False-Positive Asymmetrical Tongue Muscle 18F-FDG Uptake in Hypoglossal Nerve Paralysis Following Lymph Node Dissection in a Pediatric Patient with Malignant Rhabdoid Tumor of the Neck
Abstract
1. Introduction
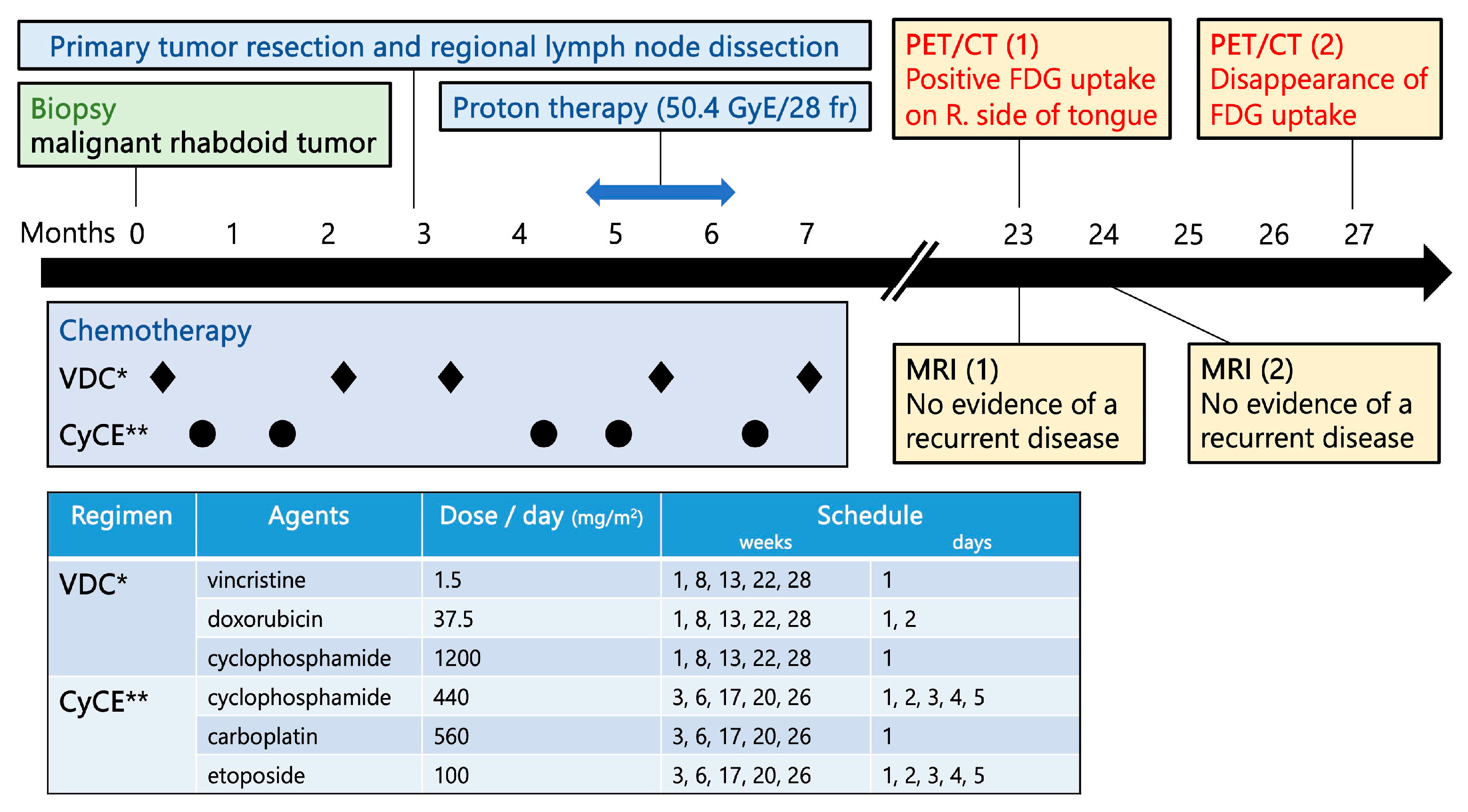
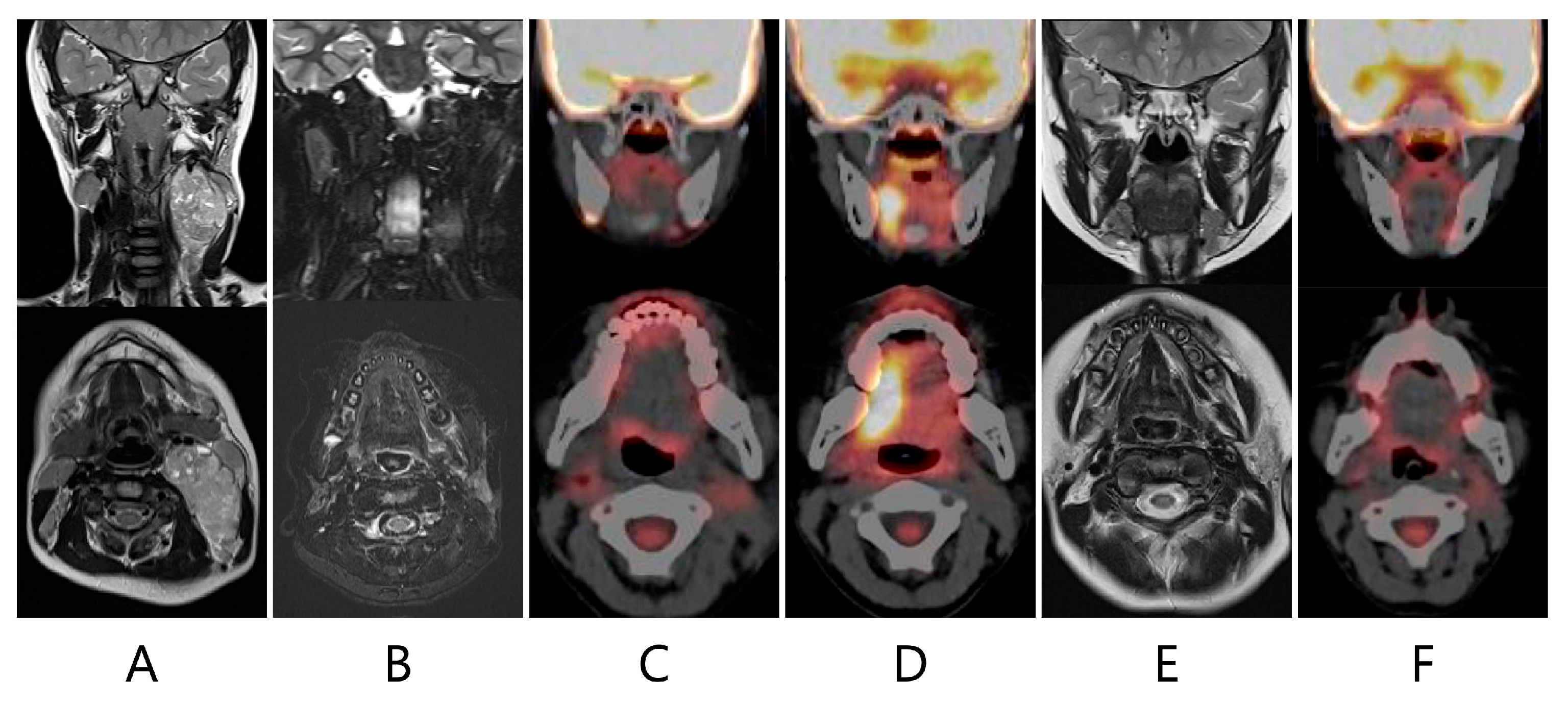
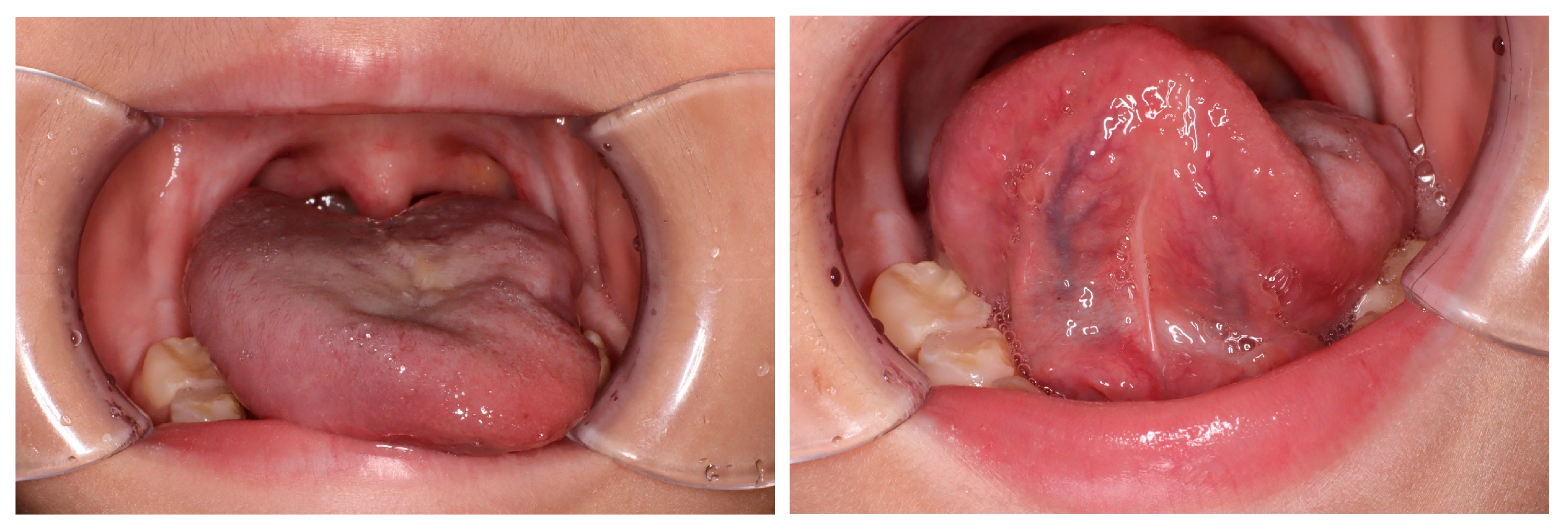
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Purohit, B.S.; Ailianou, A.; Dulguerov, N.; Becker, C.D.; Ratib, O.; Becker, M. FDG-PET/CT pitfalls in oncological head and neck imaging. Insights Imaging 2014, 5, 585–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, M.K.; Pfannenberg, C.; Öksüz, M. Nonspecific FDG uptake in the tongue mimicking the primary tumor in a patient with cancer of unknown primary. Clin. Imaging 2011, 35, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timbang, M.R.; Trosman, S.J.; Lorenz, R.R. Hypoglossal nerve paralysis results in hypermetabolic activity on positron emission tomography/computed tomography in the contralateral tongue. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 1382–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, B.; Stiller, C.; Bourdeaut, F. Extracranial rhabdoid tumours: What we have learned so far and future directions. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, e329–e336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, B.; De Salvo, G.L.; Orbach, D.; De Paoli, A.; Kelsey, A.; Mudry, P.; Francotte, N.; Van Noesel, M.; Bisogno, G.; Casanova, M.; et al. Outcome of extracranial malignant rhabdoid tumours in children registered in the European Paediatric Soft Tissue Sarcoma Study Group Non-Rhabdomyosarcoma Soft Tissue Sarcoma 2005 Study-EpSSG NRSTS 2005. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 60, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madigan, C.E.; Armenian, S.H.; Malogolowkin, M.H.; Mascarenhas, L. Extracranial malignant rhabdoid tumors in childhood: The Childrens Hospital Los Angeles experience. Cancer 2007, 110, 2061–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Yang, S.; Cai, S.; Ma, X.; Qin, H.; Zhang, W.; Fu, L.; Zeng, Q.; Wen, M.; Peng, X.; et al. Clinical