Overviews of Internet of Things Applications in China’s Hospitality Industry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Room Automation
1.2. Predictive Maintenance
1.3. Mobile Interaction
1.4. Hyper-Personalization
1.5. APIs and Third-Party Integrations
2. Background on the Foundation of Internet of Things (IoT)
2.1. Architecture of Internet of Thing
2.2. Technical Support for Internet of Thing
2.3. China’s Development of the Internet of Things
2.4. Hospitality Industry Reform
2.5. Application of IoT in the Hospitality Industry—Chain Analysis
2.5.1. Upstream of Hospitality Industry Chain—Chips
2.5.2. Upstream of Hospitality Industry Chain—IoT Modules
2.5.3. Midstream of Hospitality Industry—Chain-Industry Cooperation and Integration
2.5.4. Downstream of Hospitality Industry Chain—Improving Hotel Operations
2.5.5. Downstream of Hospitality Industry Chain—Enhance Hotel User Experience
- Before check-in
- After check-in
- After check-out
3. Hypothesis
3.1. IoT Can Help Hospitality Industry Revolutionize the Supply Chain to Reduce Hotel Costs
3.2. The Drivers of IoT Adoption in the Hospitality Industry Depend on the Development of the Communications Industry and the Pandemic
3.3. Factors Limiting the Development of IoT in the Hospitality Industry May Be due to Lack of Intelligence, Lack of Serviceability, Privacy Issues, and Lack of Financial Follow-Up
4. China’s IoT Hospitality Industry Policy Analysis
5. IoT Has Been Revolutionizing the Supply Chain of Hospitality Industry to Reduce Costs
5.1. IoT Improve the Efficiency and Reduce the Cost of the Hotels Supply Chain
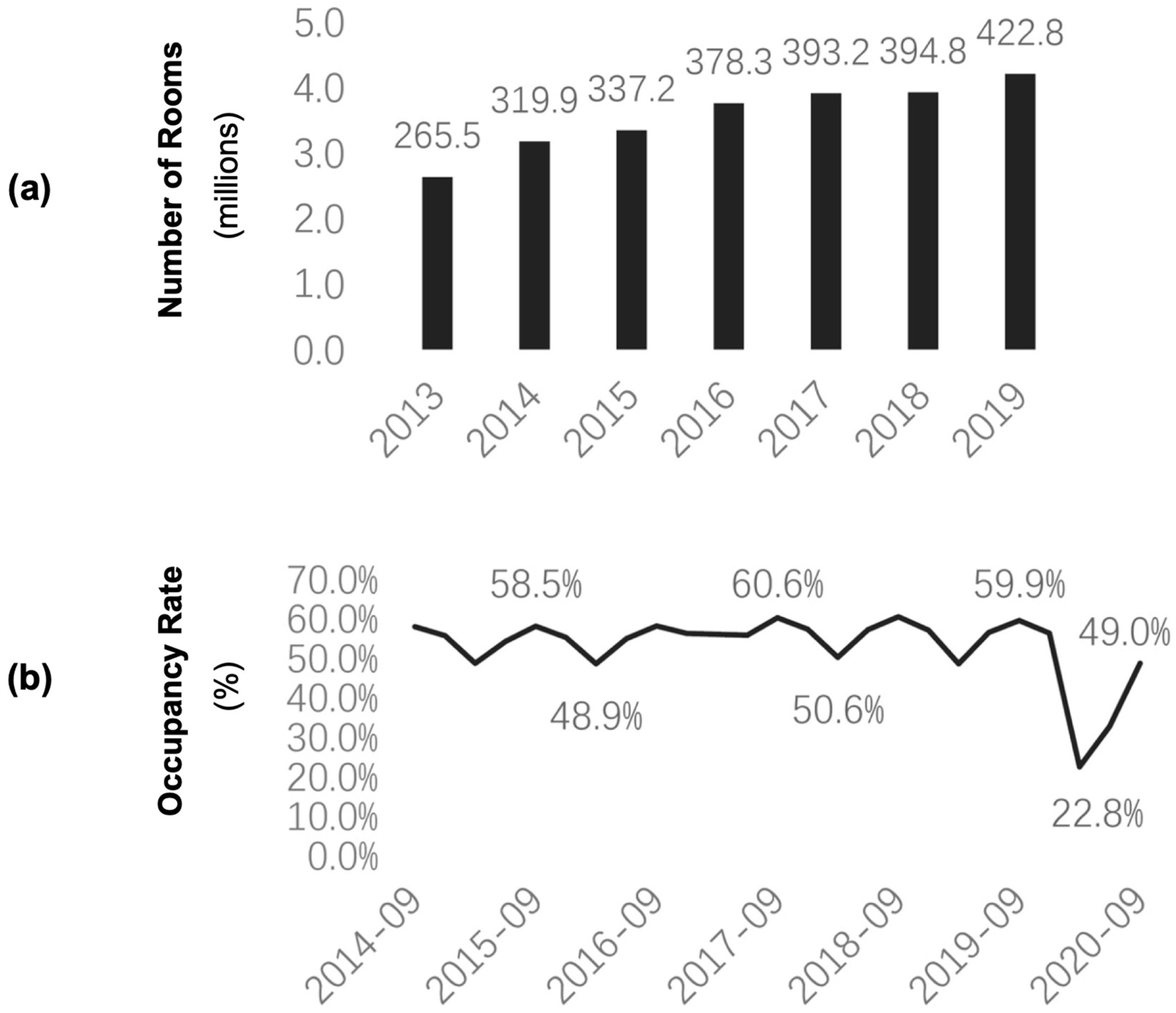
5.2. IoT Improvements to Hotel Costs in 2021
6. Drivers of IoT Adoption in Hospitality Industry Depend on the Development of the Communications Industry and the Pandemic
6.1. Communications Development Drives IoT in the Hospitality Industry
