Thermal Behavior of Passive Intelligent Radiant Cooling Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
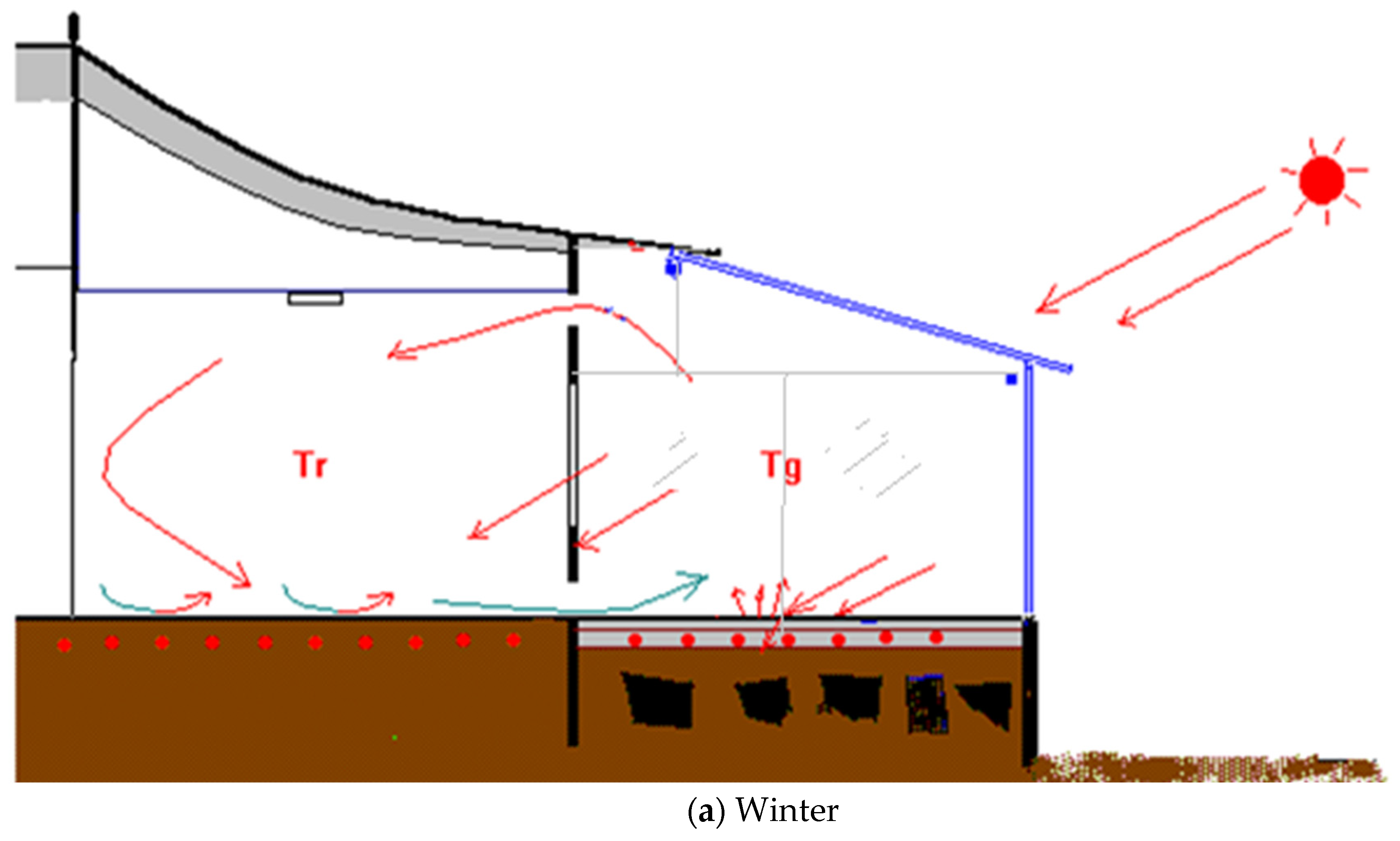
2.1. Principle of Passive Intelligent Radiant Cooling
2.2. Description of the Passive Intelligent Radiant Cooling System
2.3. Research Methodologies
3. Thermal Behavior of the Radiant Cooling System
3.1. Evaluation of Mean Radiant Temperature (MRT) and Operative Temperature (OT)
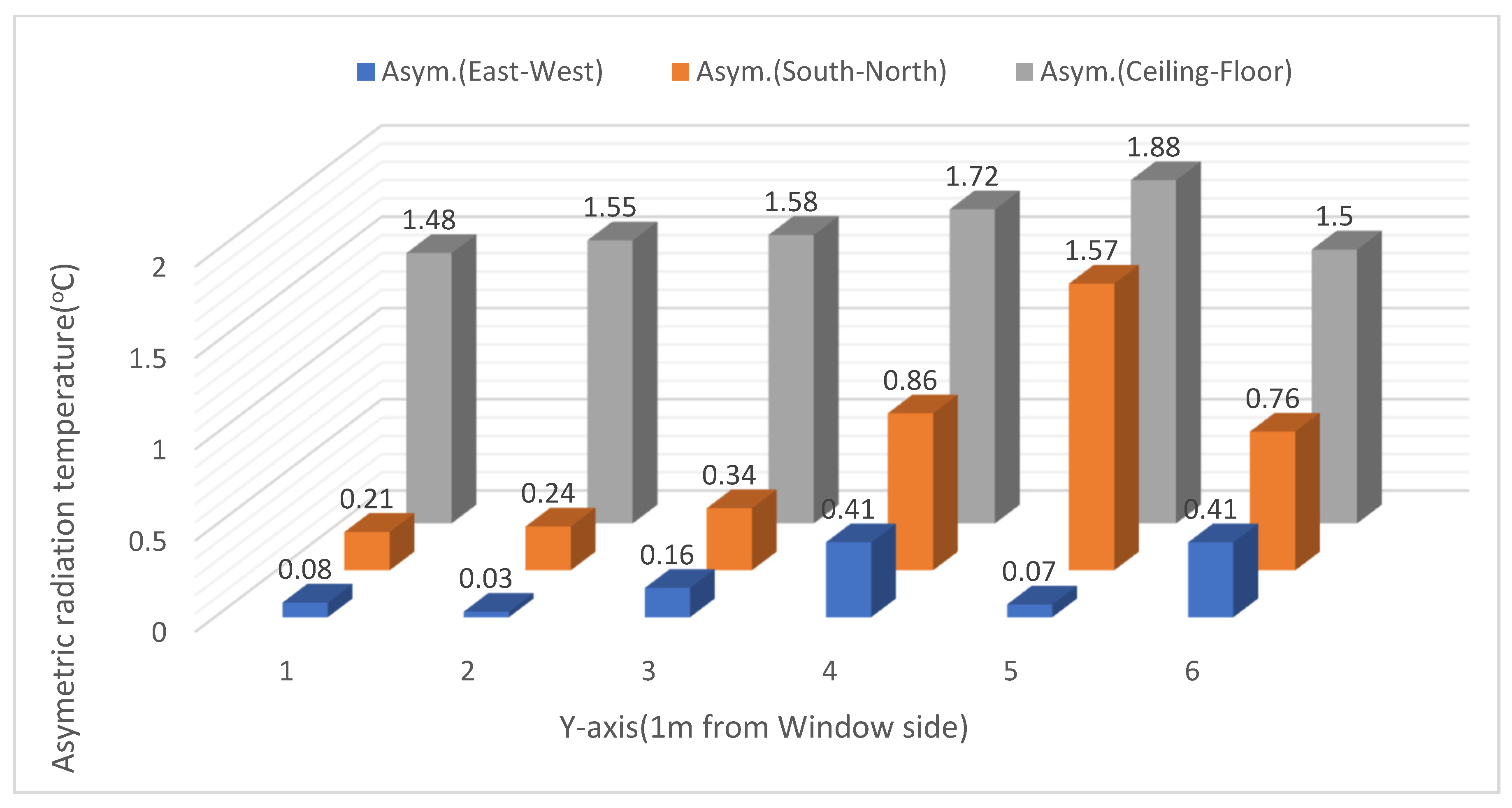
3.2. Asymmetric Radiation
