Biodegradation Kinetics of Phenol and 4-Chlorophenol in the Presence of Sodium Salicylate in Batch and Chemostat Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model Development
2.1. Kinetic Model for Single Phenol and SA Biodegradation in a Batch Reactor
2.2. Kinetic Model for Phenol and SA Biodegradation in a Batch Reactor
2.3. Kinetic Model for 4-CP and SA Biodegradation in a Batch reactor
2.4. Kinetic Model for Phenol and SA in a Chemostat System
2.5. Kinetic Model for SA and 4-CP in a Chemostat System
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Culture Activation
3.2. Nutrient Medium
3.3. Batch Experiments
3.4. Chemostat Experiments
3.5. Analytical Methods
4. Results and Discussion
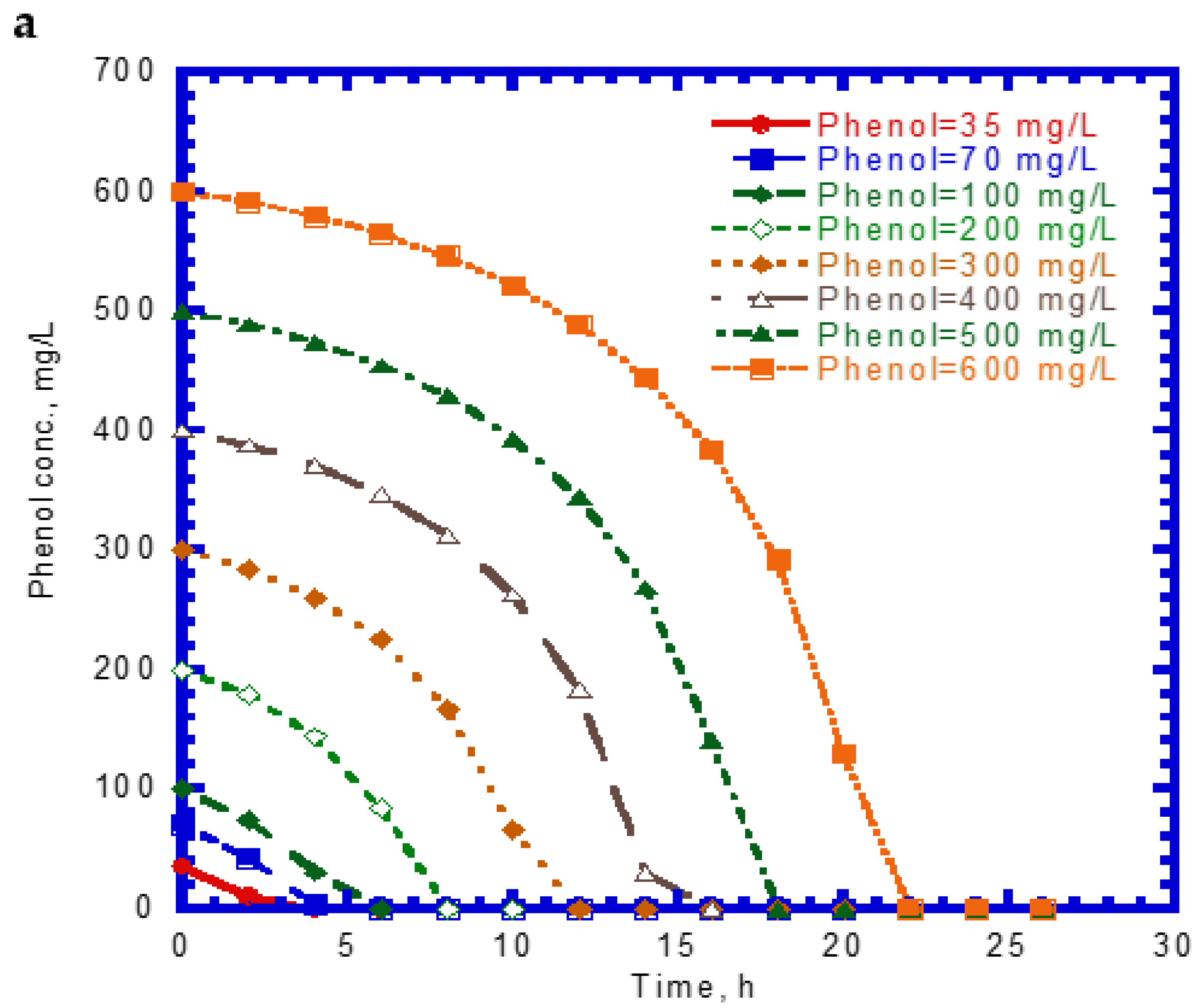
4.1. Biodegradation of Single Phenol and SA
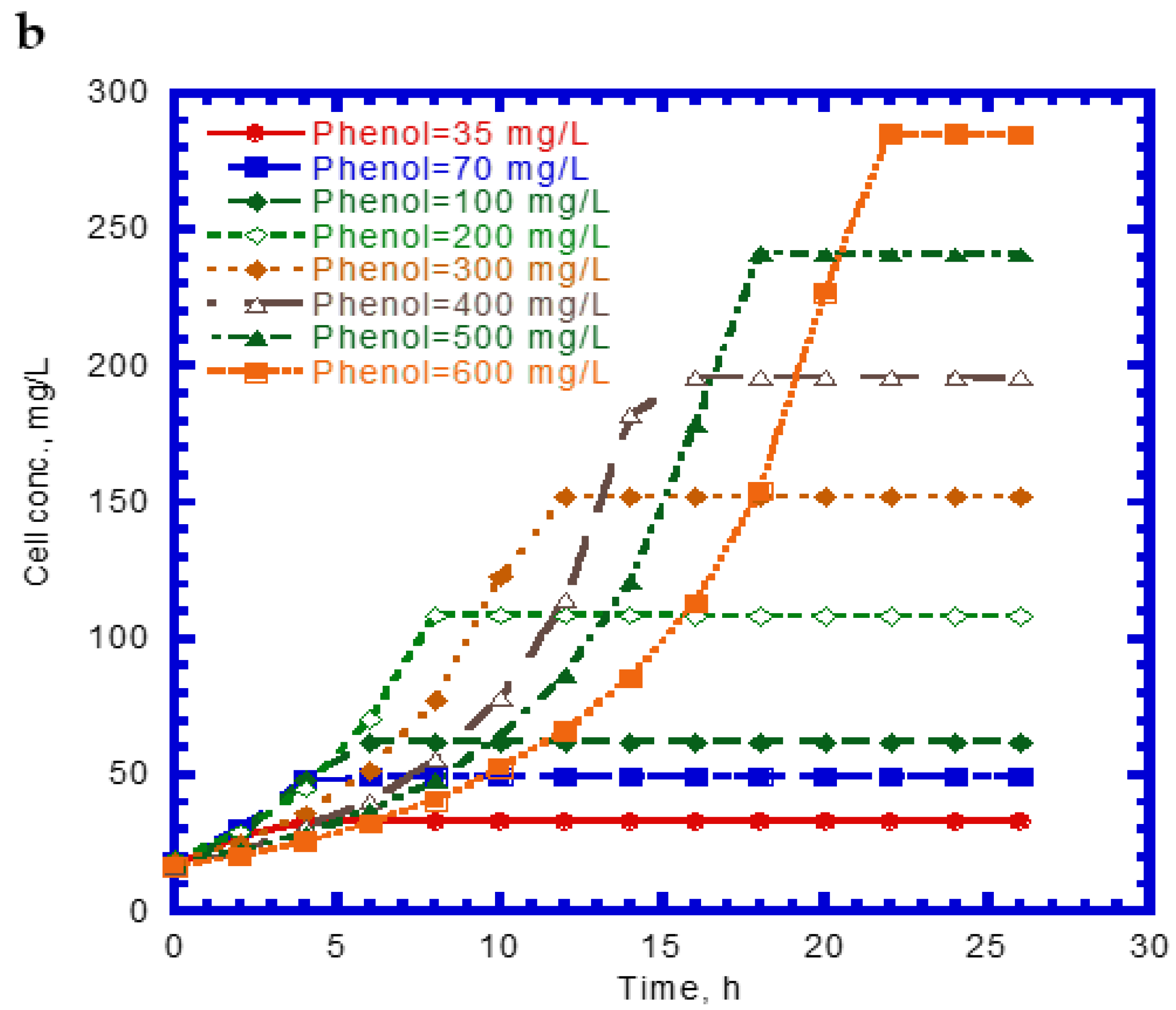
4.2. Cell Growth Kinetics on Single Phenol and SA
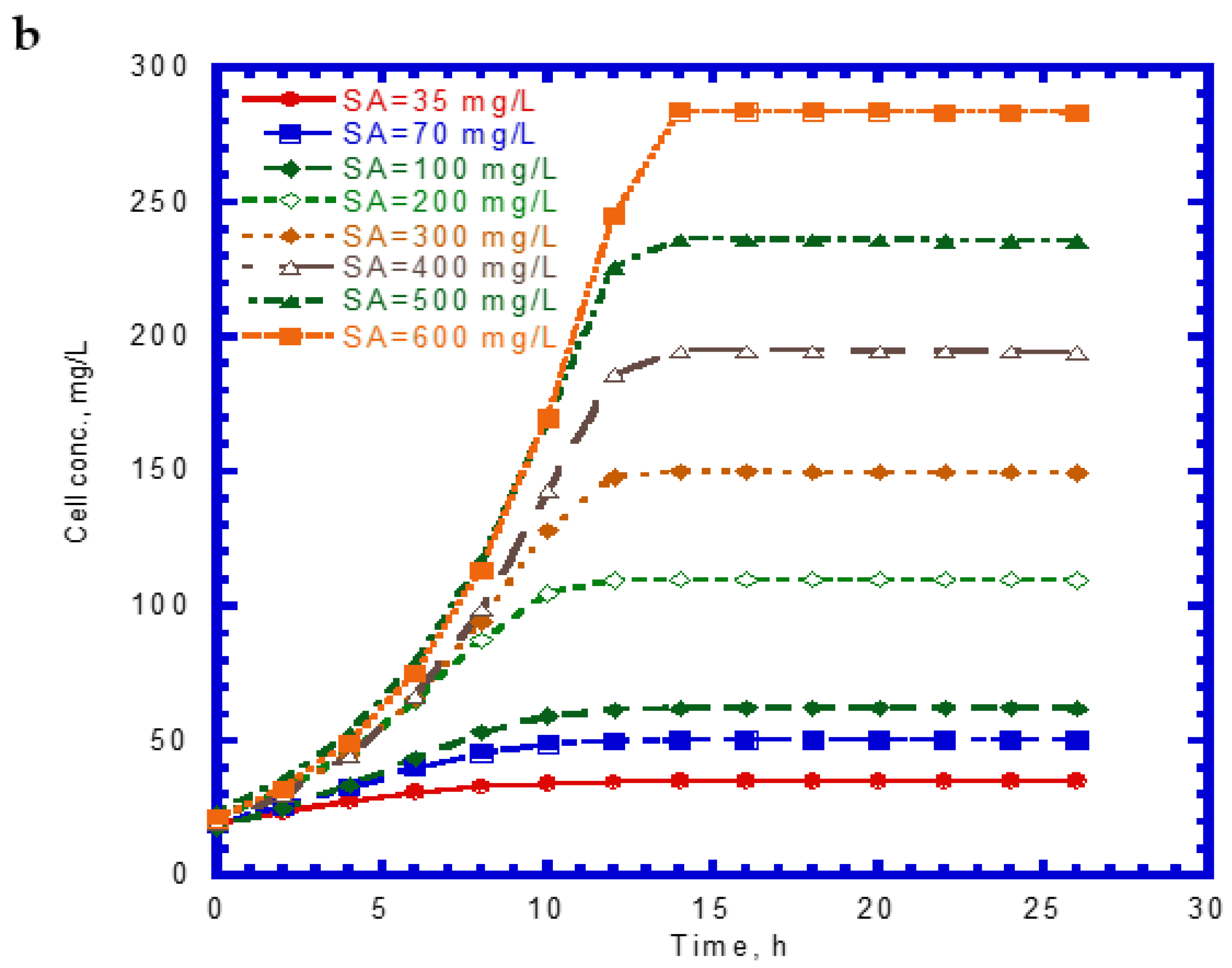
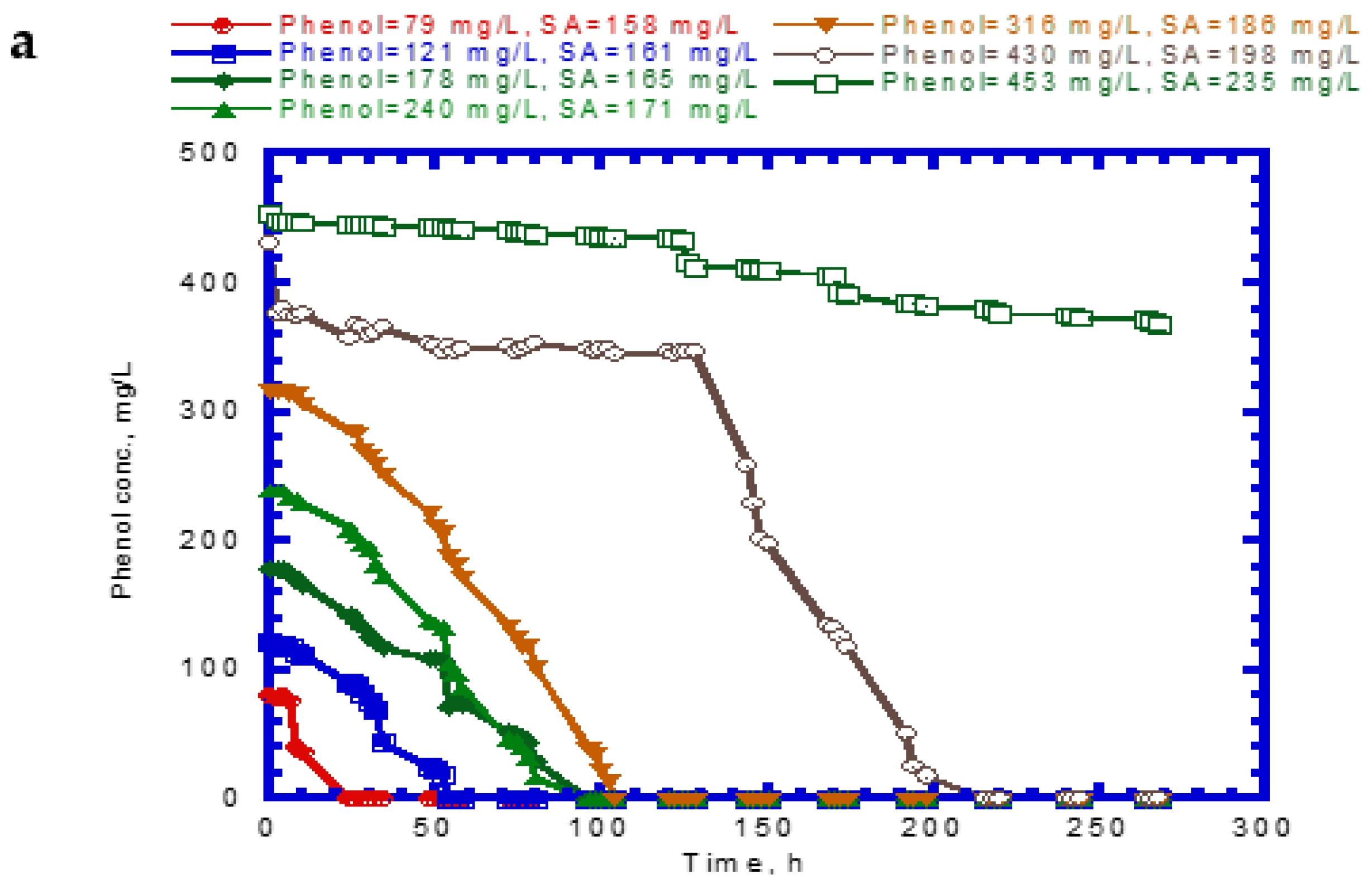
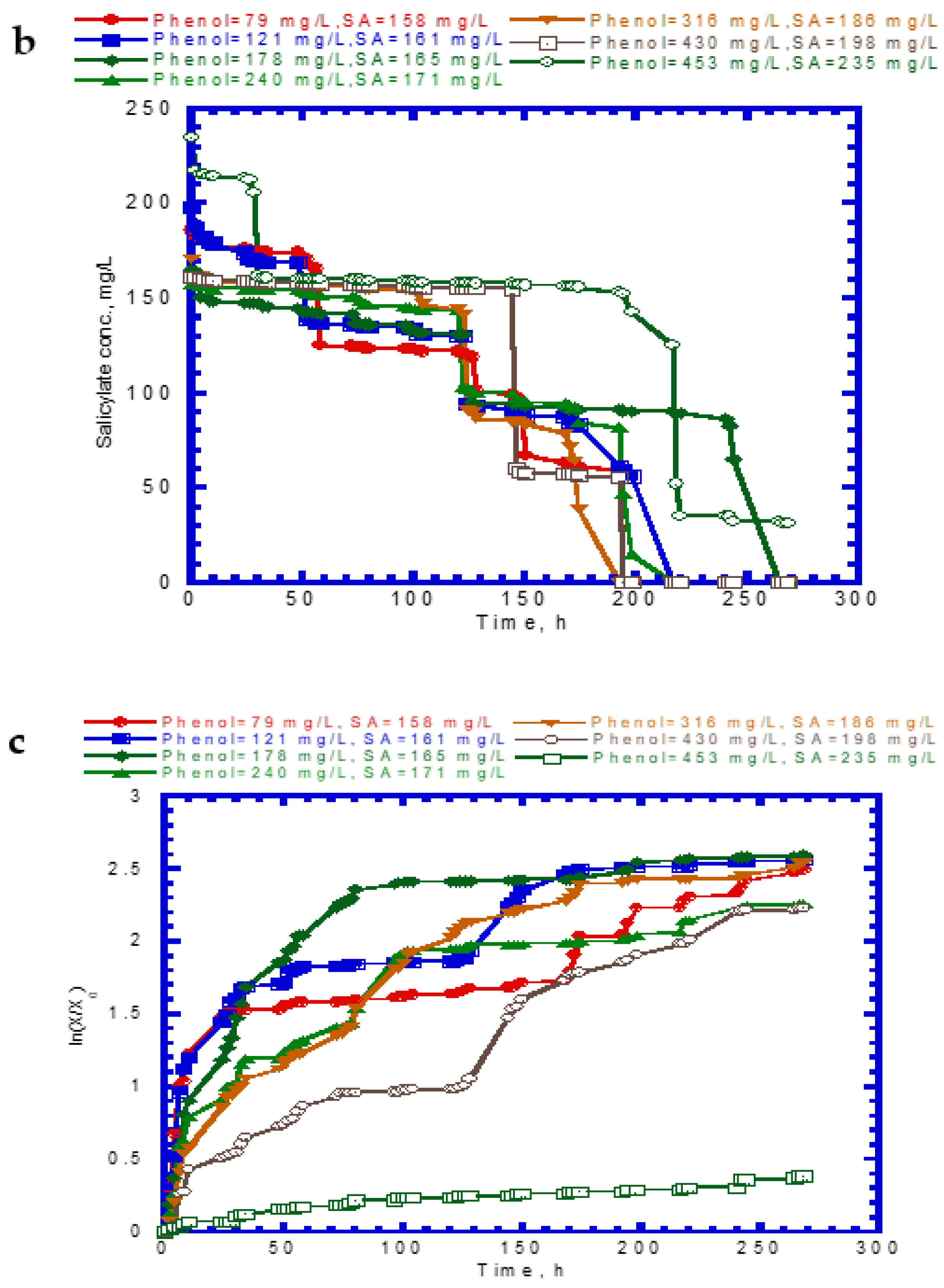
4.3. Cell Growth on Binary Substrates of Phenol and SA
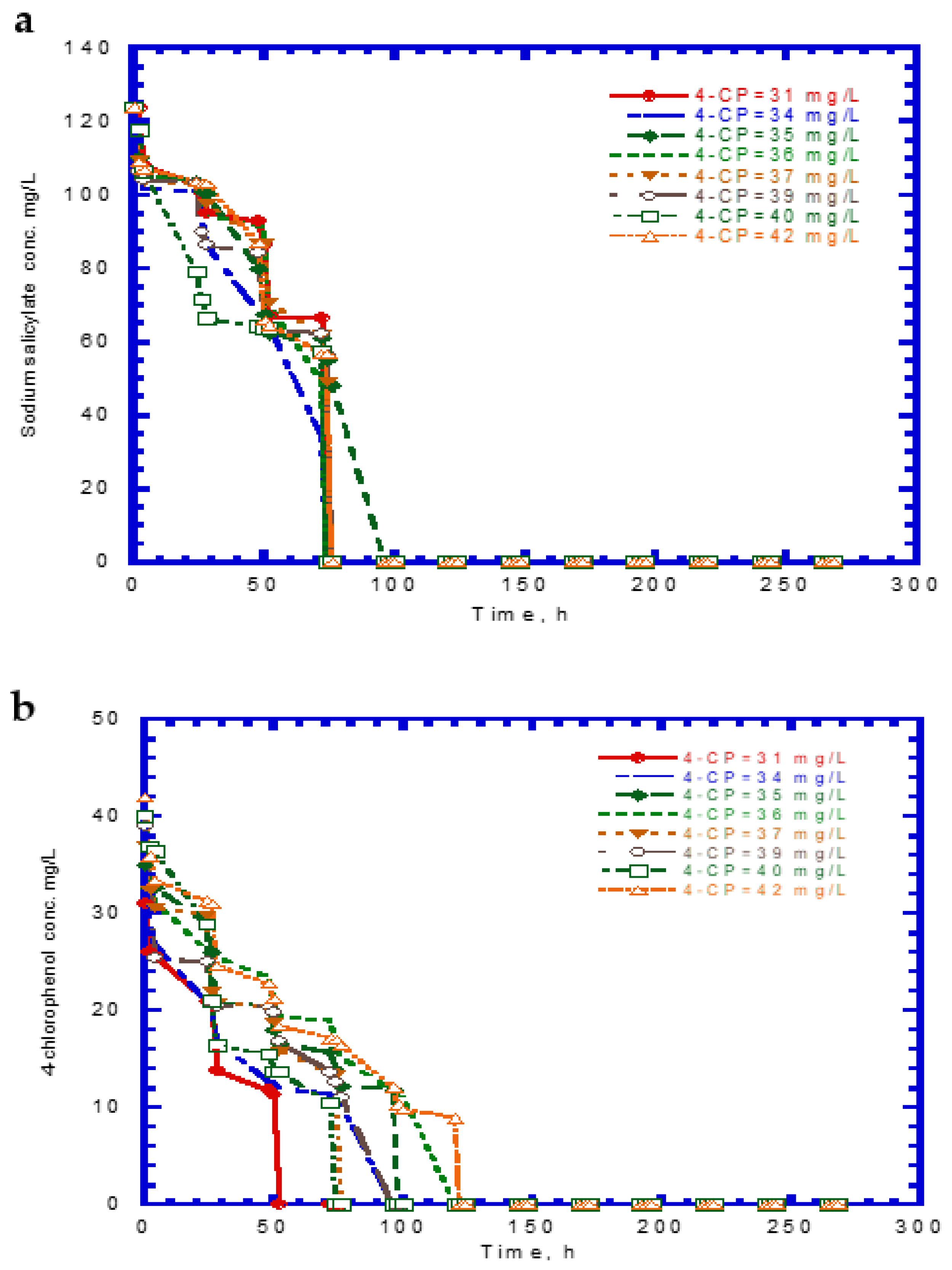
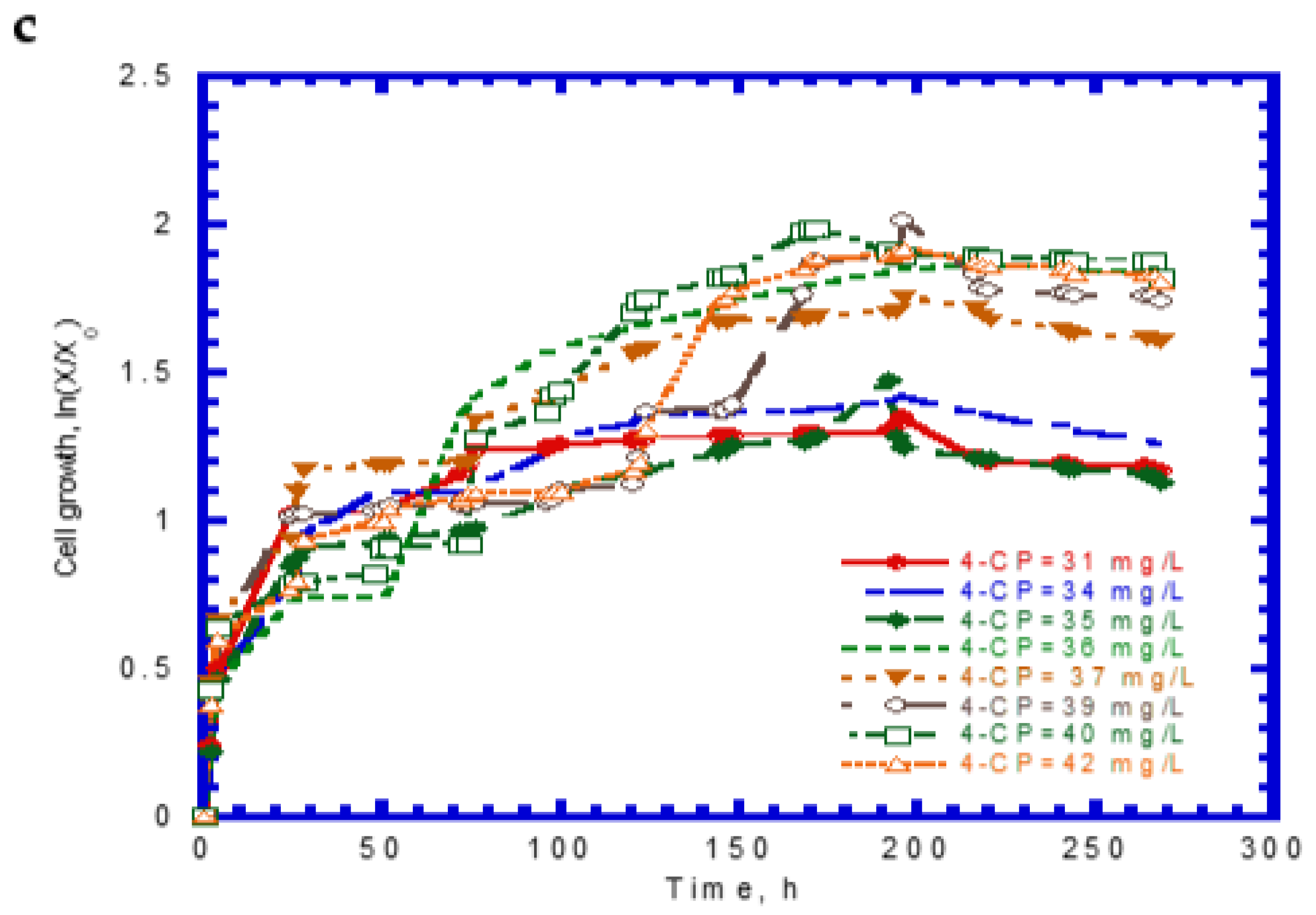
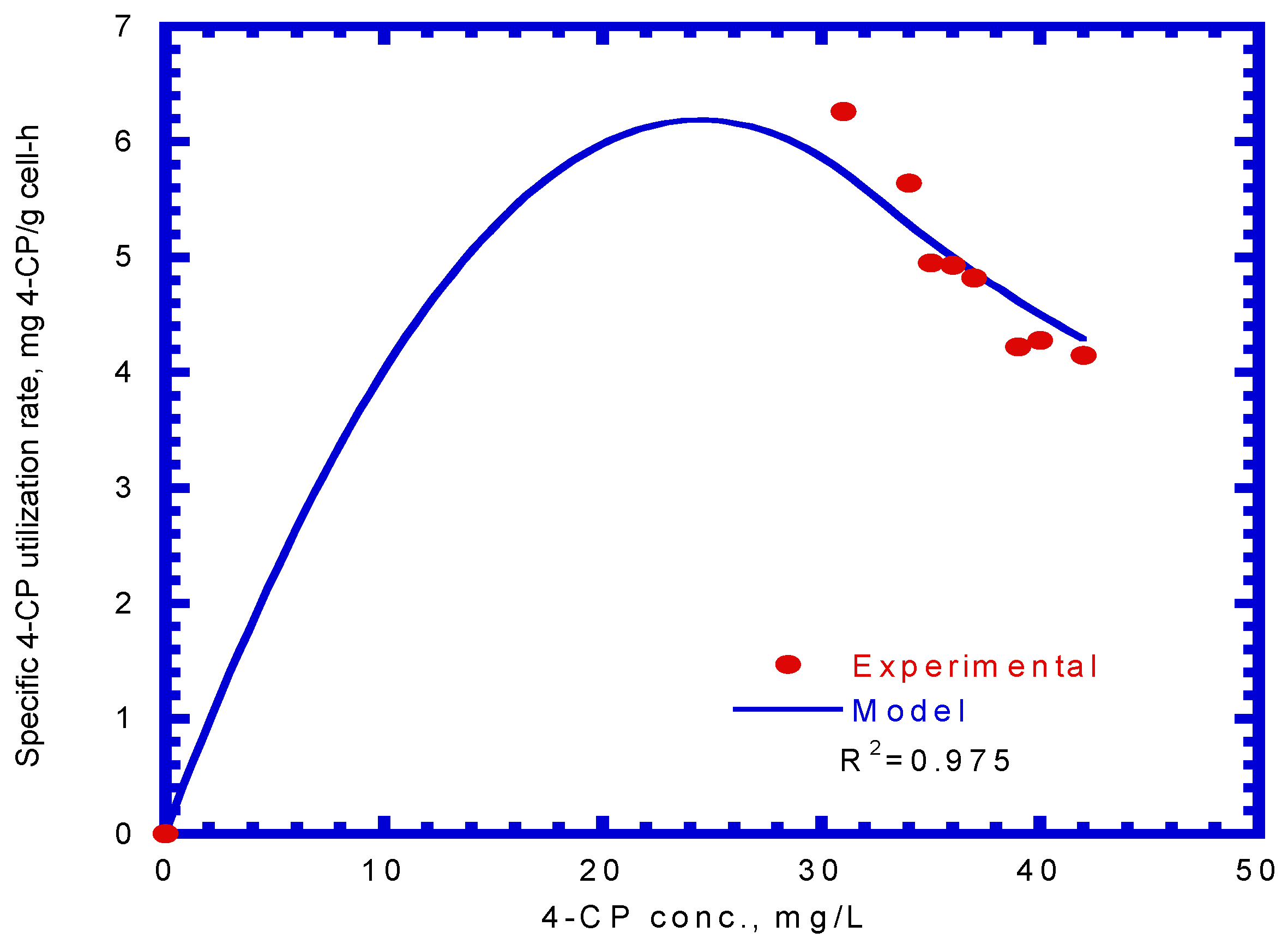
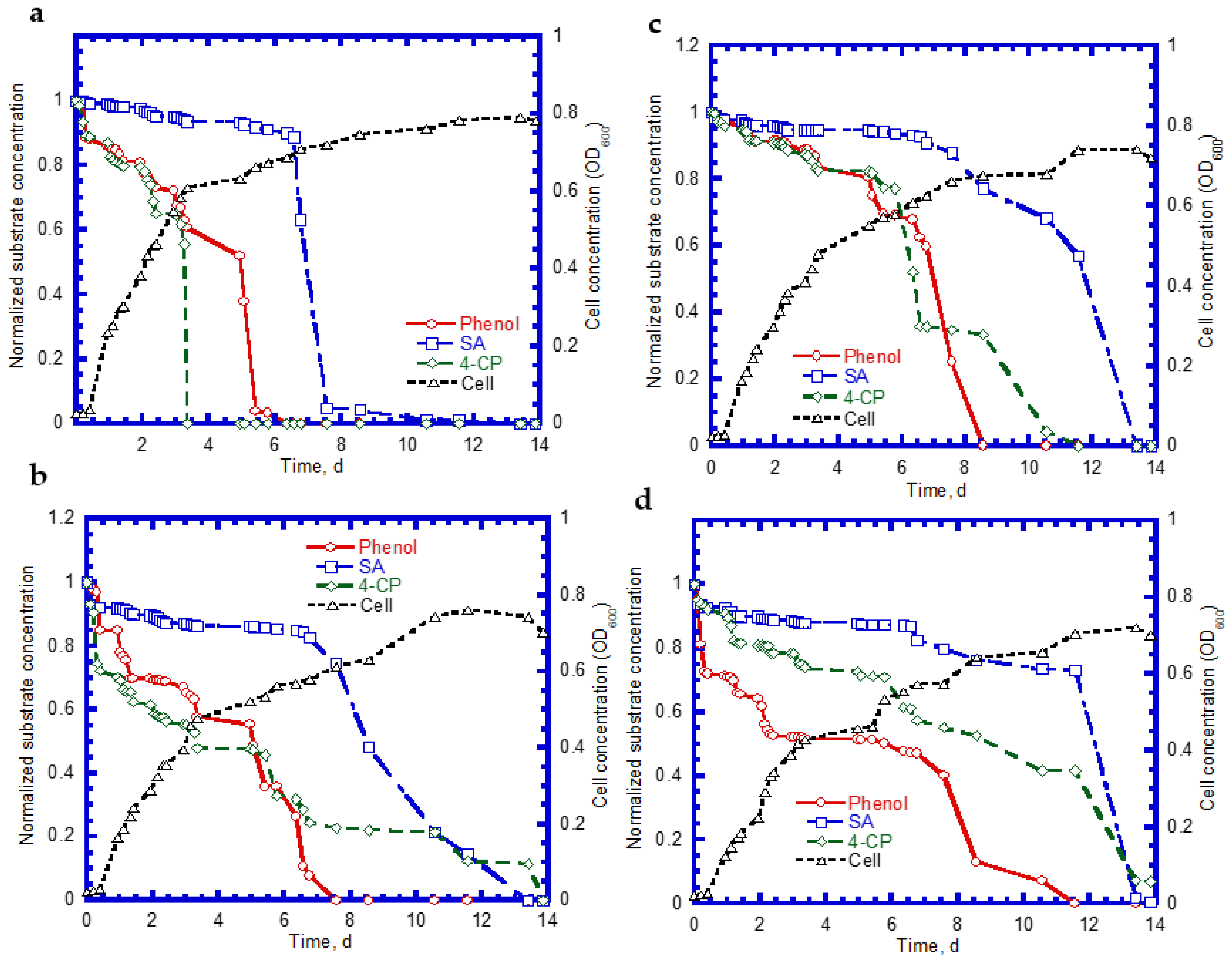
4.4. Biodegradation of Binary Substrates of SA and 4-CP
4.5. Biodegradation of Ternary Substrates of SA, Phenol, and 4-CP
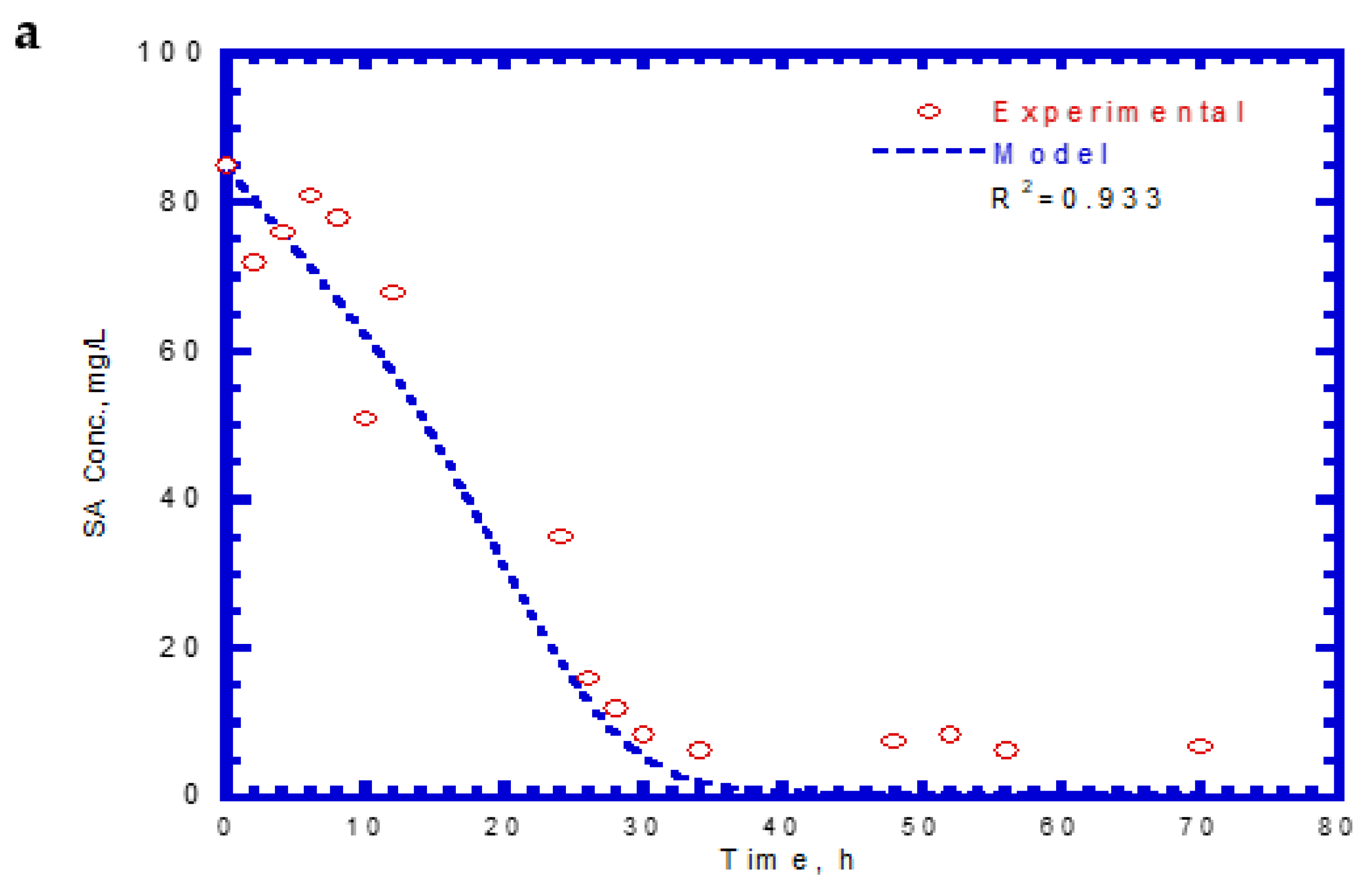
4.6. Biodegradation of Binary Substrates in the Chemostat System
5. Practical Implications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dey, A.; Sarkar, P.; Das, A. View of studies on biodegradation of 4-chlorophenol and 4-nitrophenol by isolated pure cultures. Eur. J. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Hao, X.; Liu, T.; Liu, W.; Xie, M.; Wang, M.; Xu, Q.; Yang, B. Rapid synergistic cloud point extraction (RS-CPE) with partial least squares (PLS) for the simultaneous determination of chlorophenols (CPs) in environmental water samples using a microplate Assay (MPA). Anal. Lett. 2020, 53, 1719–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, E.; Abbasi, F.; Baghapour, M.A.; Shirdareh, M.R.; Shooshtarian, M.R. 4-chlorophenol removal by air lift packed bed bioreactor and its modeling by kinetics and numerical model (artificial neural network). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedyan, H.; Assadi, A.; Amin, M. Effects of 4-chlorophenol loadings on acclimation of biomass with optimized fixed time sequencing batch reactor. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2008, 5, 225–234. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, P.K.; Bae, H. Bacterial degradation of chlorophenols and their derivatives. Microb. Cell Factories 2014, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, P.; Sreekrishnan, T.R.; Shaikh, Z.A. Evaluating the effects on performance and biomass of hybrid anaerobic reactor while treating effluents having glucose with increasing concentrations of 4-chlorophenols. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2643–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.Y.; Juang, R.S. Biodegradation of phenol and sodium salicylate mixtures by suspended Pseudomonas putida CCRC 14365. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 138, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandhibigraha, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Bandyopadhyay, T.; Bhunia, B. A kinetic study of 4-chlorophenol biodegradation by the novel isolated Bacillus subtilis in batch shake flask. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 25, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dizicheh, A.A.; Bayat, M.; Alimohmmadi, M.; Hashemi, J. Survey bioremediation of 4-Chlorophenol by yeast and mold isolated from industrial and petroleum wastewaters (Imam Khomeini seaport, Mahshahr). Int. J. Mol. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 957–966. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Arya, D.; Malhotra, A.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, B. Biodegradation of dual phenolic substrates in simulated wastewater by Gliomastix indicus MTCC 3869. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dursun, G.; Çiçek, H.; Dursun, A.Y. Adsorption of phenol from aqueous solution by using carbonized beet pulp. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 125, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ra, J.S.; Oh, S.Y.; Lee, B.C.; Kim, S.D. The effect of suspended particles coated by humic acid on the toxicity of pharmaceuticals, estrogens, and phenolic compounds. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durruty, I.; Okada, E.; González, J.F.; Murialdo, S.E. Multisubstrate monod kinetics model for simultaneous degradation of chlorophenol mixtures. Biotechnol. Bioprocess. Eng. 2011, 16, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, S.; Li, M.; Liao, Y.; Qin, Q.; Sun, S.; Tan, Y. In-situ preparation of biochar-loaded particle electrode and its application in the electrochemical degradation of 4-chorophenol in wastewater. Chemosphere 2020, 273, 128506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonwani, R.K.; Giri, B.S.; Das, T.; Singh, R.S.; Rai, B.N. Biodegradation of fluorine by neoteric LDPE immobilized Pseudomonas NRSS3 in a packed bed bioreactor and analysis of external mass transfer correlation. Process Biochem. 