Abstract
Enzyme inhibitors are frequently used to treat viral illnesses. Protease inhibitors are a promising class for combating novel and life-threatening viral infections. This research aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of lopinavir/ritonavir monotherapy or lopinavir/ritonavir plus interferon for the treatment of COVID-19. The PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library databases were searched for English articles with full texts available online. ReviewManager software was used to conduct a meta-analysis, subgroup analysis, and sensitivity analysis. Following the creation of the protocol, the collected sources were sorted into categories and evaluated for quality. Risk and hazard ratios and the random effects model were implemented, with statistical heterogeneity assigned using the Higgins I2 statistic. Lopinavir/ritonavir, with or without interferon, was associated with a nonsignificant higher mortality rate (odds ratio [OR] 1.29; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.95 to 1.761; p = 0.1), as was clinical improvement (OR 1.2; 95% CI 0.8 to 1.84; p = 0.36). The difference in the length of hospital stay was in favor of the control group but statistically insignificant (standardized mean difference [SMD] 0.07; 95% CI −0.44 to 0.57; p = 0.79). The pooled data showed that lopinavir/ritonavir, with or without interferon, was associated with a significantly higher number of adverse events than placebo (OR 1.2; 95% CI 1.09 to 2.34; p = 0.02). Serious adverse events were insignificantly increased in the treated group over the control group (OR 1.2; 95% CI 0.96 to 2.12; p = 0.08). In the subgroup analysis, it was found that interferon used with lopinavir/ritonavir did not have a statistically significant effect on mortality rates (OR 1.75; 95% CI 0.87 to 3.55; p = 0.37), adverse effects (OR 1.20; 95% CI 0.75 to 1.91; p = 0.27), or serious adverse effects (OR 1.86; 95% CI 1.17 to 2.96; p = 0.33). Treatment with lopinavir/ritonavir alone or in combination with interferon for COVID-19 did not significantly outperform placebo in this study. Large randomized clinical trials are required to evaluate lopinavir/ritonavir in conjunction with interferon for the treatment of COVID-19. Such studies would benefit greatly from being conducted in a double-blind fashion at multiple locations.
1. Introduction
Over the past two decades, significant health issues have been caused by three members of the betacoronavirus genus: SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2 [1]. On 12 March 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared that COVID-19 cases had reached the level of a pandemic and become a global public health emergency. As of 19 December 2022, 647,972,911 verified cases had been registered worldwide and 6,642,832 deaths due to COVID-19 had been recorded [2]. Some of the clinical symptoms of COVID-19 include a high temperature, trouble breathing, dyspnea, fatigue, and coughing [3]. Most people infected with COVID-19 experience mild symptoms or have a rapid recovery, although a small percentage of those infected go on to develop multiorgan failure or severe pneumonia and some die [4,5].
While there have been extensive efforts to find effective treatments for SARS-CoV-2 infections all around the world, only a small number of drugs have been approved for use in an emergency setting and none have garnered universal acceptance as cures. Accordingly, research into potential pharmacological treatments for COVID-19 continues. Antiviral drugs such as remdesivir, favipiravir, ribavirin, chloroquine, interferons, protease inhibitors, neuraminidase inhibitors, fusion and entry inhibitors, and hemagglutinin inhibitors have been repurposed to treat COVID-19 [6,7,8,9]. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States has given the dual protease inhibitor lopinavir/ritonavir the green light for treating acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) [10]. Additionally, the drug has demonstrated antiviral activity against MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV [11,12]. The effective treatment of COVID-19 infection has been demonstrated with purine and pyrimidine derivatives, including acyclovir, ganciclovir, and lopinavir [13,14]. Other promising drugs for COVID-19 are simeprevir [15], paxlovid (nirmatrelvir/ritonavir) [16], and molnupiravir [17].
Interferons are important components of the immune system in the fight against viruses [18]. Type I, II, and III interferons were recognized in the past, and the type IV interferon was discovered very recently [19]. Type I interferons inhibited SARS-CoV-2 multiplication in vitro utilizing Vero E6 cells in plaque reduction, viral antigen expression, and viral load reduction experiments [20]. When compared with SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2 is more susceptible to the effects of type I interferons [21]. Interferon-β has been shown to provide considerable benefits in terms of the time it takes for clinical improvements to occur, but not in terms of reducing mortality rates or shortening hospital stays for COVID-19 patients [22,23]. However, this study’s findings were constrained by confounding variables, varying interferon doses, and significant heterogeneity.
The purpose of this research was to examine how effective lopinavir/ritonavir was on its own and in conjunction with interferon in treating patients with COVID-19. Few studies have been performed on the safety and efficacy of lopinavir/ritonavir alone or in combination with interferon. This study evaluated the efficacy of lopinavir/ritonavir with or without interferon versus placebo, standard care, and other antiviral medications, as measured by 28-day mortality rates, clinical response rates, and the length of hospitalization. The number of patients who reported mild or severe adverse effects when taking lopinavir/ritonavir with or without interferon was also compared with the number of people who reported such effects while taking a placebo, receiving normal care, or taking other antiviral medication.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Question and Guidelines
While conducting this study, the researchers used data from systematic reviews and meta-analyses [24] and relied on the guidelines and recommendations of the Cochrane community [25].
The research question was structured according to the patient/population, intervention, comparison, and outcomes (PICO) model. The population was COVID-19 patients. The intervention was lopinavir/ritonavir with or without interferon. Comparisons were made among patients receiving placebo, standard care, and other antiviral drugs. The primary outcome(s) were mortality rates at day 28 and rates of clinical improvement. The secondary outcomes were the length of hospital stay, adverse events, and serious adverse events. The research question was, “Is the use of lopinavir/ritonavir, with or without interferon, safe and effective compared with placebo, standard care, and other antiviral drugs in managing COVID-19 patients”?
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
The articles that were selected for review for this study were in English and published between 1 January 2020 and 1 December 2022. The length of time it took to finish the study was not relevant. The demographics, research design, and purpose of each article were taken into consideration when determining whether it should be included in the study. An included research article had to satisfy the following conditions: (1) It had to be a randomized clinical trial (RCT). (2) It had to compare laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 patients who were given lopinavir/ritonavir as a single therapy or together with interferon with those who were given placebo, no antiviral agent, or other antiviral agents for COVID-19 treatment. (3) It had to examine at least one of the primary outcomes. The mortality rate on day 28 of treatment was the main safety-linked outcome of concern. After treatment, clinical improvement was the main efficacy-linked outcome of concern. (4) It had to be written in English and published. (5) No specific criteria were used to limit the age of the study population; therefore, all participants were regarded as eligible in terms of age.
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
All non-original publications such as reviews, letters to the editor, conference papers, and comments on published articles were excluded from this study. In addition, articles for which the full text was not available, animal studies, case studies, study protocols, non−peer reviewed journal articles, and studies that could not be sourced in the English language were excluded.
2.4. Search Strategy
To find pertinent articles up to December 2022, a systematic search was performed in PubMed, Scopus, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, and the Web of Science. Additional studies cited in the included studies and the reviews’ reference lists were searched manually. Only papers having an English abstract or full text were included in the search. The search strategy for pertinent articles on PubMed was (Coronavirus OR COVID-19 OR SARS-CoV-2) AND (lopinavir/ritonavir OR lopinavir/ritonavir AND interferon). A similar strategy was followed while searching other databases.
2.5. Quality Assessment
The Cochrane risk-of-bias tool for randomized controlled studies was used to assess the quality of the included studies because only randomized controlled trials were included in this review.
2.6. Data Extraction
Data extraction was performed after studies were chosen from the databases and their methodological quality was evaluated. Microsoft Excel was used to create a consistent data-collecting format for gathering the following data: author and year of publication, location of the study, number of participants, patient age, participant gender (male), and the study’s measured outcome(s). Two researchers independently carried out these steps.
2.7. Data Synthesis
Dichotomous data were converted into pooled odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Using the inverse variance approach, the standardized mean difference (SMD) was calculated by pooling the effect sizes for each continuous variable. When they were not reported, the means and standard deviations were computed using ranges, medians, interquartile ranges (IQRs), and sample sizes [26]. Mantel–Haenszel ORs and count data were used to display the results for tolerability (at least one event had to be observed to be included in the analysis). The assumption behind the random effects model was that the disparities between the research populations would result in some fluctuation in the size of the effect between trials [27]. Meta-analysis was performed if there were results from at least two studies on the targeted outcomes.
Heterogeneity was examined using the Cochrane Q test and the I2 statistic, which evaluated the heterogeneity of the study data. Heterogeneity of less than 25% was categorized as low, between 26% and 74% as moderate, and higher than 75% as high [28]. Sensitivity and subgroup analyses were carried out when appropriate and applicable in order to identify potential sources of heterogeneity. For all statistical analyses, ReviewManager (RevMan) software version 5.4.1 was used.
