Parent and Peer Emotion Responsivity Styles: An Extension of Gottman’s Emotion Socialization Parenting Typologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Emotion Socialization
1.2. The Role of Parents in Emotion Socialization
1.3. The Role of Peers in Emotion Socialization
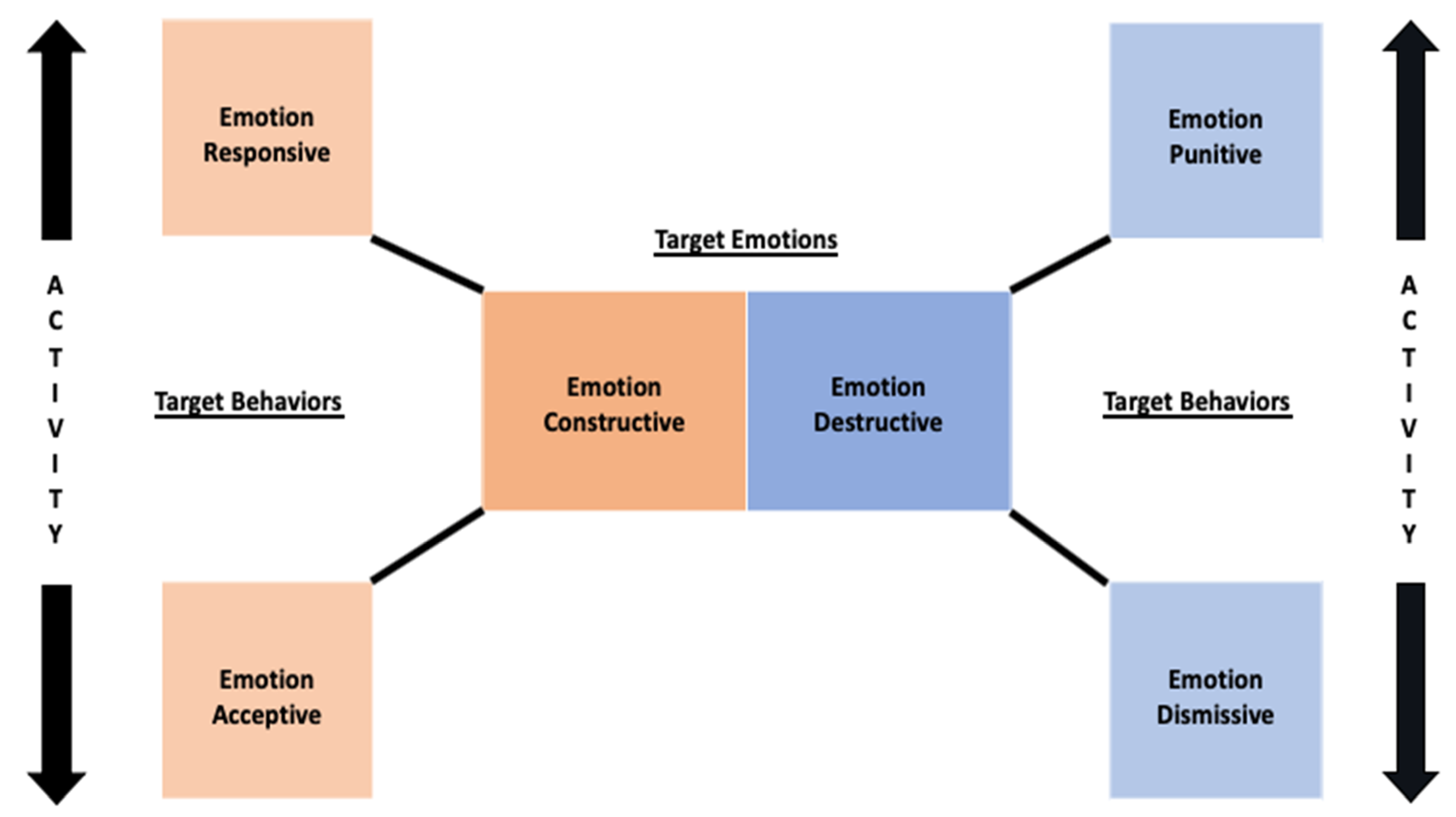
2. Key Concepts and Propositions
2.1. Positive Responsivity Styles
2.1.1. Emotion Constructive
2.1.2. Emotion Responsive
2.1.3. Emotion Acceptive
2.2. Negative Responsivity Styles
2.2.1. Emotion Destructive
2.2.2. Emotion Punitive
2.2.3. Emotion Dismissive
3. Guiding Theoretical Frameworks
4. Theoretical Assumptions
5. Research Methods for Implementation
6. Implications and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spinrad, T.L.; Morris, A.S.; Luthar, S.S. Introduction to the special issue: Socialization of emotion and self-regulation: Understanding processes and application. Dev. Psychol. 2020, 56, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiente, C.; Swanson, J.; DeLay, D.; Fraser, A.M.; Parker, J.H. Emotion-related socialization in the classroom: Considering the roles of teachers, peers, and the classroom context. Dev. Psychol. 2020, 56, 578–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottman, J.M.; Katz, L.F.; Hooven, C. Parental meta-emotion philosophy and the emotional life of families: Theoretical models and preliminary data. J. Fam. Psychol. 1996, 10, 243–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottman, J.M.; Katz, L.F.; Hooven, C. Meta-Emotion: How Families Communicate Emotionally; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottman, J. Raising an Emotionally Intelligent Child; Simon and Schuster: New York, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, A.S.; Cui, L.; Jespersen, J.E.; Criss, M.M.; Cosgrove, K.T. The Socialization of Emotion Regulation. In Cambridge Handbook of Parenting: Interdisciplinary Research and Application; Mendez, J., Morris, A.S., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg, N.; Cumberland, A.; Spinrad, T.L. Parental socialization of emotion. Psychol. Inq. 1998, 9, 241–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, A.S.; Silk, J.S.; Steinberg, L.; Myers, S.S.; Robinson, L.R. The role of the family context in the development of emotion regulation. Soc. Dev. 2007, 16, 361–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg-Nielsen, T.S.; Vikan, A.; Dahl, A.A. Parenting related to child and parental psychopathology: A descriptive review of the literature. Clin. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2002, 7, 529–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silk, J.S.; Shaw, D.S.; Prout, J.T.; O’Rourke, F.; Lane, T.J.; Kovacs, M. Socialization of emotion and offspring internalizing symptoms in mothers with childhood-onset depression. J. Appl. Dev. Psychol. 