3.3. Cooling Capacity
4. Experiment and Simulation Results
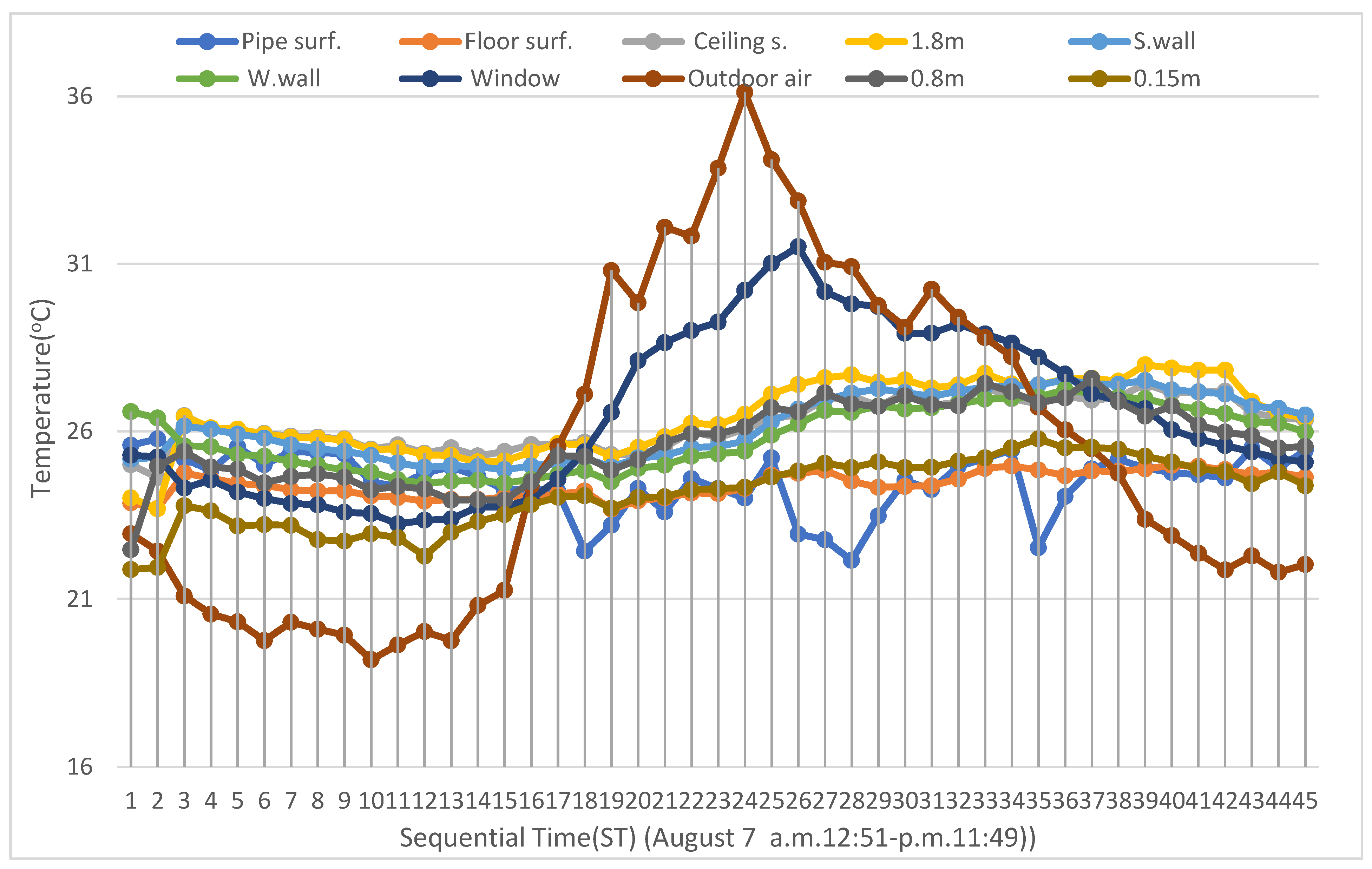
4.1. Radiant Cooling Concept and Experiment Results for the Target House
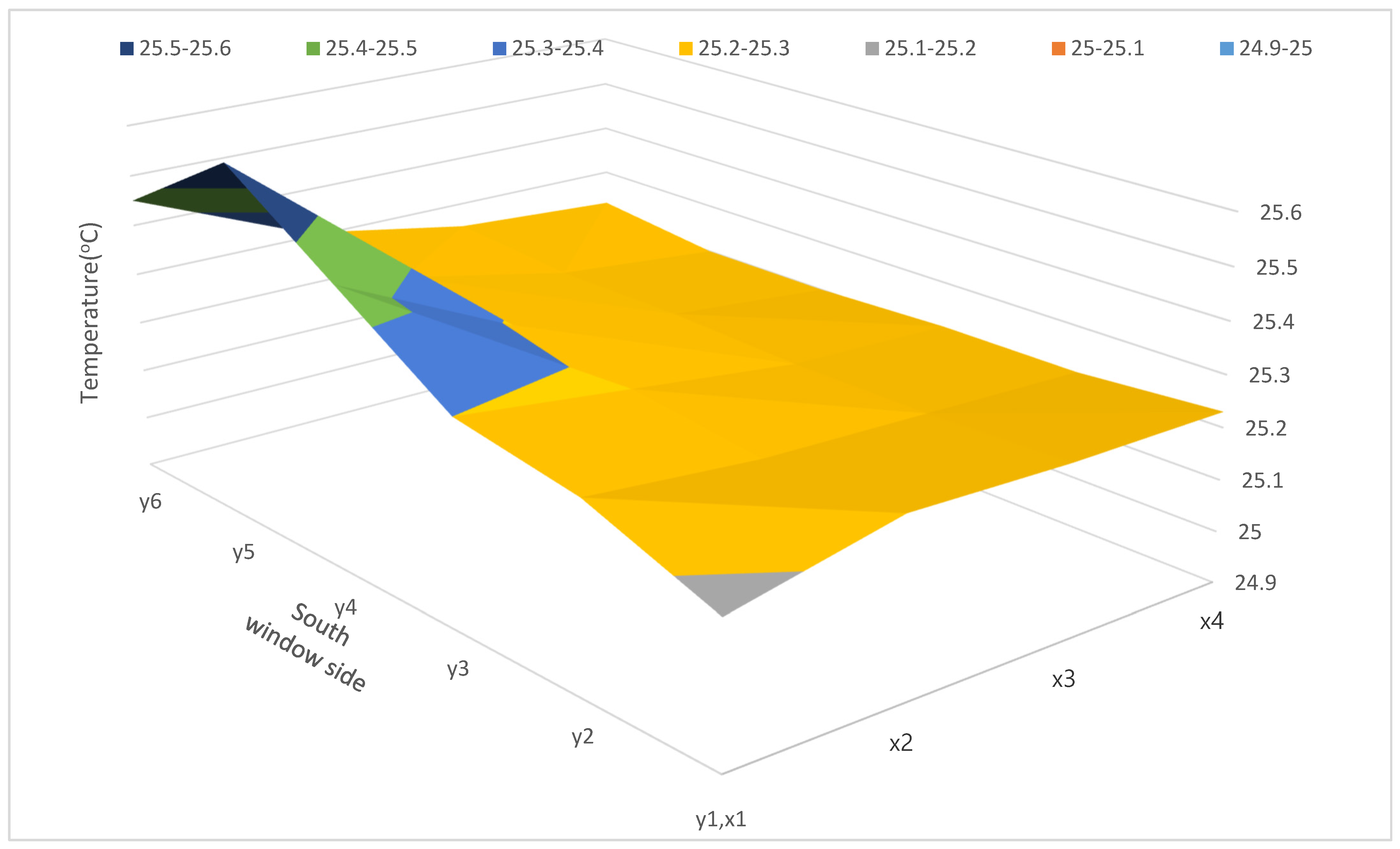
4.2. Mean Radiant Temperature (MRT) and Operative Temperature (OT) Calculation
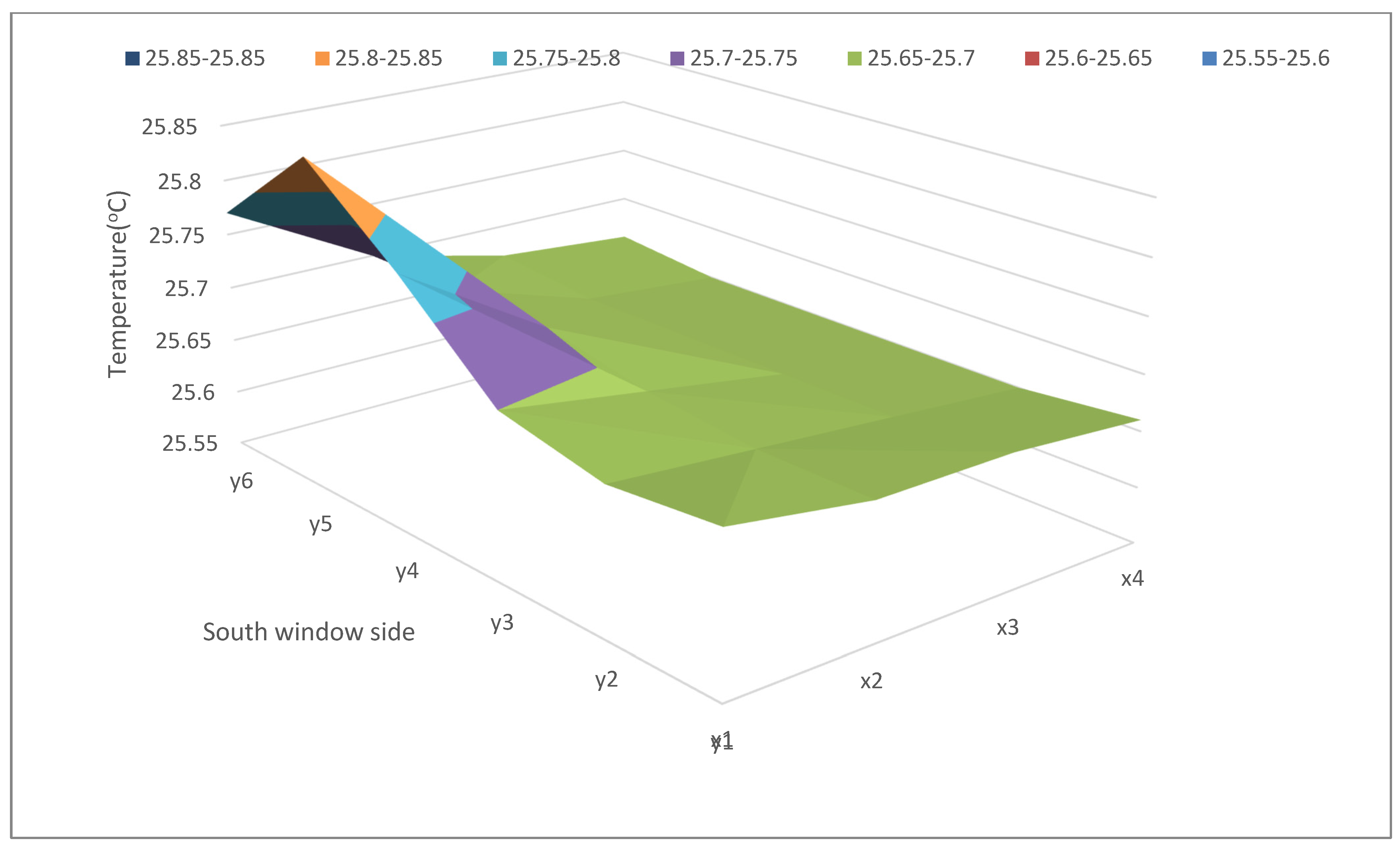
4.3. Asymmetric Radiation Simulation
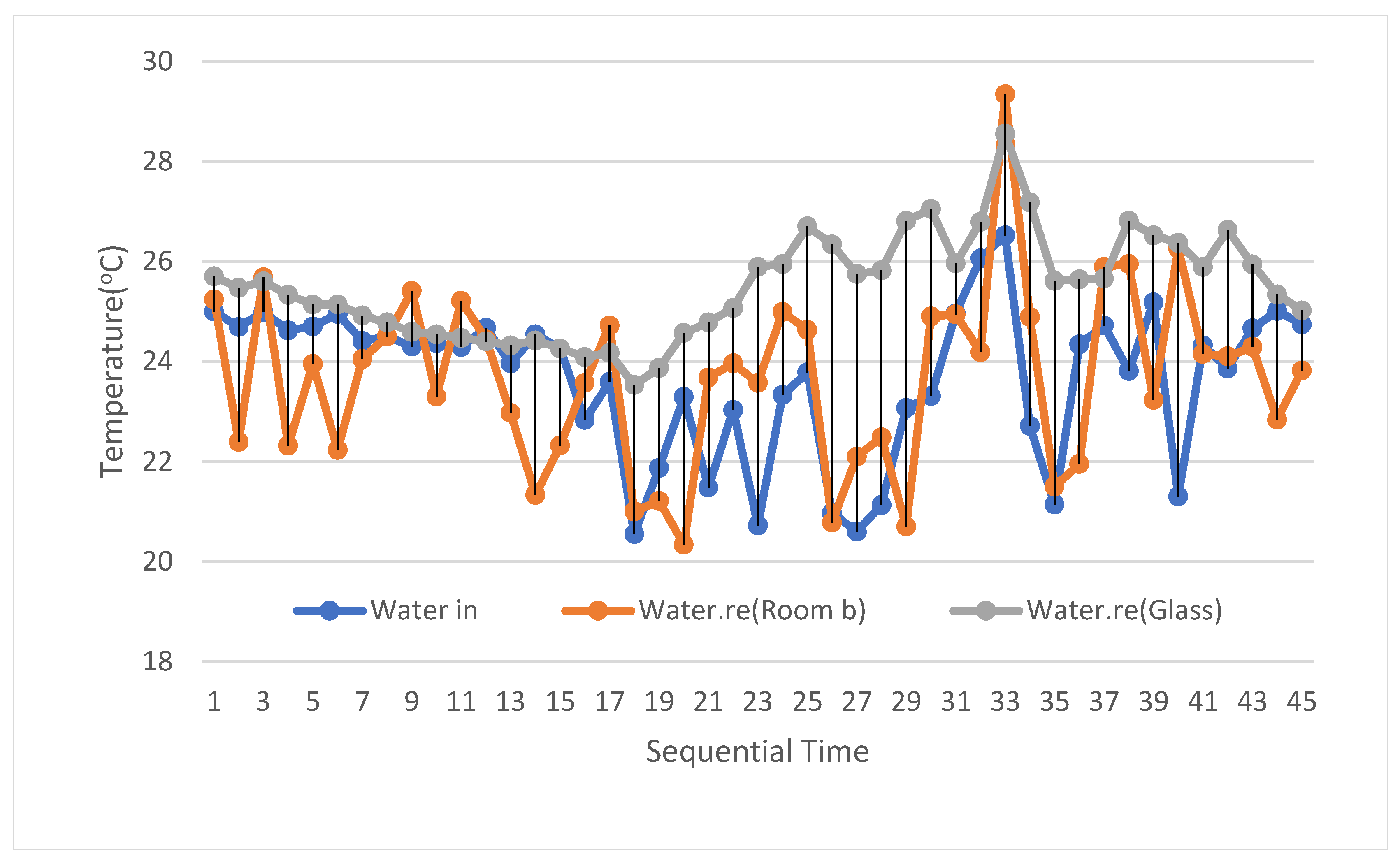
4.4. The Cooling Capacity of the Passive Intelligent Radiant Cooling System
