Secondary Narcolepsy as Worsening Sign in a Pediatric Case of Optic Pathway Glioma
Abstract
1. Introduction
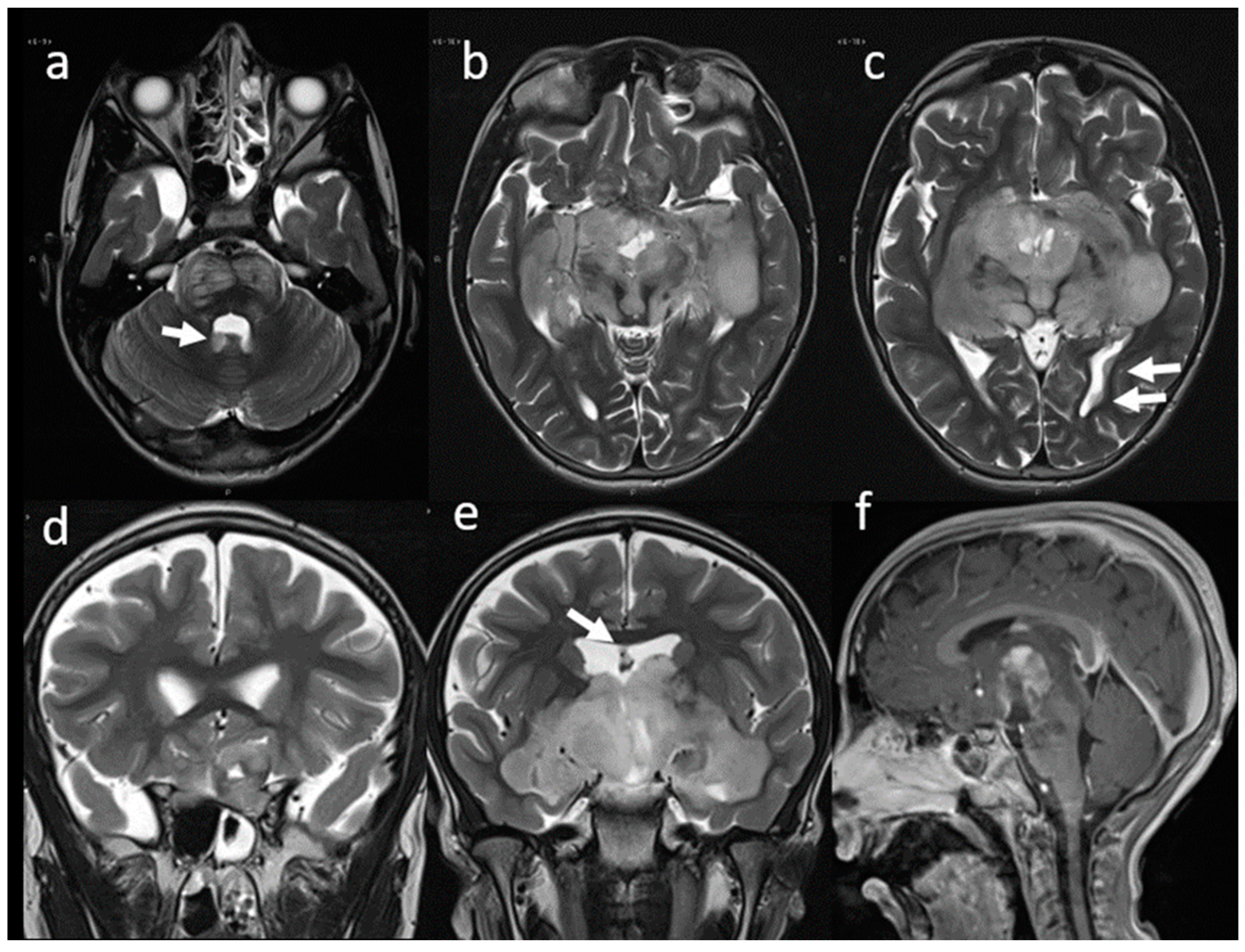
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaleyias, J.; Manley, P.; Kothare, S.V. Sleep Disorders in Children With Cancer. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2012, 19, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulrooney, D.A.; Ness, K.K.; Neglia, J.P.; Whitton, J.A.; Green, D.M.; Zeltzer, L.K.; Robison, L.L.; Mertens, A.C. Fatigue and Sleep Disturbance in Adult Survivors of Childhood Cancer: A Report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study (CCSS). Sleep 2008, 31, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, L.M.; Nixon, G.M.; Davey, M.J.; Downie, P.A.; Horne, R.S.C. Sleep and Fatigue in Pediatric Oncology: A Review of the Literature. Sleep Med. Rev. 2015, 24, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, K. Sleep-Related Disturbances among Adolescents with Cancer: A Systematic Review. Sleep Med. 2014, 15, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogavero, M.P.; Bruni, O.; DelRosso, L.M.; Ferri, R. Neurodevelopmental Consequences of Pediatric Cancer and Its Treatment: The Role of Sleep. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, T.S.; Shade, M.Y.; Breton, G.; Gilbert, M.R.; Mahajan, A.; Scheurer, M.E.; Vera, E.; Berger, A.M. Sleep-Wake Disturbance in Patients with Brain Tumors. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 19, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, M.; Lewinter, K.; Ward, S.; Perez, I. Sleep Disorders in Children with Central Nervous System Tumors. OBM Neurobiol. 2018, 2, 017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, R.; Pitts, J.; Patterson, M.C.; Lloyd, R.; Keating, G.; Kotagal, S. Secondary Narcolepsy in Children. J. Child Neurol. 2021, 36, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.B.; Merchant, T.E.; Sadighi, Z.S.; Bello, M.S.; Lu, Z.; Sykes, A.; Wise, M.S.; Crabtree, V.M.; Zabrowski, J.; Simmons, A.; et al. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Response to Treatment for Hypersomnia of Central Origin in Survivors of Childhood Brain Tumors. J. Neurooncol. 2018, 136, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, C.; Pizza, F.; Antelmi, E.; Folli, M.C.; Plazzi, G. Narcolepsy Treatment: Pharmacological and Behavioral Strategies in Adults and Children. Sleep Breath. 2020, 24, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrell, B.N.; Wise, M.; Schoumacher, R.A.; Pritchard, M.; West, N.; Ness, K.K.; Crabtree, V.M.; Merchant, T.E.; Morris, B. Excessive Daytime Sleepiness and Sleep-Disordered Breathing Disturbances in Survivors of Childhood Central Nervous System Tumors: CNS Tumor and Sleep. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2012, 58, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, L. Pediatric Narcolepsy: Clinical and Therapeutical Approaches. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 112, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamji, M.F.; Benoit, B.G. Syndromic and Sporadic Pediatric Optic Pathway Gliomas: Review of Clinical and Histopathological Differences and Treatment Implications. Neurosurg. Focus 2007, 23, E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalil, A.; Ramaswamy, V. Low Grade Gliomas in Children. J. Child Neurol. 