Integrated Reservoir Model and Differential Stimulation Modes of Low Permeability Porous Carbonate Reservoir: A Case Study of S Reservoir in X Oilfield in Iraq
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Field and Geological Description
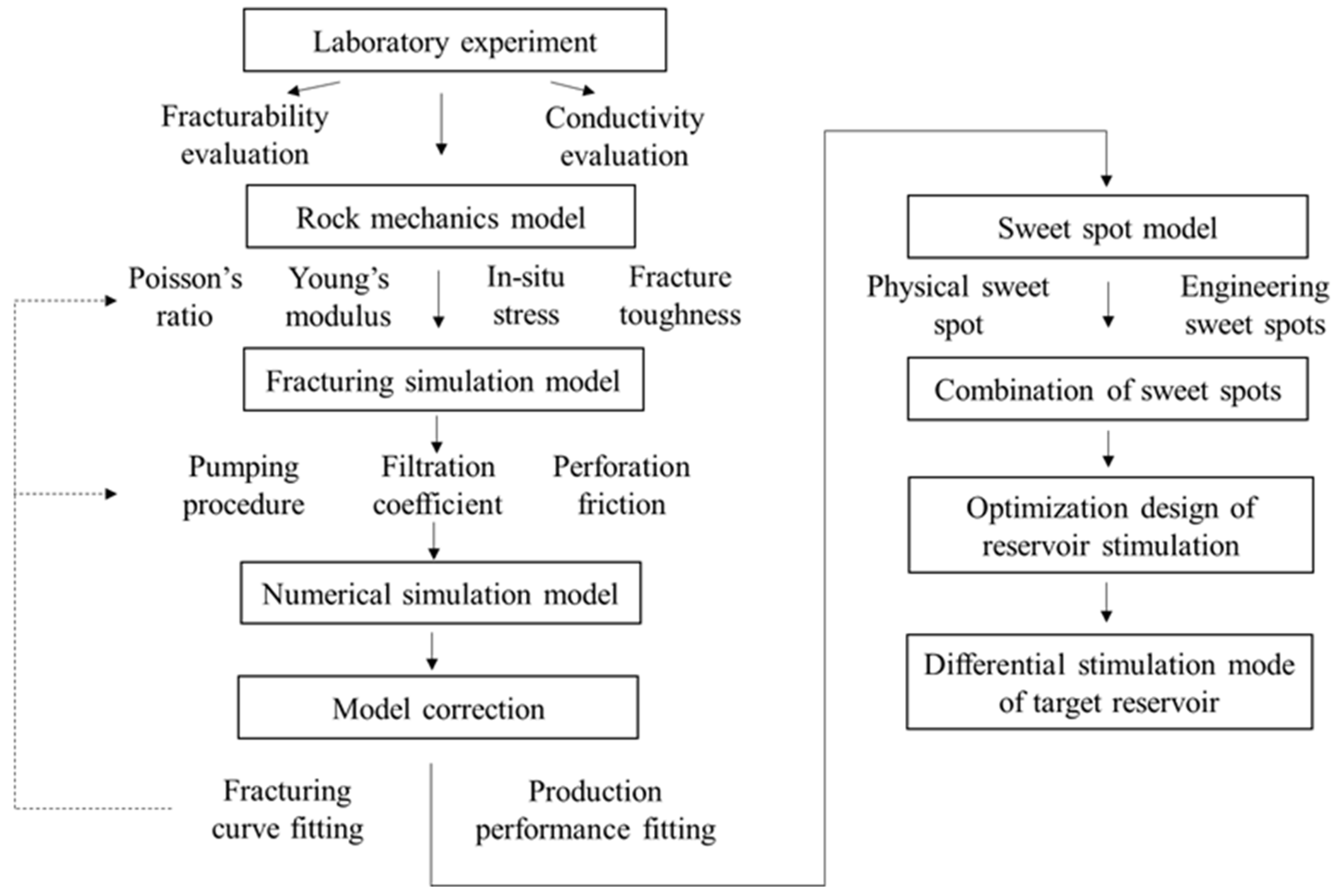
3. Improved Integrated Strategy of Reservoir Stimulation
4. Stimulation Evaluation by Laboratory Experiment
4.1. Evaluation of Fracturing Feasibility
4.2. Evaluation of Conductivity
5. Differential Stimulation Modes Based on Sweet Spot Type
5.1. Evaluation of Conductivity
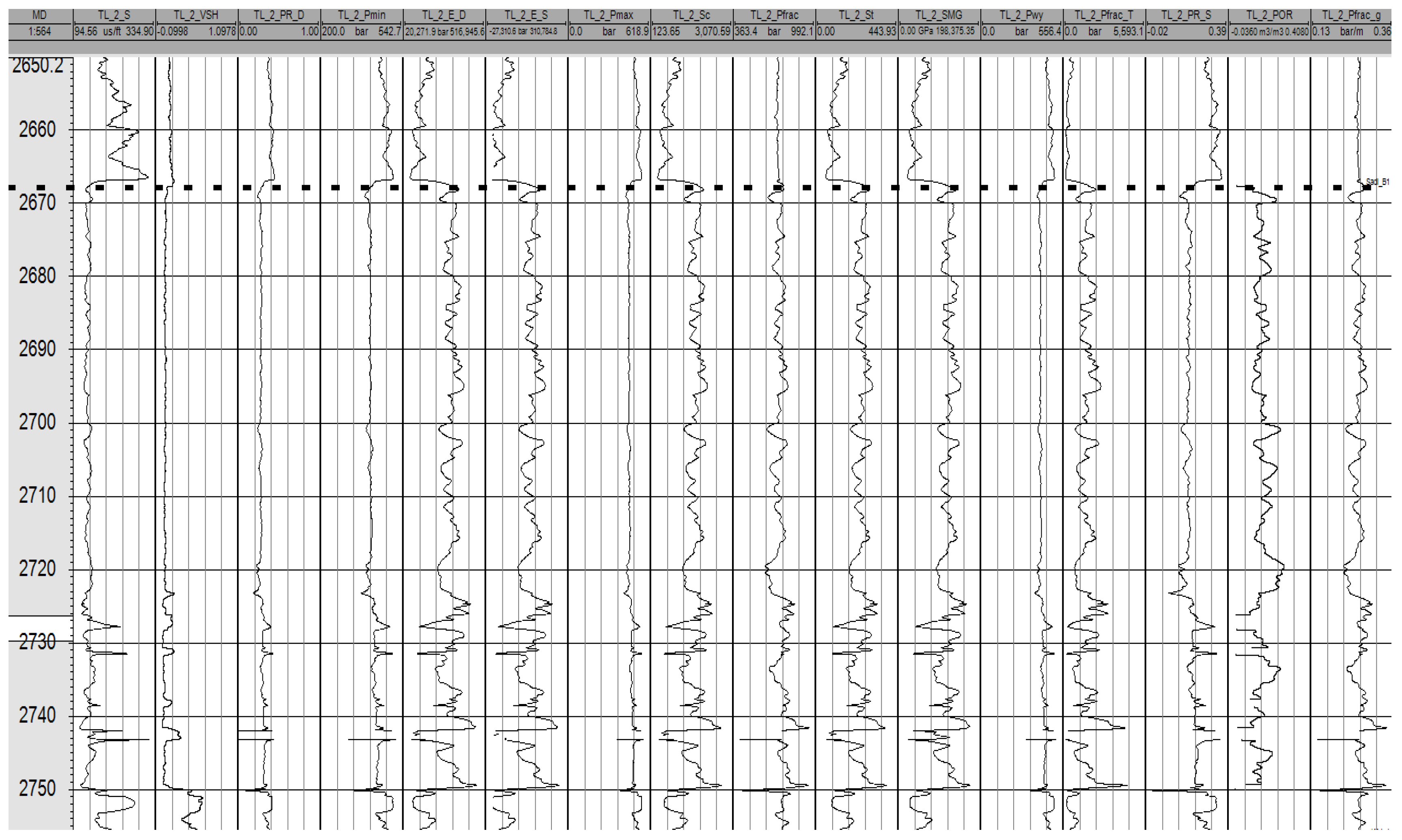
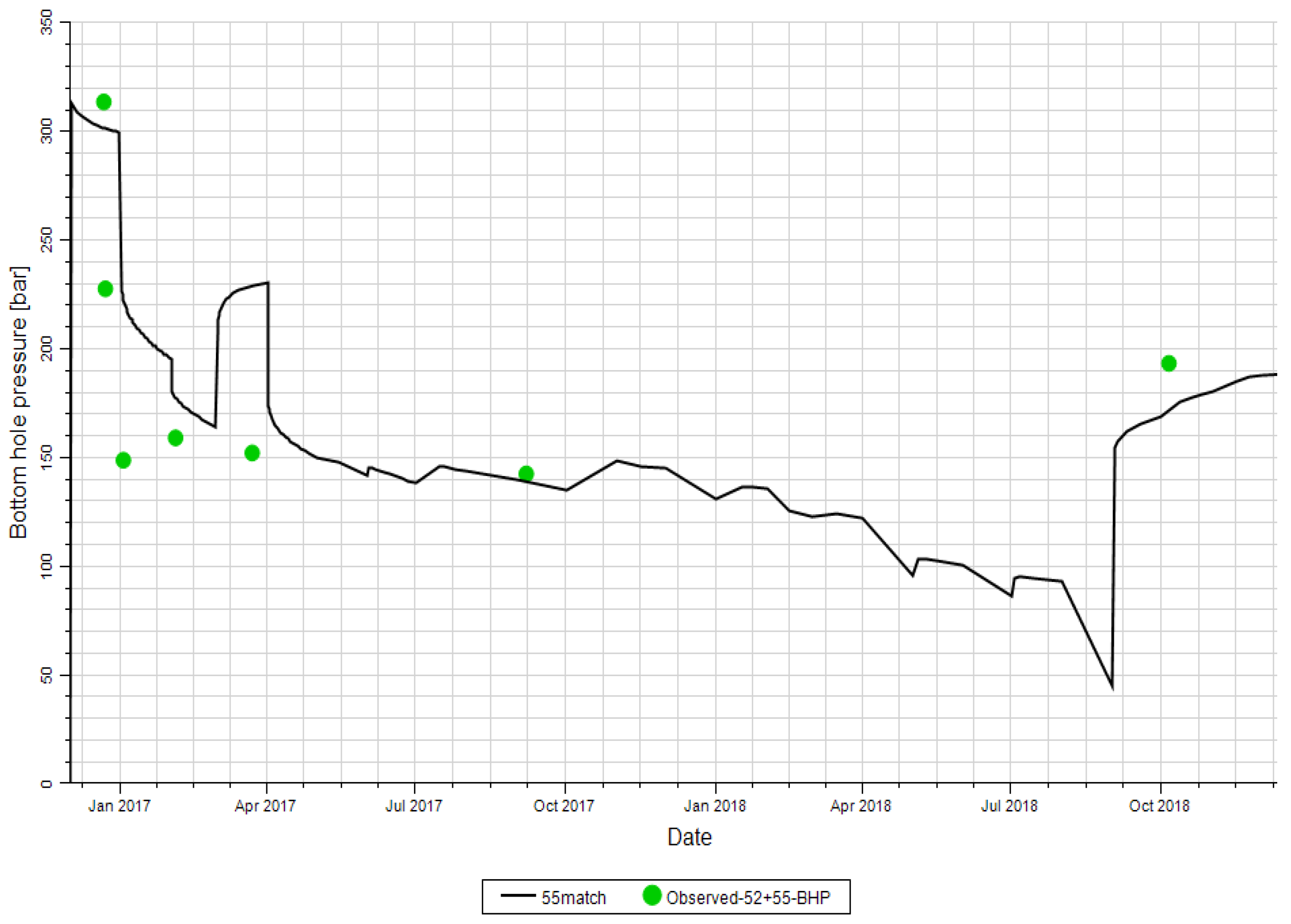
5.2. Correction of Integrated Stimulation Model
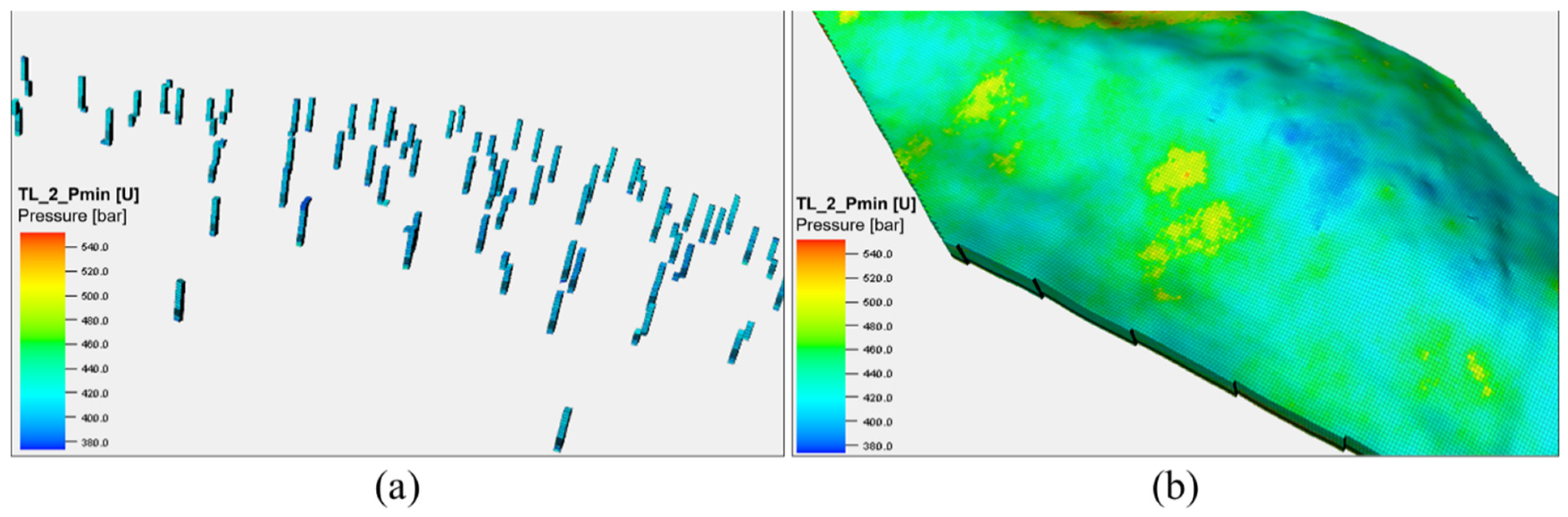
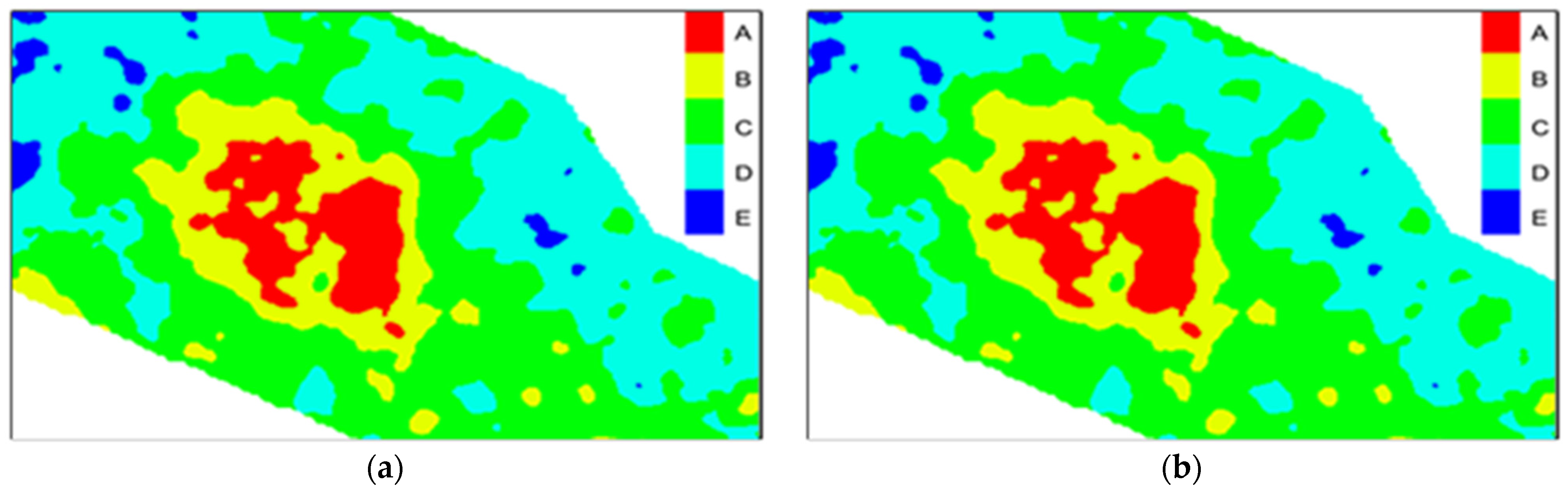
5.3. Establishment of Sweet Spot Models
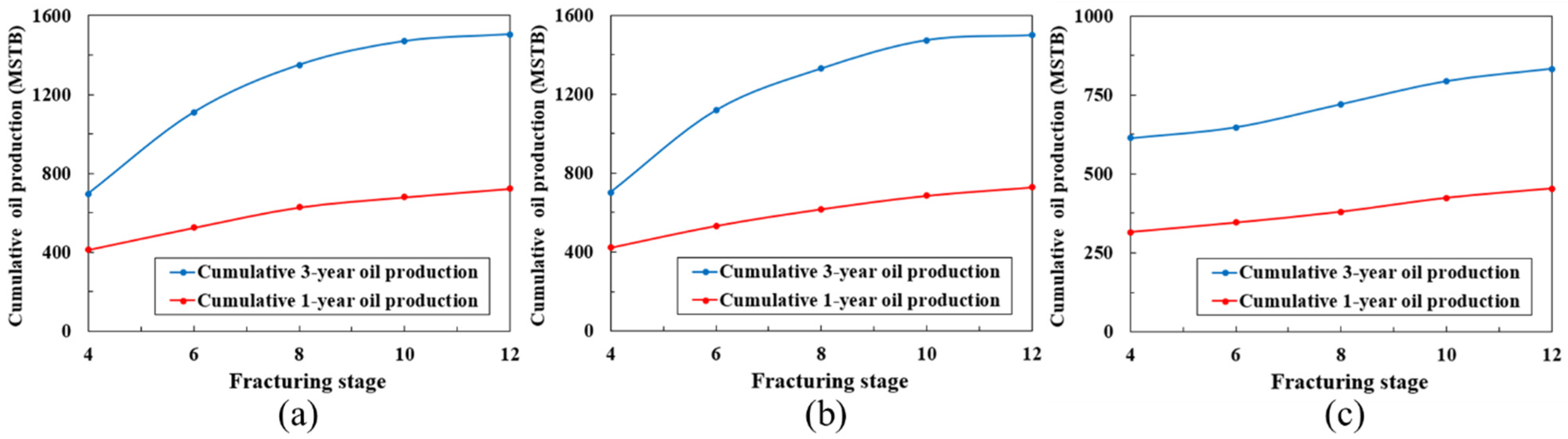
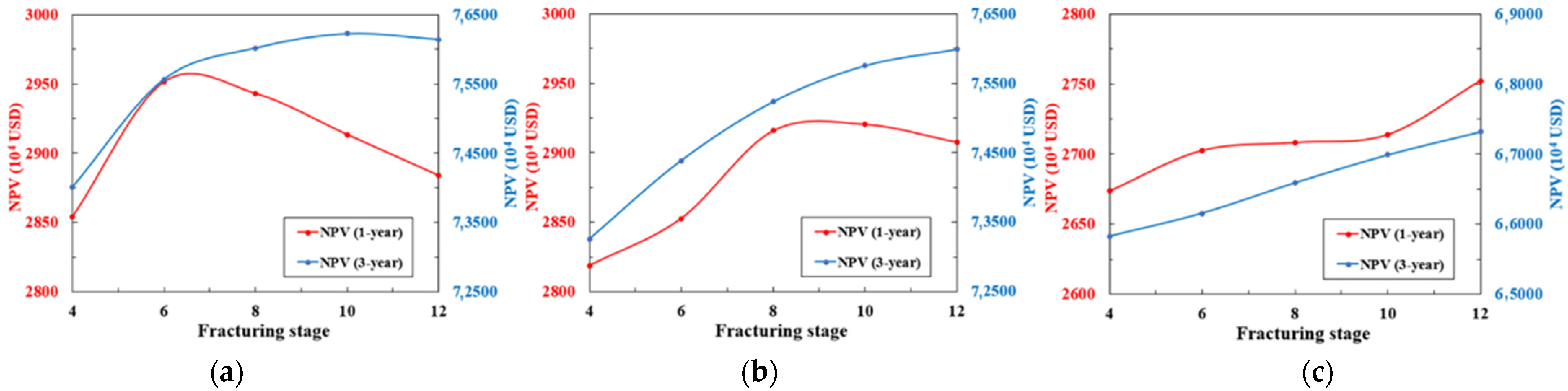
5.4. Differential Stimulation Modes
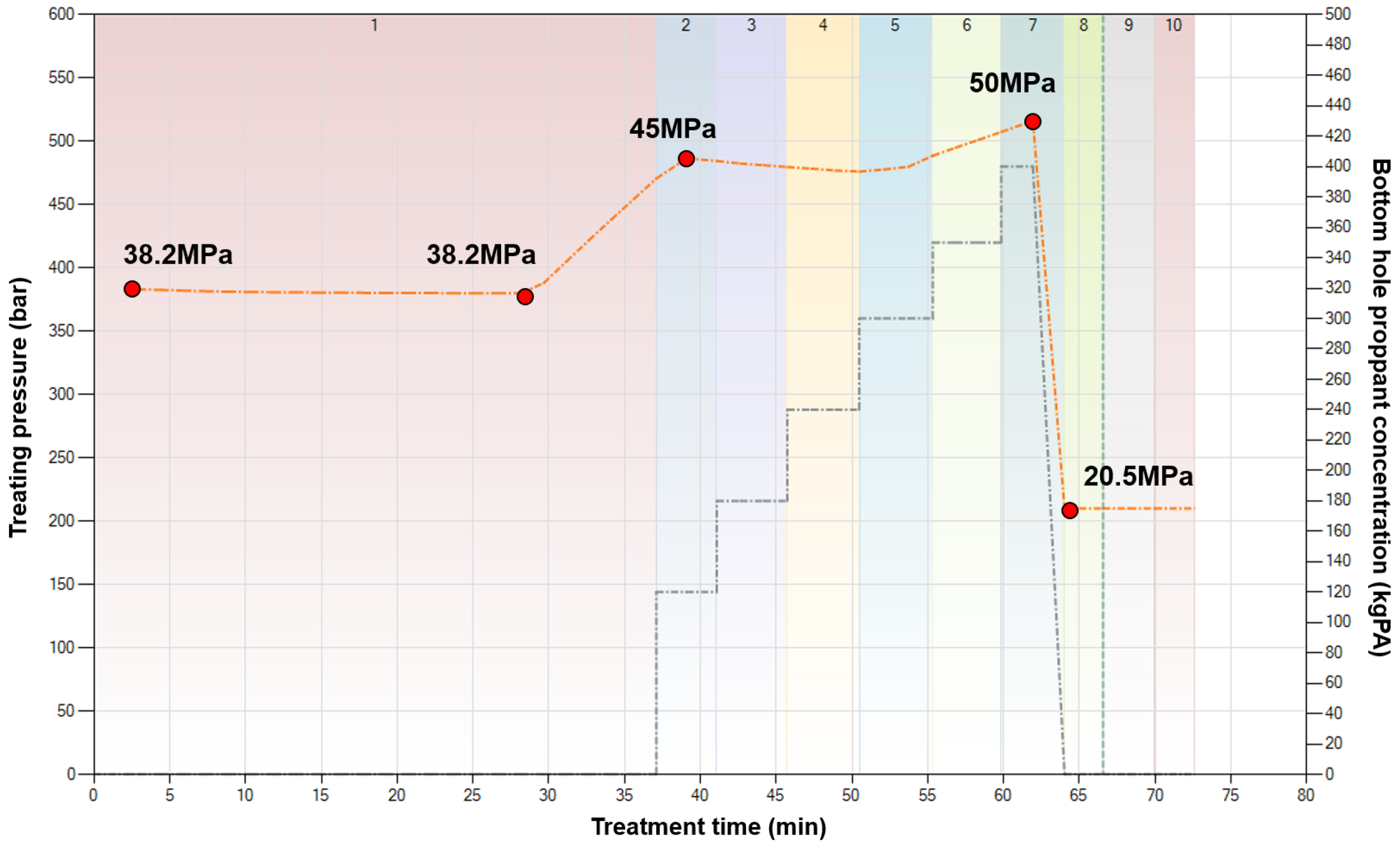
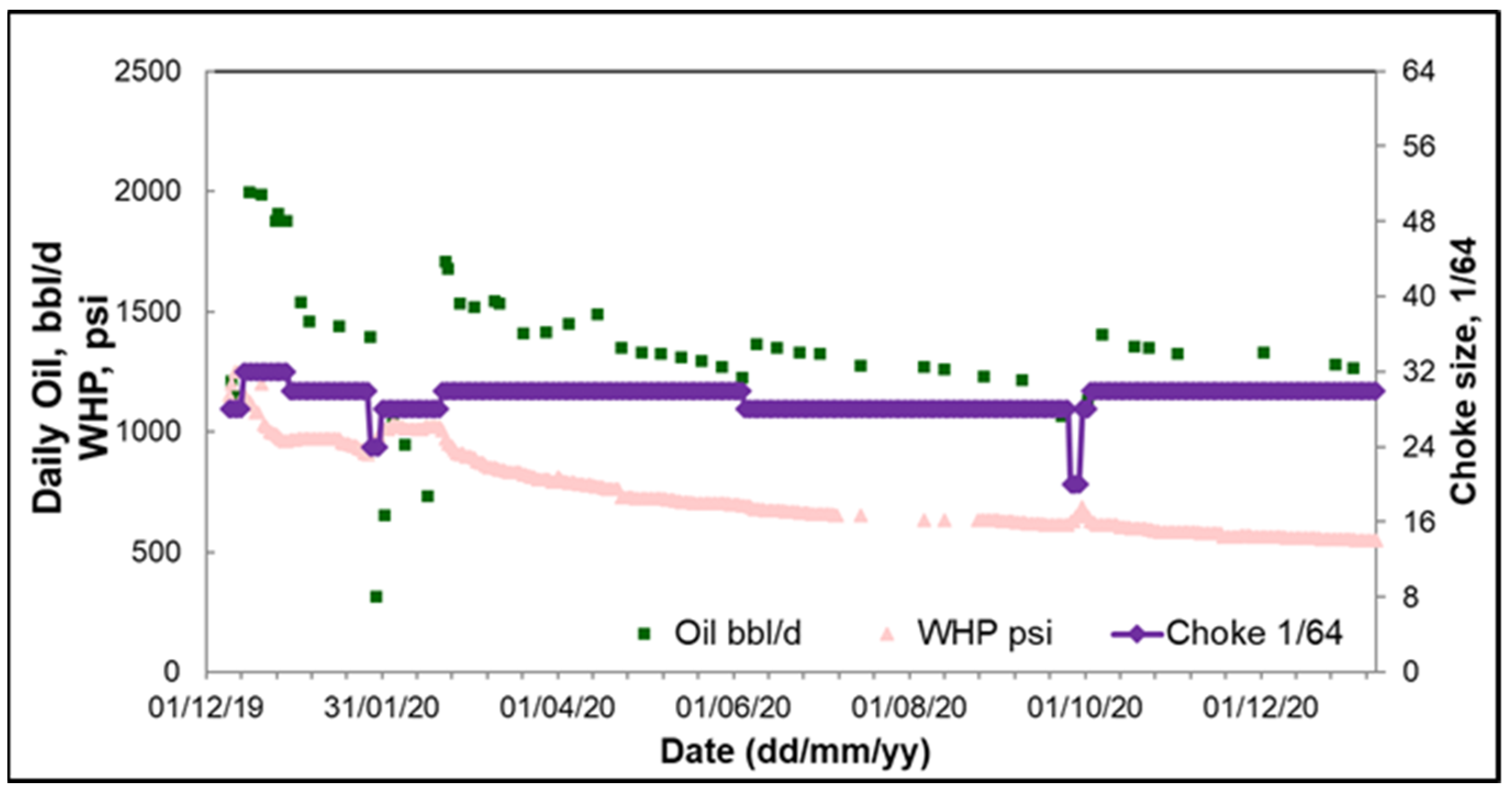
6. Field Application
7. Conclusions
- The target reservoir can be stimulated by hydraulic fracturing. The larger the proppant particle size, the better the fracture conductivity after fracturing.
- Through the fitting of the fracturing operation curve and production dynamic curve, the integrated reservoir model is corrected, and differential stimulation modes are proposed, targeted for the three types of stimulation areas.
