioniemi, A.; Tanner, M.; Isola, J. Clinicopathological and prognostic correlations of HER3 expression and its degradation regulators, NEDD4-1 and NRDP1, in primary breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghoff, A.S.; Bartsch, R.; Preusser, M.; Ricken, G.; Steger, G.G.; Bago-Horvath, Z.; Rudas, M.; Streubel, B.; Dubsky, P.; Gnant, M.; et al. Co-overexpression of HER2/HER3 is a predictor of impaired survival in breast cancer patients. Breast 2014, 23, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, A.; Bhattarai, S.; Sahoo, B.; Mongan, N.P.; Alsaleem, M.; Green, A.R.; Aleskandarany, M.; Ellis, I.O.; Pattni, S.; Li, X.B.; et al. Combined HER3-EGFR score in triple-negative breast cancer provides prognostic and predictive significance superior to individual biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wege, A.K.; Chittka, D.; Buchholz, S.; Klinkhammer-Schalke, M.; Diermeier-Daucher, S.; Zeman, F.; Ortmann, O.; Brockhoff, G. HER4 expression in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer is associated with decreased sensitivity to tamoxifen treatment and reduced overall survival of postmenopausal women. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, J.M.; Collier, K.A.; Barros Costa, R.L.; Taxter, T.; Kalyan, A.; Leite, C.A.; Chae, Y.K.; Giles, F.J.; Carneiro, B.A. A comprehensive review of heregulins, HER3, and HER4 as potential therapeutic targets in cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 89284–89306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabindran, S.K.; Discafani, C.M.; Rosfjord, E.C.; Baxter, M.; Floyd, M.B.; Golas, J.; Hallett, W.A.; Johnson, B.D.; Nilakantan, R.; Overbeek, E.; et al. Antitumor activity of HKI-272, an orally active, irreversible inhibitor of the HER-2 tyrosine kinase. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3958–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwak, E.L.; Sordella, R.; Bell, D.W.; Godin-Heymann, N.; Okimoto, R.A.; Brannigan, B.W.; Harris, P.L.; Driscoll, D.R.; Fidias, P.; Lynch, T.J.; et al. Irreversible inhibitors of the EGF receptor may circumvent acquired resistance to gefitinib. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 7665–7670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, M.; Holmes, F.A.; Ejlertsen, B.; Delaloge, S.; Moy, B.; Iwata, H.; von Minckwitz, G.; Chia, S.K.L.; Mansi, J.; Barrios, C.H.; et al. Neratinib after trastuzumab-based adjuvant therapy in HER2-positive breast cancer (ExteNET): 5-year analysis of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1688–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, C.; Oliveira, M.; Feng, Y.H.; Dai, M.S.; Chen, S.W.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Kim, S.B.; Moy, B.; Delaloge, S.; Gradishar, W.; et al. Neratinib Plus Capecitabine Versus Lapatinib Plus Capecitabine in HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer Previously Treated With >/= 2 HER2-Directed Regimens: Phase III NALA Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3138–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, V.M.; Bhola, N.E.; Bauer, J.A.; Formisano, L.; Lee, K.M.; Hutchinson, K.E.; Witkiewicz, A.K.; Moore, P.D.; Estrada, M.V.; Sanchez, V.; et al. Kinome-Wide RNA Interference Screen Reveals a Role for PDK1 in Acquired Resistance to CDK4/6 Inhibition in ER-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2488–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Chen, X.; Sanders, M.E.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Shyr, Y.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2750–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lyons, T.G. Targeted Therapies for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol 2019, 20, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanizaki, J.; Okamoto, I.; Fumita, S.; Okamoto, W.; Nishio, K.; Nakagawa, K. Roles of BIM induction and survivin downregulation in lapatinib-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells with HER2 amplification. Oncogene 2011, 30, 4097–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gong, Y.; Somwar, R.; Politi, K.; Balak, M.; Chmielecki, J.; Jiang, X.; Pao, W. Induction of BIM is essential for apoptosis triggered by EGFR kinase inhibitors in mutant EGFR-dependent lung adenocarcinomas. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, J. MEK inhibition overcomes everolimus resistance in gastric cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharm. 2020, 85, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atefi, M.; von Euw, E.; Attar, N.; Ng, C.; Chu, C.; Guo, D.; Nazarian, R.; Chmielowski, B.; Glaspy, J.A.; Comin-Anduix, B.; et al. Reversing melanoma cross-resistance to BRAF and MEK inhibitors by co-targeting the AKT/mTOR pathway. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Scott, S.; Evans, K.W.; Yuca, E.; Saridogan, T.; Zheng, X.; Wang, H.; Korkut, A.; Cruz Pico, C.X.; Demirhan, M.; et al. Combining Neratinib with CDK4/6, mTOR, and MEK Inhibitors in Models of HER2-positive Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, V.; Scaltriti, M.; Prudkin, L.; Eichhorn, P.J.; Ibrahim, Y.H.; Chandarlapaty, S.; Markman, B.; Rodriguez, O.; Guzman, M.; Rodriguez, S.; et al. PI3K inhibition results in enhanced HER signaling and acquired ERK dependency in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2547–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, Y.; Morita, T.Y.; Ohashi, A.; Haeno, H.; Hakozaki, Y.; Fujii, M.; Kashima, Y.; Kobayashi, S.S.; Mukohara, T. Combination treatment with a PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway inhibitor overcomes resistance to anti-HER2 therapy in PIK3CA-mutant HER2-positive breast cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernieri, C.; Milano, M.; Brambilla, M.; Mennitto, A.; Maggi, C.; Cona, M.S.; Prisciandaro, M.; Fabbroni, C.; Celio, L.; Mariani, G.; et al. Resistance mechanisms to anti-HER2 therapies in HER2-positive breast cancer: Current knowledge, new research directions and therapeutic perspectives. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2019, 139, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, F.; O′Regan, R.; Ozguroglu, M.; Toi, M.; Xu, B.; Jerusalem, G.; Masuda, N.; Wilks, S.; Arena, F.; Isaacs, C.; et al. Everolimus for women with trastuzumab-resistant, HER2-positive, advanced breast cancer (BOLERO-3): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.; Moy, B.; Mansi, J.; Ejlertsen, B.; Holmes, F.A.; Chia, S.; Iwata, H.; Gnant, M.; Loibl, S.; Barrios, C.H.; et al. Final Efficacy Results of Neratinib in HER2-positive Hormone Receptor-positive Early-stage Breast Cancer From the Phase III ExteNET Trial. Clin. Breast Cancer 2021, 21, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulfkuhle, J.D.; Yau, C.; Wolf, D.M.; Vis, D.J.; Gallagher, R.I.; Brown-Swigart, L.; Hirst, G.; Voest, E.E.; DeMichele, A.; Hylton, N.; et al. Evaluation of the HER/PI3K/AKT Family Signaling Network as a Predictive Biomarker of Pathologic Complete Response for Patients With Breast Cancer Treated With Neratinib in the I-SPY 2 TRIAL. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, N.; Tovey, H.; Pearson, A.; Cutts, R.; Toms, C.; Proszek, P.; Hubank, M.; Dowsett, M.; Dodson, A.; Daley, F.; et al. Homologous recombination DNA repair deficiency and PARP inhibition activity in primary triple negative breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, N.M.; Robson, M.E.; Ventz, S.; Santa-Maria, C.A.; Nanda, R.; Marcom, P.K.; Shah, P.D.; Ballinger, T.J.; Yang, E.S.; Vinayak, S.; et al. TBCRC 048: Phase II Study of Olaparib for Metastatic Breast Cancer and Mutations in Homologous Recombination-Related Genes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 4274–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, C.J.; Ashworth, A. BRCAness revisited. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Liu, H.; Pearson, T.; Iwase, T.; Fuson, J.; Lalani, A.S.; Eli, L.D.; Diala, I.; Tripathy, D.; Lim, B.; et al. PI3K and MAPK Pathways as Targets for Combination with the Pan-HER Irreversible Inhibitor Neratinib in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer and TNBC by Kinome RNAi Screening. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070740
Lee J, Liu H, Pearson T, Iwase T, Fuson J, Lalani AS, Eli LD, Diala I, Tripathy D, Lim B, et al. PI3K and MAPK Pathways as Targets for Combination with the Pan-HER Irreversible Inhibitor Neratinib in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer and TNBC by Kinome RNAi Screening. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(7):740. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070740
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jangsoon, Huey Liu, Troy Pearson, Toshiaki Iwase, Jon Fuson, Alshad S. Lalani, Lisa D. Eli, Irmina Diala, Debu Tripathy, Bora Lim, and et al. 2021. "PI3K and MAPK Pathways as Targets for Combination with the Pan-HER Irreversible Inhibitor Neratinib in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer and TNBC by Kinome RNAi Screening" Biomedicines 9, no. 7: 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070740
APA StyleLee, J., Liu, H., Pearson, T., Iwase, T., Fuson, J., Lalani, A. S., Eli, L. D., Diala, I., Tripathy, D., Lim, B., & Ueno, N. T. (2021). PI3K and MAPK Pathways as Targets for Combination with the Pan-HER Irreversible Inhibitor Neratinib in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer and TNBC by Kinome RNAi Screening. Biomedicines, 9(7), 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070740