6.2. Epidemic Drives the Development of IoT in Hospitality Industry
7. Factors Limiting the Development of IoT in Hospitality Industry
7.1. Constraints to the Application of IoT in Hospitality Industry in China
7.2. Investment Risks in the Application of IoT in Hospitality Industry in China
- 1.
- The rapid development of mobile communication and Internet has built the foundation for the application of the IoT in hotels.
- 2.
- The demand for contactless services in hotels has increased, and the application of IoT in hotels has achieved new growth opportunities in the post-pandemic period.
- 3.
- The development of the Internet of Things in hotels will move towards the humanization of equipment and services.
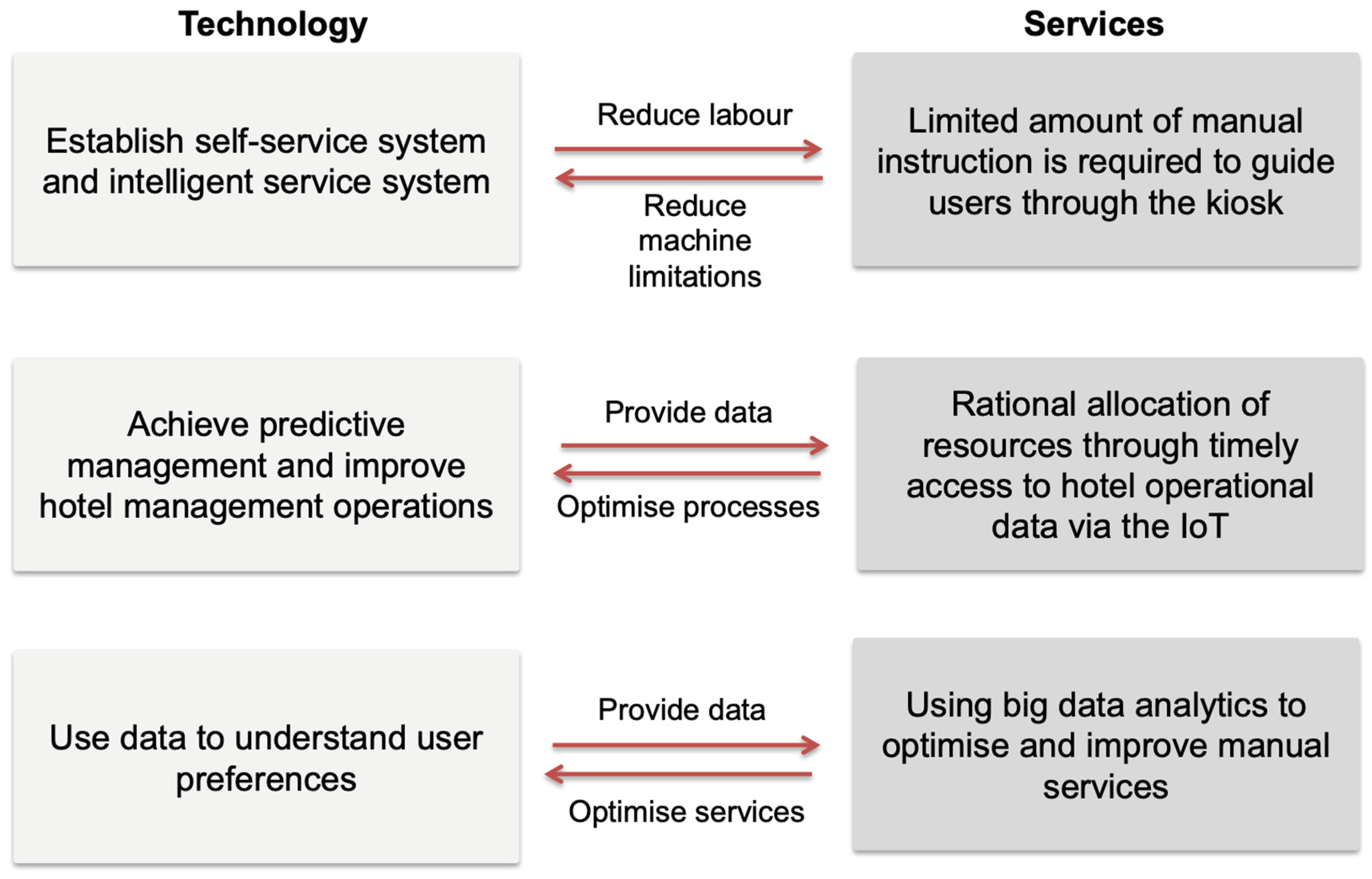
8. Trends in the IoT Application in Hospitality Industry—The Integration of Technology and Services
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- China’s NB-IoT industry chain matures. China Telecom. Newsl. 2017, 21, 2.
