Cerebrovascular Autoregulation in Preterm Infants Using Heart Rate or Blood Pressure: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
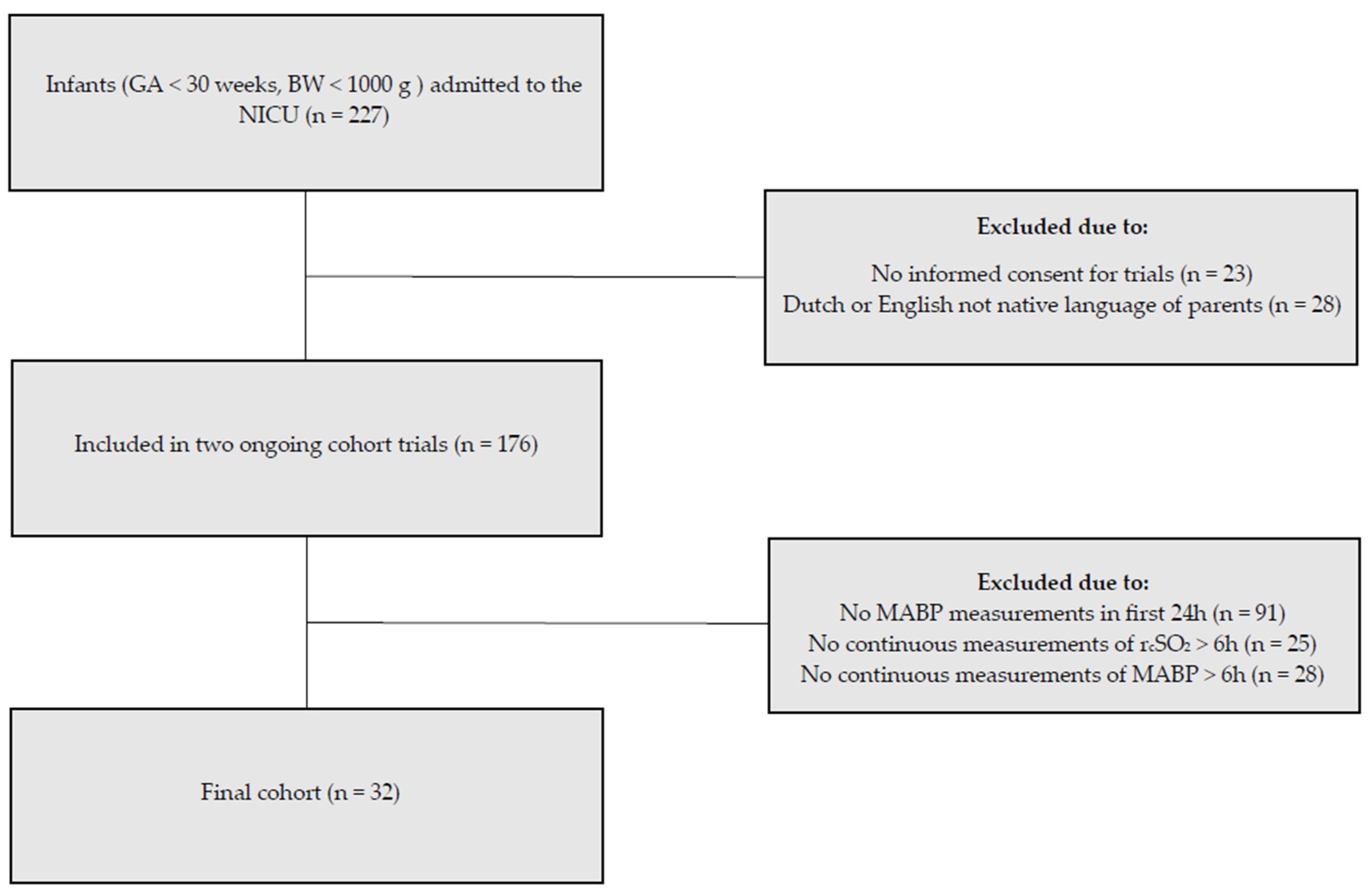
2.1. Patient Population and Data Collection
2.2. Difference in Cerebrovascular Autoregulation Assessment Based on MABP HR
2.3. Short-Term Cerebral Injury
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Cerebrovascular Autoregulation Assessment Using Either MABP or HR
3.3. Impaired Cerebrovascular Autoregulation and Short-Term Cerebral Injury
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rhee, C.J.; da Costa, C.S.; Austin, T.; Brady, K.M.; Czosnyka, M.; Lee, J.K. Neonatal cerebrovascular autoregulation. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 84, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thewissen, L.; Naulaers, G.; Hendrikx, D.; Caicedo, A.; Barrington, K.; Boylan, G.; Cheung, P.Y.; Corcoran, D.; El-Khuffash, A.; Garvey, A.; et al. Cerebral oxygen saturation and autoregulation during hypotension in extremely preterm infants. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 90, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, A.L.; Mayer, B.; Bassler, D.; Hummler, H.D.; Fuchs, H.W.; Bryant, M.B. Cerebral Oxygenation in Preterm Infants Developing Cerebral Lesions. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 809248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimatti, A.G.; Martini, S.; Galletti, S.; Vitali, F.; Aceti, A.; Frabboni, G.; Faldella, G.; Corvaglia, L. Cerebral Oxygenation and Autoregulation in Very Preterm Infants Developing IVH During the Transitional Period: A Pilot Study. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korcek, P.; Stranak, Z.; Sirc, J.; Naulaers, G. The role of near-infrared spectroscopy monitoring in preterm infants. J. Perinatol. 2017, 37, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, S.M.; Prakash, S.S.; Verma, S.; Desai, P.; Kazmi, S.; Mally, P.V. Near-infrared spectroscopy in the medical management of infants. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care 2022, 52, 101291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, H.; Gregas, M.C.; Limperopoulos, C.; Zaretskaya, I.; Bassan, H.; Soul, J.S.; Di Salvo, D.N.; du Plessis, A.J. Elevated Cerebral Pressure Passivity Is Associated With Prematurity-Related Intracranial Hemorrhage. Pediatrics 2009, 124, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, L.W.; Roberts, G.; Anderson, P.J.; Collaborative, V.I. Changing long-term outcomes for infants 500–999 g birth weight in Victoria, 1979–2005. Arch. Dis. Child.-Fetal 2011, 96, F443–F447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooi, E.M.W.; Richter, A.E. Cerebral Autoregulation in Sick Infants: Current Insights. Clin. Perinatol. 