Recent Regulation in Credit Risk Management: A Statistical Framework
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Modelling Income Volatility and Early Recognition of Credit Risk
3. Analyzing the Optimization Problem for Continuous Asset Distribution
3.1. Considering a Shifted Exponential Distribution for Modelling the Net Asset Value
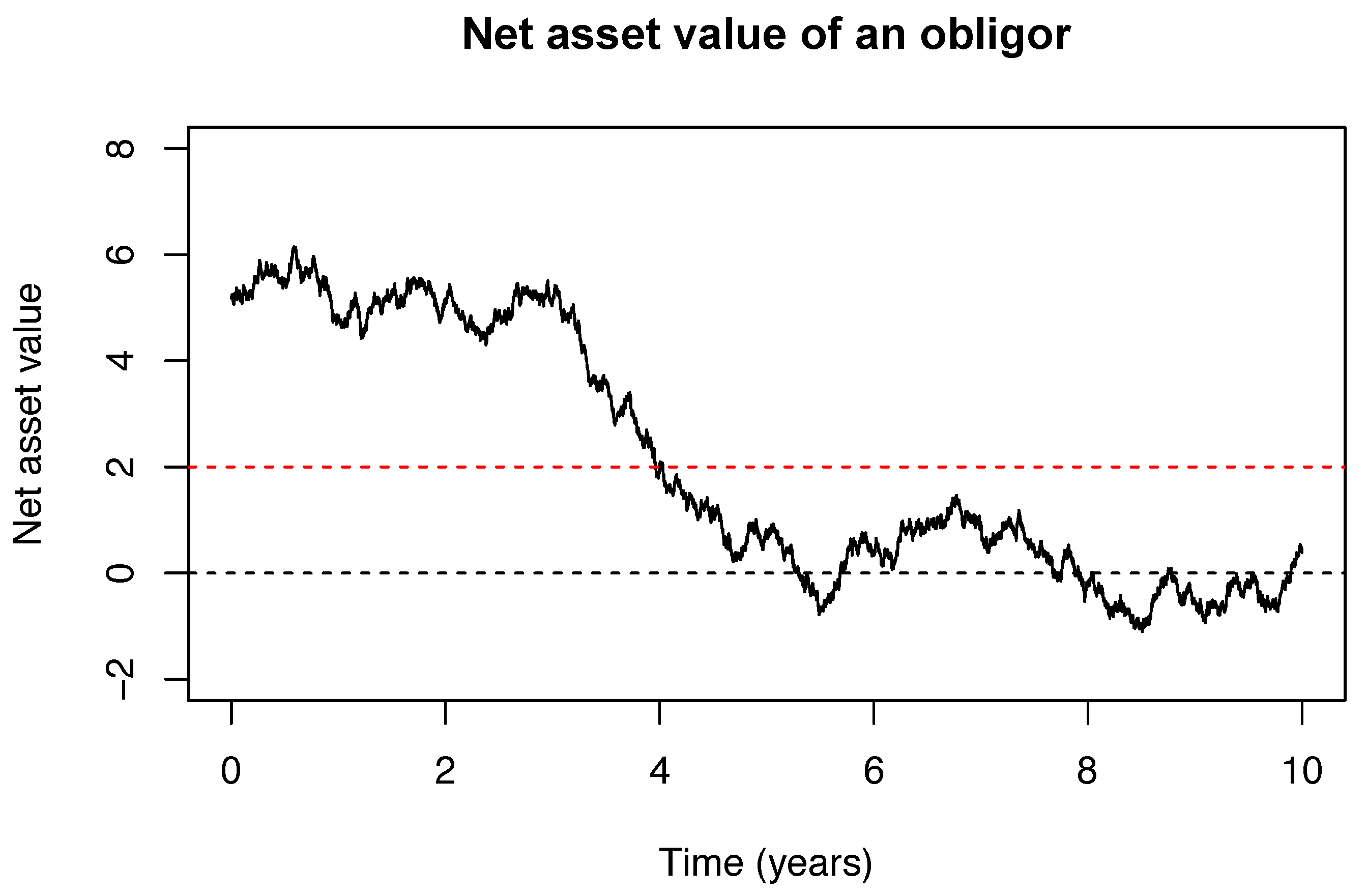
3.2. Modelling the Net Asset Value with Brownian Motion
4. Analyzing the Optimization Problem for Discrete Asset Distribution
4.1. Specific Increments
4.2. General Increments
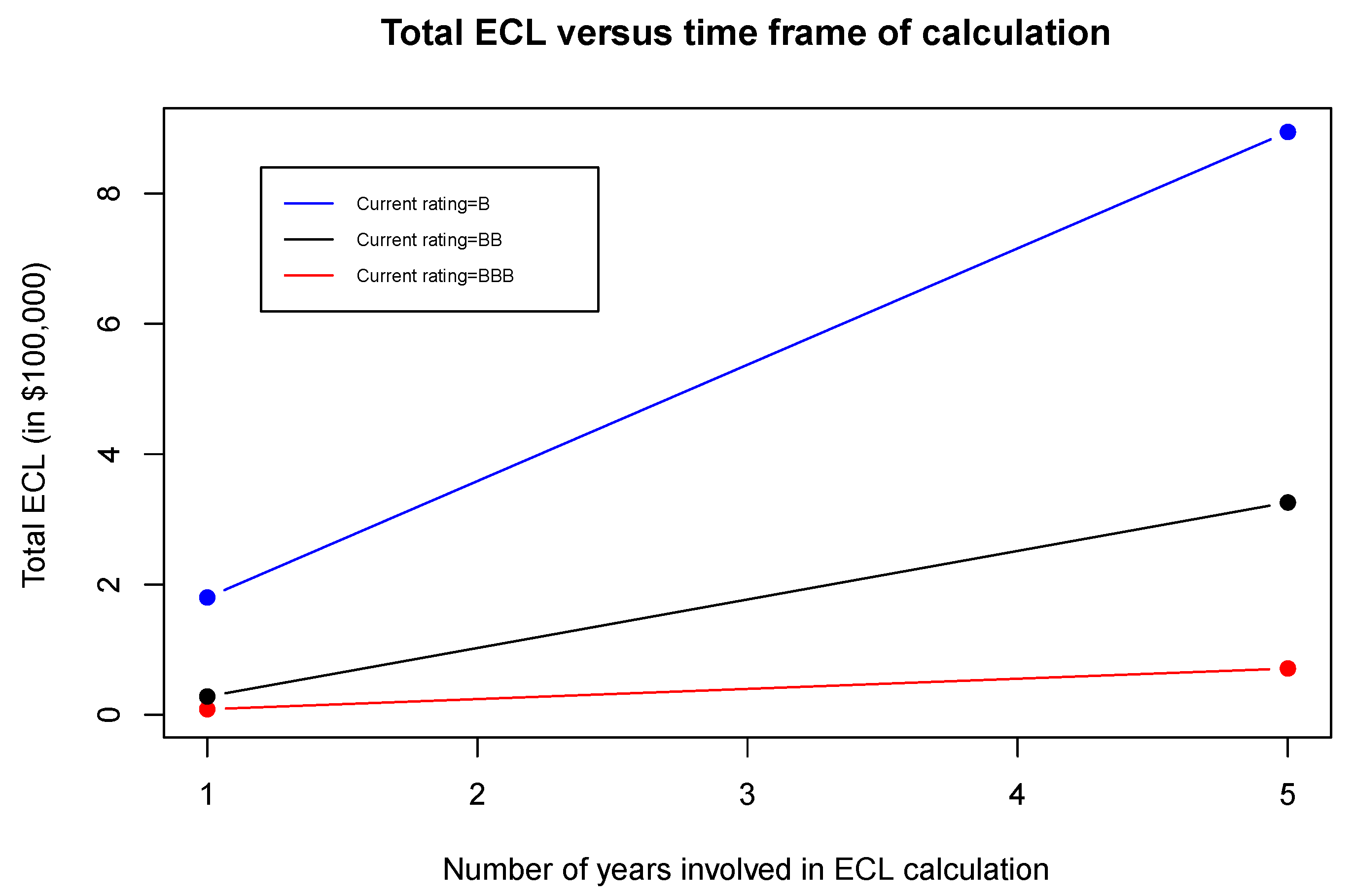
5. Relating Our Model to the European Union Stress Test and Standard and Poor’s Default Data
5.1. Selection of in Comparison to European Union Framework
5.2. Analyzing the Income Volatility Portion with Default Data by Standard and Poor’s
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EaD | exposure at default |
| ECL | expected credit loss |
| EU | European Union |
| IFRS | International Financial Reporting Standard |
| LGD | loss given default |
| PD | probability of default |
References
- Angilella, Silvia, and Sebastiano Mazzù. 2017. A credit risk model with an automatic override for innovative small and medium-sized enterprises. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basel Committee on Banking Supervision. 2005. An Explanatory Note on the Basel II IRB Risk Weight Functions. Bank for International Settlements. Available online: www.bis.org (accessed on 5 April 2019).
- Basel Committee on Banking Supervision. 2015. Guidance on Credit Risk and Accounting for Expected Credit Losses. Bank for International Settlements. Available online: www.bis.org (accessed on 5 April 2019).
