Biphasic Effects of Blue Light Irradiation on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Isolation and Cell Culture
2.2. Blue Light Irradiation
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.5. Reactive Oxygen Species Measurements
2.5.1. Measurement Using The Redox Sensor
2.5.2. Measurement Using the 2′,7′-Dichlor-dihydrofluorescein-diacetate (DCFH-DA) Dye
2.6. Apoptosis Assay
2.7. Migration Assays
2.7.1. Wound Healing Assay
2.7.2. Transwell Assay
2.8. Angiogenic Assays
2.8.1. Tube Formation Assay
2.8.2. Spheroid Sprouting Assay
2.9. RNA Isolation and Sequencing
3. Bioinformatic Analysis of RNA Sequencing
3.1. Real-time Quantitative PCR
3.2. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Effects of Blue Light Irradiation on Cell Viability and Proliferation
4.2. Effect of Blue Light on Cell Redox Change and Apoptosis
4.3. Effect of Blue Light on Cell Migration
4.4. Effect of Blue Light on the Angiogenic Potential of HUVECs
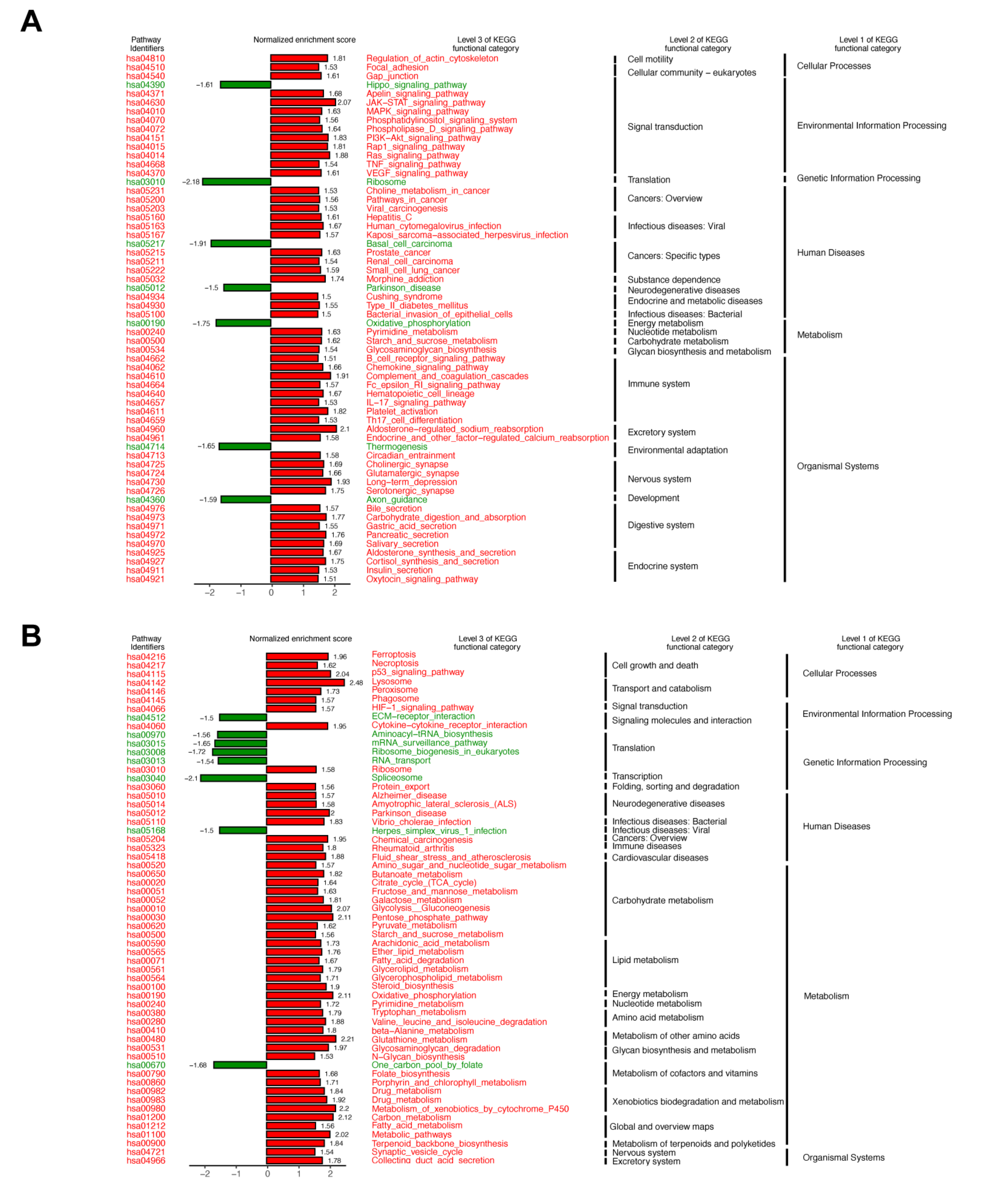
4.5. Gene Expression Analysis from RNA-Sequencing
4.6. Real-Time PCR Verifies Genes in Enriched Pathways
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carmeliet, P.; Jain, R.K. Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature 2011, 473, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carmeliet, P. Mechanisms of angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosino, P.; Papa, A.; Buonauro, A.; Mosella, M.; Calcaterra, I.; Spedicato, G.A.; Maniscalco, M.; Di Minno, M.N.D. Clinical assessment of endothelial function in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: A meta-analysis with meta-regressions. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, e13552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guffey, J.S.; Wilborn, J. In Vitro Bactericidal Effects of 405-nm and 470-nm Blue Light. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2006, 24, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omi, T.; Bjerring, P.; Sato, S.; Kawana, S.; Hankins, R.; Honda, M. 420 nm intense continuous light therapy for acne. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2004, 6, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnitkind, E.; Yaping, E.; Geen, S.; Shalita, A.R.; Lee, W.-L. Anti-inflammatory properties of narrow-band blue light. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2006, 5, 605–610. [Google Scholar]
- Pfaff, S.; Liebmann, J.; Born, M.; Merk, H.F.; Von Felbert, V. Prospective Randomized Long-Term Study on the Efficacy and Safety of UV-Free Blue Light for Treating Mild Psoriasis Vulgaris. Dermatology 2015, 231, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Chawla, D.; Deorari, A. Cochrane Neonatal Group Light-emitting diode phototherapy for unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia in neonates. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 2011, CD007969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaw, U.; Ilyas, M.; Bullock, T.; Rittwage, L.; Riha, M.; Vidimos, A.; Hu, B.; Warren, C.B.; Maytin, E.V. A regimen to minimize pain during blue light photodynamic therapy of actinic keratoses: Bilaterally controlled, randomized trial of simultaneous versus conventional illumination. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dungel, P.; Hartinger, J.; Chaudary, S.; Slezak, P.; Hofmann, A.; Hausner, T.; Strassl, M.; Wintner, E.; Redl, H.; Mittermayr, R. Low level light therapy by LED of different wavelength induces angiogenesis and improves ischemic wound healing. Lasers Surg. Med. 2014, 46, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, M.; Broja, M.; Sansone, R.; Gröne, M.; Skene, S.; Liebmann, J.; Suschek, C.V.; Born, M.; Kelm, M.; Heiss, C. Blue light exposure decreases systolic blood pressure, arterial stiffness, and improves endothelial function in humans. