Bioleaching and Selective Precipitation for Metal Recovery from Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
2.3. Batch Mode Bioleaching
2.4. Semi-Continuous Mode Bioleaching
2.5. Chemical Analysis
2.6. Kinetic Analysis
2.7. Preparation of the Synthetic Metal Solutions
2.8. Selective Chemical Precipitation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of BOF Slag
3.2. Batch Mode Bioleaching of BOF Slag
3.3. Semi-Continuous Mode Bioleaching of BOF Slag
3.4. Selective Chemical Precipitation for Metal Recovery
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steffen, W.; Broadgate, W.; Deutsch, L.; Gaffney, O.; Ludwig, C. The trajectory of the anthropocene: The great acceleration. Anthr. Rev. 2015, 2, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedmann, T.O.; Schandl, H.; Lenzen, M.; Moran, D.; Suh, S.; West, J.; Kanemoto, K. The material footprint of nations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 6271–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ali, S.H.; Giurco, D.; Arndt, N.; Nickless, E.; Brown, G.; Demetriades, A.; Durrheim, R.; Enriquez, M.A.; Kinnaird, J.; Littleboy, A.; et al. Mineral supply for sustainable development requires resource governance. Nature 2017, 543, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, R.A. The coming copper peak. Science 2014, 343, 722–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohr, S.; Giurco, D.; Retamal, M.; Mason, L.; Mudd, G. Global projection of lead-zinc supply from known resources. Resources 2018, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cossu, R.; Williams, I.D. Urban mining: Concepts, terminology, challenges. Waste Manag. 2015, 45, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Mathews, J.A.; Li, J. Urban Mining of E-Waste is Becoming More Cost-Effective Than Virgin Mining. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4835–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esguerra, J.L.; Laner, D.; Svensson, N.; Krook, J. Landfill mining in Europe: Assessing the economic potential of value creation from generated combustibles and fines residue. Waste Manag. 2021, 126, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerbach, R.; Ratering, S.; Bokelmann, K.; Gellermann, C.; Brämer, T.; Baumann, R.; Schnell, S. Bioleaching of valuable and hazardous metals from dry discharged incineration slag. An approach for metal recycling and pollutant elimination. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, H.I.; Funari, V.; Dinelli, E.; Soavi, F. Enhanced electrodialytic bioleaching of fly ashes of municipal solid waste incineration for metal recovery. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 345, 136188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremser, K.; Thallner, S.; Strbik, D.; Spiess, S.; Kucera, J.; Vaculovic, T.; Vsiansky, D.; Haberbauer, M.; Mandl, M.; Guebitz, G.M. Leachability of metals from waste incineration residues by iron- and sulfur-oxidizing bacteria. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Rastegar, S.O.; Mousavi, S.M.; Li, M.; Zhou, M. Advances in bioleaching for recovery of metals and bioremediation of fuel ash and sewage sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 261, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Wang, S.Y. Effects of solid content and substrate concentration on bioleaching of heavy metals from sewage sludge using Aspergillus niger. Metals 2019, 9, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.Y.; Cheng, Y.K. Effects of sulfur dosage and inoculum size on pilot-scale thermophilic bioleaching of heavy metals from sewage sludge. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocheng, H.; Su, C.; Jadhav, U.U. Bioleaching of metals from steel slag by Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans culture supernatant. Chemosphere 2014, 117, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestola, E.A.; Kuusenaho, M.K.; Närhi, H.M.; Tuovinen, O.H.; Puhakka, J.A.; Plumb, J.J.; Kaksonen, A.H. Acid bioleaching of solid waste materials from copper, steel and recycling industries. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 103, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremser, K.; Gerl, P.; Pellis, A.; Guebitz, G.M. A new bioleaching strategy for the selective recovery of aluminum from multi-layer beverage cans. Waste Manag. 2021, 120, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremser, K.; Thallner, S.; Schoen, H.; Weiss, S.; Hemmelmair, C.; Schnitzhofer, W.; Aldrian, A.; Guebitz, G.M. Stirred-tank and heap-bioleaching of shredder-light-fractions (SLF) by acidophilic bacteria. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 193, 105315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srichandan, H.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, P. Hydrometallurgy Bioleaching approach for extraction of metal values from secondary solid wastes: A critical review. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 189, 105122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethurajan, M.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Nancharaiah, Y.V. Biotechnology in the management and resource recovery from metal bearing solid wastes: Recent advances. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 211, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voestalpine AG LD-Schlacke Daten und Fakten. Available online: www.voestalpine.com (accessed on 12 January 2022).
