Volatility Spillovers among Sovereign Credit Default Swaps of Emerging Economies and Their Determinants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Econometric Methodology
3.1. Time-Domain Approach of Diebold and Yilmaz (2012)
3.2. Frequency Connectedness Approach
4. Data and Preliminary Statistics
5. Empirical Results and Discussion
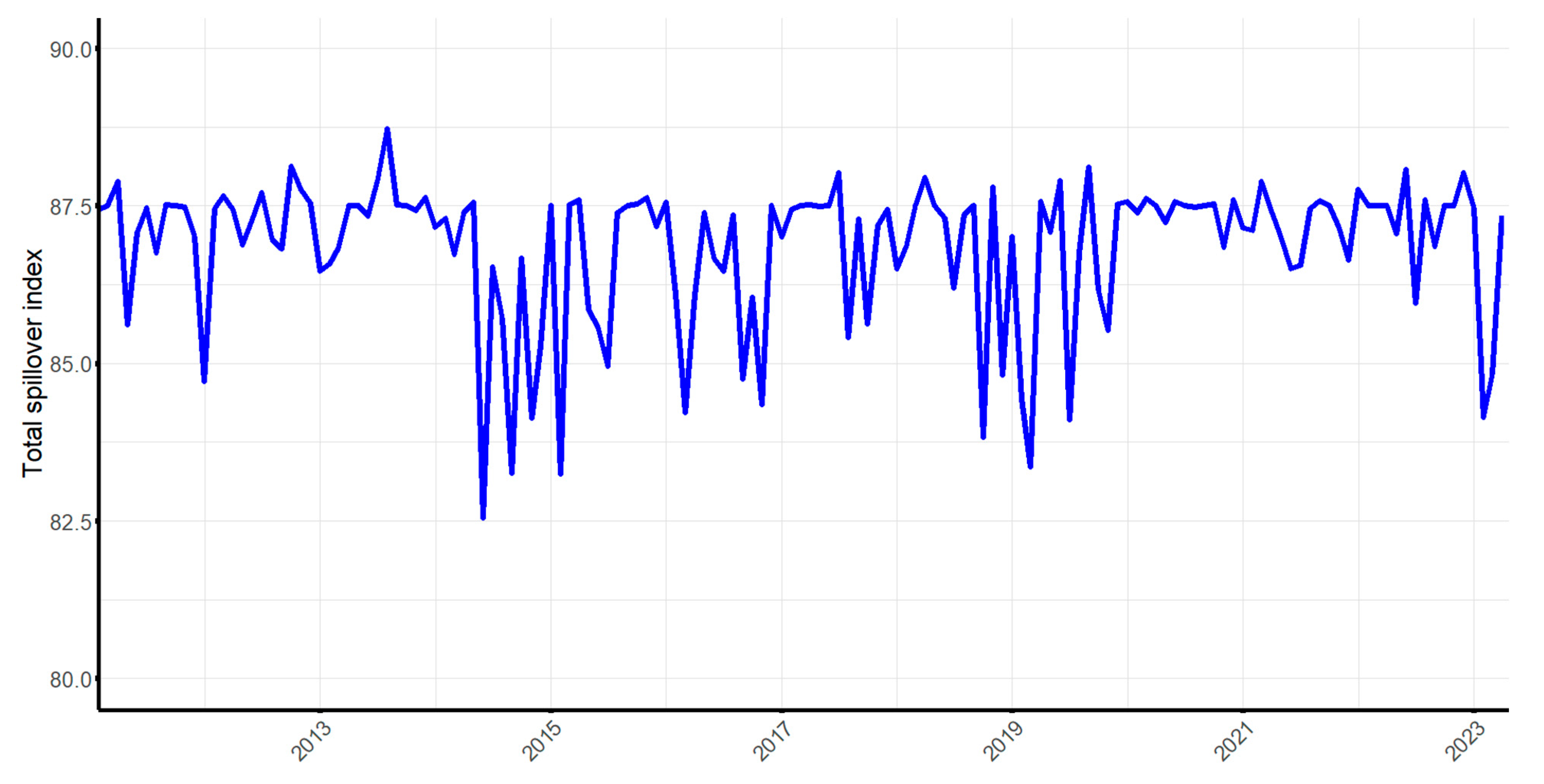
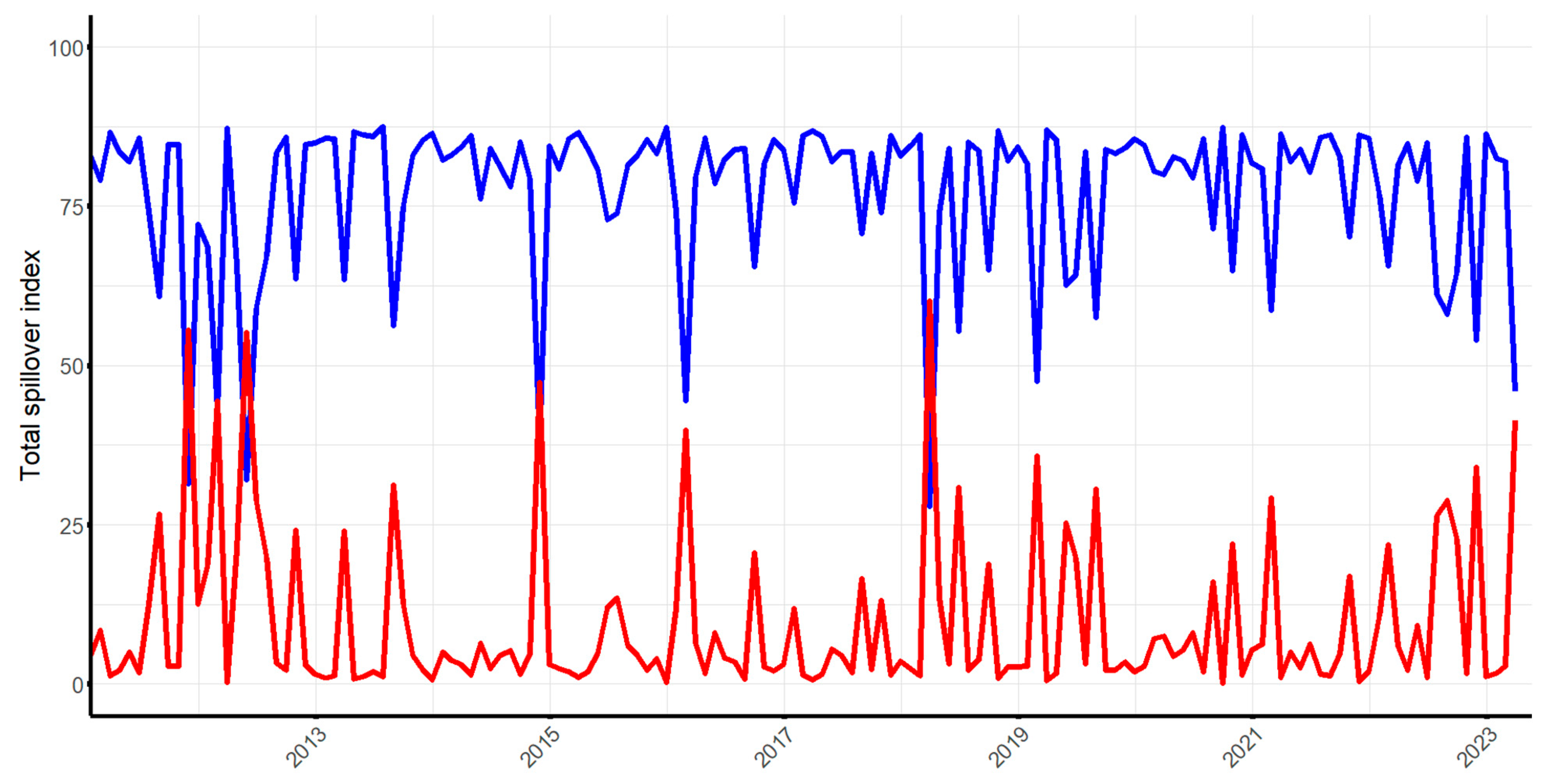
5.1. Time -Domain Spillover Analysis
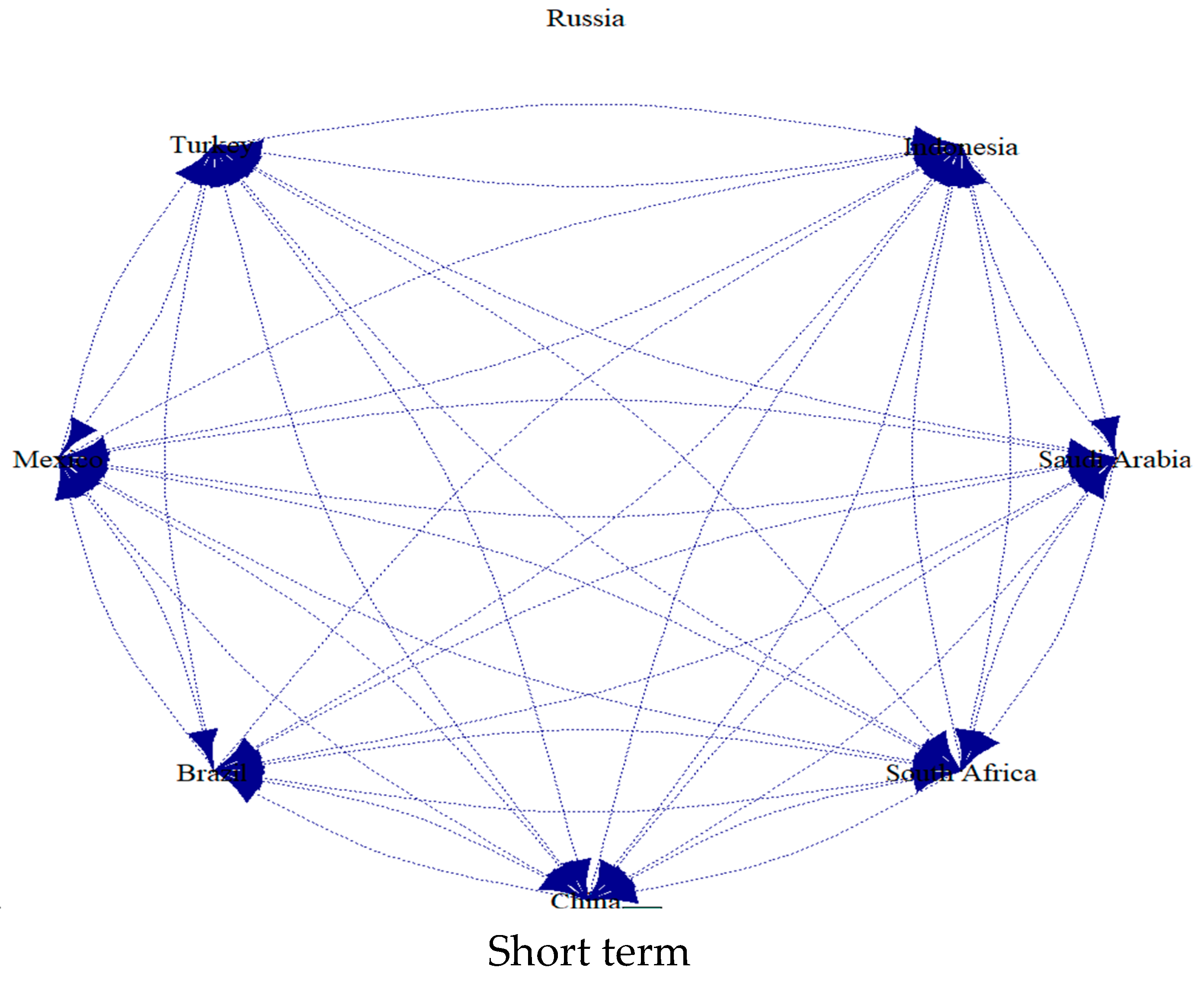
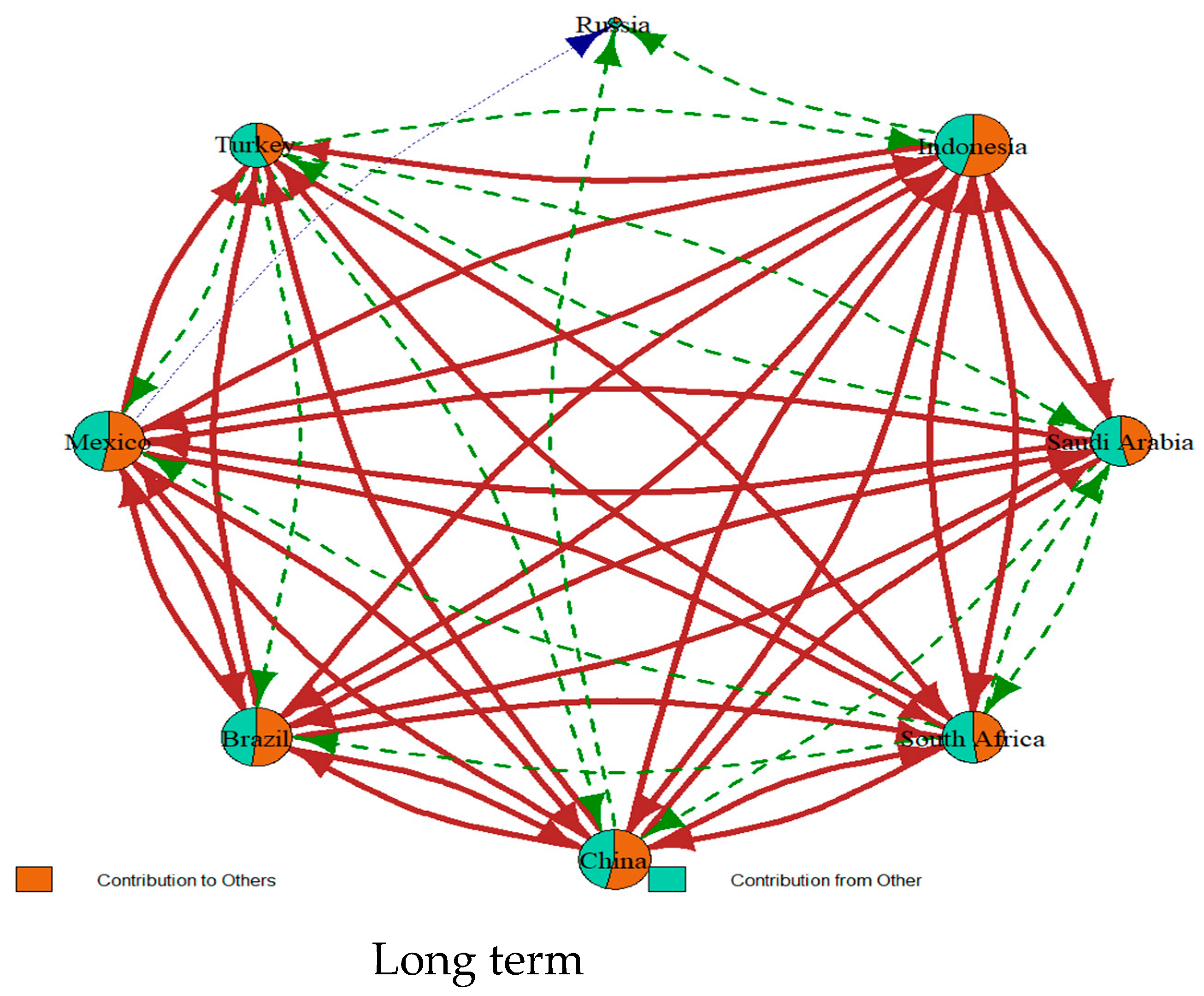
5.2. Frequency-Domain Spillover Analysis
5.3. The Impact of Global Uncertainty Factors on SCDS Spillovers
6. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abed, R. E., Sahar Boukadida, and Warda Jaidane. 2019. Financial Stress Transmission from Sovereign Credit Market to Financial Market: A Multivariate FIGARCH-DCC Approach. Global Business Review 20: 1122–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, Fathi, and Nader Naifar. 2006. The Determinants of Credit Default Swap Rates: An Explanatory Study. International Journal of Theoretical and Applied Finance 9: 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstad, Marlene, Eli Remolona, and Jimmy Shek. 2016. How do global investors differentiate between sovereign risks? The new normal versus the old. Journal of International Money and Finance 66: 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, Patrick, Hamid Boustanifar, Johannes Breckenfelder, and Jan Schnitzler. 2018. Sovereign to Corporate Risk Spillovers. Journal of Money, Credit and Banking 50: 857–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, Patrick, Valeri Sokolovski, Marti G. Subrahmanyam, and Davide Tomio. 2020. In Sickness and in Debt: The COVID-19 Impact on Sovereign Credit Risk. SSRN Electronic Journal. Available online: https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3613432 (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Baffes, John, Alain N. Kabundi, Peter S. O. Nagle, and Franziska Ohnsorge. 