Crude Oil Degradation by a Novel Strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa AQNU-1 Isolated from an Oil-Contaminated Lake Wetland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Water Sampling
2.2. Isolation and Selection of Crude Oil-Degrading Bacteria
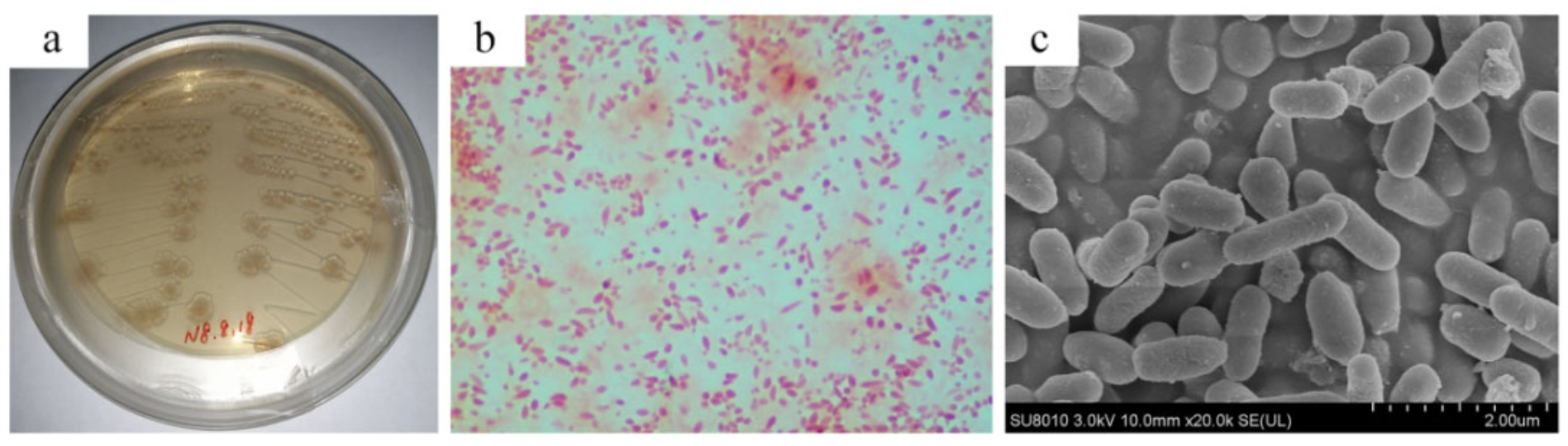
2.3. Analysis of Morphological Observation
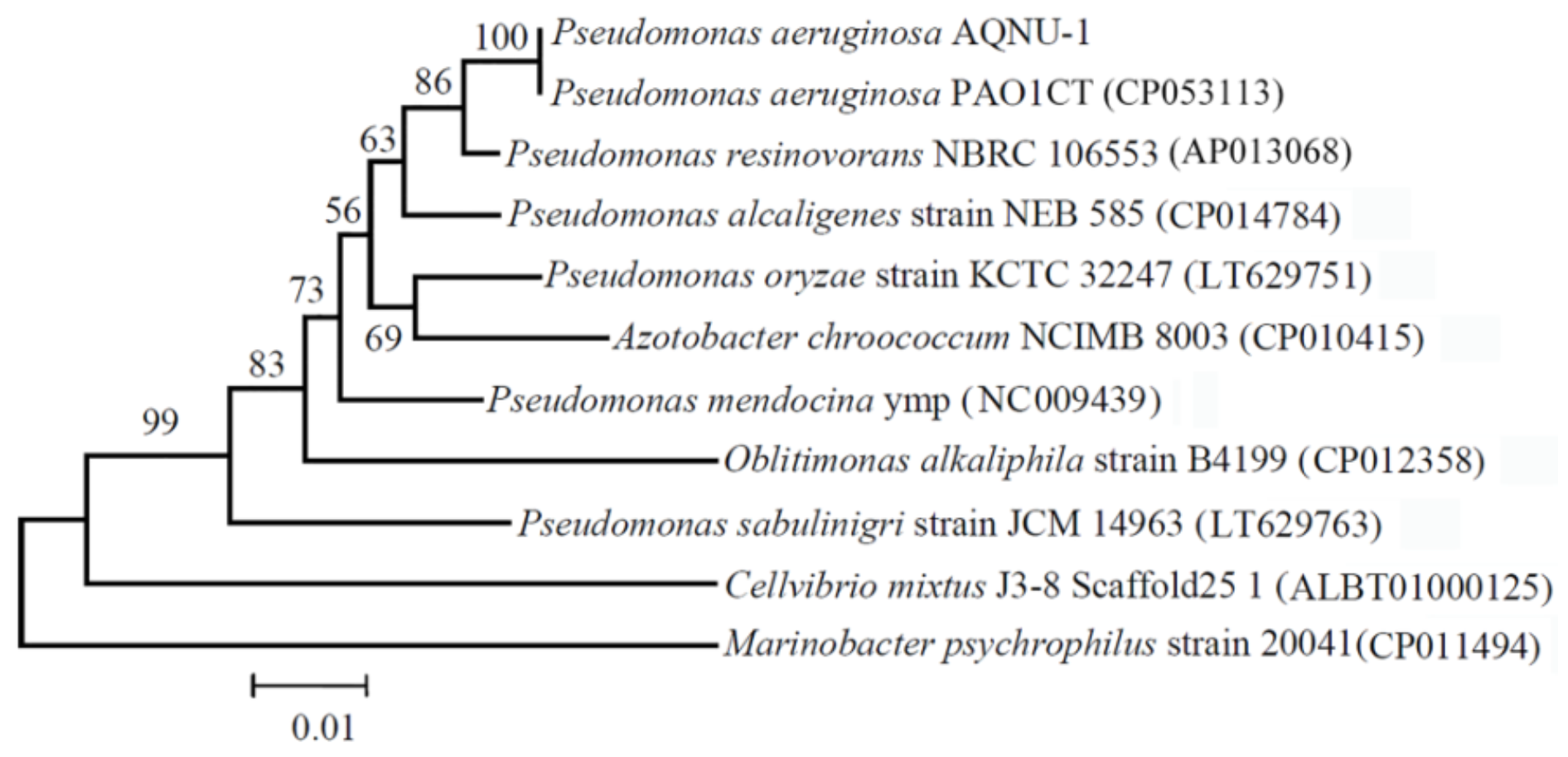
2.4. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.5. Carbon Source Utilization
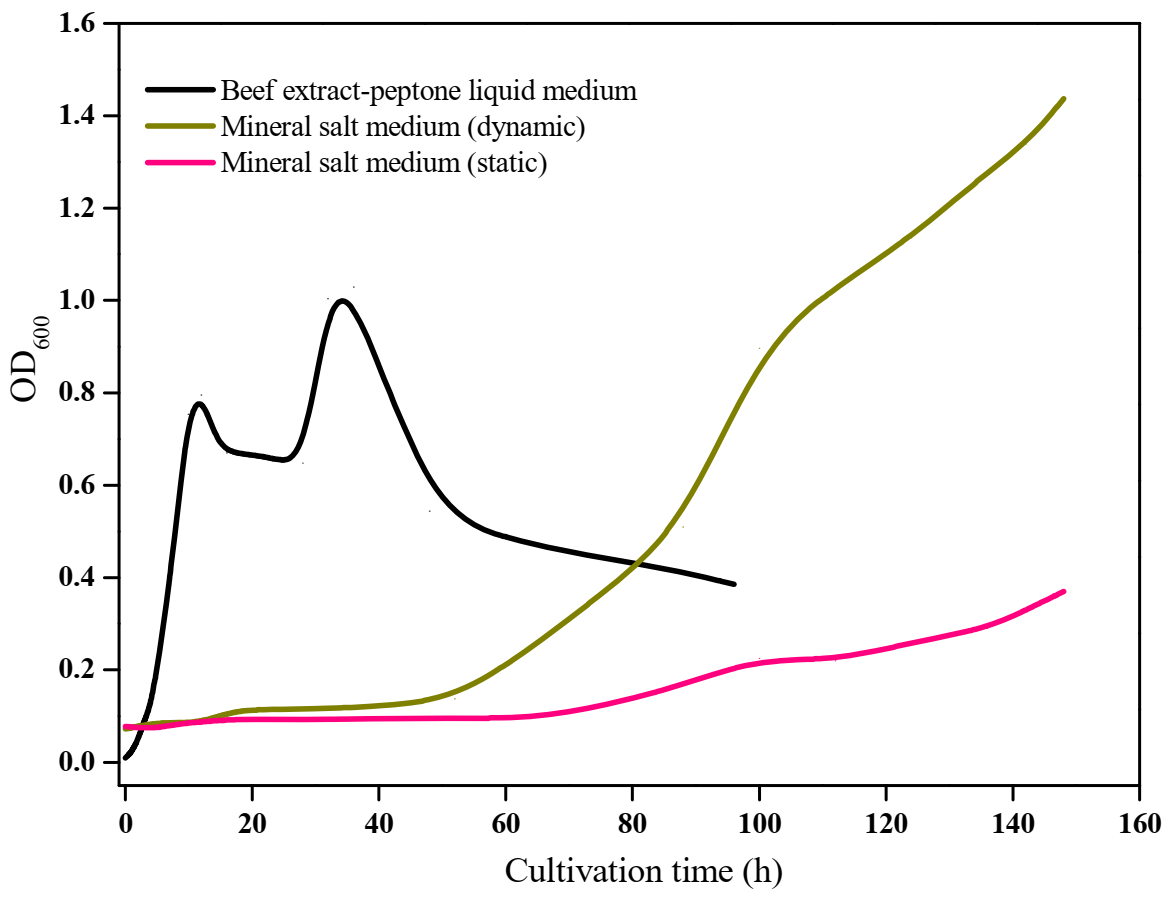
2.6. Growth Assay with Different Mediums
2.7. Degradation Properties
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Identification of a Crude Oil-Degrading Strain
3.2. Growth Characterization
3.3. Carbon Source Utilization
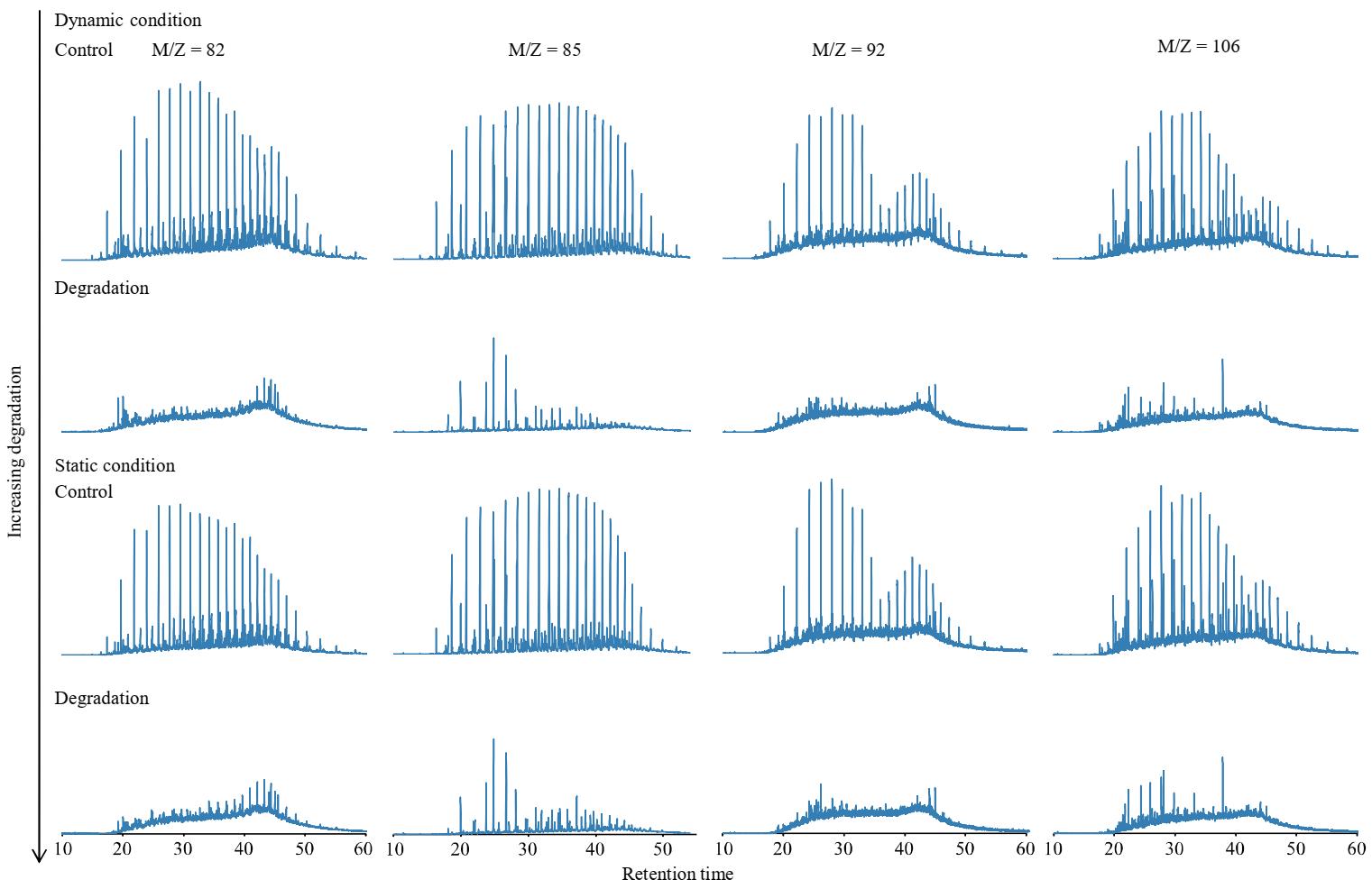
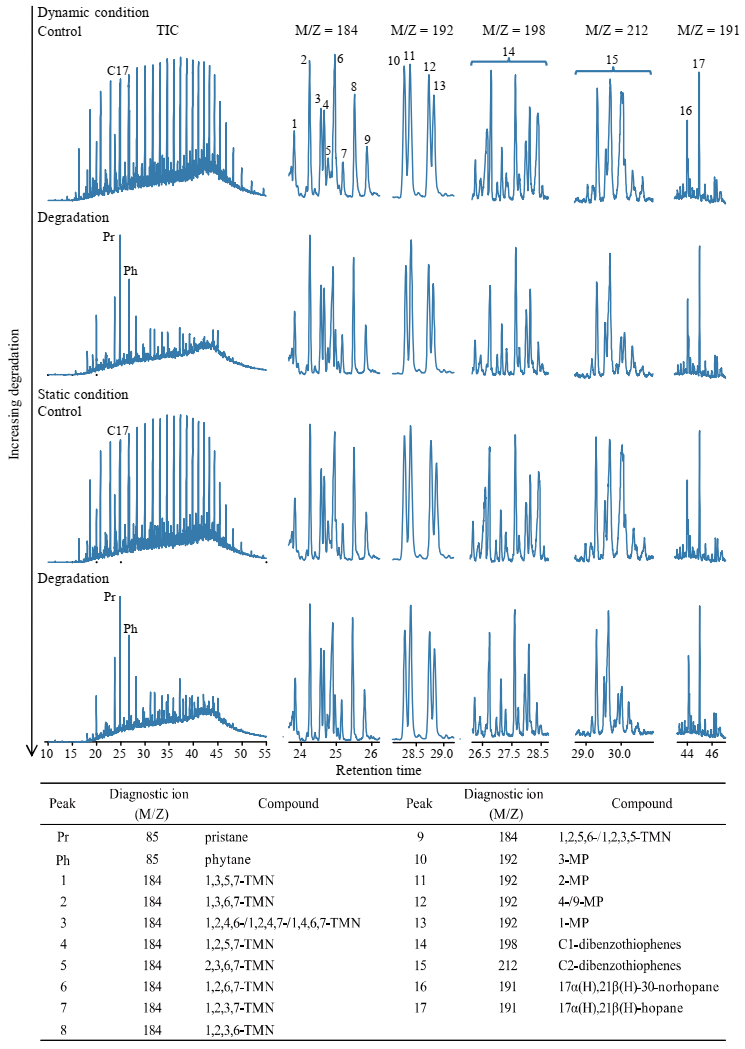
3.4. Crude Oil Degradation under Dynamic and Static Cultivation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Phulpoto, I.A.; Hu, B.W.; Wang, Y.F.; Ndayisenga, F.; Li, J.M.; Yu, Z.S. Effect of natural microbiome and culturable biosurfactants-producing bacterial consortia of freshwater lake on petroleum-hydrocarbon degradation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Han, I.; Kang, B.R.; Kim, S.H.; Sul, W.J.; Lee, T.K. Degradation of crude oil in a contaminated tidal flat area and the resilience of bacterial community. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abena, M.T.B.; Chen, G.Q.; Chen, Z.Y.; Zheng, X.C.; Li, S.S.; Li, T.T.; Zhong, W.H. Microbial diversity changes and enrichment of potential petroleum hydrocarbon degraders in crude oil-, diesel-, and gasoline-contaminated soil. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.G.; Liu, M.Z.; Chen, H.H.; Hou, G.H. Source identification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in different ecological wetland components of the Qinkenpao Wetland in Northeast China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 102, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.X.; Luo, Y.M.; Teng, Y.; Li, Z.G.; Ma, L.Q. Bioremediation of oily sludge-contaminated soil by stimulating indigenous microbes. Environ. Geochem. Health 2010, 32, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dua, M.; Singh, A.; Sethunathan, N.; Johri, A.K. Biotechnology and bioremediation: Successes and limitations. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 59, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.Q.; He, Y.; Huang, L.; Jiang, D.W.; Lu, W.Y. n-Hexadecane and pyrene biodegradation and metabolization by Rhodococcus sp. T1 isolated from oil contaminated soil. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 27, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varjani, S.J.; Upasani, V.N. Biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons by oleophilic strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa NCIM 5514. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 222, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshirsagar, S.D.; Mattam, A.J.; Jose, S.; Ramachandrarao, B.; Velankar, H.R. Heavy hydrocarbons as selective substrates for isolation of asphaltene degraders: A substrate-based bacterial isolation strategy for petroleum hydrocarbon biodegradation. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.Q.; Li, Y.P.; Huang, C.; Chen, F.L.; Ma, Y.L. Genome sequence and metabolic analysis of a fluoranthene-degrading strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa DN1. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvanitis, N.; Katsifas, E.A.; Chalkou, K.I.; Meintanis, C.; Karagouni, A.D. A refinery sludge deposition site: Presence of nahH and alkJ genes and crude oil biodegradation ability of bacterial isolates. Biotechnol. Lett. 2008, 30, 2105–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneiker, S.; Santos, V.A.M.D.; Bartels, D.; Bekel, T.; Brecht, M.; Buhrmester, J.; Chernikova, T.N.; Denaro, R.; Ferrer, M.; Gertler, C.; et al. Genome sequence of the ubiquitous hydrocarbon-degrading marine bacterium Alcanivorax borkumensis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.N.; Yao, J.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Liu, J.L. Biodegradation of pyrene by Pseudomonas sp. JPN2 and its initial degrading mechanism study by combining the catabolic nahAc gene and structure-based analyses. Chemosphere 2016, 164, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, X.Q.; Yang, W.; Xu, F.; Wang, W.; Feng, L.; Bartlam, M.; Wang, L.; Rao, Z.H. Crystal structure of long-chain alkane monooxygenase (LadA) in complex with coenzyme FMN: Unveiling the long-chain alkane hydroxylase. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 376, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, M.Q.; Fu, D.F.; Chakraborty, R.; Singh, R.P.; Terry, N. Enhanced crude oil depletion by constructed bacterial consortium comprising bioemulsifier producer and petroleum hydrocarbon degraders. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Esmail, G.A.; Arasu, M.V. Enhanced production of biosurfactant from Bacillus subtilis strain Al-Dhabi-130 under solid-state fermentation using date molasses from Saudi Arabia for bioremediation of crude-oil-contaminated soils. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Puri, S.; Thakur, I.S.; Kaur, J. Enhanced pyrene degradation by a biosurfactant producing Acinetobacter baumannii BJ5: Growth kinetics, toxicity and substrate inhibition studies. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, R.; Ali, M.I.; Ali, N.; Badshah, M.; Iqbal, M.; Jamal, A.; Huang, Z.X. Crude oil biodegradation potential of biosurfactant-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Meyerozyma sp. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakshi; Singh, S.K.; Haritash, A.K. Catabolic enzyme activities during biodegradation of three-ring PAHs by novel DTU-1Y and DTU-7P strains isolated from petroleum-contaminated soil. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 3101–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Pan, J.C.; Ma, Y.L. Elucidation of multiple alkane hydroxylase systems in biodegradation of crude oil n-alkane pollution by Pseudomonas aeruginosa DN1. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Chen, W.W.; Wang, Y.B.; Guo, J.; Zhang, H.K.; Hu, X.K. Nutrient depletion is the main limiting factor in the crude oil bioaugmentation process. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 100, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.Q.; Zhang, B.Y.; Zhu, Z.W.; Song, X.; Cai, Q.H.; Chen, B.; Dong, G.H.; Ye, X.D. Microbial eco-physiological strategies for salinity-mediated crude oil biodegradation. Sci. Total Enviro. 