Abstract
SiO2 and MnO are the essential components dictating flux O potential subject to submerged arc welding. Due to the lack of thermodynamic data on the flux properties in early trials, the roles of SiO2 and FeO in the determination of the flux O potential remain nebulous, and conclusions are often conflicting with each other. Within this framework, through the analysis of the fluxes of 23 formulas at the full coverage of acid and basic fluxes with a basicity index spanning from 0.5 to 5.6, attempts are made to obtain a better understanding of the thermodynamic interconnection between oxides (SiO2 and FeO) and the flux O potential, and to clarify the controversial conclusions raised by different investigators. In particular, a thermodynamic approach has been proposed to simulate the equilibrium FeO activity, during which no measurement of the slag composition is needed. It is revealed that the simulated equilibrium FeO activity is feasible to evaluate the flux potential for both acid and basic fluxes, which may pave a vital way to save the experimental resources on the flux design and analysis.
1. Introduction
Submerged arc welding (SAW) has become the backbone of metal joining in heavy manufacturing industries owing to its high deposition rate [1]. During the SAW process, the arc plasma and weld pool are shielded beneath the flux and molten slag (the flux indicates the granules before welding, while the slag indicates the molten or solidified flux) [2]. Flux serves vital functions in SAW process, such as atmospheric protection, arc stabilization, weld metal (WM) composition control, etc. [3] Due to complex chemical interactions between the arc plasma, flux (slag), and weld pool, the flux essentially affects the WMs composition, which further dictates the final mechanical properties [2,4].
O is an important element pertinent to the qualities of the weldment [5,6]. Excessive O may incur unexpected issues, including an enhanced porosity, reduced toughness, and depreciated hardenability [7,8]. When the O content in WM is too low, a poor impact toughness is expected since there are insufficient inclusions to promote the formation of the acicular ferrite (an interlocking microstructure nucleating on nonmetallic that can effectively inhibit the propagation of the cracks in metal) [5,9,10].
It has been well known that oxides tend to decompose, release O2, and improve the O level in the weld pool under the presence of the arc plasma [7,8,11]. Generally, flux serves as the main source of the O uptake for the submerged arc-welded metal [12]. In SAW metallurgy, a concept of the flux O potential has been employed to describe the driving force for the O transfer from the flux to the WM [6,13]. Due to incomplete understandings of the flux’s thermodynamic properties in early trials, the predicting for the flux O potential relies on the empirical ideas drawn from steelmaking, viz. the basicity [14,15]. The most widely applied basicity index (BI) equation has been proposed by Tuliani et al. [16], as illustrated by Equation (1) (wt pct), to estimate the flux O potential. BI is an empirical value to estimate the flux O potential. In general, the higher the BI, the fewer the nonmetallic inclusions in the WM [4].
The oxygen-free compound most frequently contained in the flux is CaF2. The basic oxides include CaO, CaF2, MgO, Na2O, K2O, MnO, and FeO, while the acid oxides include SiO2, Al2O3, Cr2O3, TiO2, and ZrO2. However, investigators have pointed out that there is no thermodynamic fundamental basis for the correlation between the BI and flux O potential, and redundant emphasis has been placed on the relationship between them [2,4].
Similar to the circumstances in steelmaking, SiO2 and FeO play vital roles in the tuning of the flux O potential [8,17,18]. SiO2, acting as a network-builder, is an indispensable component for the flux since it dominates the viscosity of the molten slag [5]. Viscosity is an important consideration for the flux’s design, the level of which must be low enough to cover the entire metal and allow gases to escape [19]. Belton et al. [20] determined the equilibrium constants of Reaction (1) (K1) up to 2000 °C (the value of an effective equilibrium temperature subject to SAW). Then, Eager [8] assumed that Reaction (2) may be considered to approach equilibrium when SiO2-enriched acid fluxes are applied, which may explain the high level of the dissolved O concentration in the WM under such welding circumstances [8,21].
Additionally, FeO is formed at the slag–metal interface inevitably during the SAW process, which further transfers to the bulk slag, even when no FeO is contained in the initial flux due to a significant O uptake from the flux [22,23,24,25]. Fe in the weld pool is oxidized via a complicated chemical interaction, especially in terms of the Reaction (4) [23,24,25]. Eagar [8] suggested that the equilibrium of the FeO reaction is not attained, and the flux O potential is controlled by the FeO activity in more basic fluxes. Then, Mitra et al. [24] revised Eagar’s assumption and postulated that Reaction (4) generally proceeds forward.
In a word, Eagar [8] speculated that the flux O potential is controlled by the SiO2 activity in acid fluxes; for more basic fluxes, the flux O potential is controlled by the FeO activity. It is noted that Eagar [8] only considered the activities of SiO2 and FeO in the bulk flux (slag). Indacochea et al. [17], on the other hand, assumed that the activity of FeO at the interface, instead of the FeO activity in the bulk slag, is more feasible to identify the flux O potential, although its value is immeasurable from technical perspectives [2].
The studies reviewed above demonstrate that the roles of SiO2 and FeO in the determination of the flux O potential remain nebulous, and conclusions are often conflicting with each other. In recent decades, thermodynamic databases for multicomponent oxide have been developed by what has come to be known as the Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry (Calphad) technique [26]. Although the temperature of the SAW is as high as 2000 °C, the applicable thermodynamic models have paved a reliable way to obtain the thermodynamic data under high temperatures [27].
The present study has been undertaken to generate a better understanding of the thermodynamic relationship between oxides (SiO2 and FeO) and the flux O potential, and try to charity the controversial conclusions raised by different investigators from the perspective of thermodynamics. To guarantee the integrality of this study, the fluxes of 23 formulas are selected at the full coverage of the acid and basic fluxes with a wide BI range from 0.5 to 5.6. The pertinent thermodynamic data regarding SiO2 and FeO are obtained from measured flux/slag compositions and reliable thermodynamic databases/models [17,28,29]. Then, the relationship between the flux O potential and the thermodynamic data on SiO2 and MnO is evaluated, which may provide insights into the control mechanism of the flux formula on the O potential subject to the SAW process.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Flux Preparation
The details of the flux preparation, welding procedure, compositions of the flux, slag, and metals (data sources) have been given elsewhere [17,28,29]. SiO2-MnO-FeO fluxes are typical acid fluxes with a low BI. Indacochea et al. [17] designed SiO2-MnO-FeO fluxes with SiO2 content holding constant at 40 wt pct; as such, the BI is restricted at a low level of 0.75. CaF2-SiO2-Na2O-Cr2O3 fluxes are typical basic fluxes with a high BI [28]. F-3-1 to F-3-5 are typical commercial fluxes with various BIs at the coverage of both acid and basic fluxes [29]. The flux formulas are summarized in Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3.