- Chaurand, P.; Rose, J.; Domas, J.; Bottero, J.Y. Speciation of Cr and V within BOF steel slag reused in road constructions. J. Geochem. Explor. 2006, 88, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUROSLAG. Euroslag Statistics; Euroslag: Duisburg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Federal Ministry for Digital and Economic Affairs. BGBl. II Nr. 181/2015; Federal Ministry for Digital and Economic Affairs: Vienna, Austria, 2014; pp. 1–220.
- Xiang, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhu, N.; Zhang, T.; Liu, W.; Wu, J.; Li, P. Bioleaching of copper from waste printed circuit boards by bacterial consortium enriched from acid mine drainage. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Yang, M.; Lin, H. Bioleaching of vanadium by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans from vanadium-bearing resources: Performance and mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Li, G.; Yan, P.; Ren, J.; Zheng, L.; Han, D.; Sun, S.; Huang, S.; Zhong, Y. Removal of metals from lead-zinc mine tailings using bioleaching and followed by sulfide precipitation. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Bermúdez, Y.; Rodríguez Rico, I.L.; Guibal, E.; Calero de Hoces, M.; Martín-Lara, M.Á. Biosorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by Sargassum muticum brown alga. Application of statistical design for process optimization. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 183, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alebrahim, M.F.; Khattab, I.A.; Cai, Q.; Sanduk, M. Practical study on the electrochemical simultaneous removal of copper and zinc from simulated binary-metallic industrial wastewater using a packed-bed cathode. Egypt. J. Pet. 2017, 26, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Modin, O.