- Michael, C. Cisco: IoT traffic is taking over; 5G, WiFi 6 are ascending: Cisco Internet Report prognosticates M2M, 5G, WiFi, broadband impact by 2023. Network World, 20 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dave, M. How the hospitality industry will profit from the IoT. Network World, 9 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nadkarni, S.; Kriechbaumer, F.; Rothenberger, M.; Christodoulidou, N. The path to the Hotel of Things: Internet of Things and Big Data converging in hospitality. J. Hosp. Tour. Technol. 2020, 11, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercan, S.; Cain, L.; Akkaya, K.; Cebe, M.; Uluagac, S.; Alonso, M.; Cobanoglu, C. Improving the service industry with hyper-connectivity: IoT in hospitality. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2021, 33, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Shukla, V.K.; Sharma, R. Convergence of IOT in Tourism Industry: A Pragmatic Analysis. J. Physics. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1714, 12037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadrista. IoT Standards with Blockchain: Enterprise Methodology for Internet of Things; Apress, L.P.: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Navio-Marco, J.; Ruiz-Gómez, L.M.; Sevilla-Sevilla, C. Progress in wireless technologies in hospitality and tourism. J. Hosp. Tour. Technol. 2019, 10, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayashree, L.S.; Selvakumar, G. Enterprise IoT Development Platforms. In Getting Started with Enterprise Internet of Things: Design Approaches and Software Architecture Models; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maamar, Z.; Faci, N.; Yahya, F. A Guiding Framework for IoT Servitization. In Next-Gen Digital Services. A Retrospective and Roadmap for Service Computing of the Future; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelet, J.É.; Lick, E.; Taieb, B. The internet of things in upscale hotels: Its impact on guests’ sensory experiences and behavior. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2021, 33, 4035–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Luo, X.; Chu, X.; Zhou, M.-T. IoT Technologies and Applications. In Fog-Enabled Intelligent IoT Systems; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Li, B. The Evolutionary Game for Collaborative Innovation of the IoT Industry under Government Leadership in China: An IoT Infrastructure Perspective. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xia, Y.; Xu, M.; Xie, J.; Luo, R.; Huang, D. Distributed and Accurate Packet Reception Rate Estimation under Cross-Technology Interference. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Communications Conference, Taipei, Taiwan, 7–11 December 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, W. Composition and Communication Analysis of M2M System in Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Electromechanical Automation (AIEA), Guangzhou, China, 14–16 May 2021; pp. 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjed, R.; Croock, M.S. Dominated destinations of tourist inside Iraq using personal information and frequency of travel. Telkomnika 2019, 17, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Y. Collision Resolution with FM0 Signal Separation for Short-Range Random Multi-Access Wireless Network. IEEE Trans. Signal Inf. Processing Over Netw. 2021, 7, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LG leads the commercial spaces in providing Display-based, Air Conditioning, and IoT solutions. HospitalityBiz, 28 June 2018.
- IoT Industry in China to 2025—Key Drivers and Barriers. Plus Company Updates, 16 August 2021.
- Li, Y.; Xiao, P.; Dai, Z.; Bi, B.; Fu, D.; Hao, Y. Opportunities and Challenges Faced by the Online Educational Services in the Post-COVID-19. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Education and Social Sciences (ESS 2021), Xi’an, China, 22–23 May 2021; pp. 148–159. [Google Scholar]
- New Sustainability Research Research from Harbin Engineering University Outlined (The Evolutionary Game for Collaborative Innovation of the IoT Industry under Government Leadership in China: An IoT Infrastructure Perspective). China Weekly News, 1 May 2020; 437.
- Wang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Gangadhari, R.K.; Li, Z. Analyzing the Adoption Challenges of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Smart Cities in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A. The Role of IoT in the Fight Against Covid-19 to Restructure the Economy. In HCI International 2021—Late Breaking Papers: HCI Applications in Health, Transport, and Industry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyeenudin, H.M.; Bindu, G.; Anandan, R. OTA and IoT Influence the Room Occupancy of a Hotel. In Data Management, Analytics and Innovation; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglogiannis, I.; Iliadis, L.; Pimenidis, E. Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations. In Proceedings of the AIAI 2020 IFIP WG 12.5 International Workshops [Electronic Resource]: MHDW 2020 and 5G-PINE 2020, Neos Marmaras, Greece, 5–7 June 2020; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Leung, V.C.M.; Li, K.; Zhang, H.; Hu, X.; Liu, Q. 6GN for Future Wireless Networks. In Proceedings of the 3rd EAI International Conference, 6GN 2020, Tianjin, China, 15–16 August 2020; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Industry News: Reliance Group’s IoT Arm Ties up with China’s Fibocom. Electronics Bazaar, 20 July 2017.
- 2020 IoT opens new opportunities for China IoT industry—Booth reservations are booming. PR Newswire, 25 November 2019.
