Cerebral White Matter Connectivity in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
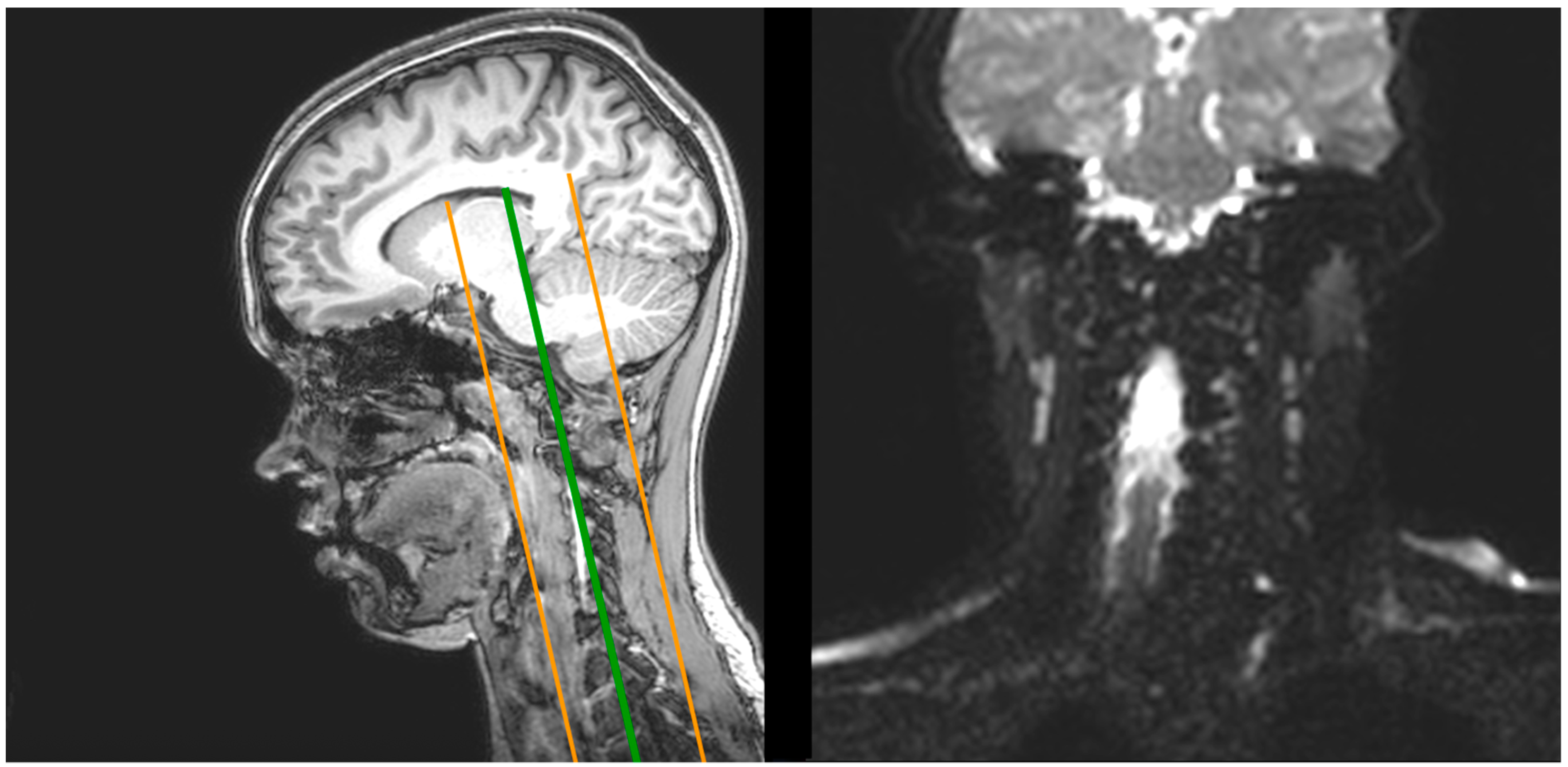
2.1. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
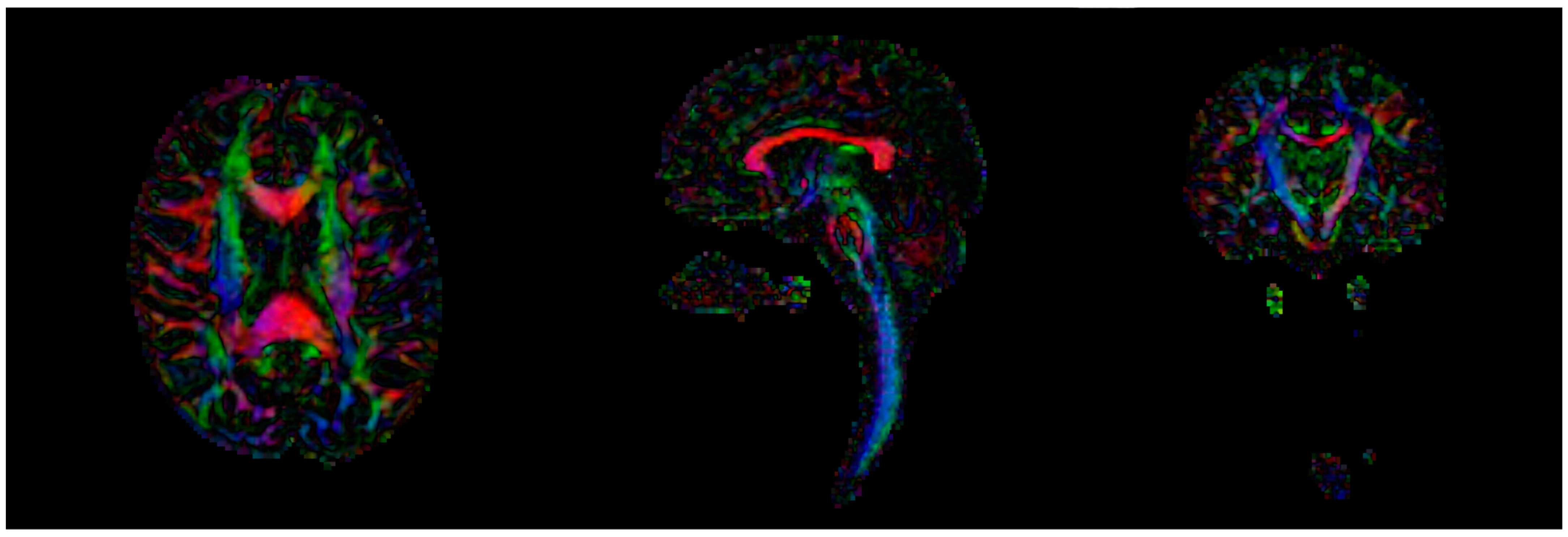
2.1.1. Image Processing
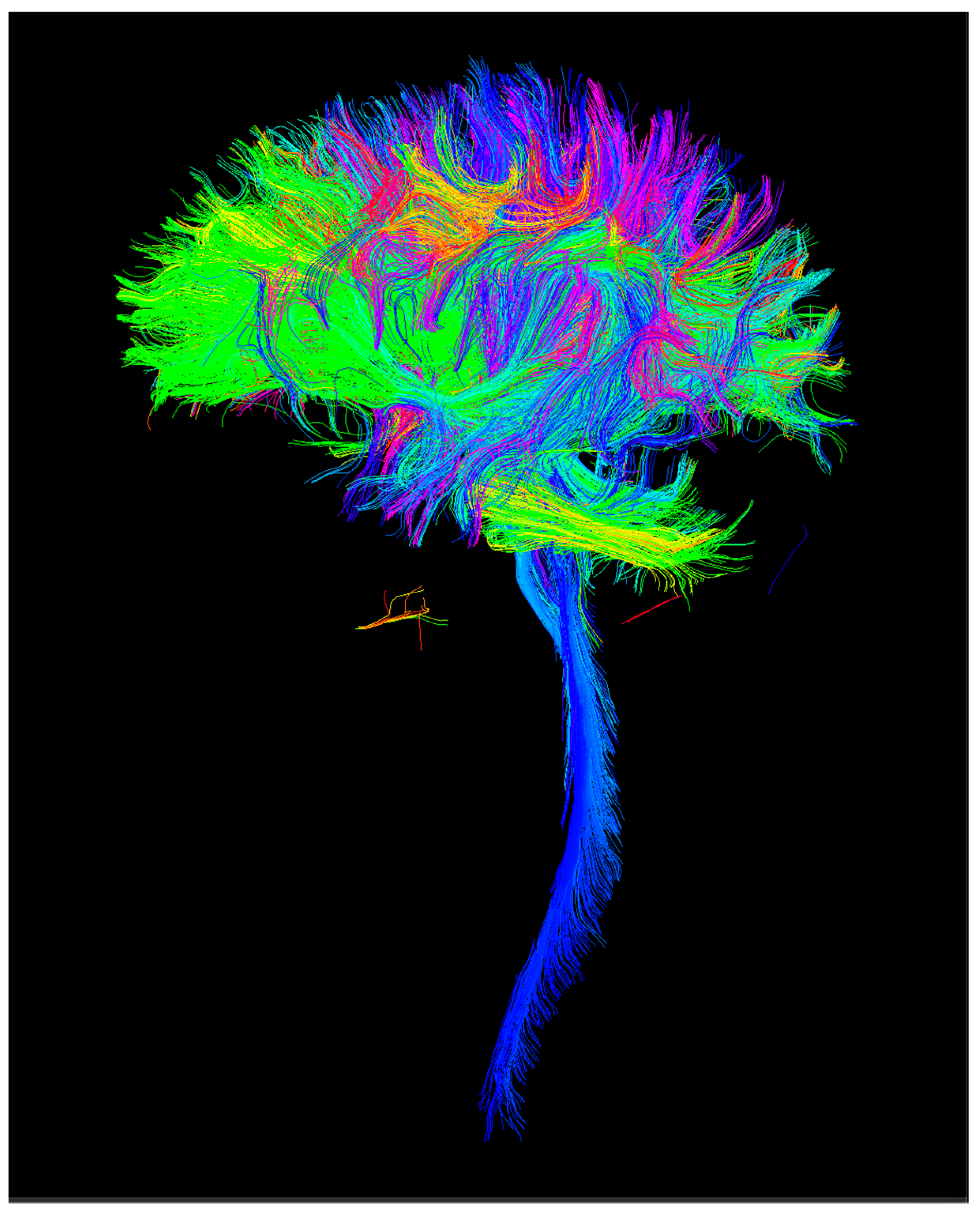
2.1.2. Connectomics
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
- (a)
- Caudal-middle-frontal cortex (left hemisphere) with superior-frontal cortex (left hemisphere);
- (b)
- Connection of the isthmus of the left cingulate gyrus with itself;
- (c)
- Connection of the right cerebellum cortex with itself.
- (a)
- Left hemispheric pericalcarine cortex with itself;
- (b)
- Left superior frontal cortex with left putamen;
- (c)
- Right superior frontal cortex with itself;
- (d)
- Insula (deep temporal lobe) with itself;
- (e)
- Superoparietal cortex with itself.
4. Discussion
Imitations of the Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, L.; Wang, D.; Chu, W.C.; Burwell, G.R.; Wong, T.T.; Heng, P.A.; Cheng, J.C. Automatic MRI segmentation and morphoanatomy analysis of the vestibular system in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. NeuroImage 2011, 54, S180–S188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznia, A.L.; Hernandez, A.K.; Lee, L.U. Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Common Questions and Answers. Am. Fam. Physician. 2020, 101, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Janicki, J.A.; Alman, B. Scoliosis: Review of diagnosis and treatment. Paediatr. Child. Health 2007, 12, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bunnell, W.P. Selective screening for scoliosis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2005, 434, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comité Nacional de Adolescencia SAP; Comité de Diagnóstico por Imágenes SAP; Sociedad Argentina de Ortopedia y Traumatología Infantil; Sociedad Argentina de Patología de la Columna Vertebral (SAPCV); Comité de Diagnóstico por Imágenes; Colaboradores. Consenso de escoliosis idiopática del adolescente [Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis]. Arch Argent Pediatr. 