2011, 32, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suveg, C.; Shaffer, A.; Morelen, D.; Thomassin, K. Links between maternal and child psychopathology symptoms: Mediation through child emotion regulation and moderation through maternal behavior. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2011, 42, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiente, C.; Lemery-Chalfant, K.; Reiser, M. Pathways to problem behaviors: Chaotic homes, parent and child effortful control, and parenting. Soc. Dev. 2007, 16, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belsky, J. The determinants of parenting: A process model. Child Dev. 1984, 55, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumrind, D. Child care practices anteceding three patterns of preschool behavior. Genet. Psychol. Monogr. 1967, 75, 43–88. [Google Scholar]
- Sameroff, A. The transactional model. In The Transactional Model of Development: How Children and Contexts Shape Each Other; American Psychological Association (APA): Washington, DC, USA, 2009; pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Bronfenbrenner, U.; Morris, P.A. The Ecology of Developmental Processes; Handbook of Child Psychology: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 993–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Tudge, J.R.H.; Mokrova, I.; Hatfield, B.E.; Karnik, R.B. Uses and misuses of bronfenbrenner’s bioecological theory of human development. J. Fam. Theory Rev. 2009, 1, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindermann, T.A. Peer Group Influences on Students’ Academic Motivation. In Handbook of Social Influences in School Contexts: Social-Emotional, Motivation, and Cognitive Outcomes; Wentzel, K.R., Ramani, G.B., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 31–47. [Google Scholar]
- Hajal, N.J.; Paley, B. Parental emotion and emotion regulation: A critical target of study for research and intervention to promote child emotion socialization. Dev. Psychol. 2020, 56, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Gatzke-Kopp, L.M.; Fosco, G.M.; Bierman, K.L. Parental support of self-regulation among children at risk for externalizing symptoms: Developmental trajectories of physiological regulation and behavioral adjustment. Dev. Psychol. 2020, 56, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberg, N.; Fabes, R.A.; Murphy, B.C. Parents’ reactions to children’s negative emotions: Relations to children’s social competence and comforting behavior. Child Dev. 1996, 67, 2227–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saarni, C.; Campos, J.J.; Camras, L.A.; Witherington, D. Emotional Development: Action, Communication, and Understanding. In Handbook of Child Psychology; Eisenberg, N., Ed.; Wiley: New York, USA, 2007; Available online: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/97804701476 (accessed on 21 January 2021).
