Adaptive Optimization Design of Building Energy System for Smart Elderly Care Community Based on Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Smart Elderly Care Community Building Energy System Design
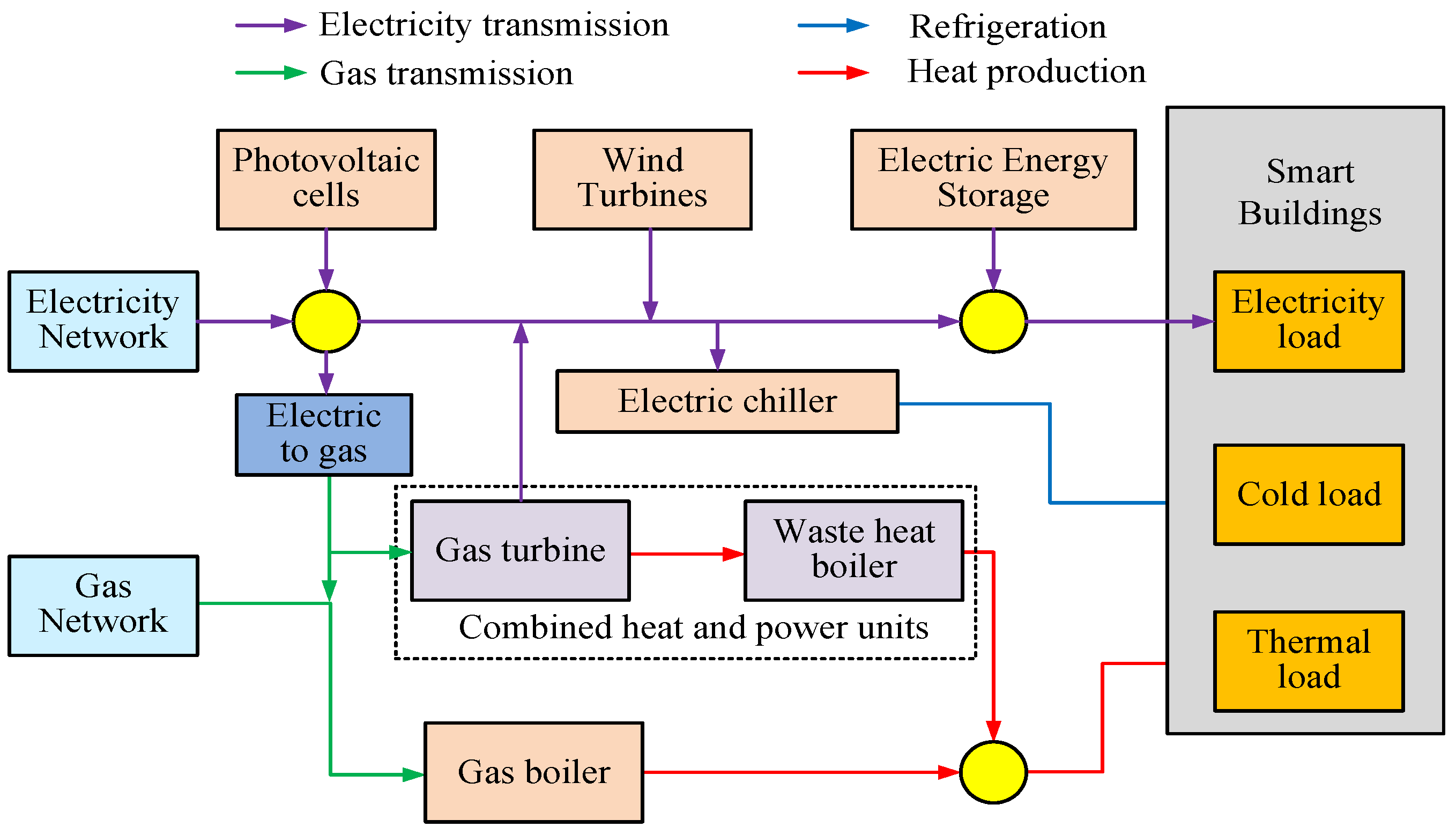