2018. The Role of Major Emerging Markets in Global Commodity Demand. World Bank Policy Research Working Paper, 8495. Washington, DC: World Bank Group. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, Scott R., Nicholas Bloom, and Steven J. Davis. 2016. Measuring Economic Policy Uncertainty. The Quarterly Journal of Economics 131: 1593–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcilar, Mehmet, Ahmed H. Elsayed, and Shawkat Hammoudeh. 2023. Financial connectedness and risk transmission among MENA countries: Evidence from connectedness network and clustering analysis. Journal of International Financial Markets, Institutions and Money 82: 101656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcilar, Mehmet, Zeynel Abidin Ozdemir, Huseyin Ozdemir, and Mark E. Wohar. 2020. Spillover effects in oil-related CDS markets during and after the sub-prime crisis. The North American Journal of Economics and Finance 54: 101249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester, Laura, and Ana González-Urteaga. 2021. Do sovereign ratings cause instability in cross-border emerging CDS markets? International Review of Economics and Finance 72: 643–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruník, Jozef, and Tomas Křehlík. 2018. Measuring the Frequency Dynamics of Financial Connectedness and Systemic Risk. Journal of Financial Econometrics 16: 271–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottero, Margherita, Simone Lenzu, and Filippo Mezzanotti. 2020. Sovereign debt exposure and the bank lending channel: Impact on credit supply and the real economy. Journal of International Economics 126: 103328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouri, Elie, Syed J. H. Shahzad, Naveed Raza, and David Roubaud. 2018. Oil volatility and sovereign risk of BRICS. Energy Economics 70: 258–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevik, Serhan, and Joao T. Jalles. 