Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Do HDL Play a Role?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Low HDL Cholesterol Phenotype in HeFH
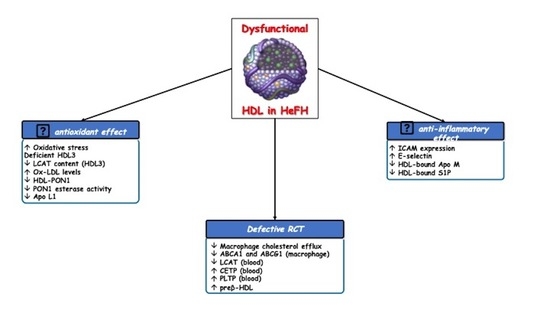
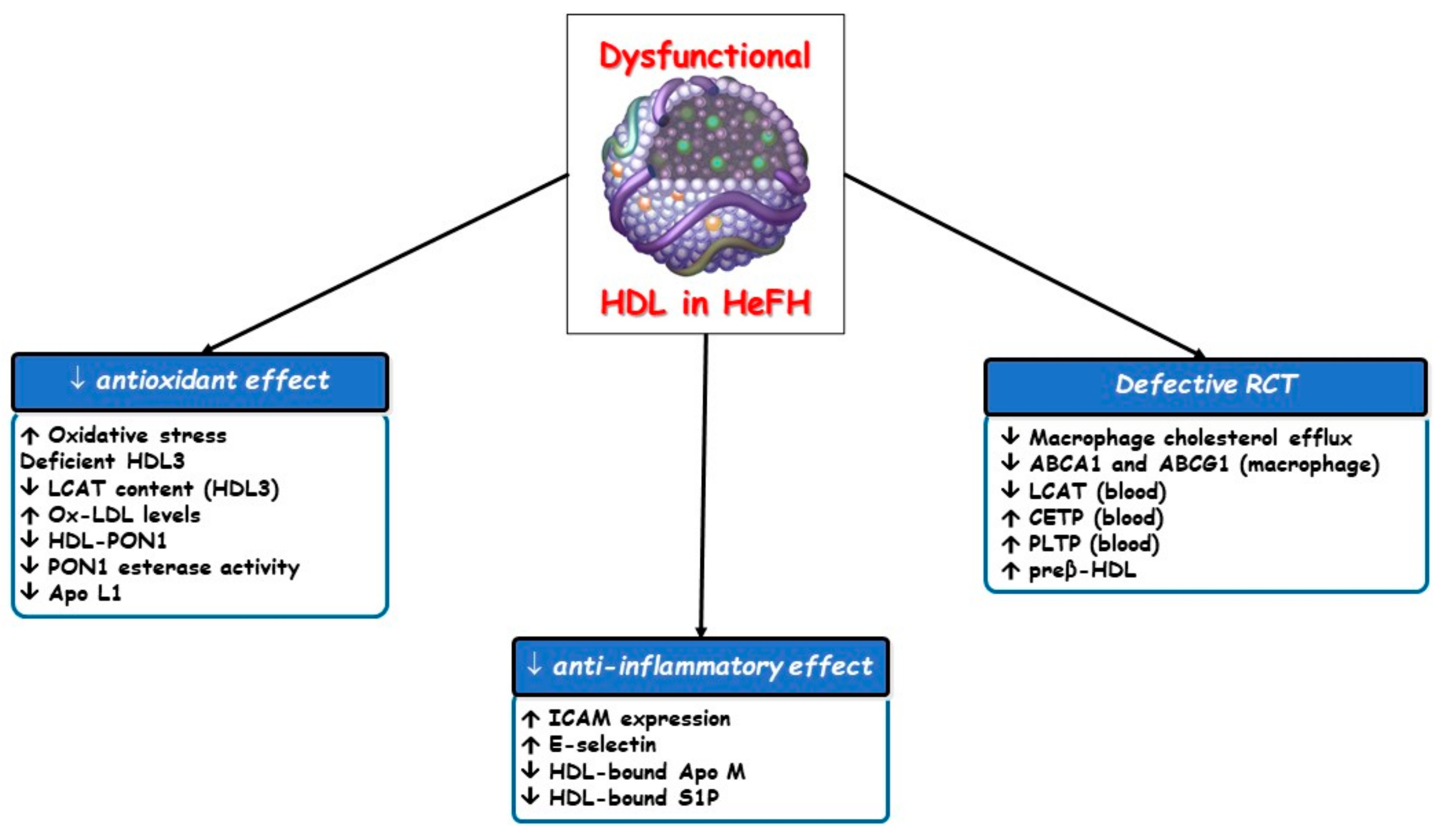
3. Dysfunctional HDL Particles in HeFH
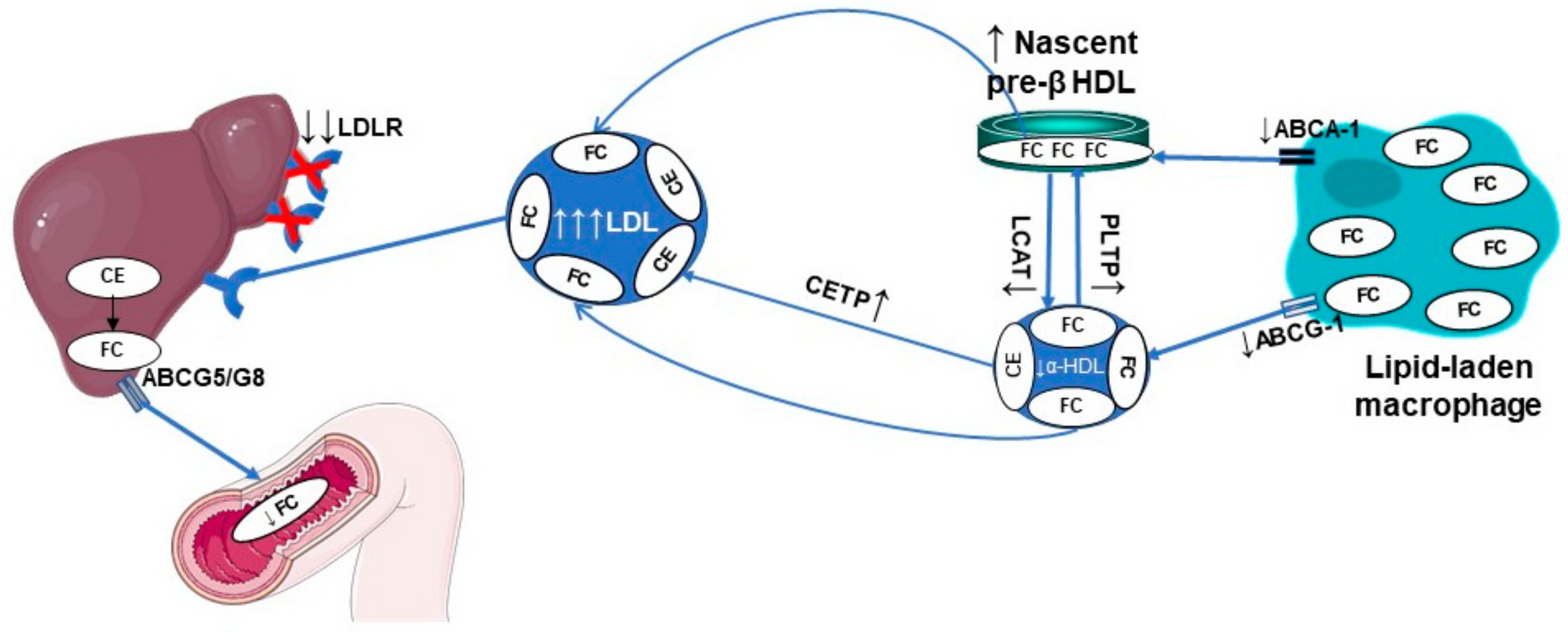
3.1. Defective Reverse Cholesterol Transport (RCT)
3.2. Other Altered HDL Atheroprotective Effects
3.3. MicroRNA Transport
4. Genetics and Epigenetics
5. Impact of Current FH Lipid-Lowering Drugs on HDL Functionality
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bleich, H.L.; Boro, E.S.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. Familial hypercholesterolemia: A genetic defect in the low-density lipoprotein receptor. N. Engl. J. Med. 1976, 294, 1386–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innerarity, T.L.; Mahley, R.W.; Weisgraber, K.H.; Bersot, T.P.; Krauss, R.M.; Vega, G.L.; Grundy, S.M.; Friedl, W.; Davignon, J.; McCarthy, B.J. Familial defective apolipoprotein B-100: A mutation of apolipoprotein B that causes hypercholesterolemia. J. Lipid Res. 1990, 31, 1337–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abifadel, M.; Rabès, J.P.; Devillers, M.; Munnich, A.; Erlich, D.; Junien, C.; Varret, M.; Boileau, C. Mutations and polymorphisms in the proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9 (PCSK9) gene in cholesterol metabolism and disease. Hum. Mutat. 2009, 30, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenarro, A.; Etxebarria, A.; de Castro-Orós, I.; Stef, M.; Bea, A.M.; Palacios, L.; Mateo-Gallego, R.; Benito-Vicente, A.; Ostolaza, H.; Tejedor, T.; et al. The p.Leu167del Mutation in APOE gene causes autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia by down-regulation of LDL receptor expression in hepatocytes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 2113–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khera, A.V.; Won, H.H.; Peloso, G.M.; Lawson, K.S.; Bartz, T.M.; Deng, X.; van Leeuwen, E.M.; Natarajan, P.; Emdin, C.A.; Bick, A.G.; et al. Diagnostic yield and clinical utility of sequencing familial hypercholesterolemia genes in patients with severe hypercholesterolemia. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 2578–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besseling, J.; Hovingh, G.K.; Huijgen, R.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Hutten, B.A. Statins in familial hypercholesterolemia: Consequences for coronary artery disease and all-cause mortality. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphries, S.E.; Cooper, J.A.; Seed, M.; Capps, N.; Durrington, P.N.; Jones, B.; McDowell, I.F.W.; Soran, H.; Neil, H.A.W.; Simon Broome Familial Hyperlipidaemia Register Group. Coronary heart disease mortality in treated familial hypercholesterolaemia: Update of the UK Simon Broome FH register. Atherosclerosis 2018, 274, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luirink, I.K.; Wiegman, A.; Kusters, D.M.; Hof, M.H.; Groothoff, J.W.; de Groot, E.; Kastelein, J.J.; Hutten, B.A. 20-Year follow-up of statins in children with familial hypercholesterolemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1547–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Calahorra, S.; Laclaustra, M.; Marco-Benedí, V.; Lamiquiz-Moneo, I.; Pedro-Botet, J.; Plana, N.; Sanchez-Hernandez, R.M.; Amor, A.J.; Almagro, F.; Fuentes, F.; et al. Effect of lipid-lowering