3.1. Building Energy System Model Construction for Smart Elderly Care Community
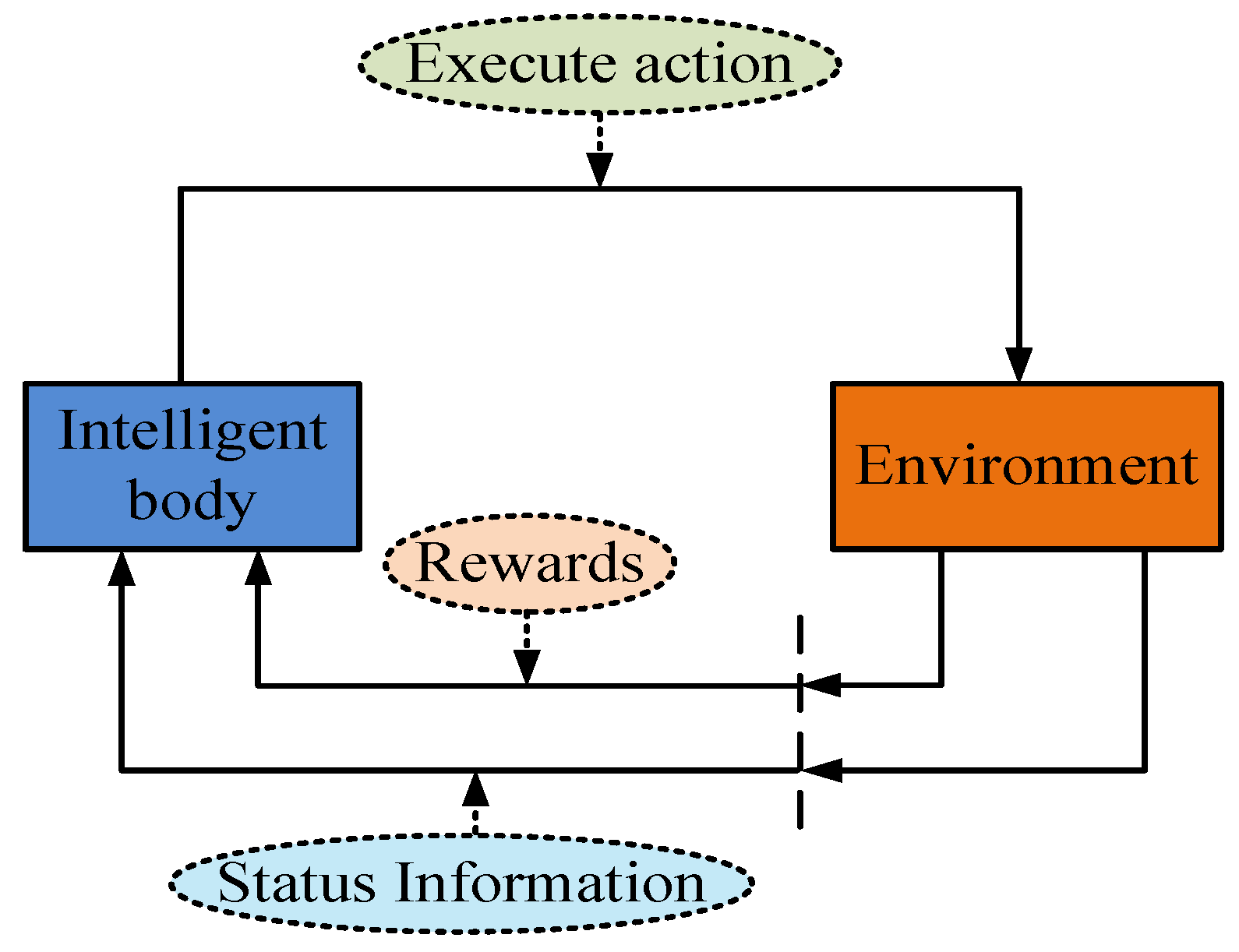