2022. This changes everything: Climate shocks and sovereign bonds. Energy Economics 107: 105856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Souza, Rodrigo, and Renee Fry-McKibbin. 2021. Global liquidity and commodity market interactions: Macroeconomic effects on a commodity exporting emerging market. International Review of Economics and Finance 76: 781–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diebold, Francis X., and Kamil Yilmaz. 2012. Better to give than to receive: Predictive directional measurement of volatility spillovers. International Journal of Forecasting 28: 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichengreen, Barry, and Poonam Gupta. 2015. Tapering talk: The impact of expectations of reduced Federal Reserve security purchases on emerging markets. Emerging Markets Review 25: 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyssell, Thomas, Hung-G. Fung, and Gaiyan Zhang. 2013. Determinants and price discovery of China sovereign credit default swaps. China Economic Review 24: 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilidis, Konstantinos. 2021. Measuring Climate Policy Uncertainty. SSRN Electronic Journal. SSRN Scholarly Paper 3847388. Available online: https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3847388 (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Ghenimi, Ameni, Hasna Chaibi, and Mohamed Omri. 2017. The effects of liquidity risk and credit risk on bank stability: Evidence from the MENA region. Borsa Istanbul Review 17: 238–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härdle, Wolfgang K., Weining Wang, and Lining Yu. 2016. TENET: Tail-Event driven NETwork risk. Journal of Econometrics 192: 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbert, Ann M., and Ivelina Pavlova. 2017. The drivers of sovereign cds spread changes: Local versus global factors. Financial Review 52: 435–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilscher, Jens, and Yves Nosbusch. 