Experimental Study on Deformation and Strength Characteristics of Interbedded Sandstone with Different Interlayer Thickness under Uniaxial and Triaxial Compression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Characteristics of the Sandstone Samples
3. Test Method
4. Analysis of Uniaxial Compression Test Results
4.1. Characteristics of Stress–Strain Curves of Interbedded Sandstone with Different Interlayer Thickness
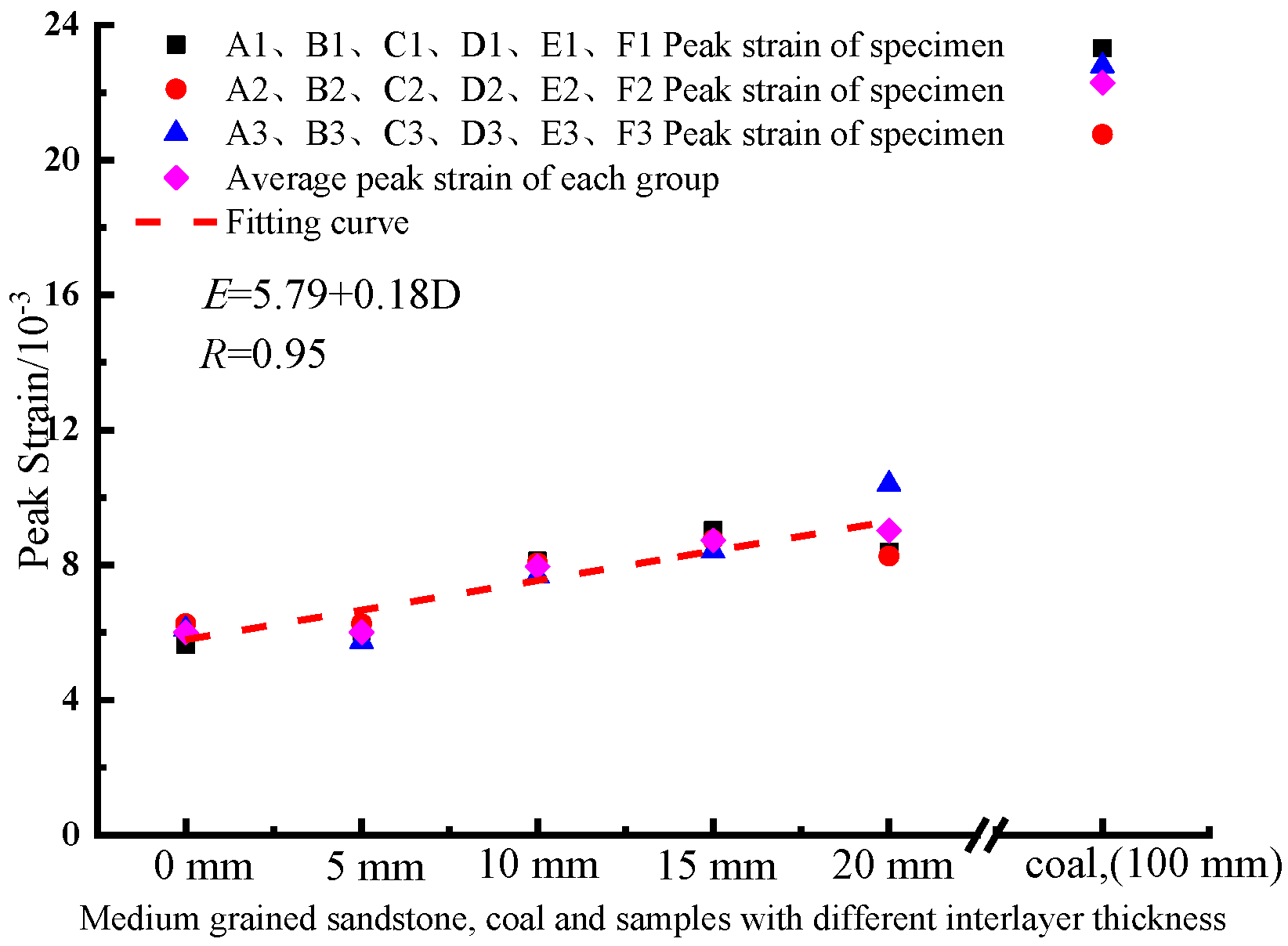
4.2. Characteristics of Uniaxial Mechanical Parameters of Interbedded Sandstone with Different Interlayer Thickness
5. Analysis of Triaxial Compression Test Results
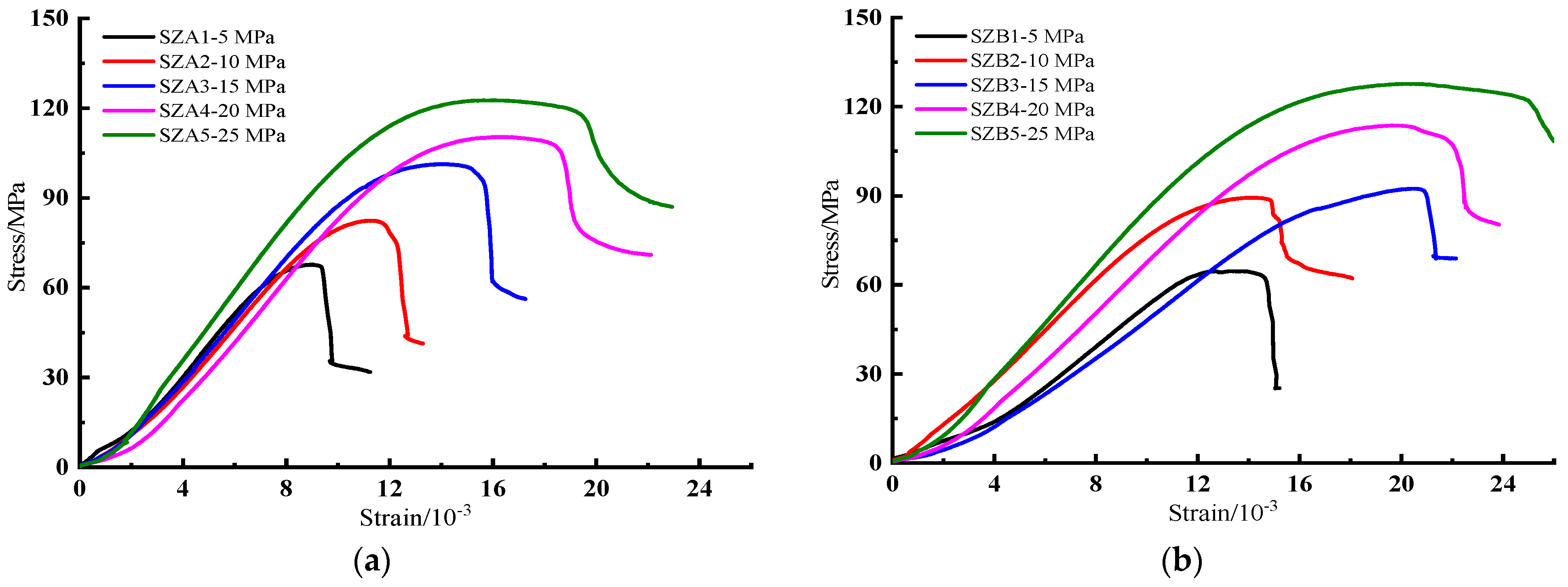
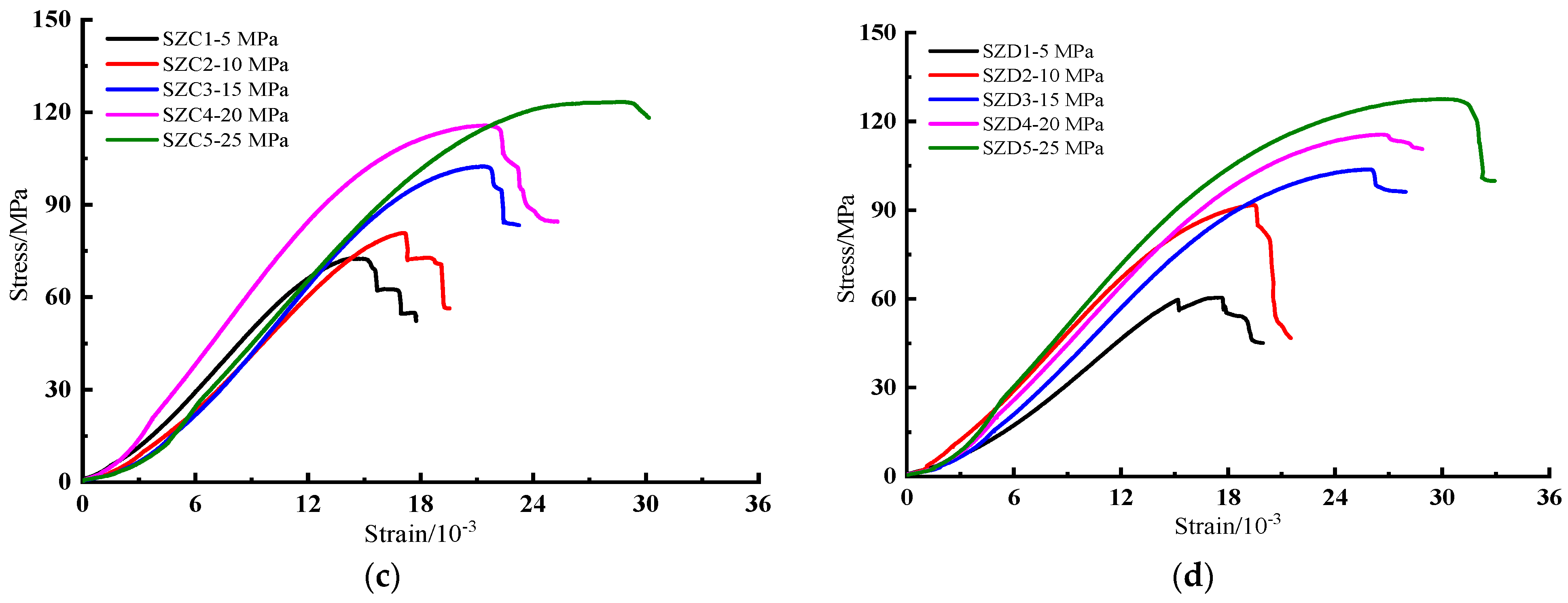
5.1. Deformation Characteristics
5.2. Strength Characteristics
- Mohr–Coulomb strength criterionwhere
- σ1: peak strength;
- σc: uniaxial compressive strength;
- φ: internal friction angle;
- σ3: confining pressure.
- (1)
- When the interlayer thickness accounts for 5% of the total height of the sample:According to the Mohr–Coulomb strength criterion, the predicted value of the uniaxial compressive strength of the interbedded medium-grained sandstone with interlayer thickness of 5 mm is 55.59 MPa, and the correlation fitting coefficient is 0.98608.
- (2)
- When the interlayer thickness accounts for 10% of the total height of the sample:According to the Mohr–Coulomb strength criterion, the predicted value of the uniaxial compressive strength of the interbedded medium-grained sandstone with interlayer thickness of 10 mm is 52.45 MPa, and the correlation fitting coefficient is 0.96465.