Table 1.
Flux formulas subject to SiO2-MnO-FeO fluxes [17].

Table 2.
Flux formulas subject to CaF2-SiO2-Na2O-Cr2O3 fluxes [28].

Table 3.
Flux formulas subject to typical commercial fluxes [29].
2.2. Thermodynamic Calculation
The Equilib module of FactSage was applied to calculate the activities of SiO2 and FeO in the bulk slag [18]:
- The FToxid database was selected to model the slag.
- The equilibrium temperature of 2000 °C was set.
- The measured slag compositions were set as the input compositions.
The gas–slag–metal equilibrium model is employed to obtain the equilibrium FeO activity at the interface [15].
- FToxid, Fstel, and FactPS databases are selected. The solution phases of ASlag-liq all oxides, S (FToxid-SLAGA), and LIQUID (FStel-Liqu) were selected to model the molten slag and metal phases.
- The equilibrium temperature of 2000 °C was set.
- The flux formulas and nominal compositions (if the dilution value is not given, it may be assumed to be 0.5) were set as the input chemistries [30].
The thermodynamic data are given in Table 4 and Table 5. The symbols used in the study are summarized in Table 6.

Table 4.
SiO2 and FeO activities in bulk slag.

Table 5.
FeO activity at interface.

Table 6.
List of symbols.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Flux O Potential vs. SiO2 and FeO Activities in Bulk Slag
It has been well established that the O potential of SiO2-enriched fluxes is in proportion to the SiO2 activity in the bulk slag due to SiO2 being a major source of the component in the flux [20,31]. Eager [8] assumed that Reaction (2) may be considered to approach equilibrium for the SiO2-enriched acid flux, and the SiO2 could be employed to quantify the flux O potential.
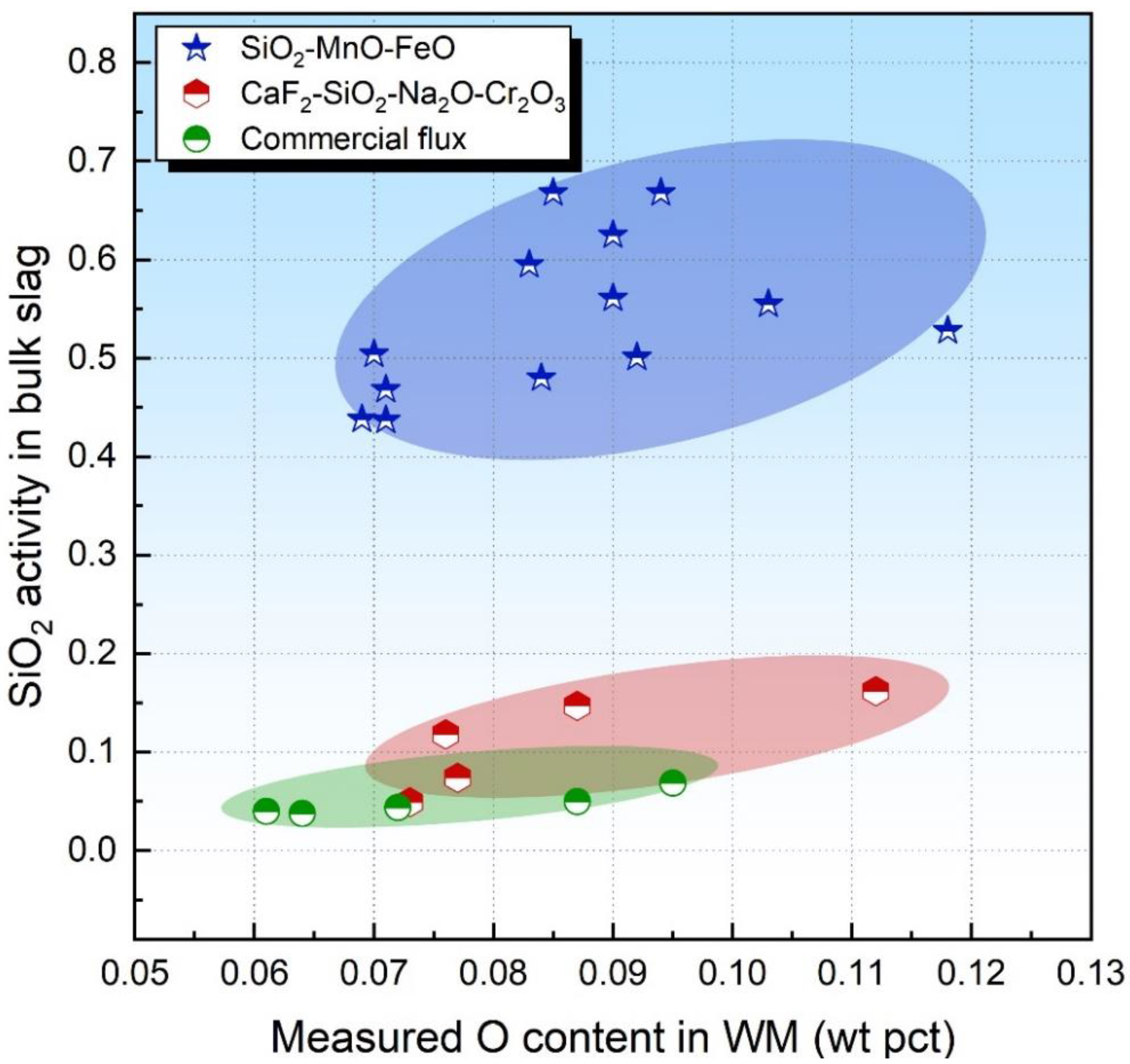
Figure 1 plots the level of the O content in the WM against the SiO2 activity in the bulk slag. It seems that no relationship between the O content and SiO2 activity is observed for both acid and basicity fluxes. Such information is expected since the thermodynamic equilibrium of Reaction (2) may not be attained, as was concluded in previous studies [17,21]. Additionally, some unstable oxides are also major sources of O for the submerged arc-welded metal due to their decomposition behaviors under the arc plasma [11]. Therefore, the sole consideration of the SiO2 activity may be insufficient to evaluate the O potential of the flux.