2016, 114, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, C.; Verma, K. Classifications in Brief: The Lenke Classification for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2018, 476, 2271–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Uhm, J.Y.; Chae, D.H.; Park, Y. Low body mass index for early screening of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A comparison based on standardized body mass index classifications. Asian Nurs. Res. 2020, 14, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, X.X.; Huang, C.A.; Lin, J.L.; Zhang, Z.J.; Shi, Y.F.; Chen, B.D.; Zhang, H.W.; Dai, Z.Y.; Yu, X.P.; Wang, X.Y. Prevalence of the thoracic scoliosis in children and adolescents candidates for strabismus surgery: Results from a 1935-patient cross-sectional study in China. Eur. Spine J. 2020, 29, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaturro, D.; Costantino, C.; Terrana, P.; Vitagliani, F.; Falco, V.; Cuntrera, D.; Sannasardo, C.E.; Vitale, F.; Letizia Mauro, G. Risk Factors, Lifestyle and Prevention among Adolescents with Idiopathic Juvenile Scoliosis: A Cross Sectional Study in Eleven First-Grade Secondary Schools of Palermo Province, Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latalski, M.; Danielewicz-Bromberek, A.; Fatyga, M.; Latalska, M.; Kröber, M.; Zwolak, P. Current insights into the aetiology of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Arch Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2017, 137, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baliyan, V.; Das, C.J.; Sharma, R.; Gupta, A.K. Diffusion weighted imaging: Technique and applications. World J. Radiol. 2016, 28, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, W.C.; Kong, Y.; Shi, L.; Hui, S.; Wang, D.; Deng, M.; Qiu, Y.; Cheng, J. Altered anisotropy and diffusivity of medulla oblongata and spinal cord in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Scoliosis 2015, 10, O45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, Y.; Shi, L.; Hui, S.C.; Wang, D.; Deng, M.; Chu, W.C.; Cheng, J.C. Variation in anisotropy and diffusivity along the medulla oblongata and the whole spinal cord in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A pilot study using diffusion tensor imaging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 1621–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joly, O.; Rousié, D.; Jissendi, P.; Rousié, M.; Frankó, E. A new approach to corpus callosum anomalies in idiopathic scoliosis using diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. Eur. Spine