4.5. Recommendations for an Energy-Efficient Dwelling with the Passive Intelligent Radiant Cooling System
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Asym | Asymmetric radiation [°C] |
| Adu | Human body surface area [m2] |
| h | Enthalpy [kJ/kg] |
| H | Height [cm] |
| m | Water flow rate [kG/s] |
| MRT | Mean radiant temperature [°C] |
| OT | Operative temperature [°C] |
| t | Temperature [°C] |
| T | Absolute temperature [°K] |
| W | Weight [Kg] |
| Ø | View factor [-] |
| Indices | |
| air | Air |
| coef | Coefficient |
| b | The human body |
| o | Opposite side |
| ot | Operative temperature |
| si | Room surface i, |
| 1 | Inlet position [-] |
| 2 | Outlet position [-] |
| u | Underside |
References
- IEA. IEA at COP26: The Role of Energy Efficient Buildings on the Path to Net-Zero-Strategies for Policymakers; IEA: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- IEA. EBC Annual Report 2020, Energy in Buildings and Communities Program; IEA: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Delmastro, C. Cooling, Tracking Report; IEA: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel, H.; Raiss, W. Heiz-und Lueftungstechnik; Springer: Berlin/Goettingen/Heidelberg, Germany, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Fanger, P.O. Thermal Comfort; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Glueck, B. Strahlungsheizung-Theorie und Paxis; Verlag, C.F., Ed.; Mueller: Karlsruhe, Germany, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Konzelmann, M.; Zoellner, G. Waermetechnische Pruefung von Fussbodenheizungen, HLH 33; Springer VDI Verlag: Dusseldorf, Germany, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Teitelbaum, E.; Chen, K.W.; Meggers, F.; Pantelic, J.; Aviv, D.; Rysanek, A. The Cold Tube: Membrane assisted radiant cooling for condensation-free outdoor comfort in the tropics. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1343, 012080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesundheit-Ingenieur (GI); R.Oldenbourg Verlag: Muenchen, Germany, 1938.
