Assessing the Utility of Hemoglobin, HALP Score, FAR Ratio, and Coagulation Parameters as Predictors for Preterm Birth
Abstract
1. Introduction
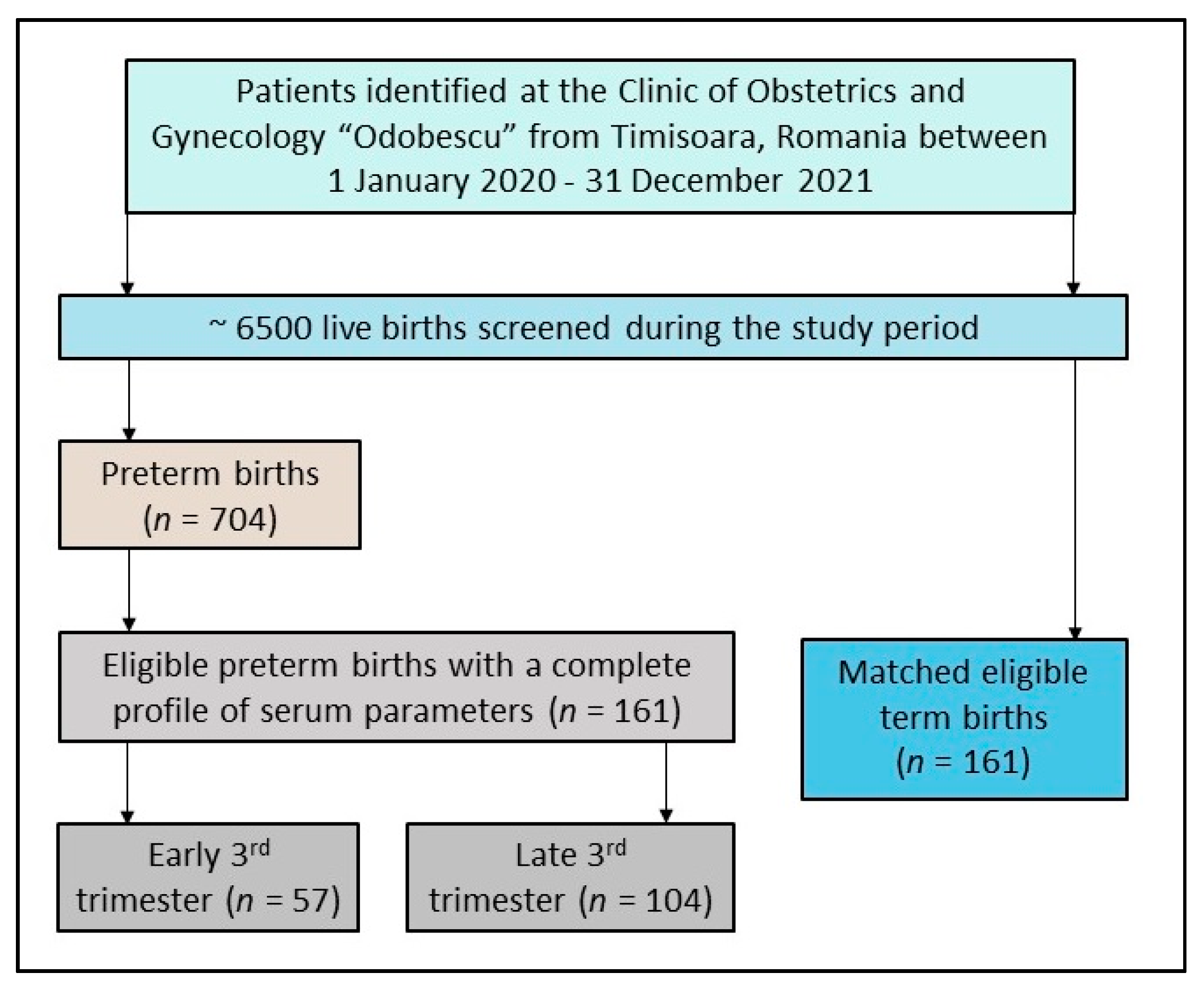
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethical Considerations
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Variables
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Background
3.2. Serum Parameters
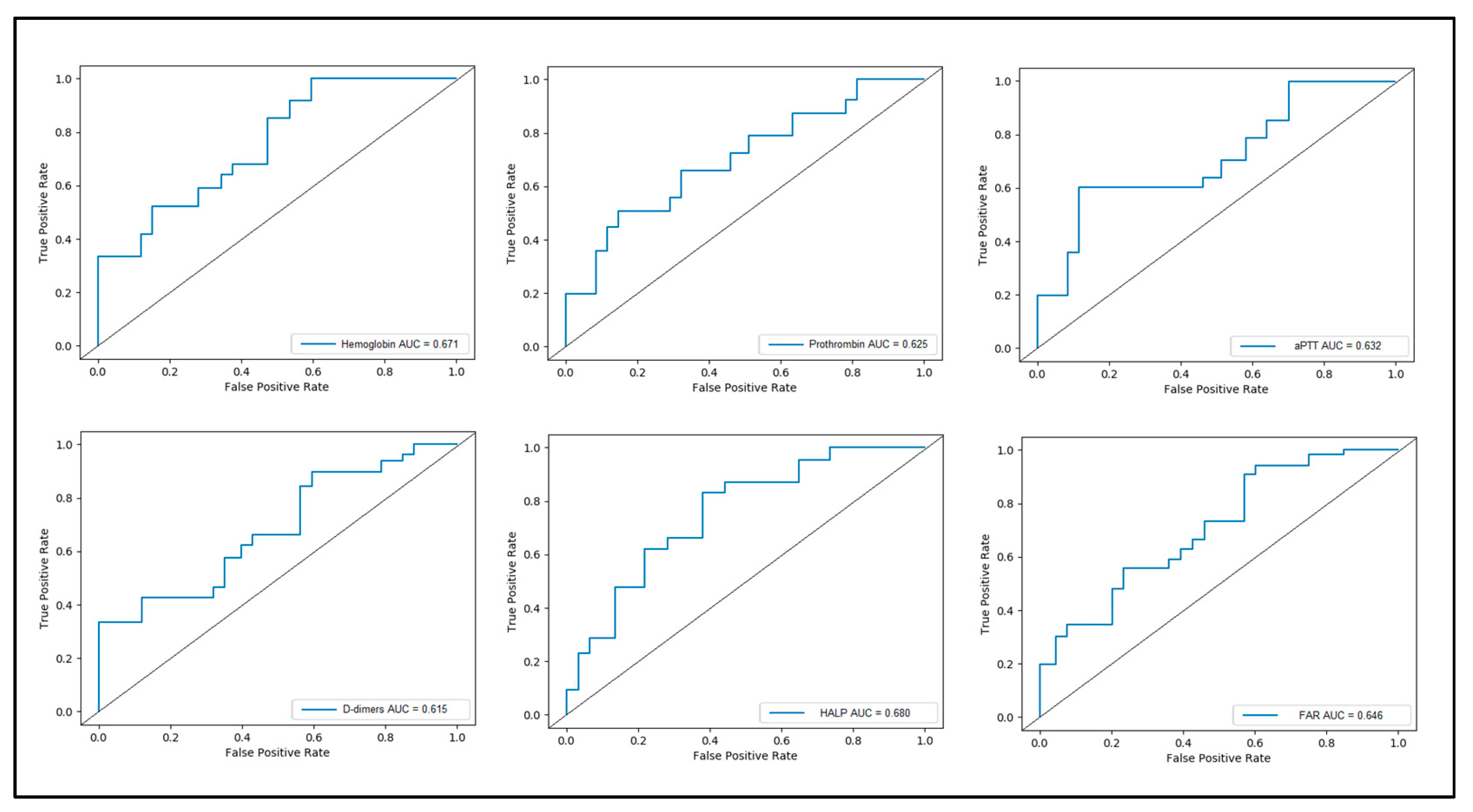
3.3. Receiver Operand Curve and Area under Curve
3.4. Risk Assessment
4. Discussion
4.1. Important Findings
4.2. Study Limitations and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samuel, T.M.; Sakwinska, O.; Makinen, K.; Burdge, G.C.; Godfrey, K.M.; Silva-Zolezzi, I. Preterm Birth: A Narrative Review of the Current Evidence on Nutritional and Bioactive Solutions for Risk Reduction. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, R.; Dey, S.K.; Fisher, S.J. Preterm labor: One syndrome, many causes. Science 2014, 345, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Oza, S.; Hogan, D.; Perin, J.; Rudan, I.; Lawn, J.E.; Cousens, S.; Mathers, C.; Black, R.E. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2000–13, with projections to inform post-2015 priorities: An updated systematic analysis. Lancet 2015, 385, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugelman, A.; Colin, A.A. Late Preterm Infants: Near Term but Still in a Critical Developmental Time Period. Pediatrics 2013, 132, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiou, H.M.; Di Quinzio, M.K.W.; Permezel, M.; Brennecke, S.P. Predicting Preterm Labour: Current Status and Future Prospects. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 435014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajantie, E.; Strang-Karlsson, S.; Evensen, K.A.I.; Haaramo, P. Adult outcomes of being born late preterm or early term–what do we know? Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019, 24, 66–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halimi Asl, A.A.; Safari, S.; Parvareshi Hamrah, M. Epidemiology and Related Risk Factors of Preterm Labor as an obstetrics emergency. Emergency 2017, 5, e3. [Google Scholar]
- Dahman, H. Risk factors associated with preterm birth: A retrospective study in Mukalla Maternity and Childhood Hospital, Hadhramout Coast/Yemen. Sudan. J. Paediatr. 2020, 20, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alijahan, R.; Hazrati, S.; Mirzarahimi, M.; Pourfarzi, F.; Hadi, P.A. Prevalence and risk factors associated with preterm birth in Ardabil, Iran. Iran. J. Reprod. Med. 2014, 12, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kemp, M.; Newnham, J.; Challis, J.; Jobe, A.; Stock, S. The clinical use of corticosteroids in pregnancy. Hum. Reprod. Updat. 