J. 2014, 23, 2643–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastwood, J.D.; Lev, M.H.; Wintermark, M.; Fitzek, C.; Barboriak, D.P.; Delong, D.M.; Lee, T.Y.; Azhari, T.; Herzau, M.; Chilukuri, V.R.; et al. Correlation of early dynamic CT perfusion imaging with whole-brain MR diffusion and perfusion imaging in acute hemispheric stroke. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2003, 24, 1869–1875. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soffia, P. Difusión por resonancia magnética: Bases y aplicaciones oncológicas en órganos extracraneanos. Rev. Chil. Radiol. 2009, 15, s17–s24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mori, S.; Barker, P.B. Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging: Its principle and applications. Anat. Rec. 1999, 257, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBihan, D.; Mangin, J.F.; Poupon, C.; Clark, C.A.; Pappata, S.; Molko, N.; Chabriat, H. Diffusion Tensor Imaging: Concepts and Applications. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2001, 13, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagmann, P.; Cammoun, L.; Gigandet, X.; Gerhard, S.; Grant, P.E.; Wedeen, V.; Meuli, R.; Thiran, J.P.; Honey, C.J.; Sporns, O. MR connectomics: Principles and challenges. J. Neurosci. Methods 2010, 15, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, S.R.; Qiu, G.X.; Zhang, J.G.; Zhuang, Q.Y. Research progress on the etiology and pathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 20, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Zhang, J. Principles of Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Its Applications to Basic Neuroscience Research. Neuron 2006, 51, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romero, C.; Ghisi, J.P.; Mazzucco, J.; Ternak, A. Imágenes con tensor de difusión en resonancia magnética. Rev. Argent. Neuroc. 2007, 21, 4499. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, W.C.; Man, G.C.; Lam, W.W.; Yeung, B.H.; Chau, W.W.; Ng, B.K.; Lam, T.P.; Lee, K.M.; Cheng, J.C. Morphological and functional electrophysiological evidence of relative spinal cord tethering in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2008, 15, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.C.; Man, G.C.; Lam, W.W.; Yeung, B.H.; Chau, W.W.; Ng, B.K.; Lam, T.P.; Lee, K.M.; Cheng, J.C. A