treatment in cardiovascular disease prevalence in familial hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis 2019, 284, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrieres, J.; Lambert, J.; Lussier-Cacan, S.; Davignon, J. Coronary artery disease in heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia patients with the same LDL receptor gene mutation. Circulation 1995, 92, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civeira, F.; Castillo, S.; Alonso, R.; Meriño-Ibarra, E.; Cenarro, A.; Artied, M.; Martín-Fuentes, P.; Ros, E.; Pocoví, M.; Mata, P. Tendon xanthomas in familial hypercholesterolemia are associated with cardiovascular risk independently of the low density lipoprotein receptor gene mutation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 1960–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jansen, A.C.M.; van Aalst-Cohen, E.S.; Tanck, M.W.; Trip, M.D.; Lansberg, P.J.; Liem, A.H.; van Lennep, H.W.; Sijbrands, E.J.; Kastelein, J.J. The contribution of classical risk factors to cardiovascular disease in familial hypercholesterolaemia: Data in 2400 patients. J. Intern. Med. 2004, 25, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.D.; Gidding, S.S.; Hegele, R.A.; Cuchel, M.A.; Barter, P.J.; Watts, G.F.; Baum, S.J.; Catapano, A.L.; Chapman, M.J.; Defesche, J.C.; et al. Defining severe familial hypercholesterolaemia and the implications for clinical management: A consensus statement from the International Atherosclerosis Society Severe Familial Hypercholesterolemia Panel. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Isla, L.P.; Alonso, R.; Mata, N.; Fernández-Pérez, C.; Muñiz, O.; Díaz-Díaz, J.L.; Saltijeral, A.; Fuentes-Jiménez, F.; de Andrés, R.; Zambón, D.; et al. Predicting cardiovascular events in familial hypercholesterolemia: The SAFEHEART registry (Spanish Familial Hypercholesterolemia Cohort Study). Circulation 2017, 135, 2133–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paquette, M.; Baass, A. Predicting cardiovascular disease in familial hypercholesterolemia. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2018, 29, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akioyamen, L.E.; Genest, J.; Chu, A.; Inibhunu, H.; Ko, D.T.; Tu, J.V. Risk factors for cardiovascular disease in heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2019, 13, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barter, P.J.; Rye, K.A. HDL cholesterol concentration or HDL function: Which matters? Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2487–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Bryan Brewer, H., Jr.; Barter, P.J.; Björkegren, J.L.M.; Chapman, M.J.; Gaudet, D.; Kim, D.S.; Niesor, E.; Rye, K.A.; Sacks, F.M.; et al. HDL and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: Genetic insights into complex biology. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macheboeuf, M. Recherches sur les phosphoaminolipides du sérum sanguin. Nature des phospholipides liés aux albumines du sérum de cheval à l’état de cenapses acido-précipitables. Bull. Soc. Chim. Biol. (Paris) 1929, 11, 485–503. [Google Scholar]