2020, 727, 138723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez García, M.; García de Llasera, M.P. A review on the enzymes and metabolites identified by mass spectrometry from bacteria and microalgae involved in the degradation of high molecular weight PAHs. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venosa, A.D.; Zhu, X.Q. Biodegradation of crude oil contaminating marine shorelines and freshwater wetlands. Spill Sci. Technol. B 2003, 8, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Yang, G.; Jia, H.; Yao, J. Impact of long-term cultivation with crude oil on wetland microbial community shifts and the hydrocarbon degradation potential. Energy Source Part A 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Yao, J.; Yuan, Z.M.; Shang, Y.F.; Chen, H.L.; Wang, F.; Masakorala, K.; Yu, C.; Cai, M.M.; Blake, R.E.; et al. Isolation and characterization of crude-oil-degrading bacteria from oil-water mixture in Dagang oilfield, China. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 87, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Kim, H.W.; Liu, C.L.; Lee, H.K. A simple method for DNA extraction from marine bacteria that produce extracellular materials. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2003, 52, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.W.; Cai, T.; Wen, W.T.; Ai, J.Z.; Ai, J.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhu, L.; George, S.C. Surfactin for enhanced removal of aromatic hydrocarbons during biodegradation of crude oil. Fuel 2020, 267, 117272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Hou, D.J.; Mao, R.; Xu, C.G. Severe biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in reservoired crude oils from the Miaoxi depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Fuel 2018, 211, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, N.; Morris, B.E.L.; Cai, M.M.; Gründger, F.; Yao, J.; Richnow, H.H.; Krüger, M. Evidence for in situ methanogenic oil degradation in the Dagang oil field. Org. Geochem. 