- (3)
- When the interlayer thickness accounts for 15% of the total height of the sample:According to the Mohr–Coulomb strength criterion, the predicted uniaxial compressive strength of the interbedded medium-grained sandstone with interlayer thickness of 15 mm is 58.09 MPa, and the correlation fitting coefficient is 0.97335.
- (4)
- When the interlayer thickness accounts for 20% of the total height of the sample:According to the Mohr–Coulomb strength criterion, the predicted value of the uniaxial compressive strength of the interbedded medium-grained sandstone with interlayer thickness of 20 mm is 52.47 MPa, and the correlation fitting coefficient is 0.94331 (Table 3).
- Rocker strength criterionwhere
- σ1: the peak strength;
- σc: the uniaxial compressive strength;
- σ3: confining pressure;
- T: uniaxial tensile strength of rock;
- b: exponent.
- (1)
- When the interlayer thickness accounts for 5% of the total height of the sample:According to the Rocker strength criterion, the predicted value of the uniaxial compressive strength of the interbedded medium-grained sandstone with interlayer thickness of 5 mm is 43.72 MPa, and the correlation fitting coefficient is 0.99389.
- (2)
- When the interlayer thickness accounts for 10% of the total height of the sample:According to the Rocker strength criterion, the predicted value of the uniaxial compressive strength of the interbedded medium-grained sandstone with interlayer thickness of 10 mm is 48.53 MPa, and the correlation fitting coefficient is 0.96544.
- (3)
- When the interlayer thickness accounts for 15% of the total height of the sample:According to the Rocker strength criterion, the predicted value of the uniaxial compressive strength of the interbedded medium-grained sandstone with interlayer thickness of 15 mm is 54.09 MPa, and the correlation fitting coefficient is 0.97522.
- (4)
- When the interlayer thickness accounts for 20% of the total height of the sample:According to the Rocker strength criterion, the predicted value of the uniaxial compressive strength of the interbedded medium-grained sandstone with interlayer thickness of 20 mm is 1.53 MPa, and the correlation fitting coefficient is 0.98369 (Table 4).
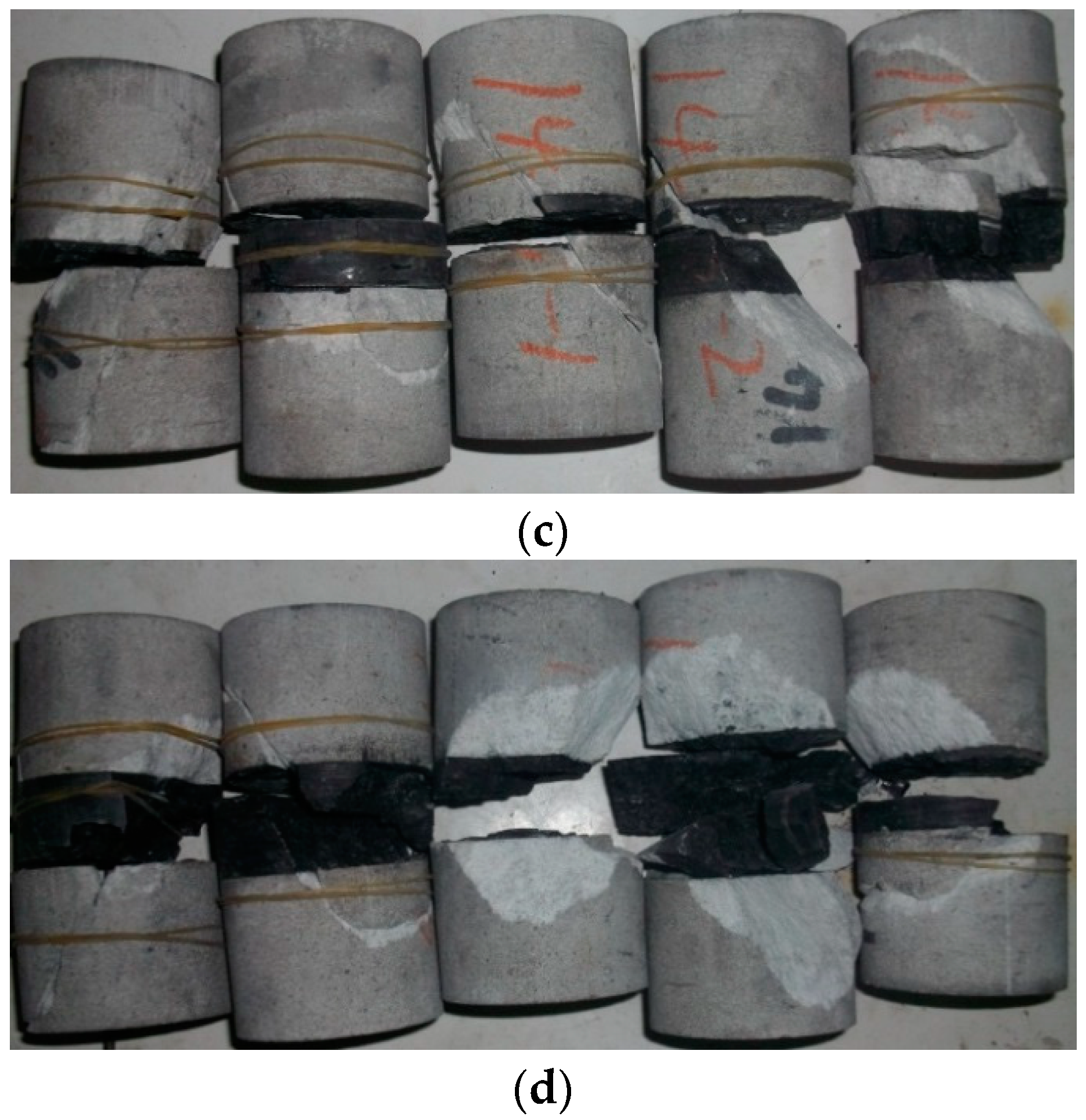
5.3. Failure Characteristics
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- When the difference between the compressive strength of the interlayer and the compressive strength of the sandstone is small, the uniaxial compressive strength of the interbedded medium-grained sandstone first decreases and then increases with the gradual increase of the interlayer thickness. In addition, the elastic modulus is negatively correlated with the interlayer thickness, while the peak strain is positively correlated with the interlayer thickness. The interlayer thickness has little effect on the triaxial compressive strength of the intercalated medium-grained sandstone.
