Binge-like Alcohol Exposure in Adolescence: Behavioural, Neuroendocrine and Molecular Evidence of Abnormal Neuroplasticity… and Return
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Drugs
2.3. Binge Alcohol Exposure
2.4. Behavioural Procedures
2.4.1. Novelty-Suppressed Feeding Test (NSFT)
2.4.2. Sucrose-Consumption Test (ST)
2.4.3. Social Interaction Test (SI)
2.4.4. Forced Swim Test (FST)
2.5. Tissue Collection
2.6. Blood Alcohol Concentration Measurements
2.7. Corticosterone Determination
2.8. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR
2.9. Immunofluorescence Experiments
2.10. Data Calibration and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Alcohol Binging during Adolescence Jeopardizes Affective Behaviour
3.2. Binge-like Alcohol Exposure during Adolescence Perturbs the Neuroendocrine Stress Response
3.3. Binging on Alcohol during Adolescence Alters Neuroplasticity in the NAc during Withdrawal
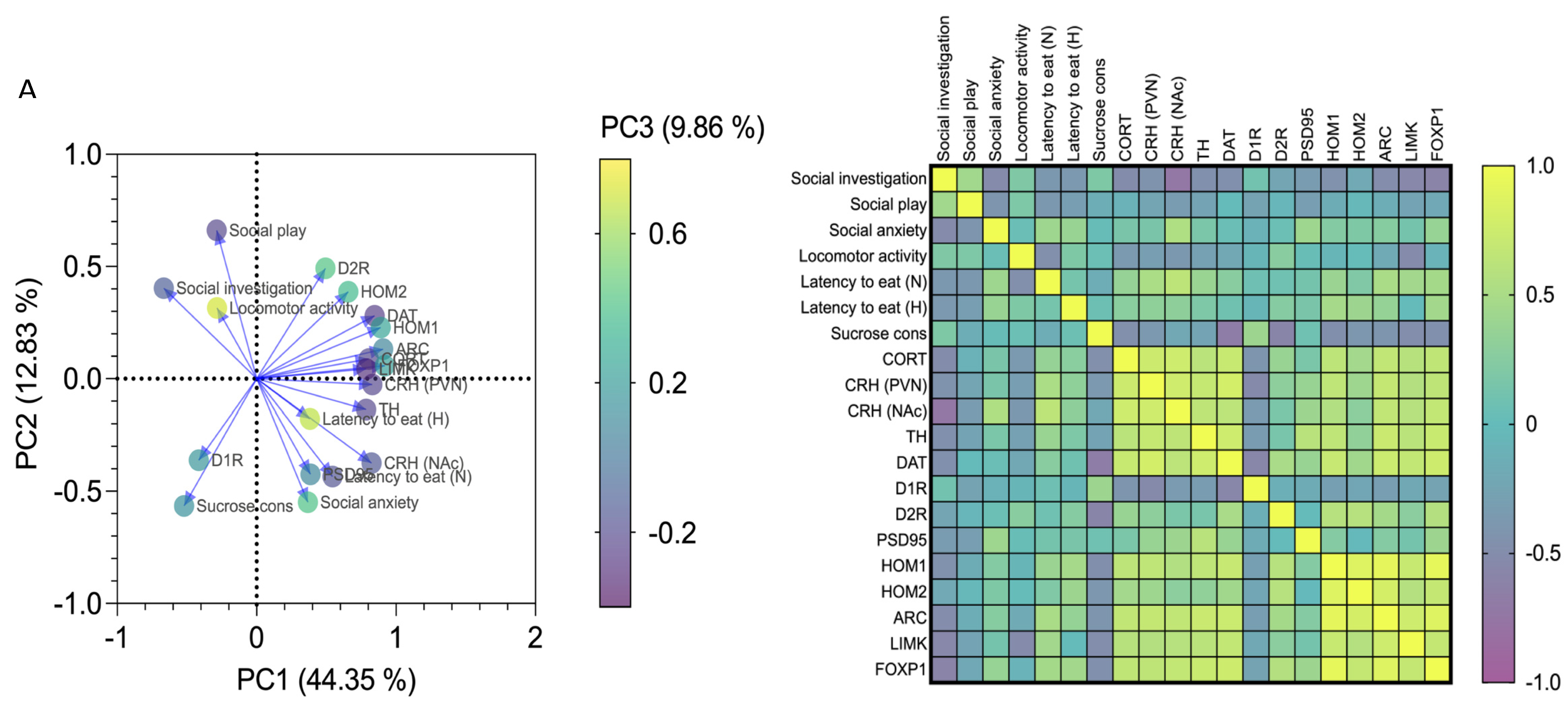
3.4. Affective and Emotional Behaviour in Binge-like Alcohol-Exposed Rats Correlates with Neuroendocrine Stress Response and Transcriptional Alterations in the NAc
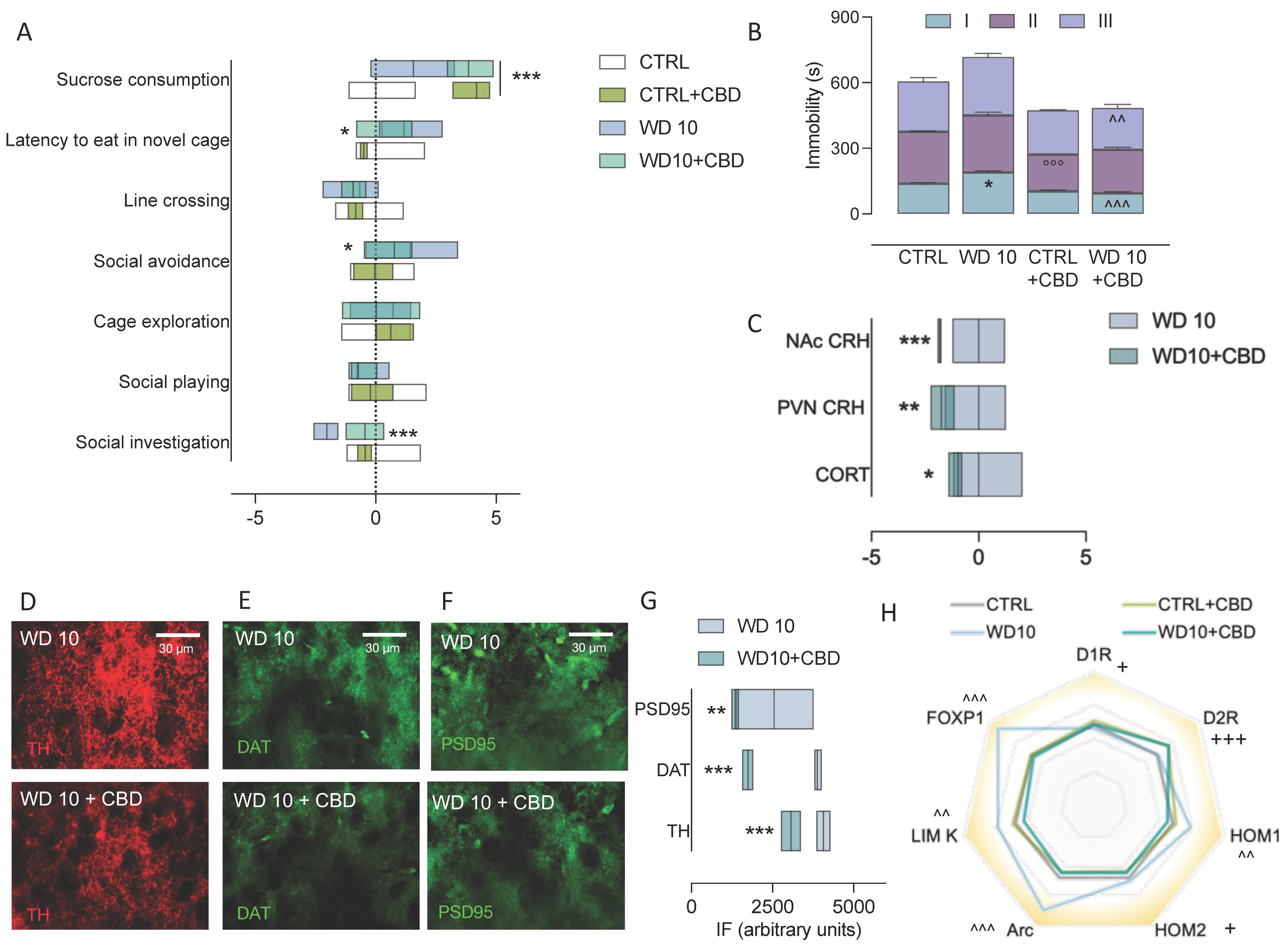
3.5. CBD Mitigates Behavioural and Neuroendocrine Dysregulation, and NAc Maladaptive Neuroplasticity in Binge-Like Alcohol-Exposed Rats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ESPAD Group. ESPAD Report 2019: Results from the European School Survey Project on Alcohol and Other Drugs; EMCDDA Joint Publications, Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shnitko, T.A.; Spear, L.P.; Robinson, N.L. Adolescent binge-like alcohol alters sensitivity to acute alcohol effects on dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens of adult rats. Psychopharmacology 2016, 233, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varlinskaya, E.I.; Spear, L.P.; Spear, N.E. Acute effects of ethanol on behavior of adolescent rats: Role of social context. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2001, 25, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spear, L.P.; Varlinskaya, E.I. Adolescence. Alcohol sensitivity, tolerance, and intake. Recent Dev. Alcohol. 2005, 17, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patrick, M.E.; Schulenberg, J.E.; Martz, M.E.; Maggs, J.L.; O’Malley, P.M.; Johnston, L.D. Extreme binge drinking among 12th-grade students in the United States: Prevalence and predictors. JAMA Pediatr. 2013, 167, 1019–1025, Erratum in 2013, 167, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. NIAAA Council Approves Definition of Binge Drinking, NIAAA Newsletter, No. 3; National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Koob, G.F.; Weiss, F. Neuropharmacology of Cocaine and Ethanol Dependence. Recent Dev. Alcohol. 1992, 10, 201–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, T.W.; Everitt, B.J. Limbic-striatal memory systems and drug addiction. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2002, 78, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodie, M.S.; Shefner, S.A.; Dunwiddie, T.V. Ethanol increases the firing rate of dopamine neurons of the rat ventral tegmental area in vitro. Brain Res. 1990, 508, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diana, M.; Pistis, M.; Muntoni, A.; Rossetti, Z.L.; Gessa, G. Marked decrease of A10 dopamine neuronal firing during ethanol withdrawal syndrome in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 221, 403–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mereu, G.; Fadda, F.; Gessa, G.L. Ethanol stimulates the firing rate of nigral dopaminergic neurons in unanesthetized rats. Brain Res. 1984, 292, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, R.A.; Weiss, F. Suppression of Ethanol-Reinforced Behavior by Naltrexone Is Associated with Attenuation of the Ethanol-Induced Increase in Dialysate Dopamine Levels in the Nucleus Accumbens. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 10663–10671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brancato, A.; Plescia, F.; Marino, R.A.M.; Maniaci, G.; Navarra, M.; Cannizzaro, C. Involvement of Dopamine D2 Receptors in Addictive-Like Behaviour for Acetaldehyde. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plescia, F.; Brancato, A.; Marino, R.A.M.; Cannizzaro, C. Acetaldehyde as a drug of abuse: Insight into AM281 administration on operant-conflict paradigm in rats. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spiga, S.; Talani, G.; Mulas, G.; Licheri, V.; Fois, G.R.; Muggironi, G.; Masala, N.; Cannizzaro, C.; Biggio, G.; Sanna, E.; et al. Hampered long-term depression and thin spine loss in the nucleus accumbens of ethanol-dependent rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E3745–E3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cannizzaro, C.; Talani, G.; Brancato, A.; Mulas, G.; Spiga, S.; De Luca, M.A.; Sanna, A.; Marino, R.A.M.; Biggio, G.; Sanna, E.; et al. Dopamine Restores Limbic Memory Loss, Dendritic Spine Structure, and NMDAR-Dependent LTD in the Nucleus Ac-cumbens of Alcohol-Withdrawn Rats. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 929–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dani, J.A.; Zhou, F.-M. Selective Dopamine Filter of Glutamate Striatal Afferents. Neuron 2004, 42, 522–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kauer, J.; Malenka, R.C. Synaptic plasticity and addiction. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorpe, H.H.A.; Hamidullah, S.; Jenkins, B.W.; Khokhar, J.Y. Adolescent neurodevelopment and substance use: Receptor ex-pression and behavioral consequences. Pharmacol Ther. 2020, 206, 107431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckley, J.T.; Laguesse, S.; Phamluong, K.; Morisot, N.; Wegner, S.A.; Ron, D. The First Alcohol Drink Triggers mTORC1-Dependent Synaptic Plasticity in Nucleus Accumbens Dopamine D1 Receptor Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crews, F.T.; Robinson, D.L.; Chandler, L.J.; Ehlers, C.L.; Mulholland, P.J.; Pandey, S.C.; Rodd, Z.A.; Spear, L.P.; Swartzwelder, H.S.; Vetreno, R.P. Mechanisms of Persistent Neurobiological Changes Following Adolescent Alcohol Exposure: NADIA Con-sortium Findings. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 43, 1806–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ernst, M.; Fudge, J.L. A developmental neurobiological model of motivated behavior: Anatomy, connectivity and ontogeny of the triadic nodes. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2009, 33, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chartier, K.G.; Hesselbrock, M.N.; Hesselbrock, V.M. Alcohol problems in young adults transitioning from adolescence to adulthood: The association with race and gender. Addict. Behav. 2011, 36, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guilarte, T.R.; McGlothan, J.L. Hippocampal NMDA receptor mRNA undergoes subunit specific changes during develop-mental lead exposure. Brain Res. 1998, 790, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.; Teicher, M. Sex differences in dopamine receptors and their relevance to ADHD. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2000, 24, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, J.E.; Marinelli, M. Age matters. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 997–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jucaite, A.; Forssberg, H.; Karlsson, P.; Halldin, C.; Farde, L. Age-related reduction in dopamine D1 receptors in the human brain: From late childhood to adulthood, a positron emission tomography study. Neuroscience 2010, 167, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, J.E.; Conrad, K.L.; Carr, S.B.; Ford, K.A.; McGehee, D.S.; Marinelli, M. Dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area fire faster in adolescent rats than in adults. J. Neurophysiol. 2012, 108, 1620–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spear, L. The adolescent brain and age-related behavioral manifestations. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2000, 24, 417–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazi, F.I.; Tomasini, E.C.; Baldessarini, R.J. Postnatal development of dopamine and serotonin transporters in rat cau-date-putamen and nucleus accumbens septi. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 254, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakemore, S.-J. Development of the Social Brain in Adolescence. J. R. Soc. Med. 2012, 105, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vilpoux, C.; Warnault, V.; Pierrefiche, O.; Daoust, M.; Naassila, M. Ethanol-sensitive brain regions in rat and mouse: A carto-graphic review, using immediate early gene expression. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 945–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varlinskaya, E.I.; Spear, L.P. Social interactions in adolescent and adult Sprague–Dawley rats: Impact of social deprivation and test context familiarity. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 188, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pattwell, S.S.; Duhoux, S.; Hartley, C.A.; Johnson, D.C.; Jing, D.; Elliott, M.D.; Ruberry, E.J.; Powers, A.; Mehta, N.; Yang, R.R.; et al. Altered fear learning across development in both mouse and human. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16318–16323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, C.S.; Lynch, K.G.; Pollock, N.K.; Clark, D.B. Gender differences and similarities in the personality correlates of adolescent alcohol problems. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2000, 14, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spear, L.P. Adolescent neurobehavioral characteristics, alcohol sensitivities, and intake: Setting the stage for alcohol use disorders? Child. Dev. Perspect. 2011, 5, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- File, S.E.; Seth, P. A review of 25 years of the social interaction test. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 463, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.; Varlinskaya, E.I.; Spear, L.P. Anxiolytic effects of the GABA(A) receptor partial agonist, L-838,417: Impact of age, test context familiarity, and stress. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2013, 109, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varlinskaya, E.I.; Doremus-Fitzwater, T.L.; Spear, L.P. Repeated restraint stress alters sensitivity to the social consequences of ethanol in adolescent and adult rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2010, 96, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Liberto, V.; Frinchi, M.; Verdi, V.; Vitale, A.; Plescia, F.; Cannizzaro, C.; Massenti, M.F.; Belluardo, N.; Mudò, G. Anxiolytic effects of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors agonist oxotremorine in chronically stressed rats and related changes in BDNF and FGF2 levels in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Psychopharmacology 2016, 234, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holleran, K.M.; Winder, D.G. Preclinical voluntary drinking models for alcohol abstinence-induced affective disturbances in mice. Genes Brain Behav. 2016, 16, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micale, V.; Di Marzo, V.; Sulcova, A.; Wotjak, C.T.; Drago, F. Endocannabinoid system and mood disorders: Priming a target for new therapies. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 138, 18–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micale, V.; Tabiova, K.; Kucerova, J.; Drago, F. Role of the endocannabinoid system in depression: From preclinical to clinical evidence. In Cannabinoid Modulation of Emotion, Memory, and Motivation; Campolongo, P., Fattore, L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 97–129. [Google Scholar]
- Hurd, Y.L.; Spriggs, S.; Alishayev, J.; Winkel, G.; Gurgov, K.; Kudrich, C.; Oprescu, A.M.; Salsitz, E. Cannabidiol for the Reduction of Cue-Induced Craving and Anxiety in Drug-Abstinent Individuals With Heroin Use Disorder: A Double-Blind Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Am. J. Psychiatry 2019, 176, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turna, J.; Syan, S.K.; Frey, B.N.; Rush, B.; Costello, M.J.; Weiss, M.; MacKillop, J. Cannabidiol as a Novel Candidate Alcohol Use Disorder Pharmacotherapy: A Systematic Review. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 43, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viudez-Martínez, A.; García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Navarron, C.; Morales-Calero, M.I.; Navarrete, F.; Torres-Suárez, A.I.; Manzanares, J. Cannabidiol reduces ethanol consumption, motivation and relapse in mice. Addict. Biol. 2017, 23, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viudez-Martínez, A.; García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Manzanares, J. Gender differences in the effects of cannabidiol on ethanol binge drinking in mice. Addict. Biol. 2019, 25, e12765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hložek, T.; Uttl, L.; Kadeřábek, L.; Balíková, M.; Lhotková, E.; Horsley, R.R.; Nováková, P.; Šíchová, K.; Štefková, K.; Tylš, F.; et al. Pharmacokinetic and behavioural profile of THC, CBD, and THC+CBD combination after pulmonary, oral, and subcutaneous administration in rats and confirmation of conversion in vivo of CBD to THC. Eur. Neuropsy-Chopharmacol. 2017, 27, 1223–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spear, L.P. Adolescent alcohol exposure: Are there separable vulnerable periods within adolescence? Physiol. Behav. 2015, 148, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varlinskaya, E.I.; Truxell, E.; Spear, L.P. Chronic intermittent ethanol exposure during adolescence: Effects on social behavior and ethanol sensitivity in adulthood. Alcohol 2014, 48, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, P.V.; Brabb, T.; Pekow, C.; Vasbinder, M.A. Administration of Substances to Laboratory Animals: Routes of Administration and Factors to Consider. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2011, 50, 600–613. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brancato, A.; Plescia, F.; Lavanco, G.; Cavallaro, A.; Cannizzaro, C. Continuous and Intermittent Alcohol Free-Choice from Pre-gestational Time to Lactation: Focus on Drinking Trajectories and Maternal Behavior. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cryan, J.F.; Page, M.E.; Lucki, I. Differential behavioral effects of the antidepressants reboxetine, fluoxetine, and moclobemide in a modified forced swim test following chronic treatment. Psychopharmacology 2005, 182, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelson, K.S.; Kalliokoski, O.; Teilmann, A.C.; Hau, J. Applicability of Commercially Available ELISA Kits for the Quantification of Faecal Immunoreactive Corticosterone Metabolites in Mice. Vivo 2016, 30, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C.R.; Emson, P.C. AChE-stained horizontal sections of the rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. J. Neurosci. Methods 1980, 3, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancato, A.; Castelli, V.; Lavanco, G.; Marino, R.A.M.; Cannizzaro, C. In utero Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol exposure confers vulnerability towards cognitive impairments and alcohol drinking in the adolescent offspring: Is there a role for neuropeptide Y? J. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 34, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badowska, D.M.; Brzózka, M.M.; Chowdhury, A.; Malzahn, D.; Rossner, M.J. Data calibration and reduction allows to visualize behavioural profiles of psychosocial influences in mice towards clinical domains. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 265, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménard, C.; Quirion, R.; Vigneault, E.; Bouchard, S.; Ferland, G.; El Mestikawy, S.; Gaudreau, P. Glutamate presynaptic vesicular transporter and postsynaptic receptor levels correlate with spatial memory status in aging rat models. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 1471–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Staay, F.J.; Schuurman, T.; van Reenen, C.G.; Korte, S.M. Emotional reactivity and cognitive performance in aversively motivated tasks: A comparison between four rat strains. Behav Brain Funct. 2009, 15, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lees, B.; Meredith, L.; Kirkland, A.E.; Bryant, B.E.; Squeglia, L.M. Effect of alcohol use on the adolescent brain and behavior. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2020, 192, 172906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, D.C.; Bruchas, M.R. A Motivational and Neuropeptidergic Hub: Anatomical and Functional Diversity within the Nucleus Accumbens Shell. Neuron 2019, 102, 529–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancato, A.; Castelli, V.; Cavallaro, A.; Lavanco, G.; Plescia, F.; Cannizzaro, C. Pre-conceptional and Peri-Gestational Maternal Binge Alcohol Drinking Produces Inheritance of Mood Disturbances and Alcohol Vulnerability in the Adolescent Off-spring. Front. Psychiatry. 2018, 23, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cannizzaro, C.; La Barbera, M.; Plescia, F.; Cacace, S.; Tringali, G. Ethanol modulates corticotropin releasing hormone release from the rat hypothalamus: Does acetaldehyde play a role? Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2010, 34, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plescia, F.; Brancato, A.; Marino, R.A.M.; Vita, C.; Navarra, M.; Cannizzaro, C. Effect of Acetaldehyde Intoxication and Withdrawal on NPY Expression: Focus on Endocannabinoidergic System Involvement. Front. Psychiatry 2014, 5, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plescia, F.; Brancato, A.; Venniro, M.; Maniaci, G.; Cannizzaro, E.; Sutera, F.M.; De Caro, V.; Giannola, L.I.; Cannizzaro, C. Acetaldehyde self-administration by a two-bottle choice paradigm: Consequences on emotional reactivity, spatial learning, and memory. Alcohol 2015, 49, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacace, S.; Plescia, F.; La Barbera, M.; Cannizzaro, C. Evaluation of chronic alcohol self-administration by a 3-bottle choice paradigm in adult male rats. Effects on behavioural reactivity, spatial learning and reference memory. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 219, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foltran, F.; Gregori, D.; Franchin, L.; Verduci, E.; Giovannini, M. Effect of alcohol consumption in prenatal life, childhood, and adolescence on child development. Nutr. Rev. 2011, 69, 642–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gellner, A.