2012, 52, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojarad, M.; Alemzadeh, A.; Ghoreishi, G.; Javaheri, M. Kerosene biodegradation ability and characterization of bacteria isolated from oil-polluted soil and water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4323–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; D’Angelo, E.M. Biogeochemical indicators to evaluate pollutant removal efficiency in constructed wetlands. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 35, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.C.; Silliman, B.R. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.L.; Sun, B.H.; Li, J.H. Influence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollution on the diversity and function of bacterial communities in urban wetlands. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 56281–56293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkem, B.M.; Halimoon, N.; Yusoff, F.M.; Johari, W.L.W.; Zakaria, M.P.; Medipally, S.R.; Kannan, N. Isolation, identification and diesel-oil biodegradation capacities of indigenous hydrocarbon-degrading strains of Cellulosimicrobium cellulans and Acinetobacter baumannii from tarball at Terengganu beach, Malaysia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 107, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.V.; Karegoudar, T.B.; Nayak, A.S. Enhanced utilization of fluorene by Paenibacillus sp. PRNK-6: Effect of rhamnolipid biosurfactant and synthetic surfactants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 151, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogan, B.W.; Sullivan, W.R.; Kayser, K.J.; Derr, K.D.; Aldrich, H.C.; Paterek, J.R. Alkanindiges illinoisensis gen. nov., sp. nov., an obligately hydrocarbonoclastic, aerobic squalane-degrading bacterium isolated from oilfield soils. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muralidharan, M.; Kavitha, R.; Kumar, P.S.; Pooja, M.; Rajagopal, R.; Gayathri, K.V. Performance evaluation and mechanism analysis of halotolerant bacterial strains and cerium oxide nanoparticle to degrade Benzo[a]pyrene. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janniche, G.S.; Spliid, H.; Albrechtsen, H.J. Microbial community-level physiological profiles (CLPP) and herbicide mineralization potential in groundwater affected by agricultural land use. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2012, 140–141, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabirova, J.S.; Becker, A.; Lünsdorf, H.; Nicaud, J.M.; Timmis, K.N.; Golyshin, P.N. Transcriptional profiling of the marine oil-degrading bacterium Alcanivorax borkumensis during growth on n-alkanes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 319, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Beilen, J.B.; Smits, T.H.M.; Roos, F.F.; Brunner, T.; Balada, S.B.; Rothlisberger, M.; Witholt, B. Identification of an amino acid position that determines the substrate range of integral membrane alkane hydroxylases. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Throne-Holst, M.; Wentzel, A.; Ellingsen, T.E.; Kotlar, H.K.; Zotchev, S.B. Identification of novel genes involved in long-chain n-alkane degradation by Acinetobacter sp. strain DSM 17874. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3327–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasian, F.; Lockington, R.; Mallavarapu, M.; Naidu, R. A aomprehensive review of aliphatic hydrocarbon biodegradation by bacteria. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 176, 670–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varjani, S.J.; Upasani, V.N. A new look on factors affecting microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon pollutants. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 120, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezza, F.A.; Chirwa, E.M.N. The role of lipopeptide biosurfactant on microbial remediation of aged polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAHs)-contaminated Soil. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 309, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasumarthi, R.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Mutnuri, S. Biodegradation of crude oil by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia fergusonii isolated from the Goan coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 76, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraro, D.J.; Okerlund, A.L.; Mowers, J.C.; Ramaswamy, S. Structural basis for regioselectivity and stereoselectivity of product formation by naphthalene 1,2-dioxygenase. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 6986–6994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Khara, P.; Roy, M.; Chakraborty, J.; Dutta, A.; Dutta, T.K. Characterization of a topologically unique oxygenase from Sphingobium sp. PNB capable of catalyzing a broad spectrum of aromatics. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2018, 111, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musumeci, M.A.; Loviso, C.L.; Lozada, M.; Ferreira, F.V.; Dionisi, H.M. Substrate specificities of aromatic ring-hydroxylating oxygenases of an uncultured gammaproteobacterium from chronically-polluted subantarctic sediments. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 137, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musumeci, M.A.; Lozada, M.; Rial, D.V.; Mac Cormack, W.P.; Jansson, J.K.; Sjöling, S.; Carroll, J.; Dionisi, H.M. Prospecting biotechnologically-relevant monooxygenases from cold sediment metagenomes: An in silico approach. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wan, Y.Y.; Wang, C.J.; Ma, Z.Y.; Liu, X.L.; Li, S.J. Biodegradation of n-alkanes in crude oil by three identified bacterial strains. Fuel 2020, 275, 117897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerniglia, C.E. Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Biodegradation 1992, 3, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.M.; Yao, J.; Yang, H.J.; Wang, R.X.; Kanaji, M. Aerobic biodegradation process of petroleum and pathway of main compounds in water flooding well of Dagang oil field. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamzah, A.; Phan, C.W.; Abu Bakar, N.F.; Wong, K.K. Biodegradation of crude oil by constructed bacterial consortia and the constituent single bacteria isolated from Malaysia. Bioremediat. J. 2013, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
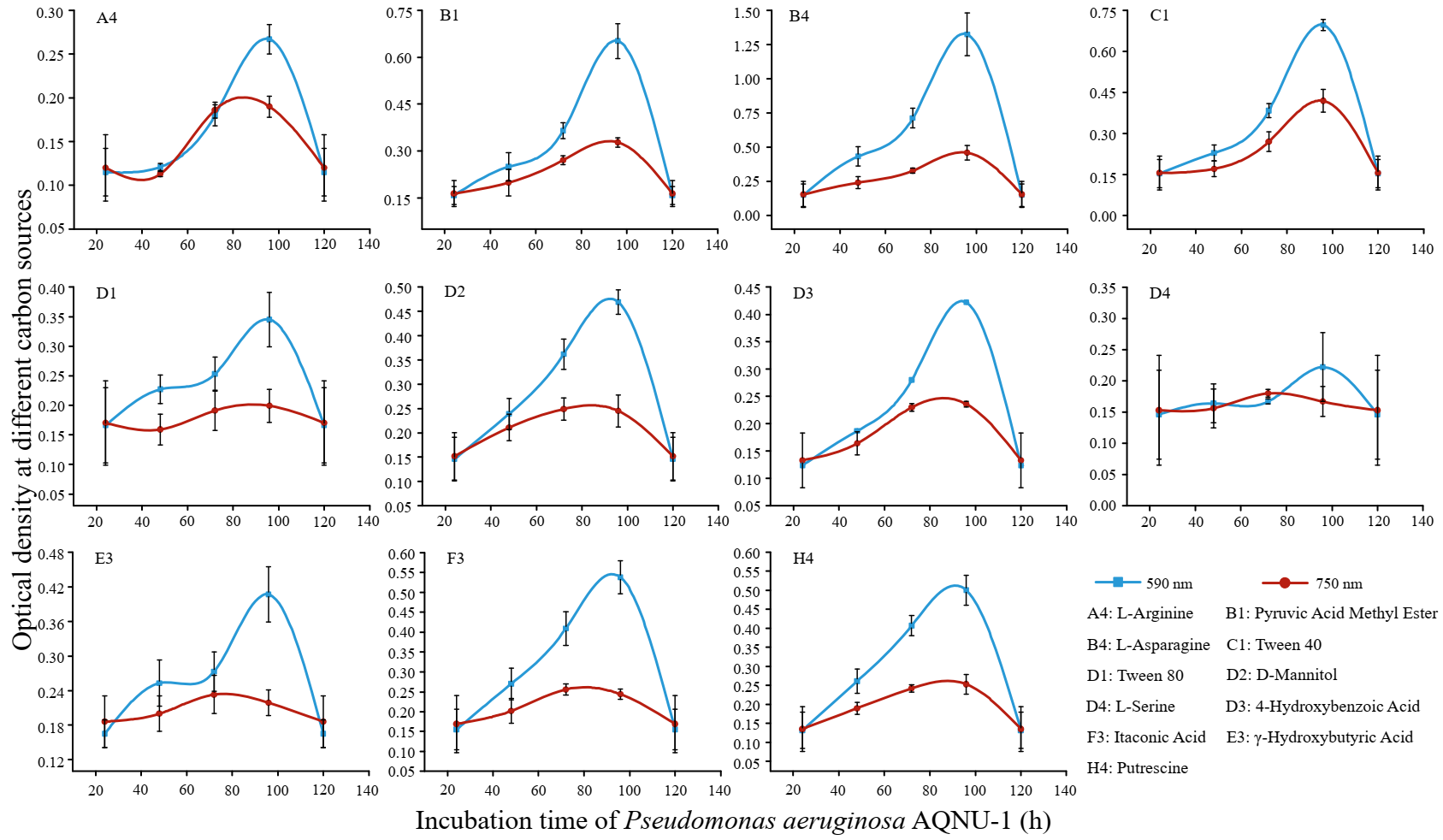
| Categories | Carbon Sources | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Carbohydrates | D-xylose |
| D-mannitol | ||
| N-acetyl-D-glucosamine | ||
| 2 | Amino acids | L-asparagine |
| L-arginine | ||
| L-serine | ||
| 3 | Carboxylic acids | γ-hydroxybutyric acid |
| Itaconic acid | ||
| Pyruvic acid methyl ester | ||