- Castelli, W.P.; Garrison, R.J.; Wilson, P.W.; Abbott, R.D.; Kalousdian, S.; Kannel, W.B. Incidence of coronary heart disease and lipo-protein cholesterol levels. The Framingham Study. JAMA 1986, 256, 2835–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration; Di Angelantonio, E.; Sarwar, N.; Perry, P.; Kaptog, S.; Ray, K.K.; Thompson, A.; Wood, A.M.; Lewington, S.; Sattar, N.; et al. Major lipids, apolipoproteins, and risk of vascular disease. JAMA 2009, 302, 1993–2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mackey, R.H.; Greenland, P.; Goff, D.C.; Lloyd-Jones, D.; Sibley, C.T.; Mora, S. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and particle concentrations, carotid atherosclerosis, and coronary events: MESA (Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seftel, H.C. HDL cholesterol in familial hypercholesterolemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1984, 310, 125. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, J.L.; Kita, T.; Brown, M.S. Defective lipoprotein receptors and atherosclerosis. Lessons from an animal counterpart of familial hypercholesterolemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1983, 309, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Real, J.T.; Chaves, F.J.; Martínez-Usó, I.; García-García, A.B.; Ascaso, J.F.; Carmena, R. Importance of HDL cholesterol levels and the total/HDL cholesterol ratio as a risk factor for coronary heart disease in molecularly defined heterozygous familial hypercho-lesterolaemia. Eur. Heart J. 2001, 22, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junyent, M.; Cofán, M.; Núñez, I.; Gilabert, R.; Zambón, D.; Ros, E. Influence of HDL cholesterol on preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in familial hypercholesterolemia. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khoury, E.; Brisson, D.; Roy, N.; Tremblay, G.; Gaudet, D. Identifying Markers of Cardiovascular Event-Free Survival in Familial Hypercholesterolemia. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvan, A.Q.; Santoro, D.; Natali, A.; Sampietro, T.; Boni, C.; Masoni, A.; Buzzigoli, G.; Ferrannini, E. Insulin sensitivity in familial hypercholesterolemia. Metabolism 1993, 42, 1359–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudet, D.; Vohl, M.C.; Perron, P.; Tremblay, G.; Gagné, C.; Lesiège, D.; Bergeron, J.; Moorjani, S.; Despréset, J.-P. Relationships of abdominal obesity and hyperinsulinemia to angiographically assessed coronary artery disease in men with known mutations in the LDL receptor gene. Circulation 1998, 97, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemello, K.; García-Nafría, J.; Gallo, A.; Martín, C.; Lambert, G.; Blom, D. Lipoprotein metabolism in familial hypercholesterolemia. J. Lipid Res. 2021, 62, 100062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frénais, R.; Ouguerram, K.; Maugeais, C.; Marchini, J.S.; Benlian, P.; Bard, J.; Magot, T.; Krempf, M. Apolipoprotein A-I kinetics in heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia: A stable isotope study. J. Lipid Res. 1999, 40, 1506–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogue, J.C.; Lamarche, B.; Gaudet, D.; Tremblay, A.J.; Després, J.P.; Bergeron, J.; Gagnéa, C.; Couturea, P. Association of heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia with smaller HDL particle size. Atherosclerosis 2007, 190, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellanger, N.; Orsoni, A.; Julia, Z.; Fournier, N.; Frisdal, E.; Duchene, E.; Bruckert, E.; Carrie, A.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Pirault, J.; et al. Atheroprotective reverse cholesterol transport pathway is defective in familial hypercholesterolemia. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cedó, L.; Plana, N.; Metso, J.; Lee-Rueckert, M.; Sanchez-Quesada, J.L.; Kovanen, P.T.; Jauhiainen, M.; Masana, L.; Escolà-Gil, J.C.; Blanco-Vaca, F. Altered HDL remodeling and functionality in familial hypercholesterolemia. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 466–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, J.C.; Goldberg, R.B.; Rubinstein, A.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Brown, W.V.; Baker, S.; Joffe, B.I.; Seftel, H.C. Plasma lipoprotein distribution of apolipoprotein E in familial hypercholesterolemia. Arteriosclerosi. 1987, 7, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miltiadous, G.; Cariolou, M.A.; Elisaf, M. HDL cholesterol levels in patients with molecularly defined familial hypercholesterole-mia. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2002, 32, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Cubedo, J.; Padro, T.; Alonso, R.; Mata, P.; Badimon, L. ApoL1 levels in high density lipoprotein and cardiovascular event presentation in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 1059–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Bryan Brewer, H., Jr.; Ansell, B.J.; Barter, P.; Chapman, M.J.; Heinecke, J.W.; Kontush, A.; Tall, A.R.; Webb, N.R. Dysfunctional HDL and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjali, S.; Momtazi, A.A.; Banach, M.; Kovanen, P.T.; Stein, E.A.; Sahebkar, A. HDL abnormalities in familial hypercholesterolemia: Focus on biological functions. Prog. Lipid Res. 2017, 67, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.K.P.; Nicholls, S.J.; Tan, J.T.M.; Bursill, C.A. The role of high-density lipoproteins in diabetes and its vascular complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rohatgi, A.; Khera, A.; Berry, J.D.; Givens, E.G.; Ayers, C.R.; Wedin, K.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Yuhanna, I.S.; Rader, D.R.; de Lemos, J.A.; et al. HDL cholesterol efflux capacity and incident cardiovascular events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2383–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padró, T.; Cubedo, J.; Camino, S.; Bejar, M.T.; Ben-Aicha, S.; Mendieta, G.; Escolà-Gil, J.C.; Escate, R.; Gutiérrez, M.; Casaní, L.; et al. Detrimental effect of hypercholesterolemia on high-density lipoprotein particle remodeling in pigs. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escolà-Gil, J.C.; Rotllan, N.; Julve, J.; Blanco-Vaca, F. Reverse cholesterol transport dysfunction is a feature of familial hypercho-lesterolemia. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2021, 23, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, L.R.; Santos, R.D.; Miname, M.H.; Deus, D.F.; Lima, E.S.; Maranhão, R.C. Transfer of lipids to high-density lipoprotein (HDL) is altered in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. Metabolism 2013, 62, 1061–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versmissen, J.; Vongpromek, R.; Yahya, R.; van der Net, J.B.; van Vark-van der Zee, L.; Blommesteijn-Touw, J.; Wattimena, D.; Rietveld, T.; Pullinger, C.R.; Christoffersen, C.; et al. Familial hypercholesterolaemia: Cholesterol efflux and coronary disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 46, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedo, L.; Metso, J.; Santos, D.; García-León, A.; Plana, N.; Sabate-Soler, S.; Rotllan, N.; Rivas-Urbina, A.; Mendez-Lara, K.A.; Tondo, M.; et al. LDL receptor regulates the reverse transport of macrophage-derived unesterified cholesterol via concerted action of the HDL-LDL axis: Insight from mouse models. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 778–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsoni, A.; Villard, E.F.; Bruckert, E.; Robillard, P.; Carrie, A.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Chapman, M.J.; Dallinga-Thie, G.M.; Le Goff, W.; Guerin, M. Impact of LDL apheresis on atheroprotective reverse cholesterol transport pathway in familial hypercholesterolemia. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bahrami, A.; Liberale, L.; Reiner, Ž.; Carbone, F.; Montecucco, F.; Sahebkar, A. Inflammatory biomarkers for cardiovascular risk stratification in familial hypercholesterolemia. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 25–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balstad, T.R.; Holven, K.B.; Ottestad, I.O.; Otterdal, K.; Halvorsen, B.; Myhre, A.M.; Ose, L.; Nenseter, M. Altered composition of HDL3 in FH subjects causing a HDL subfraction with less atheroprotective function. Clin. Chim. Acta 2005, 359, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, H.; Saheb, S.; Couturier, M.; Atassi, M.; Orsoni, A.; Carrié, A.; Therond, P.; Chantepie, S.; Robillard, P.; Bruckert, E.; et al. Small, dense high-density lipoprotein 3 particles exhibit defective antioxidative and anti-inflammatory function in familial hypercholesterolemia: Partial correction by low-density lipoprotein apheresis. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2016, 10, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swertfeger, D.K.; Rebholz, S.; Li, H.; Shah, A.S.; Davidson, W.S.; Lu, L.J. Feasibility of a plasma bioassay to assess oxidative protection of low-density lipoproteins by high-density lipoproteins. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2018, 12, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hine, D.; Mackness, B.; Mackness, M. Coincubation of PON1, APO A1, and LCAT increases the time HDL is able to prevent LDL oxidation. IUBMB Life 2011, 64, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, P.R.; Jannes, C.E.; Marsiglia, J.D.; Krieger, J.E.; Santos, R.D.; Pereira, A.C. Predictors of cardiovascular events after one year of molecular screening for Familial hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis 2016, 250, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van den Berg, E.H.; Gruppen, E.G.; James, R.W.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Dullaart, R.P.F. Serum paraoxonase 1 activity is paradoxically maintained in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease despite low HDL cholesterol. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Himbergen, T.M.; Roest, M.; de Graaf, J.; Jansen, E.H.J.M.; Hattori, H.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Voorbij, H.A.; Stalenhoef, A.F.; van Tits, L.J. Indications that paraoxonase-1 contributes to plasma high density lipoprotein levels in familial hypercholesterolemia. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Idrees, M.; Siddiq, A.R.; Ajmal, M.; Akram, M.; Khalid, R.R.; Hussain, A.; Qamar, R.; Bokhari, H. Decreased serum PON1 arylesterase activity in familial hypercholesterolemia patients with a mutated LDLR gene. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2018, 41, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desgagné, V.; Bouchard, L.; Guerin, R. MicroRNAs in lipoprotein and lipid metabolism: From biological function to clinical ap-plication. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 667–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desgagné, V.; Guérin, R.; Guay, S.P.; Boyer, M.; Hutchins, E.; Picard, S.; Maréchal, A.; Corbin, F.; Van Keuren-Jensen, K.; Arsenault, B.J.; et al. Human high-density lipoprotein microtranscriptome is unique and suggests an extended role in lipid metabolism. Epigenomics 2019, 11, 917–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, K.C.; Palmisano, B.T.; Shoucri, B.M.; Shamburek, R.D.; Remaley, A.T. MicroRNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Agostino, M.; Martino, F.; Sileno, S.; Barillà, F.; Beji, S.; Marchetti, L.; Gangi, F.M.; Persico, L.; Picozza, M.; Montali, A.; et al. Circulating miR-200c is up-regulated in paediatric patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia and correlates with miR-33a/b levels: Implication of a ZEB1-dependent mechanism. Clin. Sci. (Lond) 2017, 131, 2397–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scicali, R.; Di Pino, A.; Pavanello, C.; Ossoli, A.; Strazzella, A.; Alberti, A.; Di Mauro, S.; Scamporrino, A.; Urbano, F.; Filippello, A.; et al. Analysis of HDL-microRNA panel in heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia subjects with LDL receptor null or defective mutation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prats-Uribe, A.; Sayols-Baixeras, S.; Fernández-Sanlés, A.; Subirana, I.; Carreras-Torres, R.; Vilahur, G.; Civeira, F.; Marrugat, J.; Fitó, M.; Hernáez, Á.; et al. High-density lipoprotein characteristics and coronary artery disease: A Mendelian randomization study. Metabolism 2020, 112, 154351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Aalst-Cohen, E.S.; Jansen, A.C.M.; Boekholdt, S.M.; Tanck, M.W.T.; Fontecha, M.R.; Cheng, S.; Li, J.; Defesche, J.C.; Kuivenhoven, J.A.; Kastelein, J.J. Genetic determinants of plasma HDL-cholesterol levels in familial hypercholesterolemia. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 13, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eichler, E.E.; Flint, J.; Gibson, G.; Kong, A.; Leal, S.M.; Moore, J.H.; Nadeau, J.H. Missing heritability and strategies for finding the underlying causes of complex disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hegele, R.A. Environmental modulation of atherosclerosis end points in familial hypercholesterolemia. Atheroscler. Suppl. 2002, 2, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Graaf, A.; Vissers, M.N.; Gaudet, D.; Brisson, D.; Sivapalaratnam, S.; Roseboom, T.J.; Jansen, A.C.; Kastelein, J.J.; Hutten, B.A. Dyslipidemia of mothers with familial hypercholesterolemia deteriorates lipids in adult offspring. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 2673–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Langmann, T.; Porsch-Ozcürümez, M.; Heimerl, S.; Probst, M.; Moehle, C.; Taher, M.; Borsukova, H.; Kielar, D.; Kaminski, W.E.; Dittrich-Wengenroth, E.; et al. Identification of sterol-independent regulatory elements in the human ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 promoter: Role of Sp1/3, E-box binding factors and an oncostatin M-responsive element. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 14443–14450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guay, S.P.; Brisson, D.; Munger, J.; Lamarche, B.; Gaudet, D.; Bouchard, L. ABCA1gene promoter DNA methylation is associated with HDL particle profile and coronary artery disease in familial hypercholesterolemia. Epigenetics 2012, 7, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guay, S.; Brisson, D.; Lamarche, B.; Marceau, P.; Vohl, M.; Gaudet, D.; Bouchard, L. DNA methylation variations at CETP and LPL gene promoter loci: New molecular biomarkers associated with blood lipid profile variability. Atherosclerosis 2013, 228, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guay, S.P.; Voisin, G.; Brisson, D.; Munger, J.; Lamarche, B.; Gaudet, D.; Bouchard, L. Epigenome-wide analysis in familial hypercholesterolemia identified new loci associated with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol concentration. Epigenomics 2012, 4, 623–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guay, S.P.; Légaré, C.; Brisson, D.; Mathieu, P.; Bossé, Y.; Gaudet, D.; Bouchard, L. Epigenetic and genetic variations at the TNNT1 gene locus are associated with HDL-C levels and coronary artery disease. Epigenomics 2016, 8, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guay, S.P.; Brisson, D.; Lamarche, B.; Gaudet, D.; Bouchard, L. Epipolymorphisms within lipoprotein genes contribute inde-pendently to plasma lipid levels in familial hypercholesterolemia. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomás, M.; Sentí, M.; García-Faria, F.; Vila, J.; Torrents, A.; Covas, M.; Marrugat, J. Effect of simvastatin therapy on paraoxonase activity and related lipoproteins in familial hypercholesterolemic patients. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 2113–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deakin, S.; Leviev, I.; Guernier, S.; James, R.W. Simvastatin modulates expression of the PON1 gene and increases serum paraoxonase: A role for sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 2083–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Himbergen, T.M.; Tits, L.J.H.; de Voorbij, H.A.M.; Graaf, J.; Stalenhoef, A.F.H.; Roest, M. The effect of statin therapy on plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels is modified by paraoxonase-1 in patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia. J. Intern. Med. 2005, 258, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastelein, J.J.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Langslet, G.; Hovingh, G.K.; Ceska, R.; Dufour, R.; Blom, D.; Civeira, F.; Krempf, M.; Lorenzato, C.; et al. ODYSSEY FH I and FH II: 78 week results with alirocumab treatment in 735 patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 43, 2996–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raal, F.J.; Stein, E.A.; Dufour, R.; Turner, T.; Civeira, F.; Burgess, L.; Langslet, G.; Scott, R.; Olsson, A.G.; Sullivan, D.; et al. PCSK9 inhibition with evolocumab (AMG 145) in heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia: (RUTHERFORD-2): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatine, M.S.; Giugliano, R.P.; Keech, A.C.; Honarpour, N.; Wiviott, S.D.; Murphy, S.