Effects of Outer Edge Bending on the Aerodynamic and Noise Characters of Axial Fan for Air Conditioners
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model and Numerical Simulation
2.1. Geometric Model and Design of Bending Orthogonal Schemes
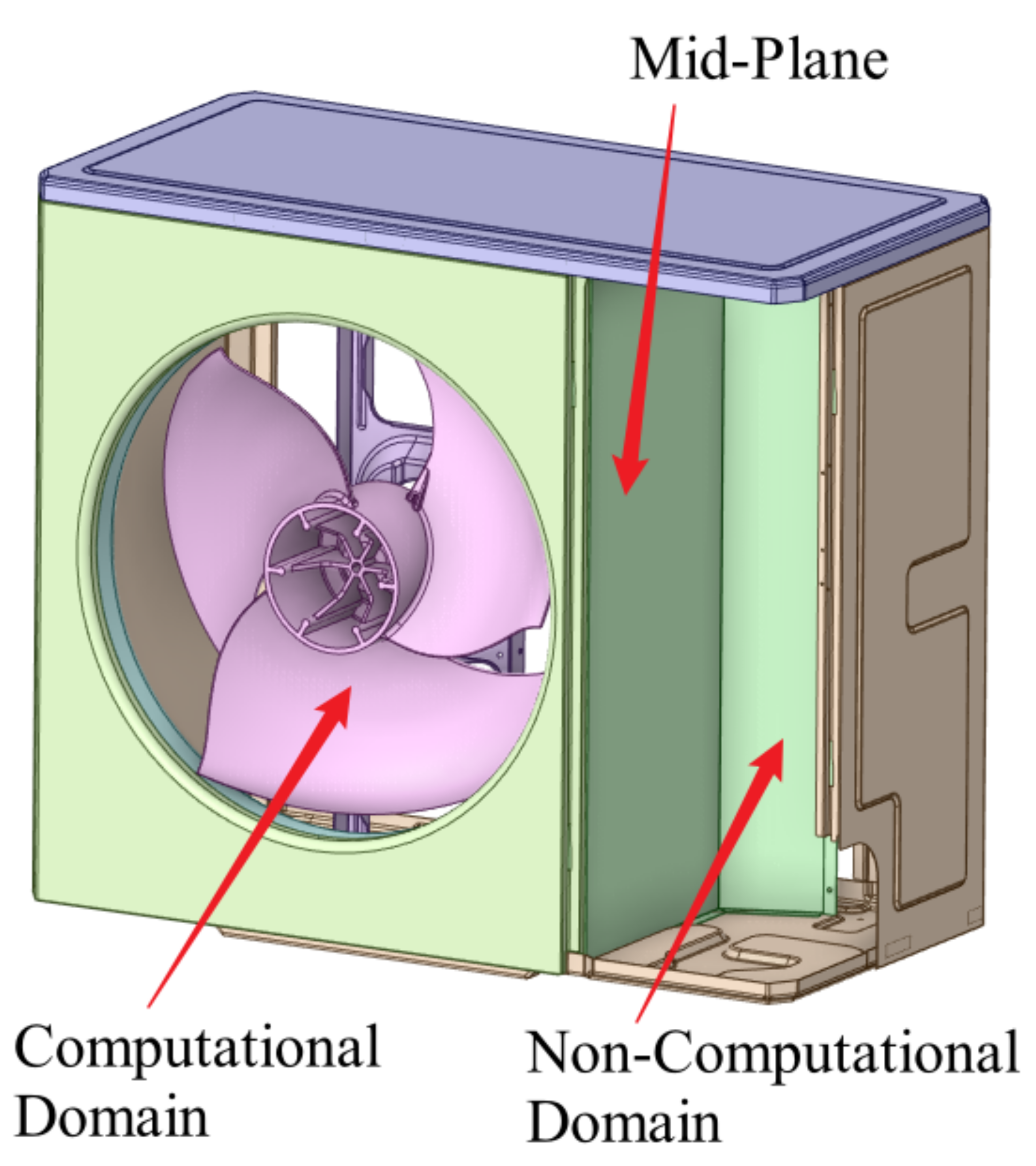
2.2. Simulation Model and Numerical Methods
2.3. Independence of Grid and Verification of Simulation Result
3. Simulation Results and Analysis
3.1. Effects of Bending Parameters on Fan Performance
3.2. Effects of Preferred Schemes on the Fan Performance
3.3. Effects of Preferred Schemes on Aerodynamic Noises
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Experimental Results of Aerodynamic Performances
4.2. Experimental Results of SPL and Sound Quality
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- After bending, the impellers’ volume flow rates were reduced to varying degrees, while their total pressure efficiency was slightly improved. However, the fan aerodynamic performance change affected by the outer edge bending is negligible. A well-designed impeller outer edge bend improves the load distribution on the blade surfaces, thereby increasing the total pressure efficiency of the impeller.