- For Type I, a better economic benefit can be achieved with the small-scale stimulation mode. Type II needs the medium-scale stimulation mode to obtain reasonable productivity, and its economic benefit is lower than that of Type I. Type III requires the large-scale stimulation mode, but the economic benefits should be above the economic limit.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiao, F.; Zhou, C.; Yang, Z. Geological theory and exploration & development practice of hydrocarbon accumulation inside continental source kitchens. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2020, 47, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, D.; Tang, Y.; He, W.; Guo, X.; Zheng, M.; Huang, L. Orderly coexistence and accumulation models of conventional and unconventional hydrocarbons in Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation, Mahu sag, Junggar Basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Hu, S.; Hou, L.; Yang, T.; Li, X.; Guo, B.; Yang, Z. Types and resource potential of continental shale oil in China and its boundary with tight oil. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2020, 47, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Xu, S.; Xing, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, S. Advances and challenges in shale oil development: A critical review. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 2020, 4, 406–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhou, C.; Jia, A.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, R.; Wu, S.; Guo, Z. Development characteristics and orientation of tight oil and gas in China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Su, H.; Liang, X.; Meng, L.; Yuan, L.; Li, X.; Liang, L. Integrated hydraulic fracturing techniques to enhance oil recovery from tight rocks. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Tao, L.; Zeng, F. Optimization of refracturing timing for horizontal wells in tight oil reservoirs: A case study of Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation, Songliao Basin, NE China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liang, X.; Niu, X.; Feng, S.; You, Y. Geological conditions for continental tight oil formation and the main controlling factors for the enrichment: A case of Chang 7 Member, Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2017, 44, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Li, J.; Wu, X.; Li, P.; Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Xie, H. Physical modeling of oil charging in tight reservoirs:A case study of Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2016, 43, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Tan, J.; Xian, C.; Fan, X.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Y. Theoretical understandings, key technologies and practices of tight conglomerate oilfield efficient development: A case study of the Mahu oilfield, Junggar Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2020, 47, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Zhen, M.; Zhang, Y. Unconventional hydrocarbon resources in China and the prospect of exploration and development. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2012, 39, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.N.; Zhang, G.S.; Yang, Z.; Tao, S.Z.; Hou, L.H.; Zhu, R.K.; Yuan, X.J.; Ran, Q.Q.; Li, D.H.; Wang, Z.P. Geological concepts, characteristics, resource potential and key techniques of unconventional hydrocarbon: On unconventional petroleum geology. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2013, 40, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, B.; Tian, C.; Zhu, Y.; Song, B.; Qian, Q. A method of production profile quick prediction based on typical curves: A case study of the Upper Shale large multi-layered sandstone reservoir, Rumaila Oilfield, Iraq. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2016, 43, 956–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zou, C.; Jia, A.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, S.; Guo, S. Development characteristics and orientation of tight oil hydrocarbon in China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 1073–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Zhou, F.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, B.; Dong, R.; Liang, T.; Li, J. Pore-scale investigation on occurrence characteristics and conformance control mechanisms of emulsion in porous media. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu El Ela, M.; Samir, M.; Abdel Monem, A.; El Tayeb, S.; Sayyouh, H. An integration between geological and reservoir engineering data to design a conceptual waterflood program. In Proceedings of the North Africa Technical Conference and Exhibition, Cairo, Egypt, 15–17 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Zhou, F.; Wang, Q.; Yu, F.; Dong, R.; Xiong, C.; Li, J.; Liang, T. Flow physics of polymer nanospheres and diluted microemulsion in fractured carbonate reservoirs: An investigation into enhanced oil recovery mechanisms. SPE J. 2021, 26, 2231–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Bian, X.; Zuo, L. Whole lifecycle geology-engineering integration of volumetric fracturing technology in unconventional reservoir. Pet. Reserv. Eval. Dev. 2021, 11, 297–304. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Xian, C.; Wu, J.; Zhao, S. Optimal key elements of geoengineering integration in Changning National Shale Gas Demonstration Zone. China Pet. Explor. 2019, 24, 174–185. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Q.; Weng, D.; Guan, B.; Mu, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Li, S. A novel approach of tight oil reservoirs stimulation based on fracture controlling optimization and design. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2020, 47, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Xu, S.; Ren, G. Hierarchical optimization of well pattern parameters in multi-stage fractured horizontal well for tight oil. Acta Pet. Sin. 2019, 40, 830–838. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.; Li, X.; Ci, H.; Lu, X.; Liu, X. Experimental and numerical simulation of water adsorption and diffusion in shale gas reservoir rocks. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 2019, 3, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Feng, Y.; Du, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, R. An embedded grid-free approach for near-wellbore streamline simulation. SPE J. 2018, 23, 567–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, M.U.; Mahmud, H.B. Sandstone matrix acidizing knowledge and future development. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2017, 7, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Sebakhy, K.; Wu, K.; Jing, G.; Chen, N.; Chen, Z.; Hong, A.; Torsæter, O. Future trends for tight oil exploitation. In Proceedings of the SPE North Africa Technical Conference and Exhibition, Cairo, Egypt, 14 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, H.; Liao, X.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, B. Evaluation of fracture networks along fractured horizontal wells in tight oil reservoirs: A case study of Jimusar oilfield in the Junggar Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2020, 41, 1288–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Olorode, O.; Wang, B.; Rashid, H.U. Three-dimensional projection-based embedded discrete-fracture model for compositional simulation of fractured reservoirs. SPE J. 2020, 25, 2143–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S. Rock mechanical parameter modeling of Fuyu tight oil reservoir in Well Block T30 of Daqing Oilfield. Pet. Geol. Oilfield Dev. Daqing 2020, 39, 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, M.; Chen, Z.; Liao, X.; Wang, J.; Shi, L. A well-testing method for parameter evaluation of multiple fractured horizontal wells with non-uniform fractures in shale oil reservoirs. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 2020, 4, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Lu, Z.; Wu, S. Sweet spot classifi cation evaluation of tight conglomerate reservoir in Mahu sag and its engineering application. China Pet. Explor. 2020, 25, 110–119. [Google Scholar]
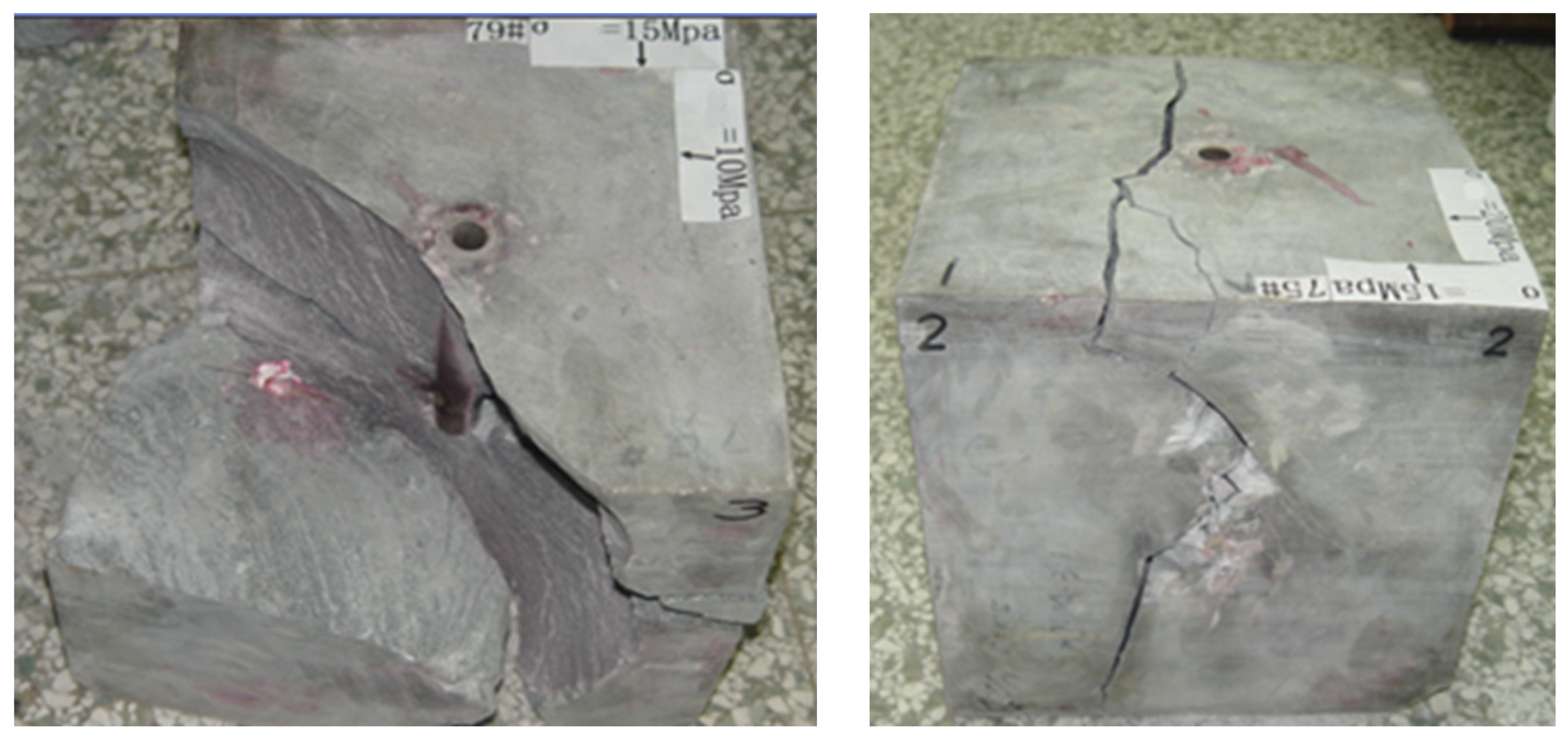