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Rauch, S.; Fedje, K.K. Bioelectrochemical recovery of Cu, Pb, Cd, and Zn from dilute solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 235–236, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, P.; Huang, J.C.; Li, A.W.F.; Wei, S. Heavy metal removal from wastewater in fluidized bed reactor. Water Res. 1999, 33, 1918–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlović, J.; Stopić, S.; Friedrich, B.; Kamberović, Ž. Selective removal of heavy metals from metal-bearing wastewater in a cascade line reactor. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2007, 14, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya-Beltrán, A.; Beard, S.; Rojas-Villalobos, C.; Issotta, F.; Gallardo, Y.; Ulloa, R.; Giaveno, A.; Degli Esposti, M.; Johnson, D.B.; Quatrini, R. Genomic evolution of the class Acidithiobacillia: Deep-branching Proteobacteria living in extreme acidic conditions. ISME J. 2021, 15, 3221–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, H.I.; Funari, V.; Mayes, W.M.; Rogerson, M.; Prior, T.J. Recovery of Al, Cr and V from steel slag by bioleaching: Batch and column experiments. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 222, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirazimi, S.M.J.; Abbasalipour, Z.; Rashchi, F. Vanadium removal from LD converter slag using bacteria and fungi. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 153, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thallner, S.; Hemmelmair, C.; Martinek, S.; Schnitzhofer, W. Bioleaching for removal of chromium and associated metals from LD slag. Solid State Phenom. 2017, 262, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.L.; Lv, S.Q.; Xia, J.L.; Nie, Z.Y.; Zhang, D.R.; Pan, X.; Liu, L.Z.; Wen, W.; Zheng, L.; Zhao, Y.D. Extraction of Al and Ce from coal fly ash by biogenic Fe3+ and H2SO4. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 370, 1407–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramov, S.; He, J.; Wimmer, D.; Lemloh, M.L.; Muehe, E.M.; Gann, B.; Roehm, E.; Kirchhof, R.; Babechuk, M.G.; Schoenberg, R.; et al. Heavy metal mobility and valuable contents of processed municipal solid waste incineration residues from Southwestern Germany. Waste Manag. 2018, 79, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, A.; Srichandan, H.; Kim, D.J. Column bioleaching of metals from refinery spent catalyst by Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans: Effect of operational modifications on metal extraction, metal precipitation, and bacterial attachment. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 242, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Lin, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y. Blank roasting and bioleaching of stone coal for vanadium recycling. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 243, 118625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikoda, B.; Potysz, A.; Kmiecik, E. Bacterial leaching of critical metal values from Polish copper metallurgical slags using Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 236, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, A.C.; Von Bernath, D.; Jerez, A.C. Heavy Metal Resistance Strategies of Acidophilic Bacteria and Their Acquisition: Importance for Biomining and Bioremediation. Biol. Res. 2013, 46, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asghari, I.; Mousavi, S.M. Effects of key parameters in recycling of metals from petroleum refinery waste catalysts in bioleaching process. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 13, 139–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

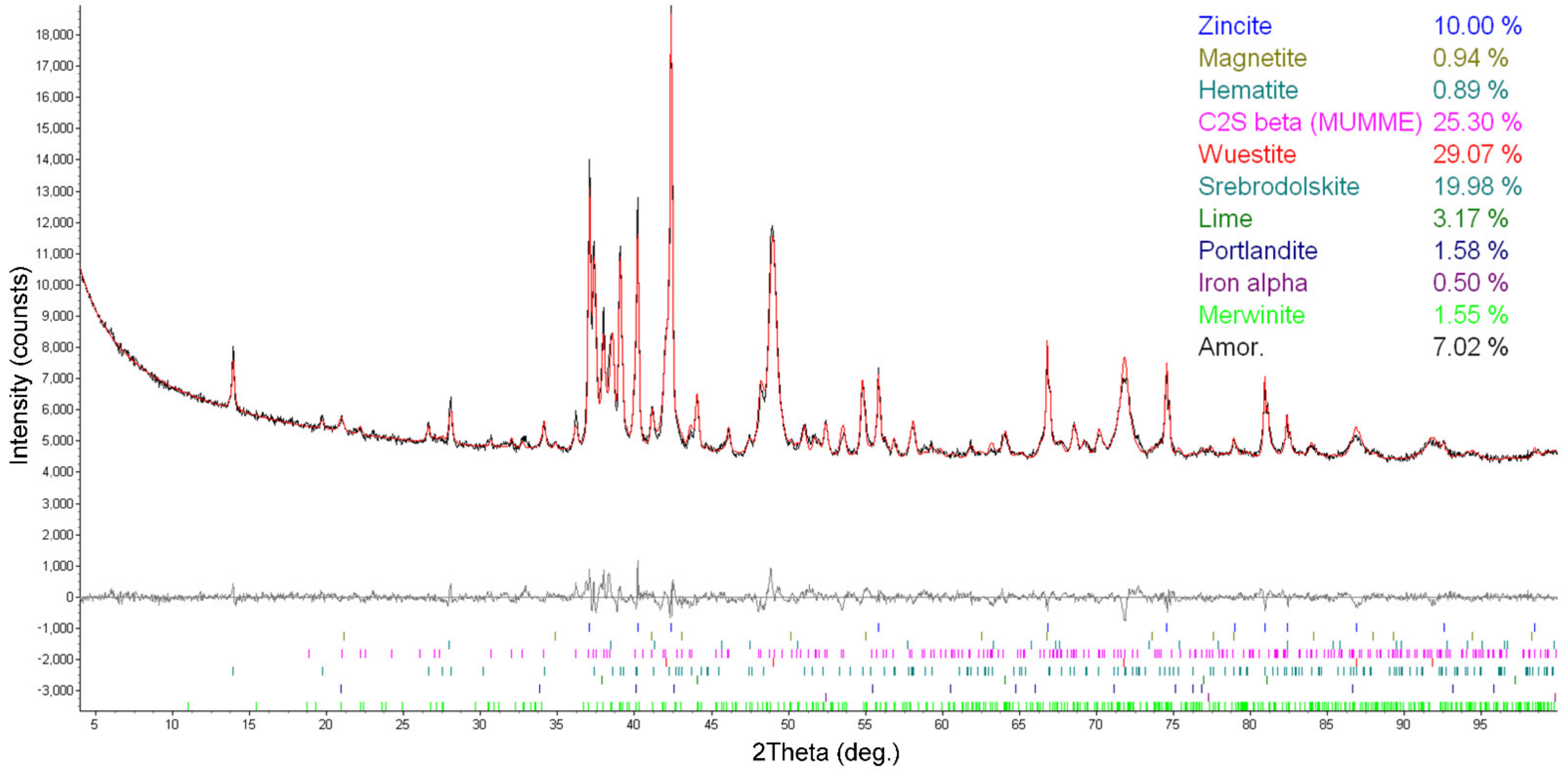

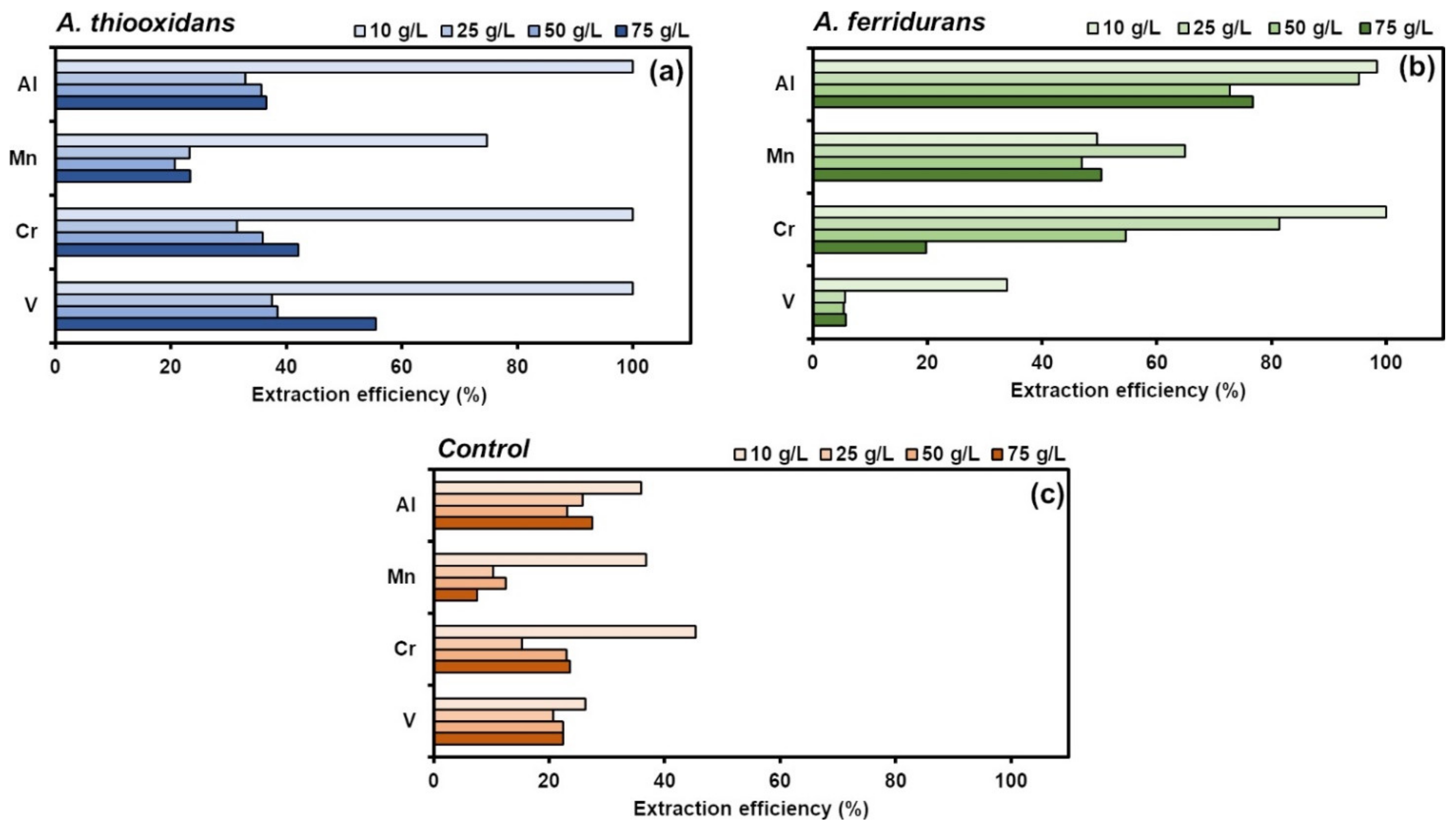
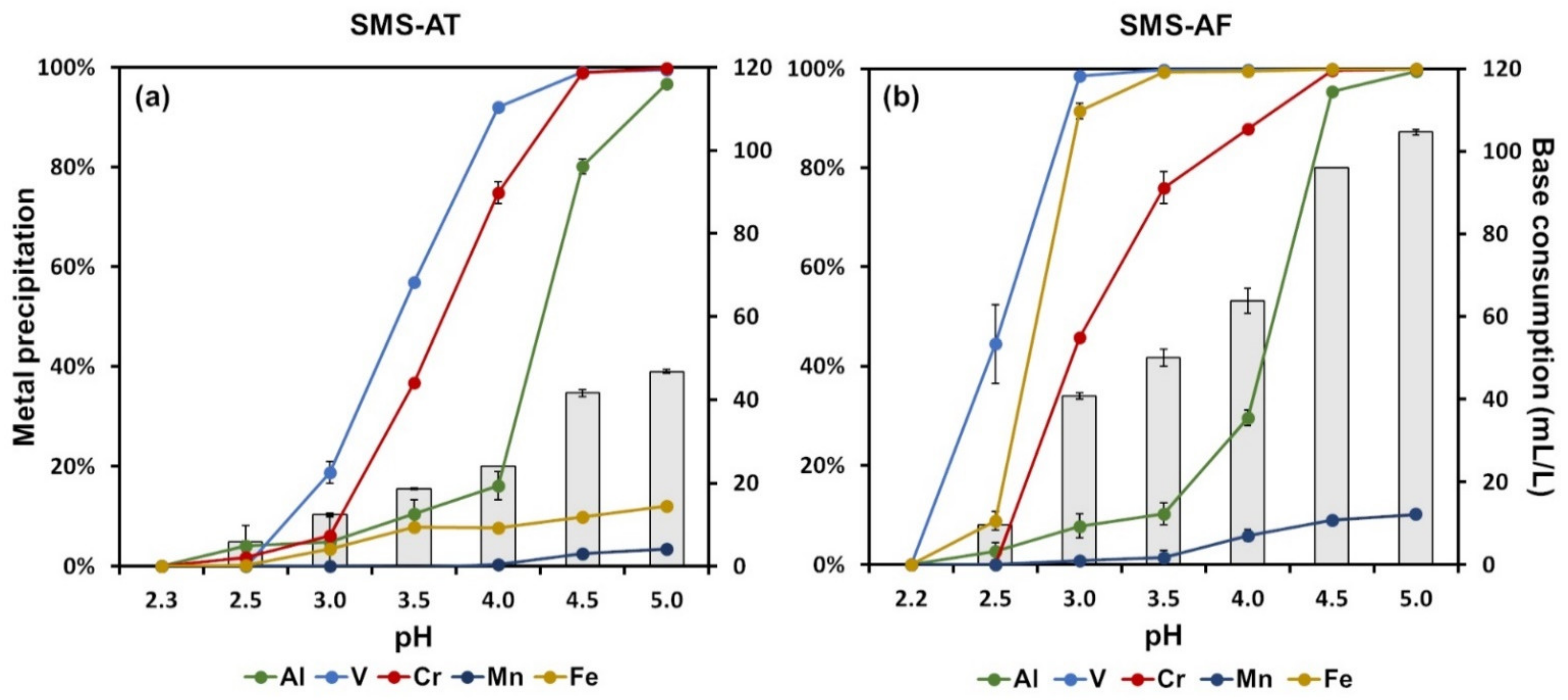