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2018, 25, 1875–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohringer, S.; Holnthoner, W.; Chaudary, S.; Slezak, P.; Priglinger, E.; Strassl, M.; Pill, K.; Mühleder, S.; Redl, H.; Dungel, P. The impact of wavelengths of LED light-therapy on endothelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorey, C.K.; Delori, F.C.; Akeo, K. Growth of cultured RPE and endothelial cells is inhibited by blue light but not green or red light. Curr. Eye Res. 1990, 9, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, E.A.; Nachman, R.L.; Becker, C.G.; Minick, C.R. Culture of Human Endothelial Cells Derived from Umbilical Veins. IDENTIFICATION BY MORPHOLOGIC AND IMMUNOLOGIC CRITERIA. J. Clin. Investig. 1973, 52, 2745–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demaison, C.; Parsley, K.L.; Brouns, G.; Scherr, M.; Battmer, K.; Kinnon, C.; Grez, M.; Thrasher, A. High-Level Transduction and Gene Expression in Hematopoietic Repopulating Cells Using a Human Imunodeficiency Virus Type 1-Based Lentiviral Vector Containing an Internal Spleen Focus Forming Virus Promoter. Hum. Gene Ther. 2002, 13, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, P.; Herskind, C.; Fleckenstein, K.; Spier, I.; Laufs, S.; Zeller, W.J.; Fruehauf, S.; Wenz, F. MDR1Gene Transfer Using a Lentiviral SIN Vector Confers Radioprotection to Human CD34+Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells. Radiat. Res. 2008, 169, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byer, S.J.; Brossier, N.M.; Peavler, L.T.; Eckert, J.M.; Watkins, S.; Roth, K.A.; Carroll, S.L. Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Invasion Requires Aberrantly Expressed EGF Receptors and Is Variably Enhanced by Multiple EGF Family Ligands. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 72, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.-X.; Xing, J.-G.; Wang, L.-L.; Jiang, H.-L.; Guo, S.-L.; Liu, R. Luteolin Inhibits Fibrillary β-Amyloid1–40-Induced Inflammation in a Human Blood-Brain Barrier Model by Suppressing the p38 MAPK-Mediated NF-κB Signaling Pathways. Molecules 2017, 22, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimaitiyiming, H.; Norman, H.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, S. CD47 Deficiency Protects Mice From Diet-induced Obesity and Improves Whole Body Glucose Tolerance and Insulin Sensitivity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carpentier, G.; Berndt, S.; Ferratge, S.; Rasband, W.; Cuendet, M.; Uzan, G.; Albanese, P. Angiogenesis Analyzer for ImageJ—A comparative morphometric analysis of “Endothelial Tube Formation Assay” and “Fibrin Bead Assay”. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-T.; Wang, J.-Y.; Lin, Y.-F.; Wo, A.M.; Chen, B.P.C.; Lee, H. Three-dimensional spheroid culture targeting versatile tissue bioassays using a PDMS-based hanging drop array. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Klapczynski, A.; Kuch, N.; Arpino, F.; Simon-Keller, K.; De La Torre, C.; Sticht, C.; Van Abeelen, F.A.; Oversluizen, G.; Gretz, N. Gene expression profiling reveals aryl hydrocarbon receptor as a possible target for photobiomodulation when using blue light. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, srep33847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Distler, E.; Klapczynski, A.; Arpino, F.; Kuch, N.; Simon-Keller, K.; Sticht, C.; Van Abeelen, F.A.; Gretz, N.; Oversluizen, G. Blue light inhibits proliferation of melanoma cells. In Proceedings of the Mechanisms of Photobiomodulation Therapy XI, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13 February 2016; Volume 9695, p. 969503. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, A.; Sticht, C.; Dweep, H.; Van Abeelen, F.A.; Gretz, N.; Oversluizen, G. Impact of blue LED irradiation on proliferation and gene expression of cultured human keratinocytes. In Proceedings of the Mechanisms for Low-Light Therapy X, San Francisco, CA, USA, 7–8 February 2015; Volume 9309, p. 930909. [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood, D.B.; Wataha, J.C.; Lewis, J.B.; Tseng, W.Y.; Messer, R.L.; Hsu, S.D. Blue light generates reactive oxygen species (ROS) differentially in tumor vs. normal epithelial cells. Dent. Mater. 2005, 21, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Esawi, M.; Arthaut, L.-D.; Jourdan, N.; D’Harlingue, A.; Link, J.; Martino, C.F.; Ahmad, M. Blue-light induced biosynthesis of ROS contributes to the signaling mechanism of Arabidopsis cryptochrome. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oron, U.; Yaakobi, T.; Oron, A.; Hayam, G.; Gepstein, L.; Rubin, O.; Wolf, T.; Ben Haim, S. Attenuation of infarct size in rats and dogs after myocardial infarction by low-energy laser irradiation. Lasers Surg. Med. 2001, 28, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzafame, R.J.; Stadler, I.; Kurtz, A.F.; Connelly, R.; Brondon, P.; Olson, D. Reciprocity of exposure time and irradiance on energy density during photoradiation on wound healing in a murine pressure ulcer model. Lasers Surg. Med. 2007, 39, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-Y.; Chen, A.C.-H.; Carroll, J.D.; Hamblin, M.R. Biphasic Dose Response in Low Level Light Therapy. Dose-Response 2009, 7, 358–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Luo, J.; Rana, J.S.; Laham, R.; Sellke, F.W.; Li, J. Involvement of COX-2 in VEGF-induced angiogenesis via P38 and JNK pathways in vascular endothelial cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 69, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.-L.; Wartmann, M.; Lin, A.Y.; Knopf, J.L.; Seth, A.; Davis, R.J. cPLA2 is phosphorylated and activated by MAP kinase. Cell 1993, 72, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förstermann, U.; Münzel, T. Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase in Vascular Disease. Circ. 2006, 113, 1708–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- NO and Angiogenesis—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14664903/ (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Opländer, C.; Deck, A.; Volkmar, C.M.; Kirsch, M.; Liebmann, J.; Born, M.; van Abeelen, F.; van Faassen, E.E.; Kröncke, K.-D.; Windolf, J.; et al. Mechanism and biological relevance of blue-light (420–453 nm)-induced nonenzymatic nitric oxide generation from photolabile nitric oxide derivates in human skin in vitro and in vivo. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 1363–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebmann, J.; Born, M.; Kolb-Bachofen, V. Blue-Light Irradiation Regulates Proliferation and Differentiation in Human Skin Cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krassovka, J.M.; Suschek, C.V.; Prost, M.; Grotheer, V.; Schiefer, J.L.; Demir, E.; Fuchs, P.C.; Windolf, J.; Stürmer, E.K.; Opländer, C. The impact of non-toxic blue light (453 nm) on cellular antioxidative capacity, TGF-β1 signaling, and myofibrogenesis of human skin fibroblasts. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B: Biol. 2020, 209, 111952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, P.-S.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, E.-M.; Hwang, H.; Ryu, H.H.; Lim, S.; Sohn, M.-H.; Jeong, H.-J. Inhibitory effect of blue light emitting diode on migration and invasion of cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 3444–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Yan, G.; Gong, R.; Zhang, L.; Liu, T.; Feng, C.; Du, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Li, Y.; et al. Effects of Blue Light Emitting Diode Irradiation On the Proliferation, Apoptosis and Differentiation of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seko, Y.; Pang, J.; Tokoro, T.; Ichinose, S.; Mochizuki, M. Blue light-induced apoptosis in cultured retinal pigment epithelium cells of the rat. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2001, 239, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-S.; Zheng, R.-L. Biphasic regulation of angiogenesis by reactive oxygen species. Die Pharm. 2006, 61, 223–229. [Google Scholar]