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
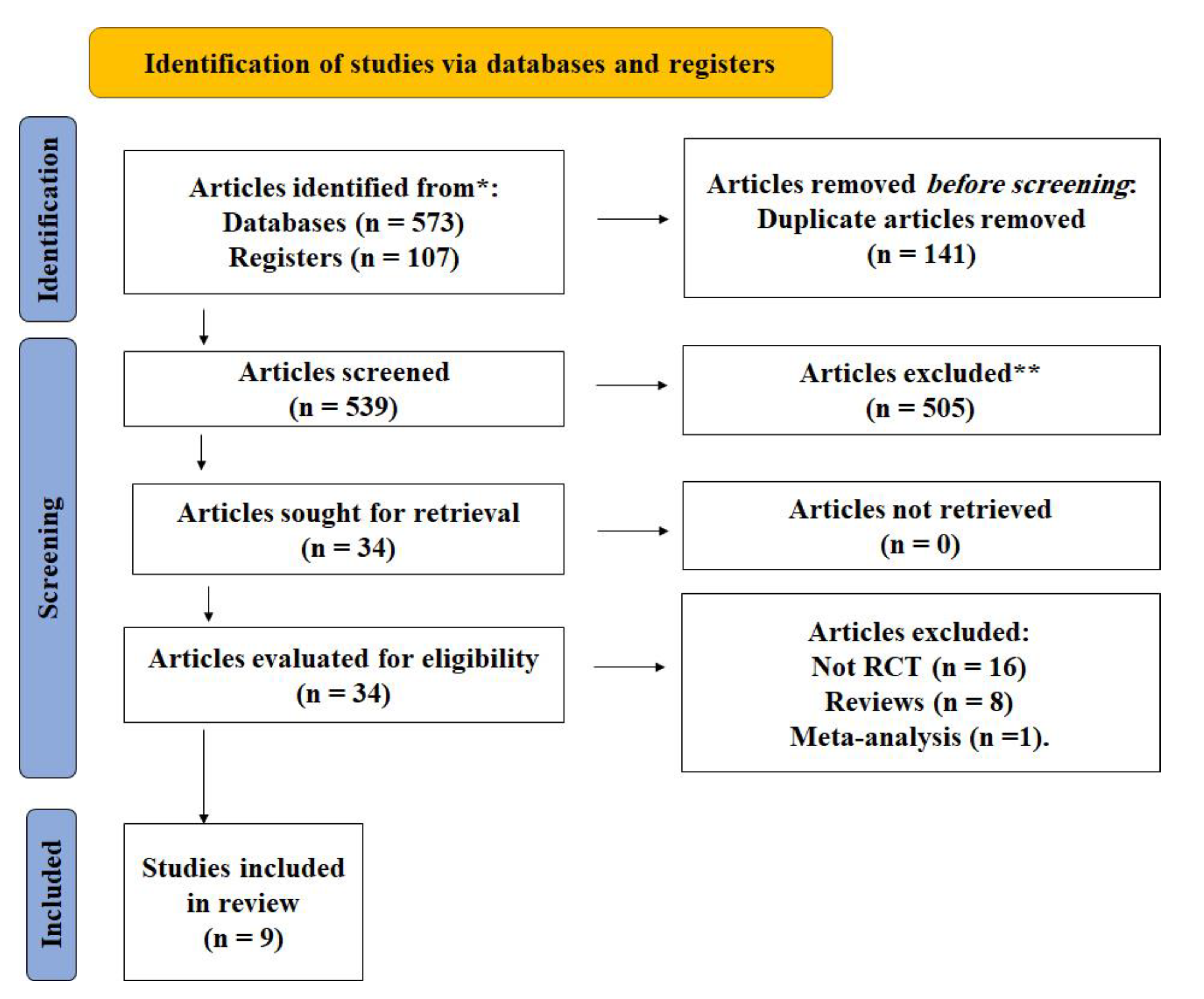
A total of 680 studies were found in the initial search of the internet databases using the aforementioned keywords. With repetitions removed, we were left with 539 studies. The titles and abstracts of the 539 studies were reviewed to select those that would be included in the meta-analysis. After the initial round of culling, just 34 publications were left; a full-text read led to the elimination of another 25 studies. In the end, 9 articles were found to have effectively met the established eligibility requirements (Table 1). Figure 1 shows the PRISMA diagram for the study selection process.

Table 1.
Characteristics of included studies considered in this study.
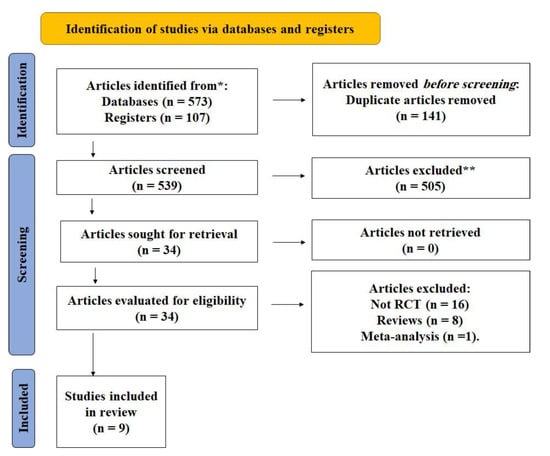
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram. * According to the inclusion criteria of articles in the study. ** The articles were excluded according to the exclusion criteria described in the methods section.
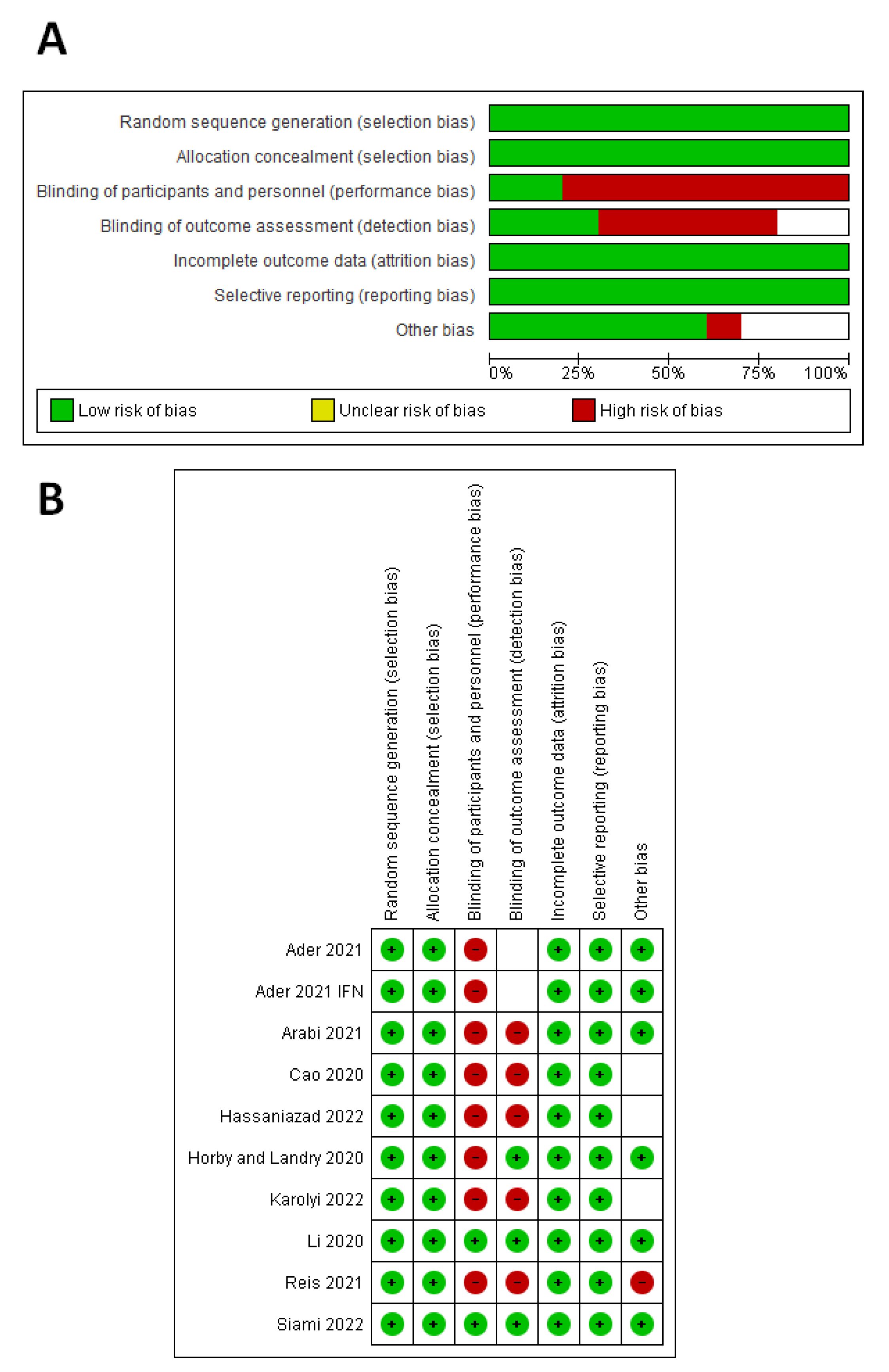
3.2. Quality Assessment Results
According to the Cochrane risk-of-bias tool (Figure 2), seven studies had a high risk of performance bias [29,30,31,32,33,34,35], five studies had a high risk of detection bias [30,31,32,34,35], and one study had an unclear risk of detection bias [29]. One study had a high risk of other biases [35], and three studies had an unclear risk of other biases [31,32,34].