- Xiaozhong, L.; Yueli, G.; Hailei, Z. Comparative research on the IOT industry competitiveness of Eastern, Central and Western China. J. Grey Syst. 2016, 28, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, D. Future Communication, Information and Computer Science. In Proceedings of the International Research Association of Information and Computer Science, Beijing, China, 22–23 May 2014; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Y.; Liqaa, N. IoT Technologies during and Beyond COVID-19: A Comprehensive Review. Future Internet 2021, 13, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. China’s manufacturing locus in 2025: With a comparison of “Made-in-China 2025” and “Industry 4.0.”. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 135, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visible energy unveils IOT products for commercial refrigeration at China refrigeration 2016: New Wi-Fi connected devices change how commercial refrigerators operate, achieving unprecedented energy savings and efficiency. PR Newswire, 11 April 2016.
- Gong, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Gu, M.; Ong, P.; Li, Y. Established and Nascent Entrepreneurs: Comparing the Mental Health, Self-Care Behaviours and Wellbeing in Singapore. Front. Sociol. 2022, 7, 843101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ning, Z.; Zhou, M.; Hu, X.; Wang, L.; Hu, B.; Kwok, R.Y.K.; Guo, Y. A Privacy-Preserving Message Forwarding Framework for Opportunistic Cloud of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 5281–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IoT Partner Programs Now Streamlining Ecosystem to Enter New Markets. Communications Today, 17 July 2019.
- Semtech’s LoRa Technology Expands Presence as Leading Internet of Things (IoT) Platform in China: Alibaba Cloud and Zhejiang Provincial Company of China Unicom deploy LoRa Technology in Hangzhou to expand China’s IoT industry. NASDAQ OMX’s News Release Distribution Channel, 9 April 2018.
- Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Hao, Y.; Xiao, P.; Liu, J. Psychosocial Impacts of Mobile Game on K12 Students and Trend Exploration for Future Educational Mobile Games. Front. Educ. 2022, 7, 843090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marriott International Teams with Samsung and Legrand to Unveil Hospitality Industry’s IoT Hotel Room of The Future, Enabling the Company To Deepen Personalized Guest Experience. Journal of Engineering; Bethesda, MD, USA, 2017; Available online: https://news.marriott.com/news/2017/11/14/marriott-international-teams-with-samsung-and-legrand-to-unveil-hospitality-industrys-iot-hotel-room-of-the-future-enabling-the-company-to-deepen-personalized-guest-experience (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Meghamala, P. The IoT in Hospitality: Advantages and Limitations. 2019. Available online: electronicsofthings.com (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Maiti, M.; Vuković, D.; Mukherjee, A.; Paikarao, P.D.; Yadav, J.K. Advanced data integration in banking, financial, and insurance software in the age of COVID-19. Softw. Pract. Exp. 2022, 52, 887–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoukry, A.; Aldeek, F. Attributes prediction from IoT consumer reviews in the hotel sectors using conventional neural network: Deep learning techniques. Electron. Commer. Res. 2019, 20, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomislav, C.; Stifanich, L.P.; Simunic, M. Internet of things (IOT) in tourism and hospitality: Opportunities and challenges. Tour. South East Eur. 2019, 5, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrag, M.A.; Shu, L.; Choo, K.K.R. Fighting COVID-19 and Future Pandemics with the Internet of Things: Security and Privacy Perspectives. IEEE-CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2021, 8, 1477–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Policy Title | Date of Issue | Issue Department |
|---|---|---|
| Notice on Furthering the Comprehensive Development of Mobile Internet of Things | 2020-05 | Ministry of Industry and Information Technology |
| Three-Year Action Plan to Expand and Upgrade Information Consumption (2018–2020) | 2018-07 | Ministry of Industry and Information Technology |
