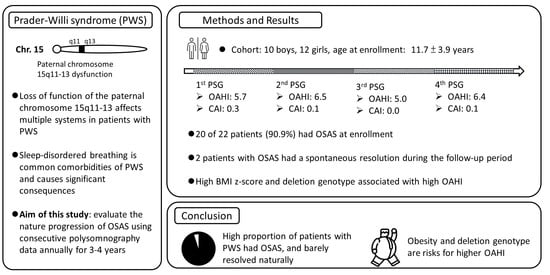
Progression of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Pediatric Patients with Prader–Willi Syndrome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Overnight PSG and Sleep Variables
2.3. Normalized Body Mass Index (BMI) Z-Score
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cassidy, S.B.; Schwartz, S.; Miller, J.L.; Driscoll, D.J. Prader–Willi syndrome. Genet. Med. 2012, 14, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nixon, G.M.; Brouillette, R.T. Sleep and breathing in Prader–Willi syndrome. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2002, 34, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donoghue, F.J.; Camfferman, D.; Kennedy, J.D.; Martin, A.J.; Couper, T.; Lack, L.D.; Lushington, K.; McEvoy, R.D. Sleep-disordered breathing in Prader–Willi syndrome and its association with neurobehavioral abnormalities. J. Pediatr. 2005, 147, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, T.; Obata, K.; Tonoki, H.; Temma, S.; Murakami, N.; Katada, Y.; Yoshino, A.; Sakazume, S.; Takahashi, E.; Sakuta, R.; et al. Cause of sudden, unexpected death of Prader–Willi syndrome patients with or without growth hormone treatment. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2005, 136, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urquhart, D.S.; Gulliver, T.; Williams, G.; Harris, M.A.; Nyunt, O.; Suresh, S. Central sleep-disordered breathing and the effects of oxygen therapy in infants with Prader–Willi syndrome. Arch. Dis. Child. 2013, 98, 592–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayat, A.; Narang, I.; Bin-Hasan, S.; Amin, R.; Al-Saleh, S. Longitudinal evaluation of sleep disordered breathing in infants with Prader–Willi syndrome. Arch. Dis. Child. 2017, 102, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedky, K.; Bennett, D.S.; Pumariega, A. Prader Willi syndrome and obstructive sleep apnea: Co-occurrence in the pediatric population. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2014, 10, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nixon, G.M.; Rodda, C.P.; Davey, M.J. Longitudinal association between growth hormone therapy and obstructive sleep apnea in a child with Prader–Willi syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Saleh, S.; Al-Naimi, A.; Hamilton, J.; Zweerink, A.; Iaboni, A.; Narang, I. Longitudinal evaluation of sleep-disordered breathing in children with Prader–Willi syndrome during 2 years of growth hormone therapy. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, 263–268.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.S.; Guilleminault, C.; Li, H.Y.; Yang, C.M.; Wu, Y.Y.; Chen, N.H. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder with obstructive sleep apnea: A treatment outcome study. Sleep Med. 2007, 8, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthopoulos, M.S.; Gallagher, P.R.; Berkowitz, R.I.; Radcliffe, J.; Bradford, R.; Marcus, C.L. Neurobehavioral functioning in adolescents with and without obesity and obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 2015, 38, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marcus, C.L.; Brooks, L.J.; Ward, S.D.; Draper, K.A.; Gozal, D.; Halbower, A.C.; Jones, J.; Lehmann, C.; Schechter, M.S.; Sheldon, S.; et al. Diagnosis and management of childhood obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Pediatrics 2012, 130, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Camacho, M.; Certal, V.; Capasso, R. Comprehensive review of surgeries for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 79, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeMarcantonio, M.A.; Darrow, D.H.; Gyuricsko, E.; Derkay, C.S. Obstructive sleep disorders in Prader–Willi syndrome: The role of surgery and growth hormone. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 74, 1270–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, S.L.; Splaingard, M.; Repaske, D.R.; Zipf, W.; Atkins, J.; Jatana, K. OUtcomes of adenotonsillectomy in patients with Prader–Willi syndrome. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 138, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, K.K.; Tomur, S.; Beckerman, R.; Cassidy, K.; Lypka, M. Orthognathic Correction in Prader-Willi Syndrome: Occlusion and Sleep Restored. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2019, 56, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushida, C.A.; Nichols, D.A.; Holmes, T.H.; Quan, S.F.; Walsh, J.K.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Simon, R.D.; Guilleminault, C.; White, D.P.; Goodwin, J.L.; et al. Effects of continuous positive airway pressure on neurocognitive function in obstructive sleep apnea patients: The Apnea Positive Pressure Long-term Efficacy Study (APPLES). Sleep 2012, 35, 1593–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulander, M.; Johansson, M.S.; Ewaldh, A.E.; Svanborg, E.; Broström, A. Side effects to continuous positive airway pressure treatment for obstructive sleep apnoea: Changes over time and association to adherence. Sleep Breath. 2014, 18, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, C.L.; Moore, R.H.; Rosen, C.L.; Giordani, B.; Garetz, S.L.; Taylor, H.G.; Mitchell, R.B.; Amin, R.; Katz, E.S.; Arens, R.; et al. A randomized trial of adenotonsillectomy for childhood sleep apnea. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2366–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.Y.; Lin, S.P.; Yen, J.L.; Lee, Y.J.; Huang, C.Y.; Hung, H.Y.; Hsu, C.; Kao, H.; Chang, J.; Chiu, N.; et al. Prader–Willi syndrome in Taiwan. Pediatr. Int. 2007, 49, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lind van Wijngaarden, R.F.A.; Siemensma, E.P.C.; Festen, D.A.M.; Otten, B.J.; van Mil, E.G.A.H.; Rotteveel, J.; Odink, R.J.H.; Bindels-de Heus, G.C.B.; Van Leeuwen, M.; Haring, D.A.J.P.; et al. Efficacy and safety of long-term continuous growth hormone treatment in children with Prader–Willi syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 4205–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iber, C.; American Academy of Sleep Medicine. The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events: Rules, Terminology and Technical Specifications; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Westchester, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon, S.H.; Kryger, M.H.; Ferber, R.; Gozal, D. Principles and Practice of Pediatric Sleep Medicine E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Chang, M.-H. New growth charts for Taiwanese children and adolescents based on World Health Organization standards and health-related physical fitness. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2010, 51, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peppard, P.E.; Young, T.; Palta, M.; Dempsey, J.; Skatrud, J. Longitudinal study of moderate weight change and sleep-disordered breathing. JAMA 2000, 284, 3015–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.S.; Tsai, W.H.; Tsai, L.P.; Wong, S.B. Clinical characteristics and epilepsy in genomic imprinting disorders: Angelman syndrome and Prader–Willi syndrome. Tzu Chi Med. J. 2020, 32, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, S.; Barthelemy, M.; Muscatelli, F.; Hilaire, G. Necdin gene, Respiratory disturbances and Prader–Willi syndrome. In Advances in Experimental Medicine & Biology; Poulin, M., Wilson, R.A., Eds.; Integration in Respiratory Control; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 605, pp. 159–164. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.N.; Hung, W.C.; Chen, C.T.; Tsai, L.P.; Lai, W.S.; Min, M.Y.; Wong, S.B. Firing activity of locus coeruleus noradrenergic neurons decreases in necdin-deficient mice, an animal model of Prader–Willi syndrome. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2020, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proffitt, J.; Osann, K.; McManus, B.; Kimonis, V.E.; Heinemann, J.; Butler, M.G.; Stevenson, D.A.; Gold, J.