detailed morphologic and functional magnetic resonance imaging study of the craniocervical junction in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 2007, 32, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saifuddin, A.; Tucker, S.; Taylor, B.A.; Noordeen, M.H.; Lehovsky, J. Prevalence and clinical significance of superficial abdominal reflex abnormalities in idiopathic scoliosis. Eur. Spine J. 2005, 14, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Shi, L.; Chu, W.C.; Paus, T.; Cheng, J.C.; Heng, P.A. A comparison of morphometric techniques for studying the shape of the corpus callosum in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Neuroimage 2009, 45, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bihan, D.; Breton, E.; Lallemand, D.; Aubin, M.L.; Vignaud, J.; Laval-Jeantet, M. Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology 1988, 168, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.K. Studying connections in the living human brain with diffusion MRI. Cortex 2008, 44, 936–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Chu, W.C.; Young, G.; Li, K.; Yeung, B.H.; Guo, L.; Man, G.C.; Lam, W.W.; Wong, S.T.; Cheng, J.C. MR analysis of regional brain volume in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Neurological manifestation of a systemic disease. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2008, 27, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, C.; Shi, L.; Hui, S.C.N.; Wang, D.; Lam, T.P.; Ip, C.B.; Ng, B.K.W.; Cheng, J.C.Y.; Chu, W.C.W. Altered White Matter Microstructure in the Corpus Callosum and Its Cerebral Interhemispheric Tracts in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Diffusion Tensor Imaging Analysis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| n | Sex and Female/Male Ratio | Age (X ± SD) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | 22 | 17/5 | 14.73 ± 3.03 |
| Controls | 18 | 8/10 | 12.33 ± 2.43 |
| T1 | dMRI | |
|---|---|---|
| Sequence type | Turbo field echo | Diffusion-weighted single shot spin echo |
| Repetition time | 8.1 ms | 9000 ms |
| Echo time | 3.7 ms | 86 ms |
| Flip angle | 8° | 90° |
| Echo train length | 170 | 59 |
| No. of slices | 240 | 140 |
| B-value | - | 1000 s/mm2 |
| No. of gradient directions | - | 61 |
| Orientation | Sagittal | Axial |
