Modelling and Scaling-Up of a Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Emulsions Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
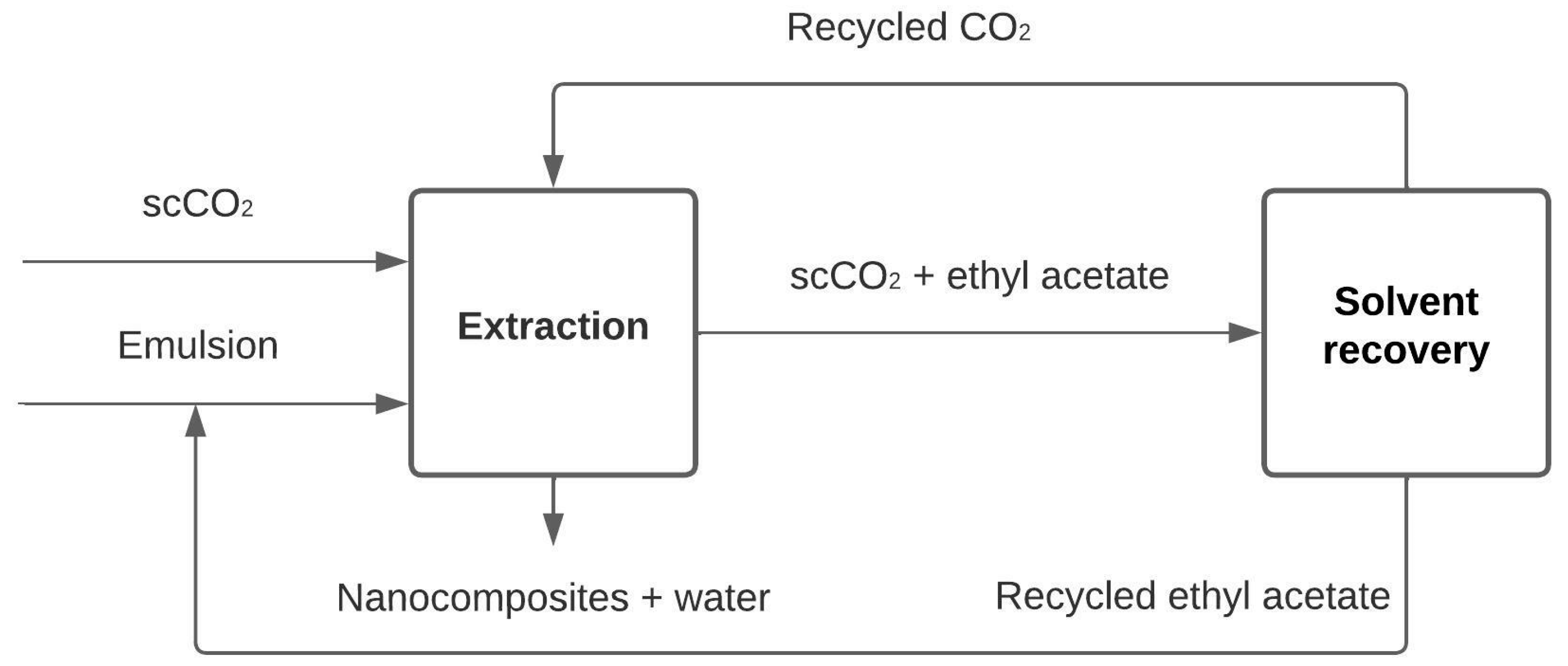
2.1. Block Diagram
2.2. Definition of Purities, Recoveries, and Key Components
2.3. Thermodynamic Modelling
2.4. High-Pressure Column Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
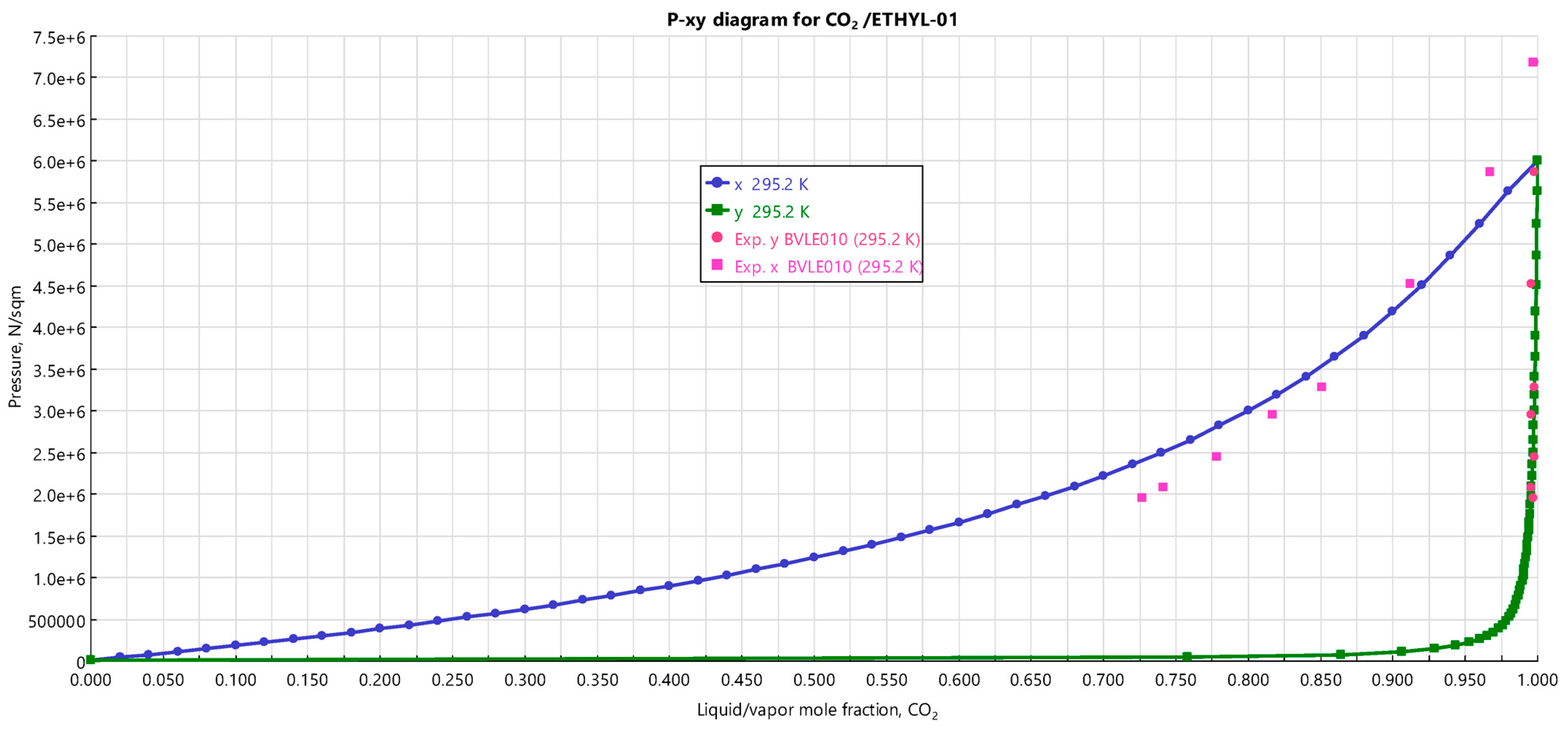
3.1. Selection of the Thermodynamic Model
3.2. Operating Conditions of the Fractionation Column
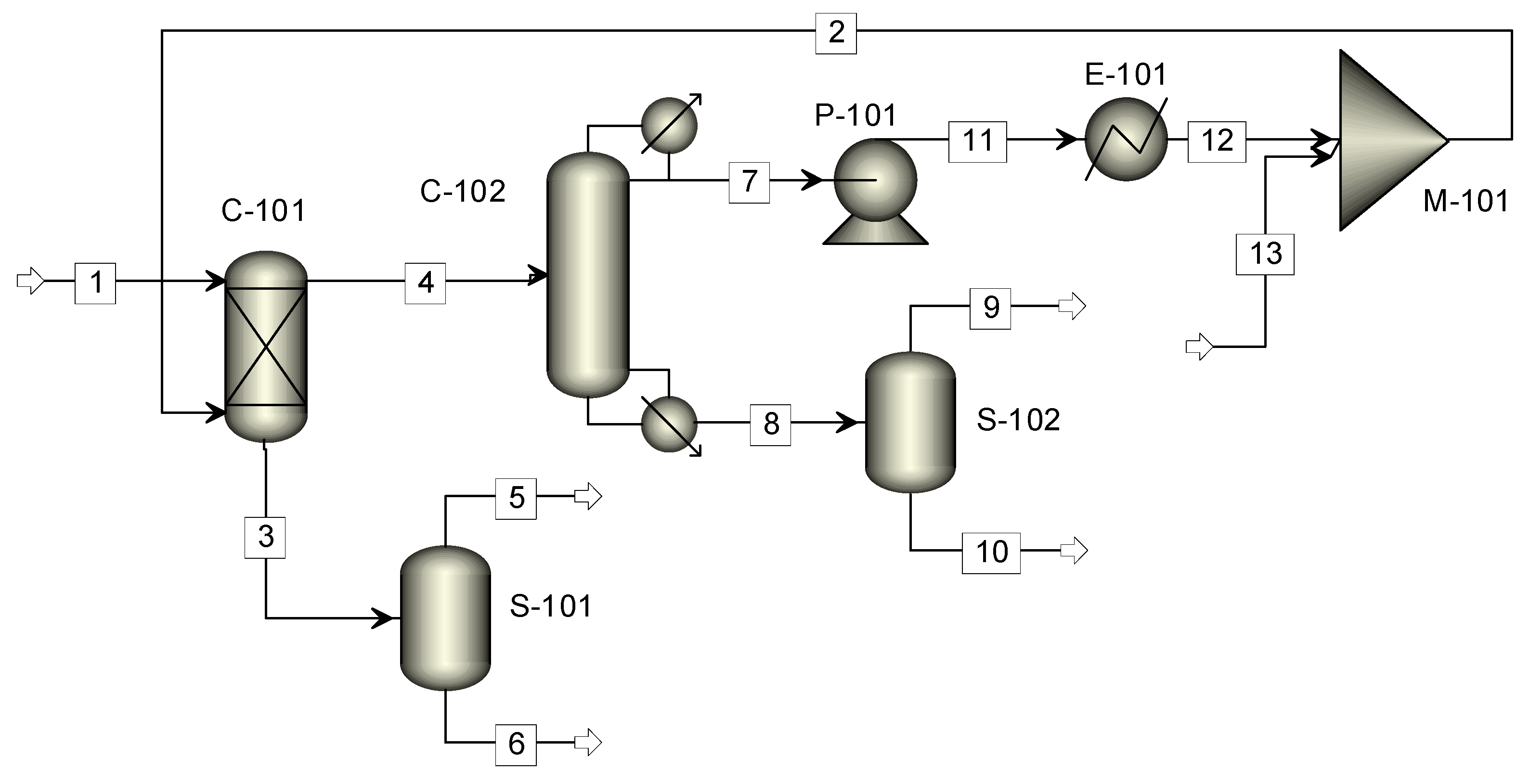
3.3. Aspen Plus® Process Simulation
3.3.1. Number of Theoretical Stages of Extract Unit
3.3.2. Design of the Integrated Process
3.4. Scale-Up
3.5. Economic Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lukic, I.; Pajnik, J.; Nisavic, J.; Tadic, V.; Vági, E.; Szekely, E.; Zizovic, I. Application of the integrated supercritical fluid extraction–impregnation process (SFE-SSI) for development of materials with antiviral properties. Processes 2022, 10, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Matis, K.A. Green separation and extraction processes: Part I. Processes 2020, 8, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, E.; Campardelli, R.; De Marco, I.; Perego, P. Optimization of PCL polymeric films as potential matrices for the loading of alpha-tocopherol by a combination of innovative green processes. Processes 2021, 9, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, H.; Hashemipour, H.; Rahimpour, E.; Rahimpour, M.R. Particle size design of acetaminophen using supercritical carbon dioxide to improve drug delivery: Experimental and modeling. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, Y. Some advances in supercritical fluid extraction for fuels, bio-materials and purification. Processes 2019, 7, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, C.; Calvo, L. The encapsulation of low viscosity omega-3 rich fish oil in polycaprolactone by supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 128, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, C.; Calvo, L. Supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions to nanoencapsulate vitamin E in polycaprolactone. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 119, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, P.; Huff, R.; Shekunov, B.Y. Drug encapsulation using supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Rao, L.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liao, X. Supercritical carbon dioxide applications in food processing. Food Eng. Rev. 2021, 13, 570–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirado, D.F.; Palazzo, I.; Scognamiglio, M.; Calvo, L.; Della Porta, G.; Reverchon, E. Astaxanthin encapsulation in ethyl cellulose carriers by continuous supercritical emulsions extraction: A study on particle size, encapsulation efficiency, release profile and antioxidant activity. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 150, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirado, D.F.; Latini, A.; Calvo, L. The encapsulation of hydroxytyrosol-rich olive oil in Eudraguard® protect via supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions. J. Food Eng. 2021, 290, 110215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, C.; Duarte, C.M.M.; Calvo, L. Performance comparison of different supercritical fluid extraction equipments for the production of vitamin E in polycaprolactone nanocapsules by supercritical fluid extraction of emulsionsc. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 122, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, P.; Huff, R.W.; Seitzinger, J.S.; Shekunov, B.Y. Composite Particles and Method for Preparing. US6966990B2, 22 November 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay, P.; Huff, R.W.; Seitzinger, J.S.; Shekunov, B.Y. Particles from Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Emulsion. US6998051B2, 14 February 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Reverchon, E.; Della Porta, G. Continuous Process for Microspheres Production by Using Expanded Fluids. US20100203145A1, 14 January 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Brunner, G. Counter-current separations. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2009, 47, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, L.; Prieto, C. The teaching of enhanced distillation processes using a commercial simulator and a project-based learning approach. Educ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 17, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tian, S.; Zhang, D.; Chang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, P. Optimization study on improving energy efficiency of power cycle system of staged coal gasification coupled with supercritical carbon dioxide. Energy 2022, 239, 122168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, C.; Calvo, L.; Duarte, C.M.M. Continuous supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions to produce nanocapsules of vitamin E in polycaprolactone. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 124, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICH Impurities: Guideline for Residual Solvents Q3C(R6); ICH: London, UK, 2016; Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/Q3C-R6_Guideline_ErrorCorrection_2019_0410_0.pdf (accessed on 22 February 2023).