| The Average Value of SB2 | The Value of Outcrop Core | |
|---|---|---|
| Gas permeability | 0.04 × 10−3 μm2 | 0.028 × 10−3 μm2 |
| Porosity | 18.7% | 15.1% |
| Young’s modulus | 14.992 GPa | 13.588 GPa |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.212 | 0.220 |
| Rock mineral analysis | 95% Calcite | 89.1% Calcite |
| Fracturing Fluid | Displacement Rate, mL/min | Vertical Stress, MPa | Horizontal Maximum Principal Stress, MPa | Horizontal Minimum Principal Stress, MPa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | slick water | 60 | 15 | 12 | 2 |
| 2# | slick water | 60 | 20 | 15 | 10 |
| Index | Design Parameters | Fracturing Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid volume (m3) | 426.1 | 463.6 |
| Pre-liquid ratio (%) | 45 | 45.3 |
| Sand amount | 57.2 | 62.0 |
| Average sand ratio (%) | 24.3 | 24.4 |
| Maximum sand ratio (%) | 41.4 | 41.4 |
| Average sand concentration (kg/m3) | 352.9 | 353.8 |
| Maximum sand concentration (kg/m3) | 600 | 600 |
| Pump injection speed (m3/min) | 5.5 | 5–5.5 |
| Mesh number of proppants | 30/50 | 30/50 |
| Level | Brittleness Index, Decimal | Minimum Horizontal Stress (MPa) | Fracture Toughness (MPa·m−0.5) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poisson’s Ratio | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | |||
| A | >0.9 | <37 | <60 | |
| <0.14 | >20 | |||
| B | 0.8–0.9 | 37–40 | 60–100 | |
| 0.14–0.18 | 18–20 | |||
| C | 0.65–0.8 | 40–43 | 100–140 | |
| 0.18–0.22 | 16–18 | |||
| D | 0.55–0.65 | 43–46 | 140–180 | |
| 0.22–0.26 | 14–16 | |||
| E | <0.55 | >46 | >180 | |
| >0.26 | <14 | |||
