The AST-120 Recovers Uremic Toxin-Induced Cognitive Deficit via NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway in Astrocytes and Microglia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. CKD Mouse Model and AST-120 Treatment
2.2. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.3. Y-Maze Spontaneous Alternation Test
2.4. Water Maze Behavioral Test
2.5. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Immunohistochemistry Staining
2.7.1. Chromogenic Detection
2.7.2. Fluorescent Detection
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Impaired Working Memory in 5/6 Partial Nephrectomy-Induced CKD Mice
3.2. Brain Levels of Indoxyl Sulfate and p-Cresol Sulfate were Increased in CKD Mice
3.3. AST-120 Reduced Brain and Serum Levels of Indoxyl Sulfate and p-Cresol Sulfate in CKD Mice and Reverted CKD-Induced Learning and Memory Impairment
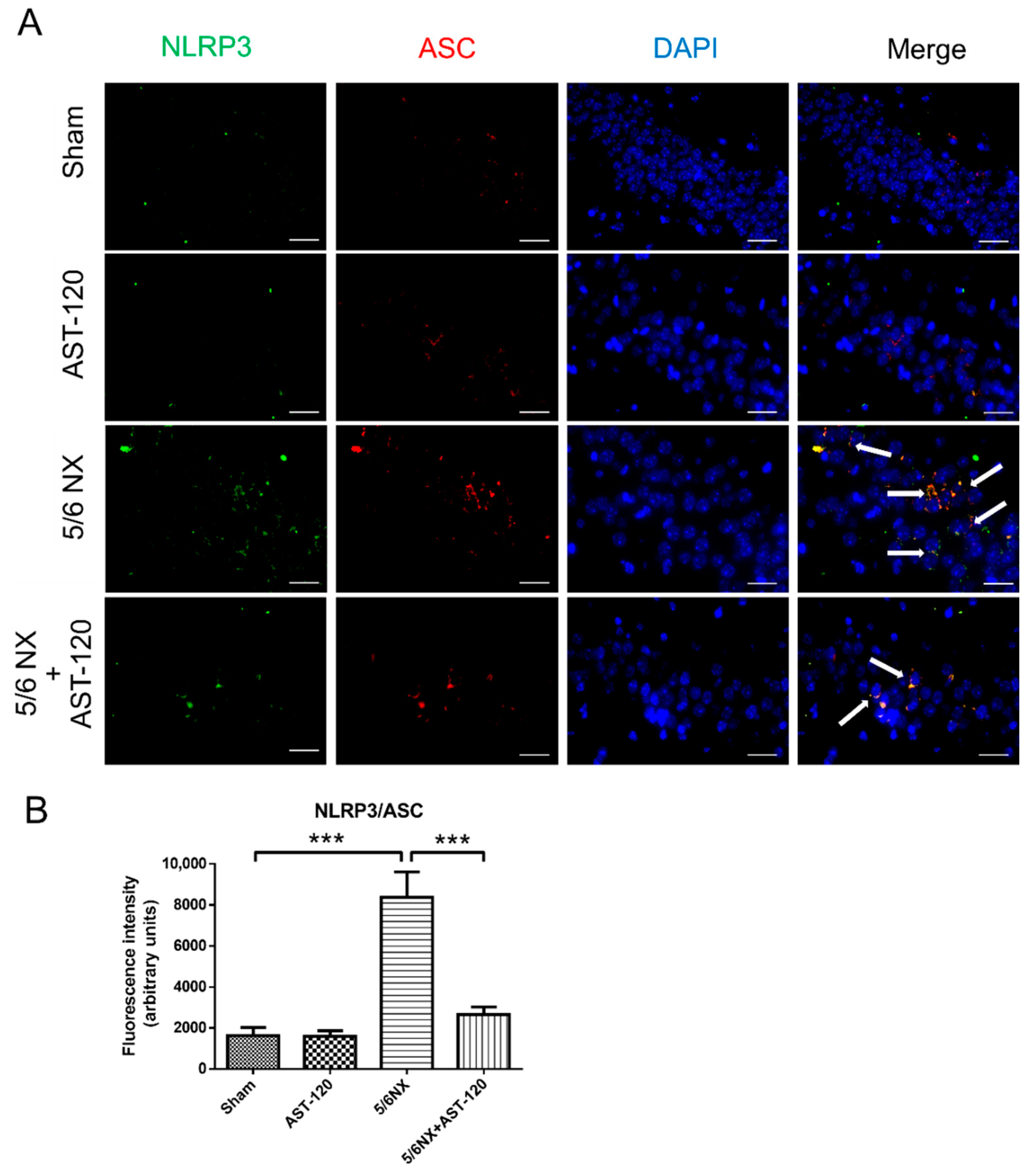
3.4. AST-120 Suppressed Hippocampal Inflammation in CKD Mice
3.5. NLRP3-Knockout Mice Maintained Cognitive Function in CKD Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bikbov, B.; Purcell, C.A.; Levey, A.S.; Smith, M.; Abdoli, A.; Abebe, M.; Adebayo, O.M.; Afarideh, M.; Agarwal, S.K.; Agudelo-Botero, M.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet 2020, 395, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bugnicourt, J.M.; Godefroy, O.; Chillon, J.M.; Choukroun, G.; Massy, Z.A. Cognitive disorders and dementia in CKD: The neglected kidney-brain axis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brines, M.L.; Ghezzi, P.; Keenan, S.; Agnello, D.; de Lanerolle, N.C.; Cerami, C.; Itri, L.M.; Cerami, A. Erythropoietin crosses the blood-brain barrier to protect against experimental brain injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10526–10531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobalava, Z.D.; Troitskaya, E.A. Asymptomatic hyperuricemia: Treatment approaches according to the risk of cardiovascular and renal events. Kardiologiia 2021, 60, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, F.F.; Chen, J.B.; Hsieh, K.C.; Liou, C.W. Cognitive changes after parathyroidectomy in patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism. Surgery 2008, 143, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchetti, M.T.; Cosola, C.; Ranieri, E.; Gesualdo, L. Protein-bound uremic toxins and immunity. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2325, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McQuillan, R.; Jassal, S.V. Neuropsychiatric complications of chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2010, 6, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, M.F.; Elias, P.K.; Seliger, S.L.; Narsipur, S.S.; Dore, G.A.; Robbins, M.A. Chronic kidney disease, creatinine and cognitive functioning. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2009, 24, 2446–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, A.C.; Tsai, S.J.; Yeh, H.L.; Chen, J.Y.; Liou, Y.J.; Hwang, J.P.; Hong, C.J. Association between renal function and cognitive performance in elderly community-dwelling men without dementia. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2010, 58, 2046–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Watanabe, T.; Nakayama, M. Cerebro-renal interactions: Impact of uremic toxins on cognitive function. Neurotoxicology 2014, 44, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prochnicki, T.; Latz, E. Inflammasomes on the crossroads of innate immune recognition and metabolic control. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 71–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsai, S.J. Effects of interleukin-1beta polymorphisms on brain function and behavior in healthy and psychiatric disease conditions. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017, 37, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; Kummer, M.P.; Stutz, A.; Delekate, A.; Schwartz, S.; Vieira-Saecker, A.; Griep, A.; Axt, D.; Remus, A.; Tzeng, T.C.; et al. NLRP3 is activated in Alzheimer’s disease and contributes to pathology in APP/PS1 mice. Nature 2013, 493, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johann, S.; Heitzer, M.; Kanagaratnam, M.; Goswami, A.; Rizo, T.; Weis, J.; Troost, D.; Beyer, C. NLRP3 inflammasome is expressed by astrocytes in the SOD1 mouse model of ALS and in human sporadic ALS patients. Glia 2015, 63, 2260–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Jiang, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Ding, C.; Tian, Z.; Zhou, R. Dopamine controls systemic inflammation through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell 2015, 160, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, X.; He, J.; Cao, X.; Zou, J.; Liu, H.; Ding, X. Effects of oral carbonic adsorbent (AST-120) on kidney of early-stage chronic kidney disease rats. Ren. Fail. 2015, 37, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakagawa, N.; Hasebe, N.; Sumitomo, K.; Fujino, T.; Fukuzawa, J.; Hirayama, T.; Kikuchi, K. An oral adsorbent, AST-120, suppresses oxidative stress in uremic rats. Am. J. Nephrol. 2006, 26, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulman, G.; Vanholder, R.; Niwa, T. AST-120 for the management of progression of chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 2014, 7, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hatakeyama, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Okamoto, A.; Imanishi, K.; Tokui, N.; Okamoto, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Sugiyama, N.; Imai, A.; Kudo, S.; et al. Effect of an oral adsorbent, AST-120, on dialysis initiation and survival in patients with chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Nephrol. 2012, 2012, 376128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraeuter, A.K.; Guest, P.C.; Sarnyai, Z. The Y-Maze for assessment of spatial working and reference memory in mice. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1916, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- D’Hooge, R.; De Deyn, P.P. Applications of the Morris water maze in the study of learning and memory. Brain Res. Rev. 2001, 36, 60–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chaudhry, M.A.; Nie, Y.; Xie, Z.; Shapiro, J.I.; Liu, J. A mouse 5/6th nephrectomy model that induces experimental uremic cardiomyopathy. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 129, 55825. [Google Scholar]
- Hamed, S.A. Neurologic conditions and disorders of uremic syndrome of chronic kidney disease: Presentations, causes, and treatment strategies. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 61–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijers, B.K.; Van Kerckhoven, S.; Verbeke, K.; Dehaen, W.; Vanrenterghem, Y.; Hoylaerts, M.F.; Evenepoel, P. The uremic retention solute p-cresyl sulfate and markers of endothelial damage. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 54, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwa, T. Indoxyl sulfate is a nephro-vascular toxin. J. Ren Nutr. 2010, 20 (Suppl. 5), S2–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto, F.C.; Barreto, D.V.; Liabeuf, S.; Meert, N.; Glorieux, G.; Temmar, M.; Choukroun, G.; Vanholder, R.; Massy, Z.A. European Uremic Toxin Work Group. Serum indoxyl sulfate is associated with vascular disease and mortality in chronic kidney disease patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schepers, E.; Meert, N.; Glorieux, G.; Goeman, J.; Van der Eycken, J.; Vanholder, R. P-cresylsulphate, the main in vivo metabolite of p-cresol, activates leucocyte free radical production. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2007, 22, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.C.; Huang, M.; Liang, S.S.; Hwang, S.J.; Tsai, J.C.; Liu, T.L.; Wu, P.H.; Yang, Y.H.; Kuo, K.C.; Kuo, M.C.; et al. Indoxyl sulfate, not p-cresyl sulfate, is associated with cognitive impairment in early-stage chronic kidney disease. Neurotoxicology 2016, 53, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayne, K.; White, J.A.; McMurran, C.E.; Rivera, F.J.; de la Fuente, A.G. Aging and neurodegenerative disease: Is the adaptive immune system a friend or foe? Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 572090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Aierken, A.; Xie, Z.; Li, N.; Zhao, J.; Qing, H. The age-related microglial transformation in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Neurobiol. Aging 2020, 92, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, D.C.; Haque, A.; Banik, N.L. Neuroinflammatory responses of microglia in central nervous system trauma. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2020, 40 (Suppl. 1), S25–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Nie, D.; Wang, L.J.; Qiu, H.C.; Ma, L.; Dong, M.X.; Tu, W.J.; Zhao, J. Microglial polarization: Novel therapeutic strategy against ischemic stroke. Aging Dis. 2021, 12, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchman, A.S.; Tanne, D.; Boyle, P.A.; Shah, R.C.; Leurgans, S.E.; Bennett, D.A. Kidney function is associated with the rate of cognitive decline in the elderly. Neurology 2009, 73, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Etgen, T.; Sander, D.; Chonchol, M.; Briesenick, C.; Poppert, H.; Forstl, H.; Bickel, H. Chronic kidney disease is associated with incident cognitive impairment in the elderly: The INVADE study. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2009, 24, 3144–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, H.C.; Xu, Y.F.; Xu, R.; Yang, Z.K.; Qu, Z.; Chen, Y.Q.; Liu, G.L.; Dong, J. Cognitive impairment and structural neuroimaging abnormalities among patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2016, 41, 986–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, E.; Saigusa, D.; Mishima, E.; Uchida, T.; Miura, D.; Morikawa-Ichinose, T.; Kisu, K.; Sekimoto, A.; Saito, R.; Oe, Y.; et al. Impact of the oral adsorbent AST-120 on organ-specific accumulation of uremic toxins: LC-MS/MS and MS imaging techniques. Toxins 2017, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.T.; Wu, P.H.; Liang, S.S.; Mubanga, M.; Yang, Y.H.; Hsu, Y.L.; Kuo, M.C.; Hwang, S.J.; Kuo, P.L. Protein-bound uremic toxins are associated with cognitive function among patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, K.; Watanabe, H.; Morisaki, T.; Matsuzaki, T.; Ohmura, T.; Hamada, A.; Saito, H. Involvement of indoxyl sulfate in renal and central nervous system toxicities during cisplatin-induced acute renal failure. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobot, M.; Thomas, L.; Moyon, A.; Fernandez, S.; McKay, N.; Balasse, L.; Garrigue, P.; Brige, P.; Chopinet, S.; Poitevin, S.; et al. Uremic toxic blood-brain barrier disruption mediated by AhR activation leads to cognitive impairment during experimental renal dysfunction. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 1509–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesso, S.; Paterniti, I.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Fujioka, M.; Autore, G.; Magnus, T.; Pinto, A.; Marzocco, S. AST-120 reduces neuroinflammation induced by indoxyl sulfate in glial cells. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, E.; Hosomi, K.; Sekimoto, A.; Mishima, E.; Oe, Y.; Saigusa, D.; Ito, S.; Abe, T.; Sato, H.; Kunisawa, J.; et al. Effects of the oral adsorbent AST-120 on fecal p-cresol and indole levels and on the gut microbiota composition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 525, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancu, I.C.; Cremers, N.; Vanrusselt, H.; Couturier, J.; Vanoosthuyse, A.; Kessels, S.; Lodder, C.; Brone, B.; Huaux, F.; Octave, J.N.; et al. Aggregated Tau activates NLRP3-ASC inflammasome exacerbating exogenously seeded and non-exogenously seeded Tau pathology in vivo. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 137, 599–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halle, A.; Hornung, V.; Petzold, G.C.; Stewart, C.R.; Monks, B.G.; Reinheckel, T.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Latz, E.; Moore, K.J.; Golenbock, D.T. The NALP3 inflammasome is involved in the innate immune response to amyloid-beta. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adesso, S.; Magnus, T.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Campolo, M.; Rissiek, B.; Paciello, O.; Autore, G.; Pinto, A.; Marzocco, S. Indoxyl Sulfate Affects glial function increasing oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in chronic kidney disease: Interaction between astrocytes and microglia. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, N.; Jeltema, D.; Duan, Y.; He, Y. The NLRP3 inflammasome: An overview of mechanisms of activation and regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karbowska, M.; Hermanowicz, J.M.; Tankiewicz-Kwedlo, A.; Kalaska, B.; Kaminski, T.W.; Nosek, K.; Wisniewska, R.J.; Pawlak, D. Neurobehavioral effects of uremic toxin-indoxyl sulfate in the rat model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherubini, E.; Miles, R. The CA3 region of the hippocampus: How is it? What is it for? How does it do it? Front. Cell Neurosci. 2015, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]








| Sham-Operation | 5/6Nx | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Post-Surgery Time | Control-4W | Control-8W | CKD-4W | CKD-8W |
| Animal Number | N = 8 | N = 8 | N = 8 | N = 8 |
| Body Weight (g) | 29.5 ± 2.1 | 29.9 ± 0.8 | 25.7 ± 0.6 | 27.9 ± 0.8 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 24.3 ± 5.0 | 20.6 ± 4.9 | 53.5 ± 12.3 a | 47.7 ± 8.6 b |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.03 ± 0.15 | 1.12 ± 0.23 | 1.85 ± 0.38 a | 2.35 ± 0.47 b |
| Indoxyl sulfate (ng/mL) | 5142.4 + 1660.0 | 4343.95 ± 2481.2 | 18,959.7 ± 5072.2 a | 18,152.5 ± 8887.5 b |
| P-cresyl sulfate (ng.mL) | 1794.9 ± 372. | 2423.3 ± 900.3 | 6413.5 ± 2184.4 a | 3892.7 ± 2822.5 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.-C.; Chen, W.-Y.; Chen, J.-B.; Lee, W.-C.; Chang, C.-C.; Tzeng, H.-T.; Huang, C.-C.; Chang, Y.-J.; Yang, J.-L. The AST-120 Recovers Uremic Toxin-Induced Cognitive Deficit via NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway in Astrocytes and Microglia. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091252
Li L-C, Chen W-Y, Chen J-B, Lee W-C, Chang C-C, Tzeng H-T, Huang C-C, Chang Y-J, Yang J-L. The AST-120 Recovers Uremic Toxin-Induced Cognitive Deficit via NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway in Astrocytes and Microglia. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(9):1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091252
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Lung-Chih, Wei-Yu Chen, Jin-Bor Chen, Wen-Chin Lee, Chiung-Chih Chang, Hong-Tai Tzeng, Chiang-Chi Huang, Ya-Jen Chang, and Jenq-Lin Yang. 2021. "The AST-120 Recovers Uremic Toxin-Induced Cognitive Deficit via NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway in Astrocytes and Microglia" Biomedicines 9, no. 9: 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091252
APA StyleLi, L.-C., Chen, W.-Y., Chen, J.-B., Lee, W.-C., Chang, C.-C., Tzeng, H.-T., Huang, C.-C., Chang, Y.-J., & Yang, J.-L. (2021). The AST-120 Recovers Uremic Toxin-Induced Cognitive Deficit via NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway in Astrocytes and Microglia. Biomedicines, 9(9), 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091252