- Kuida, K.; Haydar, T.; Kuan, C.-Y.; Gu, Y.; Taya, C.; Karasuyama, H.; Su, M.S.-S.; Rakic, P.; Flavell, R.A. Reduced Apoptosis and Cytochrome c–Mediated Caspase Activation in Mice Lacking Caspase 9. Cell 1998, 94, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hakem, R.; Hakem, A.; Duncan, G.S.; Henderson, J.T.; Woo, M.; Soengas, M.; Elia, A.; De La Pompa, J.L.; Kagi, D.; Khoo, W.; et al. Differential Requirement for Caspase 9 in Apoptotic Pathways In Vivo. Cell 1998, 94, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westphal, D.; Kluck, R.; Dewson, G. Building blocks of the apoptotic pore: How Bax and Bak are activated and oligomerize during apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pawlowski, J.; Kraft, A.S. Bax-induced apoptotic cell death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 529–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halstead, F.D.; Ahmed, Z.; Bishop, J.R.B.; Oppenheim, B.A. The potential of visible blue light (405 nm) as a novel decontamination strategy for carbapenemase-producing enterobacteriaceae (CPE). Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2019, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Espada, R.; Liu, X.; Goh, X.S.; Dai, T. Antimicrobial Blue Light Inactivation of Polymicrobial Biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Solution Components | Concentration | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| 40% acrylamide | 20% | Bio-Rad, Munich, Germany |
| 2% bis-acrylamide | 0.05% | Bio-Rad, Munich, Germany |
| 16% PFA | 4% | Electron Microscopy Sciences, Hatfield, USA |
| Sodium acrylate | 10% | Sigma-Aldrich, Munich, Germany |
| 10% VA-044 | 0.1% | FUJIFILM, Osaka, Japan |
| 10× PBS | 1× | Sigma-Aldrich, Munich, Germany |
| Gene Symbol | Qiagen Category Number |
|---|---|
| VEGFA | QT01010184 |
| KDR | QT00069818 |
| NOS3 | QT00089033 |
| PLA2G4A | QT00085813 |
| PTGS2 | QT00040586 |
| CDKN1A | QT00044233 |
| TP53 | QT02377634 |
| CDK2AP1 | QT00226198 |
| CASP9 | QT00036267 |
| BAX | QT00031192 |
| GAPDH | QT01192646 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kan, K.; Mu, Y.; Bouschbacher, M.; Sticht, C.; Kuch, N.; Sigl, M.; Rahbari, N.; Gretz, N.; Pallavi, P.; Keese, M. Biphasic Effects of Blue Light Irradiation on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070829
Kan K, Mu Y, Bouschbacher M, Sticht C, Kuch N, Sigl M, Rahbari N, Gretz N, Pallavi P, Keese M. Biphasic Effects of Blue Light Irradiation on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(7):829. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070829
Chicago/Turabian StyleKan, Kejia, Yifei Mu, Marielle Bouschbacher, Carsten Sticht, Natalia Kuch, Martin Sigl, Nuh Rahbari, Norbert Gretz, Prama Pallavi, and Michael Keese. 2021. "Biphasic Effects of Blue Light Irradiation on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells" Biomedicines 9, no. 7: 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070829
APA StyleKan, K., Mu, Y., Bouschbacher, M., Sticht, C., Kuch, N., Sigl, M., Rahbari, N., Gretz, N., Pallavi, P., & Keese, M. (2021). Biphasic Effects of Blue Light Irradiation on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Biomedicines, 9(7), 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070829







