Ultrasound and Microbubbles for Targeted Drug Delivery to the Lung Endothelium in ARDS: Cellular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Endothelial Activation and Leakage during Inflammation
1.1.1. Pulmonary Endothelial Inflammation and Vascular Permeability
1.1.2. Pulmonary Endothelial Dysfunction—Coagulation
1.2. Current Therapies Targeting the Endothelium
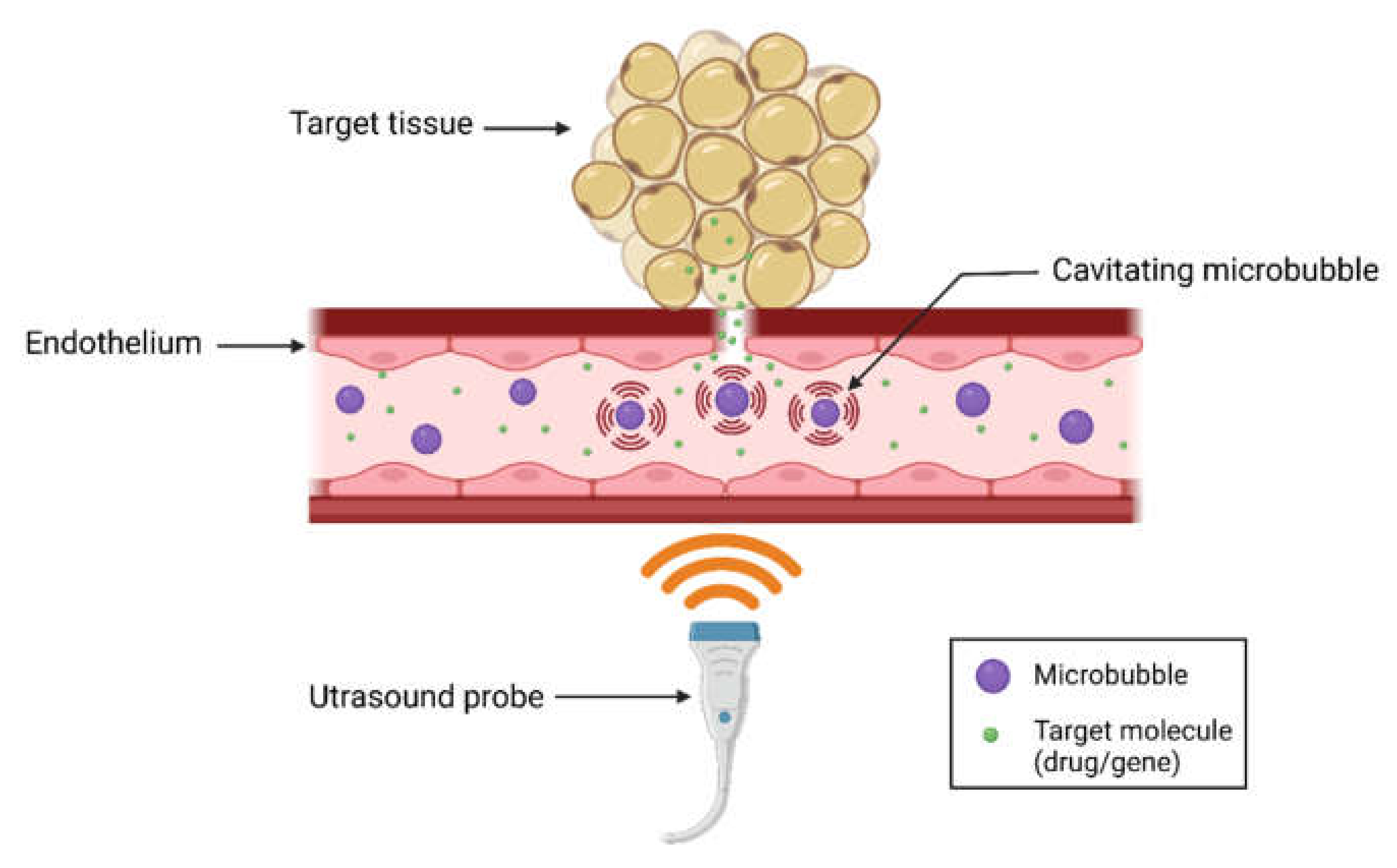
2. Introduction to Ultrasound-Microbubble Mediated Therapy
2.1. Mechanisms of USMB-Mediated Intracellular Delivery
2.1.1. Sonoporation
Acoustic Microstreaming
Shock Waves and Liquid Microjets
2.1.2. Endocytosis
Biological Mechanisms of USMB-Induced Endocytosis
Physical Mechanisms of USMB-Induced Endocytosis
2.1.3. Cargo Delivery Using USMB—On, Inside, or Around?
Electrostatic or Covalent Binding of Cargo to the Microbubble Shell
Embedding Cargo Inside the Microbubble Shell
Co-Administration of Cargo and Microbubbles
2.1.4. Modification of the Microbubble to Enhance Delivery
2.2. A New Frontier? Ultrasound and Microbubble Treatment of the Injured Lung
3. Future Directions—Challenges and Opportunities
3.1. Trade off of Increased Leakage vs. Cargo Delivery
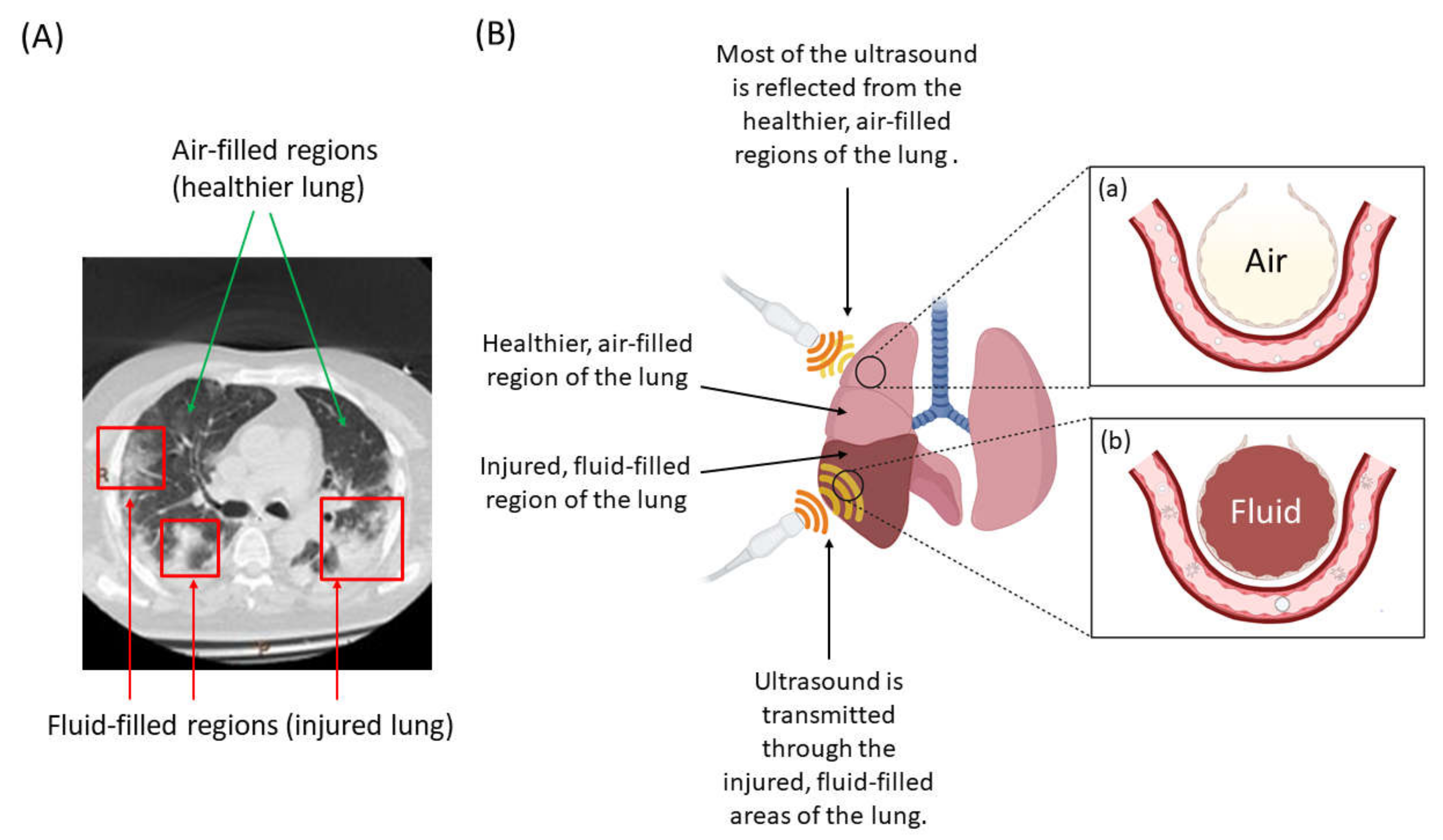
3.2. Tissue (Depth) Penetration and Specificity for the Lung
3.3. Optimizing Bubble Size and Charge for Delivery
3.4. Emerging Techniques to Control Bubble Sizes and Charge
3.5. Clinical Trials of USMB Treatment for ARDS
4. Conclusions—A New Technique Provides New Opportunities
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sturtzel, C. Endothelial Cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1003, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filewod, N.C.; Lee, W.L. Inflammation without Vascular Leakage. Science Fiction No Longer? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 1472–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, N.M.; Steinberg, B.E.; Slutsky, A.S.; Lee, W.L. Broken Barriers: A New Take on Sepsis Pathogenesis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 88ps25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.L.; Slutsky, A.S. Sepsis and Endothelial Permeability. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 689–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ARDS Definition Task Force; Ranieri, V.M.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ferguson, N.D.; Caldwell, E.; Fan, E.; Camporota, L.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012, 307, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellani, G.; Laffey, J.G.; Pham, T.; Fan, E.; Brochard, L.; Esteban, A.; Gattinoni, L.; van Haren, F.; Larsson, A.; McAuley, D.F.; et al. Epidemiology, Patterns of Care, and Mortality for Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 Countries. JAMA 2016, 315, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassiliou, A.G.; Kotanidou, A.; Dimopoulou, I.; Orfanos, S.E. Endothelial Damage in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latreille, E.; Lee, W.L. Interactions of Influenza and SARS-CoV-2 with the Lung Endothelium: Similarities, Differences, and Implications for Therapy. Viruses 2021, 13, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, B.J.; Jurd, K.M. Endothelial Cell Activation. A Central Pathophysiological Process. BMJ 1998, 316, 1328–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavard, J.; Gutkind, J.S. VEGF Controls Endothelial-Cell Permeability by Promoting the Beta-Arrestin-Dependent Endocytosis of VE-Cadherin. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, F.; Winderlich, M.; Holm, M.; Frye, M.; Rivera-Galdos, R.; Vockel, M.; Linnepe, R.; Ipe, U.; Stadtmann, A.; Zarbock, A.; et al. Leukocyte Extravasation and Vascular Permeability Are Each Controlled in Vivo by Different Tyrosine Residues of VE-Cadherin. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, M.; Gillespie, M.K.; Ackerson, L.; Moore, F.A.; Moore, E.E.; Parsons, P.E. Endothelial Cell Activity Varies in Patients at Risk for the Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 24, 1782–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, A.M.; Cronen, C.; Müller, K.-M.; Kirkpatrick, C.J. Heterogeneous Expression of Cell Adhesion Molecules by Endothelial Cells in ARDS. J. Pathol. 2002, 198, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Griensven, M.; Probst, C.; Müller, K.; Hoevel, P.; Pape, H.-C. Leukocyte-Endothelial Interactions via ICAM-1 Are Detrimental in Polymicrobial Sepsis. Shock 2006, 25, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, S.C.; Haslett, C.; Dransfield, I.; Robertson, C.E.; Carter, D.C.; Ross, J.A.; Grant, I.S.; Tedder, T.F. Role of Selectins in Development of Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Lancet 1994, 344, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraway, M.S.; Welty-Wolf, K.E.; Kantrow, S.P.; Huang, Y.C.; Simonson, S.G.; Que, L.G.; Kishimoto, T.K.; Piantadosi, C.A. Antibody to E- and L-Selectin Does Not Prevent Lung Injury or Mortality in Septic Baboons. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 157, 938–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridings, P.C.; Windsor, A.C.; Jutila, M.A.; Blocher, C.R.; Fisher, B.J.; Sholley, M.M.; Sugerman, H.J.; Fowler, A.A. A Dual-Binding Antibody to E- and L-Selectin Attenuates Sepsis-Induced Lung Injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 152, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C. The Role of Inflammatory Cytokines in Endothelial Dysfunction. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2008, 103, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprague, A.H.; Khalil, R.A. Inflammatory Cytokines in Vascular Dysfunction and Vascular Disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meduri, G.U.; Kohler, G.; Headley, S.; Tolley, E.; Stentz, F.; Postlethwaite, A. Inflammatory Cytokines in the BAL of Patients with ARDS. Persistent Elevation over Time Predicts Poor Outcome. Chest 1995, 108, 1303–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.Y.; Goodman, R.B.; Steinberg, K.P.; Ruzinski, J.T.; Radella, F.; Park, D.R.; Pugin, J.; Skerrett, S.J.; Hudson, L.D.; Martin, T.R. Cytokine Balance in the Lungs of Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 1896–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teijaro, J.R.; Walsh, K.B.; Cahalan, S.; Fremgen, D.M.; Roberts, E.; Scott, F.; Martinborough, E.; Peach, R.; Oldstone, M.B.A.; Rosen, H. Endothelial Cells Are Central Orchestrators of Cytokine Amplification during Influenza Virus Infection. Cell 2011, 146, 980–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McVey, M.J.; Steinberg, B.E.; Goldenberg, N.M. Inflammasome Activation in Acute Lung Injury. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2021, 320, L165–L178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Kouadir, M.; Song, H.; Shi, F. Recent Advances in the Mechanisms of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Its Inhibitors. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The REMAP-CAP Investigators. Interleukin-6 Receptor Antagonists in Critically Ill Patients with Covid. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, P.; Caraffa, A.; Gallenga, C.E.; Ross, R.; Kritas, S.K.; Frydas, I.; Younes, A.; Ronconi, G. Coronavirus-19 (SARS-CoV-2) Induces Acute Severe Lung Inflammation via IL-1 Causing Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: A Promising Inhibitory Strategy. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 1971–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, P.; Pregliasco, F.E.; Calvisi, V.; Calvisi, V.; Caraffa, A.; Gallenga, C.E.; Kritas, S.K.; Ronconi, G. Monoclonal Antibody Therapy in COVID. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2021, 35, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, N.; Jeltema, D.; Duan, Y.; He, Y. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, T.L.; Swartz, T.H. Targeting the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Severe COVID. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunwell, J.R.; Stephenson, S.T.; Mohammad, A.F.; Jones, K.; Mason, C.; Opolka, C.; Fitzpatrick, A.M. Differential Type I Interferon Response and Primary Airway Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Release in Children with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, E.A.; He, X.-Y.; Denorme, F.; Campbell, R.A.; Ng, D.; Salvatore, S.P.; Mostyka, M.; Baxter-Stoltzfus, A.; Borczuk, A.C.; Loda, M.; et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Contribute to Immunothrombosis in COVID-19 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Blood 2020, 136, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, C.; Palaniyar, N.; Otulakowski, G.; Khan, M.A.; Post, M.; Kuebler, W.M.; Tanswell, K.; Belcastro, R.; Masood, A.; Engelberts, D.; et al. Mechanical Ventilation Induces Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation. Anesthesiology 2015, 122, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vestweber, D.; Winderlich, M.; Cagna, G.; Nottebaum, A.F. Cell Adhesion Dynamics at Endothelial Junctions: VE-Cadherin as a Major Player. Trends Cell Biol. 2009, 19, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corada, M.; Mariotti, M.; Thurston, G.; Smith, K.; Kunkel, R.; Brockhaus, M.; Lampugnani, M.G.; Martin-Padura, I.; Stoppacciaro, A.; Ruco, L.; et al. Vascular Endothelial-Cadherin Is an Important Determinant of Microvascular Integrity in Vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9815–9820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broermann, A.; Winderlich, M.; Block, H.; Frye, M.; Rossaint, J.; Zarbock, A.; Cagna, G.; Linnepe, R.; Schulte, D.; Nottebaum, A.F.; et al. Dissociation of VE-PTP from VE-Cadherin Is Required for Leukocyte Extravasation and for VEGF-Induced Vascular Permeability in Vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 2393–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, D.; Küppers, V.; Dartsch, N.; Broermann, A.; Li, H.; Zarbock, A.; Kamenyeva, O.; Kiefer, F.; Khandoga, A.; Massberg, S.; et al. Stabilizing the VE-Cadherin-Catenin Complex Blocks Leukocyte Extravasation and Vascular Permeability. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 4157–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindle, N.P.J.; Saharinen, P.; Alitalo, K. Signaling and Functions of Angiopoietin-1 in Vascular Protection. Circ. Res. 2006, 98, 1014–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, N.A.M.; van Leeuwen, A.L.I.; van Strien, W.W.J.; Majolée, J.; Szulcek, R.; Vonk, A.B.A.; Hordijk, P.L.; Boer, C.; van den Brom, C.E. Microcirculatory Perfusion Disturbances Following Cardiac Surgery with Cardiopulmonary Bypass Are Associated with in Vitro Endothelial Hyperpermeability and Increased Angiopoietin-2 Levels. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Heijden, M.; van NieuwAmerongen, G.P.; Koolwijk, P.; van Hinsbergh, V.W.M.; Groeneveld, A.B.J. Angiopoietin-2, Permeability Oedema, Occurrence and Severity of ALI/ARDS in Septic and Non-Septic Critically Ill Patients. Thorax 2008, 63, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, K.; Liaw, P.C.; Mullington, J.M.; Shih, S.-C.; Okada, H.; Bodyak, N.; Kang, P.M.; Toltl, L.; Belikoff, B.; Buras, J.; et al. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Is an Important Determinant of Sepsis Morbidity and Mortality. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 1447–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, C.E.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L.; Zhao, Y.-Y. Mechanisms of Endothelial Regeneration and Vascular Repair and Their Application to Regenerative Medicine. Am. J. Pathol. 2021, 191, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, C.; Tauseef, M.; Farazuddin, M.; Yazbeck, P.; Amin, M.-R.; Avin, V.B.; Sharma, T.; Mehta, D. MicroRNA-150 Suppression of Angiopoetin-2 Generation and Signaling Is Crucial for Resolving Vascular Injury. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Y. MiR-150 Attenuates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury via Targeting AKT. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 75, 105794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-Y.; Gao, X.-P.; Zhao, Y.D.; Mirza, M.K.; Frey, R.S.; Kalinichenko, V.V.; Wang, I.-C.; Costa, R.H.; Malik, A.B. Endothelial Cell-Restricted Disruption of FoxM1 Impairs Endothelial Repair Following LPS-Induced Vascular Injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 2333–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, D.X.; Yin, J.; Hu, G.; Evans, C.E.; Zhao, Y.