- Bluhm, Christian, and Ludger Overbeck. 2003. Systematic risk in homogeneous credit portfolios. In Credit Risk: Measurement, Evaluation and Management (Contributions to Economics). Edited by Georg Bol, Gholamreza Nakhaeizadeh, Svetlozar T. Rachev, Thomas Ridder and Karl-Heinz Vollmer. Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer, pp. 35–48. [Google Scholar]
- Bluhm, Christian, Ludger Overbeck, and Christoph Wagner. 2010. An Introduction to Credit Risk Modeling, 2nd ed. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC. [Google Scholar]
- Bohn, Jeffrey R., and Roger M. Stein. 2009. Active Credit Portfolio Management in Practice. Hoboken: Wiley Finance. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, Benjamin H., and Gerald A. Edwards Jr. 2017. The New Era of Expected Credit Loss Provisioning. BIS Quarterly Review. Available online: www.bis.org (accessed on 5 April 2019).
- Crook, Jonathan N., David B. Edelman, and Lyn C. Thomas. 2007. Recent developments in consumer credit risk assessment. European Journal of Operational Research 183: 1447–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst & Young. 2015. Accounting for Share-Based Payments under IFRS 2—The Essential Guide. Available online: www.ey.com (accessed on 5 April 2019).
- European Banking Authority. 2017. Report on Results from the Second EBA Impact Assessment of IFRS 9. Available online: www.eba.europa.eu (accessed on 5 April 2019).
- European Banking Authority. 2018. 2018 EU-Wide Stress Test. European Union. Available online: www.eba.europa.eu (accessed on 5 April 2019).
- Frei, Christoph, and Marcus Wunsch. 2018. Moment estimators for autocorrelated time series and their application to default correlations. Journal of Credit Risk 14: 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordy, Michael B. 2000. A comparative anatomy of credit risk models. Journal of Banking and Finance 24: 119–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallenberg, Olav. 2002. Foundations of Modern Probability, 2nd ed. Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P. Ravi, and Vadlamani Ravi. 2007. Bankruptcy prediction in banks and firms via statistical and intelligent techniques—A review. European Journal of Operational Research 180: 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, Filippo, Alfonso Natale, Theodore Pepanides, Enrico Risso, and Gerhard Schröck. 2017. IFRS 9: A Silent Revolution in Banks’ Business Models. New York: McKinsey & Company. [Google Scholar]
- McNeil, Alexander J., Rüdiger Frey, and Paul Embrechts. 2015. Quantitative Risk Management: Concepts, Techniques and Tools, rev. ed. Princeton: Princeton University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Merton, Robert C. 1974. On the pricing of corporate debt: The risk structure of interest rates. Journal of Finance 29: 449–70. [Google Scholar]
- Miu, Peter, and Bogie Ozdemir. 2009. Stress-testing probability of default and migration rate with respect to Basel II requirements. Journal of Risk Model Validation 3: 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miu, Peter, and Bogie Ozdemir. 2017. Adapting the Basel II advanced internal-ratings-based models for International Financial Reporting Standard 9. Journal of Credit Risk 13: 53–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PricewaterhouseCoopers. 2016. The Wait Is Nearly Over? IFRS 17 Is Coming, Are You Prepared for It? Available online: www.pwc.com (accessed on 5 April 2019).
- PricewaterhouseCoopers. 2018. Revenue from Contracts with Customers. Available online: www.pwc.com (accessed on 5 April 2019).
- Randall, Mark, and Sandra Thompson. 2017. IFRS 9 Impairment: Significant Increase in Credit Risk: PwC in Depth. Available online: www.pwc.com (accessed on 5 April 2019).
- Simons, Dietske, and Ferdinand Rolwes. 2009. Macroeconomic default modeling and stress testing. International Journal of Central Banking 5: 177–204. [Google Scholar]
- Skoglund, Jimmy, and Wei Chen. 2016. The application of credit risk models to macroeconomic scenario analysis and stress testing. Journal of Credit Risk 12: 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard and Poor’s. 2018. Default, Transition, and Recover: 2017 Annual Global Corporate Default Study and Rating Transitions. Available online: www.spratings.com (accessed on 5 April 2019).
- Stulz, Rene M. 2015. Risk-taking and risk management by banks. Journal of Applied Corporate Finance 27: 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Bill Huajian, and Zunwei Du. 2015. Stress testing and modeling of rating migration under the Vasicek model framework: Empirical approaches and technical implementation. Journal of Risk Model Validation 9: 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| IFRS 9 | Loan Type | ECL |
|---|---|---|
| bucket 1 | performing | one-year |
| bucket 2 | underperforming | lifetime |
| bucket 3 | impaired | lifetime |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ewanchuk, L.; Frei, C. Recent Regulation in Credit Risk Management: A Statistical Framework. Risks 2019, 7, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks7020040
Ewanchuk L, Frei C. Recent Regulation in Credit Risk Management: A Statistical Framework. Risks. 2019; 7(2):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks7020040
Chicago/Turabian StyleEwanchuk, Logan, and Christoph Frei. 2019. "Recent Regulation in Credit Risk Management: A Statistical Framework" Risks 7, no. 2: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks7020040
APA StyleEwanchuk, L., & Frei, C. (2019). Recent Regulation in Credit Risk Management: A Statistical Framework. Risks, 7(2), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks7020040