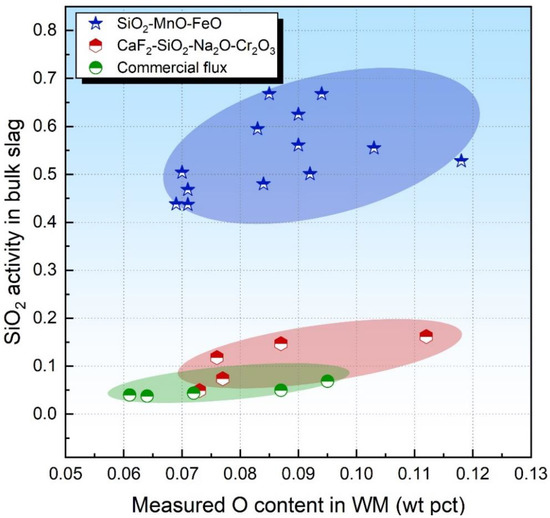
Figure 1.
SiO2 activity in bulk slag as a function of measured O content in WM.
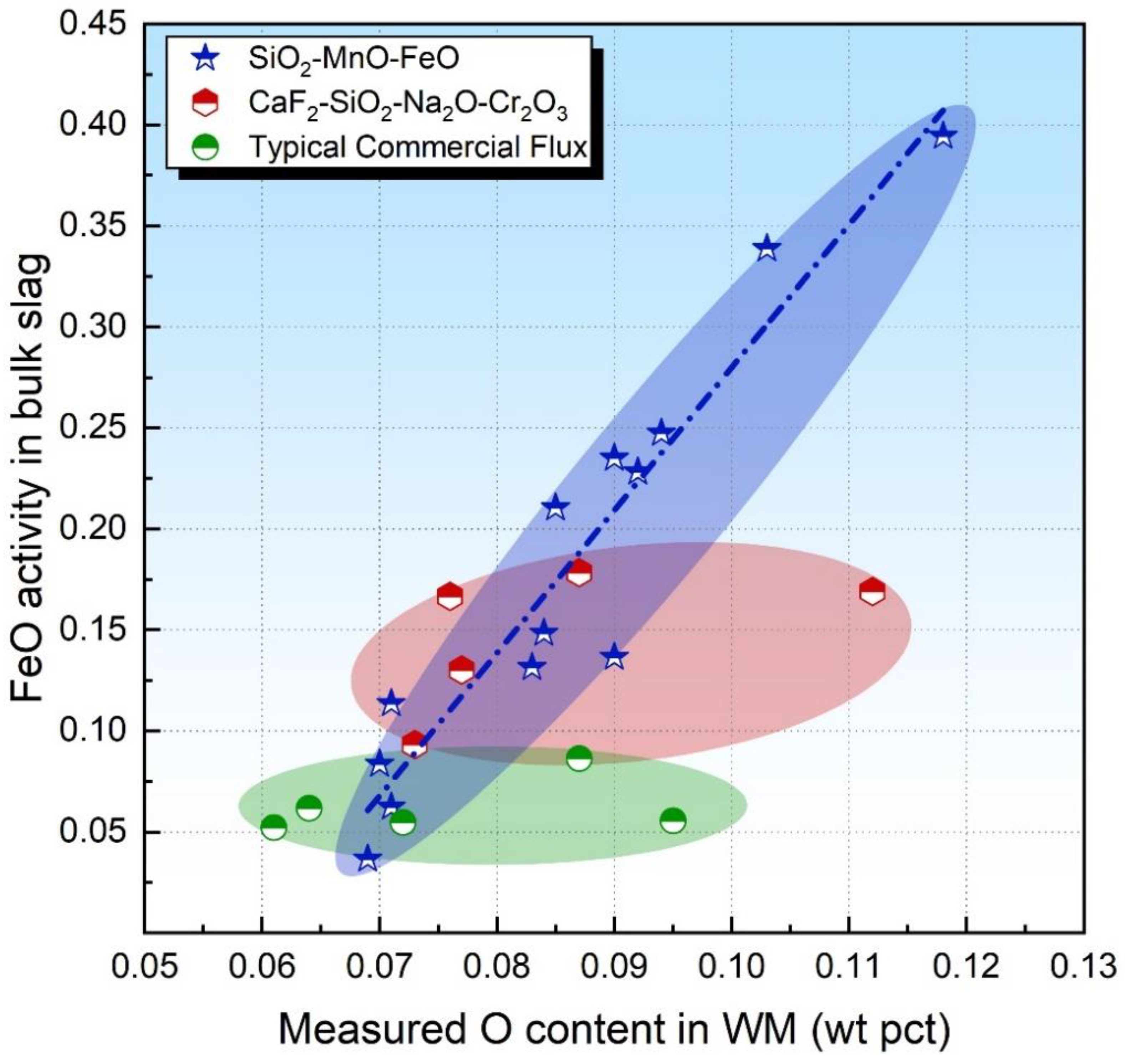
Indacochea et al. [17] postulated that FeO should diffuse faster than SiO2 so that Reaction (4) would be less kinetically constrained than those involving SiO2, viz. Reaction (2). Therefore, the activity of FeO in the bulk slag may be more feasible to evaluate the flux O potential. With this in mind, the FeO activity in the bulk slag is plotted in Figure 2 as a function of the O content in WM.
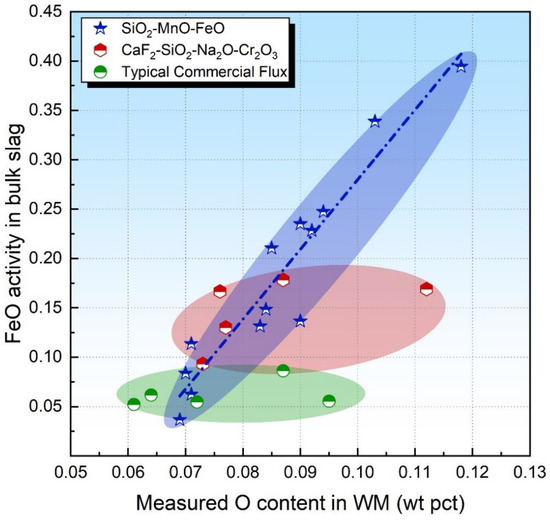
Figure 2.
FeO activity in bulk slag as a function of measured O content in WM.
