Evaluating the Efficacy of Intelligent Methods for Maximum Power Point Tracking in Wind Energy Harvesting Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Research Background
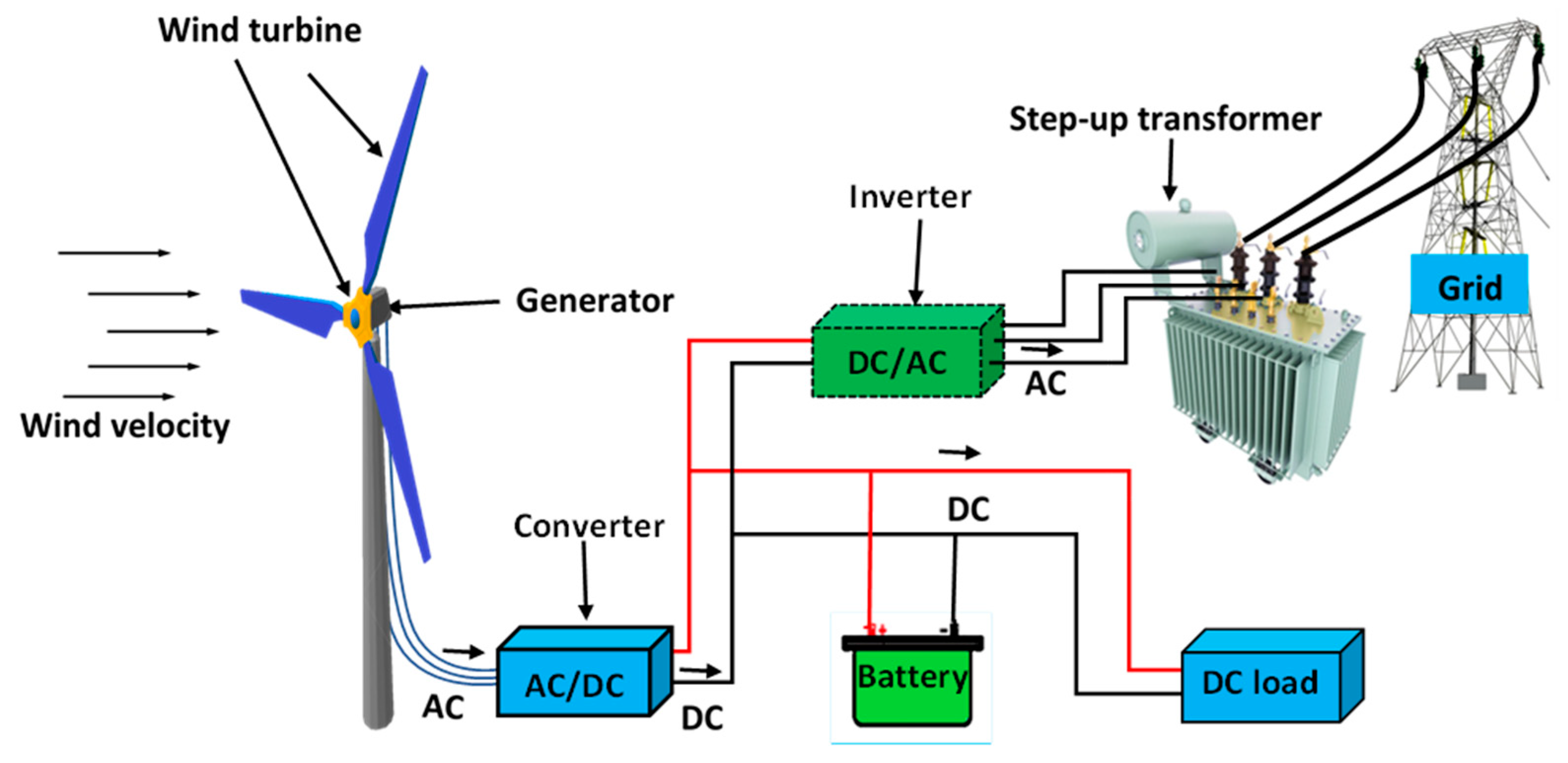
3. Modeling of WEHS
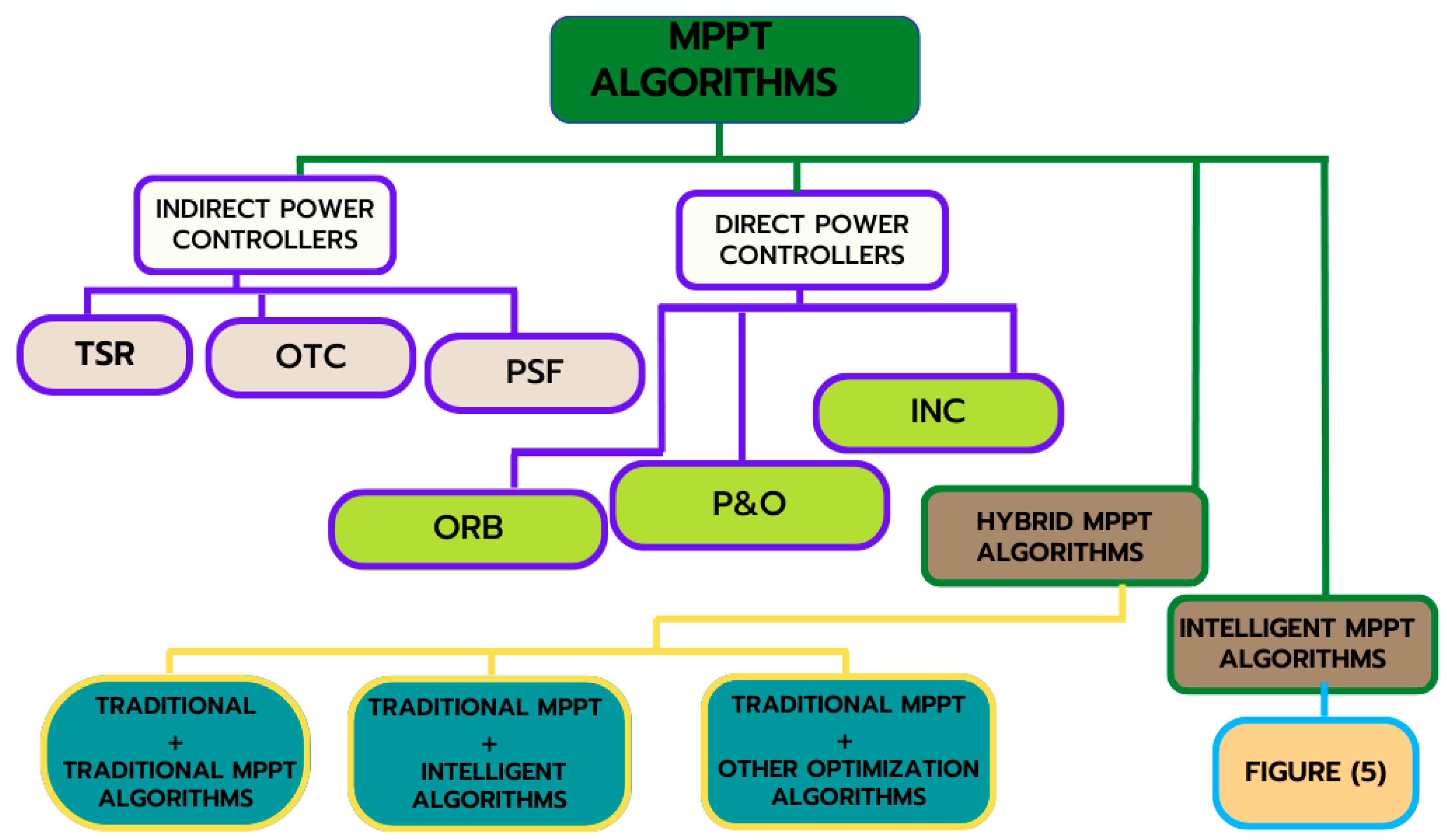
4. MPPT Methods for WEHS
4.1. Traditional MPPT Methods for WEHS
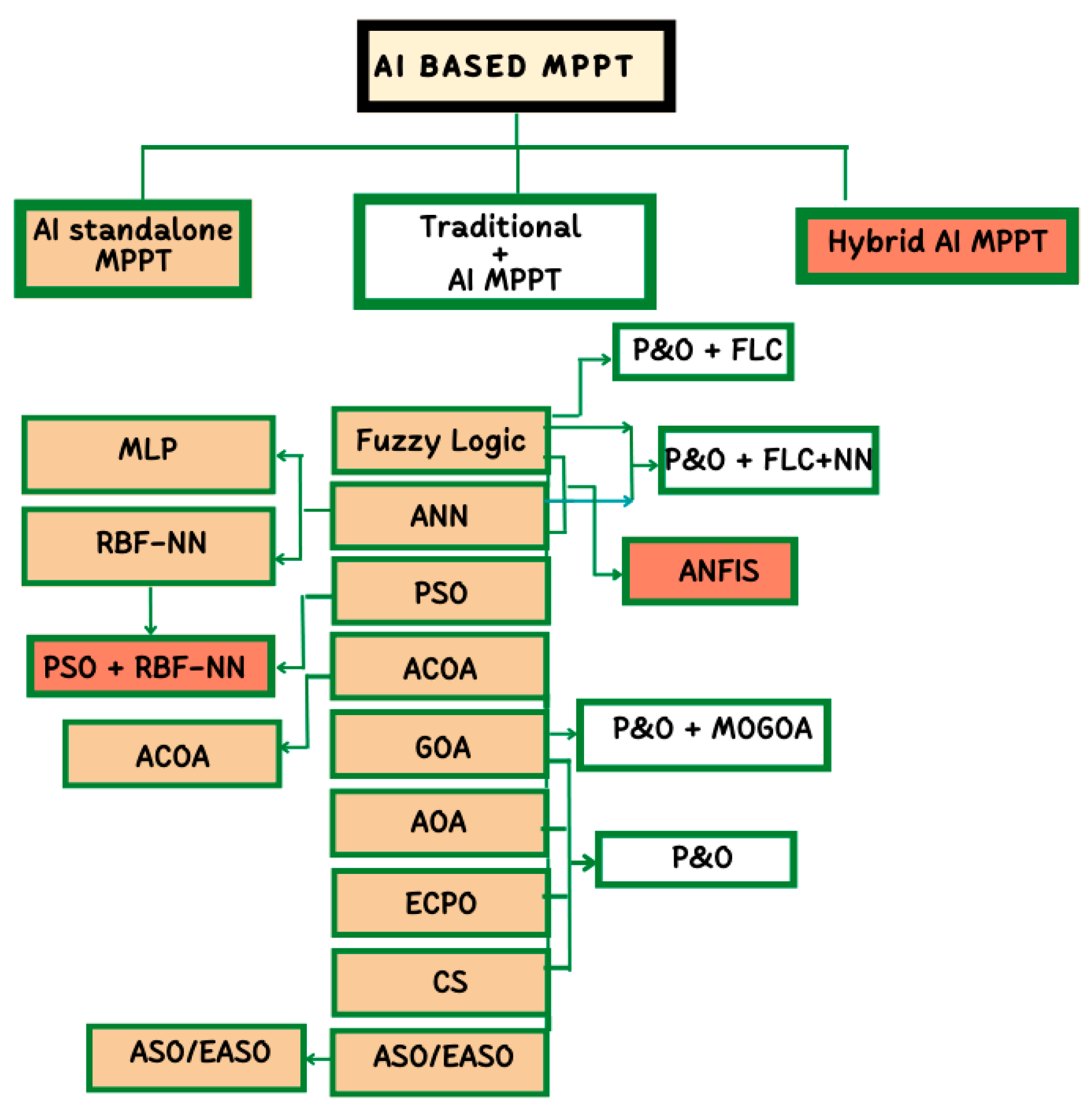
4.2. Intelligent-Based MPPT Methods
4.2.1. The Fuzzy Logic-Based MPPT Controllers
4.2.2. The Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) Based MPPT Controller

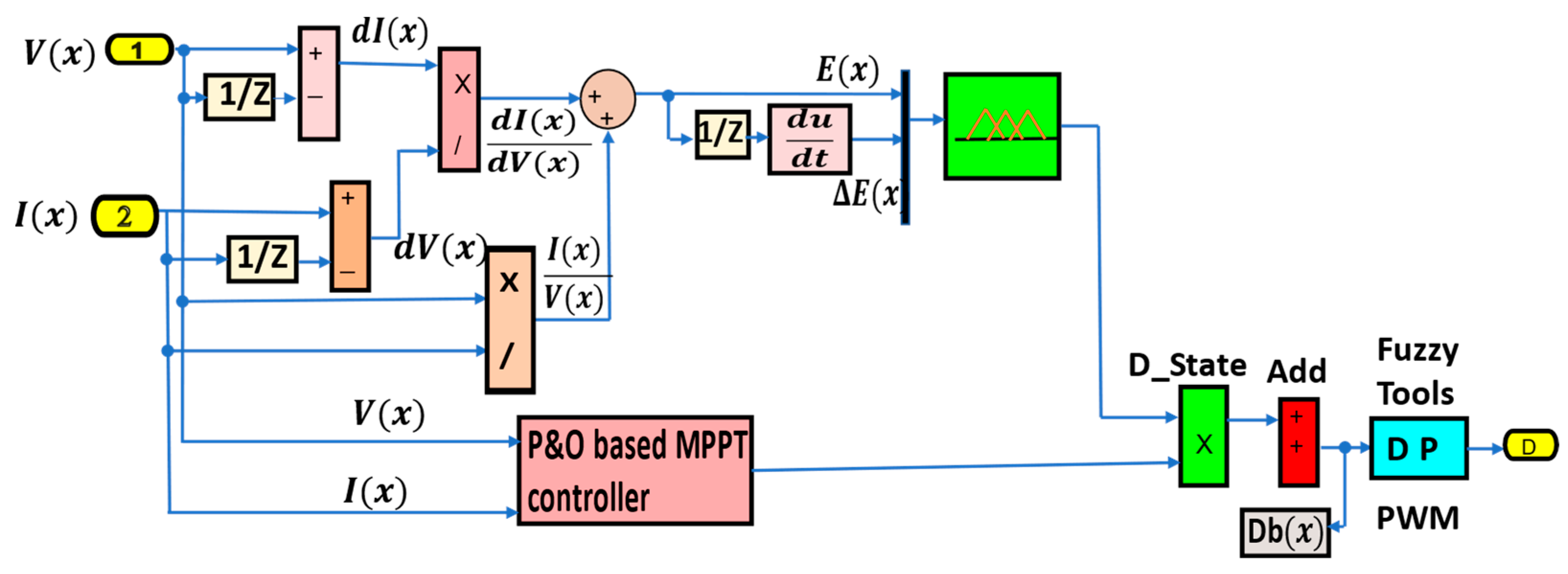
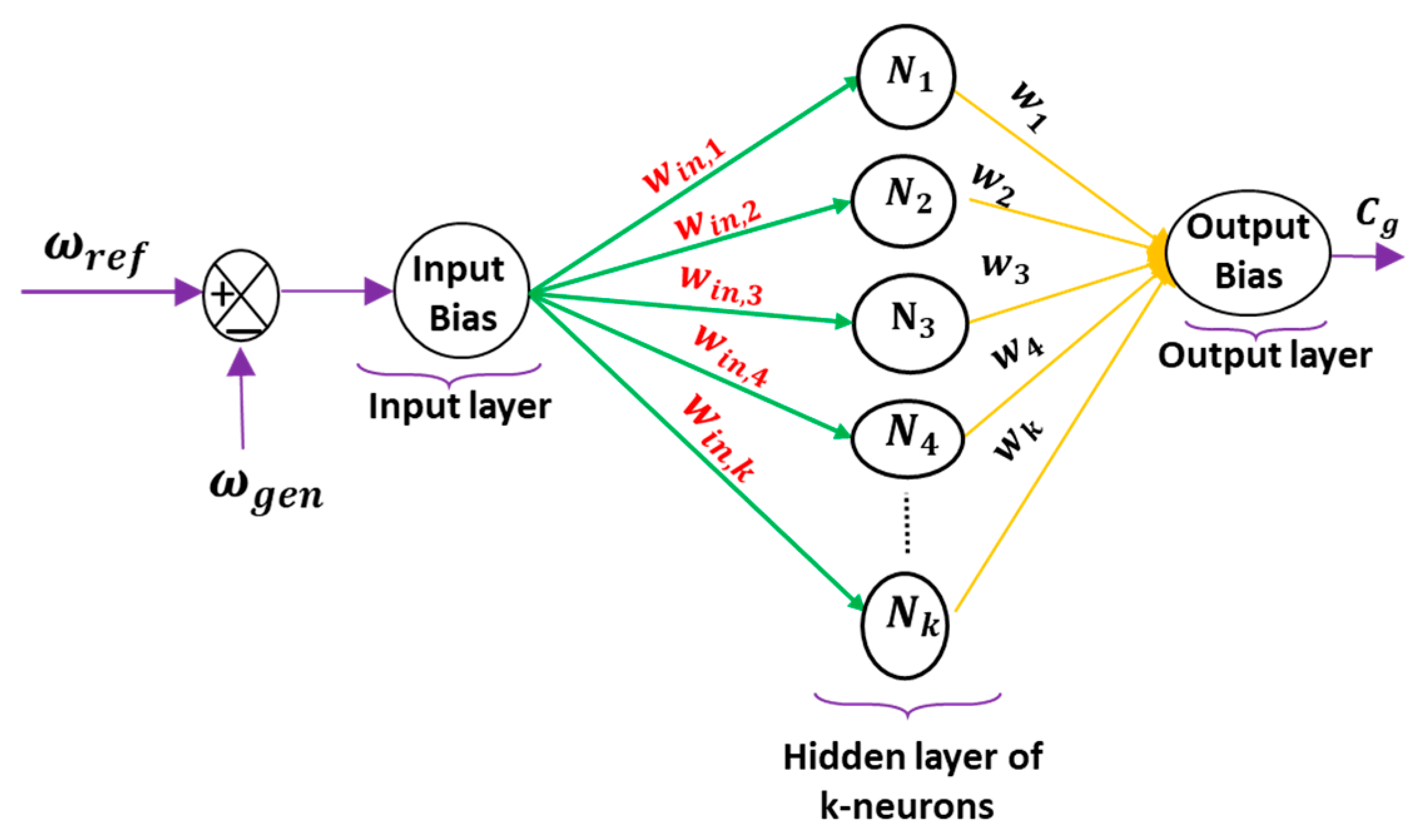
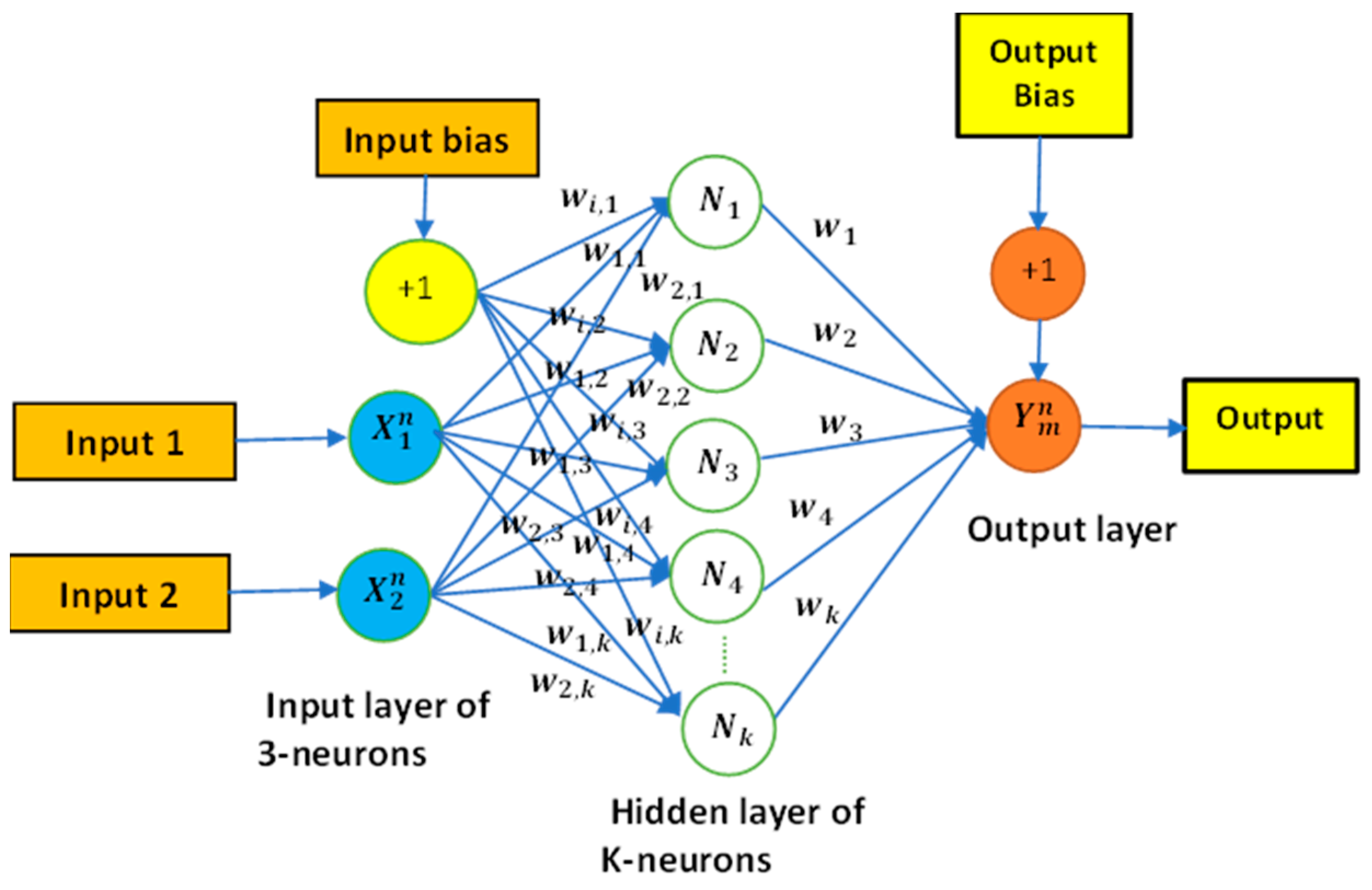
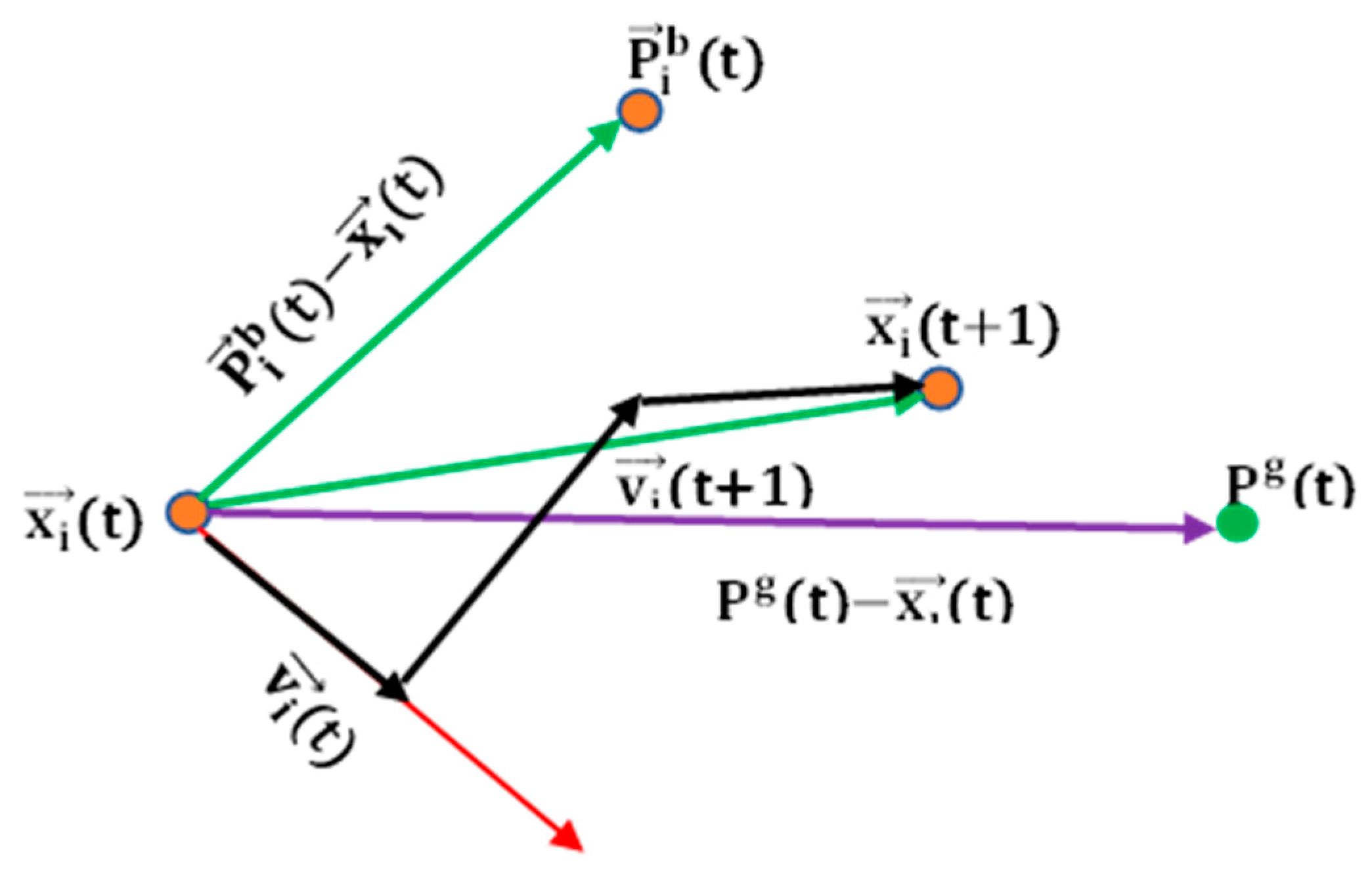
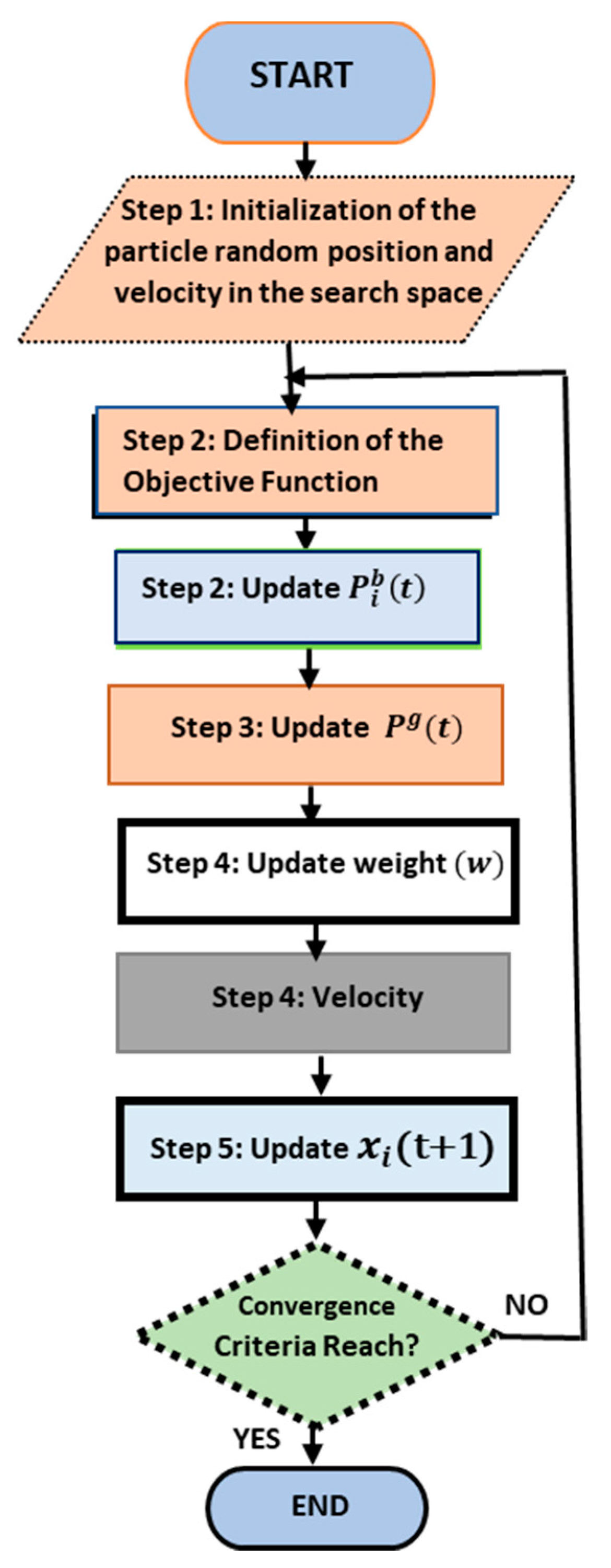
4.2.3. MPPT Using PSO Algorithms
4.2.4. MPPT Method Using Other Optimization Algorithms
4.3. The Hybrid MPPT Techniques
4.3.1. The Hybrid-Traditional MPPT
4.3.2. Hybrid Methods (Traditional and Intelligent)
4.3.3. Hybrid Methods (Intelligent and Intelligent)
5. Discussions
5.1. Intelligent-Based MPPT Models
5.2. Hybrid Methods (Traditional and Intelligent-Based MPPT)
5.3. Hybrid Methods (Intelligent and Intelligent)
6. Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roga, S.; Bardhan, S.; Kumar, Y.; Dubey, S.K. Recent technology and challenges of wind energy generation: A review. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 52, 102239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famoso, F.; Brusca, S.; D’Urso, D.; Galvagno, A.; Chiacchio, F. A novel hybrid model for the estimation of energy conversion in a wind farm combining wake effects and stochastic dependability. Appl. Energy 2020, 280, 115967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Flores, D.R.; Duran-Gomez, J.L.; Chacon-Murguia, M.I. A Mechanical Sensorless MPPT Algorithm for a Wind Energy Conversion System based on a Modular Multilayer Perceptron and a Processor-in-the-Loop Approach. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2020, 186, 106409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.D.; Chang, C.C.W.; Bhuiyan, M.A.S.; Minhad, K.N.; Ali, K. Advancements of wind energy conversion systems for low-wind urban environments: A review. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 3406–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, D.A.; Yaw, C.T.; Koh, S.P.; Tiong, S.K.; Alkahtani, A.A.; Yusaf, T. Design and Optimization of a Small-Scale Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine Blade for Energy Harvesting at Low Wind Profile Areas. Energies 2022, 15, 3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jia, J.; Zheng, L.; Yi, W.; Zhang, Z. Maximum power point tracking algorithms for wind power generation system: Review, comparison and analysis. Energy Sci. Eng. 2022, 11, 430–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, S.M.R.; Goto, H.; Guo, H.J.; Ichinokura, O. Review and critical analysis of the research papers published till date on maximum power point tracking in wind energy conversion system. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Atlanta, GA, USA, 12–16 September 2010; pp. 4075–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, H.H.H.; Youssef, A.R.; Mohamed, E.E.M. State of the art perturb and observe MPPT algorithms based wind energy conversion systems: A technology review. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 126, 106598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, J.; Nasikkar, P.; Kotecha, K.; Varadarajan, V. A review of maximum power point tracking algorithms for wind energy conversion systems. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J. Review of Recent Trends in Optimization Techniques for Hybrid Renewable Energy System. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 1459–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J.; Mathew, L. Comparative Study of Optimization Techniques for Renewable Energy System. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2020, 27, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, B.; Aggarwal, M. A Comprehensive Review of Traditional and Smart MPPT Techniques in PMSG based Wind Energy Conversion System. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Power Electronics, Control and Automation (ICPECA), New Delhi, India, 16–17 November 2019; Volume 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.Z.; Baloch, M.H.; Gul, M.; Kaloi, G.S.; Chauhdary, S.T.; Memon, A.A. A research on conventional and modern algorithms for maximum power extraction from wind energy conversion system: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 5020–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apata, O.; Oyedokun, D.T.O. An overview of control techniques for wind turbine systems. Sci. Afr. 2020, 10, e00566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, M.; Feng, R. Research on the economy of implementing the MPPT for wind-solar hybrid power generation system: A review. In Proceedings of the 2022 41st Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Hefei, China, 25–27 July 2022; Volume 2022, pp. 5339–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Chatterjee, K. A review of conventional and advanced MPPT algorithms for wind energy systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 957–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Yang, Z.; Cao, B. A new maximum power point tracking control scheme for wind generation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Power System Technology, Kunming, China, 13–17 October 2002; Volume 1, pp. 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, S. Extreme learning machine based wind speed estimation and sensorless control for wind turbine power generation system. Neurocomputing 2013, 102, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, B.; Liu, X. Adaptive neuro-fuzzy algorithm to estimate effective wind speed and optimal rotor speed for variable-speed wind turbine. Neurocomputing 2018, 272, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitharthan, R.; Karthikeyan, M.; Sundar, D.S.; Rajasekaran, S. Adaptive hybrid intelligent MPPT controller to approximate effectual wind speed and optimal rotor speed of variable speed wind turbine. ISA Trans. 2020, 96, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Zhu, T.; Wang, J.; Shu, H.; Yu, T.; Zhang, X.; Yao, W.; Sun, L. Comprehensive overview of maximum power point tracking algorithms of PV systems under partial shading condition. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 121983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.A.; Yatim, A.H.M.; Tan, C.W. An online Optimum-Relation-Based Maximum Power Point Tracking Algorithm for Wind Energy Conversion System. In Proceedings of the 2014 Australasian universities power engineering conference (AUPEC), Perth, Australia, 28 September–1 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.; Rashid, M.A.; Mohamed, S.B.; Yaakob, S.B. A novel maximum power point tracking algorithm for wind energy conversion system. Eng. Lett. 2019, 27, 822–830. [Google Scholar]