| Elements (mg/g) | The Average Values and Standard Deviations (n = 3) |
|---|---|
| Fe | 225.70 ± 4.97 |
| Mn | 51.46 ± 0.95 |
| Al | 9.21 ± 0.62 |
| Cr | 1.30 ± 0.00 |
| V | 0.67 ± 0.03 |
| Acid Consumption | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Slag Concentration (g/L) | Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans | Acidithiobacillus ferridurans | Control |
| (mL 18 M H2SO4/g Slag) | |||
| 10 | - | - | 0.44 |
| 25 | 0.05 | - | 0.27 |
| 50 | 0.31 | 0.07 | 0.25 |
| 75 | 0.49 | 0.19 | 0.23 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kremser, K.; Thallner, S.; Spiess, S.; Kucera, J.; Vaculovic, T.; Všianský, D.; Haberbauer, M.; Guebitz, G.M. Bioleaching and Selective Precipitation for Metal Recovery from Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag. Processes 2022, 10, 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10030576
Kremser K, Thallner S, Spiess S, Kucera J, Vaculovic T, Všianský D, Haberbauer M, Guebitz GM. Bioleaching and Selective Precipitation for Metal Recovery from Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag. Processes. 2022; 10(3):576. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10030576
Chicago/Turabian StyleKremser, Klemens, Sophie Thallner, Sabine Spiess, Jiri Kucera, Tomas Vaculovic, Dalibor Všianský, Marianne Haberbauer, and Georg M. Guebitz. 2022. "Bioleaching and Selective Precipitation for Metal Recovery from Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag" Processes 10, no. 3: 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10030576
APA StyleKremser, K., Thallner, S., Spiess, S., Kucera, J., Vaculovic, T., Všianský, D., Haberbauer, M., & Guebitz, G. M. (2022). Bioleaching and Selective Precipitation for Metal Recovery from Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag. Processes, 10(3), 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10030576