As is illustrated in Figure 2, the FeO activity in the bulk slag is proportional to the O content in WM for acid fluxes (see the blue dot dash line), which is consistent with the assumption raised by Indacochea et al. [17] Therefore, the FeO activity in the bulk slag can be applied to evaluate the flux O potential for FeO and SiO2-ernriched acid fluxes in addition to the SiO2 activity. For basic fluxes, the FeO activity in the bulk slag fails to identify the flux O potential (see the red and green shaded area in Figure 2) since Reaction (4) generally proceeds forward, as was assumed by Mitra et al. [24]
3.2. Flux O Potential vs. FeO Uptake in Bulk Slag
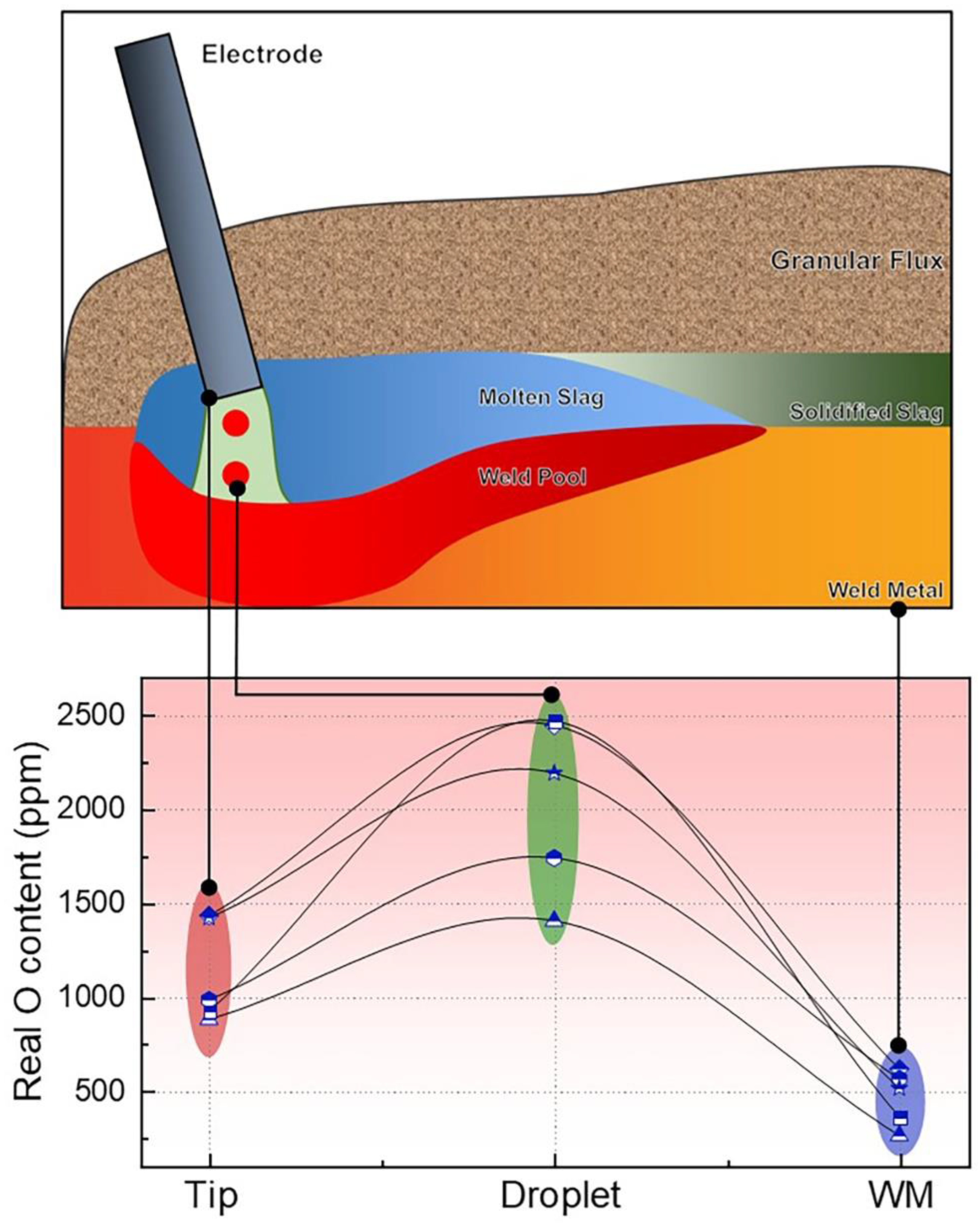
Since the arc plasma, molten slag, and weld pool are shielded under the flux, it is impossible to capture the gases and molten slag for analytical purposes [13,14]. Hence, in-depth investigations regarding Reaction (4) remain nebulous. Lau et al. [7,32] have confirmed that significant levels of O were analyzed within the overall SAW process (from the electrode tip and droplet to the weld pool); they also revealed that the O content in the droplet is about one order of magnitude higher than that in the WM, as shown in Figure 3.
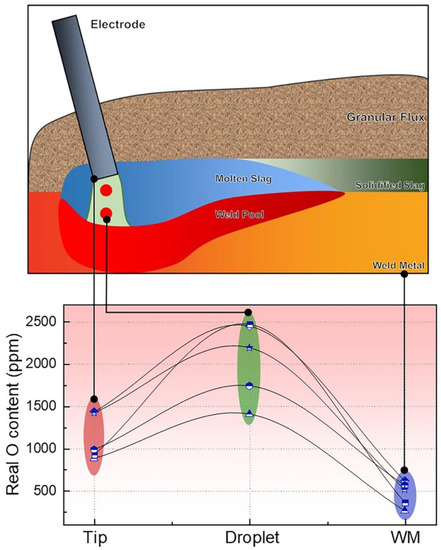
Figure 3.
O levels at various stages subject to SAW process (ppm) [7,32].