- (2)
- The deviation of the fitted uniaxial compressive strength of the Rocker strength criterion when the thickness of the interlayer is small is relatively small, and the prediction result of the Mohr–Coulomb strength criterion for the uniaxial compressive strength of medium-grained sandstones with different interlayer thicknesses is relatively good. For the prediction of the tensile strength of rocks with interlayers, the Rocker strength criterion shows superiority.
- (3)
- The development of cracks in medium-grained sandstone is hindered due to the existence of the interlayer, but this effect is weakened with the gradual increase of the interlayer thickness. The confining pressure and interlayer thickness also have significant effects on some failure characteristics of the interlayer. With the increase of confining pressure and interlayer thickness, the cracks in the interlayer gradually increase. They develop from vertical cracks to cracks in different directions, and the area of the fracture zone also increases gradually.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| σc | uniaxial compressive strength |
| εc | peak strain |
| E | elastic modulus |
| μ | Poisson’s ratio |
| σ1 | peak strength |
| σ3 | confining pressure |
| σR | residual strength |
| φ | internal friction angle |
| R2 | correlation fit coefficient |
| T | uniaxial tensile strength of rock |
References
- Li, H.M.; Li, H.G.; Song, G.J.; Wang, K.L. Physical and mechanical properties of the coal-bearing strata rock in Shendong coal field. J. China Coal Soc. 2016, 41, 2661–2671. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.G.; Li, H.M.; Li, C.X.; Chen, S.L. Study on the Acoustic Emission Characteristics in the Rupture Process of Medium Grain Sandstone with Natural Structural Plane. Min. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 45, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Huamin, L.; Qunlei, Z.; Chuang, L.; Lulu, S.; Huigui, L. Analysis on overburden strata movement and mine strata pressure behavior of high cutting mining in ultra thick seam. Coal Sci. Technol. 2017, 45, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.F.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, K.Z.; Xu, Y.L.; Li, H.G. Fracture characteristics and determination of support working resistance of key strata under shallow buried short-distance multi-seam goaf. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2018, 35, 332–338. [Google Scholar]