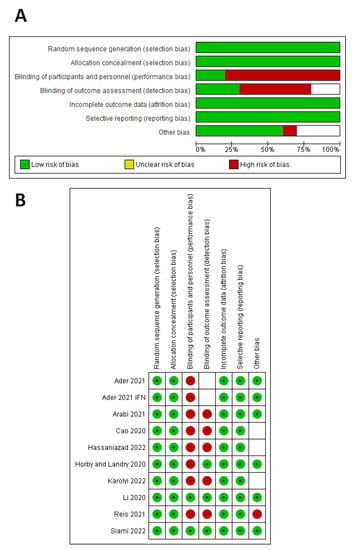
Figure 2.
Quality assessment of the included studies. (A) Risk-of-bias graph. (B) Risk-of-bias summary for each study.
3.3. Measured Outcomes
3.3.1. Mortality Rate on Day 28
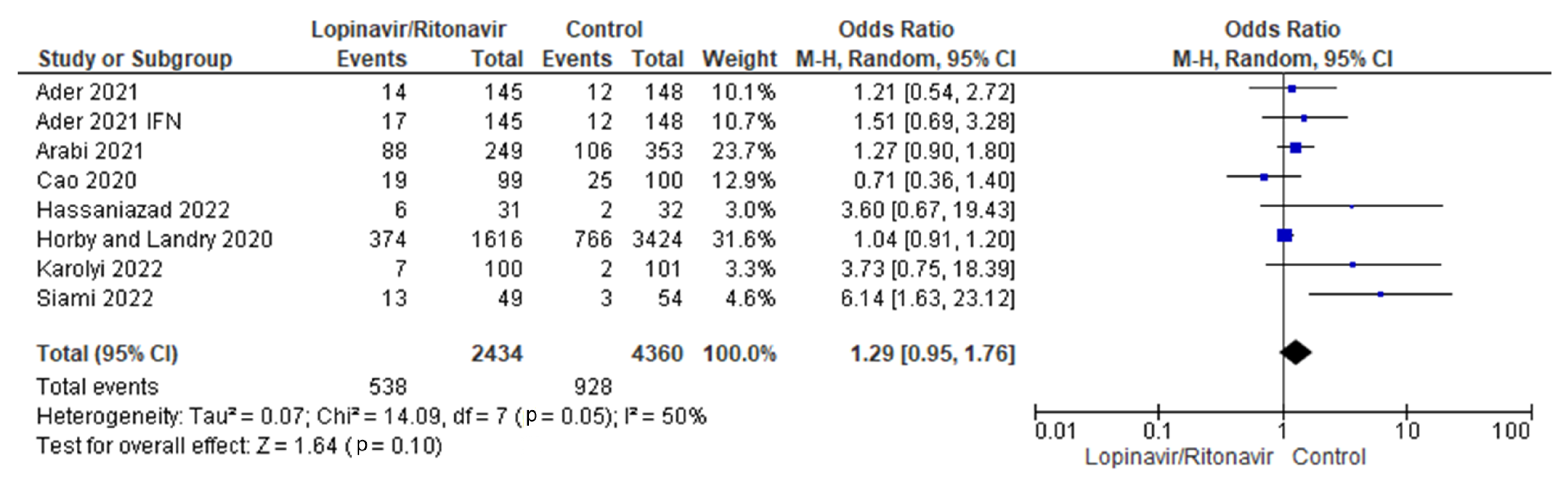
Seven randomized trials were combined for this meta-analysis [29,30,31,32,33,34,36]. The control group consisted of 4360 patients, while the intervention group had 2434 individuals. The findings of the I2 statistic, at 50%, showed that the heterogeneity of the seven studies pooled in this analysis was moderate.
According to the combined data, the groups that took lopinavir/ritonavir with or without interferon had a higher mortality rate (22.1%) than the control group (21.2%). When the lopinavir/ritonavir groups with or without interferon were compared with the control group, the difference in mortality incidence was an OR of 1.29, with a 95% CI of 0.95 to 1.76, favoring the control group. However, because the p-value was higher than the established threshold (p = 0.10), these findings were not statistically significant. A forest plot of the analysis is presented in Figure 3.
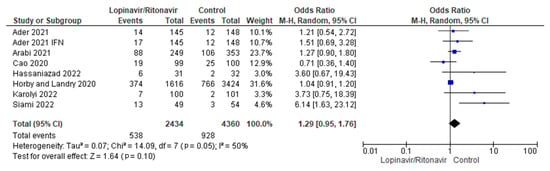
Figure 3.
Forest plot analysis for mortality incidence. The sizes of the blue squares reflect the relative weight of the individual trials. The combined point estimate is shown as a black diamond. The diamond and the squares (together with the 95% CIs) located beyond the vertical line (indicating the unit value) show that a result was statistically significant.
3.3.2. Clinical Improvement
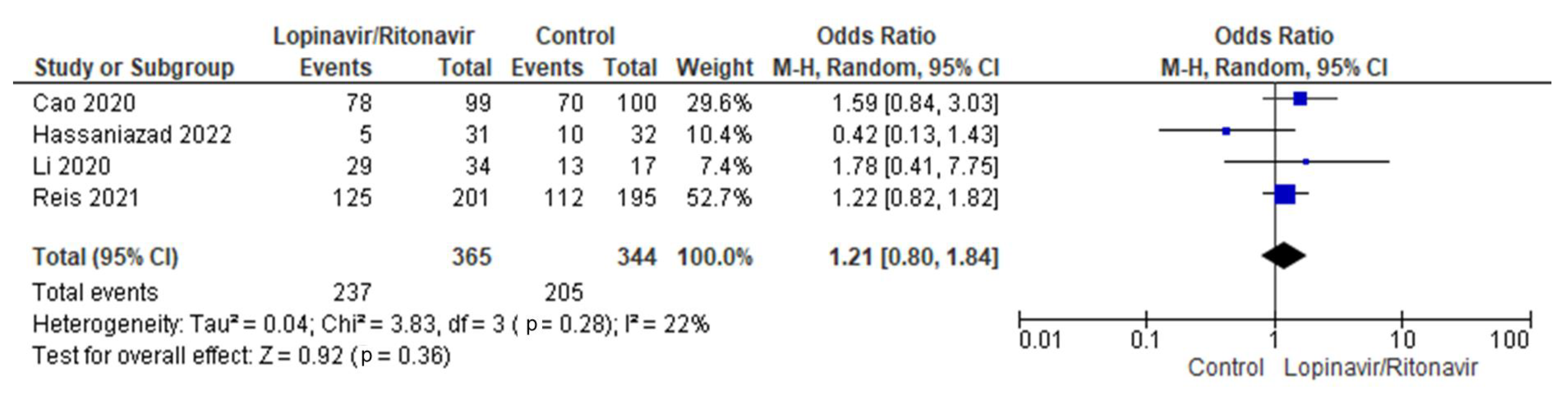
Four randomized trials were merged for analysis in this meta-analysis [31,32,35,37]. There were 344 patients in the control group and 365 in the intervention group overall. The I2 statistic results, at 22%, showed that the four studies aggregated in this analysis had low heterogeneity. In comparison with the control group, more COVID-19 patients receiving lopinavir/ritonavir with or without interferon experienced clinical remission. The difference between the COVID-19 groups receiving lopinavir/ritonavir with or without interferon and the control group in terms of clinical improvement was an OR of 1.21, with a 95% CI of 0.80 to 1.84, favoring the groups receiving lopinavir/ritonavir with or without interferon. However, because the p-value was greater than the established cutoff point (p = 0.36), these findings were not statistically significant. Figure 4 shows a forest plot of the analysis.
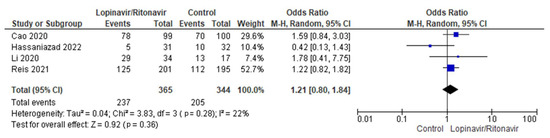
Figure 4.