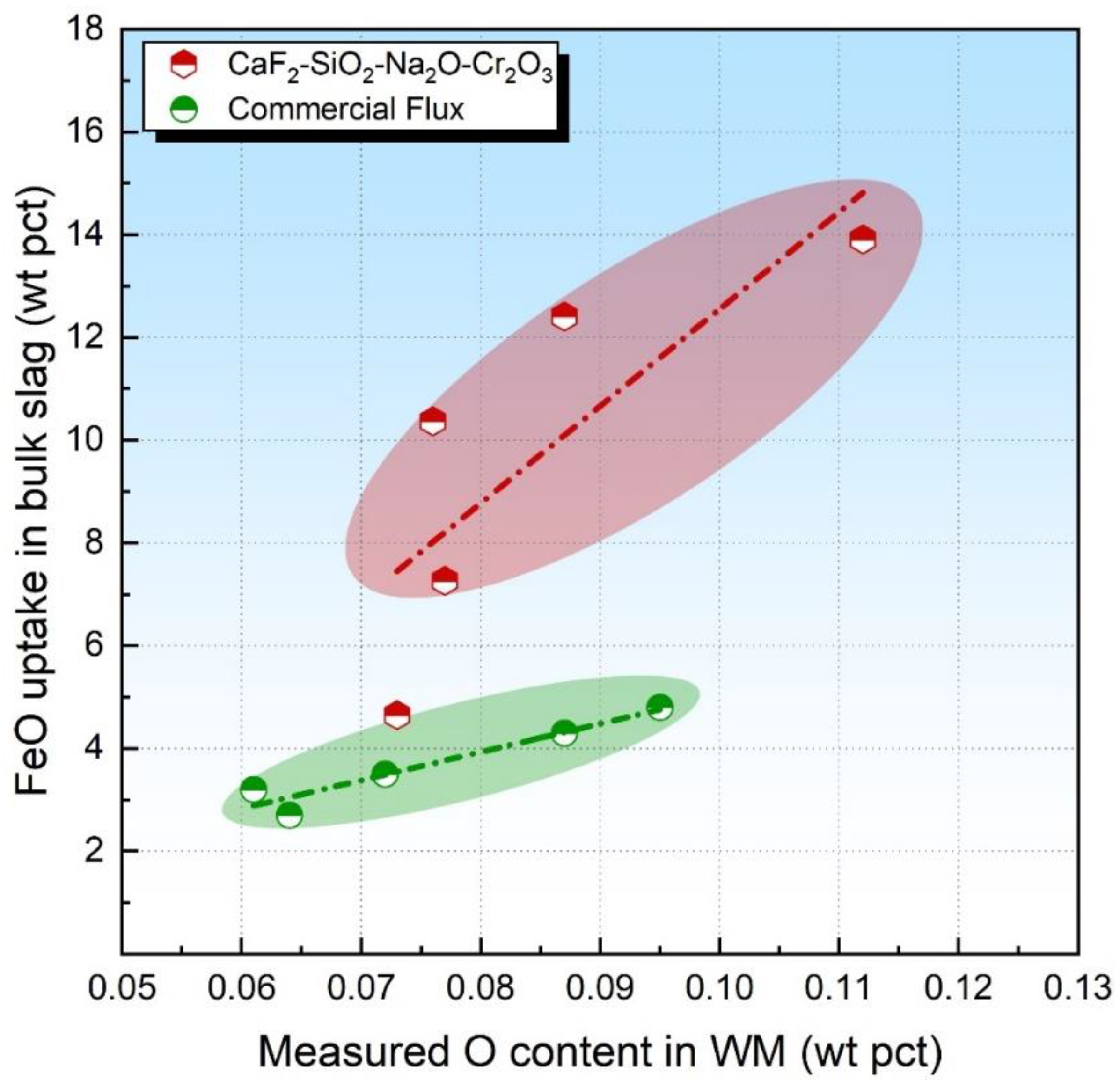
Due to the large quantities of O initially dissolved in the molten metal at high temperatures under the arc cavity, Reaction (4) would be driven to the right side; that is, the higher the flux O potential, the higher the FeO uptake in the slag is expected to be [29,33]. The fact that Reaction (4) only proceeds forward was also confirmed in our previous study [28]. The level of FeO uptake in the bulk slag has been plotted in Figure 4. It is seen that, for the FeO-free flux, the O content in WM is proportional to the FeO analyzed in the slag, as shown by the red and green dashed dotted lines.
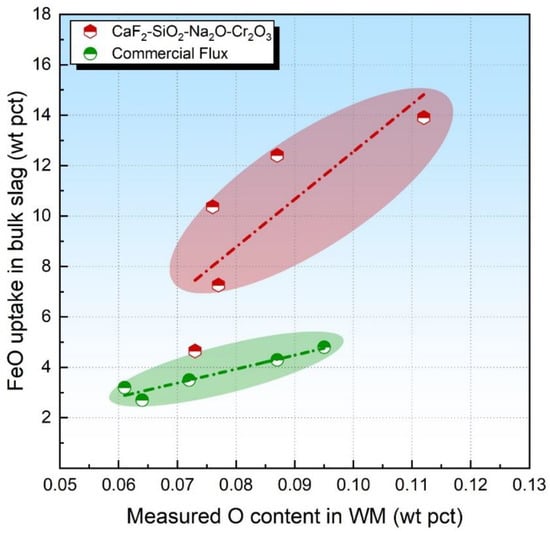
Figure 4.
FeO content in bulk slag as a function of measured O content in WM.
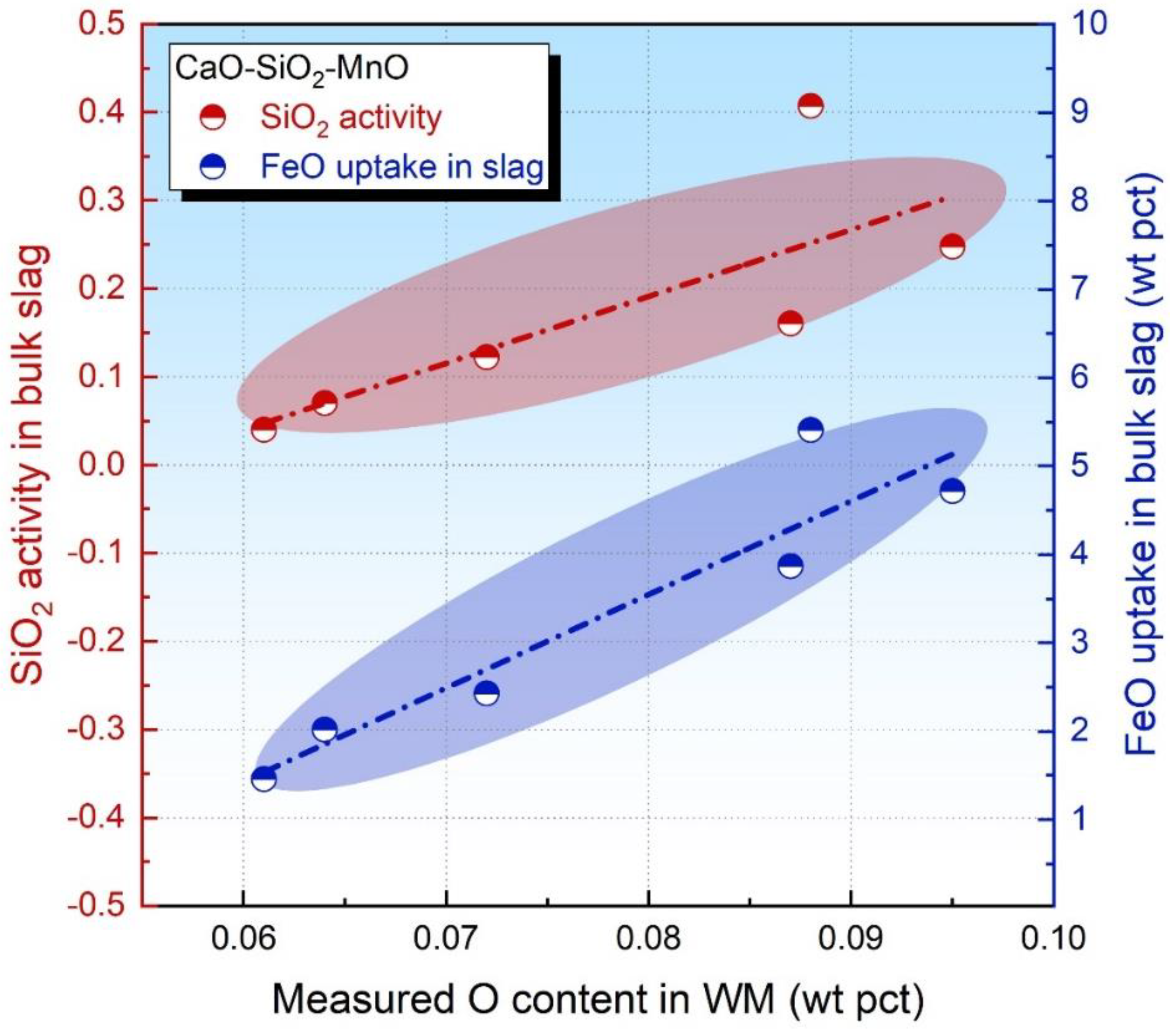
To further verify the assumptions in parts 3.1 and 3.2, the CaO-SiO2-MnO fluxes designed in our previous study are referenced since this flux series is rendered to be FeO-free acid in nature yet with a high level of SiO2 [18]. The SiO2 activity in the bulk slag and FeO uptake level in the slag has been given elsewhere [18]. Then, these data are plotted in Figure 5 as a function of the measured O content.