- (2)
- Simulation and experimental results showed that the smooth transition of the outer edge bending in a large radial range minimizes the volume flow rate attenuation caused by outer edge bending. The impeller’s total pressure efficiency was improved by a large degree of bending in a small radial range. The orthogonal parameter analysis showed that the bending degree affects fan efficiency more than the circumferential starting and radial relative positions.
- (3)
- Fan blade design with a significant degree of bending in a small radial range could effectively weaken the tip vortex strength, reduce the pressure pulsation on the blade tip, and reduce the SPL of the fan. For the Case-10 solution with the best noise-reduction effect, the noise of Case-Basic was reduced by 0.54~2.68 dB(A) under the same volumetric flow, and the total pressure efficiency of the rated working condition was increased by 0.68%.
- (4)
- The bending characteristics mainly reduced fans’ broadband noise among 200~1000 Hz, and the improvement of discrete noise was relatively limited. An analysis of the sound quality showed that the rationally designed outer edge bending scheme had lower loudness and roughness, which effectively improved the sound quality of fan noise.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, S.C.; Park, K.S.; Kim, K.W. The Study on Affecting Subject Accomplishment by Noise. J. Ergon. Soc. Korea 2010, 29, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K. Sources, Effects, and Control of Noise in Indoor/Outdoor Living Environments. J. Ergon. Soc. Korea 2015, 34, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stansfeld, S.A.; Matheson, M.P. Noise pollution: Non-auditory effects on health. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ising, H.; Gunther, T. Interaction between noise-induced stress and magnesium losses: Relevance for long-term health effects. In Proceedings of the INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference Proceedings, Budapest, Hungary, 25 August 1997; pp. 1258–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Z. Prediction and measurement of axial flow fan aerodynamic and aeroacoustic performance in a split-type air-conditioner outdoor unit. Int. J. Refrig. 2013, 36, 1098–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, C.-M.; Furukawa, M.; Inoue, M. Analysis of Vortical Flow Field in a Propeller Fan by LDV Measurements and LES—Part II: Unsteady Nature of Vortical Flow Structures Due to Tip Vortex Breakdown. J. Fluids Eng. 2001, 123, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, C.-M.; Furukawa, M.; Inoue, M. Analysis of Vortical Flow Field in a Propeller Fan by LDV Measurements and LES—Part I: Three-Dimensional Vortical Flow Structures. J. Fluids Eng. 2001, 123, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.L.; Tian, J.; Ouyang, H.; Chen, J.P.; Chen, Z.J. Investigation of air-flow fields and aeroacoustic noise in outdoor unit for split-type air conditioner. Noise Control. Eng. J. 2006, 54, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.L.; Chen, J.P.; Chen, Z.J.; Tian, J.; Hua, O.Y.; Du, Z.H. Experimental and numerical study on aeroacoustic sound of axial flow fan in room air conditioner. Appl. Acoust. 2007, 68, 458–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.J.; Ouyang, H.; Du, Z.H. Experimental and numerical investigation of noise generated by rotor blade passing an exhaust grille. Noise Control. Eng. J. 2008, 56, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, T.; Ouyang, H.; Wu, Y.D. Experimental and numerical study on aerodynamic noise of outdoor unit of room air conditioner with different grilles. Int. J. Refrig. 2009, 32, 1112–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, B.; Chu, W.L.; Zhang, H.G. Tip leakage flow and aeroacoustics analysis of a low-speed axial fan. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 98, 105700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vad, J. Aerodynamic effects of blade sweep and skew in low-speed axial flow rotors at the design flow rate: An overview. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part. A 2008, 222, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Ouyang, H.; Du, Z.-H. Internal flow Mechanism and Experimental Research of low Pressure Axial fan with Forward-Skewed Blades. J. Hydrodyn. 