Testicular Torsion in the Absence of Severe Pain: Considerations for the Pediatric Surgeon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Sudden, severe, persistent, unilateral scrotal pain;
- Vegetative symptoms such as nausea and emesis;
- Visible displacement of the testicle, either in rotation or height;
- Swelling and/or tenderness of the scrotal sac;
- Absence of cremasteric reflex.
- Testicular torsion;
- Torsion of appendix testis;
- Hydrocele;
- Varicocele;
- Scrotal hernia;
- Epididymitis/orchitis;
- Tumor;
- Trauma.
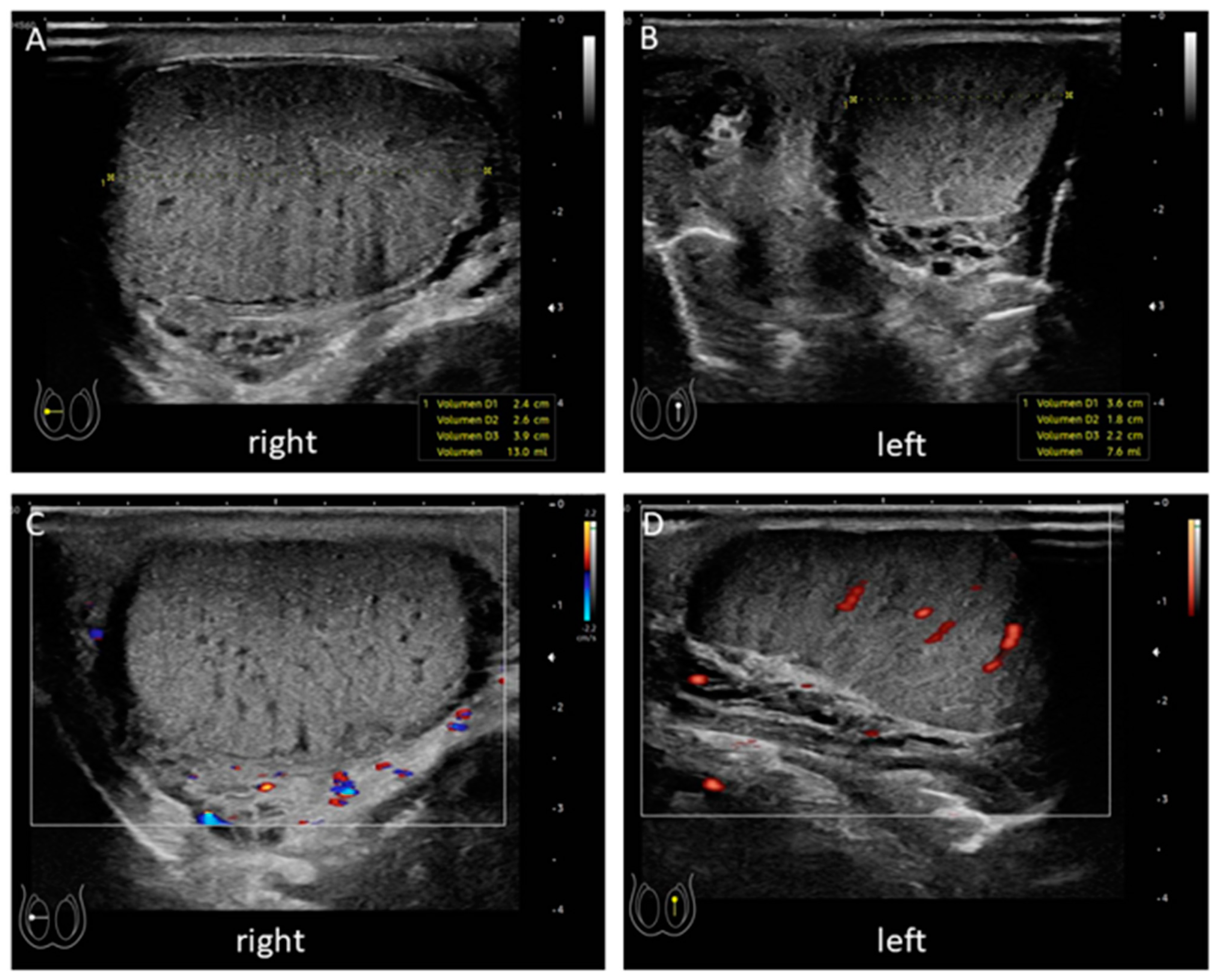
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bowlin, P.R.; Gatti, J.M.; Murphy, J.P. Pediatric Testicular Torsion. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 97, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, V.J.; Kieran, K.; Arlen, A.M. Testicular torsion: Diagnosis, evaluation, and management. Am. Fam. Physician 2013, 88, 835–840. [Google Scholar]
- Ringdahl, E.; Teague, L. Testicular torsion. Am. Fam Physician 2006, 74, 1739–1743. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, R.C.N. Torsion of the testis and allied conditions. Br. J. Surg. 2005, 63, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.C.; Lautz, T.B.; Meeks, J.J.; Maizels, M. Pediatric Testicular Torsion Epidemiology Using a National Database: Incidence, Risk of Orchiectomy and Possible Measures Toward Improving the Quality of Care. J. Urol. 2011, 186, 2009–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muttarak, M.; Lojanapiwat, B. The painful scrotum: An ultrasonographical approach to diagnosis. Singap. Med. J. 2005, 46, 352. [Google Scholar]
- Nandi, B.; Murphy, F.L. Neonatal testicular torsion: A systematic literature review. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2011, 27, 1037–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seng, Y.J.; Moissinac, K. Trauma induced testicular torsion: A reminder for the unwary. J. Accid Emerg. Med. 2000, 17, 381–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Bi, Y. Pediatric Trauma-Induced Testicular Torsion: A Surgical Emergency. Urol. Int. 2021, 105, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi, K.; Dumble, C.; Hutson, J.M.; Mushtaq, I.; Mirjalili, S.A. The bell-clapper deformity of the testis: The definitive pathological anatomy. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laher, A.; Ragavan, S.; Mehta, P.; Adam, A. Testicular Torsion in the Emergency Room: A Review of Detection and Management Strategies. Open Access Emerg. Med. 2020, 12, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.K.; Höllwarth, M.E. Acute Scrotum. In Pediatric Surgery, Diagnosis and Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 928–929. [Google Scholar]
- Mellick, L.B.; Sinex, J.E.; Gibson, R.W.; Mears, K. A Systematic Review of Testicle Survival Time After a Torsion Event. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2017, 35, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, R.P. Torsion of the testicle in childhood. A painless emergency requiring contralateral orchiopexy. JAMA 1961, 178, 702–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thinyu, S.; Muttarak, M. Role of ultrasonography in diagnosis of scrotal disorders: A review of 110 cases. Biomed. Imaging Interv. J. 2009, 5, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klinke, M.; Elrod, J.; Stiel, C.; Ghadban, T.; Wenskus, J.; Herrmann, J.; Junge, C.-M.; Reinshagen, K.; Boettcher, M. The BAL-Score Almost Perfectly Predicts Testicular Torsion in Children: A Two-Center Cohort Study. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 601892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheth, K.R.; Keays, M.; Grimsby, G.M.; Granberg, C.F.; Menon, V.S.; DaJusta, D.G.; Ostrov, L.; Hill, M.; Sanchez, E.; Kuppermann, D.; et al. Diagnosing Testicular Torsion before Urological Consultation and Imaging: Validation of the TWIST Score. J. Urol. 2016, 195, 1870–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridgway, A.; Hulme, P. BET 2: Twist score in cases of suspected paediatric testicular torsion. Emerg. Med. J. 2018, 35, 574.2–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunther, P.; Schenk, J.P. Testicular torsion: Diagnosis, differential diagnosis, and treatment in children. Radiologe 2006, 46, 590–595. [Google Scholar]