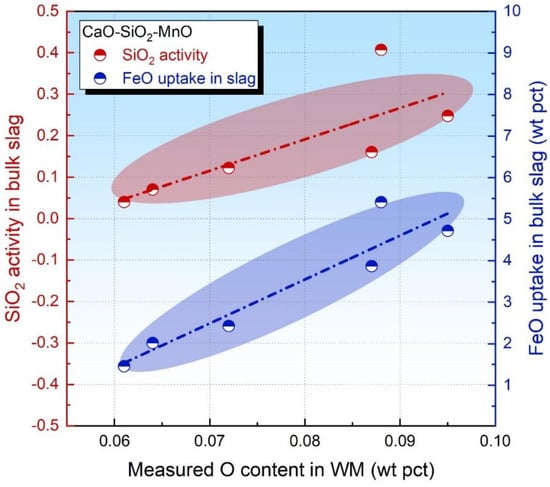
Figure 5.
Oxide activity in bulk slag as a function of measured O content in WM [18].
From an observation of Figure 5, both the SiO2 activity and FeO uptake level in the slag are proportional to the measured O content in WM. Therefore, both these values are capable of evaluating the level of the flux O potential. Nonetheless, it should be pointed out that the FeO activity in the bulk slag is more feasible for such an estimation in comparison to the SiO2 activity since Reaction (4) is less kinetically restricted than Reaction (2) due to SiO2 being the primary network builder for the molten slag [34,35]
3.3. Flux O Potential FeO Activity at Slag–Metal Interface
Although the mechanisms of the Fe transfer in the SAW process remain ambiguous, the present study, coupled with the results in previous findings, demonstrated that the level of FeO uptake in the slag is generally potential to the level of flux O [36,37,38]. The investigation over the relationship between the FeO activity and flux O potential is technically restricted since:
- The molten slag and weld pool are shielded under the flux, making the FeO activity unmeasurable.
- Although Chai et al. [30,39] developed the slag–metal equilibrium model to quantify the relationship between the flux O potential and oxide activity, the interaction items subject to various chemical interactions are neglected.
- The impact of gas formation on the transfer behaviors in SAW was not considered.
- The measurement in terms of the slag is needed to obtain the FeO uptake level.
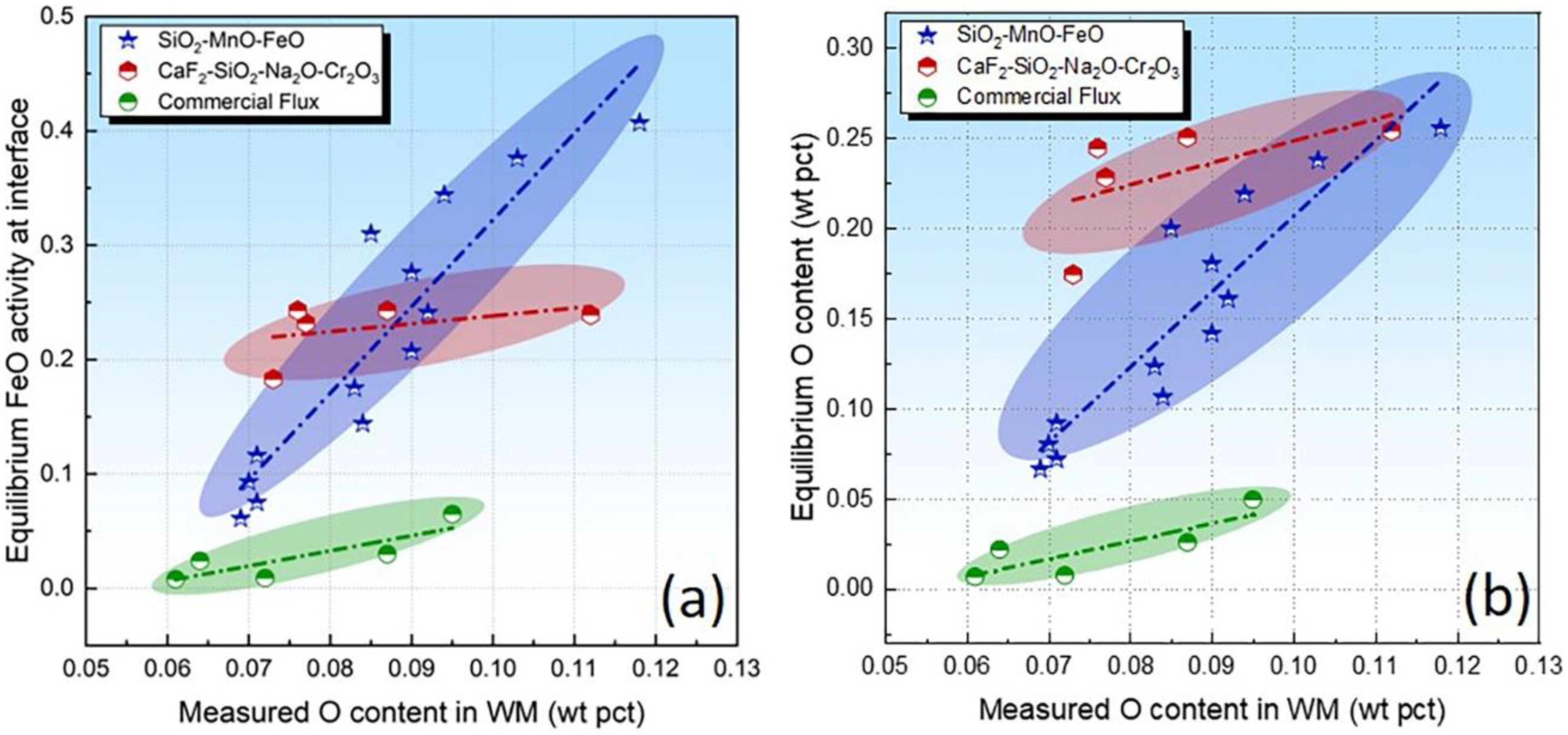
Overall equilibrium is not attained due to the high-temperature gradients in the SAW. Nonetheless, one could assume that the thermodynamic equilibrium is attained locally because the high temperatures and high surface/volume ratio counteract the short time available for the completion of chemical reactions [3,4,17]. Recently, the so-called gas–slag–metal equilibrium has been developed to analyze the scientific issues of thermodynamics in SAW [15,40]. Despite the high temperature of the SAW process, the Calphad technique is capable of extending the thermodynamic data to higher temperatures via applicable thermodynamic models [27]. The FeO activity at the interface has been plotted in Figure 6a. It is seen that, for each flux series, the level of equilibrium FeO is generally proportional to the O content in the WM (flux O potential).