-Y. Endothelial Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Is Required for Vascular Repair and Resolution of Inflammatory Lung Injury through Forkhead Box Protein M. Am. J. Pathol. 2019, 189, 1664–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yang, T.; Fei, Z. MiR-26a-5p Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Targeting the Connective Tissue Growth Factor. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Xu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, F.; Mao, L.; Li, H.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, D.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor-2Alleviates the Capillary Leakage and Inflammation in Sepsis. Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Ramchandran, R.; Shaaya, M.; Huang, L.; Ebenezer, D.L.; Jiang, Y.; Komarova, Y.; Vogel, S.M.; Malik, A.B.; Minshall, R.D.; et al. Phospholipase D2 Restores Endothelial Barrier Function by Promoting PTPN14-Mediated VE-Cadherin Dephosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 7669–7685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlinski, R.; Pedersen, B.; Schabbauer, G.; Tencati, M.; Holscher, T.; Boisvert, W.; Andrade-Gordon, P.; Frank, R.D.; Mackman, N. Role of Tissue Factor and Protease-Activated Receptors in a Mouse Model of Endotoxemia. Blood 2004, 103, 1342–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantzeskaki, F.; Armaganidis, A.; Orfanos, S.E. Immunothrombosis in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Cross Talks between Inflammation and Coagulation. Respiration 2017, 93, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, S.M.; Gao, X.; Mehta, D.; Ye, R.D.; John, T.A.; Andrade-Gordon, P.; Tiruppathi, C.; Malik, A.B. Abrogation of Thrombin-Induced Increase in Pulmonary Microvascular Permeability in PAR-1 Knockout Mice. Physiol. Genom. 2000, 4, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ware, L.B.; Bastarache, J.A.; Wang, L. Coagulation and Fibrinolysis in Human Acute Lung Injury—New Therapeutic Targets? Keio J. Med. 2005, 54, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, G.E.; de Moerloose, P.; Bulla, O.; Lou, J.; Lei, Z.; Reber, G.; Mili, N.; Ricou, B.; Morel, D.R.; Suter, P.M. Haemostatic Properties of Human Pulmonary and Cerebral Microvascular Endothelial Cells. Thromb. Haemost. 1997, 77, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katneni, U.K.; Alexaki, A.; Hunt, R.C.; Schiller, T.; DiCuccio, M.; Buehler, P.W.; Ibla, J.C.; Kimchi-Sarfaty, C. Coagulopathy and Thrombosis as a Result of Severe COVID-19 Infection: A Microvascular Focus. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 120, 1668–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, M.; Verleden, S.E.; Kuehnel, M.; Haverich, A.; Welte, T.; Laenger, F.; Vanstapel, A.; Werlein, C.; Stark, H.; Tzankov, A.; et al. Pulmonary Vascular Endothelialitis, Thrombosis, and Angiogenesis in Covid. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juffermans, N.P.; van den Brom, C.E.; Kleinveld, D.J.B. Targeting Endothelial Dysfunction in Acute Critical Illness to Reduce Organ Failure. Anesth. Analg. 2020, 131, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.G.; Liu, F.; Verin, A.D.; Birukova, A.; Dechert, M.A.; Gerthoffer, W.T.; Bamberg, J.R.; English, D. Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Promotes Endothelial Cell Barrier Integrity by Edg-Dependent Cytoskeletal Rearrangement. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, M.Z.; Joshi, J.C.; Balaji, R.V.A.; Maienschein-Cline, M.; Richard, L.P.; Asrar, B.M. Mehta Dolly Programming to S1PR1+ Endothelial Cells Promote Restoration of Vascular Integrity. Circ. Res. 2021, 129, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trieu, M.; van Meurs, M.; van Leeuwen, A.L.I.; Van Slyke, P.; Hoang, V.; Geeraedts, L.M.G.; Boer, C.; van den Brom, C.E. Vasculotide, an Angiopoietin-1 Mimetic, Restores Microcirculatory Perfusion and Microvascular Leakage and Decreases Fluid Resuscitation Requirements in Hemorrhagic Shock. Anesthesiology 2018, 128, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumpers, P.; Gueler, F.; David, S.; Slyke, P.V.; Dumont, D.J.; Park, J.-K.; Bockmeyer, C.L.; Parikh, S.M.; Pavenstadt, H.; Haller, H.; et al. The Synthetic Tie2 Agonist Peptide Vasculotide Protects against Vascular Leakage and Reduces Mortality in Murine Abdominal Sepsis. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, M.G.; Armstrong, S.M.; Wang, C.; Hwang, D.; Leong-Poi, H.; Advani, A.; Advani, S.; Zhang, H.; Szaszi, K.; Tabuchi, A.; et al. The Tie2-Agonist Vasculotide Rescues Mice from Influenza Virus Infection. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Lee, S.-J.; Kim, K.E.; Lee, H.S.; Oh, N.; Park, I.; Ko, E.; Oh, S.J.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, D.; et al. Amelioration of Sepsis by TIE2 Activation–Induced Vascular Protection. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 335ra55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauschildt, J.; Schrimpf, C.; Thamm, K.; Retzlaff, J.; Idowu, T.O.; von Kaisenberg, C.; Haller, H.; David, S. Dual Pharmacological Inhibition of Angiopoietin-2 and VEGF-A in Murine Experimental Sepsis. J. Vasc. Res. 2020, 57, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frye, M.; Dierkes, M.; Küppers, V.; Vockel, M.; Tomm, J.; Zeuschner, D.; Rossaint, J.; Zarbock, A.; Koh, G.Y.; Peters, K.; et al. Interfering with VE-PTP Stabilizes Endothelial Junctions in Vivo via Tie-2 in the Absence of VE-Cadherin. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 2267–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Frye, M.; Lee, B.L.; Reinardy, J.L.; McClung, J.M.; Ding, K.; Kojima, M.; Xia, H.; Seidel, C.; Lima e Silva, R.; et al. Targeting VE-PTP Activates TIE2 and Stabilizes the Ocular Vasculature. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4564–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Kalin, G.T.; Shi, D.; Kalinichenko, V.V. Nanoparticle Delivery Systems with Cell-Specific Targeting for Pulmonary Diseases. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2021, 64, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.R.; Raftis, J.B.; Langrish, J.P.; McLean, S.G.; Samutrtai, P.; Connell, S.P.; Wilson, S.; Vesey, A.T.; Fokkens, P.H.B.; Boere, A.J.F.; et al. Inhaled Nanoparticles Accumulate at Sites of Vascular Disease. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 4542–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, A.W.; Kalinichenko, V.V.; Shi, D. Highly Efficient In Vivo Targeting of the Pulmonary Endothelium Using Novel Modifications of Polyethylenimine: An Importance of Charge. Adv. Health Mater. 2018, 7, e1800876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolte, C.; Ustiyan, V.; Ren, X.; Dunn, A.W.; Pradhan, A.; Wang, G.; Kolesnichenko, O.A.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, D.; et al. Nanoparticle Delivery of Proangiogenic Transcription Factors into the Neonatal Circulation Inhibits Alveolar Simplification Caused by Hyperoxia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, A.; Dunn, A.; Ustiyan, V.; Bolte, C.; Wang, G.; Whitsett, J.A.; Zhang, Y.; Porollo, A.; Hu, Y.-C.; Xiao, R.; et al. The S52F FOXF1 Mutation Inhibits STAT3 Signaling and Causes Alveolar Capillary Dysplasia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwakil, M.M.A.; Khalil, I.A.; Elewa, Y.H.A.; Kusumoto, K.; Sato, Y.; Shobaki, N.; Kon, Y.; Harashima, H. Lung-Endothelium-Targeted Nanoparticles Based on a PH-Sensitive Lipid and the GALA Peptide Enable Robust Gene Silencing and the Regression of Metastatic Lung Cancer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1807677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Li, S.; Hu, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Kang, X.; Qi, J.; Lu, X.; Wu, J.; Du, Y.; et al. Combined Delivery of Angiopoietin-1 Gene and Simvastatin Mediated by Anti-Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 Antibody-Conjugated Ternary Nanoparticles for Acute Lung Injury Therapy. Nanomedicine 2019, 15, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roki, N.; Tsinas, Z.; Solomon, M.; Bowers, J.; Getts, R.C.; Muro, S. Unprecedently High Targeting Specificity toward Lung ICAM-1 Using 3DNA Nanocarriers. J.Control. Release 2019, 305, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muro, S.; Mateescu, M.; Gajewski, C.; Robinson, M.; Muzykantov, V.R.; Koval, M. Control of Intracellular Trafficking of ICAM-1-Targeted Nanocarriers by Endothelial Na+/H+ Exchanger Proteins. Am. J. Physiol. Lung. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2006, 290, L809–L817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashbaugh, D.G.; Bigelow, D.B.; Petty, T.L.; Levine, B.E. Acute Respiratory Distress in Adults. Lancet 1967, 2, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzenstein, A.L.; Bloor, C.M.; Leibow, A.A. Diffuse Alveolar Damage—The Role of Oxygen, Shock, and Related Factors. A Review. Am. J. Pathol. 1976, 85, 209–228. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.; Thrall, B.D.; Miller, D.L. Transfection of a Reporter Plasmid into Cultured Cells by Sonoporation in Vitro. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1997, 23, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.-H.; Harvey, B.K.; Borden, M.A. State-of-the-Art of Microbubble-Assisted Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4393–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, L.; Folliero, V.; Palomba, L.; Zannella, C.; Isticato, R.; Di Francia, R.; Berretta, M.; de Sio, I.; Adinolfi, L.E.; Morelli, G.; et al. Sonoporation by Microbubbles as Gene Therapy Approach against Liver Cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 32182–32190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wamel, A.; Kooiman, K.; Harteveld, M.; Emmer, M.; ten Cate, F.J.; Versluis, M.; de Jong, N. Vibrating Microbubbles Poking Individual Cells: Drug Transfer into Cells via Sonoporation. J. Control Release 2006, 112, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooiman, K.; Foppen-Harteveld, M.; van der Steen, A.F.W.; de Jong, N. Sonoporation of Endothelial Cells by Vibrating Targeted Microbubbles. J. Control Release 2011, 154, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullick Chowdhury, S.; Lee, T.; Willmann, J.K. Ultrasound-Guided Drug Delivery in Cancer. Ultrasonography 2017, 36, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooiman, K.; Vos, H.J.; Versluis, M.; de Jong, N. Acoustic Behavior of Microbubbles and Implications for Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 72, 28–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doinikov, A.A.; Bouakaz, A. Acoustic Microstreaming around a Gas Bubble. J.Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 127, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brujan, E.A.; Ikeda, T.; Matsumoto, Y. Jet Formation and Shock Wave Emission during Collapse of Ultrasound-Induced Cavitation Bubbles and Their Role in the Therapeutic Applications of High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound. Phys. Med. Biol. 2005, 50, 4797–4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roovers, S.; Segers, T.; Lajoinie, G.; Deprez, J.; Versluis, M.; De Smedt, S.C.; Lentacker, I. The Role of Ultrasound-Driven Microbubble Dynamics in Drug Delivery: From Microbubble Fundamentals to Clinical Translation. Langmuir 2019, 35, 10173–10191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presset, A.; Bonneau, C.; Kazuyoshi, S.; Nadal-Desbarats, L.; Mitsuyoshi, T.; Bouakaz, A.; Kudo, N.; Escoffre, J.-M.; Sasaki, N. Endothelial Cells, First Target of Drug Delivery Using Microbubble-Assisted Ultrasound. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020, 46, 1565–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijering, B.D.M.; Henning, R.H.; Van Gilst, W.H.; Gavrilovic, I.; Van Wamel, A.; Deelman, L.E. Optimization of Ultrasound and Microbubbles Targeted Gene Delivery to Cultured Primary Endothelial Cells. J. Drug. Target. 2007, 15, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teupe, C.; Richter, S.; Fisslthaler, B.; Randriamboavonjy, V.; Ihling, C.; Fleming, I.; Busse, R.; Zeiher, A.M.; Dimmeler, S. Vascular Gene Transfer of Phosphomimetic Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase (S1177D) Using Ultrasound-Enhanced Destruction of Plasmid-Loaded Microbubbles Improves Vasoreactivity. Circulation 2002, 105, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, L.C.; Dhanaliwala, A.H.; Klibanov, A.L.; Hossack, J.A.; Wamhoff, B.R. Focused Ultrasound-Mediated Drug Delivery from Microbubbles Reduces Drug Dose Necessary for Therapeutic Effect on Neointima Formation--Brief Report. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 2853–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mehier-Humbert, S.; Bettinger, T.; Yan, F.; Guy, R.H. Plasma Membrane Poration Induced by Ultrasound Exposure: Implication for Drug Delivery. J. Control Release 2005, 104, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Kumon, R.E.; Cui, J.; Deng, C.X. The Size of Sonoporation Pores on The Cell Membrane. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2009, 35, 1756–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.-Z.; Luo, Y.-K.; Lu, C.-T.; Xu, J.-F.; Tang, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, H.-D. Phospholipids-Based Microbubbles Sonoporation Pore Size and Reseal of Cell Membrane Cultured in Vitro. J. Drug. Target. 2008, 16, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prentice, P.; Cuschieri, A.; Dholakia, K.; Prausnitz, M.; Campbell, P. Membrane Disruption by Optically Controlled Microbubble Cavitation. Nat. Phys. 2005, 1, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, K.; Cui, J.; Ye, J.Y.; Deng, C.X. Controlled Permeation of Cell Membrane by Single Bubble Acoustic Cavitation. J. Control Release 2012, 157, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, W.; Zhang, D.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Tu, J. The Correlation between Acoustic Cavitation and Sonoporation Involved in Ultrasound-Mediated DNA Transfection with Polyethylenimine (PEI) in Vitro. J. Control Release 2010, 145, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlicher, R.K.; Radhakrishna, H.; Tolentino, T.P.; Apkarian, R.P.; Zarnitsyn, V.; Prausnitz, M.R. Mechanism of Intracellular Delivery by Acoustic Cavitation. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2006, 32, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, N.; Okada, K.; Yamamoto, K. Sonoporation by Single-Shot Pulsed Ultrasound with Microbubbles Adjacent to Cells. Biophys. J. 2009, 96, 4866–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wan, J.M.F.; Yu, A.C.H. Membrane Perforation and Recovery Dynamics in Microbubble-Mediated Sonoporation. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2013, 39, 2393–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouakaz, A.; Zeghimi, A.; Doinikov, A.A. Sonoporation: Concept and Mechanisms. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 880, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Theoretical Study on Shear Stress Generated by Microstreaming Surrounding Contrast Agents Attached to Living Cells. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2002, 28, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novell, A.; Collis, J.; Doinikov, A.A.; Ooi, A.; Manasseh, R.; Bouakazaz, A. Theoretical and Experimental Evaluation of Microstreaming Created by a Single Microbubble: Application to Sonoporation. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium, Orlando, FL, USA, 18–21 October 2011; pp. 1482–1485. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Ross, J.P.; Chiu, J.-F. Reparable Sonoporation Generated by Microstreaming. J.Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 111, 1460–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žnidarčič, A.; Mettin, R.; Cairós, C.; Dular, M. Attached Cavitation at a Small Diameter Ultrasonic Horn Tip. Phys. Fluids 2014, 26, 023304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, J. Acoustic Microstreaming around an Isolated Encapsulated Microbubble. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 125, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doinikov, A.A.; Palanchon, P.; Kaddur, K.; Bouakaz, A. Theoretical Exploration of Shear Stress Generated by Oscillating Microbubbles on the Cell Membrane in the Context of Sonoporation. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium, Roma, Italy, 20–23 September 2009; pp. 1215–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Mobadersany, N.; Sarkar, K. Acoustic Microstreaming near a Plane Wall Due to a Pulsating Free or Coated Bubble: Velocity, Vorticity and Closed Streamlines. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 875, 781–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karshafian, R.; Bevan, P.D.; Williams, R.; Samac, S.; Burns, P.N. Sonoporation by Ultrasound-Activated Microbubble Contrast Agents: Effect of Acoustic Exposure Parameters on Cell Membrane Permeability and Cell Viability. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2009, 35, 847–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.J.; Feshitan, J.A.; Baseri, B.; Wang, S.; Tung, Y.-S.; Borden, M.A.; Konofagou, E.E. Microbubble-Size Dependence of Focused Ultrasound-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Opening in Mice in Vivo. IEEE Trans Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, P.; Jin, L.; Li, F.; Han, T.; Du, L.; Yu, A.C.H. The Relationship between Microbubble Size and Heterogeneous Sonoporation at the Single-Cell Level. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Tours, France, 18–21 September 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Koshiyama, K.; Kodama, T.; Yano, T.; Fujikawa, S. Structural Change in Lipid Bilayers and Water Penetration Induced by Shock Waves: Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Biophys. J. 2006, 91, 2198–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshiyama, K.; Kodama, T.; Yano, T.; Fujikawa, S. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Structural Changes of Lipid Bilayers Induced by Shock Waves: Effects of Incident Angles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2008, 1778, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshiyama, K.; Yano, T.; Kodama, T. Self-Organization of a Stable Pore Structure in a Phospholipid Bilayer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 018105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, A.; Lauterborn, W.; Timm, R. Optical and Acoustic Investigations of the Dynamics of Laser-Produced Cavitation Bubbles near a Solid Boundary. J. Fluid Mech. 1989, 206, 299–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohl, C.; Kurz, T.; Geisler, R.; Lindau, O.; Lauterborn, W. Bubble Dynamics, Shock Waves and Sonoluminescence. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1999, 357, 269–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentacker, I.; De Cock, I.; Deckers, R.; De Smedt, S.C.; Moonen, C.T.W. Understanding Ultrasound Induced Sonoporation: Definitions and Underlying Mechanisms. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2014, 72, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohl, C.-D.; Arora, M.; Ikink, R.; de Jong, N.; Versluis, M.; Delius, M.; Lohse, D. Sonoporation from Jetting Cavitation Bubbles. Biophys. J. 2006, 91, 4285–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijering, B.D.M.; Juffermans, L.J.M.; van Wamel, A.; Henning, R.; Zuhorn, I.; Emmer, M.; Versteilen, A.M.G.; Paulus, W.J.; van Gilst, W.; Kooiman, K.; et al. Ultrasound and Microbubble-Targeted Delivery of Macromolecules Is Regulated by Induction of Endocytosis and Pore Formation. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derieppe, M.; Rojek, K.; Escoffre, J.-M.; de Senneville, B.D.; Moonen, C.; Bos, C. Recruitment of Endocytosis in Sonopermeabilization-Mediated Drug Delivery: A Real-Time Study. Phys. Biol. 2015, 12, 046010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekri, F.; Delos Santos, R.C.; Karshafian, R.; Antonescu, C.N. Ultrasound Microbubble Treatment Enhances Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis and Fluid-Phase Uptake through Distinct Mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cock, I.; Zagato, E.; Braeckmans, K.; Luan, Y.; de Jong, N.; De Smedt, S.C.; Lentacker, I. Ultrasound and Microbubble Mediated Drug Delivery: Acoustic Pressure as Determinant for Uptake via Membrane Pores or Endocytosis. J. Control Release 2015, 197, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.; Han, T.; Yu, A.C.H.; Xu, L. Mechanistic Understanding the Bioeffects of Ultrasound-Driven Microbubbles to Enhance Macromolecule Delivery. J. Control Release 2018, 272, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paula, D.M.B.; Valero-Lapchik, V.B.; Paredes-Gamero, E.J.; Han, S.W. Therapeutic Ultrasound Promotes Plasmid DNA Uptake by Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis. J. Gene Med. 2011, 13, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, J.; Ellisman, M.; Steinau, H.-U.; Stefan, E.; Dudda, M.; Hauser, M. Ultrasound Enhanced Endocytotic Activity of Human Fibroblasts. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2009, 35, 2084–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basta, G.; Venneri, L.; Lazzerini, G.; Pasanisi, E.; Pianelli, M.; Vesentini, N.; Del Turco, S.; Kusmic, C.; Picano, E. In Vitro Modulation of Intracellular Oxidative Stress of Endothelial Cells by Diagnostic Cardiac Ultrasound. Cardiovasc. Res. 2003, 58, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apodaca, G. Modulation of Membrane Traffic by Mechanical Stimuli. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2002, 282, F179–F190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlahakis, N.E.; Schroeder, M.A.; Pagano, R.E.; Hubmayr, R.D. Deformation-Induced Lipid Trafficking in Alveolar Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2001, 280, L938–L946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Lee, S.S.; Moon, H.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, H.J. PD-L1 Targeting Immune-Microbubble Complex Enhances Therapeutic Index in Murine Colon Cancer Models. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettinger, T.; Tranquart, F. Design of Microbubbles for Gene/Drug Delivery. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 880, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.S.; Panje, C.; Pysz, M.A.; Paulmurugan, R.; Rosenberg, J.; Gambhir, S.S.; Schneider, M.; Willmann, J.K. Cationic versus Neutral Microbubbles for Ultrasound-Mediated Gene Delivery in Cancer. Radiology 2012, 264, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, Z.; Ren, P.; You, M.; Zhang, J.; Fang, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Yan, F.; Zheng, H.; et al. Localized Delivery of ShRNA against PHD2 Protects the Heart from Acute Myocardial Infarction through Ultrasound-Targeted Cationic Microbubble Destruction. Theranostics 2017, 7, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentacker, I.; De Geest, B.G.; Vandenbroucke, R.E.; Peeters, L.; Demeester, J.; De Smedt, S.C.; Sanders, N.N. Ultrasound-Responsive Polymer-Coated Microbubbles That Bind and Protect DNA. Langmuir 2006, 22, 7273–7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borden, M.A.; Caskey, C.F.; Little, E.; Gillies, R.J.; Ferrara, K.W. DNA and Polylysine Adsorption and Multilayer Construction onto Cationic Lipid-Coated Microbubbles. Langmuir 2007, 23, 9401–9408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escoffre, J.-M.; Mannaris, C.; Geers, B.; Novell, A.; Lentacker, I.; Averkiou, M.; Bouakaz, A. Doxorubicin Liposome-Loaded Microbubbles for Contrast Imaging and Ultrasound-Triggered Drug Delivery. IEEE Trans Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2013, 60, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenkel, P.A.; Chen, S.; Thai, T.; Shohet, R.V.; Grayburn, P.A. DNA-Loaded Albumin Microbubbles Enhance Ultrasound-Mediated Transfection in Vitro. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2002, 28, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, E.K.; De Cock, I.; Keravnou, C.; Gallagher, M.K.; Keller, S.B.; Zheng, Y.; Averkiou, M. Engineered 3D Microvascular Networks for the Study of Ultrasound-Microbubble-Mediated Drug Delivery. Langmuir 2019, 35, 10128–10138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omata, D.; Hagiwara, F.; Munakata, L.; Shima, T.; Kageyama, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Azuma, T.; Takagi, S.; Seki, K.; Maruyama, K.; et al. Characterization of Brain-Targeted Drug Delivery Enhanced by a Combination of Lipid-Based Microbubbles and Non-Focused Ultrasound. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 2827–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Nan, S.