2015, 22, 240–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Zhu, M.; Zhuo, B.; Li, L.; Chen, H.; Xu, L.; Wu, Z.; Cheng, F.; Xu, L.; Yan, J. Use of complete blood count for predicting preterm birth in asymptomatic pregnant women: A propensity score-matched analysis. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, R.; Rath, W.; Abele, H.; Garnier, Y.; Kuon, R.-J.; Maul, H. Reducing the Risk of Preterm Birth by Ambulatory Risk Factor Management. Dtsch. Ärzteblatt Int. 2019, 116, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinall, J.; Miller, S.P.; Bjornson, B.H.; Fitzpatrick, K.P.; Poskitt, K.J.; Brant, R.; Synnes, A.R.; Cepeda, I.L.; Grunau, R.E. Invasive Procedures in Preterm Children: Brain and Cognitive Development at School Age. Pediatrics 2014, 133, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Ananth, C.V.; Li, Z.; Smulian, J.C. Maternal anaemia and preterm birth: A prospective cohort study. Leuk. Res. 2009, 38, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasim, T.; Bushra, N.; Tajammul, A.; Humayun, S.; Rasool, S.; Shahbaz, F.; Riaz, A.; Siddique, F.; Khawaja, K.I.; Fatima, A.; et al. Ferritin screening and Iron treatment for maternal anemia and fetal growth restriction prevention—A multicenter randomized controlled trial (FAIR Study). Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 39, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrubaru, I.; Motoc, A.; Moise, M.L.; Miutescu, B.; Citu, I.M.; Pingilati, R.A.; Popescu, D.-E.; Dumitru, C.; Gorun, F.; Olaru, F.; et al. The Predictive Role of Maternal Biological Markers and Inflammatory Scores NLR, PLR, MLR, SII, and SIRI for the Risk of Preterm Delivery. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.-A.; Munoz, F.M.; Gonik, B.; Frau, L.; Cutland, C.; Mallett-Moore, T.; Kissou, A.; Wittke, F.; Das, M.; Nunes, T.; et al. Preterm birth: Case definition & guidelines for data collection, analysis, and presentation of immunisation safety data. Vaccine 2016, 34, 6047–6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timircan, M.; Bratosin, F.; Vidican, I.; Suciu, O.; Turaiche, M.; Bota, A.V.; Mitrescu, S.; Marincu, I. Coping Strategies and Health-Related Quality of Life in Pregnant Women with SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Medicina 2021, 57, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, F.; Chen, H.; Chen, Q.; Chen, D.; Chen, Y.; Sagnelli, M.; Chen, G.; Zhao, B.; Luo, Q. Second-trimester and third-trimester maternal lipid profiles significantly correlated to LGA and macrosomia. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2021, 304, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.-B.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Wang, W.; Pan, Y.-Y. The Hemoglobin, Albumin, Lymphocyte, and Platelet (HALP) Score in Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer Before First-Line Treatment with Etoposide and Progression-Free Survival. Experiment 2019, 25, 5630–5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leetanaporn, K.; Hanprasertpong, J. Predictive Value of the Hemoglobin-Albumin-Lymphocyte-Platelet (HALP) Index on the Oncological Outcomes of Locally Advanced Cervical Cancer Patients. Cancer Manag. Res. 2022, 14, 1961–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, L.; Hu, L. The value of the combination of hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte and platelet in predicting platinum-based chemoradiotherapy response in male patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 46, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, D.; Zhang, C.-J.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yang, K.-W.; Yu, X.-T.; Gong, Y.; Li, X.-S.; He, Z.-S.; Zhou, L.-Q. Prognostic significance of the combination of preoperative hemoglobin and albumin levels and lymphocyte and platelet counts (HALP) in patients with renal cell carcinoma after nephrectomy. BMC Urol. 2018, 18, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seong, W.J.; Chong, G.O.; Hong, D.G.; Lee, T.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Cho, Y.L.; Chun, S.S.; Park, I.S. Clinical significance of serum albumin level in pregnancy-related hypertension. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2010, 36, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, T.; Watanabe, K.; Kinoshita, H.; Iwasaki, A.; Owaki, Y.; Matsushita, H.; Wakatsuki, A. Hypoalbuminemia is related to endothelial dysfunction resulting from oxidative stress in parturients with preeclampsia. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2021, 83, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, S.; Azami, M.; Badfar, G.; Parizad, N.; Sayehmiri, K. The relationship between maternal anemia during pregnancy with preterm birth: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2019, 33, 2679–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardic, C.; Usta, O.; Omar, E.; Yıldız, C.; Memis, E.; Öztürk, G.Z. Relationship between anaemia during pregnancy and preterm delivery. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2019, 39, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunuwar, D.R.; Singh, D.R.; Chaudhary, N.K.; Pradhan, P.M.S.; Rai, P.; Tiwari, K. Prevalence and factors associated with anemia among women of reproductive age in seven South and Southeast Asian countries: Evidence from nationally representative surveys. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitasari, C.; Andayasari, L. Young Mothers, Parity and the Risks of Anemia in the Third Trimester of Pregnancy. Health Sci. J. Indones. 2015, 6, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Owais, A.M.; Umay, K. Effect of maternal anaemia on APGAR score of Newborn. J. Rawalpindi Med. Coll. (JRMC) 2015, 19, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, N.; Yadav Shree, N.; Kalra Suresh, K.; Pathak, S.; Gupta Binod, K.; Shrestha, S.; Patel, M.; Satia, I.; Sadhra, S.; Bolton Charlotte, E.; et al. Prognostic Factors Associated with Small for Gestational Age Babies in a Tertiary Care Hospital of Western Nepal: A Cross-sectional Study. Health Sci. Rep. 2021, 4, e250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badfar, G.; Shohani, M.; Soleymani, A.; Azami, M. Maternal anemia during pregnancy and small for gestational age: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2018, 32, 1728–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivan, E.A.; Mangaiarkkarasi, A. Evaluation of anaemia in booked antenatal mothers during the last trimester. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2013, 7, 2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suryanarayana, R.; Chandrappa, M.; Santhuram, A.N.; Prathima, S.; Sheela, S. Prospective study on prevalence of anemia of pregnant womenand its outcome: A community based study. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2017, 6, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keren-Politansky, A.; Breizman, T.; Brenner, B.; Sarig, G.; Drugan, A. The coagulation profile of preterm delivery. Thromb. Res. 2014, 133, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochart, A.; Nuytten, A.; Pierache, A.; Bauters, A.; Rauch, A.; Wibaut, B.; Susen, S.; Goudemand, J. Hemostatic profile of infants with spontaneous prematurity: Can we predict intraventricular hemorrhage development? Ital. J. Pediatr. 2019, 45, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neary, E.; McCallion, N.; Kevane, B.; Cotter, M.; Egan, K.; Regan, I.; Kirkham, C.; Mooney, C.; Coulter-Smith, S.; Áinle, F.N. Coagulation indices in very preterm infants from cord blood and postnatal samples. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 2021–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monagle, P.; Massicotte, P. Developmental haemostasis: Secondary haemostasis. Semin, Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011, 16, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, A.T.; Andreasen, B.H.; Salvig, J.D.; Hvas, A.-M. Changes in fibrin D-dimer, fibrinogen, and protein S during pregnancy. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2010, 71, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variables | Prematurity (n = 161) | No Prematurity (n = 161) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), mean ± SD | 29.4 ± 4.8 | 29.6 ± 4.9 | 0.711 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2), mean ± SD | 26.3 ± 3.5 | 24.3 ± 3.4 | <0.001 |
| Gravidity | 0.801 | ||
| 1 | 107 (66.5%) | 103 (64.0%) | |
| 2 | 34 (21.1%) | 39 (24.2%) | |
| ≥3 | 20 (12.4%) | 19 (11.8%) | |
| Parity | 0.505 | ||
| 1 | 122 (75.8%) | 127 (78.9%) | |
| ≥2 | 39 (24.2%) | 34 (21.1%) | |
| Number of comorbidities * | 0.430 | ||
| 0 | 118 (73.3%) | 126 (78.3%) | |
| 1 | 34 (21.1%) | 25 (15.5%) | |
| ≥2 | 9 (5.6%) | 10 (6.2%) | |
| Substance use during pregnancy | |||
| Smoking | 18 (11.2%) | 8 (5.0%) | 0.040 |
| Alcohol consumption | 7 (4.3%) | 6 (3.7%) | 0.777 |
| Obstetrical characteristics | |||
| Moment of birth (weeks of gestation), mean ± SD | 35.3 ± 4.1 | 37.9 ± 4.8 | <0.001 |
| Premature rupture of membranes | 17 (10.6%) | 4 (2.5%) | 0.003 |
| Abnormal placental implantation | 16 (9.9%) | 9 (5.6%) | 0.144 |
| Cesarean delivery | 17 (10.6%) | 33 (20.5%) | 0.013 |
| Urinary tract infections | 41 (25.5%) | 26 (16.1%) | 0.039 |
| Pregnancy loss/miscarriage | 6 (3.7%) | 4 (2.5%) | 0.520 |
| History of abortion | 9 (5.6%) | 7 (4.3%) | 0.608 |
| Distribution of premature births during the third trimester | - | ||
| Early third trimester (28–31 weeks) | 57 (35.4%) | - | |
| Late third trimester (32–36 weeks) | 104 (64.6%) | - |
| Variables | Normal Range * | Prematurity (n = 161) | No Prematurity (n = 161) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White blood cell count (×109/L) | 4.5–11.0 | 9.24 ± 5.31 | 8.23 ± 5.08 | 0.082 |
| Lymphocytes (×109/L) | 1.0–4.8 | 0.78 ± 0.49 | 1.06 ± 0.76 | <0.001 |
| Platelets (×109/L) | 150–450 | 216 ± 68.4 | 214 ± 71.0 | 0.247 |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 120–160 | 113 ± 24.7 | 139 ± 28.5 | <0.001 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 30–50 | 31.4 ± 7.0 | 36.6 ± 6.4 | <0.001 |
| PT (sec.) | 12.5–13.5 | 12.9 ± 1.8 | 13.3 ± 1.7 | 0.041 |
| aPTT (sec.) | 25–35 | 26.7 ± 2.3 | 27.9 ± 2.1 | <0.001 |