2020, 47, 449–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, E.; Baerts, W.; Caicedo Dorado, A.; Naulaers, G.; van Bel, F.; Lemmers, P.M.A. Cerebrovascular autoregulation in preterm fetal growth restricted neonates. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2019, 104, F467–F472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chock, V.Y.; Ramamoorthy, C.; Van Meurs, K.P. Cerebral autoregulation in neonates with a hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus. J. Pediatr. 2012, 160, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, F.Y.; Leung, T.S.; Austin, T.; Wilkinson, M.; Meek, J.H.; Wyatt, J.S.; Walker, A.M. Impaired autoregulation in preterm infants identified by using spatially resolved spectroscopy. Pediatrics 2008, 121, e604–e611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, S.B.; Lakhani, A.; Viscardi, R.M. The association between carbon dioxide, cerebral blood flow, and autoregulation in the premature infant. J. Perinatol. 2021, 41, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindan, V.; Govindan, R.; Massaro, A.N.; Al-Shargabi, T.; Andescavage, N.N.; Vezina, G.; Murnick, J.; Wang, Y.; Metzler, M.; Cristante, C.; et al. Cerebral venous volume changes and pressure autoregulation in critically ill infants. J. Perinatol. 2020, 40, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooi, E.M.W.; Verhagen, E.A.; Elting, J.W.J.; Czosnyka, M.; Austin, T.; Wong, F.Y.; Aries, M.J.H. Measuring cerebrovascular autoregulation in preterm infants using near-infrared spectroscopy: An overview of the literature. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2017, 17, 801–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, S.; Czosnyka, M.; Smielewski, P.; O’Reilly, H.; Brady, K.; Austin, T. Heart rate passivity of cerebral tissue oxygenation is associated with predictors of poor outcome in preterm infants. Acta Paediatr. 2014, 103, e374–e382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunsch, C.L.; Mebius, M.J.; Berger, R.M.F.; Bos, A.F.; Kooi, E.M.W. Early Cerebrovascular Autoregulation in Neonates with Congenital Heart Disease. Children 2022, 9, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, S.; Czosnyka, M.; Smielewski, P.; Iommi, M.; Galletti, S.; Vitali, F.; Paoletti, V.; Camela, F.; Austin, T.; Corvaglia, L. Clinical determinants of cerebrovascular reactivity in very preterm infants during the transitional period. Pediatr. Res. 2022, 92, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dokkum, N.H.; de Kroon, M.L.A.; Dijk, P.H.; Kraft, K.E.; Reijneveld, S.A.; Bos, A.F. Course of Stress during the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Stay in Preterm Infants. Neonatology 2022, 119, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, K.M.; Lee, J.K.; Kibler, K.K.; Smielewski, P.; Czosnyka, M.; Easley, R.B.; Koehler, R.C.; Shaffner, D.H. Continuous time-domain analysis of cerebrovascular autoregulation using near-infrared spectroscopy. Stroke 2007, 38, 2818–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnemore, A.; Groves, A. Physiology of the fetal and transitional circulation. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015, 20, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papile, L.A.; Burstein, J.; Burstein, R.; Koffler, H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: A study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. J. Pediatr. 1978, 92, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, A.J.; Groenendaal, F.; Benders, M.J.; de Vries, L.S. Early and late complications of germinal matrix-intraventricular haemorrhage in the preterm infant: What is new? Neonatology 2014, 106, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, L.S.; Eken, P.; Dubowitz, L.M. The spectrum of leukomalacia using cranial ultrasound. Behav. Brain Res. 1992, 49, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoftiezer, L.; Hof, M.H.P.; Dijs-Elsinga, J.; Hogeveen, M.; Hukkelhoven, C.; van Lingen, R.A. From population reference to national standard: New and improved birthweight charts. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 2019, 220, 383.E1–383.E17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panerai, R.B.; Dineen, N.E.; Brodie, F.G.; Robinson, T.G. Spontaneous fluctuations in cerebral blood flow regulation: Contribution of PaCO2. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2010, 109, 1860–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, Y.; Fraisse, A.; Erdeve, O.; Atasay, B. Echocardiographic Diagnosis and Hemodynamic Evaluation of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Extremely Low Gestational Age Newborn (ELGAN) Infants. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 573627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Y.; Czosnyka, M.; Donnelly, J.; Budohoski, K.P.; Varsos, G.V.; Nasr, N.; Brady, K.M.; Reinhard, M.; Hutchinson, P.J.; Smielewski, P. Comparison of frequency and time domain methods of assessment of cerebral autoregulation in traumatic brain injury. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, S.; Thewissen, L.; Austin, T.; da Costa, C.S.; de Boode, W.P.; Dempsey, E.; Kooi, E.; Pellicer, A.; Rhee, C.J.; Riera, J.; et al. Near-infrared spectroscopy monitoring of neonatal cerebrovascular reactivity: Where are we now? Pediatr. Res. 2023, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soul, J.S.; Hammer, P.E.; Tsuji, M.; Saul, J.P.; Bassan, H.; Limperopoulos, C.; Disalvo, D.N.; Moore, M.; Akins, P.; Ringer, S.; et al. Fluctuating pressure-passivity is common in the cerebral circulation of sick premature infants. Pediatr. Res. 2007, 61, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Votava-Smith, J.K.; Statile, C.J.; Taylor, M.D.; King, E.C.; Pratt, J.M.; Nelson, D.P.; Michelfelder, E.C. Impaired cerebral autoregulation