-L.; Bai, W.-K.; Hu, B. Low-Frequency Ultrasound Combined with Microbubbles Improves Gene Transfection in Prostate Cancer Cells in Vitro and in Vivo. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, F.S.; Jankowski, R.J.; Klibanov, S.; Pina, M.L.; Alber, S.M.; Watkins, S.C.; Brandenburger, G.H.; Wagner, W.R. Microbubbles Targeted to Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 Bind to Activated Coronary Artery Endothelial Cells. Circulation 1998, 98, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Gustafsson, B.; Aldi, S.; Dusart, P.; Egri, G.; Butler, L.M.; Bone, D.; Dähne, L.; Hedin, U.; Caidahl, K. Molecular Imaging of a New Multimodal Microbubble for Adhesion Molecule Targeting. Cel. Mol. Bioeng. 2019, 12, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro, O.; Aguilar, R.J.; Tejera, E.; Megías, D.; de Torres-Alba, F.; Evangelista, A.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. Specific Targeting of Human Inflamed Endothelium and in Situ Vascular Tissue Transfection by the Use of Ultrasound Contrast Agents. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2009, 2, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shentu, W.-H.; Yan, C.-X.; Liu, C.-M.; Qi, R.-X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.-X.; Zhou, L.-M.; You, X.-D. Use of Cationic Microbubbles Targeted to P-Selectin to Improve Ultrasound-Mediated Gene Transfection of HVEGF165 to the Ischemic Myocardium. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2018, 19, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Deng, Q.; Hu, B.; Wang, Y.-J.; Chen, J.-L.; Cui, J.-J.; Cao, S.; Song, H.-N. Ultrasound Combined with Targeted Cationic Microbubble-mediated Angiogenesis Gene Transfection Improves Ischemic Heart Function. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 2293–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baston, C.; West, T.E. Lung Ultrasound in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Beyond. J.Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, E1763–E1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperandeo, M.; Varriale, A.; Sperandeo, G.; Filabozzi, P.; Piattelli, M.L.; Carnevale, V.; Decuzzi, M.; Vendemiale, G. Transthoracic Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Pulmonary Fibrosis: Our Experience. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2009, 35, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, V.; Perlas, A. Basics of Ultrasound Imaging. In Atlas of Ultrasound-Guided Procedures in Interventional Pain Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama, M.G.; Mintsopoulos, V.; Raheel, H.; Goldenberg, N.M.; Batt, J.E.; Brochard, L.; Kuebler, W.M.; Leong-Poi, H.; Karshafian, R.; Lee, W.L. Lung Ultrasound and Microbubbles Enhance Aminoglycoside Efficacy and Delivery to the Lung in Escherichia Coli-Induced Pneumonia and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espitalier, F.; Darrouzain, F.; Escoffre, J.-M.; Ternant, D.; Piver, E.; Bouakaz, A.; Remerand, F. Enhanced Amikacin Diffusion with Ultrasound and Microbubbles in a Mechanically Ventilated Condensed Lung Rabbit Model. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 10, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Chen, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, C.; Wei, P.; Xiao, D.; Han, B. Sinapultide-Loaded Microbubbles Combined with Ultrasound to Attenuate Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2020, 14, 5611–5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lu, D.-S.; Zhang, D.-Q.; Wang, X.; Ming, Y.; Wu, Z.-Y. Targeted Antagonism of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Reduces Mortality of Mice with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Curr. Med. Sci. 2020, 40, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, D.; Hynynen, K. Acute Inflammatory Response Following Increased Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability Induced by Focused Ultrasound Is Dependent on Microbubble Dose. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3989–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, D.; Oakden, W.; Hynynen, K. Investigating the Effects of Dexamethasone on Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability and Inflammatory Response Following Focused Ultrasound and Microbubble Exposure. Theranostics 2020, 10, 1604–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helfield, B.; Chen, X.; Watkins, S.C.; Villanueva, F.S. Biophysical Insight into Mechanisms of Sonoporation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9983–9988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadakos, P.J.; Gestring, M.L. (Eds.) Lung Ultrasound. In Encyclopedia of Trauma Care; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; p. 896. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, A.; Dalvi, S.V. Microbubble Formulations: Synthesis, Stability, Modeling and Biomedical Applications. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 301–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Negishi, Y. Microbubbles and Nanobubbles with Ultrasound for Systemic Gene Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.-Y.; Liang, K.; Qiu, R.-X. Targeted Gene Delivery in Tumor Xenografts by the Combination of Ultrasound-Targeted Microbubble Destruction and Polyethylenimine to Inhibit Survivin Gene Expression and Induce Apoptosis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 29, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.-K.Y.; Pham, B.; Zong, Y.; Perez, C.; Maris, D.O.; Hemphill, A.; Miao, C.H.; Matula, T.J.; Mourad, P.D.; Wei, H.; et al. Microbubbles and Ultrasound Increase Intraventricular Polyplex Gene Transfer to the Brain. J. Control Release 2016, 231, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devulapally, R.; Lee, T.; Barghava-Shah, A.; Sekar, T.V.; Foygel, K.; Bachawal, S.V.; Willmann, J.K.; Paulmurugan, R. Ultrasound-Guided Delivery of Thymidine Kinase-Nitroreductase Dual Therapeutic Genes by PEGylated-PLGA/PIE Nanoparticles for Enhanced Triple Negative Breast Cancer Therapy. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 1051–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liufu, C.; Li, Y.; Tu, J.; Zhang, H.