Thrombospondin-1 Airway Expression and Thrombospondin-1 Gene Variants Are Associated with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Extremely Low-Birth-Weight Infants: A Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Genotyping
2.4. Tracheal Aspirate Analysis
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
3.2. TSP-1 Genotyping
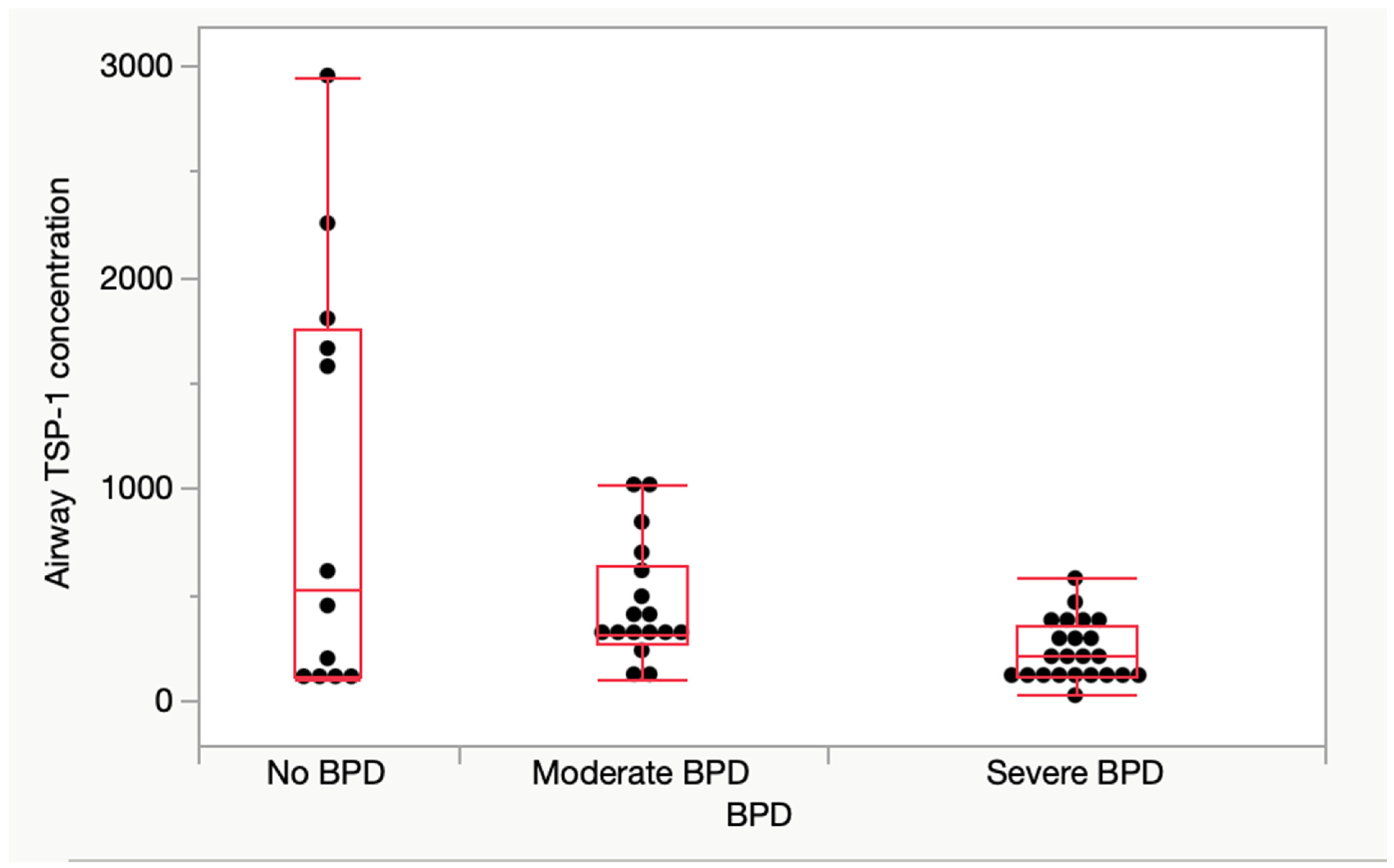
3.3. Airway TSP-1 Protein Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BPD | Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia |
| ELBW | Extremely Low Birth Weight |
| TSP-1 | Thrombospondin-1 |
| SNP | Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism |
| TGF-β | Transforming Growth Factor Beta |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| BASCs | Bronchioalveolar Stem Cells |
| ATII | Alveolar Type II |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| NE | Neutrophil Elastase |
| CG | Cathepsin G |
| CTGF | Connective Tissue Growth Factor |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| LSKL | Leucine–Serine–Lysine–Leucine |
| LAP | Latency-Associated Peptide |
| RS | Reference SNP Cluster ID |
References
- Thébaud, B.; Goss, K.N.; Laughon, M.; Whitsett, J.A.; Abman, S.H.; Steinhorn, R.H.; Aschner, J.L.; Davis, P.G.; McGrath-Morrow, S.A.; Soll, R.F.; et al. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, R.D.; Jobe, A.H.; Koso-Thomas, M.; Bancalari, E.; Viscardi, R.M.; Hartert, T.V.; Ryan, R.M.; Kallapur, S.G.; Steinhorn, R.H.; Konduri, G.G.; et al. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: Executive Summary of a Workshop. J. Pediatr. 2018, 197, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thébaud, B.; Abman, S.H. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: Where have all the vessels gone? Roles of angiogenic growth factors in chronic lung disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 175, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Xu, J.; Gao, Q.; Mao, X.; Yin, J.; Lu, K.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, R. IL-33-induced neutrophil extracellular traps degrade fibronectin in a murine model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Cell Death Discov. 2020, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surate Solaligue, D.E.; Rodríguez-Castillo, J.A.; Ahlbrecht, K.; Morty, R.E. Recent advances in our understanding of the mechanisms of late lung development and bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2017, 313, L1101–L1153. [Google Scholar]
- Lal, C.V.; Bhandari, V.; Ambalavanan, N. Genomics, microbiomics, proteomics, and metabolomics in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin. Perinatol. 2018, 42, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Brune, J.E.; Chang, M.Y.; Reeves, S.R.; Altemeier, W.A.; Frevert, C.W. Defining the versican interactome in lung health and disease. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2022, 323, C249–C276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paepe, M.E.; Greco, D.; Mao, Q. Angiogenesis-related gene expression profiling in ventilated preterm human lungs. Exp. Lung. Res. 2010, 36, 399–410. [Google Scholar]