-K.; Voelter, J.; Schmidt, U.; Beins, E.C.; Stein, V.; Philipsen, A.; Hurlemann, R. Molecular and neurocircuitry mechanisms of social avoidance. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 78, 1163–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoman, D.B.; Sansone, C.; Pasupathi, M. Talking about interest: Exploring the role of social interaction for regulating motivation and the interest experience. J. Happiness Stud. 2006, 8, 335–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstensen, L.L. A life-span approach to social motivation. In Motivation and Self-Regulation Across the Life Span; Heckhausen, J., Dweck, C.S., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998; pp. 341–364. [Google Scholar]
- Carlton, C.N.; Sullivan-Toole, H.; Ghane, M.; Richey, J.A. Reward Circuitry and Motivational Deficits in Social Anxiety Disorder: What Can Be Learned From Mouse Models? Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holleran, K.M.; Wilson, H.H.; Fetterly, T.; Bluett, R.; Centanni, S.W.; Gilfarb, R.; Rocco, L.E.R.; Patel, S.; Winder, D.G. Ketamine and MAG Lipase Inhibitor-Dependent Reversal of Evolving Depressive-Like Behavior During Forced Abstinence From Alcohol Drinking. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 2062–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, T.Y.; Renoir, T.; Du, X.; Lawrence, A.J.; Hannan, A. Depression-related behaviours displayed by female C57BL/6J mice during abstinence from chronic ethanol consumption are rescued by wheel-running. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2013, 37, 1803–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, J.R.; Schroeder, J.P.; Nixon, K.; Besheer, J.; Crews, F.T.; Hodge, C.W. Abstinence following alcohol drinking produces depression-like behavior and reduced hippocampal neurogenesis in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 1209–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jury, N.J.; DiBerto, J.F.; Kash, T.L.; Holmes, A. Sex differences in the behavioral sequelae of chronic ethanol exposure. Alcohol 2016, 58, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pleil, K.E.; Lowery-Gionta, E.G.; Crowley, N.A.; Li, C.; Marcinkiewcz, C.A.; Rose, J.H.; McCall, N.M.; Maldonado-Devincci, A.M.; Morrow, A.L.; Jones, S.R.; et al. Effects of chronic ethanol exposure on neuronal function in the prefrontal cortex and extended amygdala. Neuropharmacology 2015, 99, 735–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sidhu, H.; Kreifeldt, M.; Contet, C. Affective Disturbances During Withdrawal from Chronic Intermittent Ethanol Inhalation in C57BL/6J and DBA/2J Male Mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 42, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koob, G.F.; Buck, C.L.; Cohen, A.; Edwards, S.; Park, P.E.; Schlosburg, J.E.; Schmeichel, B.; Vendruscolo, L.F.; Wade, C.L.; Whitfield, T.W.; et al. Addiction as a stress surfeit disorder. Neuropharmacology 2013, 76, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molendijk, M.L.; de Kloet, E.R. Coping with the forced swim stressor: Current state-of-the-art. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 364, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, H.; Tsuda, A.; Oguchi, M.; Ida, Y.; Tanaka, M. Is immobility of rats in the forced swim test “behavioral despair”? Physiol. Behav. 1988, 42, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybycien-Szymanska, M.M.; Giffin-Rao, Y.S.; Pak, T.R. Binge-pattern alcohol exposure during puberty induces sexually dimorphic changes in genes regulating the HPA axis. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2010, 298, E320–E328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Przybycien-Szymanska, M.M.; Mott, N.N.; Pak, T.R. Alcohol Dysregulates Corticotropin-Releasing-Hormone (CRH) Promoter Activity by Interfering with the Negative Glucocorticoid Response Element (nGRE). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.; Friedman, A.K.; Sun, H.; A Heller, E.; Ku, S.M.; Juarez, B.; Burnham, V.L.; Mazei-Robison, M.; Ferguson, D.; Golden, S.; et al. Stress and CRF gate neural activation of BDNF in the mesolimbic reward pathway. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 17, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Arias, M.; Navarrete, F.; Blanco-Gandia, M.C.; Arenas, M.C.; Bartoll-Andrés, A.; Aguilar, M.A.; Rubio, G.; Miñarro, J.; Manzanares, J. Social defeat in adolescent mice increases vulnerability to alcohol consumption. Addict. Biol. 2016, 21, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, B.J.; Neff, N.H.; Hadjiconstantinou, M. Enhanced dopamine uptake in the striatum following repeated restraint stress. Synapse 2005, 57, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamone, J.D.; Correa, M. The Mysterious Motivational Functions of Mesolimbic Dopamine. Neuron 2012, 76, 470–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wise, R.A. Rewards wanted: Molecular mechanisms of motivation. Discov. Med. 2004, 4, 180–186. [Google Scholar]