Forest plot analysis of clinical improvement. The sizes of the blue squares reflect the relative weight of the individual trials. The combined point estimate is shown as a black diamond. The diamond and squares (together with the 95% CIs) located beyond the vertical line (indicating the unit value) show that a result was statistically significant.
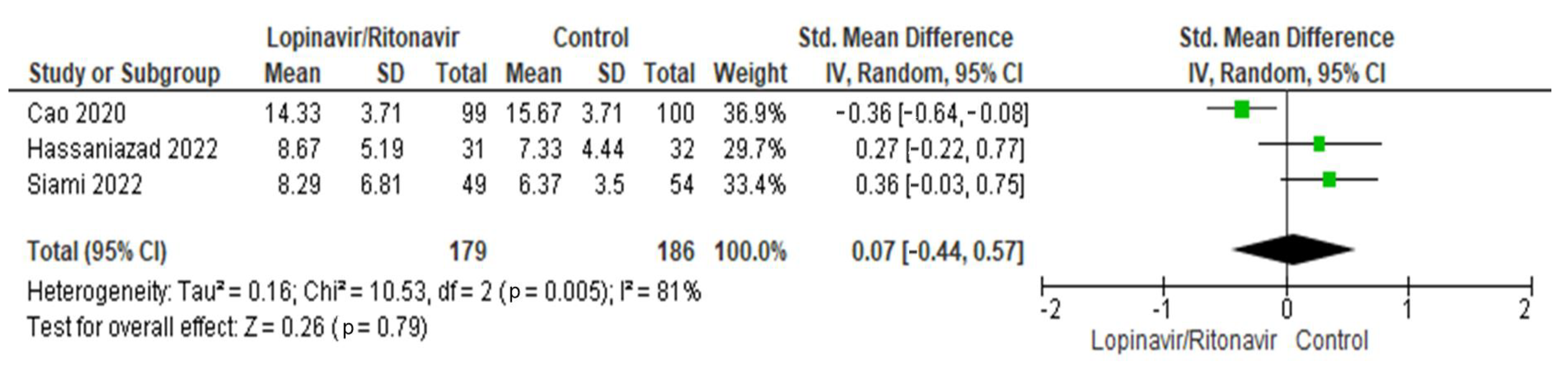
3.3.3. Length of Hospital Stay (Days)
Three papers were included for the analysis of this characteristic [31,32,36]. There were 179 patients in total in the lopinavir/ritonavir group and 186 patients overall in the control group. High levels of heterogeneity were seen in the three studies. The I2 statistic results, at 81%, demonstrated this. The difference in length of hospital stay was an SMD of 0.07 (95% CI −0.44 to 0.57), in favor of the control group. A p-value of 0.79, which was above the threshold of 0.05, indicated that the difference was statistically insignificant. Figure 5 includes a graphic display of the forest plot used in this analysis.
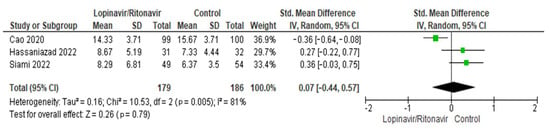
Figure 5.
Forest plot analysis for length of hospital stay. The sizes of the green squares reflect the relative weight of the individual trials. The combined point estimate is shown as a black diamond. The diamond and squares (together with the 95% CIs) located beyond the vertical line (indicating the unit value) show that a result was statistically significant.
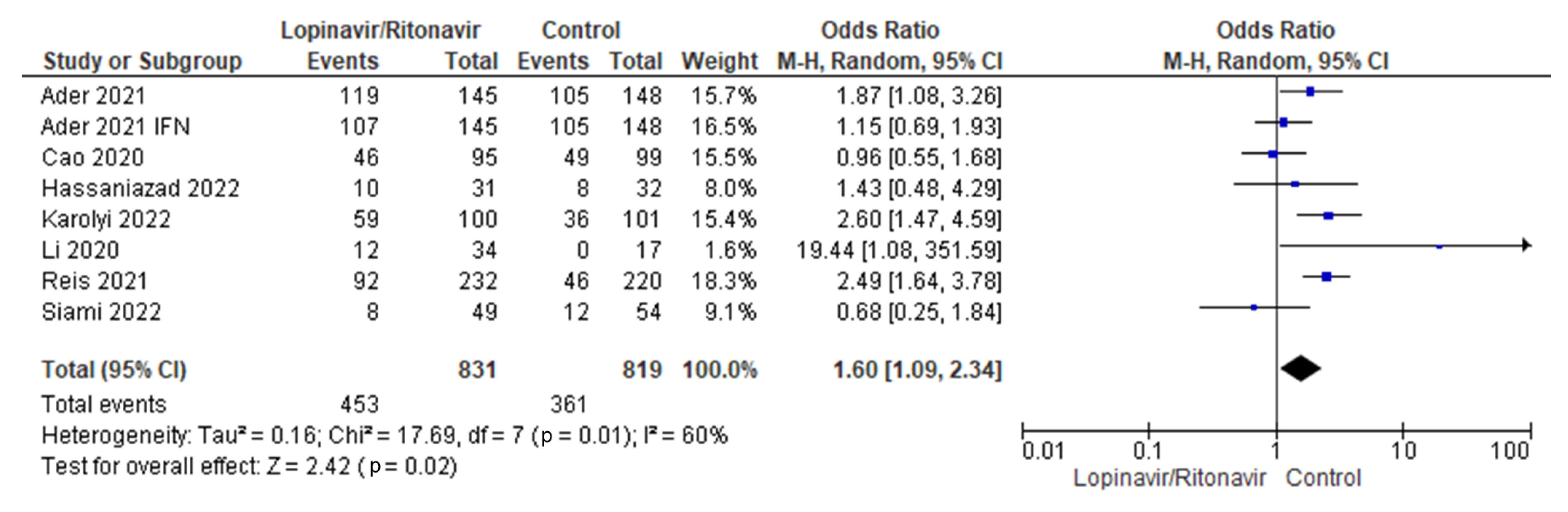
3.3.4. Adverse Events
Seven studies were considered for the analysis of adverse events [29,31,32,34,35,36,37]. There were 679 patients with COVID-19 who received lopinavir/ritonavir with or without interferon and 1213 people in the control group. Low levels of heterogeneity were present across the seven studies. The I2 statistic was 0%. According to the pooled data, the groups that received lopinavir/ritonavir with or without interferon had a disproportionately high number of side effects compared with the control group. With a 95% CI of 1.09 to 2.34, the control group was better off than the experimental group in terms of the outcomes of adverse events in COVID-19 patients. The p-value was less than the chosen threshold (p = 0.02), making these findings statistically significant. Figure 6 shows the forest plot used for this analysis.
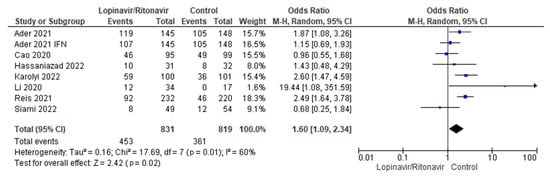
Figure 6.
Forest plot analysis of adverse events. The sizes of the blue squares reflect the relative weight of the individual trials. The combined point estimate is shown as a black diamond. The diamond and squares (together with the 95% CIs) located beyond the vertical line (indicating the unit value) show that a result was statistically significant.