- Kazmi, S.M.R.; Goto, H.; Guo, H.J.; Ichinokura, O. A novel algorithm for fast and efficient speed-sensorless maximum power point tracking in wind energy conversion systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjefar, S.; Ghassemi, A.A.; Ahmadi, M.M. Improving efficiency of two-type maximum power point tracking methods of tip-speed ratio and optimum torque in wind turbine system using a quantum neural network. Energy 2014, 67, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Meng, H.; Hu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Wang, W. A novel MPPT method for enhancing energy conversion efficiency taking power smoothing into account. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 101, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Jiang, Z.; Pan, L. Recurrent neural network based adaptive integral sliding mode power maximization control for wind power systems. Renew. Energy 2020, 145, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, Y.; Rekioua, D. High performance of Maximum Power Point Tracking Using Ant Colony algorithm in wind turbine. Renew. Energy 2018, 126, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, A.; Alharbi, A.G.; Alshammari, S.; Hasanien, H.M. Archimedes optimization algorithm based maximum power point tracker for wind energy generation system. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2022, 13, 101548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falehi, D. An innovative optimal RPO-FOSMC based on multi-objective grasshopper optimization algorithm for DFIG-based wind turbine to augment MPPT and FRT capabilities. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 130, 109407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wei, P.; Gong, X.; Meng, X.; Shan, D.; Zhu, J. Enhanced Atom Search Optimization Based Optimal Control Parameter Tunning of PMSG for MPPT. Energy Eng. J. Assoc. Energy Eng. 2022, 119, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaichi, I.; Semmah, A.; Wira, P. Control of doubly fed induction generator with maximum power point tracking for variable speed wind energy conversion systems. Period. Polytech. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2020, 64, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Agrawal, H.P.; Shah, A.; Bansal, H.O. Maximum power point tracking in wind energy conversion system using radial basis function based neural network control strategy. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2019, 36, 100533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J.; Kumar, D.; Narayan, Y.; Malik, H.; Márquez, F.P.G.; Muñoz, C.Q.G. A Novel Artificial Intelligence Maximum Power Point Tracking Technique for Integrated PV-WT-FC Frameworks. Energies 2022, 15, 3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhipa, A.A.; Kumar, V.; Joshi, R.R.; Chakrabarti, P.; Jasinski, M.; Burgio, A.; Leonowicz, Z.; Jasinska, E.; Soni, R.; Chakrabarti, T. Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system-based maximum power tracking controller for variable speed wecs. Energies 2021, 14, 6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.A.; Yatim, A.H.M.; Tan, C.W.; Saidur, R. A review of maximum power point tracking algorithms for wind energy systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 3220–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelqawee, M.; Yousef, A.Y.; Hasaneen, K.M.; Nashed, M.N.F.; Hamed, H.G. Standalone wind energy conversion system control using new maximum power point tracking technique. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. Certif. J. 2019, 9, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Pande, J.; Nasikkar, P. A Maximum Power Point Tracking Technique for a Wind Power System Based on the Trapezoidal Rule. Energies 2023, 16, 2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malobe, P.A.; Djondine, P.; Eloundou, P.N.; Ndongo, H.A. A Novel Hybrid MPPT for Wind Energy Conversion Systems Operating under Low Variations in Wind Speed. Energy Power Eng. 2020, 12, 716–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, A.; Zakaria, M.N.; Sulaiman, S.; Ahmad, W.F.W. A comparison of feed-forward back-propagation and radial basis artificial neural networks: A Monte Carlo study. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Symposium on Information Technology, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 15–17 June 2010; Volume 2, pp. 994–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kůrková, V. Kolmogorov’s theorem and multilayer neural networks. Neural Netw. 1992, 5, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J. An AIAPO MPPT controller based real time adaptive maximum power point tracking technique for wind turbine system. ISA Trans. 2022, 123, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sompracha, C.; Jayaweera, D.; Tricoli, P. Particle swarm optimisation technique to improve energy efficiency of doubly-fed induction generators for wind turbines. J. Eng. 2019, 2019, 4890–4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lin, T.; Wen, C.; Song, Y. Design of a Unified Power Controller for Variable-Speed Fixed-Pitch Wind Energy Conversion System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 4899–4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaicharoenaudomrung, K.; Areerak, K.; Areerak, K.; Bozhko, S.; Hill, C.I. Maximum Power Point Tracking for Stand-Alone Wind Energy Conversion System Using FLC-P&O Method. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2020, 15, 1723–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.; Mathew, L.; Alotaibi, M.A.; Malik, H.; Nassar, M.E. Fuzzy-Logic-Based Comparative Analysis of Different Maximum Power Point Tracking Controllers for Hybrid Renewal Energy Systems. Mathematics 2022, 10, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouz, S.; Messalti, S.; Harrag, A. A Novel Hybrid MPPT Controller Using (P&O)-neural Networks for Variable Speed Wind Turbine Based on DFIG. Model. Meas. Control A 2019, 92, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.; Al-Hadhrami, T.; Tan, C.W.; Yatim, A.H. Towards green energy for smart cities: Particle swarm optimization based MPPT approach. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 58427–58438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ref. | Types and Numbers of MPPT Technique Covered | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional | AI-Based | Hybrid (Conventional + Conventional) | Hybrid (AI + Conventional) | Hybrid (AI + AI) | |
| [8] |  | FLC&NN | P&O+OTC, ORB, PSF | ~ |  |
| [9] |  | FLC&NN | P&O+OTC, ORB, PSF | P&O+FLC, NN, PFS+NN, ORB+PSO |  |
| [10] |  | FLC&NN | P&O+PSF |  |  |
| [11] | P&O, IC | RBN, PSO, ESN ~ | RBF+PSF | P&O+FLC (Partially) |  |
| [12] |  | ANN, PSO FLC, WOA, GWOA | / |  |  |