2016, 31, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opocher, E.; Kremer, L.C.M.; Da Dalt, L.; van de Wetering, M.D.; Viscardi, E.; Caron, H.N.; Perilongo, G. Prognostic Factors for Progression of Childhood Optic Pathway Glioma: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Cancer 2006, 42, 1807–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farazdaghi, M.K.; Katowitz, W.R.; Avery, R.A. Current Treatment of Optic Nerve Gliomas. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2019, 30, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, I.; Helleringer, M.; Joud, A.; Chastagner, P.; Thomas, R.; Klein, O. Optic Pathway Tumor in Children: Toward a New Classification for Neurosurgical Use. Neurochirurgie 2020, 67, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binning, M.J.; Liu, J.K.; Kestle, J.R.W.; Brockmeyer, D.L.; Walker, M.L. Optic Pathway Gliomas: A Review. Neurosurg. Focus 2007, 23, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papini, C.; Dineen, R.A.; Walker, D.A.; Thomas, S.; Pitchford, N.J. Neuropsychological Outcomes of Children with Optic Pathway Glioma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, I.; Albanese, A. Endocrine Long-Term Follow-Up of Children with Neurofibromatosis Type 1 and Optic Pathway Glioma. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2017, 87, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadighi, Z.; Curtis, E.; Zabrowksi, J.; Billups, C.; Gajjar, A.; Khan, R.; Qaddoumi, I. Neurologic Impairments from Pediatric Low-Grade Glioma by Tumor Location and Timing of Diagnosis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, e27063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnekow, A.K.; Walker, D.A.; Kandels, D.; Picton, S.; Perilongo, G.; Grill, J.; Stokland, T.; Sandstrom, P.E.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; Pietsch, T.; et al. A European Randomised Controlled Trial of the Addition of Etoposide to Standard Vincristine and Carboplatin Induction as Part of an 18-Month Treatment Programme for Childhood (≤16 Years) Low Grade Glioma—A Final Report. Eur. J. Cancer Oxf. Engl. 2017, 81, 206–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocca, F.; Pizza, F.; Ricci, E.; Plazzi, G. Narcolepsy during Childhood: An Update. Neuropediatrics 2015, 46, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, A.M. Narcolepsy in Children and Adults: A Guide to Improved Recognition, Diagnosis and Management. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plazzi, G.; Clawges, H.M.; Owens, J.A. Clinical Characteristics and Burden of Illness in Pediatric Patients with Narcolepsy. Pediatr. Neurol. 2018, 85, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevsimalova, S. Narcolepsy in Childhood. Sleep Med. Rev. 2009, 13, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, S.; Kanbayashi, T. Symptomatic Narcolepsy, Cataplexy and Hypersomnia, and Their Implications in the Hypothalamic Hypocretin/Orexin System. Sleep Med. Rev. 2005, 9, 269–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornum, B.R. Narcolepsy Type I as an Autoimmune Disorder. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2021, 181, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassetti, C.L.A.; Adamantidis, A.; Burdakov, D.; Han, F.; Gay, S.; Kallweit, U.; Khatami, R.; Koning, F.; Kornum, B.R.; Lammers, G.J.; et al. Narcolepsy—Clinical Spectrum, Aetiopathophysiology, Diagnosis and Treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 519–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, A.G.; Muir, K.; Hukin, J.; Desautels, A.; Martel, V.; Perreault, S. Narcolepsy and Hypothalamic Region Tumors: Presentation and Evolution. Pediatr. Neurol. 2018, 84, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, I.A.; Mehler, M.F. Epigenetics of Sleep and Chronobiology. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2014, 14, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, L.; Main, K.M.; Sehested, A.; Mathiasen, R.; Feldt-Rasmussen, U.; Klose, M.; Kotagal, S.; Jennum, P.J. Brain Tumours Result in Sleep Disorders in Children and Adolescents. Sleep Med. 2021, 88, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arand, D.L.; Bonnet, M.H. The Multiple Sleep Latency Test. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 160, pp. 393–403. ISBN 978-0-444-64032-1. [Google Scholar]
- Mandrell, B.N.; LaRosa, K.; Hancock, D.; Caples, M.; Sykes, A.; Lu, Z.; Wise, M.S.; Khan, R.B.; Merchant, T.E.; McLaughlin-Crabtree, V. Predictors of Narcolepsy and Hypersomnia Due to Medical Disorder in Pediatric Craniopharyngioma. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 148, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, G.M.; Bendel, A.E.; Neglia, J.P.; Moertel, C.L.; Mahowald, M. Sleep in Children With Neoplasms of the Central Nervous System: Case Review of 14 Children. Pediatrics 2003, 112, e46–e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripley, B.; Overeem, S.; Fujiki, N.; Nevsimalova, S.; Uchino, M.; Yesavage, J.; Monte, D.D.; Dohi, K.; Melberg, A.; Lammers, G.J.; et al. CSF Hypocretin/Orexin Levels in Narcolepsy and Other Neurological Conditions. Neurology 2001, 57, 2253–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plazzi, G.; Ruoff, C.; Lecendreux, M.; Dauvilliers, Y.; Rosen, C.L.; Black, J.; Parvataneni, R.; Guinta, D.; Wang, Y.G.; Mignot, E. Treatment of Paediatric Narcolepsy with Sodium Oxybate: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomised-Withdrawal Multicentre Study and Open-Label Investigation. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2018, 2, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, G.; Brand, S.R. Sleep in Children with Cancer: Case Review of 70 Children Evaluated in a Comprehensive Pediatric Sleep Center. Support. Care Cancer 2011, 19, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, H.L. Increased Daytime Sleepiness in Patients with Childhood Craniopharyngioma and Hypothalamic Tumor Involvement: Review of the Literature and Perspectives. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 2010, 519607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manley, P.E.; McKendrick, K.; McGillicudy, M.; Chi, S.N.; Kieran, M.W.; Cohen, L.E.; Kothare, S.; Michael Scott, R.; Goumnerova, L.C.; Sun, P.; et al. Sleep Dysfunction in Long Term Survivors of Craniopharyngioma. J. Neurooncol. 2012, 108, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, G.M.; Shor, A.C.; Geller, T.J. Sleep in Children with Cancer. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2008, 20, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, L.; Klose, M.; Feldt-Rasmussen, U.; Jennum, P. Polysomnographic Findings in Craniopharyngioma Patients. Sleep Breath. 2017, 21, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, L.; Jennum, P.; Gammeltoft, S.; Poulsgaard, L.; Feldt-Rasmussen, U.; Klose, M. Sleep-Wake and Melatonin Pattern in Craniopharyngioma Patients. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 170, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.W.; Jung, H.W.; Lee, Y.A.; Shin, C.H.; Yang, S.W.; Cheon, J.-E.; Kim, I.-O.; Phi, J.H.; Kim, S.-K.; Wang, K.-C. Tumor Origin and Growth Pattern at Diagnosis and Surgical Hypothalamic Damage Predict Obesity in Pediatric Craniopharyngioma. J. Neurooncol. 2013, 113, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, H.L.; Handwerker, G.; Wollny, B.; Faldum, A.; Sörensen, N. Melatonin Secretion and Increased Daytime Sleepiness in Childhood Craniopharyngioma Patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 3993–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebhardt, U.; Handwerker, G.; Müller-Stöver, S.; Sörensen, N.; Müller, H. Secondary Narcolepsy May Be a Causative Factor of Increased Daytime Sleepiness in Obese Patients with Childhood Craniopharyngioma. Neuropediatrics 2006, 37, P84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachibana, N.; Taniike, M.; Okinaga, T.; Ripley, B.; Mignot, E.; Nishino, S. Hypersomnolence and Increased REM Sleep with Low Cerebrospinal Fluid Hypocretin Level in a Patient after Removal of Craniopharyngioma. Sleep Med. 2005, 6, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Blank, P.; Bandopadhayay, P.; Haas-Kogan, D.; Fouladi, M.; Fangusaro, J. Management of Pediatric Low-Grade Glioma. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2019, 31, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, R.J.; Pfister, S.; Bouffet, E.; Avery, R.; Bandopadhayay, P.; Bornhorst, M.; Bowers, D.C.; Ellison, D.; Fangusaro, J.; Foreman, N.; et al. Pediatric Low-Grade Gliomas: Implications of the Biologic Era. Neuro-Oncology 2016, 19, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryall, S.; Tabori, U.; Hawkins, C. Pediatric Low-Grade Glioma in the Era of Molecular Diagnostics. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazow, M.A.; Hoffman, L.; Schafer, A.; Osorio, D.S.; Boué, D.R.; Rush, S.; Wright, E.; Lane, A.; DeWire-Schottmiller, M.D.; Smolarek, T.; et al. Characterizing Temporal Genomic Heterogeneity in Pediatric Low-Grade Gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penman, C.L.; Faulkner, C.; Lowis, S.P.; Kurian, K.M. Current Understanding of BRAF Alterations in Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Therapeutic Targeting in Pediatric Low-Grade Gliomas. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olow, A.; Mueller, S.; Yang, X.; Hashizume, R.; Meyerowitz, J.; Weiss, W.; Resnick, A.C.; Waanders, A.J.; Stalpers, L.J.A.; Berger, M.S.; et al. BRAF Status in Personalizing Treatment Approaches for Pediatric Gliomas. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5312–5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.S.; Devesa, S.C.; Ince, W.; Borg, A.; Aquilina, K. A Systematic Review of Ongoing Clinical Trials in Optic Pathway Gliomas. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 1869–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, M.L.; Barnes, P.D.; Billett, A.L.; Leong, T.; Shrieve, D.C.; Scott, R.M.; Tarbell, N.J. Childhood Optic Chiasm Gliomas: Radiographic Response Following Radiotherapy and Long-Term Clinical Outcome. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 1997, 39, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouladi, M.; Wallace, D.; Langston, J.W.; Mulhern, R.; Rose, S.R.; Gajjar, A.; Sanford, R.A.; Merchant, T.E.; Jenkins, J.J.; Kun, L.E.; et al. Survival and Functional Outcome of Children with Hypothalamic/Chiasmatic Tumors. Cancer 2003, 97, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergthold, G.; Bandopadhayay, P.; Bi, W.L.; Ramkissoon, L.; Stiles, C.; Segal, R.A.; Beroukhim, R.; Ligon, K.L.; Grill, J.; Kieran, M.W. Pediatric Low-Grade Gliomas: How Modern Biology Reshapes the Clinical Field. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Rev. Cancer 2014, 1845, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Authors | N Patient | Median Age | Location of Tumor/Diagnosis | Sleep-Wake Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pickering et al. (2021) [32] | 61 | 12.4 years | 66% sleep-wake regulatory areas (brain stem, basal forebrain, hypothalamus, thalamus); 34% other areas | 90% of sleep disorders 8% narcolepsy |
| Mandrell et al. (2020) [11] | 110 | 10.3 years | Sellar/parasellar region | 27% narcolepsy 35% hypersomnia |
| Weil et al. (2018) [30] | 1 | 11 years | Sellar/parasellar region | narcolepsy |
| Rosen et al. (2011) [38] | 70 | 10 years | 68% CNS (hypothalamus/brainstem, posterior fossa, cortex) 32% no CNS (leukemia, upper airway, kidney) | 80% narcolepsy in CNS location |
| Rosen et al. (2003) [35] | 14 | 11 years | Sellar/parasellar region | 55% narcolepsy |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laus, B.; Caroleo, A.M.; Colafati, G.S.; Carai, A.; Moavero, R.; Ferilli, M.A.N.; Valeriani, M.; Mastronuzzi, A.; Cacchione, A. Secondary Narcolepsy as Worsening Sign in a Pediatric Case of Optic Pathway Glioma. Children 2022, 9, 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9101455
Laus B, Caroleo AM, Colafati GS, Carai A, Moavero R, Ferilli MAN, Valeriani M, Mastronuzzi A, Cacchione A. Secondary Narcolepsy as Worsening Sign in a Pediatric Case of Optic Pathway Glioma. Children. 2022; 9(10):1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9101455
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaus, Beatrice, Anna Maria Caroleo, Giovanna Stefania Colafati, Andrea Carai, Romina Moavero, Michela Ada Noris Ferilli, Massimiliano Valeriani, Angela Mastronuzzi, and Antonella Cacchione. 2022. "Secondary Narcolepsy as Worsening Sign in a Pediatric Case of Optic Pathway Glioma" Children 9, no. 10: 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9101455
APA StyleLaus, B., Caroleo, A. M., Colafati, G. S., Carai, A., Moavero, R., Ferilli, M. A. N., Valeriani, M., Mastronuzzi, A., & Cacchione, A. (2022). Secondary Narcolepsy as Worsening Sign in a Pediatric Case of Optic Pathway Glioma. Children, 9(10), 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9101455