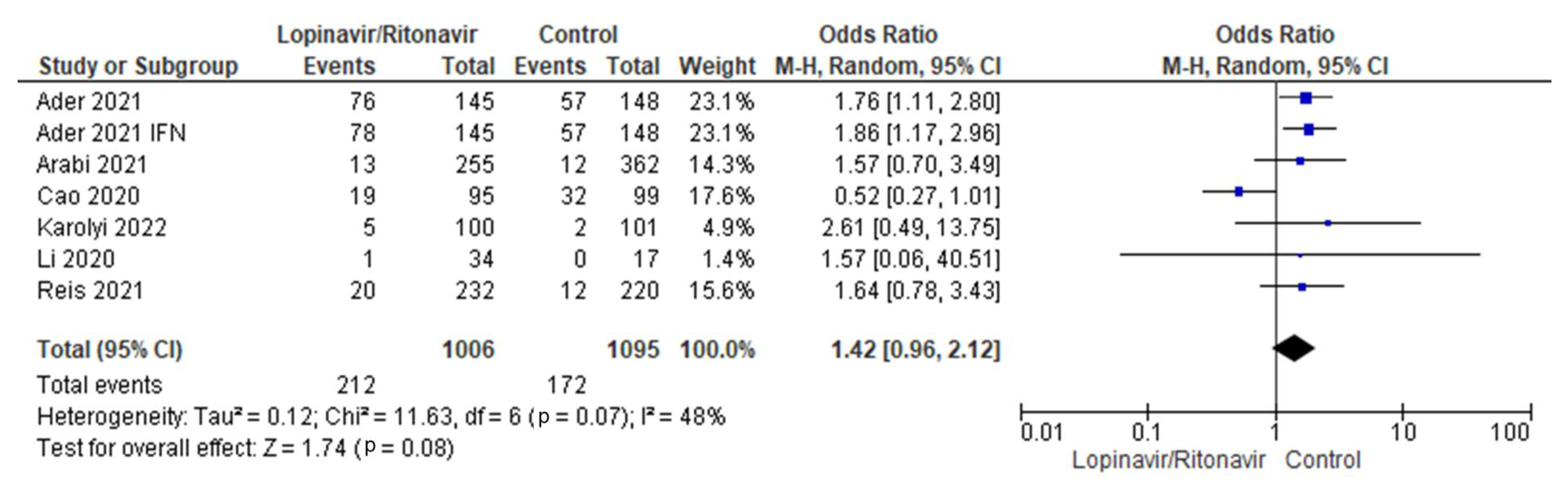
3.3.5. Serious Adverse Events
There were six studies of serious adverse events included in this meta-analysis [29,31,34,35,36,37]. There were 1213 patients in the control group and 679 in the COVID-19 cohort who received lopinavir/ritonavir with or without interferon. The six studies had a moderate amount of heterogeneity. The I2 statistic of 48% supported this. The combined data demonstrated that, in comparison with the control group, the groups that received lopinavir/ritonavir with or without interferon had a greater frequency of serious adverse events. The control group fared better than the experimental group in terms of the outcomes of serious adverse events in COVID-19 patients, with an OR of 1.42 and a 95% CI of 0.96 to 2.12. Since the p-value was higher (0.08) than the chosen threshold, these results were statistically insignificant. A forest plot for the analysis is presented in Figure 7.
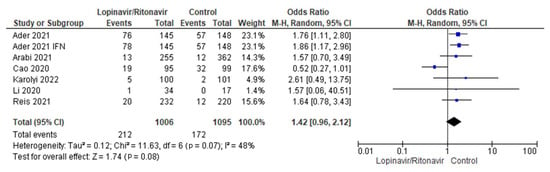
Figure 7.
Forest plot analysis of serious adverse events. The combined point estimate is shown as a black diamond. The diamond and squares (together with the 95% CIs) located beyond the vertical line (indicating the unit value) show that a result was statistically significant.
3.4. Subgroup Analysis
A subgroup analysis based on treatment with lopinavir/ritonavir as a single therapy or with interferon was performed.
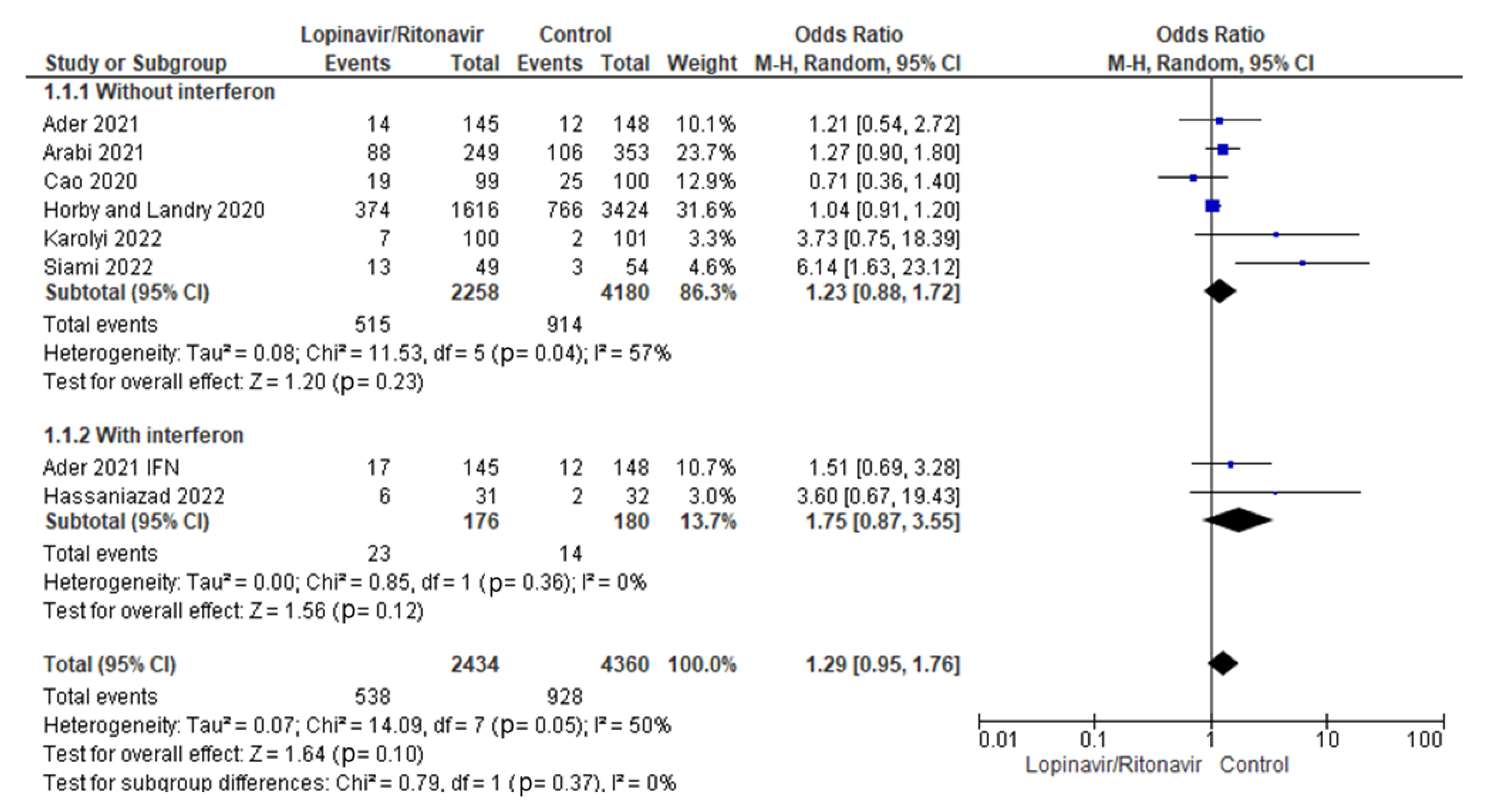
3.4.1. Mortality Rates
A subgroup study was conducted to determine whether the addition of interferon to the standard treatment of lopinavir/ritonavir for COVID-19 reduced mortality rates. The statistical results showed that the OR of mortality incidence for COVID-19 patients treated with lopinavir/ritonavir alone was 1.23 (95% CI 0.88 to 1.72) and the OR of mortality incidence for COVID-19 patients treated with lopinavir/ritonavir plus interferon was 1.75 (95% CI 0.87 to 3.55). Figure 8 displays the results of the test for subgroup differences, which revealed that there was no statistically significant subgroup effect (p = 0.37) when using interferon in conjunction with lopinavir/ritonavir for the management of COVID-19 patients.
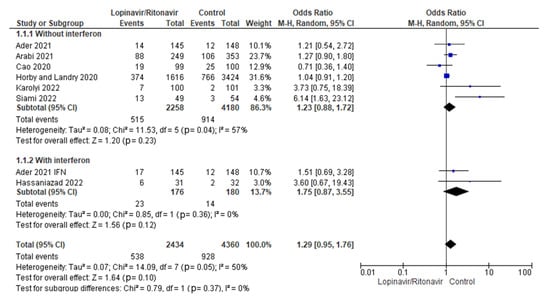
Figure 8.
Subgroup analysis for mortality rates. The sizes of the blue squares reflect the relative weight of the individual trials. The combined point estimates are shown as black diamonds. The diamonds and squares (together with the 95% CIs) located beyond the vertical line (indicating the unit value) show that a result was statistically significant.