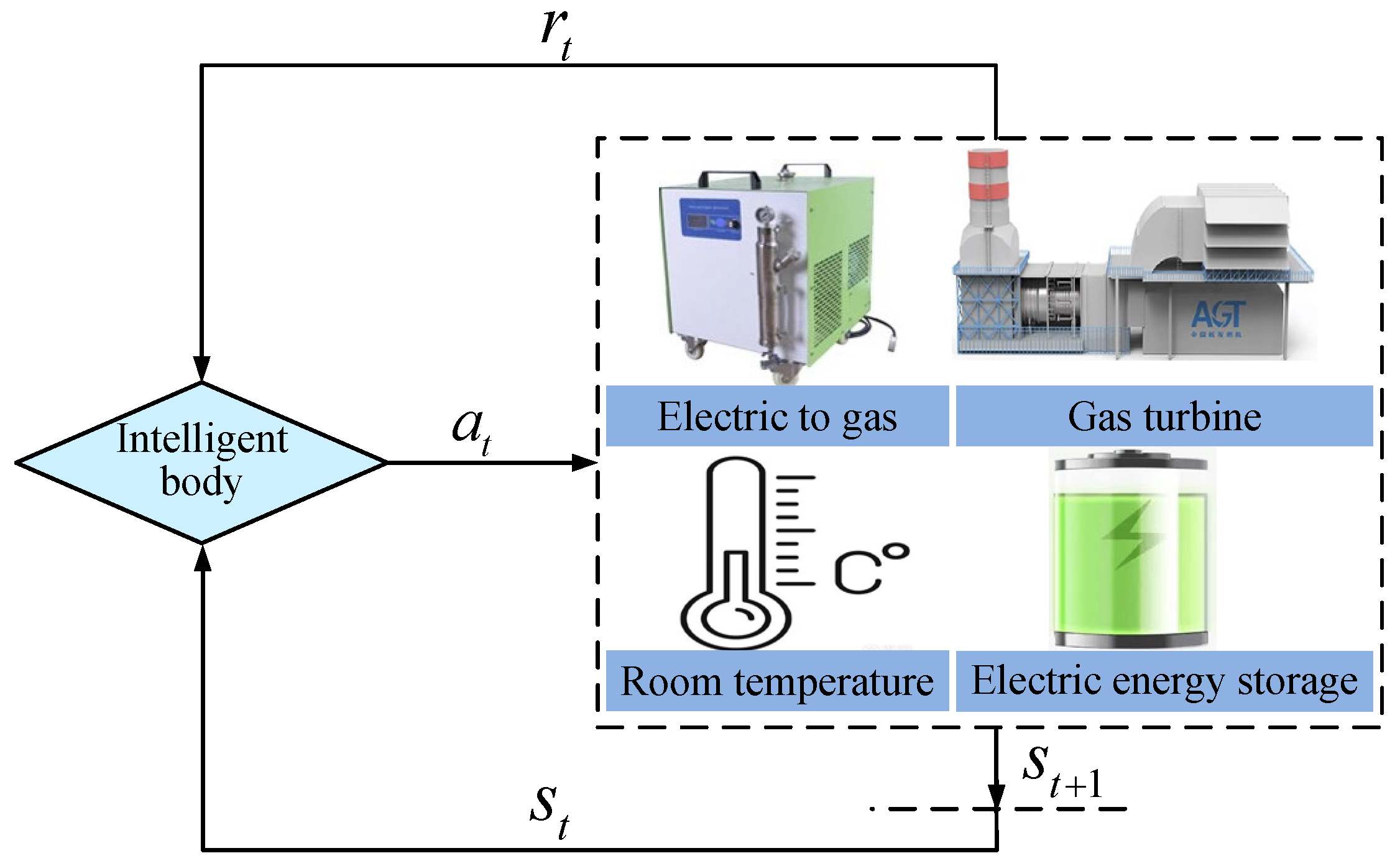
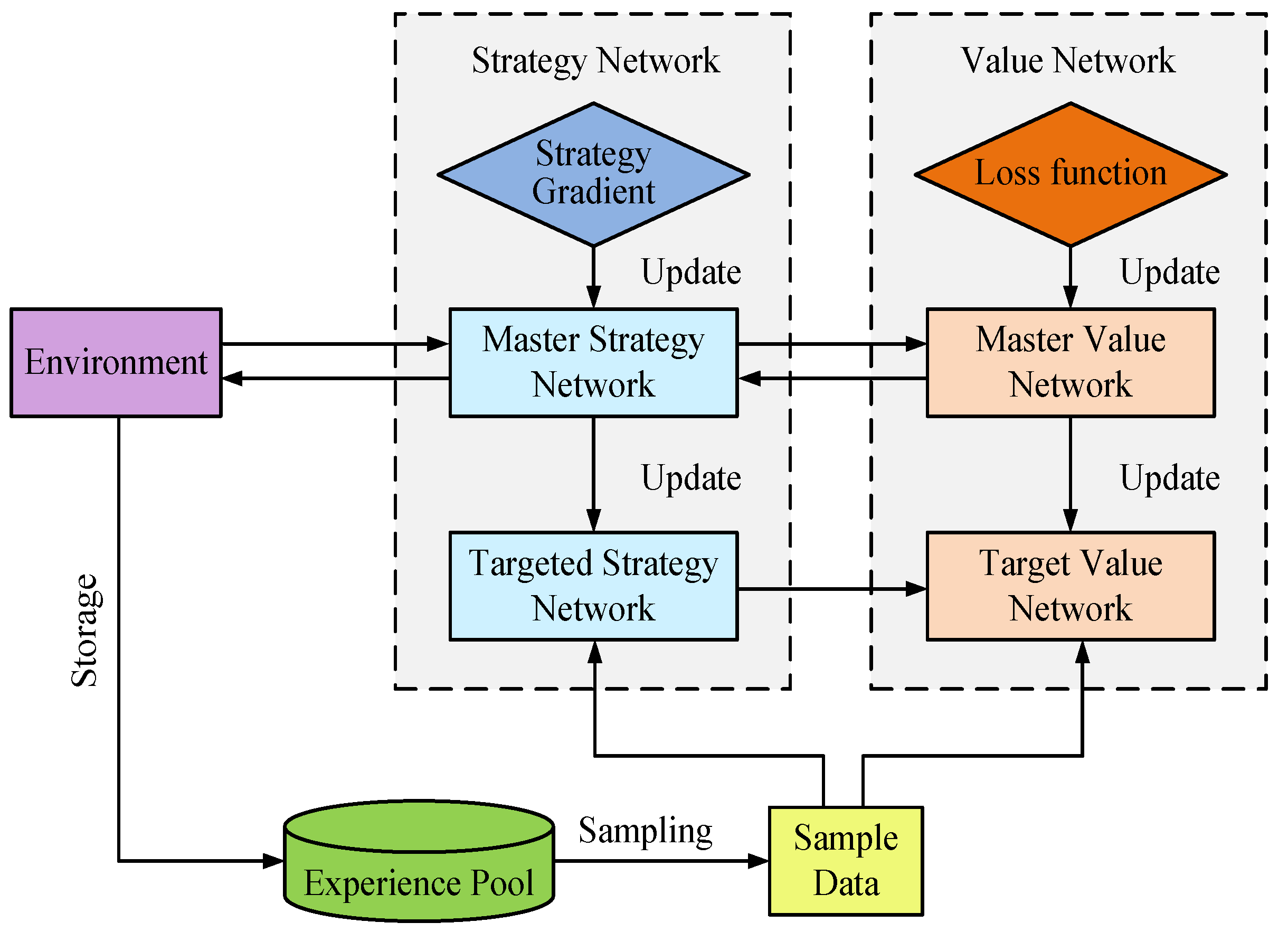
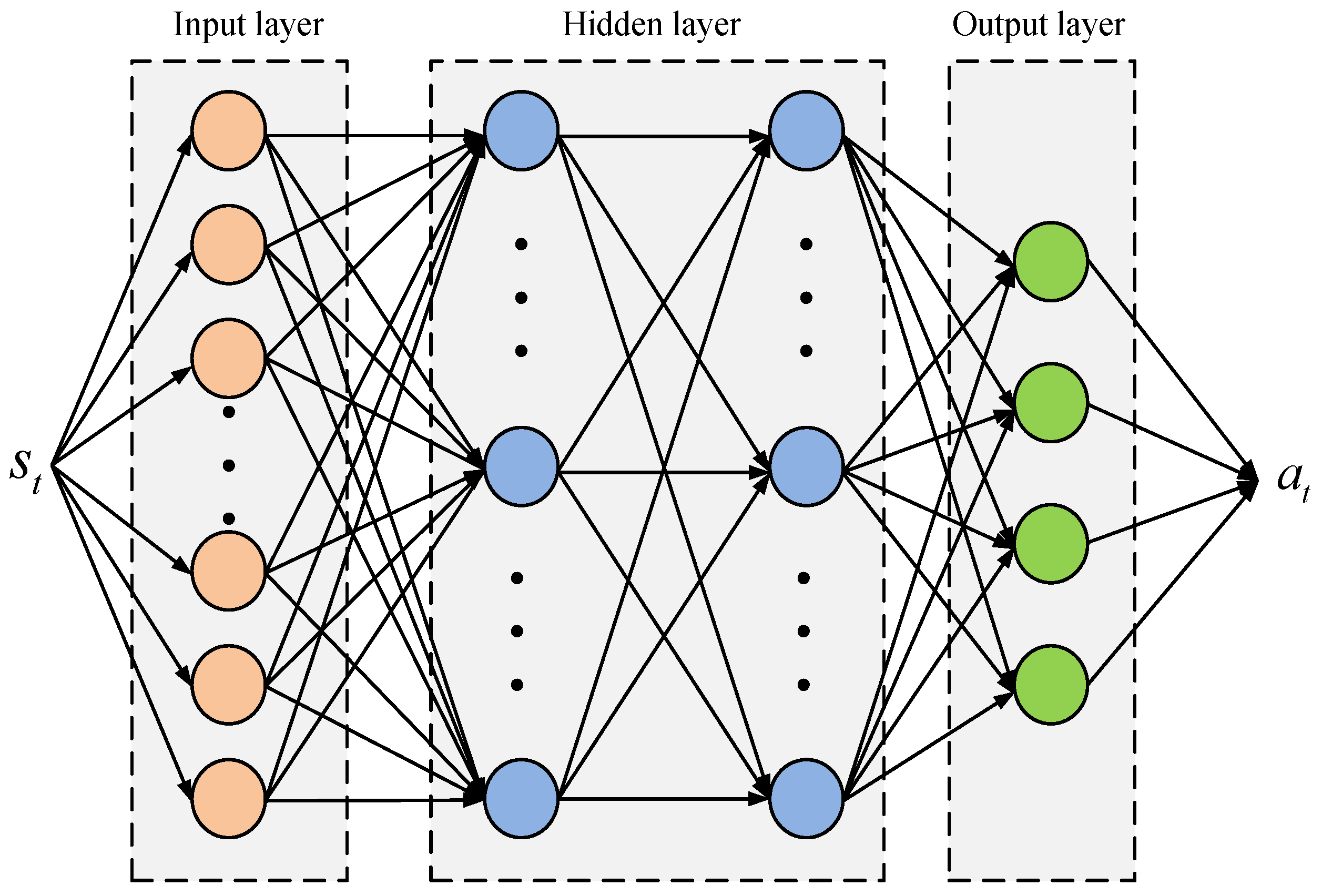