2010. Determinants of Sovereign Risk: Macroeconomic Fundamentals and the Pricing of Sovereign Debt. Review of Finance 14: 235–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Biliang, Xing Tang, Lin Yin, and Qian Liu. 2021. Emerging Markets Redefined: Comprehensive Measurement and Future Prospects. Global Journal of Emerging Market Economies 13: 165–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamber, Gunes, Özer Karagedikli, and Michael Ryan. 2016. International Spill-Overs of Uncertainty Shocks: Evidence from a FAVAR. (Working Paper No. 61/2016). Centre for Applied Macroeconomic Analysis, Crawford School of Public Policy. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2848034 (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Liu, Weifeng, Warwick J. McKibbin, Adele C. Morris, and Peter J. Wilcoxen. 2020. Global economic and environmental outcomes of the Paris Agreement. Energy Economics 90: 104838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Yang, and Bruce Morley. 2012. Sovereign credit default swaps and the macroeconomy. Applied Economics Letters 19: 129–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longstaff, Francis A., Jun Pan, Lasse H. Pedersen, and Kenneth J. Singleton. 2011. How Sovereign Is Sovereign Credit Risk? American Economic Journal: Macroeconomics 3: 75–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollum, David L., Wenji Zhou, Christoph Bertram, Harmen-S. de Boer, Valentina Bosetti, Sebastian Busch, Jacques Després, Laurent Drouet, Johannes Emmerling, Marianne Fay, and et al. 2018. Energy investment needs for fulfilling the Paris Agreement and achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. Nature Energy 3: 589–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merton, Robert C. 1974. On the Pricing of Corporate Debt: The Risk Structure of Interest Rates. Journal of Finance 29: 449. [Google Scholar]
