Intelligent Remote Photoplethysmography-Based Methods for Heart Rate Estimation from Face Videos: A Survey
Abstract
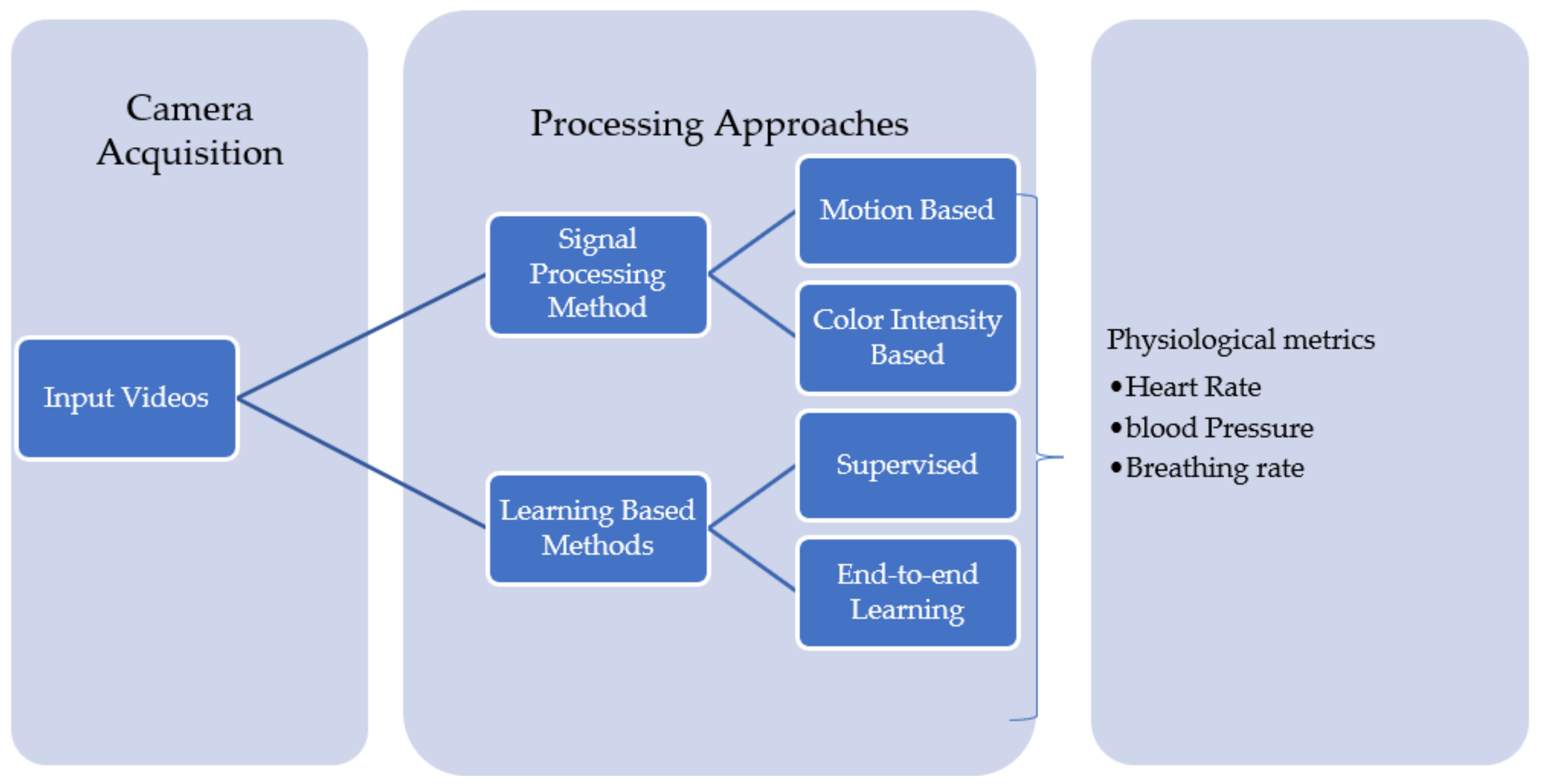
:1. Introduction
2. Outline
3. Motivations and Problem Statement
- To discuss rPPG measurement using signal processing methods as well as its recent furtherance in the deep learning environment;
- To harness the insight into the challenges on rPPG, and we anticipate some suggestions on the future direction.