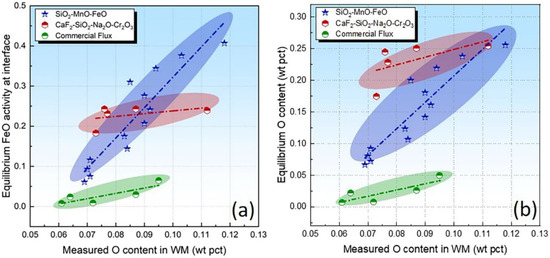
Figure 6.
Equilibrium FeO activity (a) and O content (b) as a function of measured O content in WM.
With hypothetical pure liquid FeO as the standard state, the activity of FeO is derived from the concentration of dissolved O in the weld pool considering the locally attained equilibrium in the SAW process, as was stated previously in this study [8,41]. The equilibrium constant in Reaction (4) is referenced from the work of Eagar [8] as Equations (5) and (6), where aO = [%O] × fO.
Considering that dilute solutions of O in melted iron behave ideally according to Henry’s law, the level of fO equals unity [41]. T is equal to 2000 °C (the most widely accepted effective equilibrium temperature for SAW) [13,15,21]. Therefore, due to the fact that the flux constitutes the major source of O for the WM, one may speculate that equilibrium FeO at the interface is proportional to the flux O potential. To charity such an assumption, we plotted the equilibrium O content as a function of the measured O content in Figure 6b. As shown in Figure 6b, the equilibrium O content is generally proportional to the measured content, which is in agreement with our previous findings [14,28,29,42,43].
It should be noted that although the level of FeO uptake in the slag is capable of evaluating the flux O potential, one needs the measurement of the slag compositions to obtain the FeO content [17]. However, owing to the Calphad technology, equilibrium FeO activity can be simulated with the elimination of the measurement for slag compositions [13] due to the initial flux formula being the input stream for the thermodynamic model.
From the perspective of the flux design, it is well known that the flux O potential should be controlled to a proper level. The results demonstrated in this study reveal that SiO2 and FeO are the essential components in the determination of the overall flux O potential. Furthermore, the evaluation of the flux O potential could be facilitated by the simulation of equilibrium FeO activity via the Calphad approach in lieu of the performance of experience, which may pave a vital way in saving resources on the flux’s design.
4. Conclusions
From thermodynamic perspectives, this study evaluates the roles of SiO2 and FeO in the flux O potential control subject to SAW at a full coverage of acid and basic fluxes with BI spanning from 0.5 to 5.6. The main conclusions are as follows:
- For SiO2-enriched acid fluxes, both activities of SiO2 and FeO in the bulk slag may be able to evaluate the flux O potential. For SiO2-enriched acid fluxes with FeO incorporated, the FeO activity in the bulk slag is more feasible than the SiO2 activity to evaluate the flux O potential since the transfer of FeO is less kinetically constrained than that of SiO2.
- For basic fluxes, the level of the FeO uptake in the slag is more suitable for the identification of the O potential in comparison to the FeO activity in the bulk slag since Reaction (4) generally proceeds forward under such circumstances.
- Although the equilibrium FeO activity is unmeasurable, the value can be simulated by the gas–slag–metal equilibrium model. Thermodynamic analysis shows that the simulated equilibrium FeO activity possesses a good generality in the evaluation of the flux potential for both acid and basic fluxes.
