Number of Kawasaki Disease Admissions Is Associated with Number of Domestic COVID-19 and Severe Enterovirus Case Numbers in Taiwan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
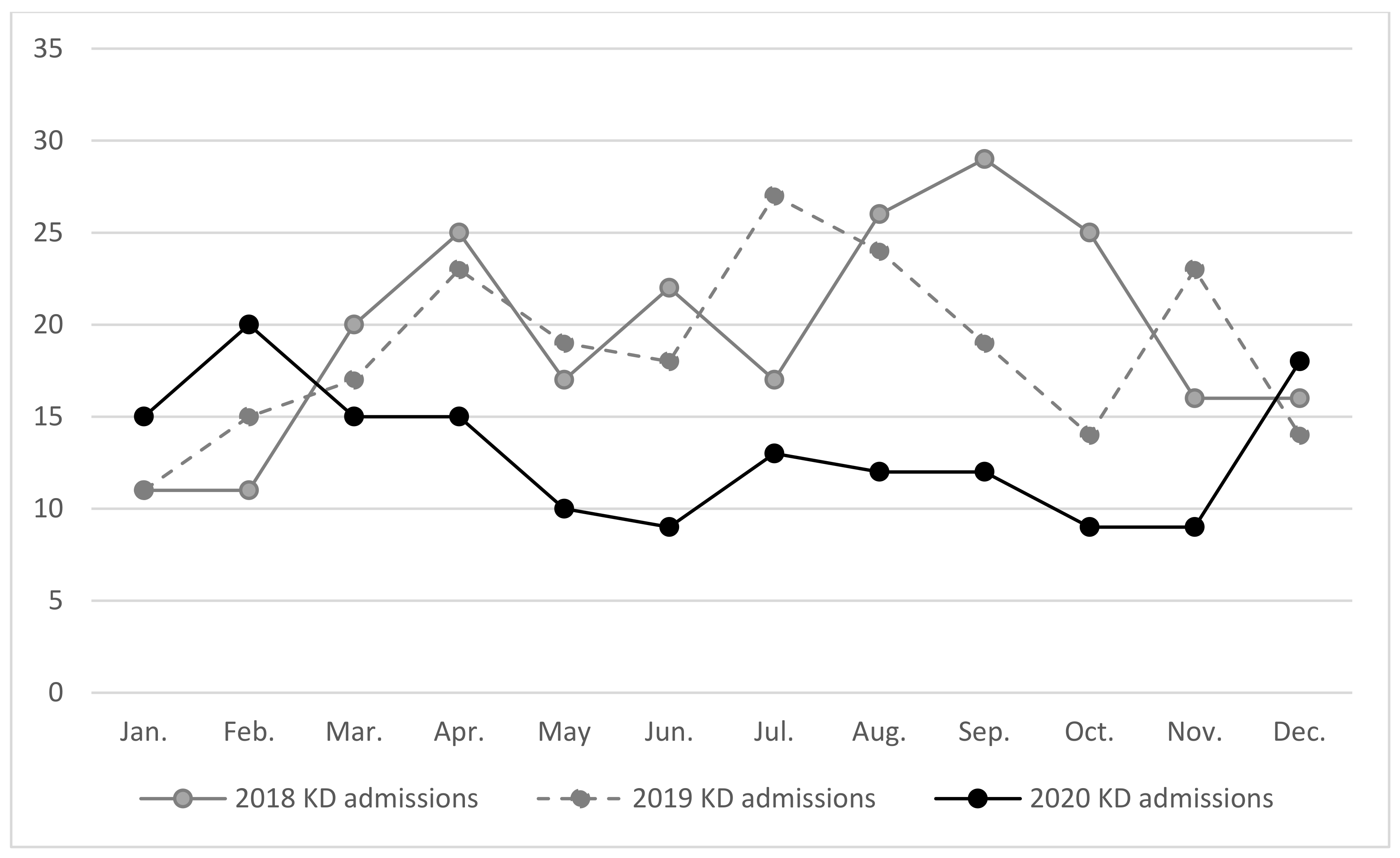
3.1. Number of KD Admissions Was Positively Correlated with Number of Domestic COVID-19 Cases and Reported Number of Severe Enterovirus Infections with Severe Complications
3.2. Number of Kawasaki Disease Admissions Were Associated with Number of Severe Enterovirus Cases in 2020
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burgner, D.; Harnden, A. Kawasaki disease: What is the epidemiology telling us about the etiology? Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 9, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.B.; Park, S.; Kwon, B.S.; Han, J.W.; Park, Y.W.; Hong, Y.M. Evaluation of the Temporal Association between Kawasaki Disease and Viral Infections in South Korea. Korean Circ. J. 2014, 44, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.Y.; Lu, C.Y.; Shao, P.L.; Lee, P.I.; Lin, M.T.; Fan, T.Y.; Cheng, A.L.; Lee, W.L.; Hu, J.J.; Yeh, S.J.; et al. Viral infections associated with Kawasaki disease. J. Formos Med. Assoc. 2014, 113, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taiwan Centers for Disease Control. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Available online: https://www.cdc.gov.tw/en/Disease/SubIndex/ (accessed on 27 November 2021).