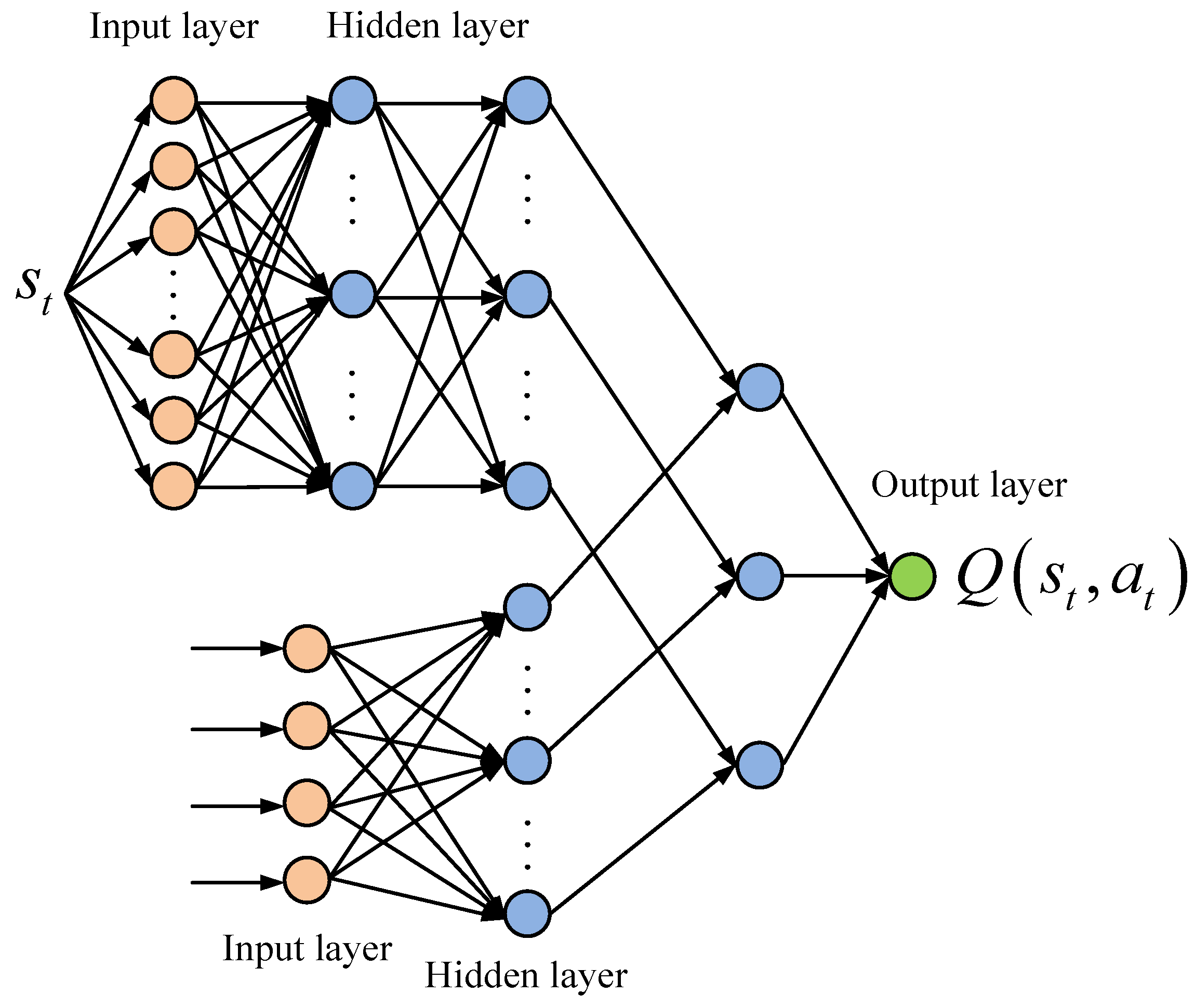
3.2. Research on Adaptive Optimization of Intelligent Building Energy Systems