- In comparison to the oxide activity (or content) in the slag, no measurement of the slag composition is needed for the calculation of the equilibrium FeO activity, which may pave a vital way to save the experimental resources on the flux’s design and analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Z. and D.Z.; methodology and software, J.Z. and D.Z.; funding acquisition, P.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 50474085), the Initial Fund of Suqian University (No. 2022XRC040), Scientific Research and Innovation Team of Suqian University (No. 2021td07), and Suqian Science & Technology Project (Nos. K202239, K202122).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sengupta, V.; Havrylov, D.; Mendez, P. Physical Phenomena in the Weld Zone of Submerged Arc Welding—A Review. Weld. J. 2019, 98, 283–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, W.; Zhang, J. Fine-tuning Weld Metal Compositions via Flux Optimization in Submerged Arc Welding: An Overview. Acta Metall. Sin. 2022, 57, 1126–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D.; Liu, S.; Frost, R.; Edwards, G.; Fleming, D. Nature and Behavior of Fluxes Used for Welding. ASM International, ASM Handbook. 1993, 6, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natalie, C.A.; Olson, D.L.; Blander, M. Physical and Chemical Behavior of Welding Fluxes. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1986, 16, 389–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallam, C.; Liu, S.; Olson, D. Flux Composition Dependence of Microstructure and Toughness of Submerged Arc HSLA Weldments. Weld. J. 1985, 64, 140–151. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Leng, J.; Wang, C. Tuning Weld Metal Mechanical Responses via Welding Flux Optimization of TiO2 Content: Application into EH36 Shipbuilding Steel. Mater. Trans. B 2019, 50, 2083–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, T.; Weatherly, G.; McLean, A. The Sources of Oxygen and Nitrogen Contamination in Submerged Arc Welding using CaO-Al2O3 Based Fluxes. Weld. J. 1985, 64, 343–347. [Google Scholar]
- Eagar, T. Sources of Weld Metal Oxygen Contamination during Submerged Arc Welding. Weld. J. 1978, 57, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Ricks, R.; Howell, P.; Barritte, G. The Nature of Acicular Ferrite in HSLA Steel Weld Metals. J. Mater. Sci. 1982, 17, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, A.; Thewlis, G.; Whiteman, J. Nature of Inclusions in Steel Weld Metals and Their Influence on Formation of Acicular Ferrite. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1987, 3, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.; Eagar, T. Slag Metal Reactions in Binary CaF2-Metal Oxide Welding Fluxes. Weld. J. 1982, 61, 229–232. [Google Scholar]
- Kou, S. Welding Metallurgy, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 22–122. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Shao, G.; Guo, Y.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Z. Facilitating Flux Design Process Geared Towards Submerged Arc Welding via Thermodynamic Approach: Case Study into CaF2–SiO2–Na2O–Al2O3–TiO2 Agglomerated Flux. Calphad 2022, 79, 102483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Coetsee, T. Assessment of Weld Metal Compositional Prediction Models Geared Towards Submerged Arc Welding: Case Studies Involving CaF2-SiO2-MnO and CaO-SiO2-MnO Fluxes. Mater. Trans. B 2021, 52, 2404–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Coetsee, T.; Basu, S.; Wang, C. Impact of Gas Formation on the Transfer of Ti and O From TiO2-bearing Basic-fluoride Fluxes to Submerged Arc Welded Metals: A Thermodynamic Approach. Calphad 2020, 71, 102195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuliani, S.; Boniszewski, T.; Eaton, N. Notch Toughness of Commercial Submerged Arc Weld Metal. Weld. Met. Fabr. 1969, 37, 327–339. [Google Scholar]
- Indacochea, J.E.; Blander, M.; Christensen, N.; Olson, D.L. Chemical Reactions During Submerged Arc Welding with FeO-MnO-SiO2 Fluxes. Metall. Trans. B 1985, 16, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Coetsee, T. Thermodynamic Evaluation of Element Transfer Behaviors for Fused CaO-SiO2-MnO Fluxes Subjected to High Heat Input Submerged Arc Welding. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2021, 52, 1937–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liby, A.; Dixon, R.; Olson, D. Welding: Theory and Practice; Elsevier Science Publishers B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; Volume 389. [Google Scholar]
- Belton, G.; Moore, T.; Tankins, E. Slag-metal Reactions in Submerged Arc Welding. Weld. J. 1963, 42, 289s–297s. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Peng, L.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Y. On the Si Content Prediction for Submerged Arc Welded Metal via Calphad Technique: A Brief Discussion. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 1856–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, U.; Eagar, T. Slag Metal Reactions during Submerged Arc Welding of Alloy Steels. Metall. Trans. A 1984, 15, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, U.; Eagar, T. Slag-metal Reactions during Welding: Part I. Evaluation and Reassessment of Existing Theories. Metall. Trans. B 1991, 22, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, U.; Eagar, T. Slag-metal Reactions During Welding: Part II. Theory. Metall. Trans. B 1991, 22, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, U.; Eagar, T. Slag-metal Reactions during Welding: Part III. Verification of the Theory. Metall. Trans. B 1991, 22, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bale, C.W.; Bélisle, E.; Chartrand, P.; Decterov, S.; Eriksson, G.; Gheribi, A.; Hack, K.; Jung, I.-H.; Kang, Y.-B.; Melançon, J. Reprint of: FactSage Thermochemical Software and Databases, 2010–2016. Calphad 2016, 55, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, I.-H. Overview of the Applications of Thermodynamic Databases to Steelmaking Processes. Calphad 2010, 34, 332–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, Q. Probing Element Transfer Behavior during the Submerged Arc Welding Process for CaF2-SiO2-Na2O-Cr2O3 Agglomerated Fluxes: A Thermodynamic Approach. Processes 2022, 10, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetsee, T.; Mostert, R.J.; Pistorius, P.G.H.; Pistorius, P.C. The Effect of Flux Chemistry on Element Transfer in Submerged Arc Welding: Application of Thermochemical Modelling. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 11, 2021–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.; Eagar, T. Slag-metal Equilibrium during Submerged Arc Welding. Metall. Trans. B 1981, 12, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indacochea, J.; Olson, D. Relationship of Weld-metal Microstructure and Penetration to Weld-metal Oxygen Content. J. Mater. Energy Syst. 1983, 5, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, T.; Weatherly, G.; McLean, A. Gas/metal/slag Reactions in Submerged Arc Welding Using CaO-Al2O3 Based Fluxes. Weld. J. 1986, 65, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Coetsee, T. Phase Chemistry of Submerged Arc Welding (SAW) Fluoride Based Slags. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 9766–9776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.; Keene, B. Physicochemical properties of molten CaF2-based slags. Int. Met. Rev. 1981, 26, 21–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K. Slag atlas. VDEh, 2nd ed.; Verlag Stahleisen GmbH: Düsseldorf, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Coetsee, T.; Wang, C. Element Transfer Behaviors of Fused CaF2-SiO2 Fluxes Subject to High Heat Input Submerged Arc Welding. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2020, 51, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Coetsee, T.; Dong, H.; Wang, C. Element Transfer Behaviors of Fused CaF2-SiO2-MnO Fluxes under High Heat Input Submerged Arc Welding. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2020, 51, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Coetsee, T.; Dong, H.; Wang, C. Element Transfer Behaviors of Fused CaF2-TiO2 Fluxes in EH36 Shipbuilding Steel During High Heat Input Submerged Arc Welding. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2020, 51, 1953–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.-S. Slag-metal Reactions during Flux Shielded Arc Welding. Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Bale, C.W.; Chartrand, P.; Degterov, S.; Eriksson, G.; Hack, K.; Mahfoud, R.B.; Melançon, J.; Pelton, A.; Petersen, S. FactSage thermochemical software and databases. Calphad 2002, 26, 189–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.; Bowman, B.; Lefrank, P. The Making, Shaping, and Treating of Steel—Steelmaking and Refining Volume; The AISE Steel Foundation: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, G.; Liu, Z.; Fan, J.; Guo, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, J. Evaluation of Flux Basicity Concept Geared toward Estimation for Oxygen Content in Submerged Arc Welded Metal. Metals 2022, 12, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S.; Shao, G.; Liu, Z. Element Transfer Behavior for CaF2-Na2O-SiO2 Agglomerated Flux Subject in Submerged Arc Welding Process. Processes 2022, 10, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).