- Naifar, Nader. 2023. Does climate change affect sovereign credit risk? International evidence. Borsa Istanbul Review 23: S84–S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naifar, Nader, and Syed J. H. Shahzad. 2021. Tail event-based sovereign credit risk transmission network during COVID-19 pandemic. Finance Research Letters 45: 102182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, Luis, Jose D. Curto, and Joao P. Nunes. 2012. The determinants of sovereign credit spread changes in the Euro-zone. Journal of International Financial Markets, Institutions and Money 22: 278–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Jun, and Kenneth J. Singleton. 2008. Default and Recovery Implicit in the Term Structure of Sovereign CDS Spreads. Journal of Finance 63: 2345–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, Winnie P., Jianfu Shen, and John E. Burnett. 2017. An empirical study of international spillover of sovereign risk to bank credit risk. Financial Review 52: 281–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, Anmar. 2023. How did advanced emerging stock markets respond to COVID-19 and the Ukraine invasion? Journal of Economic and Financial Sciences 16: a820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remolona, Eli, Michela Scatigna, and Eliza Wu. 2008. The Dynamic Pricing of Sovereign Risk in Emerging Markets: Fundamentals and Risk Aversion. The Journal of Fixed Income 17: 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Xiaohang, Xiao Zhang, Cheng Yan, and Giray Gozgor. 2022. Climate policy uncertainty and firm-level total factor productivity: Evidence from China. Energy Economics 113: 106209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikhotso, Prayer M., and Beatrice D. Simo-Kengne. 2022. Dependence Structures between Sovereign Credit Default Swaps and Global Risk Factors in BRICS Countries. Journal of Risk and Financial Management 15: 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabkha, Saker, Christian de Peretti, and Dorra Mezzez Hmaied. 