in preoperative newborn infants with congenital heart disease. J. Thorac. Cardiov Surg. 2017, 154, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, N.; Gunn, A.J.; Bennet, L.; Dhillon, S.K.; Davidson, J.O. Preventing Brain Injury in the Preterm Infant-Current Controversies and Potential Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballabh, P. Intraventricular Hemorrhage in Premature Infants: Mechanism of Disease. Pediatr. Res. 2010, 67, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahya, K.P.; Suryawanshi, P. Neonatal periventricular leukomalacia: Current perspectives. Res. Rep. Neonatol. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, E.A.; Hummel, L.A.; Bos, A.F.; Kooi, E.M. Near-infrared spectroscopy to detect absence of cerebrovascular autoregulation in preterm infants. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 125, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Clinical Characteristics | N (%) or Mean ± SD or Median (Interquartile Range) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gestational age (weeks + days) | 25 + 5/7 (24 + 6/7–27 + 5/7) | ||
| Birth weight (g) | 902 ± 244 | ||
| Male | 16 (50%) | ||
| Multiple pregnancy | 14 (43.8%) | ||
| Head circumference (cm) | 23.4 ± 1.7 | ||
| Apgar scores at 5 min | 7 (5–8) | ||
| SGA | 4 (12.5%) | ||
| HsPDA | 15 (46.9%) | ||
| NEC | 7 (21.9%) | ||
| EONS | 2 (6.3%) | ||
| Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | |
| Sedatives | 9 (28.1%) | 11 (34.4%) | 8 (25%) |
| Inotropes | 1 (3.1%) | 4 (12.5%) | 2 (6.3%) |
| Mortality during NICU admission | 4 (12.5%) | ||
| Measurement Variables | Day 1 (n = 32) | Day 2 (n = 24) | Day 3 (n = 28) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MABP (mmHg) | 34 ± 4 | 37 ± 5 | 38 ± 6 |
| HR (bpm) | 150 ± 2 | 155 ± 5 | 157 ± 10 |
| RcSO2 (%) | 79 ± 7 | 80 ± 7 | 78 ± 7 |
| SpO2 (%) | 94 ± 3 | 94 ± 2 | 93 ± 2 |
| (n = 32) | (n = 32) | (n = 32) | |
| Mechanical ventilation | 20 (62.5%) | 17 (53.1%) | 15 (46.9%) |
| Peak FiO2 | 0.46 [0.32–0.69] | 0.32 [0.21–0.66] | 0.35 [0.25–0.50] |
| (n = 30) | (n = 25) | (n = 28) | |
| PCO2 (kPa) | 5.3 ± 1.1 | 5.6 ± 1.1 | 5.9 ± 1.0 |
| Measurement Variables | Day 1 (n = 32) | Day 2 (n = 24) | Day 3 (n = 28) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean COx | 0.07 ± 0.11 * | 0.06 ± 0.12 * | 0.02 ± 0.15 |
| Mean TOHRx | −0.03 ± 0.11 | −0.05 ± 0.10 | −0.01 ± 0.11 |
| Agreement on impaired CAR (%) | |||
| TOHRx cc cut-off 0.3 | 67.6 ± 17.3 | 72.1 ± 11.9 | 70.1 ± 12.7 |
| TOHRx cc cut-off −0.3 | 69.6 ± 12.5 | 65.7 ± 12.3 | 69.4 ± 12.1 |
| Sonographic Characteristics | First cUS on Day 1–3 | cUS on Day 7–10 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cerebral injury on cUS as defined | 20 (62.5%) | |||
| IVH | 20 (62.5%) | 25 (78.1%) | ||
| Side | ||||
| Right-sided | 5 (25%) | 3 (12%) | ||
| Left-sided | 1 (5%) | 2 (8%) | ||