and Prognostic Characteristics of 53 Cases of Extracranial Malignant Rhabdoid Tumor in Children. A Single-Institute Experience from 2007 to 2017. Oncologist 2019, 24, e551–e558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemes, K.; Bens, S.; Kachanov, D.; Teleshova, M.; Hauser, P.; Simon, T.; Tippelt, S.; Woessmann, W.; Beck, O.; Flotho, C.; et al. Clinical and genetic risk factors define two risk groups of extracranial malignant rhabdoid tumours (eMRT/RTK). Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 142, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, E.M.; Goerres, G.W.; Burger, C.; von Schulthess, G.K.; Steinert, H.C. Recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy in patients with lung cancer: Detection with PET-CT image fusion—Report of six cases. Radiology 2002, 224, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Shah, S.; Gnanasegaran, G.; Rajkotia, S.; Purandare, N.; Puranik, A.; Rangarajan, V. PET/CT Normal Variants and Pitfalls in Pediatric Disorders. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 51, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, T.; Voth, E.; Berthold, F. Asymmetric salivary gland 123I-meta-iodobenzylguanidine uptake in a patient with cervical neuroblastoma and Horner syndrome. Med. Pediatr. Oncol. 2001, 36, 489–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, T.; Yu, C.; Rossleigh, M.; Pereira, J.; Cohn, R. False-positive MIBG uptake in pneumonia in a patient with stage IV neuroblastoma. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2010, 35, 743–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazarika, M.; Rahman, T.; Sarma, A.; Krishnatreya, M. Malignant rhabdoid tumor of the tongue: A rare occurrence. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2014, 18, 312–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohan, E.J.; Wirth, G.A. Anatomy of the neck. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2014, 41, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, I.; Hughes, C.; Brigger, M.T. Pediatric head and neck malignancies: Incidence and trends, 1973-2010. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 152, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Person, L.; Lacour, B.; Faure, L.; Guissou, S.; Poulalhon, C.; Orbach, D.; Goujon, S.; Berger, C.; Clavel, J.; Desandes, E. Childhood head and neck cancer in France: Incidence, survival and trends from 2000 to 2015. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 150, 110858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilja-Fischer, J.K.; Schrøder, H.; Nielsen, V.E. Pediatric malignancies presenting in the head and neck. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 118, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junn, J.C.; Soderlund, K.A.; Glastonbury, C.M. Imaging of Head and Neck Cancer With CT, MRI, and US. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 51, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, T.; Master, Z.; Kannan, S.; Agarwal, J.P.; Ghsoh-Laskar, S.; Rangarajan, V.; Murthy, V.; Budrukkar, A. Diagnostic performance of post-treatment FDG PET or FDG PET/CT imaging in head and neck cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2011, 38, 2083–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, C.; Lee, J.H.; Tetzner, U.; Seidel, S.; Kim, S.Y. Comparison of diffusion-weighted MR imaging and (18)F Fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT in detection of residual or recurrent tumors and delineation of their local spread after (chemo) radiotherapy for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 130, 109157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klenk, C.; Gawande, R.; Uslu, L.; Khurana, A.; Qiu, D.; Quon, A.; Donig, J.; Rosenberg, J.; Luna-Fineman, S.; Moseley, M.; et al. Ionising radiation-free whole-body MRI versus (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT scans for children and young adults with cancer: A prospective, non-randomised, single-centre study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, D.M.; Blackledge, M.; Padhani, A.R.; Takahara, T.; Kwee, T.C.; Leach, M.O.; Collins, D.J. Whole-body diffusion-weighted MRI: Tips, tricks, and pitfalls. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 199, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, D.; Elliston, C.; Hall, E.; Berdon, W. Estimated risks of radiation-induced fatal cancer from pediatric CT. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2001, 176, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallory, M.D.; Travers, C.; Cravero, J.P.; Kamat, P.P.; Tsze, D.; Hertzog, J.H. Pediatric Sedation/Anesthesia for MRI: Results from the Pediatric Sedation Research Consortium. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023, 57, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.Z.; Zhu, M.; Bulas, D. Techniques for minimizing sedation in pediatric MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 50, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matsumoto, Y.; Matsui, M.; Makidono, A.; Makimoto, A.; Yuza, Y. False-Positive Asymmetrical Tongue Muscle 18F-FDG Uptake in Hypoglossal Nerve Paralysis Following Lymph Node Dissection in a Pediatric Patient with Malignant Rhabdoid Tumor of the Neck. Children 2024, 11, 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11030348
Matsumoto Y, Matsui M, Makidono A, Makimoto A, Yuza Y. False-Positive Asymmetrical Tongue Muscle 18F-FDG Uptake in Hypoglossal Nerve Paralysis Following Lymph Node Dissection in a Pediatric Patient with Malignant Rhabdoid Tumor of the Neck. Children. 2024; 11(3):348. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11030348
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatsumoto, Yuta, Motohiro Matsui, Akari Makidono, Atsushi Makimoto, and Yuki Yuza. 2024. "False-Positive Asymmetrical Tongue Muscle 18F-FDG Uptake in Hypoglossal Nerve Paralysis Following Lymph Node Dissection in a Pediatric Patient with Malignant Rhabdoid Tumor of the Neck" Children 11, no. 3: 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11030348
APA StyleMatsumoto, Y., Matsui, M., Makidono, A., Makimoto, A., & Yuza, Y. (2024). False-Positive Asymmetrical Tongue Muscle 18F-FDG Uptake in Hypoglossal Nerve Paralysis Following Lymph Node Dissection in a Pediatric Patient with Malignant Rhabdoid Tumor of the Neck. Children, 11(3), 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11030348