2019. International risk spillover in sovereign credit markets: An empirical analysis. Managerial Finance 45: 1020–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolbov, Mikhail. 2017. Determinants of sovereign credit risk: The case of Russia. Post-Communist Economies 29: 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Xin, Shupei Huang, Brian M. Lucey, and Haizhong An. 2023. The impacts of climate policy uncertainty on stock markets: Comparison between China and the US. International Review of Financial Analysis 88: 102671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Lu, and Shigeyuki Hamori. 2023. Modeling the global sovereign credit network under climate change. International Review of Financial Analysis 87: 102618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenios, Stavros A. 2022. The risks from climate change to sovereign debt. Climatic Change 172: 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
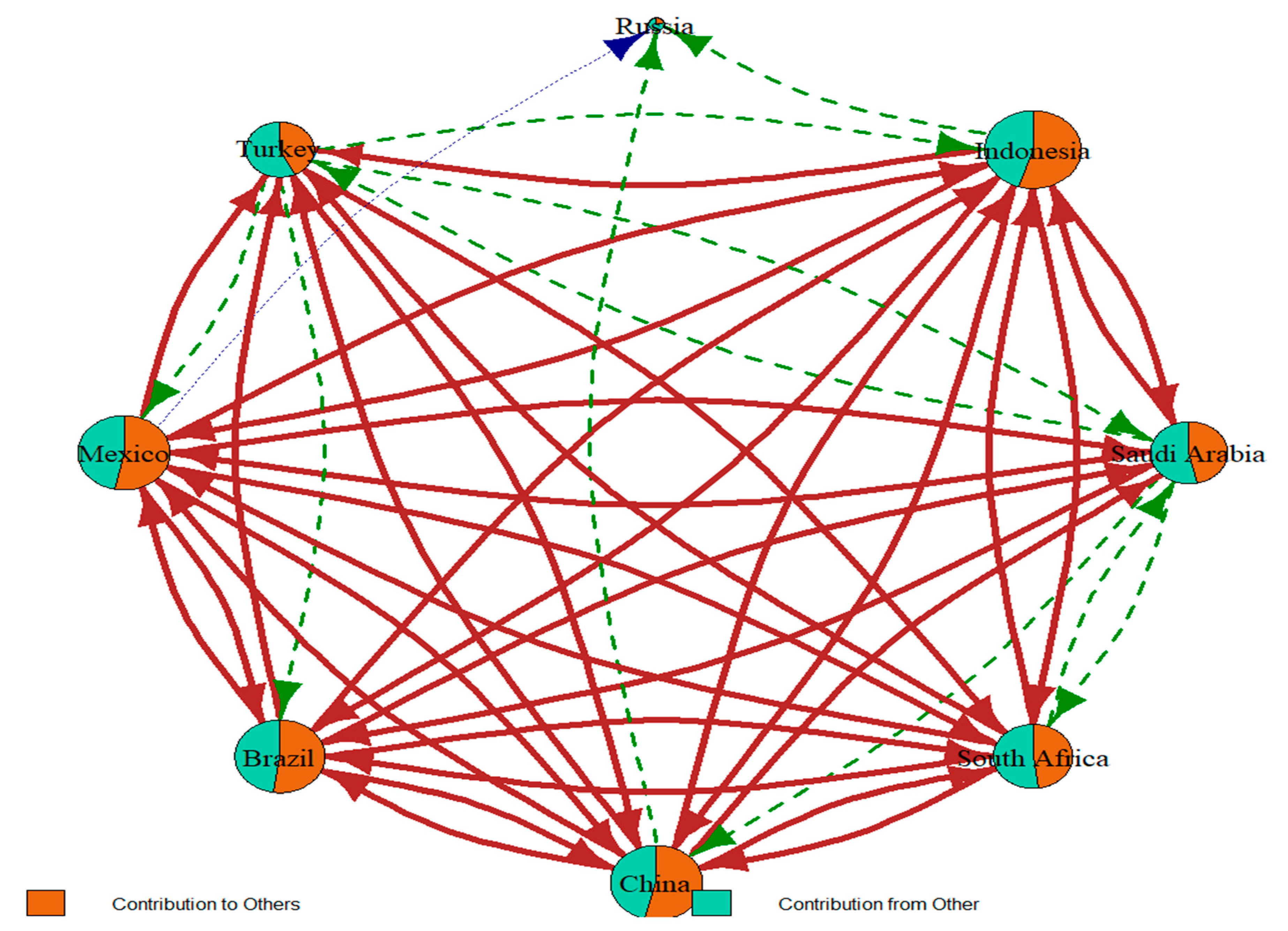
| Saudi Arabia | Indonesia | Russia | Turkey | Mexico | Brazil | China | South Africa | FROM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saudi Arabia | 22.91 | 14.84 | 0.60 | 6.76 | 16.81 | 16.80 | 12.22 | 9.05 | 9.64 |
| Indonesia | 11.41 | 18.62 | 1.33 | 9.20 | 15.52 | 14.77 | 16.58 | 12.57 | 10.17 |
| Russia | 1.90 | 5.25 | 76.70 | 1.37 | 3.51 | 2.40 | 6.95 | 1.92 | 2.91 |
| Turkey | 7.83 | 13.71 | 0.55 | 27.00 | 11.82 | 11.32 | 13.82 | 13.95 | 9.12 |
| Mexico | 13.70 | 16.44 | 0.93 | 8.23 | 18.71 | 17.97 | 13.88 | 10.13 | 10.16 |
| Brazil | 13.99 | 16.17 | 0.64 | 8.12 | 18.32 | 19.10 | 13.56 | 10.10 | 10.11 |
| China | 9.91 | 17.54 | 1.82 | 10.07 | 13.75 | 12.90 | 20.34 | 13.67 | 9.96 |
| South Africa | 8.98 | 15.87 | 0.52 | 11.66 | 12.21 | 12.02 | 16.31 | 22.43 | 9.70 |
| TO | 8.47 | 12.48 | 0.80 | 6.93 | 11.49 | 11.02 | 11.67 | 8.92 | 71.77 |