Based on the DDPG Algorithm
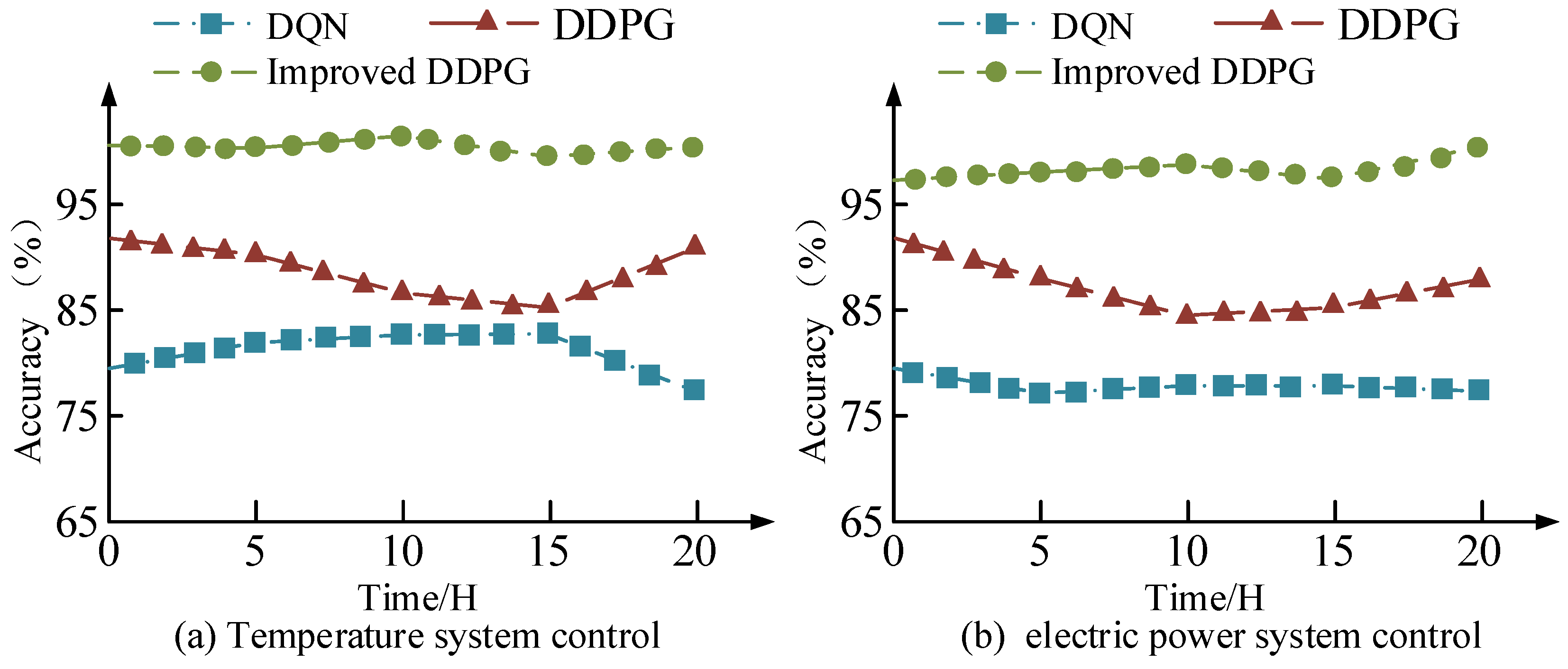
4. Analysis of Adaptive Optimization Results for Building