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, P.; Chen, Z. Echogenic PEGylated PEI-Loaded Microbubble As Efficient Gene Delivery System. IJN 2019, 14, 8923–8941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panje, C.M.; Wang, D.S.; Pysz, M.A.; Paulmurugan, R.; Ren, Y.; Tranquart, F.; Tian, L.; Willmann, J.K. Ultrasound-Mediated Gene Delivery with Cationic versus Neutral Microbubbles: Effect of DNA and Microbubble Dose on in Vivo Transfection Efficiency. Theranostics 2012, 2, 1078–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirsi, S.R.; Hernandez, S.L.; Zielinski, L.; Blomback, H.; Koubaa, A.; Synder, M.; Homma, S.; Kandel, J.J.; Yamashiro, D.J.; Borden, M.A. Polyplex-Microbubble Hybrids for Ultrasound-Guided Plasmid DNA Delivery to Solid Tumors. J. Control Release 2012, 157, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.; Wu, M.D.; Cigarroa, G.; Belcik, J.T.; Ammi, A.; Moccetti, F.; Lindner, J.R. Influence of DNA-Microbubble Coupling on Contrast Ultrasound-Mediated Gene Transfection inMuscleand Liver. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2016, 29, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, K.W.; Borden, M.A.; Zhang, H. Lipid-Shelled Vehicles: Engineering for Ultrasound Molecular Imaging and Drug Delivery. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, A.-H.; Ho, H.-C.; Lin, Y.-C.; Chen, H.-K.; Wang, C.-H. Effects of Microbubble Size on Ultrasound-Induced Transdermal Delivery of High-Molecular-Weight Drugs. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.L.; Lu, X.; Fabiilli, M.; Dou, C. Influence of Microbubble Size and Pulse Amplitude on Hepatocyte Injury Induced by Contrast-Enhanced Diagnostic Ultrasound. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, R.; Bisazza, A.; Lembo, D. Micro- and Nanobubbles: A Versatile Non-Viral Platform for Gene Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayier, B.; Deng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Mu, Y.; Yan, F. Biosynthetic Nanobubbles for Targeted Gene Delivery by Focused Ultrasound. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 14757–14768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, R.; Bisazza, A.; Trotta, M.; Argenziano, M.; Civra, A.; Donalisio, M.; Lembo, D. New Chitosan Nanobubbles for Ultrasound-Mediated Gene Delivery: Preparation and in Vitro Characterization. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 3309–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- du Toit, L.C.; Govender, T.; Pillay, V.; Choonara, Y.E.; Kodama, T. Investigating the Effect of Polymeric Approaches on Circulation Time and Physical Properties of Nanobubbles. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jawadi, S.; Thakur, S.S. Ultrasound-Responsive Lipid Microbubbles for Drug Delivery: A Review of Preparation Techniques to Optimise Formulation Size, Stability and Drug Loading. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 585, 119559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnyawali, V.; Moon, B.-U.; Kieda, J.; Karshafian, R.; Kolios, M.C.; Tsai, S.S.H. Honey, I Shrunk the Bubbles: Microfluidic Vacuum Shrinkage of Lipid-Stabilized Microbubbles. Soft. Matter. 2017, 13, 4011–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumi, C.T.; Da Silva, W.J.; Schneider, F.K.; Maia, J.M.; Morales, R.E.M.; Filho, W.D.A. Micropipette-Based Microfluidic Device for Monodisperse Microbubbles Generation. Micromachines 2018, 9, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulsipher, K.W.; Hammer, D.A.; Lee, D.; Sehgal, C.M. Engineering Theranostic Microbubbles Using Microfluidics for Ultrasound Imaging and Therapy: A Review. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 2441–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Salari, A.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; Kerr, L.; Darbandi, A.; de Leon, A.C.; Exner, A.A.; Kolios, M.C.; Yuen, D.; et al. Microfluidic Generation of Monodisperse Nanobubbles by Selective Gas Dissolution. Small 2021, e2100345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimcevski, G.; Kotopoulis, S.; Bjånes, T.; Hoem, D.; Schjøtt, J.; Gjertsen, B.T.; Biermann, M.; Molven, A.; Sorbye, H.; McCormack, E.; et al. A Human Clinical Trial Using Ultrasound and Microbubbles to Enhance Gemcitabine Treatment of Inoperable Pancreatic Cancer. J. Control Release 2016, 243, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yan, K.; Shen, L.; Yang, W.; Gong, J.; Ding, K. Clinical Study of Ultrasound and Microbubbles for Enhancing Chemotherapeutic Sensitivity of Malignant Tumors in Digestive System. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 30, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubenfeld, G.D. Confronting the Frustrations of Negative Clinical Trials in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Ann. ATS 2015, 12, S58–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Medium | Acoustic Impedance |
|---|---|
| Lung | 0.18 × 106 Rayls |
| Air | 0.0004 ×106 Rayls |
| Blood | 1.65 ×106 Rayls |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanwal, R.; Joshi, K.; Ditmans, M.; Tsai, S.S.H.; Lee, W.L. Ultrasound and Microbubbles for Targeted Drug Delivery to the Lung Endothelium in ARDS: Cellular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070803
Sanwal R, Joshi K, Ditmans M, Tsai SSH, Lee WL. Ultrasound and Microbubbles for Targeted Drug Delivery to the Lung Endothelium in ARDS: Cellular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(7):803. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070803
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanwal, Rajiv, Kushal Joshi, Mihails Ditmans, Scott S. H. Tsai, and Warren L. Lee. 2021. "Ultrasound and Microbubbles for Targeted Drug Delivery to the Lung Endothelium in ARDS: Cellular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities" Biomedicines 9, no. 7: 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070803
APA StyleSanwal, R., Joshi, K., Ditmans, M., Tsai, S. S. H., & Lee, W. L. (2021). Ultrasound and Microbubbles for Targeted Drug Delivery to the Lung Endothelium in ARDS: Cellular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Biomedicines, 9(7), 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070803