- Bhandari, V.; Gruen, J.R.; Jang, K.L.; Göpel, W.; Hallman, M.; Lavoie, P.M. Genetics of bronchopulmonary dysplasia: When things do not match up, it is only the beginning. J. Pediatr. 2019, 208, 298–299. [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein, P. Diversity of function is inherent in matricellular proteins: An appraisal of thrombospondin 1. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 130, 503–506. [Google Scholar]
- Lawler, P.R.; Lawler, J. Molecular basis for the regulation of angiogenesis by thrombospondin-1 and -2. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isenberg, J.S.; Roberts, D.D. THBS1 (thrombospondin-1). Atlas. Genet. Cytogenet. Oncol. Haematol. 2020, 24, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, A.; Rogers, N.M.; Ghimire, K. Thrombospondin-1 CD47 Signalling: From Mechanisms to Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacurari, M.; Kafoury, R.; Turner, T.; Taylor, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Thrombospondin-1 and microRNA-1 expression in response to multiwalled carbon nanotubes in alveolar epithelial cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 1596–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozo, F.; Hooper, S.B.; Wallace, M.J. Thrombospondin-1 expression and localization in the developing ovine lung. J. Physiol. 2007, 584, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenina, O.I.; Ustinov, V.; Krukovets, I.; Marinic, T.; Topol, E.J.; Plow, E.F. Polymorphisms A387P in thrombospondin-4 and N700S in thrombospondin-1 perturb calcium binding sites. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1893–1895. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.J.; Wei, C.Y.; Li, W.B.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Tang, M.X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, M. Association between single nucleotide polymorphisms in thrombospondins genes and coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis. Thromb. Res. 2015, 136, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, W.; Hoppmann, P.; de Waha, A.; Schömig, A.; Kastrati, A. Polymorphisms in thrombospondin genes and myocardial infarction: A case-control study and a meta-analysis of available evidence. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narizhneva, N.V.; Byers-Ward, V.J.; Quinn, M.J.; Zidar, F.J.; Plow, E.F.; Topol, E.J.; Byzova, T.V. Molecular and functional differences induced in thrombospondin-1 by the single nucleotide polymorphism associated with the risk of premature, familial myocardial infarction. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 21651–21657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alehagen, U.; Shamoun, L.; Wågsäter, D. Increased cardiovascular mortality in females with the a/a genotype of the SNPs rs1478604 and rs2228262 of thrombospondin-1. BMC Med. Genet. 2020, 21, 179. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Shi, Z.; Li, Q.; Dai, X.; Pan, C.; Ma, Y.; Yan, R.; Fei, D.; Xie, J. A novel growth-friendly system alleviates pulmonary dysplasia in early-onset scoliosis combined with thoracic insufficiency syndrome: Radiological, pathological, and transcriptomic assessments. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27887. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Yang, S.; Li, Q.; Ren, Z.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Gu, X.; Liu, F.; Mu, J.; et al. Association of THBS1 genetic variants and mRNA expression with the risks of ischemic stroke and long-term death after stroke. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 1006473. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Takahashi, K.; Pasic, L.; Narui, C.; Ellinger, P.; Grundmann, M.; Takahashi, T. The effects of CD148 Q276P/R326Q polymorphisms in A431D epidermoid cancer cell proliferation and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling. Cancer Rep. 2022, 5, e1566. [Google Scholar]
- Amatya, S.; Rajbhandari, S.; Pradhan, S.; Trinh, V.; Paudel, U.; Parton, L.A. Hedgehog signaling pathway gene variant influences bronchopulmonary dysplasia in extremely low birth weight infants. World J. Pediatr. 2021, 17, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras-Ruiz, L.; Ryan, D.S.; Sia, R.K.; Bower, K.S.; Dartt, D.A.; Masli, S. Polymorphism in THBS1 gene is associated with post-refractive surgery chronic ocular surface inflammation. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Bhang, D.H.; Beede, A.; Huang, T.L.; Stripp, B.R.; Bloch, K.D.; Wagers, A.J.; Tseng, Y.H.; Ryeom, S.; Kim, C.F. Lung stem cell differentiation in mice directed by endothelial cells via a BMP4-NFATc1-thrombospondin-1 axis. Cell 2014, 156, 440–455. [Google Scholar]
- Sozo, F.; Wallace, M.J.; Zahra, V.A.; Filby, C.E.; Hooper, S.B. Gene expression profiling during increased fetal lung expansion identifies genes likely to regulate development of the distal airways. Physiol. Genom. 2006, 24, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Shiraishi, K.; Shah, P.P.; Morley, M.P.; Loebel, C.; Santini, G.T.; Katzen, J.; Basil, M.C.; Lin, S.M.; Planer, J.D.; Cantu, E.; et al. Biophysical forces mediated by respiration maintain lung alveolar epithelial cell fate. Cell 2023, 186, 1478–1492.e1415. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, S.; Roberts, D.D. Emerging functions of thrombospondin-1 in immunity. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 155, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.; Olonisakin, T.; Bain, W.; Zupetic, J.; Brown, R.; Hulver, M.; Xiong, Z.; Tejero, J.; Shanks, R.M.; Bomberger, J.M.; et al. Thrombospondin-1 protects against pathogen-induced lung injury by limiting extracellular matrix proteolysis. J. Clin. Investig. Insight 2018, 3, e96914. [Google Scholar]
- Peñaloza, H.F.; Olonisakin, T.F.; Bain, W.G.; Qu, Y.; van der Geest, R.; Zupetic, J.; Hulver, M.; Xiong, Z.; Newstead, M.W.; Zou, C.; et al. Thrombospondin-1 Restricts Interleukin-36γ-Mediated Neutrophilic Inflammation during Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pulmonary Infection. mBio 2021, 12, 10–1128. [Google Scholar]
- Lawler, J.; Sunday, M.; Thibert, V.; Duquette, M.; George, E.L.; Rayburn, H.; Hynes, R.O. Thrombospondin-1 is required for normal murine pulmonary homeostasis and its absence causes pneumonia. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 982–992. [Google Scholar]