| Bilateral | 14 (70%) | 20 (80%) | ||
| Grade | Right side | Left side | Right side | Left side |
| I | 12 (63.2%) | 8 (53.3%) | 10 (43.5%) | 13 (59.1%) |
| II | 3 (15.8%) | 4 26.7%) | 4 (17.4%) | 4 (18.2%) |
| III | 4 (21.1%) | 3 (20.0%) | 9 (39.1%) | 5 (21.9%) |
| Worsening of IVH | 13 (40.6%) | |||
| PVHI | 5 (15.6%) | 7 (24.1%) | ||
| PVL | 10 (31.3%) | |||
| Side | ||||
| Bilateral | 10 (100%) | |||
| Grade | ||||
| I | 10 (100%) | |||
| Day | Measurement Variable | No Cerebral Injury on cUS (n = 12) | Cerebral Injury on cUS (n = 20) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RcSO2 (%) | 80.9 ± 6.4 | 77.0 ± 6.4 | 0.111 |
| COx | 0.09 ± 0.10 | 0.07 ± 0.12 | 0.589 | |
| TOHRx | −0.03 ± 0.12 | −0.03 ± 0.11 | 0.914 | |
| %TimeCARi with MABP (%) | 27.0 ± 13.8 | 25.6 ± 13.1 | 0.774 | |
| %TimeCARi with HR (%) | ||||
| TOHRx cc cut-off 0.3 | 13.7 ± 8.1 | 12.2 ± 8.6 | 0.631 | |
| TOHRx cc cut-off −0.3 | 18.2 ± 13.3 | 17.4 ± 13.3 | 0.884 | |
| 2 | (n = 7) | (n = 17) | ||
| RcSO2 (%) | 79.7 ± 8.8 | 79.7 ± 6.4 | 0.494 | |
| COx | 0.03 ± 0.12 | 0.07 ± 0.13 | 0.304 | |
| TOHRx | 0.00 ± 0.07 | −0.07 ± 0.11 | 0.081 | |
| %TimeCARi with MABP (%) | 21.5 ± 8.3 | 26.6 ± 13.3 | 0.274 | |
| %TimeCARi with HR (%) | ||||
| TOHRx cc cut-off 0.3 | 14.6 ± 7.1 | 11.5 ± 8.9 | 0.381 | |
| TOHRx cc cut-off −0.3 | 13.2 ± 10.2 | 21.3 ± 12.1 | 0.118 | |
| 3 | (n = 10) | (n = 18) | ||
| RcSO2 (%) | 79.4 ± 4.9 | 77.4 ± 8.1 | 0.714 | |
| COx | 0.06 ± 0.16 | 0.00 ± 0.15 | 0.296 | |
| TOHRx | −0.01 ± 0.10 | −0.02 ± 0.11 | 0.751 | |
| %TimeCARi with MABP (%) | 26.7 ± 15.6 | 21.6 ± 11.5 | 0.332 | |
| %TimeCARi with HR | ||||
| TOHRx cc cut-off 0.3 | 15.7 ± 9.2 | 14.1 ± 12.0 | 0.731 | |
| TOHRx cc cut-off −0.3 | 16.6 ± 9.4 | 17.4 ± 10.7 | 0.928 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lahr, B.E.; Brunsch, C.L.; Dikkers, R.; Bos, A.F.; Kooi, E.M.W. Cerebrovascular Autoregulation in Preterm Infants Using Heart Rate or Blood Pressure: A Pilot Study. Children 2024, 11, 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11070765
Lahr BE, Brunsch CL, Dikkers R, Bos AF, Kooi EMW. Cerebrovascular Autoregulation in Preterm Infants Using Heart Rate or Blood Pressure: A Pilot Study. Children. 2024; 11(7):765. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11070765
Chicago/Turabian StyleLahr, Bineta E., Celina L. Brunsch, Riksta Dikkers, Arend F. Bos, and Elisabeth M. W. Kooi. 2024. "Cerebrovascular Autoregulation in Preterm Infants Using Heart Rate or Blood Pressure: A Pilot Study" Children 11, no. 7: 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11070765
APA StyleLahr, B. E., Brunsch, C. L., Dikkers, R., Bos, A. F., & Kooi, E. M. W. (2024). Cerebrovascular Autoregulation in Preterm Infants Using Heart Rate or Blood Pressure: A Pilot Study. Children, 11(7), 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11070765