Energy Systems Based on the DDPG Algorithm
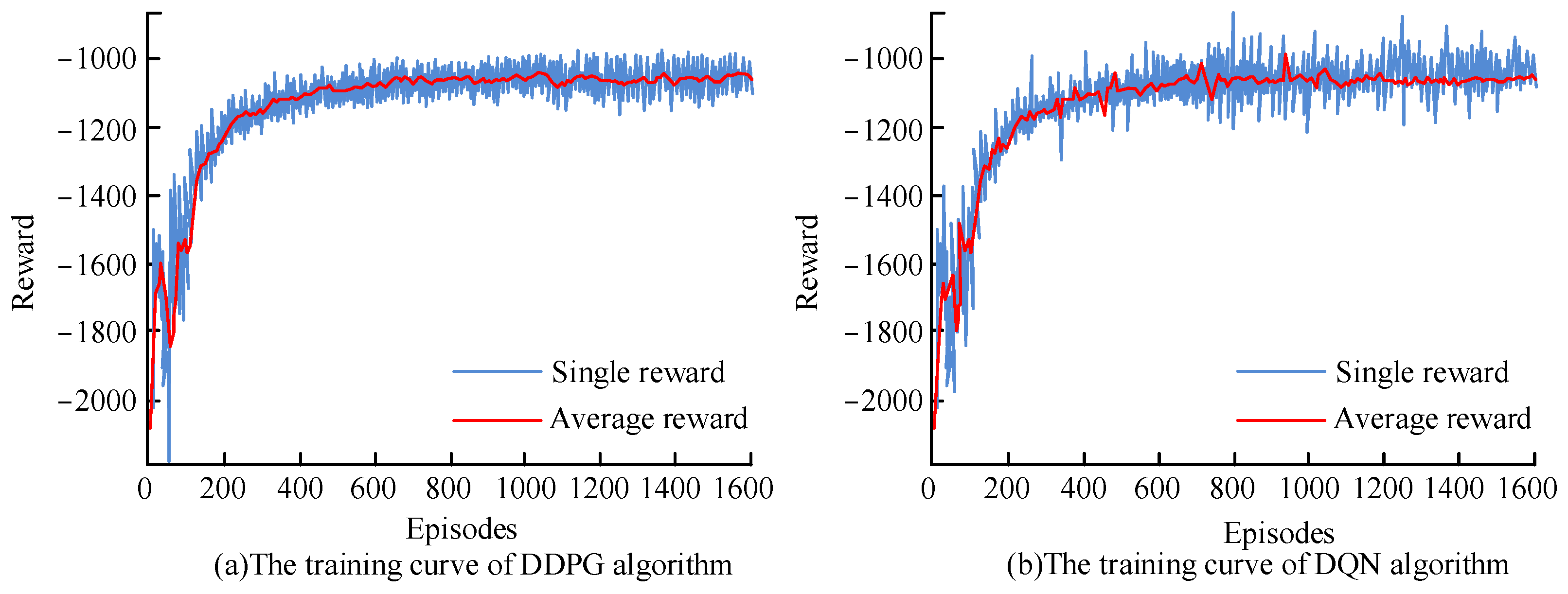
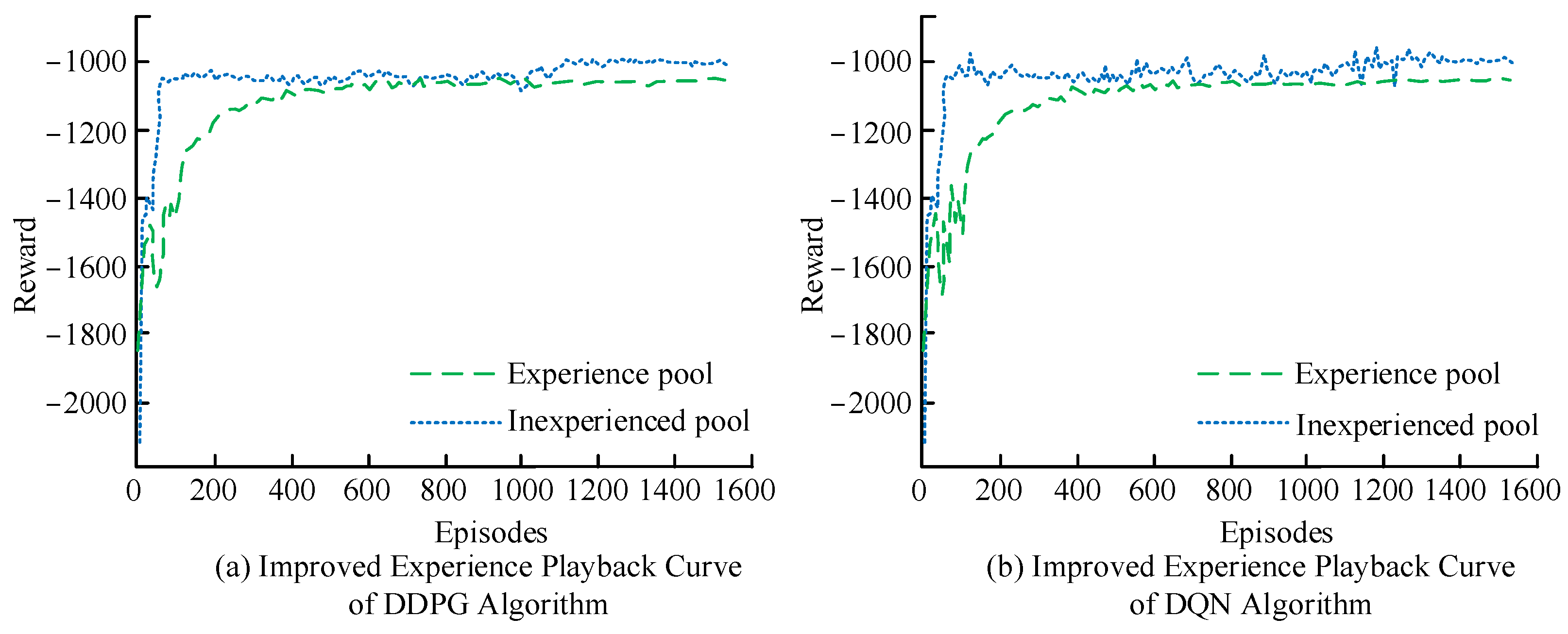