- Ruschkowski, B.A.; Esmaeil, Y.; Daniel, K.; Gaudet, C.; Yeganeh, B.; Grynspan, D.; Jankov, R.P. Thrombospondin-1 Plays a Major Pathogenic Role in Experimental and Human Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.H.; Dhaliwal, R.; Kantores, C.; Ivanovska, J.; Gosal, K.; McNamara, P.J.; Letarte, M.; Jankov, R.P. Rho-kinase inhibitor prevents bleomycin-induced injury in neonatal rats independent of effects on lung inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 50, 61–73. [Google Scholar]
- Dakshinamurti, S. Thrombospondin in the Puzzle of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, 610–612. [Google Scholar]
- Ezzie, M.E.; Piper, M.G.; Montague, C.; Newland, C.A.; Opalek, J.M.; Baran, C.; Ali, N.; Brigstock, D.; Lawler, J.; Marsh, C.B. Thrombospondin-1-deficient mice are not protected from bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 44, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Warburton, D.; Kaartinen, V. When the lung is stretched, could it be thrombospondin via TGFbeta1 peptide activation? J. Physiol. 2007, 584, 365. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, S.; Roberts, D.D. Why do humans need thrombospondin-1? J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 17, 485–493. [Google Scholar]
- Tabary, M.; Gheware, A.; Peñaloza, H.F.; Lee, J.S. The matricellular protein thrombospondin-1 in lung inflammation and injury. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2022, 323, C857–C865. [Google Scholar]
- Dylag, A.M.; Misra, R.S.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; Poole, C.; Huyck, H.L.; Jehrio, M.G.; Haak, J.; Deutsch, G.H.; Dvorak, C.; Olson, H.M.; et al. New insights into the natural history of bronchopulmonary dysplasia from proteomics and multiplexed immunohistochemistry. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2023, 325, L419–L433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.S.Y.; Picard, D.; Hawkins, C.E.; Lu, M.; Pfister, S.; Korshunov, A.; Roussel, M.F.; Wechsler-Reya, R.J.; Henkin, J.; Bouffet, E.; et al. Thrombospondin-1 mimetics are promising novel therapeutics for MYC-associated medulloblastoma. Neurooncol. Adv. 2021, 3, vdab002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No BPD (n = 30) | BPD (n = 67) | p-Value | Corrected p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA, weeks., median (IQR) | 27 (25,28) | 25 (24,26) | 0.008 | 0.16 | |
| BW, g, mean (SD) | 820 (153) | 712 (155) | 0.002 | 0.04 | |
| SGA, n (%) | 5 (17) | 12 (18) | 0.91 | 1 | |
| Male gender, n (%) | 12 (40) | 38 (57) | 0.11 | 1 | |
| Race, n (%) | NH white | 8 (27) | 22(33) | 0.52 | 1 |
| NH black | 11 (37) | 16(24) | |||
| Hispanic | 7 (23) | 17 (25) | |||
| Other | 4 (13) | 12 (18) | |||
| Maternal age, mean (SD) | 28 (7) | 28 (7) | 0.97 | 1 | |
| C section delivery, n (%) | 22 (75) | 44 (71) | 0.62 | 1 | |
| Multiple birth, n (%) | 11 (37) | 16 (25) | 0.23 | 1 | |
| Inborn, n (%) | 22 (76) | 48 (76) | 0.97 | 1 | |
| Antenatal steroids, n (%) | 26 (90) | 57 (86) | 0.65 | 1 | |
| PROM, n (%) | 6 (22) | 14 (23) | 0.97 | 1 | |
| Chorioamnionitis, n (%) | 5 (17) | 7 (11) | 0.37 | 1 | |