| [13] |  | FLC&NN |  | PSF+FLC |  |
| [14] |  | FLC, NN&GA |  |  |  |
| [6] | ~ | FLC, NN | P&O+PSF, OTC+P&O |  |  |
| [15] |  | FLC, NN |  |  |  |
| MPPT Technique | Advantages | Major Drawbacks | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| TSR | TSR is highly efficient, has high convergence speed, and quickly responds to wind speed changes [37]. Additionally, the TSR method is simple, and no memory is required for the process | The need for a mechanical sensor to measure wind speed results in inaccuracies, leading to increased costs for installation and maintenance. | A novel approach was developed to estimate wind speed, which removed inaccuracies associated with mechanical sensors. The algorithm’s speed to track MPP was enhanced, and the technique was made simpler [18,19,20]. |
| OTC | The OTC method is highly efficient and flexible, with stable torque regulation and easy application. It is also practical as it does not require real-time wind speed measurement, allowing for quick adjustments to changes in wind speed. | The mechanical sensor used for wind speed measurement and knowledge of wind turbine characteristics is necessary. In addition, the turbine’s large inertia causes a sluggish response to torque commands, resulting in slow MPP tracking during sudden changes in wind speed. Moreover, measuring electromagnetic torque and turbine speed can increase the system cost and its dependency on generator parameters. | A quantum neural network (QNN) was introduced into the OTC method by [25] and efficiency improvement was recorded more than with conventional OTC and NN. Reference [26] proposed a fuzzy inference-based MPPT method to improve the OTC method. This method enhances the MPPT efficiency under fluctuating wind speeds while ensuring system stability. |
| PSF | PSF has moderate performance under fluctuating wind speeds and high convergence speeds. The system cost is less compared to the TSR method. | The use of a mechanical sensor to measure wind speed introduces inaccuracies. Additionally, PSF is less efficient and more complex than the TSR and OTC methods. Moreover, it requires knowledge of wind turbine characteristics, and can cause the generator to stall when there are sudden changes in wind speed. | The modified PSF as reported by [7] has solved the issue of generator stalling but raises further issues, such as overshoot of the control variables and greater difficulty in tracking the MPP. |
| P&O | The proposed method eliminates the need for a mechanical sensor and requires less memory, making it simple to implement. Additionally, it does not require any prior knowledge of the system parameters and characteristics, resulting in lower overall system costs. Although its performance under intermittent wind speed is moderate, it is still a viable option. | Large step size causes oscillation around the maximum power point (MPP) while smaller step size leads to slower response. Both scenarios result in a loss of MPP tracking and reduced efficiency, particularly at varying wind speeds. In addition, the convergence speed is slow. | The drawbacks can be addressed by adopting the followings: Variable, Adaptive, and hybrid step sizes concept [9]. The step size was calculated using trapezoidal rule in [38] which successfully reduce computational complexity of the algorithms and eliminated power oscillation at the MPP. |