| Three-Year Action Plan to Promote the Development of a New Generation of Artificial Intelligence Industries (2018–2020) | 2017-12 | Ministry of Industry and Information Technology |
| The 13th Five-Year Plan for the Internet of Things (2016–2020) | 2016-12 | State Council of China |
| Smart Manufacturing Development Plan (2016–2020) | 2016-12 | Ministry of Industry and Information Technology & Ministry of Finance |
| The 12th Five-Year Plan for the Development of the Internet of Things | 2011-12 | Ministry of Industry and Information Technology |
| Major Categories | Subdivision | Market Costs | Cost Breakdown | Solutions | Costs after Optimization | Savings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy costs | Energy | 6% of operating costs | Water, electricity, gas, etc. | Using the wireless controller | 4% of operating costs | ≈25% |
| Labor costs | Staff | 48,260 RMB/year | Salaries, social security, overheads | Robotic assistance | 24,000–36,000 RMB/year | ≈40% |
| Room Distribution | Approx. 16.8 RMB per hour | Labor costs | Robot-assisted delivery | Approx. 2.7–4.2 RMB per hour | ≈80% | |
| Restaurant Services | Per 6 people | Labor costs | Robots instead of manual labor | 1 unit | ≈80% | |
| Management costs | Transport delivery | Approx. 2–2.5 RMB/set | Vehicles, drivers, fuel costs | RFID chip implantation without handover | Approx. 0.6–0.7 RMB/set | ≈65% |
| Stock Turnaround | 360 RMB/set | Towel replacement cycle 1 year, bedding 1.5 years | Scheduling of cloths via app, on demand | 250 RMB/set | ≈30% | |
| Laundry | 360 RMB/set | 3 times stock availability | Three levels of procurement based on demand | 220 RMB/set | ≈70% |
| Constraints | Specific Issues | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Insufficient intelligence | Smart devices are only semi-intelligent and semi-manual, and cannot completely replace manual labor. | The layout of the hotel rooms and the positions of the furniture are different, and the machine cannot adapt to them independently, so manual intervention is required. |
| Lack of sense of service | IoT devices lack a sense of service and are more about problem solving. | Unable to recognize expressions and tone of voice; unable to provide accurate service. |
| Privacy issues | IoT enables customer personalization through big data collection, but also inadvertently invades customer privacy. | There is a large number of camera equipment, terminals, and sensors. |
| Inadequate financial follow-up | Smart hotels are larger and more costly in terms of investment and have certain capital requirements. | Requires large amounts of electrical energy, highly stable network environment, and high-quality system maintenance. |
| Risks | Main Content | Risk Index | Impact Index | Risk Control Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Competition risk | Market homogenization is evident, and competition is becoming fierce. | 70% | 70% |
|
| Construction or renovation cost risk | The high construction cost will bring some economic pressure and cash flow risk. | 40% | 70% |
|
| Security risk | IoT hotel cyber security is a crucial aspect. | 30% | 60% |
|
| Market risk | A single intelligent hotel IoT transformation does not attract customers. | 20% | 30% |
|
| Technical risk | The IoT industry is rapidly renewing and there is a risk of rapid obsolescence of the original IoT devices and service systems, etc. | 10% | 10% |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, M.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Shi, A.; Gu, M.; Li, Y. Overviews of Internet of Things Applications in China’s Hospitality Industry. Processes 2022, 10, 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10071256
Chen M, Jiang Z, Xu Z, Shi A, Gu M, Li Y. Overviews of Internet of Things Applications in China’s Hospitality Industry. Processes. 2022; 10(7):1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10071256
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Mengyuan, Zheng Jiang, Zezheng Xu, Aihua Shi, Mingyan Gu, and Yuanzhe Li. 2022. "Overviews of Internet of Things Applications in China’s Hospitality Industry" Processes 10, no. 7: 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10071256
APA StyleChen, M., Jiang, Z., Xu, Z., Shi, A., Gu, M., & Li, Y. (2022). Overviews of Internet of Things Applications in China’s Hospitality Industry. Processes, 10(7), 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10071256







