Numerical Description of Jet and Duct Ventilation in Underground Garage after LPG Dispersion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Study
2.2. Numerical Model
3. Results and Discussion
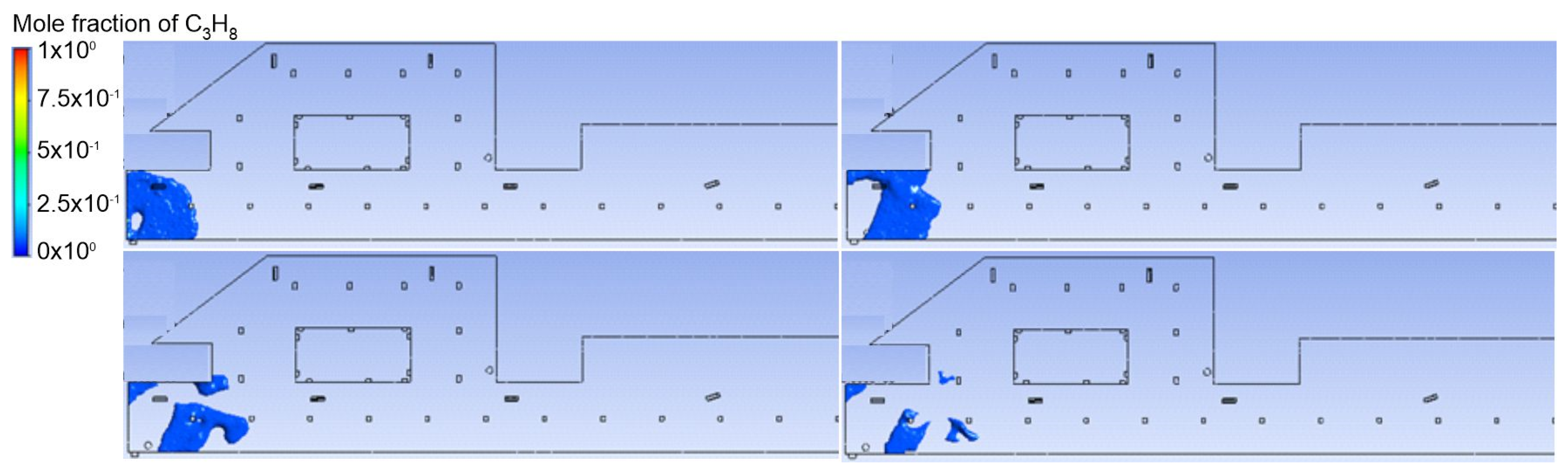
3.1. Duct Ventilation
3.2. Jet Ventilation
3.3. Limitations to the Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yassin, M.F. Experimental study on contamination of building exhaust emissions in urban environment under changes of stack locations and atmospheric stability. Energy Build. 2013, 62, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabunshchikov, Y.A.; Shkarpet, V.E.; Kapko, D.V.; Brodach, M.M.; Kochariantc, K.V. Installing Local Recirculation Air Diffusers During Building Deep Renovation Reduces Energy Consumption of Ventilation Systems. Energy Procedia 2016, 96, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantinou, K.; Chaloulakou, A.; Duci, A.; Vlachakis, N.; Markatos, N. Air quality in an underground garage: Computational and experimental investigation of ventilation effectiveness. Energy Build. 2003, 35, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladyszewska-Fiedoruk, K.; Nieciecki, M. Indoor air quality in a multi-car garage. Energy Procedia 2016, 95, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tsai, P.-Y.; Weisel, C.P. Penetration of Evaporative Emissions into a Home from an M85-Fueled Vehicle Parked in an Attached Garage. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2000, 50, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majder-Lopatka, M.; Wesierski, T.; Dmochowska, A.; Salamonowicz, Z.; Polanczyk, A. The influence of hydrogen on the indications of the electrochemical carbon monoxide sensors. Sustainability 2020, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhu, Z.; Jiao, Z.; Mi, H.; Wang, Q. Characteristics of fire and smoke in the natural gas cabin of urban underground utility tunnels based on CFD simulations. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 109, 103748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterman, S.; Jia, C.; Hatzivasilis, G. Migration of volatile organic compounds from attached garages to residences: A major exposure source. Environ. Res. 2007, 104, 224–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faramarzi, A.; Lee, J.; Stephens, B.; Heidarinejad, M. Assessing ventilation control strategies in underground parking garages. Build. Simul. 2021, 14, 701–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroidis, I.; Griffiths, R.F.; Jones, C.D.; Biltoft, C. Experimental investigation of the residence of contaminants in the wake of an obstacle under different stability conditions. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckland, I.G. Explosions of gas layers in a room size chamber. Inst. Chem. Eng. Symp. Ser. 1980, 58, 289–304. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, Y.W.N.Y.; Chow, W.-k.; Show, C.L.; Cheng, F.M. Numerical simulations on explosion of leaked liquefied petroleum gas in a garage. Build. Simul. 2017, 10, 755–768. [Google Scholar]
- Krawczyk, D.A. Theoretical and real effect of thermal modernization 2—A case study. Energy Build 2014, 81, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano EmrysScarponi, G.E.; Pastor, E.; Planas, E.; Cozzani, V. Analysis of the impact of wildland-urban-interface fires on LPG domestic tanks. Saf. Sci. 2020, 124, 104588. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, W.K. On ventilation design for underground car parks. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 1995, 10, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamonowicz, Z.; Majder-Lopatka, M.; Dmochowska, A.; Piechota-Polanczyk, A.; Polanczyk, A. Numerical Analysis of Smoke Spreading in a Medium-High Building under Different Ventilation Conditions. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannaa, S.R.; Hansenb, O.R.; Ichard, M.; Strimaitisc, D. CFD model simulation of dispersion from chlorine railcar releases in industrial and urban areas. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanczyk, A.; Salamonowicz, Z. Computational modeling of gas mixture dispersion in a dynamic setup – 2d and 3d numerical approach. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 44, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieminska-Stolarska, A.; Polanczyk, A.; Zbicinski, I. 3-D CFD simulations of hydrodynamics in the Sulejow dam reservoir. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2015, 63, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, Z.; Qian, X.; Huang, P. Long-term consequence and vulnerability assessment of thermal radiation hazard from LNG explosive fireball in open space based on full-scale experiment and PHAST. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2017, 46, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoman, D.C.; O’Kula, K.R.; Laul, J.C.; Davis, M.W.; Knecht, K.D. Comparison of ALOHA and EPIcode for Safety Analysis Applications. J. Chem. Health Saf. 2006, 13, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanczyk, A.; Wawrzyniak, P.; Zbicinski, I. CFD analysis of dust explosion relief system in the counter-current industrial spray drying tower. Dry. Technol. 