| Acquisition duration | 359 s | 696 s |
| Connection | Parameter | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Global connectivity | FA | 3.8·10−6 |
| Caudal-middle-frontal cortex (left hemisphere) to superior-frontal cortex (left hemisphere) | FA | <0.0092 |
| Connection of the isthmus of the left cingulate gyrus with itself | FA | <0.0092 |
| Connection of the right cerebellum cortex with itself | FA | <0.0092 |
| Left hemispheric pericalcarine cortex to itself | FA (adjusted average) | 0.003806 |
| Left superior frontal superior cortex with left putamen | FA (adjusted average) | 0.005745 |
| Right superior frontal superior cortex with itself | FA (adjusted average) | 0.008644 |
| Insula (deep temporal lobe) with itself | FA (adjusted average) | 0.008463 |
| Superoparietal cortex with itself | FA (adjusted average) | 0.003526 |
| Supramarginal cortex | Number of tractography lines | <0.0062 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noriega-Gonzalez, D.C.; Crespo, J.; Ardura, F.; Calabia-del Campo, J.; Alberola-Lopez, C.; de Luis-García, R.; Caballero-García, A.; Córdova, A. Cerebral White Matter Connectivity in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Children 2022, 9, 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9071023
Noriega-Gonzalez DC, Crespo J, Ardura F, Calabia-del Campo J, Alberola-Lopez C, de Luis-García R, Caballero-García A, Córdova A. Cerebral White Matter Connectivity in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Children. 2022; 9(7):1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9071023
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoriega-Gonzalez, David C., Jesús Crespo, Francisco Ardura, Juan Calabia-del Campo, Carlos Alberola-Lopez, Rodrigo de Luis-García, Alberto Caballero-García, and Alfredo Córdova. 2022. "Cerebral White Matter Connectivity in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study" Children 9, no. 7: 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9071023
APA StyleNoriega-Gonzalez, D. C., Crespo, J., Ardura, F., Calabia-del Campo, J., Alberola-Lopez, C., de Luis-García, R., Caballero-García, A., & Córdova, A. (2022). Cerebral White Matter Connectivity in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Children, 9(7), 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9071023