-A. Contributing factors of mortality in Prader–Willi syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2019, 179, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Hsu, W.C.; Ko, J.Y.; Yeh, T.H.; Lin, M.T.; Kang, K.T. Adenotonsillectomy for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in children with Prader–Willi syndrome: A meta-analysis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 162, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, A.C.; Dai, X.; Walsh, J.M.; Sterni, L.M.; Prichett, L.; Boss, E.F.; Seal, S.M.; Ryan, M.A. Outcomes of adenotonsillectomy for obstructive sleep apnea in Prader–Willi syndrome: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudewyns, A.; Verhulst, S.; Maris, M.; Saldien, V.; Van de Heyning, P. Drug-induced sedation endoscopy in pediatric obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Med. 2014, 15, 1526–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, M.C.; Hsu, Y.B.; Lan, M.Y.; Chiu, T.J.; Huang, T.T.; Wong, S.B.; Chen, Y.C.; Tsai, L.P. Drug-induced sleep endoscopy in children with Prader–Willi syndrome. Sleep Breath. 2016, 20, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Álvarez, M.L.; Cordero-Guevara, J.A.; Terán-Santos, J.; Gonzalez-Martinez, M.; Jurado-Luque, M.J.; Corral-Peñafiel, J.; Duran-Cantolla, J.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Gozal, D. Obstructive sleep apnea in obese community-dwelling children: The NANOS study. Sleep 2014, 37, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, M.S.; Zhang, H.L.; Cai, X.H.; Lin, Y.; Liu, P.N.; Zhang, Y.B.; Hu, W.Z.; Li, C.C.; Xiao, Y.F. Obesity in children with different risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea: A community-based study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2016, 175, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Álvarez, M.L.; Terán-Santos, J.; Navazo-Egüia, A.I.; Martinez, M.G.; Jurado-Luque, M.J.; Corral-Peñafiel, J.; Duran-Cantolla, J.; Cordero-Guevara, J.A.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Gozal, D. Treatment outcomes of obstructive sleep apnoea in obese community-dwelling children: The NANOS study. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verhulst, S.L.; Franckx, H.; Van Gaal, L.; De Backer, W.; Desager, K. The effect of weight loss on sleep-disordered breathing in obese teenagers. Obesity 2009, 17, 1178–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, J.V.; Whittington, J.E.; Holland, A.J.; McAllister, C.J.; Goldstone, A.P. The transition between the phenotypes of Prader–Willi syndrome during infancy and early childhood. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2010, 52, e88–e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, N.E.; Kuppens, R.J.; Siemensma, E.P.C.; Tummers-de Lind van Wijngaarden, R.F.A.; Festen, D.A.M.; Bindels-de Heus, G.C.B.; Bocca, G.; Haring, D.A.J.P.; Hoorweg-Nijman, J.J.G.; Houdijk, E.C.A.M.; et al. Eight years of growth hormone treatment in children with Prader–Willi syndrome: Maintaining the positive effects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 4013–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cassidy, S.B.; Driscoll, D.J. Prader–Willi syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 17, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkia, M.; Michaud, S.; Berthier, M.T.; Giguère, Y.; Stewart, L.; Deladoëy, J.; Deal, C.; Van Vliet, G.; Chanoine, J.P. Thyroid function from birth to adolescence in Prader-Willi syndrome. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diene, G.; Mimoun, E.; Feigerlova, E.; Caula, S.; Molinas, C.; Grandjean, H.; Tauber, M. Endocrine disorders in children with Prader-Willi syndrome--data from 142 children of the French database. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2010, 74, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrias, A.; Grugni, G.; Crinò, A.; Di Candia, S.; Chiabotto, P.; Cogliardi, A.; Chiumello, G.; De Medici, C.; Spera, S.; Gargantini, L.; et al. Assessment of central adrenal insufficiency in children and adolescents with Prader-Willi syndrome. Clin. Endocrinol. 2012, 76, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lind van Wijngaarden, R.F.; Otten, B.J.; Festen, D.A.; Joosten, K.F.; de Jong, F.H.; Sweep, F.C.; Hokken-Koelega, A. High prevalence of central adrenal insufficiency in patients with Prader-Willi syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillessen-Kaesbach, G.; Robinson, W.; Lohmann, D.; Kaya-Westerloh, S.; Passarge, E.; Horsthemke, B. Genotype-phenotype correlation in a series of 167 deletion and non-deletion patients with Prader–Willi syndrome. Hum. Genet. 