4. Remote Photoplethysmography
5. Remote Methods for HR Detection
5.1. Signal Processing Methods
- (1).
- Pre-processing;
- (2).
- Signal extraction;
- (3).
- Heart rate estimation (post-processing).
5.1.1. Pre-Processing
Face Detection and ROI Tracking
Raw Signal Trace Extraction
5.1.2. Signal Extraction
Filtering
Dimensionality Reduction
- Blind source separation;
- Model-based methods;
- Design-based methods.
5.1.3. Heart Rate Estimation
5.2. Learning-Based Methods
5.2.1. Supervised Learning Methods
5.2.2. End-to-End Learning-Based Approach
- It requires a large volume of training data;
- Poor performance under realistic conditions;
- Low accuracy due to compression;
- Complexity due to intermediate steps.
6. Datasets
7. Challenges
7.1. Data Implication
7.2. Privacy Concern
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biswas, D.; Simoes-Capela, N.; Van Hoof, C.; Van Helleputte, N. Heart Rate Estimation from Wrist-Worn Photoplethysmography: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 6560–6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalise, L.; Bernacchia, N.; Ercoli, I.; Marchionni, P. Heart rate measurement in neonatal patients using a web camera. In Proceedings of the MeMeA 2012—2012 IEEE Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications, Budapest, Hungary, 18–19 May 2012; pp. 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, S.; Caldato, C.; Greenwood, D.C.; Bartoli, N.; Pensabene, V.; Actis, P. Remote heart rate monitoring—Assessment of the Face reader rPPg by Noldus. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuncoro, C.B.D.; Luo, W.-J.; Kuan, Y.-D. Wireless Photoplethysmography Sensor for Continuous Blood Pressure Bio signal Shape Acquisition. J. Sens. 2020, 2020, 7192015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilmisson, H.; Berman, S.; Magnusdottir, S. Sleep apnea diagnosis in children using software-generated apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) derived from data recorded with a single photoplethysmogram sensor (PPG): Results from the Childhood Adenotonsillectomy Study (CHAT) based on cardiopulmonary coupling analysis. Sleep Breath. 2020, 24, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, N.; Guragain, B.; Verma, A.; Archer, L.; Tavakolian, K. Blending Human and Machine: Feasibility of Measuring Fatigue Through the Aviation Headset. Hum. Factors 2020, 62, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Laurentius, T.; Bollheimer, C.; Leonhardt, S.; Antink, C.H. Noncontact Monitoring of Heart Rate and Heart Rate Variability in Geriatric Patients Using Photoplethysmography Imaging. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021, 25, 1781–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasangohar, F.; Davis, E.; Kash, B.A.; Shah, S.R. Remote patient monitoring and telemedicine in neonatal and pediatric settings: Scoping literature review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2018, 20, e295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poh, M.Z.; McDuff, D.J.; Picard, R.W. Advancements in noncontact, multiparameter physiological measurements using a webcam. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sinhal, R.; Singh, K.; Raghuwanshi, M.M. An Overview of Remote Photoplethysmography Methods for Vital Sign Monitoring. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2020, 992, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Hung, C.-C.; Zhao, C.; Lin, C.-L.; Hsu, B.-Y. Learning based Remote Photoplethysmography for Physiological Signal Feedback Control in Fitness Training. In Proceedings of the 15th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Kristiansand, Norway, 9–13 November 2020; pp. 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaunseder, S.; Trumpp, A.; Wedekind, D.; Malberg, H. Cardiovascular assessment by imaging photoplethysmography-a review. Biomed. Tech. 2018, 63, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.W.; Wu, B.J.; Wu, B.F. A Heart Rate Monitoring Framework for Real-World Drivers Using Remote Photoplethysmography. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021, 25, 1397–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.F.; Chu, Y.W.; Huang, P.W.; Chung, M.L. Neural Network Based Luminance Variation Resistant Remote-Photoplethysmography for Driver’s Heart Rate Monitoring. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 57210–57225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, W.F.C.; Lakens, D. Addressing Reproducibility Issues in Remote Photoplethysmography (rPPG) Research: An Investigation of Current Challenges and Release of a Public Algorithm Benchmarking Dataset. 25 June 2021. Available online: https://data.4tu.nl/repository/uuid:2ac74fbd-2276-44ad-aff1-2f68972b7b51 (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Gupta, Y.; Kaur, A.; Arora, A.; Kapoor, S.; Gupta, M. Heart-Rate Evaluation Using Remote Photoplethysmography—A Case Study. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Innovative Computing & Communications (ICICC), Delhi, India, 18 May 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDuff, D.J.; Estepp, J.R.; Piasecki, A.M.; Blackford, E.B. A survey of remote optical photoplethysmography imaging methods. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS, Milano, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 6398–6404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouast, P.V.; Adam, M.T.P.; Chiong, R.; Cornforth, D.; Lux, E. Remote heart rate measurement using low-cost RGB face video: A technical literature review. Front. Comput. Sci. 2018, 12, 858–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Kooij, K.M.; Naber, M. An open-source remote heart rate imaging method with practical apparatus and algorithms. Behav. Res. Methods 2019, 51, 2106–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Pun, T.; Chanel, G. A comparative survey of methods for remote heart rate detection from frontal face videos. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, J. Photoplethysmography and its application in clinical physiological measurement. Physiol. Meas. 2007, 28, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Yan, B.P.-Y.; Dai, W.-X.; Ding, X.-R.; Zhang, Y.-T.; Zhao, N. Multi-wavelength photoplethysmography method for skin arterial pulse extraction. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Haan, G.; Van Leest, A. Improved motion robustness of remote-PPG by using the blood volume pulse signature. Physiol. Meas. 2014, 35, 1913–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsbusch, M.; Blazek, V. Contactless mapping of rhythmical phenomena in tissue perfusion using PPGI. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2002: Physiology and Function from Multidimensional Images, San Diego, CA, USA, 24–26 February 2002; Volume 4683, p. 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevin Zhou, S.; Chellappa, R.; Ramanathan, N. Unconstrained Face Recognition from a Single Image. In The Essential Guide to Image Processing, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, I.; Rawson, A.J.; Schroeder, H.A.; Joseph, N.R. Studies on the estimation of cardiac output in man, and of abnormalities in cardiac function, from the heart’s recoil and the blood’s impacts; the ballistocardiogram. Am. J. Physiol.-Leg. Content 1939, 127, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da He, D.; Winokur, E.S.; Sodini, C.G. A continuous, wearable, and wireless heart monitor using head ballistocardiogram (BCG) and head electrocardiogram (ECG). In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 4729–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, G.; Durand, F.; Guttag, J. Detecting pulse from head motions in video. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 18–23 June 2013; pp. 3430–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viola, P.; Jones, M.J. Robust Real-Time Face Detection. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 57, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Yu, M. Video-based heart rate measurement using head motion tracking and ICA. In Proceedings of the 2013 6th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, CISP, Hangzhou, China, 16–18 December 2013; Volume 1, pp. 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inan, O.T. Recent advances in cardiovascular monitoring using ballistocardiography. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 5038–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidis, I.; Dowdall, J.; Sun, N.; Puri, C.; Fei, J.; Garbey, M. Interacting with human physiology. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2007, 108, 150–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkruysse, W.; Svaasand, L.O.; Nelson, J.S. Remoteplethysmography imaging using ambient light. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 21434–21445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cootes, T.F.; Edwards, G.J.; Taylor, C.J. Active appearance models. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Freiburg, Germany, 2–6 June 1998; pp. 484–498. [Google Scholar]