- He, M.M.; Chen, Y.S.; Li, N.; Zhu, C.H. Deformation and energy characteristics of sandstone subjected to uniaxial cyclic loading. J. China Coal Soc. 2015, 40, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, P.; Jiaqi, Z.; Quanle, Z.; Junhui, M. Fatigue deformation characteristics and damage model of sandstone subjected to uniaxial step cyclic loading. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2017, 46, 8–17. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Yang, H.; Haque, E.; Wang, G. Effect of Joint Orientation on the Breakage Behavior of Jointed Rock Mass Loaded by Disc Cutters. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2021, 54, 2087–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Q.; Mao, X.B.; Shi, H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.L. Hysteresis failure behavior of argillaceous sandstone under cyclic loading, load-holding and unloading. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2018, 35, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Deng, R.; Fu, X.; Wang, C. Experimental study of deformation and strength properties of simulated columnar jointed rock masses under conventional triaxial compression. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2015, 34, 2817–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.H.; Xiong, L.X. Uniaxial compression test of single-joint fractured rock mass considering the influence of thickness and length of joint surface and numerical simulation. J. Geol. Hazards Environ. Preserv. 2019, 30, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.F.; Liu, S.; Ren, D.; Liu, X.L. Numerical simulation of uniaxial compression of jointed rock mass based on FLAC3D Beijing Society of mechanics. In Proceedings of the 22nd Annual Conference of Beijing Society of Mechanics, Beijing Mechanical Society, Beijing, China, 22–27 August 2016; pp. 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Zhou, Z.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, D.; Cheng, S. Strength reduction model for jointed rock masses and peridynamics simulation of uniaxial compression testing. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resour. 2021, 7, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.T.; Zhang, Y.; Gang, M.A.; Zhang, Y. Experimental and Simulation Study on Fracture Characteristics of Sandstone under Cyclic Loading. J. Hunan Univ. 2021, 48, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q.; Cao, P.; Liu, Y.; Cao, R.; Li, J. Mechanical behaviour of a jointed rock mass with a circular hole under compression-shear loading: Experimental and numerical studies. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2021, 114, 102998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; Xia, C.C.; Wang, X.D.; Zhou, J.F.; Zhang, C.S. Experimental study on deformation and strength properties of jointed marble specimens. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2008, 27, 2118–2123. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.F.; Xiong, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Qi, Y.; Li, T.; Xu, X.L. Shear strength parameters of jointed rock mass based on single test sample method. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2020, 42, 1509–1515. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, S. Influence of weak inclusions on the fracturing and fractal behavior of a jointed rock mass containing an opening: Experimental and numerical studies. Comput. Geotech. 2021, 132, 104011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.X.; Cao, P.; Pu, C.Z. Effect of the density and inclination of joints on the strength and deformation properties of rock-like specimens under uniaxial compression. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing 2017, 39, 494–501. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.Q.; Tao, Y.; Tang, J.Z. Experimental study of triaxial strength and deformation of single jointed sandstone under cyclic loading. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2020, 49, 819–882. [Google Scholar]
- China National Standardization Administration Committee. GB/T 23561.1—2009 Determination Method of Physical and Mechanical Properties of Coal and Rock; China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Su, C.D.; Fu, Y.S. Experimental study of triaxial compression deformation and strength characteristics of red sandstone. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2014, 33 (Suppl. 1), 3164–3169. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China. SL264—2001 Water Conservancy and Hydropower Engineering Specifications for Rock Tests; Water Power Press: Beijing, China, 2001. (In Chinese)
- Carter, B.J.; Duncan, E.S.; Lajtai, E.Z. Fitting strength criteria to intact rock. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 1991, 9, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