1995, 96, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, L.C.S.; Manning, K.E.; Whittington, J.E.; Holland, A.J. Mechanistic insights into the genetics of affective psychosis from Prader–Willi syndrome. Lancet Psychiatry 2018, 5, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaditis, A.G.; Alonso Alvarez, M.L.; Boudewyns, A.; Alexopoulos, E.I.; Ersu, R.; Joosten, K.; Larramona, H.; Miano, S.; Narang, I.; Trang, H.; et al. Obstructive sleep disordered breathing in 2- to 18-year-old children: Diagnosis and management. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chervin, R.D.; Ellenberg, S.S.; Hou, X.; Marcus, C.L.; Garetz, S.L.; Katz, E.S.; Hodges, E.K.; Mitchell, R.B.; Jones, D.T.; Arens, R.; et al. PRognosis for spontaneous resolution of osa in children. Chest 2015, 148, 1204–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| 1st PSG | 2nd PSG | 3rd PSG | 4th PSG | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 22 | 22 | 22 | 18 |
| Age (years) | 11.7 ± 3.9 | 13.1 ± 4.1 | 14.4 ± 4.3 | 15.8 ± 4.5 |
| Female (%) | 12 (54.5) | 12 (54.5) | 12 (54.5) | 10 (55.6) |
| Del/non-Del | 17/5 | 17/5 | 17/5 | 15/3 |
| BMI | 22.8 ± 4.5 | 23.1 ± 4.1 | 23.8 ± 4.5 | 25.9 ± 6.4 |
| BMI z-score | 1.7 ± 1.3 | 1.6 ± 1.3 | 1.7 ± 1.5 | 2.3 ± 2.2 |
| GH Tx (%) | 18 (81.8) | 18 (81.8) | 18 (81.8) | 16 (88.9) |
| Total sleep time (m) | 414.6 ± 69.4 | 421.4 ± 52.2 | 393.0 ± 100.2 | 388.7 ± 73.6 |
| Sleep efficiency (%) | 87.4 ± 6.5 | 83.9 ± 8.3 | 79.8 ± 18.0 | 81.0 ± 12.2 |
| Awake (%) | 10.2 ± 6.1 | 12.5 ± 8.3 | 18.9 ± 16.7 | 17.6 ± 11.0 |
| Stage 1 (%) | 8.3 ± 4.2 | 7.6 ± 4.0 | 8.0 ± 5.5 | 9.5 ± 6.1 |
| Stage 2 (%) | 47.0 ± 11.8 | 45.1 ± 12.5 | 45.4 ± 16.5 | 46.6 ± 9.4 |
| SWS (%) | 23.2 ± 11.7 | 26.4 ± 11.6 | 24.6 ± 12.0 | 22.3 ± 10.3 |
| REM (%) | 20.4 ± 7.1 | 20.8 ± 5.9 | 21.9 ± 6.5 | 21.5 ± 4.8 |
| CAI (/h) | 0.3 ± 0.5 | 0.1 ± 0.2 | 0.0 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 |
| OAHI (/h) | 5.7 ± 6.4 | 6.5 ± 6.8 | 5.0 ± 3.5 | 6.4 ± 5.7 |
| Oxygen concentration nadir (%) | 83.1 ± 6.8 | 83.3 ± 6.5 | 82.8 ± 5.2 | 81.4 ± 9.8 |
| Arousal index (/h) | 12.5 ± 9.7 | 10.7 ± 7.6 | 8.0 ± 4.3 | 8.8 ± 6.1 |
| No OSAS (%) | 2 (9.1) | 1 (4.5) | 2 (9.1) | 1 (5.6) |
| Mild OSAS (%) | 8 (36.4) | 10 (45.5) | 10 (45.5) | 7 (38.9) |
| Moderate OSAS (%) | 11 (50) | 9 (40.9) | 8 (36.4) | 7 (38.9) |
| Severe OSAS (%) | 1 (4.5) | 2 (9.1) | 2 (9.1) | 3 (16.7) |
| Parameter | Estimate | Wald χ2 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −7.602 | 0.829 | 0.363 |
| Sex a | 2.294 | 0.282 | 0.595 |
| Age | 0.116 | 0.062 | 0.803 |
| BMI z-score | 4.883 | 16.852 | <0.001 ** |
| PSG Time | 0.259 | 0.101 | 0.751 |
| Genotype b | −3.728 | 4.086 | 0.043 * |
| GH Tx c | 4.886 | 1.511 | 0.219 |
| BMI z-score × PSG Time | −0.476 | 3.585 | 0.058 |
| Genotype × PSG Time | 0.478 | 0.158 | 0.691 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wong, S.-B.; Yang, M.-C.; Tzeng, I.-S.; Tsai, W.-H.; Lan, C.-C.; Tsai, L.-P. Progression of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Pediatric Patients with Prader–Willi Syndrome. Children 2022, 9, 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9060912
Wong S-B, Yang M-C, Tzeng I-S, Tsai W-H, Lan C-C, Tsai L-P. Progression of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Pediatric Patients with Prader–Willi Syndrome. Children. 2022; 9(6):912. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9060912
Chicago/Turabian StyleWong, Shi-Bing, Mei-Chen Yang, I-Shiang Tzeng, Wen-Hsin Tsai, Chou-Chin Lan, and Li-Ping Tsai. 2022. "Progression of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Pediatric Patients with Prader–Willi Syndrome" Children 9, no. 6: 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9060912
APA StyleWong, S.-B., Yang, M.-C., Tzeng, I.-S., Tsai, W.-H., Lan, C.-C., & Tsai, L.-P. (2022). Progression of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Pediatric Patients with Prader–Willi Syndrome. Children, 9(6), 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9060912