Enhancement of Digestion Resistance and Glycemic Control of Corn Starch through Conjugation with Gallic Acid and Quercetin Using the Free Radical Grafting Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Phenolic–Starch Complexes Preparation
2.2. Determination of DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
2.3. Determination of Water Solubility Index and Swelling Power
2.4. Determination of Pasting Properties
2.5. Determination of Resistance Starch Content
2.6. Determination of In Vivo Postprandial Glycemic Responses
2.7. UPLC-Q-TOF-MS Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
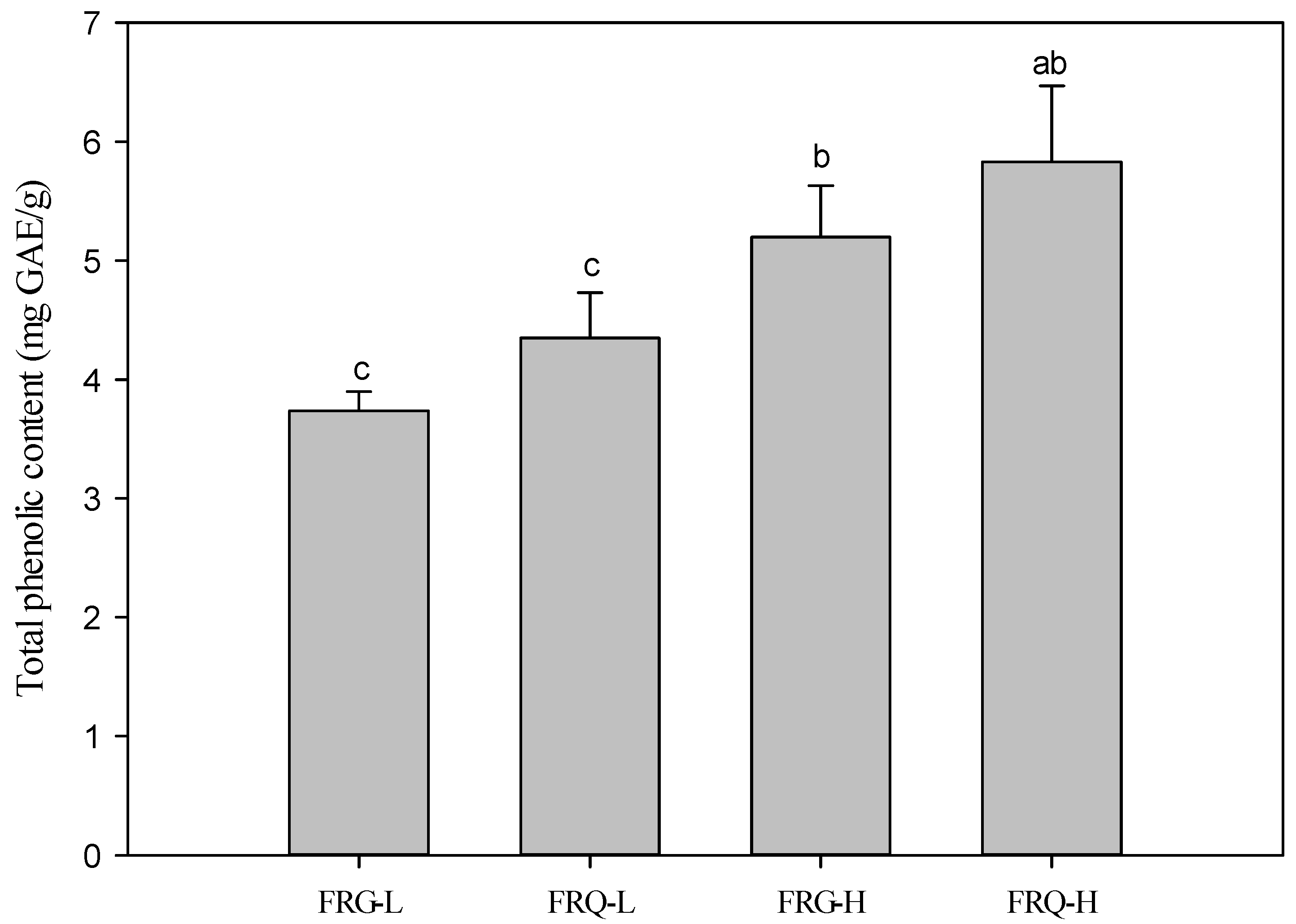
3.1. Phenolic Compound-Binding Capacity in the Complex
3.2. Antioxidant Activity of Phenolic–Starch Complexes
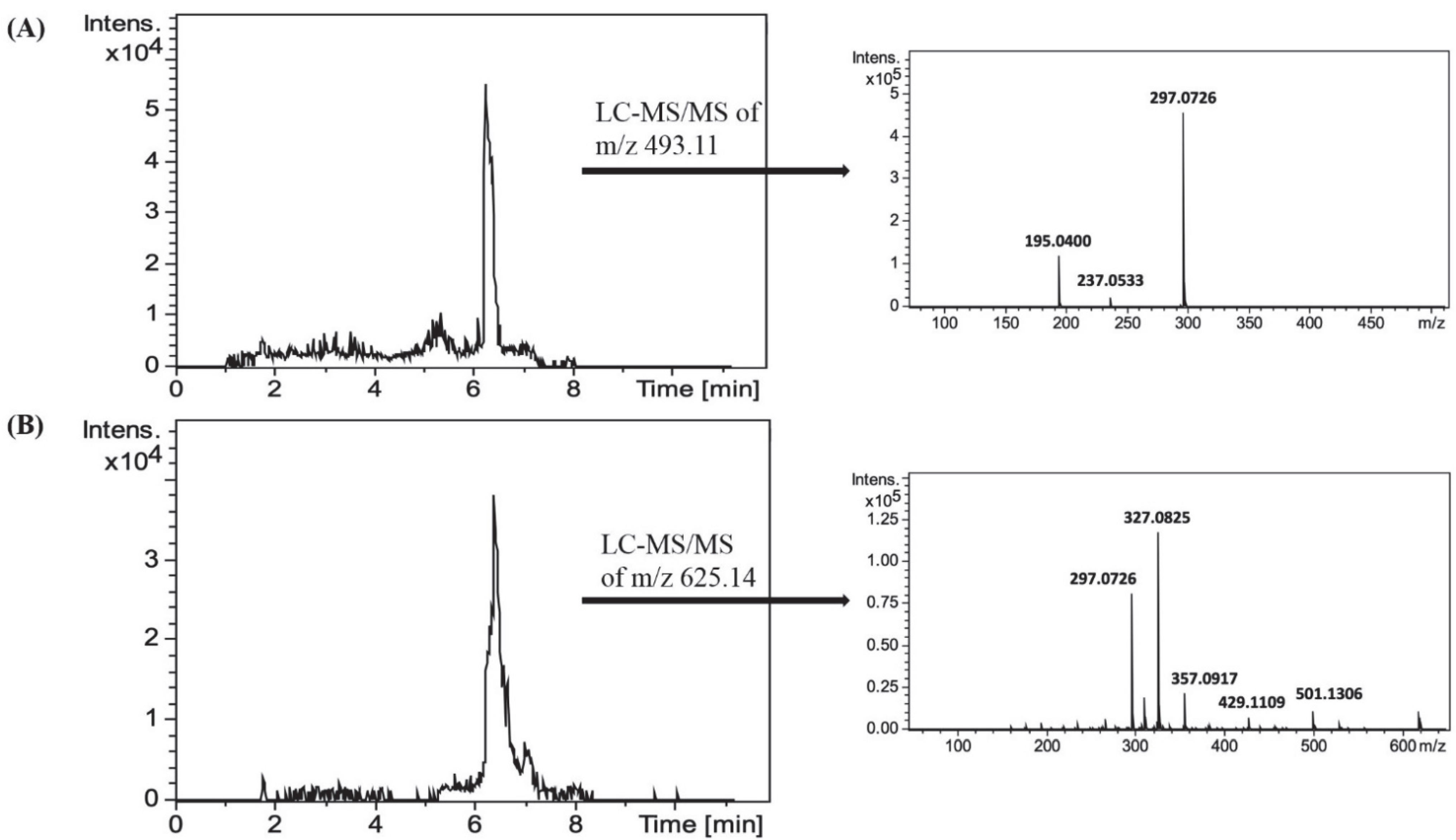
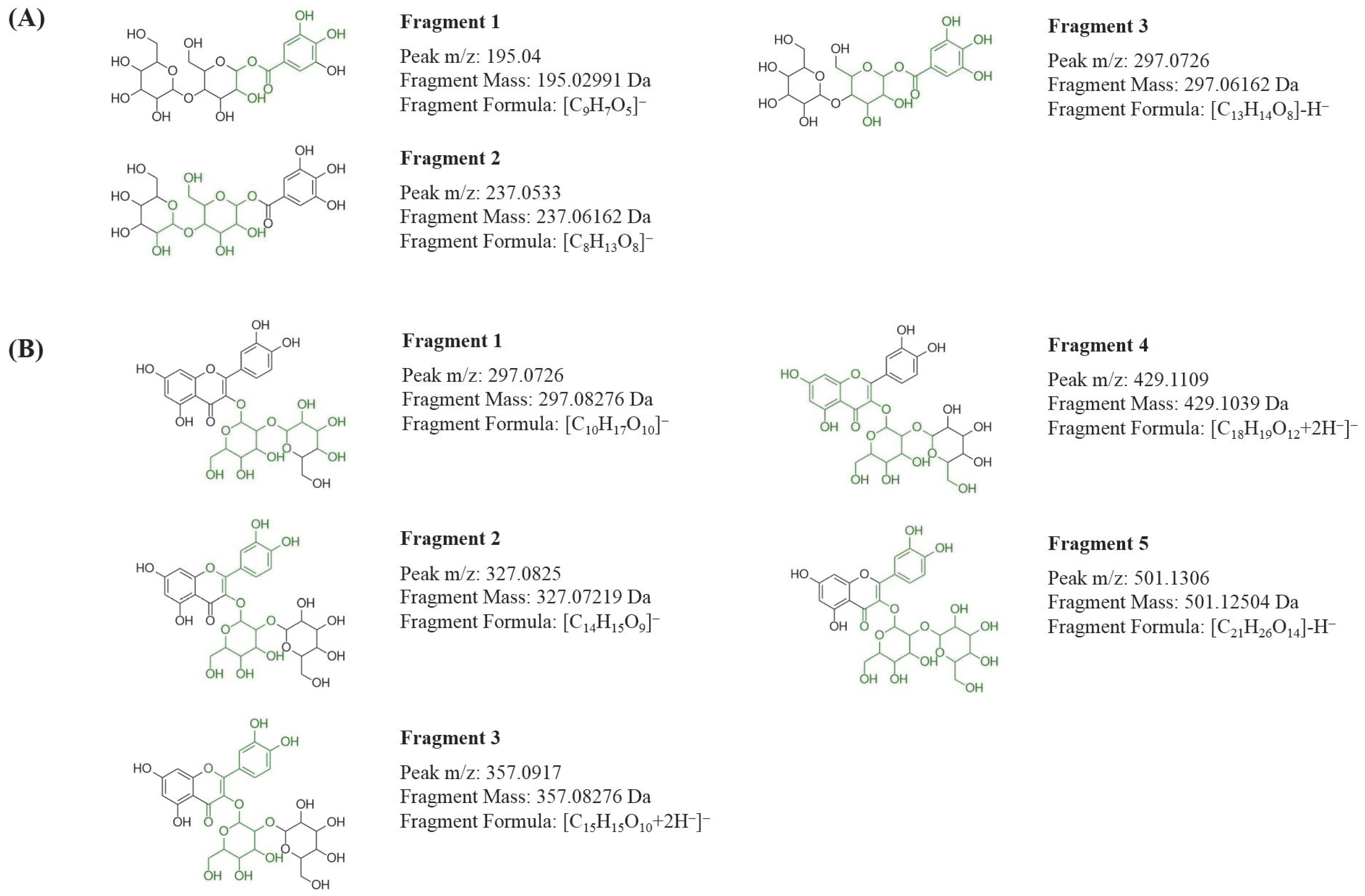
3.3. Characterization of Interactions by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS
3.4. Resistant to Starch Digestibility
3.5. In Vivo Starch Digestibility
3.6. Swelling Ability and Water Solubility Index
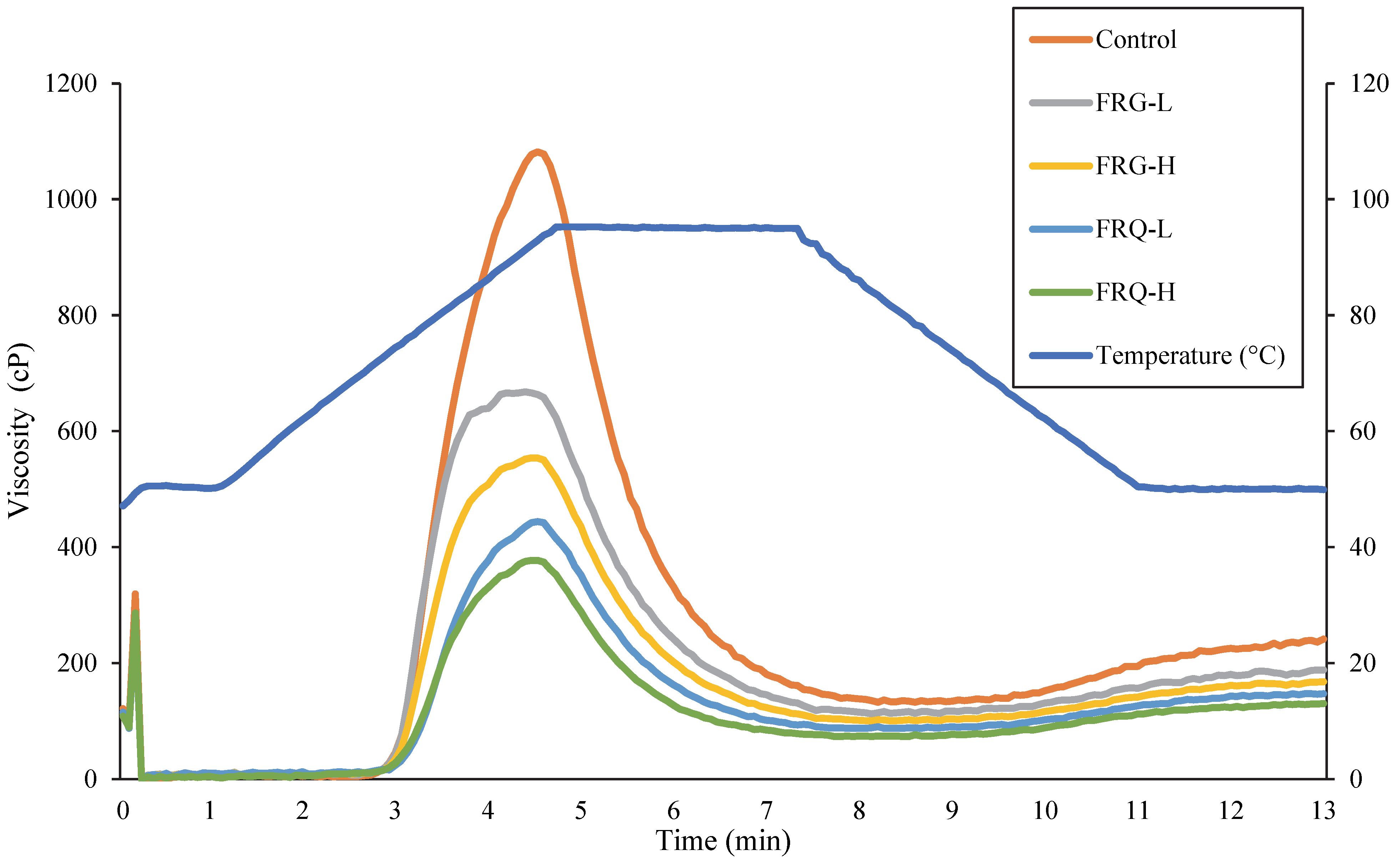
3.7. Pasting Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Church, T.; Martin, C.K. The obesity epidemic: A consequence of reduced energy expenditure and the uncoupling of energy intake? Obesity 2018, 26, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raigond, P.; Ezekiel, R.; Raigond, B. Resistant starch in food: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 1968–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birt, D.F.; Boylston, T.; Hendrich, S.; Jane, J.L.; Hollis, J.; Li, L.; McClelland, J.; Moore, S.; Phillips, G.J.; Rowling, M.; et al. Resistant starch: Promise for improving human health. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 587–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.Y.; Sun, N.N.; Chau, C.F. Application of corona electrical discharge plasma on modifying the physicochemical properties of banana starch indigenous to Taiwan. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, S.; Vittorio, O.; Cirillo, G.; Boyer, C. Enhancing the therapeutic effects of polyphenols with macromolecules. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 1529–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spizzirri, U.G.; Parisi, O.I.; Iemma, F.; Cirillo, G.; Puoci, F.; Curcio, M.; Picci, N. Antioxidant–polysaccharide conjugates for food application by eco-friendly grafting procedure. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 7, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, G.; Puoci, F.; Iemma, F.; Curcio, M.; Parisi, O.I.; Spizzirri, U.G.; Altimari, I.; Picci, N. Starch-quercetin conjugate by radical grafting: Synthesis and biological characterization. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2012, 17, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woranuch, S.; Yoksan, R.; Akashi, M. Ferulic acid-coupled chitosan: Thermal stability and utilization as an antioxidant for biodegradable active packaging film. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arizmendi-Cotero, D.; Villanueva-Carvajal, A.; Gómez-Espinoza, R.M.; Dublán-García, O.; Dominguez-Lopez, A. Radical scavenging activity of an inulin-gallic acid graft and its prebiotic effect on Lactobacillus acidophilus in vitro growth. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 29, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Koecher, K.; Hansen, L.; Ferruzzi, M.G. Phenolics from whole grain oat products as modifiers of starch digestion and intestinal glucose transport. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 6831–6839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Yong, H.; Kan, J.; Zhang, N.; Jin, C. Preparation, characterization, digestibility and antioxidant activity of quercetin grafted Cynanchum auriculatum starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Vásquez, M.J.; Valenzuela-Buitimea, E.L.; Plascencia-Jatomea, M.; Encinas-Encinas, J.C.; Rodríguez-Félix, F.; Sánchez-Valdes, S.; Rosas-Burgos, E.C.; Ocaño-Higuera, V.M.; Graciano-Verdugo, A.Z. Functionalization of chitosan by a free radical reaction: Characterization, antioxidant and antibacterial potential. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 155, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, N.; Deng, Z.; Tang, C.; Liu, C.; Luo, S.; Chen, T.; Hu, X. Formation, structure and properties of the starch-polyphenol inclusion complex: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuberti, G.; Rocchetti, G.; Lucini, L. Interactions between phenolic compounds, amylolytic enzymes and starch: An updated overview. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2020, 31, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabehdar, S.K.; Aghjehgheshlagh, F.M.; Navidshad, B.; Mahdavi, A.; Staji, H. In vitro antimicrobial effect of phenolic extracts and resistant starch on Escherichia coli, Streptococcus spp., Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus spp. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2019, 25, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pu, H.; Liu, S.; Kan, J.; Jin, C. Synthesis, characterization, bioactivity and potential application of phenolic acid grafted chitosan: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 999–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, M.; Puoci, F.; Iemma, F.; Parisi, O.I.; Cirillo, G.; Spizzirri, U.G.; Picci, N. Covalent insertion of antioxidant molecules on chitosan by a free radical grafting procedure. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 5933–5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lu, J.F.; Kan, J.; Wen, X.Y.; Jin, C.H. Synthesis, characterization and in vitro anti-diabetic activity of catechin grafted inulin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 64, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H.L.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhang, Y.; He, C.; Ji, X.; Li, H. Antioxidant activity of ethanolic extract of Cortex fraxini and use in peanut oil. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardestani, A.; Yazdanparast, R. Antioxidant and free radical scavenging potential of Achillea santolina extracts. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Huang, Y.W.; Wu, M.Z.; Wu, T.Y.; Lai, P.S.; Sun, N.N.; Saw, C.Y.; Li, C.W.; Chau, C.F. Enhanced resistance to amylolysis in rice kernels through interaction with chlorogenic acid. Processes 2021, 9, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.; Altman, D.; Campbell, M.; Royston, P. Analysis of serial measurements in medical research. BMJ 1990, 300, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopjar, M.; Lončarić, A.; Mikulinjak, M.; Šrajbek, Ž.; Šrajbek, M.; Pichler, A. Evaluation of antioxidant interactions of combined model systems of phenolics in the presence of sugars. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 1934578X1601101008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Jiménez, J.; Saura-Calixto, F. Macromolecular antioxidants or non-extractable polyphenols in fruit and vegetables: Intake in four European countries. Int. Food Res. J. 2015, 74, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ma, Q.; Cheng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Sun, J. Development of chitosan/potato peel polyphenols nanoparticles driven extended-release antioxidant films based on potato starch. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 31, 100793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tian, J.; Fang, H.; Zhang, H.; Kong, X.; Wu, D.; Zheng, J.; Liu, D.; Ye, X.; Chen, S. Physicochemical and digestion properties of potato starch were modified by complexing with grape seed proanthocyanidins. Molecules 2020, 25, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Si, H.; Jia, Z.; Liu, D. Dietary anti-aging polyphenols and potential mechanisms. Antioxidants 2020, 10, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Caravaca, A.M.; López-Cobo, A.; Verardo, V.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A. HPLC-DAD-q-TOF-MS as a powerful platform for the determination of phenolic and other polar compounds in the edible part of mango and its by-products (peel, seed, and seed husk). Electrophoresis 2016, 37, 1072–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, J.; Shahidi, F. Identification and quantification of soluble and insoluble-bound phenolics in lentil hulls using HPLC-ESI-MS/MS and their antioxidant potential. Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, H.A.R.; Gutiérrez, T.J.; Bello-Pérez, L.A. Can starch-polyphenol V-type complexes be considered as resistant starch? Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 124, 107226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oboh, G.; Ademosun, A.O.; Ayeni, P.O.; Omojokun, O.S.; Bello, F. Comparative effect of quercetin and rutin on α-amylase, α-glucosidase, and some pro-oxidant-induced lipid peroxidation in rat pancreas. Comp. Clin. Path. 2015, 24, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleixandre, A.; Gil, J.V.; Sineiro, J.; Rosell, C.M. Understanding phenolic acids inhibition of α-amylase and α-glucosidase and influence of reaction conditions. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, P.; Vijayakumar, S.; Kothandaraman, S.; Palani, M. Anti-diabetic activity of quercetin extracted from Phyllanthus emblica L. fruit: In silico and in vivo approaches. J. Pharm. Anal. 2018, 8, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Tang, G.; Zhang, C.; Wang, N.L.; Feng, Y. Gallic acid and diabetes mellitus: Its association with oxidative stress. Molecules 2021, 26, 7115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.J.; Wang, L. Physicochemical properties of common and waxy corn starches oxidized by different levels of sodium hypochlorite. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 52, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaratne, A.; Corke, H. Influence of prior acid treatment on acetylation of wheat, potato and maize starches. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.; Huang, L.; Jia, X.; Huang, F.; Liu, L. Physicochemical interactions between rice starch and different polyphenols and structural characterization of their complexes. LWT 2020, 125, 109227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, R.E.; Willett, J.L. Water soluble oxidized starches by peroxide reactive extrusion. Ind. Crops. Prod. 1997, 7, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunaratne, R.; Zhu, F. Physicochemical interactions of maize starch with ferulic acid. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Dai, M.; Huang, Y.; Jin, R.; Shang, D. Effects of high pressure homogenization on rheological properties of rice starch. CYTA J. Food 2019, 17, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rosa Zavareze, E.; Dias, A.R.G. Impact of heat-moisture treatment and annealing in starches: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, N.; Sharma, S.; Sahni, P.; Singh, B.; Sharma, S.P. Nutritional composition, techno-functionality, in-vitro starch digestibility, structural characteristics and storage stability of sweet potato flour and mash supplemented specialty pasta. LWT 2022, 168, 113886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, P.V.; Morita, N. Physicochemical properties of hydroxypropylated and cross-linked starches from A-type and B-type wheat starch granules. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 59, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Cai, Y.Z.; Sun, M.; Corke, H. Effect of phytochemical extracts on the pasting, thermal, and gelling properties of wheat starch. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Hu, X.; Luo, S.; Liu, W.; Chen, J.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, C. Properties of starch after extrusion: A review. Starke 2018, 70, 1700110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petchoo, J.; Jittinandana, S.; Tuntipopipat, S.; Ngampeerapong, C.; Tangsuphoom, N. Effect of partial substitution of wheat flour with resistant starch on physicochemical, sensorial and nutritional properties of breadsticks. Int. J. Food Sci. 2021, 56, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Samples | Resistant Starch (g/100 g) | AUC# |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 3.0 ± 0.4 d | 416 ± 16 b |
| FRG-L | 6.9 ± 1.2 c | 405 ± 27 b |
| FRQ-L | 7.7 ± 1.0 c | 389 ± 17 ab |
| FRG-H | 11.6 ± 1.3 b | 383 ± 33 ab |
| FRQ-H | 15.3 ± 1.0 a | 367 ± 13 a |
| Samples | Swelling Power (g/g) | Water Solubility (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 12.0 ± 0.8 cd | 30.1 ± 2.0 c |