| D-dimers (ng/mL) | <250 | 229 ± 52 | 216 ± 36 | 0.009 |
| Fibrinogen (g/L) | 2–4 | 5.13 ± 0.88 | 3.10 ± 0.72 | <0.001 |
| HALP score | ≥24 | 12.82 ± 3.16 | 23.96 ± 4.28 | <0.001 |
| FAR score | <0.1 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 0.08 ± 0.03 | <0.001 |
| Variables | AUC | 95% CI | SE | % | % | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | Sensitivity | Specificity | ||||
| Hemoglobin | 0.671 | 0.554 | 0.819 | 0.076 | 73% | 65% | 0.001 |
| PT | 0.625 | 0.526 | 0.802 | 0.073 | 62% | 69% | 0.042 |
| aPTT | 0.632 | 0.561 | 0.886 | 0.070 | 68% | 64% | 0.045 |
| D-dimers | 0.615 | 0.487 | 0.731 | 0.071 | 66% | 60% | 0.039 |
| HALP | 0.680 | 0.548 | 0.835 | 0.084 | 75% | 69% | 0.001 |
| FAR | 0.646 | 0.533 | 0.774 | 0.080 | 68% | 64% | 0.020 |
| Adjusted Factors | Odds Ratio | (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin | 3.28 | 1.62–5.36 | 0.001 |
| PT | 2.11 | 1.09–4.91 | 0.038 |
| aPTT | 3.24 | 2.01–6.13 | <0.001 |
| D-dimers | 4.26 | 1.24–6.58 | 0.005 |
| HALP | 6.09 | 1.99–10.24 | <0.001 |
| FAR | 5.30 | 1.75–8.87 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hrubaru, I.; Motoc, A.; Dumitru, C.; Bratosin, F.; Fericean, R.M.; Alambaram, S.; Citu, I.M.; Chicin, G.N.; Erdelean, I.; Gorun, F.; et al. Assessing the Utility of Hemoglobin, HALP Score, FAR Ratio, and Coagulation Parameters as Predictors for Preterm Birth. Children 2023, 10, 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10030527
Hrubaru I, Motoc A, Dumitru C, Bratosin F, Fericean RM, Alambaram S, Citu IM, Chicin GN, Erdelean I, Gorun F, et al. Assessing the Utility of Hemoglobin, HALP Score, FAR Ratio, and Coagulation Parameters as Predictors for Preterm Birth. Children. 2023; 10(3):527. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10030527
Chicago/Turabian StyleHrubaru, Ingrid, Andrei Motoc, Catalin Dumitru, Felix Bratosin, Roxana Manuela Fericean, Satish Alambaram, Ioana Mihaela Citu, Gratiana Nicoleta Chicin, Izabella Erdelean, Florin Gorun, and et al. 2023. "Assessing the Utility of Hemoglobin, HALP Score, FAR Ratio, and Coagulation Parameters as Predictors for Preterm Birth" Children 10, no. 3: 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10030527
APA StyleHrubaru, I., Motoc, A., Dumitru, C., Bratosin, F., Fericean, R. M., Alambaram, S., Citu, I. M., Chicin, G. N., Erdelean, I., Gorun, F., Citu, C., & Popa, Z. L. (2023). Assessing the Utility of Hemoglobin, HALP Score, FAR Ratio, and Coagulation Parameters as Predictors for Preterm Birth. Children, 10(3), 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10030527