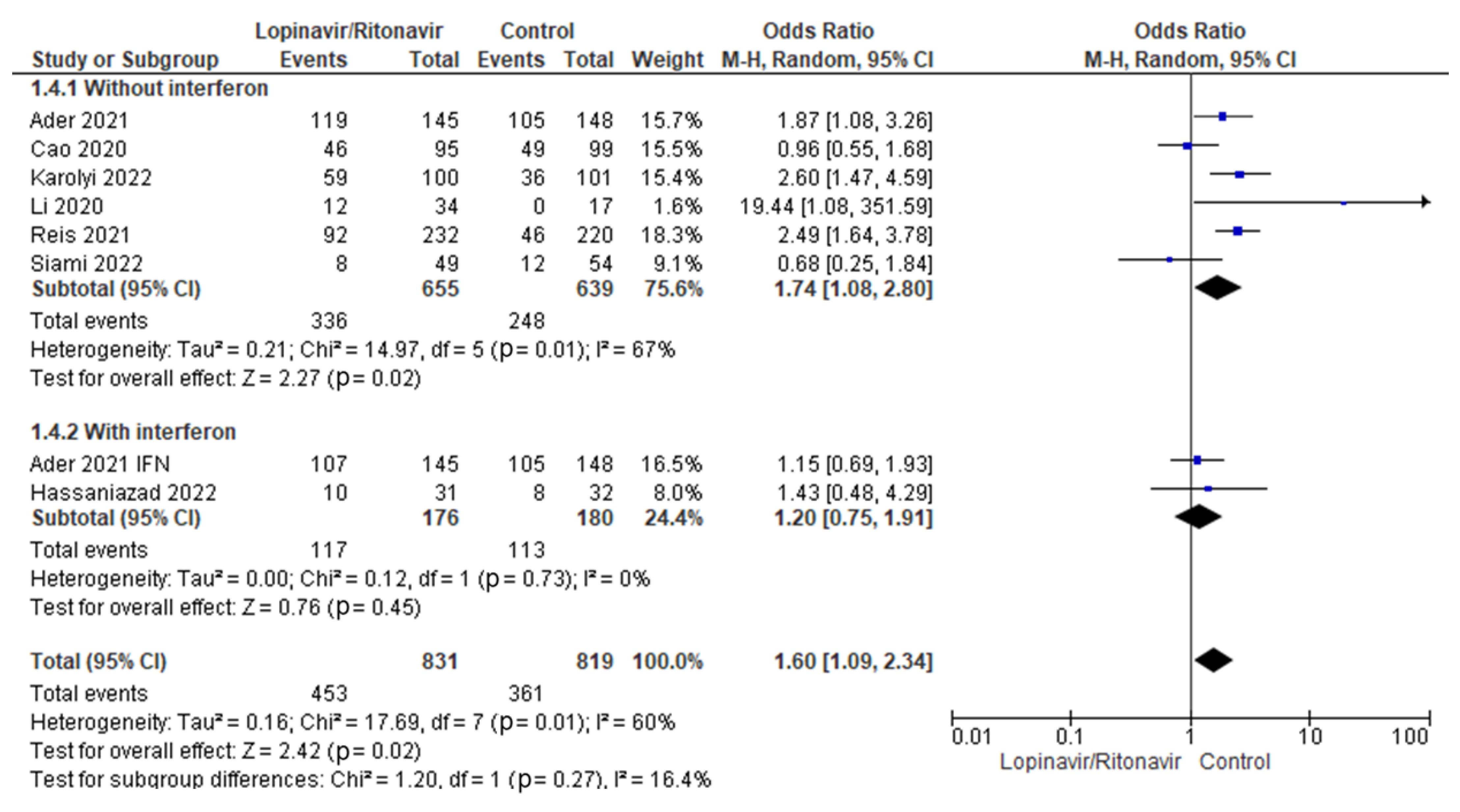
3.4.2. Adverse Events
Interferon’s potential impact on adverse events in COVID-19 patients treated with lopinavir/ritonavir was tested in a subgroup analysis. In COVID-19 patients, the statistical results showed that the OR for adverse event incidence was 1.74 (95% CI 1.08 to 2.80) for lopinavir/ritonavir alone and 1.20 (95% CI 0.75 to 1.91) for lopinavir/ritonavir with interferon. Figure 9 displays the results for the subgroup differences; this test showed that there was no statistically significant subgroup effect (p = 0.27), indicating that interferon did not have a statistically significant effect on adverse events when used in combination with lopinavir/ritonavir to manage patients with COVID-19.
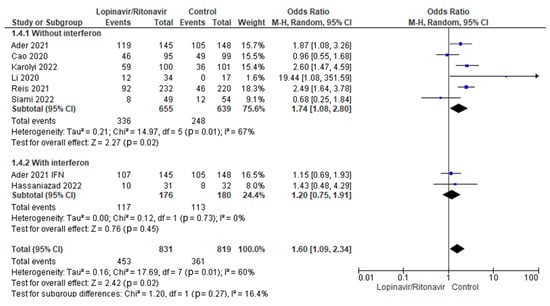
Figure 9.
Subgroup analysis for adverse events. The sizes of the blue squares reflect the relative weight of the individual trials. The combined point estimates are shown as black diamonds. The diamonds and squares (together with the 95% CIs) located beyond the vertical line (indicating the unit value) show that a result was statistically significant.
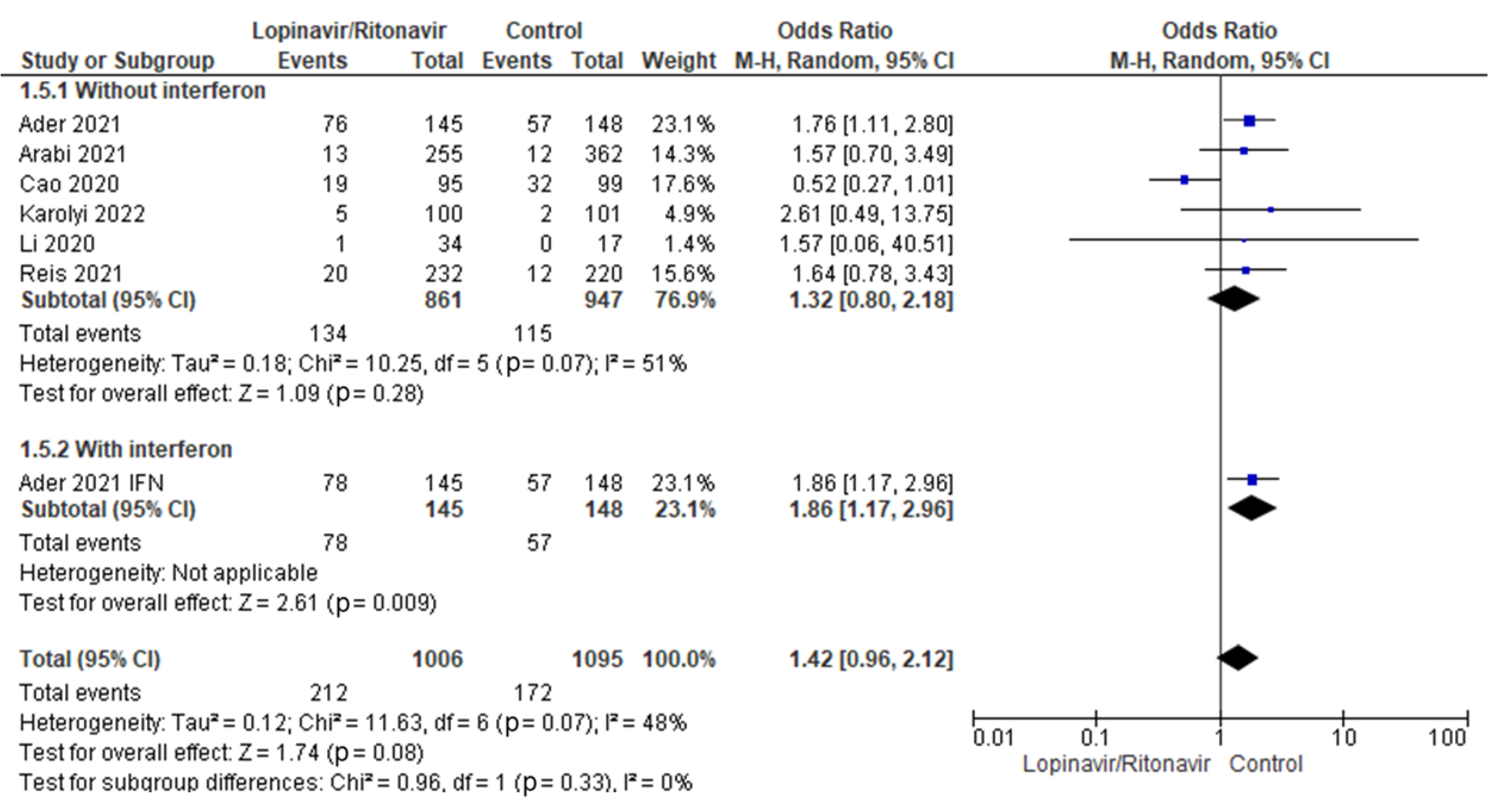
3.4.3. Serious Adverse Events
A subgroup analysis was performed to test whether interferon had an effect on serious adverse events when used with lopinavir/ritonavir for treating COVID-19 patients. Statistical results showed that the OR for of adverse events incidence in COVID-19 patients was 1.32 (95% CI 0.80 to 2.18) for lopinavir/ritonavir alone and 1.86 (95% CI 1.17 to 2.96) for lopinavir/ritonavir with interferon. Figure 10 displays the results of the test for subgroup differences, which showed that there was no statistically significant subgroup effect (p = 0.33), indicating that adding interferon to lopinavir/ritonavir for the management of COVID-19 patients did not result in a statistically significant increase in the rate of serious adverse events.