| FRG-L | 12.7 ± 0.9 bc | 46.0 ± 2.0 a |
| FRQ-L | 11.5 ± 0.2 d | 42.6 ± 0.6 b |
| FRG-H | 14.3 ± 0.5 a | 48.2 ± 3.4 a |
| FRQ-H | 13.2 ± 0.7 b | 47.7 ± 2.2 a |
| Samples | Peak Viscosity (cP) | Breakdown Viscosity (cP) | Final Viscosity (cP) | Setback Viscosity (cP) | Pasting Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1066 ± 7 e | 950 ± 7 e | 221 ± 2 e | 109 ± 3 d | 72.5 ± 0.3 a |
| FRG-L | 640 ± 6 d | 552 ± 4 d | 163 ± 3 d | 75 ± 2 c | 72.9 ± 0.4 a |
| FRQ-L | 424 ± 3 c | 359 ± 2 bc | 126 ± 2 b | 62 ± 4 a | 75.9 ± 0.4 c |
| FRG-H | 416 ± 3 b | 356 ± 7 b | 132 ± 2 c | 69 ± 3 b | 74.5 ± 0.3 b |
| FRQ-H | 352 ± 3 a | 306 ± 2 a | 111 ± 3 a | 60 ± 4 a | 76.0 ± 0.1 c |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, T.-Y.; Sun, N.-N.; Chan, Z.; Chen, C.-J.; Wu, Y.-C.; Chau, C.-F. Enhancement of Digestion Resistance and Glycemic Control of Corn Starch through Conjugation with Gallic Acid and Quercetin Using the Free Radical Grafting Method. Processes 2022, 10, 2610. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10122610
Wu T-Y, Sun N-N, Chan Z, Chen C-J, Wu Y-C, Chau C-F. Enhancement of Digestion Resistance and Glycemic Control of Corn Starch through Conjugation with Gallic Acid and Quercetin Using the Free Radical Grafting Method. Processes. 2022; 10(12):2610. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10122610
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Tsung-Yen, Nan-Nong Sun, Zu Chan, Chao-Jung Chen, Yi-Ching Wu, and Chi-Fai Chau. 2022. "Enhancement of Digestion Resistance and Glycemic Control of Corn Starch through Conjugation with Gallic Acid and Quercetin Using the Free Radical Grafting Method" Processes 10, no. 12: 2610. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10122610
APA StyleWu, T.-Y., Sun, N.-N., Chan, Z., Chen, C.-J., Wu, Y.-C., & Chau, C.-F. (2022). Enhancement of Digestion Resistance and Glycemic Control of Corn Starch through Conjugation with Gallic Acid and Quercetin Using the Free Radical Grafting Method. Processes, 10(12), 2610. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10122610