- Koschenz, M.; Lehman, B. Thermoaktive Bauteilsysteme Tabs; EMPA: Dübendorf, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pirvaram, A.; Talebzadeh, N.; Leung, S.N.; O’Brien, P.G. Radiative cooling for buildings: A review of techno-enviro-economics and life-cycle assessment methods. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 162, 112415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietschel, H.; Fitzner, K. Raumklimatechnik-Band2: Raumluft- und Raumkueltechnik; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume VDI. [Google Scholar]
- Daniels, K. The Technology of Ecological Building; Birkhaeuser Verlag: Basel, Switzerland; Boston, MA, USA; Berlin, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, S.H. Radiant Cooling and Heating System for Zero Energy Solar Architecture, SWC 2021; ISES: Freiburg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, S.H.; Sohn, J.R. A Radiant Floor Cooling System for the Use of Natural Energy by Convergence of Traditional Ondol and Hot Water Ondol Heating System; KFMA: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, S.H. Warm and Cold-Water Cycle Structure of Boiler; Korean Intellectual Property Office: Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 7730; Ergonomics of the Thermal Environment—Analytical Determination and Interpretation of Thermal Comfort using Calculation of the PMV and PPD Indices and Local Thermal Comfort Criteria. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005.
- Yoo, S.H. Mathematical Solutions for Mean Radiant Temperature Calculation in a Rectangular or Non-rectangular Geometry. Int. J. Adv. Mech. Civ. Eng. 2018, 5, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- DIN4715/1; Raumkuehlflaechen, Teil 1: Leistungsmessung bei Freier Stroemung Pruefregeln. Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 1994.
- ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 55-2004; Thermal Environmental Conditions for Human Occupancy. American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc.: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2004.
- Özbey, M.F.; Turhan, C. A comprehensive comparison and accuracy of different methods to obtain mean radiant temperature in an indoor environment. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2022, 31, 101295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.H.; Choi, H.J. Solar architecture integrated bi-facial photovoltaic system as a shade. Processes 2021, 9, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Measurement Factor (Position) | Method | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Outdoor air temperature (1.5 m) | Data logger (Datascan 7020) + T-type thermocouple | ±0.75% |
| Vertical room temperature (Floor surface, 0.1 m, 0.8 m, 2.3 m, and ceiling surface) | ||
| Vertical floor temperature (Floor surface, 0.15 m, 0.8 m) | ||
| Inside surface temperature (South wall, south window, west wall, north wall, floor surface 1, 2, 3, 4) | ||
| Inside temperature of the glass house -Surface (Floor, south, east, and inclined glass ceiling) -Vertical air (0.1 m, 0.8 m, 2.3 m) - Inlet and outlet water temperature (Pipe surface temp.) | ||
| Glove temperature (Room and glasshouse) (0.8 m) | Glove thermometer + T-type thermocouple | |
| Room humidity (0.15 m) | Asman humidity meter + T-type thermocouple |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoo, S.-H. Thermal Behavior of Passive Intelligent Radiant Cooling Systems. Processes 2022, 10, 2666. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10122666
Yoo S-H. Thermal Behavior of Passive Intelligent Radiant Cooling Systems. Processes. 2022; 10(12):2666. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10122666
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoo, Seung-Ho. 2022. "Thermal Behavior of Passive Intelligent Radiant Cooling Systems" Processes 10, no. 12: 2666. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10122666
APA StyleYoo, S.-H. (2022). Thermal Behavior of Passive Intelligent Radiant Cooling Systems. Processes, 10(12), 2666. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10122666