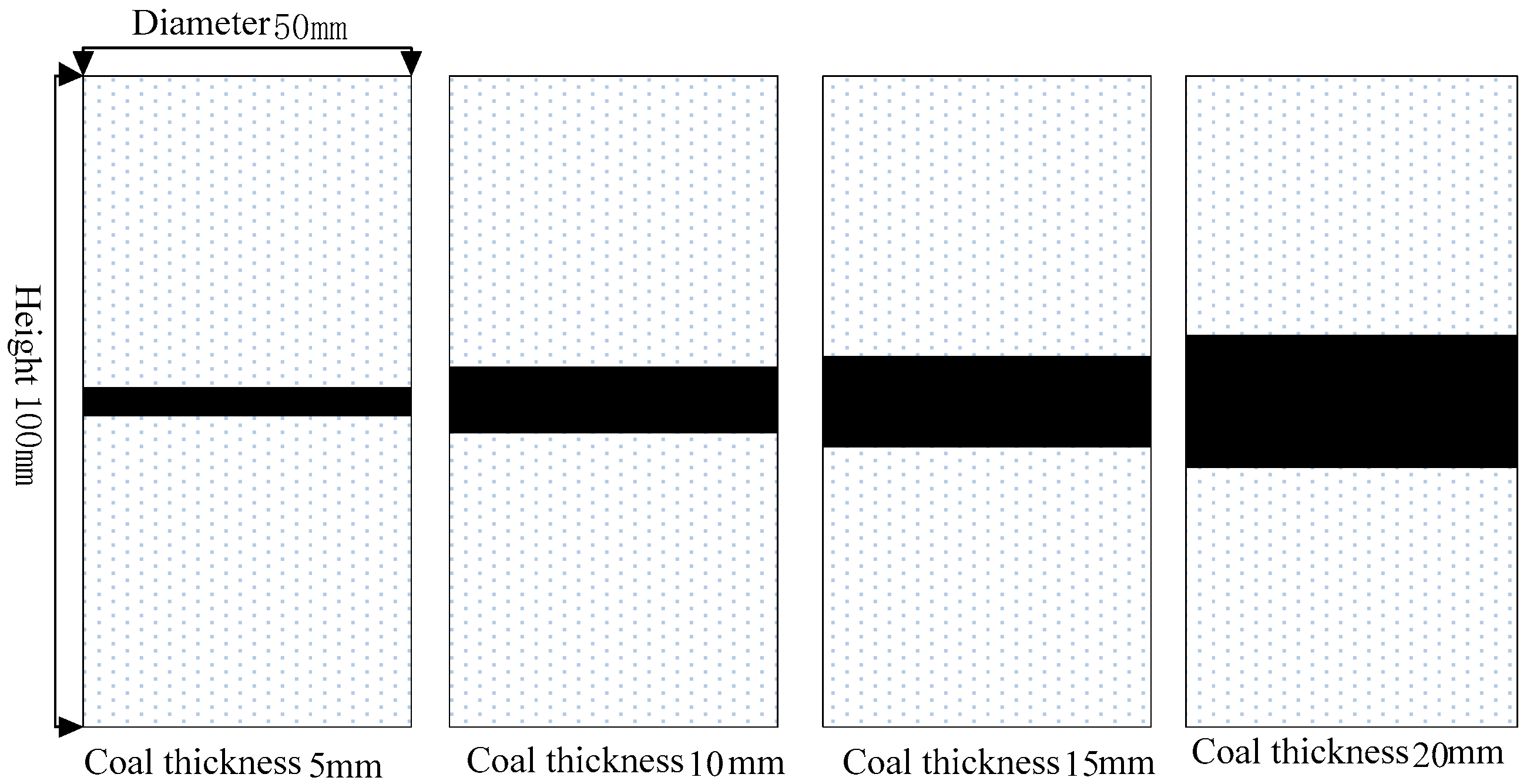
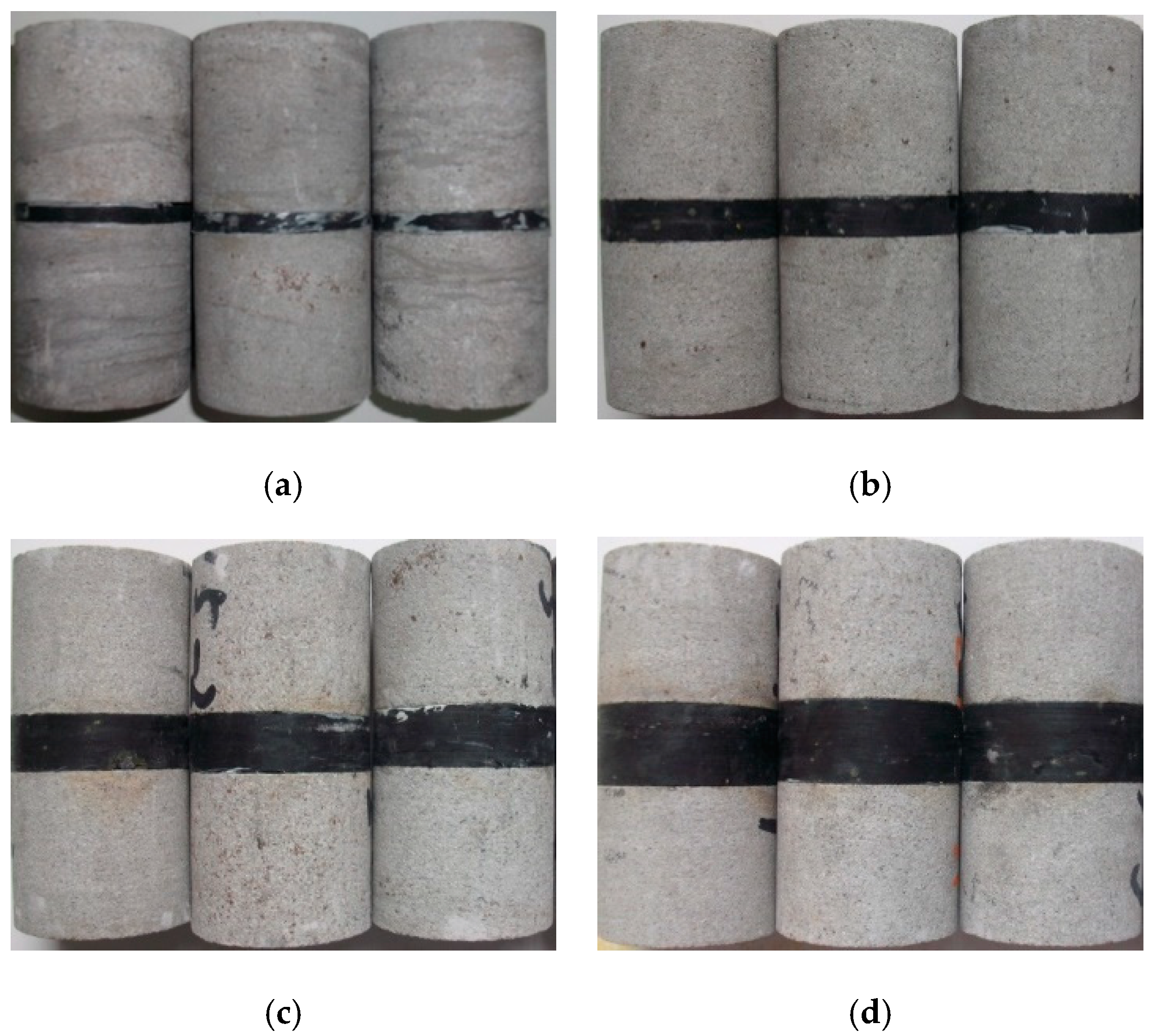
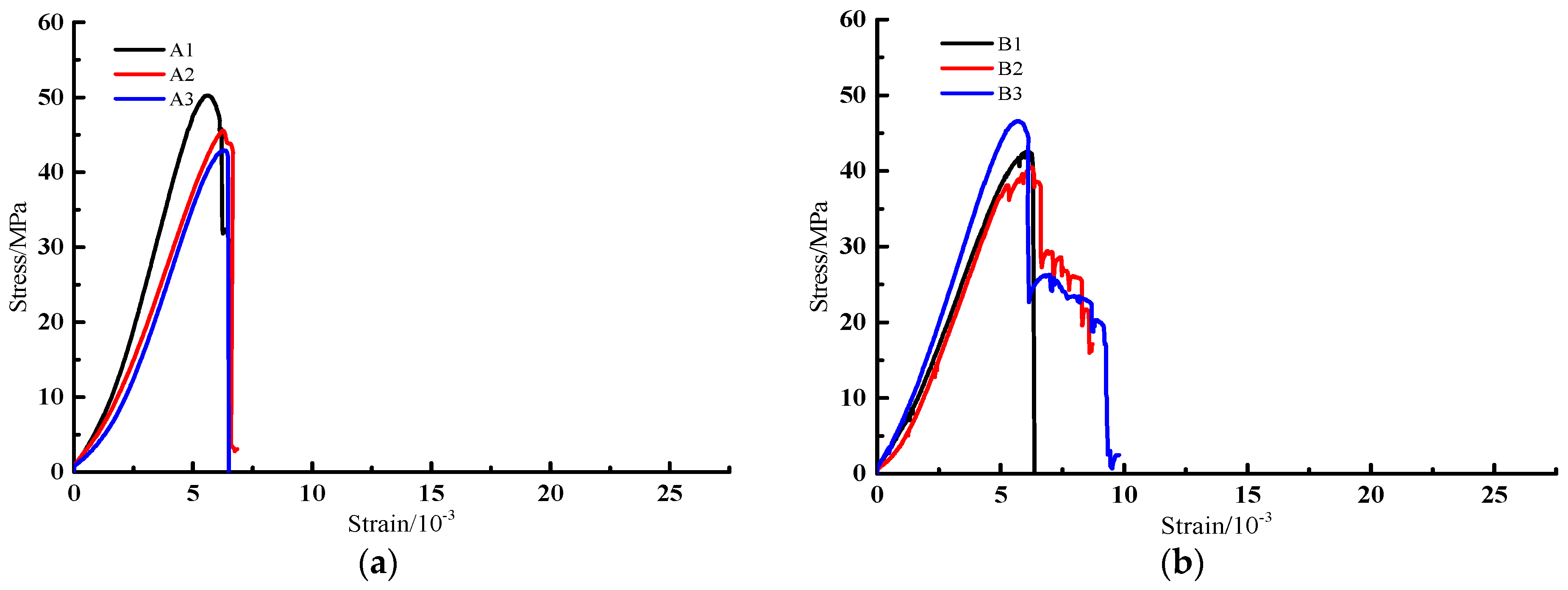
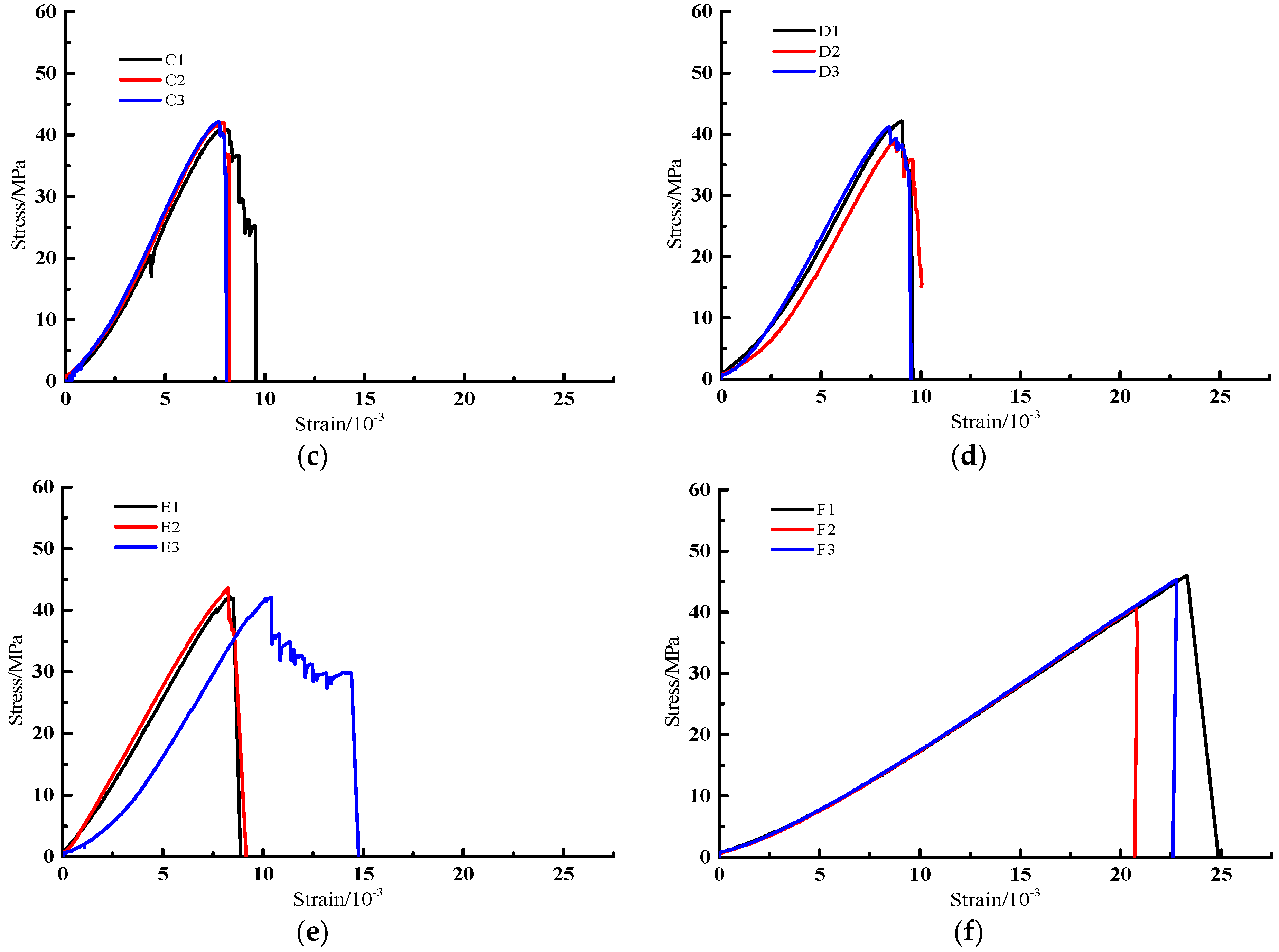




| Lithology | Interlayer Thickness/mm | Number | H/mm | D/mm | σc/MPa | εc/10−3 | E/GPa | μ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium-grained sandstone | 0 | A1 | 98.30 | 49.50 | 50.24 | 5.63 | 11.68 | 0.192 |
| 0 | A2 | 96.20 | 49.70 | 45.55 | 6.26 | 8.90 | 0.251 | |
| 0 | A3 | 99.20 | 50.10 | 50.76 | 6.10 | 9.49 | 0.262 | |
| 5 | B1 | 98.10 | 49.90 | 40.89 | 6.03 | 8.68 | 0.312 | |
| 5 | B2 | 98.10 | 49.70 | 40.47 | 6.26 | 8.78 | 0.266 | |
| 5 | B3 | 97.90 | 49.80 | 46.60 | 5.73 | 9.84 | 0.194 | |
| 10 | C1 | 98.80 | 49.90 | 40.89 | 8.12 | 6.55 | 0.264 | |
| 10 | C2 | 98.70 | 50.10 | 41.21 | 8.06 | 6.51 | 0.305 | |
| 10 | C3 | 98.60 | 49.70 | 42.14 | 7.67 | 6.77 | 0.309 | |
| 15 | D1 | 100.70 | 49.70 | 42.13 | 9.03 | 5.76 | 0.311 | |
| 15 | D2 | 100.50 | 49.80 | 38.79 | 8.74 | 5.68 | 0.303 | |
| 15 | D3 | 99.30 | 49.70 | 41.17 | 8.41 | 5.93 | 0.220 | |
| 20 | E1 | 100.70 | 49.70 | 41.87 | 8.39 | 5.35 | 0.216 | |
| 20 | E2 | 100.50 | 49.80 | 43.62 | 8.26 | 5.83 | 0.208 | |
| 20 | E3 | 99.30 | 49.70 | 42.07 | 10.40 | 5.40 | 0.298 | |
| Coal | - | F1 | 99.20 | 49.90 | 45.99 | 23.31 | 2.13 | 0.146 |
| - | F2 | 101.00 | 49.70 | 40.84 | 20.76 | 2.12 | 0.358 | |
| - | F3 | 99.30 | 49.80 | 45.38 | 22.79 | 2.15 | 0.341 |
| Lithology | Number | Interlayer Thickness/mm | H/mm | D/mm | σ3/MPa | σ1/MPa | σR/MPa | εc/10−3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium-grained sandstone | SZA-1 | 5 | 99.20 | 50.10 | 5 | 67.69 | 31.83 | 8.88 |
| SZA-2 | 5 | 98.58 | 49.80 | 10 | 82.43 | 41.39 | 11.38 | |
| SZA-3 | 5 | 99.96 | 50.20 | 15 | 101.33 | 56.21 | 14.10 | |
| SZA-4 | 5 | 98.80 | 49.70 | 20 | 110.36 | 71.01 | 16.44 | |
| SZA-5 | 5 | 99.10 | 50.40 | 25 | 122.51 | 87.01 | 16.61 | |
| SZB-1 | 10 | 99.50 | 49.60 | 5 | 64.63 | 25.22 | 13.24 | |
| SZB-2 | 10 | 99.42 | 50.30 | 10 | 89.40 | 62.15 | 14.11 | |
| SZB-3 | 10 | 98.86 | 50.70 | 15 | 92.44 | 68.89 | 20.55 | |
| SZB-4 | 10 | 98.82 | 49.70 | 20 | 113.70 | 80.32 | 20.02 | |
| SZB-5 | 10 | 99.62 | 49.80 | 25 | 127.68 | 102.96 | 20.64 | |
| SZC-1 | 15 | 100.10 | 49.80 | 5 | 72.65 | 53.87 | 14.33 | |
| SZC-2 | 15 | 98.62 | 49.90 | 10 | 80.82 | 56.42 | 17.11 | |
| SZC-3 | 15 | 99.22 | 49.80 | 15 | 102.42 | 83.35 | 21.20 | |