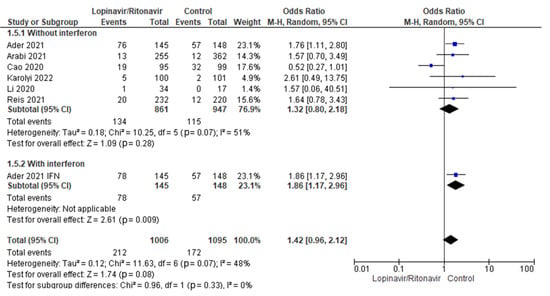
Figure 10.
Subgroup analysis of serious adverse events. The sizes of the blue squares reflect the relative weight of the individual trials. The combined point estimates are shown as black diamonds. The diamonds and squares (together with the 95% CIs) located beyond the vertical line (indicating the unit value) show that a result was statistically significant.
4. Discussion
To combat COVID-19, we urgently need effective and safe medications, and thus researchers are looking into every possibility in a range of assessment frameworks. The pharmaceutical combination lopinavir/ritonavir was among the first to be used to treat SARS-CoV-2 because of its efficacy in treating SARS-CoV [38]. Both medications function by inhibiting the activity of a specific protein in the body; in this case, it is the protease in the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV protease) [39]. Ritonavir is recommended alongside lopinavir in modest doses because it enhances pharmacokinetics [40]. Ritonavir also prevents the CYP450-mediated metabolism of other protease inhibitors, and this improves bioavailability and reduces the dosage and frequency of administration of the second protease inhibitor [41,42].
The clinical efficacy and safety of the lopinavir/ritonavir combination have not been established, despite the fact that they have proved to be effective binders against the viral protease. There is conflicting evidence as to whether or not lopinavir/ritonavir inhibits the major protease activity of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro [43,44]. Lopinavir/ritonavir was effective on SARS-CoV-2 replication in vitro. However, it did not extrapolate to sufficient serum levels to kill the virus in clinical cases [45]. In another in vitro study, lopinavir/ritonavir effectively suppressed SARS-CoV-2 at the usual plasma levels [46]. Our study therefore attempted to determine the efficacy, safety, and justification for using lopinavir/ritonavir as a single therapy or in combination with interferon by pooling data on the following outcomes: mortality rates, length of hospital stay, clinical efficacy, safety, and major adverse events.
Of the nine trials considered here, seven provided death rates. The effect of lopinavir/ritonavir on mortality rates in COVID-19 patients relative to the control group was statistically significant in only one experiment [36]. In this trial, the group that received lopinavir/ritonavir had a higher mortality rate (26.5%) than the control group (5.6%). Six studies found no significant impact of lopinavir/ritonavir as a single therapy or when combined with interferon on mortality rates as compared with the control group. There was no discernible difference in mortality rates between the experimental and control groups in this meta-analysis (OR 1.29; 95% CI 0.95 to 1.76). This study’s results were in line with those of a previous meta-analysis and systematic review by Bhattacharyya et al., who also concluded that lopinavir/ritonavir monotherapy did not significantly reduce mortality rates when compared with placebo or treatment with other drugs [41].
Regarding clinical remission, treatment with lopinavir/ritonavir resulted in greater clinical improvement in COVID-19 patients than in control individuals in three studies. However, one trial found that lopinavir/ritonavir with interferon was likely to enhance clinical outcomes in a limited proportion of patients as compared with the control individuals. The results from all four trials that reported data on clinical improvement showed that the difference between the two treatment arms was statistically insignificant. Similarly, patients with COVID-19 who received lopinavir/ritonavir as monotherapy or in combination with interferon fared no better than those who received placebo or alternative COVID-19 therapeutic options (p = 0.36), according to pooled data from the studies included in this meta-analysis. The heterogeneity test returned a low I2 result of 22%.
The current meta-analysis found that lopinavir/ritonavir with or without interferon did not reduce the length of the hospital stay, although these findings were not statistically significant when compared with the control individuals (SMD 0.07; 95% CI 0.44 to 0.57). The length of hospital stay in the lopinavir/ritonavir arm was significantly shorter than in the control arm in one of the included studies [31]. The overall heterogeneity of the included studies was substantial. A sensitivity analysis revealed that excluding a single research study [31] significantly impacted the mean time of hospitalization. Amani et al. conducted a meta-analysis of three studies and found no statistically significant difference in hospitalization duration between the group who received lopinavir/ritonavir alone and the group that received the combination treatment [47]. Another prior study discovered that lopinavir/ritonavir as a single medication was associated with significantly shorter hospital stays than the comparison group [41].
In terms of safety, this study investigated the association between lopinavir/ritonavir as a single therapy or with interferon and adverse events or serious adverse events in COVID-19 patients compared with the control individuals. Lopinavir/ritonavir with or without interferon was associated with a significantly higher number of adverse events in COVID-19 patients, such as moderate to severe kidney injury, compared with the control individuals (p = 0.02). Common adverse events of lopinavir/ritonavir in patients with COVID-19 are gastrointestinal disturbances, in particular diarrhea, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, hepatic disorders, and pancreatitis [47]. This investigation discovered no significant difference between the two groups in terms of major adverse events. The occurrence of adverse events was more likely with lopinavir/ritonavir alone in COVID-19 patients (OR = 1.74, 95% CI 1.08 to 2.80) compared with lopinavir/ritonavir with interferon (OR = 1.20, 95% CI 0.75 to 1.91), although this was not statistically significant (p = 0.27). The findings were similar for serious adverse events.
The fact that this study only included randomized clinical trials and recent studies was its main strength. It is also worth noting that out of the nine RCTs included in this study, only two investigated the efficacy and safety of lopinavir/ritonavir with interferon in managing COVID-19. Before drawing conclusions about the efficacy and safety of lopinavir/ritonavir plus interferon, more research is necessary.
5. Conclusions
This study compared lopinavir/ritonavir with or without interferon to placebo and conventional treatment in terms of mortality rates, clinical improvement, length of hospital stay, and the appearance of mild or severe side effects. In the current meta-analysis, patients with COVID-19 receiving lopinavir/ritonavir with or without interferon showed no improvement in mortality rates, clinical status, or length of hospital stay compared with groups receiving a placebo. In terms of safety, this study discovered that groups receiving lopinavir/ritonavir with or without interferon had more adverse events and serious adverse events than groups receiving placebo. Large randomized clinical trials are needed to assess the efficacy and safety of lopinavir/ritonavir with interferon in the treatment of COVID-19. These studies work best when conducted in a double-blind fashion at multiple locations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.K. and M.A.M.; methodology, M.K.; software, M.K.; validation, M.K., H.M.A.E.-L. and M.M.; formal analysis, M.K.; investigation, K.N.V. and I.A.; resources, M.K.; data curation, M.K. and H.S.E.-B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.K.; writing—review and editing, K.M.A.K.; funding acquisition, M.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was funded by the Deputyship for Research and Innovation, Ministry of Education, Saudi Arabia, through project number INST002.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available in the manuscript and supplementary material.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deputyship for Research and Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia, for funding this research work (project number INST002).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rabaan, A.A.; Al-Ahmed, S.H.; Haque, S.; Sah, R.; Tiwari, R.; Malik, Y.S.; Dhama, K.; Yatoo, M.I.; Bonilla-Aldana, D.K.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J. SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-COV: A comparative overview. Infez. Med. 2020, 28, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. COVID-19 Dashboard. 2022. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Adhikari, S.P.; Meng, S.; Wu, Y.-J.; Mao, Y.-P.; Ye, R.-X.; Wang, Q.-Z.; Sun, C.; Sylvia, S.; Rozelle, S.; Raat, H. Epidemiology, causes, clinical manifestation and diagnosis, prevention and control of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) during the early outbreak period: A scoping review. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggioni, C.; Comberiati, P.; Giovannini, M.; Agache, I.; Akdis, M.; Alves-Correia, M.; Antó, J.M.; Arcolaci, A.; Azkur, A.K.; Azkur, D. A compendium answering 150 questions on COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2. Allergy 2020, 75, 2503–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Eijk, L.E.; Binkhorst, M.; Bourgonje, A.R.; Offringa, A.K.; Mulder, D.J.; Bos, E.M.; Kolundzic, N.; Abdulle, A.E.; van der Voort, P.H.; Olde Rikkert, M.G. COVID-19: Immunopathology, pathophysiological mechanisms, and treatment options. J. Pathol. 2021, 254, 307–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frediansyah, A.; Tiwari, R.; Sharun, K.; Dhama, K.; Harapan, H. Antivirals for COVID-19: A critical review. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2021, 9, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsafi, R.; Alghamdi, S.; Asif, M. Antiviral Drugs and Their Roles in the Treatment of Coronavirus Infection. In Antiviral Drugs; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kandeel, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Tani, H.; Kobayashi, A.; Gohda, J.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Park, B.K.; Kwon, H.-J.; Inoue, J.-I.; Alkattan, A. Discovery of new fusion inhibitor peptides against SARS-CoV-2 by targeting the spike S2 subunit. Biomol. Ther. 2021, 29, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Q.; Xia, S.; Lu, L. Coronavirus Entry Inhibitors. In Virus Entry Inhibitors; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 101–121. [Google Scholar]