- Kazemi, V.; Sullivan, J. One millisecond face alignment with an ensemble of regression trees. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Qiao, Y. Joint Face Detection and Alignment Using Multi-Task Cascaded Convolutional Networks. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 1499–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomasi, C.; Kanade, T. Detection and tracking of point features. Tech. Rep. Int. J. Comput. Vision 1991, 9, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, R.J.; Sezan, M.I.; Matthews, K.E. A robust real-time face tracking algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Chicago, IL, USA, 4–7 October 1998; Volume 1, pp. 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, D.; Park, K. ROI analysis for remote photoplethysmography on facial video. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS, Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 4938–4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gastel, M.; Stuijk, S.; de Haan, G. Robust respiration detection from remote photoplethysmography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, M.A.; Malik, G.S.; Saad, N.; Karasfi, B.; Ali, Y.S.; Fofi, D. Optimal source selection for image photoplethysmography. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Taipei, Taiwan, 23–26 May 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasli, H.E.; Gudi, A.; Uyl, M.D. Remote ppg based vital sign measurement using adaptive facial regions Vicarious Perception Technologies Intelligent Systems Lab Amsterdam, University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 1410–1414. [Google Scholar]
- ElMaghraby, A.; Abdalla, M.; Enany, O.; El Nahas, M.Y. Detect and Analyze Face Parts Information using Viola- Jones and Geometric Approaches. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2014, 101, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holton, B.D.; Mannapperuma, K.; Lesniewski, P.J.; Thomas, J.C. Signal recovery in imaging photoplethysmography. Physiol. Meas. 2013, 34, 1499–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousefsaf, F.; Maaoui, C.; Pruski, A. Continuous wavelet filtering on webcam photoplethysmographic signals to remotely assess the instantaneous heart rate. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2013, 8, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Wang, Z.J.; Miao, C. Non-contact driver cardiac physiological monitoring using video data. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE China Summit and International Conference on Signal and Information Processing, ChinaSIP 2015, Chengdu, China, 12–15 July 2015; pp. 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poh, M.Z.; McDuff, D.J.; Picard, R.W. Non-contact, automated cardiac pulse measurements using video imaging and blind source separation. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 10762–10774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, C.; Ohta, Y. Heart rate measurement based on a time-lapse image. Med. Eng. Phys. 2007, 29, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djeldjli, D.; Bousefsaf, F.; Maaoui, C.; Bereksi-Reguig, F. Imaging Photoplethysmography: Signal Waveform Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Data Acquisition and Advanced Computing Systems: Technology and Applications, IDAACS 2019, Metz, France, 18–21 September 2019; Volume 2, pp. 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedekind, D.; Trumpp, A.; Gaetjen, F.; Rasche, S.; Matschke, K.; Malberg, H.; Zaunseder, S. Assessment of blind source separation techniques for video-based cardiac pulse extraction. J. Biomed. Opt. 2017, 22, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mannapperuma, K.; Holton, B.D.; Lesniewski, P.J.; Thomas, J.C. Performance limits of ICA-based heart rate identification techniques in imaging photoplethysmography. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lewandowska, M.; Rumiński, J.; Kocejko, T.; Nowak, J. Measuring pulse rate with a webcam—A non-contact method for evaluating cardiac activity. In Proceedings of the 2011 Federated Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems, FedCSIS, Szczecin, Poland, 18–21 September 2011; pp. 405–410. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Chen, J.; Zhao, G.; Pietikäinen, M. Remote heart rate measurement from face videos under realistic situations. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 4264–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.R.; Gupta, K. Color Intensity: A Study of RPPG Algorithm for Heart Rate Estimation Color Intensity: A Study of RPPG Algorithm for Heart Rate Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Computational Performance Evaluation (ComPE), Shillong, India, 1–3 December 2021; pp. 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Haan, G.; Jeanne, V. Robust pulse rate from chrominance-based rPPG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 2878–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Stuijk, S.; De Haan, G. A Novel Algorithm for Remote Photoplethysmography: Spatial Subspace Rotation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 1974–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDuff, D.; Gontarek, S.; Picard, R.W. Improvements in remote cardiopulmonary measurement using a five-band digital camera. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 2593–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDuff, D.; Gontarek, S.; Picard, R.W. Remote detection of photoplethysmographic systolic and diastolic peaks using a digital camera. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 2948–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Kwan, B.; Lim, C.; Wong, S.; Paramesran, R. Video-based heart rate measurement using a short-time Fourier transform. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing and Communication Systems, Okinawa, Japan, 12–15 November 2013; pp. 704–707. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Po, L.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, R. Motion-Resistant Remote Imaging Photoplethysmography Based on the Optical Properties of Skin. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2015, 25, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, R.; Nasrollahi, K.; Moeslund, T.B. Improved pulse detection from head motions using DCT. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP), Lisbon, Portugal, 5–8 June 2014; IEEE: Lisbon, Portugal, 2014; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; He, T.; Gao, L.; Xu, X.; Hanjalic, A.; Shen, H.T. Unified Binary Generative Adversarial Network for Image Retrieval and Compression. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 2243–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monkaresi, H.; Calvo, R.A.; Yan, H. A machine learning approach to improve contactless heart rate monitoring using a webcam. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2014, 18, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aha, D.W.; Kibler, D.; Albert, M.K. Instance-Based Learning Algorithms. Mach. Learn. 1991, 6, 37–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spetlik, R.; Franc, V.; Cech, J.; Matas, J. Visual heart rate estimation with convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference 2018, BMVC 2018, Newcastle, UK, 3–6 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Estepp, J.R.; Blackford, E.B.; Meier, C.M. Recovering pulse rate during motion artifact with a multi-imager array for non-contact imaging photoplethysmography. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, San Diego, CA, USA, 5–8 October 2014; pp. 1462–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, M.; Peng, B.; Wang, W.; Dong, J. An Accurate LSTM Based Video Heart Rate Estimation Method. In Proceedings of the Chinese Conference on Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision (PRCV), Xi’an, China, 8–11 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Kao, Y.; Hsu, C. Vision-Based Heart Rate Estimation via a Two-Stream Cnn Zhi-Kuan Wang Ying Kao Chiou-Ting Hsu Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 3327–3331. [Google Scholar]
- Paracchini, M.; Marcon, M.; Villa, F.; Zappa, F.; Tubaro, S. Biometric Signals Estimation Using Single Photon Camera and Deep Learning. Sensors 2020, 20, 6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabokrou, M.; Pourreza, M.; Li, X.; Fathy, M.; Zhao, G. Deep-HR: Fast heart rate estimation from face video under realistic conditions. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 186, 115596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, Y.Y.; Lee, Y.A.; Hsu, C.T.; Chang, S.H. Siamese-rPPG network: Remote photoplethysmography signal estimation from face videos. In Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on Applied Computing, Brno, Czech Republic, 30 March–3 April 2020; pp. 2066–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 11206, pp. 356–373. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, X.; Han, H.; Shan, S.; Chen, X. SynRhythm: Learning a Deep Heart Rate Estimator from General to Specific. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Beijing, China, 18–20 August 2018; pp. 3580–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Shan, S.; Han, H.; Chen, X. RhythmNet: End-to-End Heart Rate Estimation from Face via Spatial-Temporal Representation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 2409–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, X.; Han, H.; Shan, S.; Chen, X. VIPL-HR: A Multi-modal Database for Pulse Estimation from Less-Constrained Face Video. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 11365, pp. 562–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Z.; Li, X.; Zhao, G. Remote photoplethysmography signal measurement from facial videos using spatio-temporal networks. In Proceedings of the 30th British Machine Vision Conference 2019, BMVC 2019, Cardiff, UK, 9–12 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, Z.; Fromm, J.; Xu, X.; Patel, S.; McDuff, D. MetaPhys: Few-shot adaptation for non-contact physiological measurement. In Proceedings of the ACM CHIL 2021—2021 ACM Conference on Health, Inference, and Learning, Virtual Event, 8–9 April 2021; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Peng, W.; Li, X.; Hong, X.; Zhao, G. Remote heart rate measurement from highly compressed facial videos: An end-to-end deep learning solution with video enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Z.; Li, X.; Niu, X.; Shi, J.; Zhao, G. AutoHR: A Strong End-to-End Baseline for Remote Heart Rate Measurement with Neural Searching. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2020, 27, 1245–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Ortega, J.; Fierrez, J.; Morales, A.; Diaz, D. A Comparative Evaluation of Heart Rate Estimation Methods using Face Videos. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 44th Annual Computers, Software, and Applications Conference, COMPSAC 2020, Madrid, Spain, 13–17 July 2020; pp. 1438–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousefsaf, F.; Pruski, A.; Maaoui, C. 3D convolutional neural networks for remote pulse rate measurement and mapping from facial video. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, M.; Qian, F.; Guo, D.; Wang, X.; He, L.; Ren, F. ETA-rPPGNet: Effective Time-Domain Attention Network for Remote Heart Rate Measurement. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 2506212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDuff, D. Deep super-resolution for recovering physiological information from videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 1448–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowara, E.M.; McDuff, D.; Veeraraghavan, A. Systematic analysis of video-based pulse measurement from compressed videos. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Ravelo-Garcia, A.G.; Morgado-Dias, F. A Motion and Illumination Resistant Non-contact Method using Undercomplete Independent Component Analysis and Levenberg-Marquardt Algorithm. In IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics; IEEE: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paracchini, M.; Marcon, M.; Villa, F.; Cusini, I.; Tubaro, S. Fast Skin Segmentation on Low-Resolution Grayscale Images for Remote PhotoPlethysmoGraphy. IEEE MultiMedia 2022, 29, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelstra, S.; Muhl, C.; Soleymani, M.; Lee, J.; Yazdani, A.; Ebrahimi, T.; Pun, T.; Nijholt, A.; Patras, I. DEAP: A Database for Emotion Analysis; Using Physiological Signals. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2012, 3, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soleymani, M.; Lichtenauer, J.; Pun, T.; Pantic, M. A multimodal database for affect recognition and implicit tagging. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2012, 3, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gudi, A.; Bittner, M.; van Gemert, J. Real-time webcam heart rate and variability estimation with clean ground truth for evaluation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanfland, S.; Paul, M. Video Format Dependency of PPGI Signals. Poster, 1–6. 2016. Available online: http://poseidon2.feld.cvut.cz/conf/poster/poster2016/proceedings/Section_BI/BI_007_Hanfland.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2022).
- Zhao, C.; Lin, C.L.; Chen, W.; Li, Z. A novel framework for remote photoplethysmography pulse extraction on compressed videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowara, E.M.; McDuff, D.; Veeraraghavan, A. A meta-analysis of the impact of skin tone and gender on non-contact photoplethysmography measurements. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 284–285. [Google Scholar]
- Dasari, A.; Prakash, S.K.A.; Jeni, L.A.; Tucker, C.S. Evaluation of biases in remote photoplethysmography methods. NPJ Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, P.; Kabra, K.; Karinca, D.; Lahiri, S.; Srivastava, D.; Kulkarni, K.; Chen, T.; Cannesson, M.; Jalilian, L.; Kadambi, A. Diverse R-PPG: Camera-based heart rate estimation for diverse subject skin-tones and scenes. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.12769. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Li, B.; Peng, J.; Jiang, W. Multi-hierarchical Convolutional Network for Efficient Remote Photoplethysmograph Signal and Heart Rate Estimation from Face Video Clips. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.02260. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Li, X. Privacy-Phys: Facial Video-Based Physiological Modification for Privacy Protection. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2022, 29, 1507–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liao, X.; Wu, M. PulseEdit: Editing Physiological Signals in Facial Videos for Privacy Protection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2022, 17, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Publication | Preprocessing | Signal Extraction and HR Estimation Methods | Database | Performance and Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Verkruysse, 2008) | Manual | Bandpass filter, FFT | Self-collected | Recorded with a simpledigital camera and ambient light, performance measured qualitatively |