2008, 20, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vad, J.; Kwedikha, A.R.A.; Horváth, C.; Balczó, M.; Lohász, M.M.; Régert, T. Aerodynamic effects of forward blade skew in axial flow rotors of controlled vortex design. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part. A 2007, 221, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Fan, F.; Zhang, R.; Li, C. Prediction of Performance of a Variable-Pitch Axial Fan with Forward-Skewed Blades. Energies 2019, 12, 2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurault, J.; Kouidri, S.; Bakir, F.; Rey, R. Experimental and numerical study of the sweep effect on three-dimensional flow downstream of axial flow fans. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2010, 21, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Gu, C.G. The Effects of Radially Distorted Incident Flow on Performance of Axial-Flow Fans with Forward-Skewed Blades. J. Turbomach. 2013, 135, 11039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Ye, J. Investigation acoustic effect of the convexity-preserving axial flow fan based on Bezier function. Comput. Fluids. 2014, 102, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulhane, N.; Patil, S.; Singh, K. Acoustic Analysis of Condenser Fan of Split Air Conditioner Using Numerical and Experimental Method. Int. J. Air Cond. Refrig. 2015, 23, 1550012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, X. Numerical investigation of aerodynamic and acoustic characteristics of bionic airfoils inspired by bird wing. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part. G 2018, 233, 4004–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkermans, R.; Stuermer, A.; Delfs, J.W. Active Flow Control for Interaction Noise Reduction of Contra-Rotating Open Rotors. AIAA J. 2016, 54, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stürmer, A.; Akkermans, R.A.D. Multidisciplinary analysis of CROR propulsion systems: DLR activities in the JTI SFWA project. CEAS Aeronaut. J. 2014, 5, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Joo, W.-G. Effect of tip clearance, winglets, and shroud height on the tip leakage in axial flow fans. Int. J. Refrig. 2018, 93, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.-G.; Jung, J.H.; Jeon, W.-H.; Joo, W.-G.; Minorikawa, G. Investigation study on the flow-induced noise by winglet and shroud shape of an axial flow fan at an outdoor unit of air conditioner. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2020, 34, 2845–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-I.; Lee, S.-Y.; Lee, K.-Y.; Yang, S.-H.; Choi, Y.-S. Numerical Investigation of Performance and Flow Characteristics of a Tunnel Ventilation Axial Fan with Thickness Profile Treatments of NACA Airfoil. Energies 2020, 13, 5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauert, J. Communication Acoustics. In Psycho-Acoustics and Sound Quality; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2005; pp. 139–162. [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano, S.; Namba, S.; Kurakata, K.; Kikuchi, Y. Evaluation of broad-band noise mixed with amplitude-modulated sounds. Acoust. Sci. Technol. 1994, 15, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Park, S.G.; Park, J.T.; Seo, K.W.; Lee, G.B.J. Comparison of the Sound Quality Characteristics for the Outdoor Unit according to the Compressor Model. In Proceedings of the International Compressor Engineering Conference, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 16–19 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann, C.; Carolus, T.; Schneider, M. A Semantic Differential for Evaluating the Sound Quality of Fan Systems. In Proceedings of the Asme Turbo Expo Turbomachinery Technical Conference & Exposition, Charlotte, NC, USA, 26–30 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Soeta, Y.; Onogawa, E. Multidimensional Psychological Evaluation of Air Conditioner Sounds and Prediction via Correlation Parameters. Front. Built Environ. 2021, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, K.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Yu, W. A perceptual dissimilarities based nonlinear sound quality model for range hood noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 144, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeta, Y.; Shimokura, R. Sound quality evaluation of air-conditioner noise based on factors of the autocorrelation function. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 124, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, F.R. Two-equation eddy-viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications. AIAA J. 1994, 32, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS, Inc. ANSYS CFX Solver Theory Guide, Release 18, 2nd ed.; ANSYS, Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Franzke, R.; Sebben, S.; Bark, T.; Willeson, E.; Broniewicz, A. Evaluation of the Multiple Reference Frame Approach for the Modelling of an Axial Cooling Fan. Energies 2019, 12, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jiang, B.Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.P.; Xiao, Q.H. Numerical and experimental investigations on non-axisymmetric D-type inlet nozzle for a squirrel-cage fan. Eng. Appl. Comp. Fluid Mech. 2021, 15, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvish, M.; Frank, S.; Paschereit, C.O. Numerical and Experimental Study on the Tonal Noise Generation of a Radial Fan. J. Turbomach. 2015, 137, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorelov, A.; Meinke, M.; Schröder, W. Effects of tip-gap width on the flow field in an axial fan. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow. 2016, 61, 466–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwicker, E. Subdivision of the Audible Frequency Range into Critical Bands (Frequenzgruppen). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1961, 33, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

















| Schemes | α (°) | r/R (%) | ΔL/LH (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case-1 | 0 | 80 | 2 |
| Case-2 | 10 | 85 | 2 |
| Case-3 | 20 | 90 | 2 |
| Case-4 | 30 | 90 | 4 |
| Case-5 | 30 | 85 | 6 |
| Case-6 | 20 | 80 | 6 |
| Case-7 | 10 | 80 | 4 |
| Case-8 | 0 | 90 | 6 |
| Case-9 | 0 | 85 | 4 |
| Case-10 | 10 | 90 | 8 |
| Case-11 | 20 | 85 | 8 |
| Case-12 | 30 | 80 | 8 |
| Case-13 | 30 | 80 | 2 |
| Case-14 | 20 | 80 | 4 |
| Case-15 | 10 | 80 | 6 |
| Case-16 | 0 | 80 | 8 |
| Case | A (α%) | B (r/R %) | C (ΔL/LH %) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case-1 | A1(0) | B1(80) | C1(2) | 61.84 |
| Case-2 | A2(10) | B2(85) | C1(2) | 61.58 |
| Case-3 | A3(20) | B3(90) | C1(2) | 61.71 |
| Case-4 | A4(30) | B3(90) | C2(4) | 61.28 |
| Case-5 | A4(30) | B2(85) | C3(6) | 61.25 |
| Case-6 | A3(20) | B1(80) | C3(6) | 61.61 |
| Case-7 | A2(10) | B1(80) | C2(4) | 61.99 |
| Case-8 | A1(0) | B3(90) | C3(6) | 62.46 |
| Case-9 | A1(0) | B2(85) | C2(4) | 62.13 |
| Case-10 | A2(10) | B3(90) | C4(8) | 63.36 |
| Case-11 | A3(20) | B2(85) | C4(8) | 62.47 |
| Case-12 | A4(30) | B1(80) | C4(8) | 62.55 |
| Case-13 | A4(30) | B1(80) | C1(2) | 61.71 |
| Case-14 | A3(20) | B1(80) | C2(4) | 62.35 |
| Case-15 | A2(10) | B1(80) | C3(6) | 62.14 |
| Case-16 | A1(0) | B1(80) | C4(8) | 62.12 |
| K1 | 62.14 | 62.04 | 61.71 | |
| K2 | 62.27 | 61.86 | 61.94 | |
| K3 | 62.04 | 62.20 | 61.87 | |
| K4 | 61.70 | / | 62.63 | |
| R | 0.57 | 0.34 | 0.91 | |
| R’ | 0.513 | 0.507 | 0.824 | |
| Optimal level | A2 > A1 > A3 > A4 | B3 > B1 > B2 | C4 > C2 > C3 > C1 | |
| Primary and secondary factors | C > A > B | |||
| Best match | C4A2B3 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Lu, Q.; Jiang, B.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Xie, J. Effects of Outer Edge Bending on the Aerodynamic and Noise Characters of Axial Fan for Air Conditioners. Processes 2022, 10, 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10040686
Li B, Lu Q, Jiang B, Yang J, Wang J, Xie J. Effects of Outer Edge Bending on the Aerodynamic and Noise Characters of Axial Fan for Air Conditioners. Processes. 2022; 10(4):686. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10040686
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bin, Qi Lu, Boyan Jiang, Jinwen Yang, Jun Wang, and Junlong Xie. 2022. "Effects of Outer Edge Bending on the Aerodynamic and Noise Characters of Axial Fan for Air Conditioners" Processes 10, no. 4: 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10040686
APA StyleLi, B., Lu, Q., Jiang, B., Yang, J., Wang, J., & Xie, J. (2022). Effects of Outer Edge Bending on the Aerodynamic and Noise Characters of Axial Fan for Air Conditioners. Processes, 10(4), 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10040686