| Saudi Arabia | Indonesia | Russia | Turkey | Mexico | Brazil | China | South Africa | FROM_ABS | FROM_WTH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saudi Arabia | 0.35 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 10.40 |
| Indonesia | 0.20 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 11.33 |
| Russia | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.79 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 2.71 |
| Turkey | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 0.41 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.12 | 8.94 |
| Mexico | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 0.12 | 0.30 | 0.28 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 11.08 |
| Brazil | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 9.31 |
| China | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 10.01 |
| South Africa | 0.13 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.34 | 0.13 | 9.57 |
| TO_ABS | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 1.01 | |
| TO_WTH | 9.36 | 11.73 | 0.96 | 6.92 | 12.10 | 11.97 | 10.46 | 9.85 | 73.35 |
| Saudi Arabia | Indonesia | Russia | Turkey | Mexico | Brazil | China | South Africa | FROM_ABS | FROM_WTH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saudi Arabia | 22.56 | 14.64 | 0.59 | 6.67 | 16.55 | 16.54 | 12.06 | 8.89 | 9.49 | 9.63 |
| Indonesia | 11.22 | 18.37 | 1.30 | 9.06 | 15.27 | 14.53 | 16.38 | 12.37 | 10.02 | 10.16 |
| Russia | 1.87 | 5.19 | 75.92 | 1.35 | 3.46 | 2.36 | 6.87 | 1.91 | 2.87 | 2.91 |
| Turkey | 7.72 | 13.53 | 0.54 | 26.59 | 11.67 | 11.17 | 13.63 | 13.75 | 9.00 | 9.13 |
| Mexico | 13.47 | 16.21 | 0.91 | 8.11 | 18.41 | 17.69 | 13.70 | 9.96 | 10.01 | 10.15 |
| Brazil | 13.80 | 15.98 | 0.63 | 8.02 | 18.08 | 18.84 | 13.42 | 9.95 | 9.98 | 10.12 |
| China | 9.76 | 17.32 | 1.79 | 9.94 | 13.55 | 12.71 | 20.10 | 13.48 | 9.82 | 9.96 |
| South Africa | 8.85 | 15.66 | 0.51 | 11.49 | 12.04 | 11.85 | 16.12 | 22.09 | 9.56 | 9.70 |