| (Poh, 2010) | Automated face tracker faces (Viola and Jones (VJ), Lienhart and Mad) | ICA, FFT | Self-collected | With movement artifacts, root mean square deviation (RMSE): 4.63 bpm |
| (Poh, 2011) | Automated face tracker | ICA, five-points moving average filter, and bandpass filter | Self-collected | RMSE: 1.24 bpm Correlation coefficient: 1.00 |
| (Lewandowska, 2011) | Manual | Principle component analysis (PCA) | Self-collected | Pulse rate from two-color channels |
| (Haan, 2013) | Automatic face detection | Chrominance-based approach (fixedsignal combination, FFT) | Self-collected | RMSE: 0.4 bpm |
| (Mannaperuma, 2015) | Automatic face detection | ICA, the channel with the strongest blood volume pulse signal is selected, inverted, and interpolated, and then peaks are detected | Self-collected | Find band camera sensor (correlation: 1.00) |
| (Wang, 2015) | Face detection by VJ | FFT, bandpass, and adaptive bandpass, motion-resistant Remote PPG method | Self-collected | Peak detection performance compared with ICA method using bland Altman plot |
| (Wang, 2015) | Manual | Spatial pruning + temporal filtering | Self-collected | SNR improvement 3.34 to 6.74 dB on state-of-the-art methods |
| (Wang, 2016) | Spatial distribution of skin pixel | 2SR algorithm | Self-collected | Results compared with ICA, CHROM, AND PBV SNR-6.55 |
| (Yu, 2019) | Spatial ROI selection and tracking | Novel semi-blind source extraction method, MAICA | UBFC-rPPG MMSE-HR | UBFC-rPPG (MAE-O.55BPM) MMSE-HR (MAE-3.91) |
| (Fouad, 2019) | Automatic face tracking | Uses BSS algorithm, FT | Self-collected | Studied factors affecting accuracy |
| (Gudi, 2020) | Active appearance model (AAM)Head orientation | Unsupervised method operates in real time FFT | PURE VIPL-HR COHAFACE | 0.34 bpm 0.57 bpm 0.46 bpm |
| Serial No | Paper | Network | Description | Datasets |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (Weixuan, 2018) | DeepPhys | First end-to-end network | RGB VIDEO 1 RGB VIDEO 11 MAHNOB-HCI IR VIDEO |
| 2 | (Niu, 2018) | SynRhythm | Transfer learning strategy and synthetic rhythm signals | MAHNOB-HCI MMSE-HR |
| 3 | (Spetlik. R, 2018) | HR-CNN | Uses 2-step CNN | MAHNOB-HCI PURE COHFACE |
| 4 | (Wang, 2020) | Two stream CNN | Two-stream end-to-end network | COHFACE |
| 5 | (Niu.X, 2020) | RhythmNet | End-to-end spatial-temporal representation | MAHNOB-HCIMMSE-HR VIPL-HR |
| 6 | (Yu.Z, 2020) | AutoHR | Neural architecture search (NAS) | MAHNOB-HCI MMSE-HR VIPL-HR |
| 7 | (Min Hu, 2021) | ETA-rPPGNet | Time domain attention mechanism | PURE MMSE-HR COHFACE UBFC-rPPG |
| 8 | (Hao LU, 2021) | NAS-HR | A neural network-based method | PURE VIPL-HR |
| Dataset | Subject | Camera | Physiological Signal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PURE | 10 Subjects 59 Videos | 480p@30fps Lossless PNG images | Ground truth PPG @60 Hz | Recorded Movement such as talking, rotation, translation |
| MAHNOB HCI | 27 Subjects 627 Videos | 780 × 580P@51fps H.264 format | Ground Truth PPG @256 Hz | Subject recorded while watching video stimuli |
| COHFACE | 40 Subjects 164 Videos | 480p@20fps MPEG4 Part 2format | Ground Truth PPG @256 Hz | Subject recorded illuminated by a spotlight and natural light |
| MMSE-HR | 40 Subjects 102 Videos | 1040 × 1392@25fps JPEG Images | Instantaneous HR@1 kHz | Part of a large multimodal corpus, subject exhibit facial expressions |
| Vicar PPG | 10 Subjects 20 Videos | 720p@30fps H.264 format | Ground Truth PPG @30 Hz | Subject recorded before and after workout |
| UBFC—RPPG | 42 Subjects 42 Videos | 480p@30fps Raw video format (lossless) | Ground Truth PPG @30/60 Hz | Subject recorded while playing game |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Premkumar, S.; Hemanth, D.J. Intelligent Remote Photoplethysmography-Based Methods for Heart Rate Estimation from Face Videos: A Survey. Informatics 2022, 9, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics9030057
Premkumar S, Hemanth DJ. Intelligent Remote Photoplethysmography-Based Methods for Heart Rate Estimation from Face Videos: A Survey. Informatics. 2022; 9(3):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics9030057
Chicago/Turabian StylePremkumar, Smera, and Duraisamy Jude Hemanth. 2022. "Intelligent Remote Photoplethysmography-Based Methods for Heart Rate Estimation from Face Videos: A Survey" Informatics 9, no. 3: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics9030057
APA StylePremkumar, S., & Hemanth, D. J. (2022). Intelligent Remote Photoplethysmography-Based Methods for Heart Rate Estimation from Face Videos: A Survey. Informatics, 9(3), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics9030057