| INC | The benefit of this method is similar to P&O method but with better convergence speed, precision, and MPPT tracking efficiency. | Slow convergence speed. Oscillation at MPP | The INC method proposed by [21] addresses the trade-off between power and convergence speed in P&O methods. Moreover, the modified INC achieves a better system with higher dynamic performance, precision, and fast convergence speed compared to P&O. |
| ORB | No need for wind speed sensors and look-up tables [16]. Furthermore, high convergence speed than that of P&O and INC. In addition, oscillations around the MPPT are absent in ORB method | Required large memory for pre-obtained optimal relation curve. Required previous knowledge of the system. | Reference [22] improved the ORB method by using the P&O method as an initialization algorithm for online MPP search at local wind speeds. This eliminated the ORB method’s drawback by extracting the necessary parameters for its operation. |
| Intelligent MPPT Type | Remarks | Algorithm Performance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| FLC | The FLC (fuzzy logic control) controller has demonstrated better power generation and faster response time when compared to other controllers such as P&O and ANN. | A power generation increase of approximately 20 W was achieved when compared to the P&O method. | [34] |
| ANN (MLP) | An Artificial neural network novel MPPT algorithm was developed Combining an intelligent modular multilayer perceptron (MLP) approach with a simplified model of WEHS. | The model in [3] has achieved an MPPT performance of 99.95% and error of 3% was recorded | [3] |
| NN (MLP) | Similar approached as in [3], The result obtained showed increased system robustness and fast power response and improved power coefficient. | The system achieved a power coefficient of 0.48 and a time response of 5 s. | [32] |
| ANN | The use of the ANN as an alternative MPPT algorithm resulted in improved MPP tracking and quicker response times compared to the P&O method. | Increase in power of approximately 30 W was achieved. | [34] |
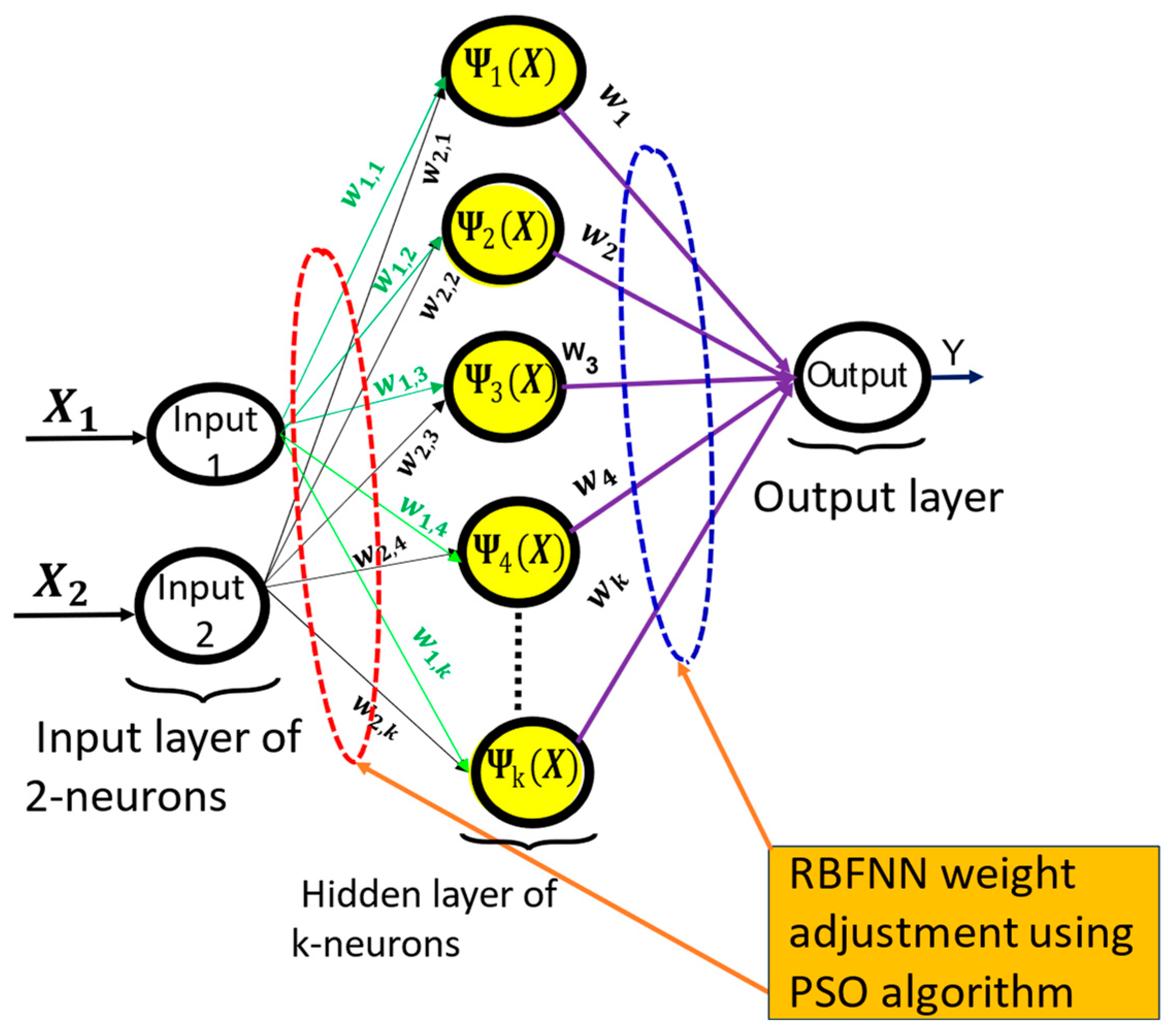
| ANN (RBF-NN) | Radial basis function-neural networks (RBF-NN) was proposed to replace the need for measurement instruments, eliminate system errors, and minimize the size and cost of the system. Compared with other AI based methods such as backpropagation of NN and FLC, the proposed RBF-NN method showed better performance. | The response times for FLC, RBF-NN, and BP-NN were 0.47, 0.46, and 0.42, respectively. However, the BP-NN method had the highest ripple factor of 4% | [33] |
| RNN | A new control strategy for wind power systems was proposed using integral sliding mode control technique based on a recurrent neural network (RNN) where optimal control signals for maximum power extraction is estimated using the RNN. Simulations show that the proposed strategy outperforms existing control strategies in power generation, disturbance rejection, and robustness to parameter variations and uncertainties. The proposed approach can improve the performance and efficiency of wind power systems. | The root mean square error (RMSE) between the optimal power and the tracked power was calculated to be 0.153. | [27] |
| Intelligent MPPT Type | Description | Algorithm Performance Evaluation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSO | An effective control MPPT algorithm based on the PSO was proposed to maximize the efficiency of fixed-pitch DFIG WT by compensating the errors in the estimation of the generator circuit parameters. Compared to the results of the conventional methods, the proposed control algorithm has improved the energy generation of the system. | More energy of 1.28% was generated | [43] |