| TO_ABS | 8.34 | 12.32 | 0.78 | 6.83 | 11.33 | 10.86 | 11.52 | 8.79 | 70.76 | |
| TO_WTH | 8.45 | 12.49 | 0.80 | 6.93 | 11.48 | 11.01 | 11.68 | 8.91 | 71.75 |
| Coefficient | Q = 0.05 | Q = 0.10 | Q = 0.25 | Q = 0.50 | Q = 0.75 | Q = 0.90 | Q = 0.95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | 0.003604 | −0.001610 | 0.001410 | −0.000808 | −0.001792 | −0.007623 * | −0.01079 *** |
| GPR | 0.030595 *** | 0.024421 *** | 0.016587 * | 0.000503 | −0.002276 | 0.005701 | 0.013200 |
| MOVE | −0.028428 | 0.018146 | 0.001033 | −0.001640 | 0.005480 | 0.008190 | 0.050487 |
| OVX | −0.043297 | −0.034522 *** | −0.009571 | 0.000583 | 0.005829 | −0.004968 | −0.036412 * |
| EPU | −0.003664 | 0.007291 | 0.003563 | 0.006466 | 0.016253 * | 0.030883 | 0.014545 |
| VIX | 0.035527 *** | 0.017979 *** | 0.007585 | 0.003489 | −0.000363 | −0.005135 | 0.002548 |
| R2 (%) | 15.47 | 14.98 | 4.97 | 0.73 | 3.04 | 6.32 | 8.86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aljarba, S.; Naifar, N.; Almeshal, K. Volatility Spillovers among Sovereign Credit Default Swaps of Emerging Economies and Their Determinants. Risks 2024, 12, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks12040071
Aljarba S, Naifar N, Almeshal K. Volatility Spillovers among Sovereign Credit Default Swaps of Emerging Economies and Their Determinants. Risks. 2024; 12(4):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks12040071
Chicago/Turabian StyleAljarba, Shumok, Nader Naifar, and Khalid Almeshal. 2024. "Volatility Spillovers among Sovereign Credit Default Swaps of Emerging Economies and Their Determinants" Risks 12, no. 4: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks12040071
APA StyleAljarba, S., Naifar, N., & Almeshal, K. (2024). Volatility Spillovers among Sovereign Credit Default Swaps of Emerging Economies and Their Determinants. Risks, 12(4), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks12040071