| Preeclampsia, n (%) | 8 (27) | 18 (27) | 0.89 | 1 | |
| Gestational diabetes, n (%) | 4 (13) | 11(16) | 0.69 | 1 | |
| 5 min APGAR < 7, n (%) | 11 (37) | 33 (50) | 0.22 | 1 | |
| Surfactant, n (%) | 26 (87) | 56 (83) | 0.92 | 1 | |
| Sepsis, n (%) | 7 (23) | 16 (24) | 0.98 | 1 | |
| Any PDA treatment, n (%) | 19 (63) | 52 (78) | 0.11 | 1 | |
| NEC, n (%) | 3 (10) | 15 (22) | 0.18 | 1 | |
| IVH grade 3 or above, n (%) | 1 (3) | 10 (15) | 0.08 | 1 | |
| rs2664139 | BPD N = 62 | No BPD N = 27 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| TT, n (%) | 45 (73%) | 15 (56%) | 0.26 |
| Tc, n (%) | 8 (13%) | 5 (18%) | |
| cc, n (%) | 9 (14%) | 7 (26%) | |
| Any minor alleles (c), n (%) | 17 (27%) | 12 (44%) | 0.11 |
| MAF | 0.35 | 0.21 | 0.13 |
| rs1478605 | BPD N = 58 | No BPD N = 24 | |
| GG, n (%) | 26 (45%) | 9 (35%) | 0.26 |
| Ga, n (%) | 18 (31%) | 5 (22%) | |
| aa, n (%) | 14 (24%) | 10 (43%) | |
| Any minor alleles (a), n (%) | 32 (57%) | 15 (65%) | 0.54 |
| MAF | 0.39 | 0.52 | 0.28 |
| rs1478604 | BPD N = 51 | No BPD N = 15 | |
| TT, n (%) | 22 (43%) | 7 (47%) | 0.27 |
| Tc, n (%) | 20 (39%) | 3 (20%) | |
| cc, n (%) | 9 (18%) | 5 (33%) | |
| Any minor alleles (c), n (%) | 29 (57%) | 8 (53%) | 0.80 |
| MAF | 0.37 | 0.43 | 0.67 |
| Genotype Distribution (rs2664139 and rs1478604) | BPD | No BPD | Unadjusted p | Adjusted p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No minor alleles (%) | 44% | 34% | 0.006 | 0.02 |
| 1 or more minor alleles (%) | 44% | 0 | ||
| Homozygous minor alleles (%) | 12% | 67% | ||
| Genotype distribution (rs1478605 and rs1478604) | BPD | No BPD | ||
| No minor alleles (%) | 52% | 44% | 0.008 | 0.04 |
| 1 or more minor alleles (%) | 36% | 0 | ||
| Homozygous minor alleles (%) | 12% | 56% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krishnan, P.; Sampath, H.; Trinh, V.; Parton, L. Thrombospondin-1 Airway Expression and Thrombospondin-1 Gene Variants Are Associated with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Extremely Low-Birth-Weight Infants: A Pilot Study. Children 2025, 12, 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12040424
Krishnan P, Sampath H, Trinh V, Parton L. Thrombospondin-1 Airway Expression and Thrombospondin-1 Gene Variants Are Associated with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Extremely Low-Birth-Weight Infants: A Pilot Study. Children. 2025; 12(4):424. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12040424
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrishnan, Parvathy, Hannah Sampath, Van Trinh, and Lance Parton. 2025. "Thrombospondin-1 Airway Expression and Thrombospondin-1 Gene Variants Are Associated with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Extremely Low-Birth-Weight Infants: A Pilot Study" Children 12, no. 4: 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12040424
APA StyleKrishnan, P., Sampath, H., Trinh, V., & Parton, L. (2025). Thrombospondin-1 Airway Expression and Thrombospondin-1 Gene Variants Are Associated with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Extremely Low-Birth-Weight Infants: A Pilot Study. Children, 12(4), 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12040424