2019, 77, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhibigraha, S.; Mandal, S.; Awasthi, M.; Bandyopadhyay, T.K.; Bhunia, B. Optimization of various process parameters for biodegradation of 4-chlorophenol using taguchi methodology. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 24, 101568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, B.; Bhunia, B.; Dutta, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Dey, A. Kinetics of phenol biodegradation at high concentration by a metabolically versatile isolated yeast Candida tropicalis PHB5. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Control Ser. 2014, 21, 1444–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Y. Effects of carbon sources on sludge performance and microbial community for 4-chlorophenol wastewater treatment in sequencing batch reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 255, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Deng, T.; Shang, Y.; Yang, K.; Wang, H. Biodegradation of phenol by entrapped cell of Debaryomyces sp. with nano-Fe3O4 under hypersaline conditions. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 123, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, R.S.; Tsai, S.Y. Growth kinetics of Pseudomonas putida in the biodegradation of single and mixed phenol and sodium salicylate. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 31, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, A.A.M.G.; Biaventura, R.A.R.; Rodrigues, A.E. Phenol biodegradation by Pseudomonas putida DSM 548 in a batch reactor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2000, 6, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, A.; Quilty, B. The enhancement of 2-chlorophenol degradation by a mixed microbial community when augmented with Pseudomonas putida CP1. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2443–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Loh, K.C.; Chua, S.S. Prediction of critical cell growth behavior of Pseudomonas putida to maximize the cometabolism of 4-chlorophenol with phenol and sodium glutamate as carbon sources. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2003, 32, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, K.C.; Yu, Y.G. Kinetics of carbazole degradation by Pseudomonas putida in presence of sodium salicylate. Water Res. 2000, 34, 4131–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, P. Experimental and kinetic study on the cometabolic biodegradation of phenol and 4-chlorophenol by psychrotrophic Pseudomonas putida LY1. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sun, Z. Exploring the effects of carbon source level on the degradation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol in the co-metabolism process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, G.; Sonwani, R.S.; Singh, R.S.; Jaiswal, R.P.; Rai, B.N. A comparative study of 4-chlorophenol biodegradation in a packed bed and moving bed bioreactor: Performance evaluation and toxicity analysis. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jia, X.; Wen, J.; Zhou, Z. Substrate interactions and kinetics study of phenolic compounds biodegradation by Pseudomonas sp. cbp1-3. Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 67, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Korus, R.A. Effects of p-cresol and chlorophenols on pentachlorophenol biodegradation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1995, 47, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittmann, B.E.; McCarty, P.L. Environmental Biotechnology: Principles and Application; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, H.; Bae, W. Optimized operational strategies based on maximum nitritation, stability, and nitrite accumulation potential in a continuous partial nitritation reactor. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 1058–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerio, H.A.; Bae, W.; Park, J.; Kim, M. Substrate uptake, loss, and reserve in ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) under different substrate availabilities. Process Biochem. 2020, 91, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Loh, K.C. Modeling the role of metabolic intermediates in kinetics of phenol biodegradation. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1999, 25, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, P.; Nguyen, D.T.T.; Loh, K.C. Biodegradation of phenol from saline wastewater using forward osmotic hollow fiber membrane bioreactor coupled chemostat. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 94, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, G.; Herrera, G.; García, M.T.; Peña, M. Biodegradation of phenolic industrial wastewater in a fluidized bed bioreactor with immobilized cells of Pseudomonas putida. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 80, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahinkaya, E.; Dilek, F.B. Effects of 2,4-chlorophenol on activated sludge. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 59, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, T.P.; Tseng, H.Y.; Juang, R.S. Mass transfer effect and intermediate detection for phenol degradation in immobilized Pseudomonas putida systems. Process Biochem. 2003, 38, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, O.J.; Kim, M.H.; Seagren, E.A.; Kim, H. Kinetics of phenol and chlorophenol utilization by Acinetobacter species. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Loh, K.C. New cell growth pattern on mixed substrates and substrate utilization in cometabolic transformation of 4-chlorophenol. Water Res. 2000, 34, 3786–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Shahane, S.; Bhunia, B.; Mishra, U.; Chaudhary, V.K.; Srivastav, A.L. Biodegradation of 4-chlorophenol in batch and continuous packed bed reactor by isolated Bacillus subtilis. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Symbol | Kinetic Constant | Value |
|---|---|---|
| SP0 | Phenol concentration in the feed (mg/L) | 192 |
| SA0 | SA concentration in the feed (mg/L) | 286 |
| μm,P | Maximum specific growth rate of cells on phenol (h−1) | 0.423 |
| YP | Growth yield of cells on phenol (mg cell/mg phenol-h) | 0.447 |
| KS,P | Half-saturation constant of phenol (mg/L) | 48.1 |
| KI,P | Inhibition constant of Phenol (mg/L) | 272.5 |
| IA1 | Inhibition of phenol degradation due to the presence of SA (dimensionless) | 0.32 |
| IB1 | Inhibition of phenol degradation due to the presence of phenol and SA (dimensionless) | 1.51 |
| μm,A | Maximum specific growth rate of cells on SA (h−1) | 0.247 |
| YA | Growth yield of cells on SA (mg cell/mg SA-h) | 0.438 |
| KS,A | Half-saturation constant of SA (mg/L) | 71.7 |
| KI,A | Inhibition constant of SA (mg/L) | 3178.2 |
| IA2 | inhibition of SA degradation due to the presence of phenol (dimensionless) | 0.14 |
| IB2 | Inhibition of SA degradation due to the presence of SA and phenol (dimensionless) | 6.6 × 10−3 |
| D | Dilution rate (h−1) | 0.04 |
| Symbol | Kinetic Constant | Value |
|---|---|---|
| SA0 | SA concentration in the feed (mg/L) | 85 |