- Hajnal, A.; Norgren, R. Accumbens dopamine mechanisms in sucrose intake. Brain Res. 2001, 904, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, J.H. Dopamine signaling in reward-related behaviors. Front. Neural Circuits 2013, 11, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Melis, M.; Spiga, S.; Diana, M. The Dopamine Hypothesis of Drug Addiction: Hypodopaminergic State. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2005, 63, 101–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campioni, M.R.; Xu, M.; McGehee, D.S. Stress-Induced Changes in Nucleus Accumbens Glutamate Synaptic Plasticity. J. Neurophysiol. 2009, 101, 3192–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheefhals, N.; MacGillavry, H.D. Functional organization of postsynaptic glutamate receptors. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 91, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gass, J.T.; Olive, M.F. Glutamatergic substrates of drug addiction and alcoholism. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 218–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iii, W.C.G.; Haun, H.L.; Hazelbaker, C.L.; Ramachandra, V.S.; Becker, H.C. Increased Extracellular Glutamate In the Nucleus Accumbens Promotes Excessive Ethanol Drinking in Ethanol Dependent Mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 39, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, W.C.; Ramachandra, V.S.; Knackstedt, L.A.; Becker, H.C. Repeated cycles of chronic intermittent ethanol exposure in-crease basal glutamate in the nucleus accumbens of mice without affecting glutamate transport. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 23, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Uys, J.D.; McGuier, N.S.; Gass, J.T.; Griffin, W.C., 3rd; Ball, L.E.; Mulholland, P.J. Chronic intermittent ethanol exposure and with-drawal leads to adaptations in nucleus accumbens core postsynaptic density proteome and dendritic spines. Addict. Biol. 2016, 21, 560–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bauer, J.; Pedersen, A.; Scherbaum, N.; Bening, J.; Patschke, J.; Kugel, H.; Heindel, W.; Arolt, V.; Ohrmann, P. Craving in Alcohol-Dependent Patients After Detoxification Is Related to Glutamatergic Dysfunction in the Nucleus Accumbens and the Anterior Cingulate Cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapasova, Z.; Szumlinski, K.K. Strain differences in alcohol-induced neurochemical plasticity: A role for accumbens gluta-mate in alcohol intake. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2008, 32, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouysségur, J.; Volmat, V.; Lenormand, P. Fidelity and spatio-temporal control in MAP kinase (ERKs) signalling. Biochem Pharmacol. 2002, 64, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Mao, L.; Tang, Q.; Samdani, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.Q. A novel Ca2+-independent signaling pathway to extracellular sig-nal-regulated protein kinase by coactivation of NMDA receptors and metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 in neurons. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 10846–10857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guzowski, J.F.; Miyashita, T.; Chawla, M.K.; Sanderson, J.; Maes, L.I.; Houston, F.P.; Lipa, P.; McNaughton, B.L.; Worley, P.F.; Barnes, C.A. Recent behavioral history modifies coupling between cell activity and Arc gene transcription in hippocampal CA1 neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stanyon, C.A.; Bernard, O. LIM-kinase1. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1999, 31, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steward, O.; Wallace, C.S.; Lyford, G.L.; Worley, P.F. Synaptic Activation Causes the mRNA for the IEG Arc to Localize Selectively near Activated Postsynaptic Sites on Dendrites. Neuron 1998, 21, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steward, O.; Worley, P.F. Selective Targeting of Newly Synthesized Arc mRNA to Active Synapses Requires NMDA Receptor Activation. Neuron 2001, 30, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, S.C.; Zhang, H.; Ugale, R.; Prakash, A.; Xu, T.; Misra, K. Effector Immediate-Early Gene Arc in the Amygdala Plays a Critical Role in Alcoholism. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 2589–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butts, A.R.; Ojelade, S.A.; Pronovost, E.D.; Seguin, A.; Merrill, C.; Rodan, A.R.; Rothenfluh, A. Altered Actin Filament Dynamics in the Drosophila Mushroom Bodies Lead to Fast Acquisition of Alcohol Consumption Preference. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 8877–8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.G.; Kulkarni, A.; Harper, M.; Konopka, G. Single-Cell Analysis of Foxp1-Driven Mechanisms Essential for Striatal Development. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 3051–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rocca, D.L.; Wilkinson, K.A.; Henley, J.M. SUMOylation of FOXP1 regulates transcriptional repression via CtBP1 to drive dendritic morphogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khandelwal, N.; Cavalier, S.; Rybalchenko, V.; Kulkarni, A.; Anderson, A.G.; Konopka, G.; Gibson, J.R. FOXP1 negatively regulates intrinsic excitability in D2 striatal projection neurons by promoting inwardly rectifying and leak potassium currents. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Becanovic, K.; Desplats, P.; Spencer, B.; Hill, A.M.; Connolly, C.; Masliah, E.; Leavitt, B.; Thomas, E.A. Forkhead box protein p1 is a transcriptional repressor of immune signaling in the CNS: Implications for transcriptional dysregulation in Huntington disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 3097–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vanderschuren, L.J.; Niesink, R.J.; Van Ree, J.M. The neurobiology of social play behavior in rats. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1997, 21, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete, F.; Aracil-Fernández, A.; Manzanares, J. Cannabidiol regulates behavioural alterations and gene expression changes induced by spontaneous cannabinoid withdrawal. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 2676–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stark, T.; Ruda-Kucerova, J.; Iannotti, F.A.; D’Addario, C.; Di Marco, R.; Pekarik, V.; Drazanova, E.; Piscitelli, F.; Bari, M.; Ba-binska, Z.; et al. Peripubertal cannabidiol treatment rescues behavioral and neurochemical ab-normalities in the MAM model of schizophrenia. Neuropharmacology 2019, 146, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogaça, M.V.; Campos, A.C.; Coelho, L.D.; Duman, R.S.; Guimarães, F.S. The anxiolytic effects of cannabidiol in chronically stressed mice are mediated by the endocannabinoid system: Role of neurogenesis and dendritic remodeling. Neuropharmacology 2018, 135, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartim, A.; Guimarães, F.; Joca, S. Antidepressant-like effect of cannabidiol injection into the ventral medial prefrontal cortex—Possible involvement of 5-HT1A and CB1 receptors. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 303, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Alfy, A.T.; Ivey, K.; Robinson, K.; Ahmed, S.; Radwan, M.; Slade, D.; Khan, I.; ElSohly, M.; Ross, S. Antidepressant-like effect of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and other cannabinoids isolated from Cannabis sativa L. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2010, 95, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abame, M.A.; He, Y.; Wu, S.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, J.; Gong, X.; Wu, C.; Shen, J. Chronic administration of synthetic cannabidiol induces antidepressant effects involving modulation of serotonin and noradrenaline levels in the hippocampus. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 744, 135594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réus, G.Z.; Stringari, R.B.; Ribeiro, K.F.; Luft, T.; Abelaira, H.M.; Fries, G.R.; Aguiar, B.W.; Kapczinski, F.; Hallak, J.E.; Zuardi, A.W.; et al. Administration of cannabidiol and imipramine induces antidepressant-like effects in the forced swimming test and increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in the rat amygdala. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2011, 23, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melas, P.; Scherma, M.; Fratta, W.; Cifani, C.; Fadda, P. Cannabidiol as a Potential Treatment for Anxiety and Mood Disorders: Molecular Targets and Epigenetic Insights from Preclinical Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viudez-Martínez, A.; García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Manzanares, J. Cannabidiol regulates the expression of hypothala-mus-pituitary-adrenal axis-related genes in response to acute restraint stress. J. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 32, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusar-Poli, P.; Allen, P.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Crippa, J.A.; Mechelli, A.; Borgwardt, S.; Martin-Santos, R.; Seal, M.L.; O’Carrol, C.; Atakan, Z.; et al. Modulation of effective connectivity during emotional processing by Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010, 13, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunasekera, B.; Diederen, K.; Bhattacharyya, S. Cannabinoids, reward processing, and psychosis. Psychopharmacology 2021, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, J.; Norris, C.; Rushlow, W.; Laviolette, S.R. Neuronal and molecular effects of cannabidiol on the mesolimbic do-pamine system: Implications for novel schizophrenia treatments. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 75, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bartolomeo, M.; Stark, T.; Maurel, O.M.; Iannotti, F.A.; Kuchar, M.; Ruda-Kucerova, J.; Piscitelli, F.; Laudani, S.; Pekarik, V.; Sa-lomone, S.; et al. Crosstalk between the transcriptional regulation of dopamine D2 and cannabinoid CB1 receptors in schizo-phrenia: Analyses in patients and in perinatal Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol-exposed rats. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 164, 105357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Whittard, J.; Higuera-Matas, A.; Morris, C.V.; Hurd, Y.L. Cannabidiol, a nonpsychotropic component of cannabis, in-hibits cue-induced heroin seeking and normalizes discrete mesolimbic neuronal disturbances. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 14764–14769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campos, A.C.; Fogaça, M.V.; Scarante, F.F.; Joca, S.; Sales, A.; Gomes, F.; Sonego, A.B.; Rodrigues, N.S.; Galve-Roperh, I.; Guimarães, F.S. Plastic and Neuroprotective Mechanisms Involved in the Therapeutic Effects of Cannabidiol in Psychiatric Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, J.; Wanat, M.; Smith, J.; Reyes, B.A.S.; Hollon, N.G.; Van Bockstaele, E.J.; Chavkin, C.; Phillips, P. Severe stress switches CRF action in the nucleus accumbens from appetitive to aversive. Nature 2012, 490, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Gene Name | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|
| Gapdh | GTTTGTGATGGGTGTGAACC (Forward) |
| CTTCTGAGTGGCAGTGATG (Reverse) | |
| Dopamine Receptor 1 | ACAGATGCATTGTTGATGAC (Forward) |
| TGCTAGTACAAATGGAGAGG (Reverse) | |
| Dopamine Receptor 2 | TTAACATCGTCTCTCTTCCA (Forward) |
| ACAGGTATAGTGATGTTACA (Reverse) | |
| Homer 1 | CTTCACAGGAATCAGCAGGAG (Forward) |
| GTCCCATTGATACTTTCTGGTG (Reverse) | |
| Homer 2 | AAGATCGCTTTGACACAGAG (Forward) |
| CTCGCTGCACTGTTCTTCCA (Reverse) | |
| Activity-Regulated Cytoskeleton Associated Protein | ACAGAGGATGAGACTGAGGCAC (Forward) TATTCAGGCTGGGTCCTGTCAC (Reverse) |
| LIM Domain Kinase 1 | ATGAGGTTGACGCTACTTTGTTG (Forward) |
| CTACACTCGCAGCACCTGAA (Reverse) | |
| Forkhead Box p1 | CACGTGGAAGAATGCAGTGC (Forward) |
| GCCTGTAAAGCTGCATTGAG (Reverse) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brancato, A.; Castelli, V.; Lavanco, G.; Tringali, G.; Micale, V.; Kuchar, M.; D’Amico, C.; Pizzolanti, G.; Feo, S.; Cannizzaro, C. Binge-like Alcohol Exposure in Adolescence: Behavioural, Neuroendocrine and Molecular Evidence of Abnormal Neuroplasticity… and Return. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091161
Brancato A, Castelli V, Lavanco G, Tringali G, Micale V, Kuchar M, D’Amico C, Pizzolanti G, Feo S, Cannizzaro C. Binge-like Alcohol Exposure in Adolescence: Behavioural, Neuroendocrine and Molecular Evidence of Abnormal Neuroplasticity… and Return. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(9):1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091161
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrancato, Anna, Valentina Castelli, Gianluca Lavanco, Giuseppe Tringali, Vincenzo Micale, Martin Kuchar, Cesare D’Amico, Giuseppe Pizzolanti, Salvatore Feo, and Carla Cannizzaro. 2021. "Binge-like Alcohol Exposure in Adolescence: Behavioural, Neuroendocrine and Molecular Evidence of Abnormal Neuroplasticity… and Return" Biomedicines 9, no. 9: 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091161
APA StyleBrancato, A., Castelli, V., Lavanco, G., Tringali, G., Micale, V., Kuchar, M., D’Amico, C., Pizzolanti, G., Feo, S., & Cannizzaro, C. (2021). Binge-like Alcohol Exposure in Adolescence: Behavioural, Neuroendocrine and Molecular Evidence of Abnormal Neuroplasticity… and Return. Biomedicines, 9(9), 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091161