- Criss, M.M.; Morris, A.S.; Ponce-Garcia, E.; Cui, L.; Silk, J.S. Pathways to adaptive emotion regulation among adolescents from low-income families. Fam. Relations 2016, 65, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.F.; Zalewski, M.; Kiff, C.J.; Moran, L.; Cortes, R.; Lengua, L.J. An empirical test of the model of socialization of emotion: Maternal and child contributors to preschoolers’ emotion knowledge and adjustment. Dev. Psychol. 2020, 56, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, N.; Morris, A.S. Children’s Emotion-Related Regulation. In Advances in Child Development and Behavior; Kail, R.V., Ed.; Academic: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; Volume 30, pp. 189–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lougheed, J.P.; Brinberg, M.; Ram, N.; Hollenstein, T. Emotion socialization as a dynamic process across emotion contexts. Dev. Psychol. 2020, 56, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, W.A.; Madsen, S.D. Parenting During Middle Childhood. In Handbook of Parenting Vol. 1: Children and Parenting, 3rd ed.; Bornstein, M.H., Ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 81–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, J. Number of Instructional Days/Hours in the School Year. 2014. Available online: http://www.ecs.org/wp-content/uploads/Number-of-Instructional-Days-Hours-in-a-School-Year_Revised.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2019).
- Pekrun, R.; Linnenbrink-Garcia, L. International Handbook of Emotions in Education; Routledge/Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raver, C.C. Emotions matter: Making the case for the role of young children’s emotional development for early school readiness. Soc. Policy Rep. 2002, 16, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothbart, M.K.; Sheese, B.E.; Posner, M.I. Executive attention and effortful control: Linking temperament, brain networks, and genes. Child Dev. Perspect. 2007, 1, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, S.R.; Coie, J.D. Peer Rejection in Childhood; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- King, K.M.; McLaughlin, K.A.; Silk, J.; Monahan, K.C. Peer effects on self-regulation in adolescence depend on the nature and quality of the peer interaction. Dev. Psychopathol. 2018, 30, 1389–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabell, A.S.; Huppert, T.J.; Fishburn, F.A.; Li, Y.; Hlutkowsky, C.O.; Jones, H.M.; Wakschlag, L.S.; Perlman, S.B. Neural correlates of early deliberate emotion regulation: Young children’s responses to interpersonal scaffolding. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2019, 40, 100708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leventon, J.S.; Merrill, N.A.; Bauer, P.J. Neural response to emotion related to narrative socialization of emotion in school-age girls. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2019, 178, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, K.H.; Bukowski, W.; Parker, J. Peer Interactions, Relationships, and Groups. In Handbook of Child Psychology, 6th ed.; Eisenberg, N., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 571–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breaux, R.P.; McQuade, J.D.; Harvey, E.A.; Zakarian, R.J. Longitudinal associations of parental emotion socialization and children’s emotion regulation: The moderating role of ADHD symptomatology. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2017, 46, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimes-Dougan, B.; Pearson, T.E.; Jappe, L.; Mathieson, L.; Simard, M.R.; Hastings, P.; Zahn-Waxler, C. Adolescent emotion socialization: A longitudinal study of friends’ responses to negative emotions. Soc. Dev. 2013, 23, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeman, J.; Shipman, K. Social-contextual influences on expectancies for managing anger and sadness: The transition from middle childhood to adolescence. Dev. Psychol. 1997, 33, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, A.; Proudfit, G.H.; Bufferd, S.J.; Kujawa, A.J.; Laptook, R.S.; Torpey, D.C.; Klein, D.N. Self-reported and observed punitive parenting prospectively predicts increased error-related brain activity in six-year-old children. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2015, 43, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, E.; Simmons, J.G.; Bousman, C.A.; Vijayakumar, N.; Bray, K.O.; Dandash, O.; Richmond, S.; Schwartz, O.; Seal, M.; Sheeber, L.; et al. The influence of maternal parenting style on the neural correlates of emotion processing in children. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2020, 59, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buss, K.A.; Goldsmith, H.H. Fear and anger regulation in infancy: Effects on the temporal dynamics of affective expression. Child Dev. 1998, 69, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silk, J.S.; Shaw, D.S.; Skuban, E.M.; Oland, A.A.; Kovacs, M. Emotion regulation strategies in offspring of childhood-onset depressed mothers. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2006, 47, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, A.S.; Silk, J.S.; Morris, M.D.S.; Steinberg, L.; Aucoin, K.J.; Keyes, A.W. The influence of mother-child emotion regulation strategies on children’s expression of anger and sadness. Dev. Psychol. 2011, 47, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferster, C.B.; Skinner, B.F. Schedules of Reinforcement; Appleton-Century-Crofts: New York, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolls, E.T. A theory of emotion, and its application to understanding the neural basis of emotion. Cogn. Emot. 1990, 4, 161–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, B.F. Contingencies of Reinforcement: A Theoretical Analysis; BF Skinner Foundation: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Pierce, W.D.; Bandura, A. Social learning theory. Can. J. Sociol. Cah. Can. Sociol. 1977, 2, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsuaki, M.N.; Shaw, D.S.; Neiderhiser, J.M.; Ganiban, J.M.; Harold, G.T.; Reiss, D.; Leve, L.D. Raised by depressed parents: Is it an environmental risk? Clin. Child Fam. Psychol. Rev. 2014, 17, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Criss, M.M.; Ratliff, E.; Wu, Z.; Houltberg, B.J.; Silk, J.S.; Morris, A.S. Longitudinal links between maternal and peer emotion socialization and adolescent girls’ socioemotional adjustment. Dev. Psychol. 2020, 56, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandell, D.L.; Belsky, J.; Burchinal, M.; Steinberg, L.; Vandergrift, N. Nichd Early Child Care Research Network. Do effects of early child care extend to age 15 years? Results from the NICHD study of early child care and youth development. Child Dev. 2010, 81, 737–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, B.S.; Lincoln, C.R. Reducing hostile parenting through computer-mediated parenting education. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2017, 73, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halberstadt, A.G.; Lozada, F.T. Emotion development in infancy through the lens of culture. Emot. Rev. 2011, 3, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElwain, N.L.; Halberstadt, A.G.; Volling, B.L. Mother and father-reported reactions to children? Negative emotions: Relations to young children? Emotional understanding and friendship quality. Child Dev. 2007, 78, 1407–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bariola, E.; Hughes, E.K.; Gullone, E. Relationships between parent and child emotion regulation strategy use: A brief report. J. Child Fam. Stud. 2011, 21, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktar, E.; Bögels, S.M. Exposure to parents’ negative emotions as a developmental pathway to the family aggregation of depression and anxiety in the first year of life. Clin. Child Fam. Psychol. Rev. 2017, 20, 369–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryce, C.I.; Bradley, R.H.; Abry, T.; Swanson, J.; Thompson, M.S. Parents’ and teachers’ academic influences, behavioral engage-ent, and first- and fifth-grade achievement. Sch. Psychol. 2019, 34, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vostanis, P.; Graves, A.; Meltzer, H.; Goodman, R.; Jenkins, R.; Brugha, T. Relationship between parental psychopathology, parenting strategies and child mental health. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2006, 41, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putnam, R.D. Our Kids: The American Dream in Crisis; Simon and Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ginott, H.G. Between Parent and Child: New Solutions to Old Problems; Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M. Parental mental health: Disruptions to parenting and outcomes for children. Child Fam. Soc. Work. 2004, 9, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magai, C.; O’Neal, C.R. Emotions as a child: Child Version. Unpublished Scale; Long Island University: Brooklyn, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Fabes, R.A.; Poulin, R.E.; Eisenberg, N.; Madden-Derdich, D.A. The Coping with Children’s Negative Emotions Scale (CCNES): Psychometric properties and relations with children’s emotional competence. Marriage Fam. Rev. 2002, 34, 285–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, V.V.; Martini, T.S. Making the child understand: Socialization of emotion in urban India. J. Fam. Psychol. 2011, 25, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, P.M.; Teti, L.O.; Zahn–Waxler, C. Mutual emotion regulation and the stability of conduct problems between preschool and early school age. Dev. Psychopathol. 2003, 15, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dix, T.; Moed, A.; Anderson, E.R. Mothers’ depressive symptoms predict both increased and reduced negative reactivity. Psychol. Sci. 2014, 25, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dix, T.; Gershoff, E.T.; Meunier, L.N.; Miller, P.C. The affective structure of supportive parenting: Depressive symptoms, immediate emotions, and child-oriented motivation. Dev. Psychol. 2004, 40, 1212–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killeen, L.A.; Teti, D.M. Mothers’ frontal EEG asymmetry in response to infant emotion states and mother–infant emotional availability, emotional experience, and internalizing symptoms. Dev. Psychopathol. 2012, 24, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leerkes, E.M.; Su, J.; Calkins, S.D.; O’Brien, M.; Supple, A.J. Maternal physiological dysregulation while parenting poses risk for infant attachment disorganization and behavior problems. Dev. Psychopathol. 2016, 29, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Austin, J.; Elliott, R.; Ellison-Wright, I.; Wan, M.W.; Drake, R.; Downey, D.; Elmadih, A.; Mukherjee, I.; Heaney, L.; et al. Neural pathways of maternal responding: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Women Ment. Heal. 2019, 22, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, J.; Kim, P.; Spicer, J.; Ho, S.; Dayton, C.; Elmadih, A.; Abel, K. Approaching the biology of human parental attachment: Brain imaging, oxytocin and coordinated assessments of mothers and fathers. Brain Res. 2014, 1580, 78–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowlby, J.A. Secure Base: Parent-Child Attachment and Healthy Human Development; Basic Books: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, S.; Muir, R.; Kerr, J. Attachment Theory: Social, Developmental, and Clinical Perspectives; Routledge: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jespersen, J.E.; Hardy, N.R.; Morris, A.S. Parent and Peer Emotion Responsivity Styles: An Extension of Gottman’s Emotion Socialization Parenting Typologies. Children 2021, 8, 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8050319
Jespersen JE, Hardy NR, Morris AS. Parent and Peer Emotion Responsivity Styles: An Extension of Gottman’s Emotion Socialization Parenting Typologies. Children. 2021; 8(5):319. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8050319
Chicago/Turabian StyleJespersen, Jens E., Nathan R. Hardy, and Amanda Sheffield Morris. 2021. "Parent and Peer Emotion Responsivity Styles: An Extension of Gottman’s Emotion Socialization Parenting Typologies" Children 8, no. 5: 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8050319
APA StyleJespersen, J. E., Hardy, N. R., & Morris, A. S. (2021). Parent and Peer Emotion Responsivity Styles: An Extension of Gottman’s Emotion Socialization Parenting Typologies. Children, 8(5), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8050319