- Yasser, S.; Said, A. Acute torsion of the testis in children and young adults: Role of high resolution and Color Doppler ultrasonography. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2015, 46, 151–157. [Google Scholar]
- Jéquier, S.; Patriquin, H.; Filiatrault, D.; Garel, L.; Grignon, A.; Jéquier, J.C.; Petitjeanroget, T. Duplex Doppler sonographic examinations of the testis in prepubertal boys. J. Ultrasound Med. 1993, 12, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomann, J.S.; Moore, C. Bedside Ultrasound of a Painful Testicle: Before and After Manual Detorsion by an Emergency Physician. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2009, 16, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotto, G.T.; Chang, S.D.; Nigro, M.K. MRI in the diagnosis of incomplete testicular torsion. Br. J. Radiol. 2010, 83, e105–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caesar, R.E.; Kaplan, G.W. Incidence of the bell-clapper deformity in an autopsy series. Urology 1994, 44, 114–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, S.V.; Hernan, H.S.; Fredotovich, N. Painless inter epididymal testicular torsion of the spermatic cord. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2007, 33, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmitz, A.-K.; Vierhaus, M.; Lohaus, A. Pain tolerance in children and adolescents: Sex differences and psychosocial influences on pain threshold and endurance. Eur. J. Pain 2012, 17, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Tumi, H.; Johnson, M.I.; Dantas, P.B.F.; Maynard, M.J.; Tashani, O.A. Age-related changes in pain sensitivity in healthy humans: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Eur. J. Pain 2017, 21, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pancekauskaitė, G.; Jankauskaitė, L. Paediatric Pain Medicine: Pain Differences, Recognition and Coping Acute Procedural Pain in Paediatric Emergency Room. Medicina 2018, 54, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schon, K.R.; Parker, A.P.J.; Woods, C.G. Congenital Insensitivity to Pain Overview. In GeneReviews® [Internet]; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Mirzaa, G., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]


| Commonly Known | Stressed in Surgical Teaching | Present Is the Presented Case |
|---|---|---|
| Sudden, severe, persistent, unilateral scrotal pain | +++ | − |
| Vegetative symptoms such as nausea and emesis | ++ | − |
| Visible displacement of the testicle, either in rotation or height | + | + |
| Swelling of the scrotal sac | + | + |
| Tenderness of the scrotal sac | + | − |
| Absence of cremasteric reflex | ++ | − |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kapp, A.; Troxler, D.; Prüfer, F.; Holland-Cunz, S.; Frech, M.; Gros, S.J. Testicular Torsion in the Absence of Severe Pain: Considerations for the Pediatric Surgeon. Children 2021, 8, 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8060429
Kapp A, Troxler D, Prüfer F, Holland-Cunz S, Frech M, Gros SJ. Testicular Torsion in the Absence of Severe Pain: Considerations for the Pediatric Surgeon. Children. 2021; 8(6):429. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8060429
Chicago/Turabian StyleKapp, Alexander, David Troxler, Friederike Prüfer, Stefan Holland-Cunz, Martina Frech, and Stephanie J. Gros. 2021. "Testicular Torsion in the Absence of Severe Pain: Considerations for the Pediatric Surgeon" Children 8, no. 6: 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8060429
APA StyleKapp, A., Troxler, D., Prüfer, F., Holland-Cunz, S., Frech, M., & Gros, S. J. (2021). Testicular Torsion in the Absence of Severe Pain: Considerations for the Pediatric Surgeon. Children, 8(6), 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8060429