| SZC-4 | 15 | 99.76 | 49.70 | 20 | 115.69 | 84.48 | 21.40 | |
| SZC-5 | 15 | 99.96 | 49.70 | 25 | 123.38 | 118.13 | 28.67 | |
| SZD-1 | 20 | 100.70 | 50.20 | 5 | 60.52 | 45.08 | 17.54 | |
| SZD-2 | 20 | 100.86 | 49.70 | 10 | 91.75 | 46.73 | 19.41 | |
| SZD-3 | 20 | 101.00 | 49.70 | 15 | 103.79 | 96.14 | 25.73 | |
| SZD-4 | 20 | 100.40 | 50.10 | 20 | 115.56 | 110.64 | 26.61 | |
| SZD-5 | 20 | 100.96 | 49.70 | 25 | 127.55 | 99.88 | 29.96 |
| Lithology | Interlayer Thickness | σc Estimate | R2 | σc Average | Deviation | Cohesion/MPa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium-grained sandstone | 5 mm | 55.59 | 2.75 | 0.98608 | 41.97 | 32.45% | 16.67 |
| 10 mm | 52.45 | 3.00 | 0.96465 | 41.41 | 26.66% | 15.14 | |
| 15 mm | 58.09 | 2.73 | 0.97335 | 40.70 | 42.73% | 17.58 | |
| 20 mm | 52.47 | 3.16 | 0.94331 | 42.52 | 23.40% | 14.76 |
| Lithology | Interlayer Thickness | σc Estimate | R2 | σc Average | Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium-grained sandstone | 5 mm | 43.73 | 0.99389 | 41.97 | 4.19% |
| 10 mm | 48.53 | 0.96544 | 41.41 | 17.19% | |
| 15 mm | 54.09 | 0.97522 | 40.70 | 32.90% | |
| 20 mm | 1.53 | 0.98369 | 42.52 | 96.40% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Wei, S.; Li, X. Experimental Study on Deformation and Strength Characteristics of Interbedded Sandstone with Different Interlayer Thickness under Uniaxial and Triaxial Compression. Processes 2022, 10, 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10020285
Li H, Wang J, Li H, Wei S, Li X. Experimental Study on Deformation and Strength Characteristics of Interbedded Sandstone with Different Interlayer Thickness under Uniaxial and Triaxial Compression. Processes. 2022; 10(2):285. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10020285
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Huigui, Jun Wang, Huamin Li, Shengjie Wei, and Xiaolong Li. 2022. "Experimental Study on Deformation and Strength Characteristics of Interbedded Sandstone with Different Interlayer Thickness under Uniaxial and Triaxial Compression" Processes 10, no. 2: 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10020285
APA StyleLi, H., Wang, J., Li, H., Wei, S., & Li, X. (2022). Experimental Study on Deformation and Strength Characteristics of Interbedded Sandstone with Different Interlayer Thickness under Uniaxial and Triaxial Compression. Processes, 10(2), 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10020285