- Martín-Muñoz, D.; Tirado, D.F.; Calvo, L. Inactivation of Legionella in aqueous media by high-pressure carbon dioxide. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2022, 180, 105431. [Google Scholar]
- Luther, S.K.; Schuster, J.J.; Leipertz, A.; Braeuer, A. Non-invasive quantification of phase equilibria of ternary mixtures composed of carbon dioxide, organic solvent and water. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2013, 84, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspen-Technology Aspen Plus V 11.0 2020. Available online: https://www.aspentech.com/en/products/engineering/aspen-plus (accessed on 22 February 2023).
- Brunner, G. Gas Extraction; Topics in Physical Chemistry; Steinkopff: Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; Volume 4, ISBN 978-3-662-07382-7. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, M.V.; Barbosa, D.; Ferreira, P.O.; Mendonça, J. High pressure phase equilibrium data for the systems carbon dioxide/ethyl acetate and carbon dioxide/isoamyl acetate at 295.2, 303.2 and 313.2 K. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2000, 175, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.L.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sato, T.; Suzuki, H.; Arai, K. Volumetric behavior of ethyl acetate, ethyl octanoate, ethyl laurate, ethyl linoleate, and fish oil ethyl esters in the presence of supercritical CO2. J. Supercrit. Fluids 1998, 13, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.B.; Mubarak, A.; Kim, J.D.; Bott, T.R. The mutual solubilities of water with supercritical and liquid carbon dioxides. J. Supercrit. Fluids 1992, 5, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakellariou, P.; Rowe, R.C.; White, E.F.T. The thermomechanical properties and glass transition temperatures of some cellulose derivatives used in film coating. Int. J. Pharm. 1985, 27, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Porta, G.; Falco, N.; Reverchon, E. Continuous supercritical emulsions extraction: A new technology for biopolymer microparticles production. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2011, 108, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Standards and Technology NIST Chemistry webBook. Available online: https://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/fluid/ (accessed on 6 July 2022).
- Falco, N.; Reverchon, E.; Della Porta, G. Continuous supercritical emulsions extraction: Packed tower characterization and application to poly(lactic- co -glycolic acid) + insulin microspheres production. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 8616–8623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budich, M.; Brunner, G. Supercritical fluid extraction of ethanol from aqueous solutions. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2003, 25, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atelier Fluides Supercritiques Equipment. Available online: https://www.atelier-fsc.com/Equipment_a23.html (accessed on 6 July 2022).
- Perrut, M. Supercritical fluid applications: Industrial developments and economic issues. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 4531–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Lab | Pilot a | Industrial a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter (m) | 0.013 | 0.058 | 0.126 |
| Height (m) | 1 | 4 | 8 |
| Volume (L) | 0.13 | 11 | 100 |
| Maximum liquid capacity a (L h−1) | 5–20 | 50 | |
| Top CO2 capacity a (kg h−1) | 80 | 600 | |
| Packing | 0.16-inch Pro-Pak | VFF Interpack (10–15 mm) | Sulzer CY |
| Production capacity (stream 6) | 0.11 | 2.2 | 33 |
| Equipment cost (EUR) | 150,000 b | 976,000 c | 3,205,000 c |
| Utilities cost (EUR /year) d | 37,284 | 74,568 | 123,736 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tirado, D.F.; Cabañas, A.; Calvo, L. Modelling and Scaling-Up of a Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Emulsions Process. Processes 2023, 11, 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041063
Tirado DF, Cabañas A, Calvo L. Modelling and Scaling-Up of a Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Emulsions Process. Processes. 2023; 11(4):1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041063
Chicago/Turabian StyleTirado, Diego F., Albertina Cabañas, and Lourdes Calvo. 2023. "Modelling and Scaling-Up of a Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Emulsions Process" Processes 11, no. 4: 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041063
APA StyleTirado, D. F., Cabañas, A., & Calvo, L. (2023). Modelling and Scaling-Up of a Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Emulsions Process. Processes, 11(4), 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041063