| 4 | Polymer | Tween 40 |
| Tween 80 | ||
| 5 | Phenolic acids | 4-hydroxybenzoic acid |
| 6 | Amine | Putrescine |
| Compound (n-Alkane) | Degradation Ratio (%) | Compound (n-Alkane) | Degradation Ratio (%) | Compound (PAHs) | Degradation Ratio (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamic | Static | Dynamic | Static | Dynamic | Static | |||
| n-C13 | 100 | 100 | n-C25 | 92 | 89 | M/Z = 138 | 37 | 65 |
| n-C14 | 100 | 100 | n-C26 | 96 | 93 | M/Z = 142 | 72 | 67 |
| n-C15 | 100 | 100 | n-C27 | 99 | 96 | M/Z = 152 | 15 | 33 |
| n-C16 | 100 | 100 | n-C28 | 100 | 95 | M/Z = 154 | 56 | 49 |
| n-C17 | 100 | 100 | n-C29 | 100 | 95 | M/Z = 154 * | 100 | 100 |
| n-C18 | 100 | 100 | n-C30 | 100 | 94 | M/Z = 168 | 72 | 61 |
| n-C19 | 98 | 98 | n-C31 | 100 | 92 | M/Z = 184 | 29 | 21 |
| n-C20 | 96 | 96 | n-C32 | 100 | 95 | M/Z = 192 | 26 | 24 |
| n-C21 | 100 | 98 | n-C33 | 100 | 93 | M/Z = 198 | 16 | 10 |
| n-C22 | 100 | 97 | n-C34 | 87 | 74 | M/Z = 212 | 25 | 27 |
| n-C23 | 93 | 94 | n-C35 | 87 | 75 | |||
| n-C24 | 98 | 96 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Yang, G.; Jia, H.; Sun, B. Crude Oil Degradation by a Novel Strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa AQNU-1 Isolated from an Oil-Contaminated Lake Wetland. Processes 2022, 10, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10020307
Liu H, Yang G, Jia H, Sun B. Crude Oil Degradation by a Novel Strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa AQNU-1 Isolated from an Oil-Contaminated Lake Wetland. Processes. 2022; 10(2):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10020307
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Haijun, Guo Yang, Hui Jia, and Bingjie Sun. 2022. "Crude Oil Degradation by a Novel Strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa AQNU-1 Isolated from an Oil-Contaminated Lake Wetland" Processes 10, no. 2: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10020307
APA StyleLiu, H., Yang, G., Jia, H., & Sun, B. (2022). Crude Oil Degradation by a Novel Strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa AQNU-1 Isolated from an Oil-Contaminated Lake Wetland. Processes, 10(2), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10020307