2013, 31, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamonowicz, Z.; Krauze, A.; Majder-Lopatka, M.; Dmochowska, A.; Piechota-Polanczyk, A.; Polanczyk, A. Numerical Reconstruction of Hazardous Zones after the Release of Flammable Gases during Industrial Processes. Processes 2021, 9, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawrzyniak, P.; Podyma, M.; Zbicinski, I.; Bartczak, Z.; Polanczyk, A.; Rabaeva, J. Model of Heat and Mass Transfer in an Industrial CounterCurrent Spray-Drying Tower. Dry. Technol. 2012, 30, 1274–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Hur, N.; Kang, S.; Lee, E.D.; Lee, K.B. A CFD simulation of hydrogen dispersion for the hydrogen leakage from a fuel cell vehicle in an underground parking garage. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 8084–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigas, F.; Sklavounos, S. Evaluation of hazards associated with hydrogen storage facilities. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2005, 30, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H.; Ran, G.; Zhang, F.; Yang, H. Augmentation of tunnel-air convective heat transfer forced by duct ventilation in a geothermal construction tunnel. Build. Environ. 2021, 205, 108219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dai, X.; Weia, J.; Ai, Z.; Fan, Y.; Tang, L.; Jin, T.; Ge, J. Numerical comparison of the efficiency of mixing ventilation and impinging jet ventilation for exhaled particle removal in a model intensive care unit. Build. Environ. 2021, 200, 107955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanczyk, A.; Salamonowicz, Z.; Majder-Lopatka, M.; Dmochowska, A.; Jarosz, W.; Matuszkiewicz, R.; Makowski, R. 3D Simulation of Chlorine Dispersion in Rrural Area. Annu. Set Environ. Prot. 2018, 20, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Bottcher, N.; Singh, A.K.; Kolditz, O.; Liedl, R. Non-isothermal, compressible gas flow for the simulation of an enhanced gas recovery application. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2012, 236, 4933–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontiggiaa, M.; Derudi, M.; Alba, M.; Scaioni, M.; Rota, R. Hazardous gas releases in urban areas: Assessment of consequences through CFD modelling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.-X.; Mo, S.-J.; Liang, D. Numerical Simulation of Natural Gas Release and Risk Zone Forecast in Urban Areas. Procedia Eng. 2014, 71, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gavelli, F.; Bullister, E.; Kytomaa, H. Application of CFD (Fluent) to LNG spills into geometrically complex environments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 159, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sklavounos, S.; Roigas, F. Simulation of Coyote series trials—Part I: CFD estimation of non-isothermal LNG releases and comparison with box-model predictions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 1434–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staveckis, A.; Borodinecs, A. Impact of impinging jet ventilation on thermal comfort and indoor air quality in office buildings. Energy Build. 2021, 235, 110738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y. Numerical and experimental investigation of thermal performance in data center with different deflectors for cold aisle containment. Build. Environ. 2021, 200, 107961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, J.T.G.; Bonilla, H.G.; Rodríguez-Betancourtt, V.M.; Bonilla, A.G.; Zamora, A.C.; Alonso, O.B.; Ortega, J.A.R. A Gas Sensor for Application as a Propane Leak Detector. J. Sens. 2021, 2021, 8871166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




















| Mesh Range | Achieved Level of Convergence |
|---|---|
| 0.20–0.15 m | non converging results |
| 0.15–0.10 m | continuity 1 × 10−5 |
| x-velocity 1 × 10−3 | |
| y-velocity 1 × 10−3 | |
| z-velocity 1 × 10−3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salamonowicz, Z.; Majder-Lopatka, M.; Dmochowska, A.; Piechota-Polanczyk, A.; Polanczyk, A. Numerical Description of Jet and Duct Ventilation in Underground Garage after LPG Dispersion. Processes 2022, 10, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10010053
Salamonowicz Z, Majder-Lopatka M, Dmochowska A, Piechota-Polanczyk A, Polanczyk A. Numerical Description of Jet and Duct Ventilation in Underground Garage after LPG Dispersion. Processes. 2022; 10(1):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10010053
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalamonowicz, Zdzislaw, Malgorzata Majder-Lopatka, Anna Dmochowska, Aleksandra Piechota-Polanczyk, and Andrzej Polanczyk. 2022. "Numerical Description of Jet and Duct Ventilation in Underground Garage after LPG Dispersion" Processes 10, no. 1: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10010053
APA StyleSalamonowicz, Z., Majder-Lopatka, M., Dmochowska, A., Piechota-Polanczyk, A., & Polanczyk, A. (2022). Numerical Description of Jet and Duct Ventilation in Underground Garage after LPG Dispersion. Processes, 10(1), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10010053