| ACOA | ACOA was developed and used to tune the PI controller to determine its optimal parameters for speed control. This approach increased the power coefficient and overall performance of the WEHS. | The system achieved a Cp of 0.453, which is slightly higher than the 0.4518 achieved using a PI controller. Additionally, an increase in power output of 150 W was obtained. | [28] |
| AOA, GOA, CSOA, ECPO, | The shortcomings of the HCS method in terms of MPP tracking speed and efficiency were successfully overcome using the AOA. Compared with other optimization methods such as CSOA, GOA, and ECPO, better performance was obtained with AOA. | The system power generation has increased to 102.20 W, 101.19 W, 78.30 W and 63.52 W respectively with AOA, GOA, ECPO and CSOA algorithm. | [29] |
| GOA and MOGOA | Fractional order sliding mode controller (FOSMC) based on the traditional P&O method was modified to incorporate the MOGOA. The successful implementation of the MOGOA significantly improved the system’s robustness as well as its dynamic performance. | The proposed algorithm achieved an integral of time multiple of absolute error (ITAE) value of 4.18 and 1.48 s for power overshoot and settling time, while the conventional and sliding mode control approaches achieved values of 5.63 and 1.64 s. | [30] |
| EASO | An optimal solution of high quality and fast system response was achieved using an EASO technique developed for PMSG-based WEHS. According to [30], the technique has a powerful global search capability to track the MPP. | The proposed method achieved an integral absolute error (IAE) control benchmark of 0.1481, which is lower than the values recorded for the PSO and GA algorithms, which were 0.182 and 0.213, respectively. | [31] |
| Type of MPPT Algorithms | Remarks | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| P&O+PSF | Improvement in power efficiency tracking was achieved with the hybrid MPPT | [44] |
| ORB+P&O | Combines ORB with a self-rotating P&O-based controller that improves the tracking speed of the hybrid MPPT. | [23] |
| P&O+OTC | The OTC was employed to detect power peak point and reduce the perturbation step size of the P&O algorithm to reach MPP. | [24] |
| Hybrid MPPT Name | Description | Algorithm Performance Evaluation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| P&O+FLC | Fuzzy logic controller (FLC) has been integrated into the adaptive P&O MPPT method which increased the computational speed of the MPPT controller. Furtherly, the new hybrid method successfully eliminated the drawbacks of both the standalone conventional adaptive P&O MPPT and the FLC. | The proposed controller yielded a power increase of 37.93% compared to the P&O method and 17.65% compared to the FLC controller. Additionally, 110 W more power was generated with the proposed controller than with the P&O method and 60 W more than the FLC controller [45]. Moreover, 36.38% of energy yield was recorded with the new controller in [46]. | [42,45,46] |
| P&O+ANN | By integrating ANN into the traditional P&O algorithm, an increase in accuracy was achieved. | The new approach effectively monitored the power coefficient at the optimal level of 0.35 and the nominal power generation of 3 MW. | [47] |