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Wasserman, S.M.; et al. Evolocumab and clinical outcomes in patients with cardiovascular disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, G.G.; Steg, P.G.; Szarek, M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Bittner, V.A.; Diaz, R.; Edelberg, J.M.; Goodman, S.G.; Hanotin, C.; Harrington, R.A.; et al. Alirocumab and cardiovascular outcomes after acute coronary syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2097–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnap, S.A.; Joshi, A.; Tsimikas, S.; Fernández-Hernando, C.; Kiechl, S.; Berry, S.E.; Hall, W.; Levkau, B.; Mayr, M. High-density lipoproteins are the main carriers of PCSK9 in the circulation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 1495–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, L.H.; Yin, R.X.; Miao, L.; Hu, X.J.; Yan, T.T.; Cao, X.L.; Wu, D.F.; Li, Q.; Pan, S.L.; Wu, J.Z. The proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 gene E670G polymorphism and serum lipid levels in the Guangxi Bai Ku Yao and Han populations. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakoski, S.G.; Lagace, T.A.; Cohen, J.C.; Horton, J.D.; Hobbs, H.H. Genetic and metabolic determinants of plasma PCSK9 levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 2537–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baass, A.; Dubuc, G.; Tremblay, M.; Delvin, E.E.; O’Loughlin, J.; Levy, E.; Davignon, J.; Lambert, M. Plasma PCSK9 is associated with age, sex, and multiple metabolic markers in a population-based sample of children and adolescents. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferri, N.; Corsini, A.; Macchi, C.; Magni, P.; Ruscica, M. Proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 and high-density lipoprotein metabolism: Experimental animal models and clinical evidence. Transl. Res. 2016, 173, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Hao, P.P.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, R.-H.; Kong, Q.-Z.; Cai, X.-J.; Zhao, Z.; Qi, J.-N.; Li, Y.; Xiao, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 monoclonal antibody in adults with familial hypercholesterolemia. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 30455–30463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qian, L.J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.M.; Chu, M.; Yao, J.; Xu, D. Therapeutic efficacy and safety of PCSK9-monoclonal antibodies on familial hypercholesterolemia and statin-intolerant patients: A meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, A.; Trigatti, B.L.; Mineo, C.; Knaack, D.; Wilkins, J.T.; Sahoo, D.; Asztalos, B.F.; Mora, S.; Cuchel, M.; Pownall, H.J.; et al. Proceedings of the ninth HDL (high-density lipoprotein) workshop: Focus on cardiovascular disease. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 2457–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pedro-Botet, J.; Climent, E.; Benaiges, D. Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Do HDL Play a Role? Biomedicines 2021, 9, 810. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070810
Pedro-Botet J, Climent E, Benaiges D. Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Do HDL Play a Role? Biomedicines. 2021; 9(7):810. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070810
Chicago/Turabian StylePedro-Botet, Juan, Elisenda Climent, and David Benaiges. 2021. "Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Do HDL Play a Role?" Biomedicines 9, no. 7: 810. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070810
APA StylePedro-Botet, J., Climent, E., & Benaiges, D. (2021). Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Do HDL Play a Role? Biomedicines, 9(7), 810. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070810