- National Development Council. Population Projections for the R.O.C. (Taiwan). Available online: https://pop-proj.ndc.gov.tw/main_en/dataSearch.aspx?uid=78&pid=78 (accessed on 27 November 2021).
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/table (accessed on 27 November 2021).
- Wang, C.J.; Ng, C.Y.; Brook, R.H. Response to COVID-19 in Taiwan: Big Data Analytics, New Technology, and Proactive Testing. JAMA 2020, 323, 1341–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.F.; Huang, Y.H.; Cheng, C.Y.; Wu, K.H.; Tang, K.S.; Chiu, I.M. Public Health Interventions for the COVID-19 Pandemic Reduce Respiratory Tract Infection-Related Visits at Pediatric Emergency Departments in Taiwan. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 604089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Huang, L.M.; Chang, I.S.; Chang, L.Y.; Chiang, B.L.; Chen, P.J.; Wu, M.H.; Lue, H.C.; Lee, C.Y. Epidemiologic features of Kawasaki disease in Taiwan, 2003–2006. Pediatrics 2009, 123, e401–e405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.M.; Kim, Y.E.; Huh, K.; Hong, J.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, M.Y.; Jung, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Jung, J.; Ahn, J.G. Reduction in Kawasaki Disease After Nonpharmaceutical Interventions in the COVID-19 Era: A Nationwide Observational Study in Korea. Circulation 2021, 143, 2508–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Kuo, H.C. Public Health Interventions for COVID-19 Reduce Kawasaki Disease in Taiwan. Children 2021, 8, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.C.; Chan, Y.Y.; Kao Yang, Y.H.; Lin, S.J.; Hung, M.J.; Chien, R.N.; Lai, C.C.; Lai, E.C. The Chang Gung Research Database—A multi-institutional electronic medical records database for real-world epidemiological studies in Taiwan. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2019, 28, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwan Centers for Disease Control. National Notifiable Disease Surveillance Report—Monthly Report. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov.tw/En/Report/MonthList/14567 (accessed on 27 November 2021).
- Katsumata, N.; Harama, D.; Toda, T.; Sunaga, Y.; Yoshizawa, M.; Kono, Y.; Hasebe, Y.; Koizumi, K.; Hoshiai, M.; Saito, T.; et al. Prevention Measures for COVID-19 and Changes in Kawasaki Disease Incidence. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 31, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iio, K.; Matsubara, K.; Miyakoshi, C.; Ota, K.; Yamaoka, R.; Eguchi, J.; Matsumura, O.; Okutani, T.; Ueda, I.; Nishiyama, M. Incidence of Kawasaki disease before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: A retrospective cohort study in Japan. BMJ Paediatr. Open. 2021, 5, e001034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Furuno, K.; Yamamura, K.; Kishimoto, J.; Mizuno, Y.; Murata, K.; Onoyama, S.; Hatae, K.; Takemoto, M.; Ishizaki, Y.; et al. Assessment of Pediatric Admissions for Kawasaki Disease or Infectious Disease During the COVID-19 State of Emergency in Japan. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e214475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koskela, U.; Helve, O.; Sarvikivi, E.; Helminen, M.; Nieminen, T.; Peltola, V.; Renko, M.; Saxén, H.; Pasma, H.; Pokka, T.; et al. Multi-inflammatory syndrome and Kawasaki disease in children during the COVID-19 pandemic: A nationwide register-based study and time series analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2021, 110, 3063–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phamduy, T.T.; Smith, S.; Herbst, K.W.; Phamduy, P.T.; Brimacombe, M.; Hogan, A.H.; Salazar, J.C.; Sturm, J. Kawasaki Disease Hospitalizations in the United States 2016–2020: A Comparison of Before and During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Era. Pediatr. Infect Dis. J. 2021, 40, e407–e412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouldali, N.; Pouletty, M.; Mariani, P.; Beyler, C.; Blachier, A.; Bonacorsi, S.; Danis, K.; Chomton, M.; Maurice, L.; Le Bourgeois, F.; et al. Emergence of Kawasaki disease related to SARS-CoV-2 infection in an epicentre of the French COVID-19 epidemic: A time-series analysis. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdoni, L.; Mazza, A.; Gervasoni, A.; Martelli, L.; Ruggeri, M.; Ciuffreda, M.; Bonanomi, E.; D’Antiga, L. An outbreak of severe Kawasaki-like disease at the Italian epicentre of the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic: An observational cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1771–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzano, A.V.; Cassano, N.; Moltrasio, C.; Verdoni, L.; Genovese, G.; Vena, G.A. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Associated with COVID-19: A Review with an Emphasis on Mucocutaneous and Kawasaki Disease-Like Findings. Dermatology 2022, 238, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, A.; Gupta, S.; Sood, M.; Sharma, S.; Verma, S. A Systematic Review of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Associated With SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Pediatr. Infect Dis. J. 2020, 39, e340–e346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Lin, K.M.; Ho, S.C.; Yan, J.H.; Lo, M.H.; Kuo, H.C. Increased Incidence of Kawasaki Disease in Taiwan in Recent Years: A 15 Years Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.H.; Huang, Y.C.; Huang, C.G.; Tsao, K.C.; Li, W.C.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Chiu, C.H.; Lin, T.Y. Clinical and epidemiologic features of Coxsackievirus A6 infection in children in northern Taiwan between 2004 and 2009. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2011, 44, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, K.P.; Wei, J.C.; Hung, Y.M.; Huang, S.H.; Chien, K.J.; Lin, C.C.; Huang, S.M.; Lin, C.L.; Cheng, M.F. Enterovirus Infection and Subsequent Risk of Kawasaki Disease: A Population-based Cohort Study. Pediatr. Infect Dis. J. 2018, 37, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Pre-COVID-19 Period (2018–2019) | Post-COVID-19 Period (2020) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual number of KD admissions | 2018: 235 2019: 224 | 2020: 157 | |
| Average KD admissions (per month) # | |||
| Jan.–Mar. | 14.17 ± 1.56 | 16.67 ± 1.67 | 0.347 |
| Apr.–Jun. | 20.67 ± 1.28 | 11.33 ± 1.86 | 0.020 * |
| Jul.–Sep. | 23.67 ± 1.93 | 12.33 ± 0.33 | 0.020 * |
| Oct.–Dec. | 18.00 ± 1.95 | 12.00 ± 3.00 | 0.019 * |
| Annual number of severe influenza cases | 2018: 52 2019: 113 | 2020: 20 | |
| Average number of severe influenza cases (per month) # | |||
| Jan.–Mar. | 10.00 ± 1.67 | 6.67 ± 5.24 | 0.439 |
| Apr.–Jun. | 4.33 ± 1.59 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.018 * |
| Jul.–Sep. | 6.50 ± 1.67 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.018 * |
| Oct.–Dec. | 6.67 ± 1.69 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | |
| Annual number of severe enterovirus cases | 2018: 38 2019: 61 | 2020: 5 | |
| Average number of severe enterovirus cases (per month) # | |||
| Jan.–Mar. | 1.83 ± 0.48 | 1.67 ± 0.33 | 0.888 |
| Apr.–Jun. | 3.83 ± 1.30 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.018 * |
| Jul.–Sep. | 6.00 ± 1.34 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.017 * |
| Oct.–Dec. | 4.83 ± 1.83 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.018 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, M.M.-H.; Yang, K.D.; Liu, S.-F.; Kuo, H.-C. Number of Kawasaki Disease Admissions Is Associated with Number of Domestic COVID-19 and Severe Enterovirus Case Numbers in Taiwan. Children 2022, 9, 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9020149
Guo MM-H, Yang KD, Liu S-F, Kuo H-C. Number of Kawasaki Disease Admissions Is Associated with Number of Domestic COVID-19 and Severe Enterovirus Case Numbers in Taiwan. Children. 2022; 9(2):149. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9020149
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Mindy Ming-Huey, Kuender D. Yang, Shih-Feng Liu, and Ho-Chang Kuo. 2022. "Number of Kawasaki Disease Admissions Is Associated with Number of Domestic COVID-19 and Severe Enterovirus Case Numbers in Taiwan" Children 9, no. 2: 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9020149
APA StyleGuo, M. M.-H., Yang, K. D., Liu, S.-F., & Kuo, H.-C. (2022). Number of Kawasaki Disease Admissions Is Associated with Number of Domestic COVID-19 and Severe Enterovirus Case Numbers in Taiwan. Children, 9(2), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9020149