| ORB+ PSO | PSO was used in the ORB algorithm to search for the maximum power coefficient. The resulting hybrid algorithm provided high efficiency | The PSO-ORBMPPT algorithm has a tracking efficiency of up to 99.4%, which is higher than that of conventional OTC and ORB MPPT algorithms. Additionally, the PSO-ORBMPPT algorithm harvests 1.9% more electrical energy than the conventional algorithms. | [48] |
| Types of Intelligent MPPT Algorithm | Description | Performance Metrics and Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| FLC, NN | The controller in [34] which combined FLC and NN has improved power harvesting capability in a hybrid renewable energy system (HRES) and shorter simulation time to catch the MPP as compared to other standalone methods such as P&O, FLC, and ANN. | Compared to the standalone P&O, FLC, and ANN methods, the hybrid method achieved an increase in power generation of 35 W, 15 W, and 5 W, respectively, in the WEHS. | [34] |
| ANFIS | An Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) (MPPT) controller for grid-connected WEHS was proposed. The method described can extract the MP from the wind by tracking the MPP independently of the wind speeds. | The ANFIS controller resulted in a 37% smaller voltage overshoot compared to the PI controller. Additionally, a power increase of approximately 7.64% was achieved. | [35] |
| RBF-NN, MPSO | RBF-NN and modified PSO were integrated into MPPT controller in [20], to replace the conventional MPPT controller. The hybrid combination was able to track the MPP of the WEHS in addition to estimating both the effective wind speed and the rotational speed of the WT. Increased in system reliability, and reduced converters loss, size, and system cost were also achieved. | The proposed hybrid method resulted in a 40% reduction in converter size and produced highest power coefficient of 0.498, whereas other methods, such as ENN+PSO, RBNN-GA, and RBFNN, achieved lower power coefficients of 0.475, 0.47, and 0.43, respectively. | [20] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Umar, D.A.; Alkawsi, G.; Jailani, N.L.M.; Alomari, M.A.; Baashar, Y.; Alkahtani, A.A.; Capretz, L.F.; Tiong, S.K. Evaluating the Efficacy of Intelligent Methods for Maximum Power Point Tracking in Wind Energy Harvesting Systems. Processes 2023, 11, 1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11051420
Umar DA, Alkawsi G, Jailani NLM, Alomari MA, Baashar Y, Alkahtani AA, Capretz LF, Tiong SK. Evaluating the Efficacy of Intelligent Methods for Maximum Power Point Tracking in Wind Energy Harvesting Systems. Processes. 2023; 11(5):1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11051420
Chicago/Turabian StyleUmar, Dallatu Abbas, Gamal Alkawsi, Nur Liyana Mohd Jailani, Mohammad Ahmed Alomari, Yahia Baashar, Ammar Ahmed Alkahtani, Luiz Fernando Capretz, and Sieh Kiong Tiong. 2023. "Evaluating the Efficacy of Intelligent Methods for Maximum Power Point Tracking in Wind Energy Harvesting Systems" Processes 11, no. 5: 1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11051420
APA StyleUmar, D. A., Alkawsi, G., Jailani, N. L. M., Alomari, M. A., Baashar, Y., Alkahtani, A. A., Capretz, L. F., & Tiong, S. K. (2023). Evaluating the Efficacy of Intelligent Methods for Maximum Power Point Tracking in Wind Energy Harvesting Systems. Processes, 11(5), 1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11051420