| Level | Permeability (mD) | Porosity (%) | Oil Saturation (%) | Effective Thickness (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | >3 | >23 | >80 | >30 |
| B | 2–3 | 20–23 | 75–80 | 25–30 |
| C | 1–2 | 17–20 | 70–75 | 20–25 |
| D | 0.1–1 | 14–17 | 65–70 | 15–20 |
| E | <0.1 | <14 | <65 | <15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Zhu, G.; An, Y.; Li, N.; Xu, W.; Wan, L.; Jin, R. Integrated Reservoir Model and Differential Stimulation Modes of Low Permeability Porous Carbonate Reservoir: A Case Study of S Reservoir in X Oilfield in Iraq. Processes 2022, 10, 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10061179
Yang J, Zhu G, An Y, Li N, Xu W, Wan L, Jin R. Integrated Reservoir Model and Differential Stimulation Modes of Low Permeability Porous Carbonate Reservoir: A Case Study of S Reservoir in X Oilfield in Iraq. Processes. 2022; 10(6):1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10061179
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jing, Guangya Zhu, Yichen An, Nan Li, Wei Xu, Li Wan, and Rongrong Jin. 2022. "Integrated Reservoir Model and Differential Stimulation Modes of Low Permeability Porous Carbonate Reservoir: A Case Study of S Reservoir in X Oilfield in Iraq" Processes 10, no. 6: 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10061179
APA StyleYang, J., Zhu, G., An, Y., Li, N., Xu, W., Wan, L., & Jin, R. (2022). Integrated Reservoir Model and Differential Stimulation Modes of Low Permeability Porous Carbonate Reservoir: A Case Study of S Reservoir in X Oilfield in Iraq. Processes, 10(6), 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10061179