- Jitta, S.R.; Salwa; Bhaskaran, N.A.; Marques, S.M.; Kumar, L. Recent advances in nanoformulation development of Ritonavir, a key protease inhibitor used in the treatment of HIV-AIDS. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momattin, H.; Mohammed, K.; Zumla, A.; Memish, Z.A.; Al-Tawfiq, J.A. Therapeutic options for Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV)–possible lessons from a systematic review of SARS-CoV therapy. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 17, e792–e798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzunova, K.; Filipova, E.; Pavlova, V.; Vekov, T. Insights into antiviral mechanisms of remdesivir, lopinavir/ritonavir and chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine affecting the new SARS-CoV-2. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhou, Q.; Li, Y.; Garner, L.V.; Watkins, S.P.; Carter, L.J.; Smoot, J.; Gregg, A.C.; Daniels, A.D.; Jervey, S. Research and development on therapeutic agents and vaccines for COVID-19 and related human coronavirus diseases. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kalyoubi, S.A.; Ragab, A.; Abu Ali, O.A.; Ammar, Y.A.; Seadawy, M.G.; Ahmed, A.; Fayed, E.A. One-pot synthesis and molecular modeling studies of new bioactive spiro-oxindoles based on uracil derivatives as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors targeting RNA polymerase and spike glycoprotein. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, H.S.; Hui, K.P.Y.; Lai, H.-M.; He, X.; Khan, K.S.; Kaur, S.; Huang, J.; Li, Z.; Chan, A.K.; Cheung, H.H.-Y. Simeprevir potently suppresses SARS-CoV-2 replication and synergizes with remdesivir. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, Y.-P.; Lee, J.-C.; Chiu, C.-W.; Lee, C.-C.; Tsai, P.-J.; Hsu, I.-L.; Ko, W.-C. Oral Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir Therapy for COVID-19: The Dawn in the Dark? Antibiotics 2022, 11, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parums, D.V. Editorial: Current Status of Oral Antiviral Drug Treatments for SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Non-Hospitalized Patients. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2022, 28, e935952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katze, M.G.; He, Y.; Gale, M. Viruses and interferon: A fight for supremacy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.N.; Gan, Z.; Hou, J.; Yang, Y.C.; Huang, L.; Huang, B.; Wang, S.; Nie, P. Identification and establishment of type IV interferon and the characterization of interferon-υ including its class II cytokine receptors IFN-υR1 and IL-10R2. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokugamage, K.G.; Hage, A.; Schindewolf, C.; Rajsbaum, R.; Menachery, V.D. SARS-CoV-2 is sensitive to type I interferon pretreatment. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokugamage, K.G.; Hage, A.; de Vries, M.; Valero-Jimenez, A.M.; Schindewolf, C.; Dittmann, M.; Rajsbaum, R.; Menachery, V.D. Type I interferon susceptibility distinguishes SARS-CoV-2 from SARS-CoV. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01410–e01420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-C.; Hsu, C.-K.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lai, C.-C.; Hung, S.-H.; Lin, W.-T. Clinical efficacy and safety of interferon-β–containing regimens in the treatment of patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2022, 20, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Saurabh, M.K.; Narasimha, V.L.; Maharshi, V. Efficacy of Interferon-β in Moderate-to-Severe Hospitalised Cases of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Drug Investig. 2021, 41, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumpston, M.S.; McKenzie, J.E.; Welch, V.A.; Brennan, S.E. Strengthening systematic reviews in public health: Guidance in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. J. Public Health 2022, 44, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Tong, T. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials revisited. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2015, 45, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. Bmj 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ader, F.; Peiffer-Smadja, N.; Poissy, J.; Bouscambert-Duchamp, M.; Belhadi, D.; Diallo, A.; Delmas, C.; Saillard, J.; Dechanet, A.; Mercier, N. An open-label randomized controlled trial of the effect of lopinavir/ritonavir, lopinavir/ritonavir plus IFN-β-1a and hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1826–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, Y.M.; Gordon, A.C.; Derde, L.P.; Nichol, A.D.; Murthy, S.; Beidh, F.A.; Annane, D.; Swaidan, L.A.; Beane, A.; Beasley, R. Lopinavir-ritonavir and hydroxychloroquine for critically ill patients with COVID-19: REMAP-CAP randomized controlled trial. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 867–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Wang, Y.; Wen, D.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Fan, G.; Ruan, L.; Song, B.; Cai, Y.; Wei, M. A trial of lopinavir–ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19. New Engl. J. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaniazad, M.; Farshidi, H.; Gharibzadeh, A.; Bazram, A.; Khalili, E.; Noormandi, A.; Fathalipour, M. Efficacy and safety of favipiravir plus interferon-beta versus lopinavir/ritonavir plus interferon-beta in moderately ill patients with COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 3184–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horby, P.W.; Mafham, M.; Bell, J.L.; Linsell, L.; Staplin, N.; Emberson, J.; Palfreeman, A.; Raw, J.; Elmahi, E.; Prudon, B. Lopinavir–ritonavir in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): A randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karolyi, M.; Pawelka, E.; Omid, S.; Koenig, F.; Kauer, V.; Rumpf, B.; Hoepler, W.; Kuran, A.; Laferl, H.; Seitz, T. Camostat Mesylate Versus Lopinavir/Ritonavir in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19—Results from a Randomized, Controlled, Open Label, Platform Trial (ACOVACT). Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 870493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, G.; Silva, E.A.d.S.M.; Silva, D.C.M.; Thabane, L.; Singh, G.; Park, J.J.; Forrest, J.I.; Harari, O.; Dos Santos, C.V.Q.; De Almeida, A.P.F.G. Effect of early treatment with hydroxychloroquine or lopinavir and ritonavir on risk of hospitalization among patients with COVID-19: The TOGETHER randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e216468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siami, Z.; Dehghan, D.; Khavandegar, A.; Lak, M.; Bakhtiyari, M. Efficacy and Safety of Atazanavir/Ritonavir versus Lopinavir/Ritonavir in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Iran. Red Crescent Med. J. 2022, 24, 1576. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Xie, Z.; Lin, W.; Cai, W.; Wen, C.; Guan, Y.; Mo, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Peng, P. Efficacy and safety of lopinavir/ritonavir or arbidol in adult patients with mild/moderate COVID-19: An exploratory randomized controlled trial. Medicine 2020, 1, 105–113.e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.; Cheng, V.; Hung, I.; Wong, M.; Chan, K.; Chan, K.; Kao, R.; Poon, L.; Wong, C.; Guan, Y. Role of lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of SARS: Initial virological and clinical findings. Thorax 2004, 59, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandwani, A.; Shuter, J. Lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of HIV-1 infection: A review. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2008, 4, 1023. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cvetkovic, R.S.; Goa, K.L. Lopinavir/ritonavir. Drugs 2003, 63, 769–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Kumar, S.; Sarma, P.; Kaur, H.; Prajapat, M.; Shekhar, N.; Bansal, S.; Avti, P.; Hazarika, M.; Sharma, S. Safety and efficacy of lopinavir/ritonavir combination in COVID-19: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression analysis. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2020, 52, 313. [Google Scholar]
- Boffito, M.; Maitland, D.; Samarasinghe, Y.; Pozniak, A. The pharmacokinetics of HIV protease inhibitor combinations. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 18, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.; Park, Y.-I.; Park, R.; Cha, Y.-E.; Namkoong, S.; Lee, J.I.; Park, J. Lopinavir-ritonavir is not an effective inhibitor of the main protease activity of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, M.; Mótyán, J.A.; Szojka, Z.I.; Golda, M.; Miczi, M.; Tőzsér, J. Analysis of the efficacy of HIV protease inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2′ s main protease. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Cao, R.; Xu, M.; Wu, Y.; Shang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Sun, Y. Comparative antiviral efficacy of viral protease inhibitors against the novel SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Virol. Sin. 2020, 35, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.K.; Seong, M.W.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, T.S.; Choe, P.G.; Song, S.H.; Kim, N.J.; Park, W.B.; Oh, M.D. In vitro activity of lopinavir/ritonavir and hydroxychloroquine against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 at concentrations achievable by usual doses. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amani, B.; Khanijahani, A.; Amani, B.; Hashemi, P. Lopinavir/ritonavir for COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 24, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).