| SCP0 | 4-CP concentration in the feed (mg/L) | 12 |
| kA | Maximum specific SA degradation rate by cells (mg SA/mg cell-h) | 0.564 |
| KS,A | Half-saturation constant of SA (mg/L) | 71.7 |
| KI,A | Inhibition constant of SA (mg/L) | 3178.2 |
| ICP | Inhibition constant of 4-CP to SA (mg/L) | 0.355 |
| kCP | Maximum specific degradation rate of 4-CP by cells (mg 4-CP/mg cell-h) | 0.189 |
| KS,CP | Half-saturation constant of 4-CP (mg/L) | 1.106 |
| KI,CP | Inhibition constant of 4-CP (mg/L) | 0.977 |
| μm,A | Maximum specific growth rate of cells on SA (h−1) | 0.247 |
| kd,A | Decay coefficient of cells on SA (h−1) | 1.635 × 10−4 |
| md,CP | Decay constant due to 4-CP (L/mg) | 6.11 |
| D | Dilution rate (h−1) | 0.04 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.-H.; Ho, B.-H. Biodegradation Kinetics of Phenol and 4-Chlorophenol in the Presence of Sodium Salicylate in Batch and Chemostat Systems. Processes 2022, 10, 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10040694
Lin Y-H, Ho B-H. Biodegradation Kinetics of Phenol and 4-Chlorophenol in the Presence of Sodium Salicylate in Batch and Chemostat Systems. Processes. 2022; 10(4):694. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10040694
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yen-Hui, and Bing-Han Ho. 2022. "Biodegradation Kinetics of Phenol and 4-Chlorophenol in the Presence of Sodium Salicylate in Batch and Chemostat Systems" Processes 10, no. 4: 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10040694
APA StyleLin, Y.-H., & Ho, B.-H. (2022). Biodegradation Kinetics of Phenol and 4-Chlorophenol in the Presence of Sodium Salicylate in Batch and Chemostat Systems. Processes, 10(4), 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10040694