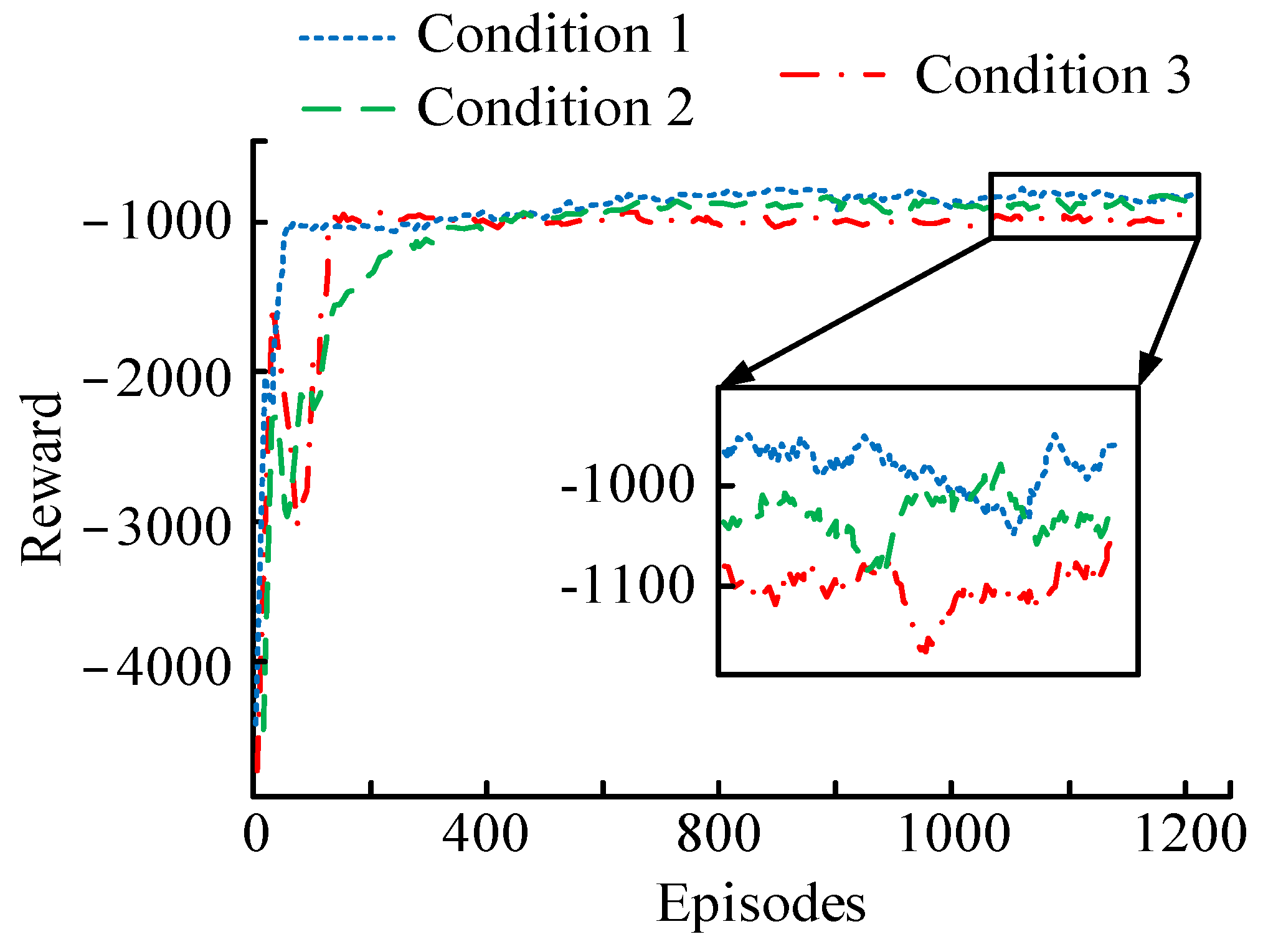
4.1. Algorithm Performance Analysis
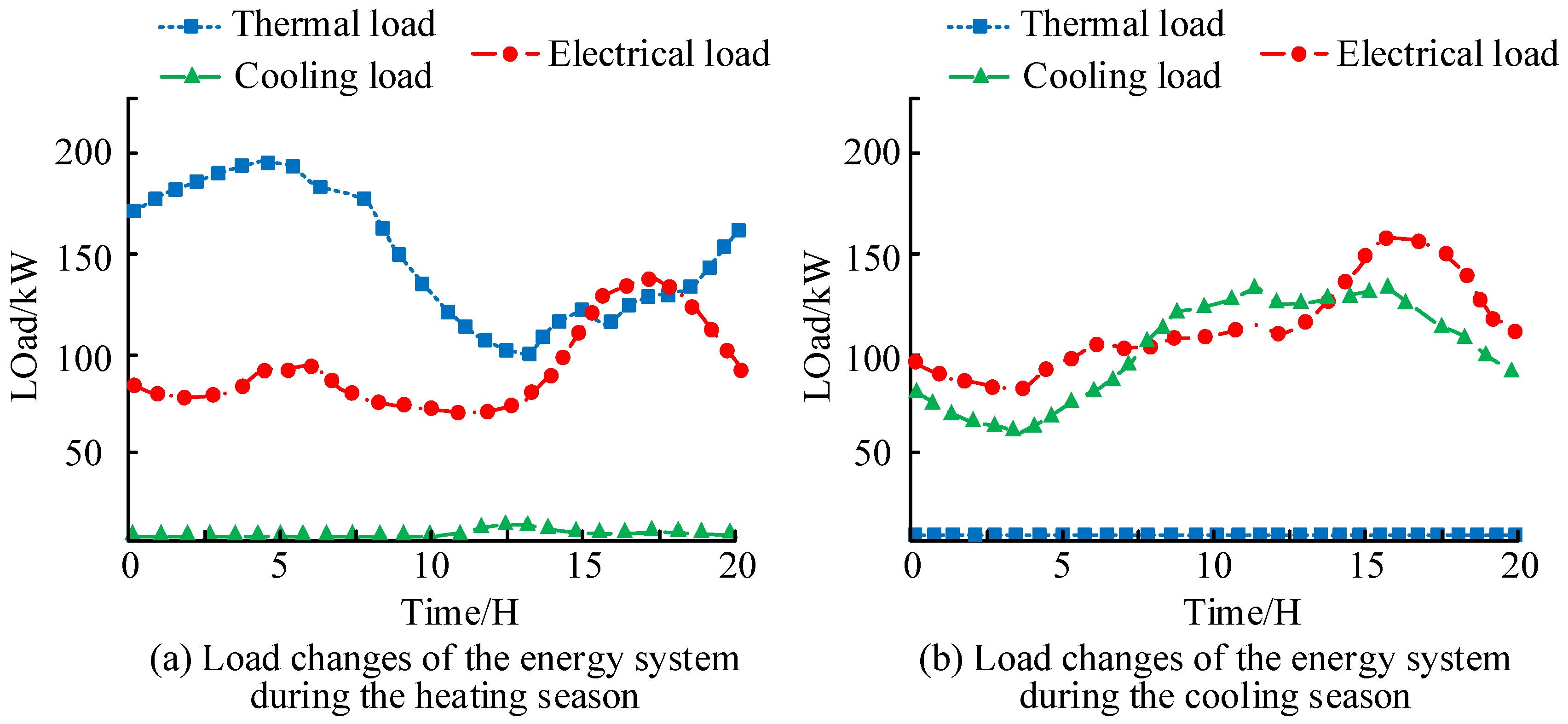
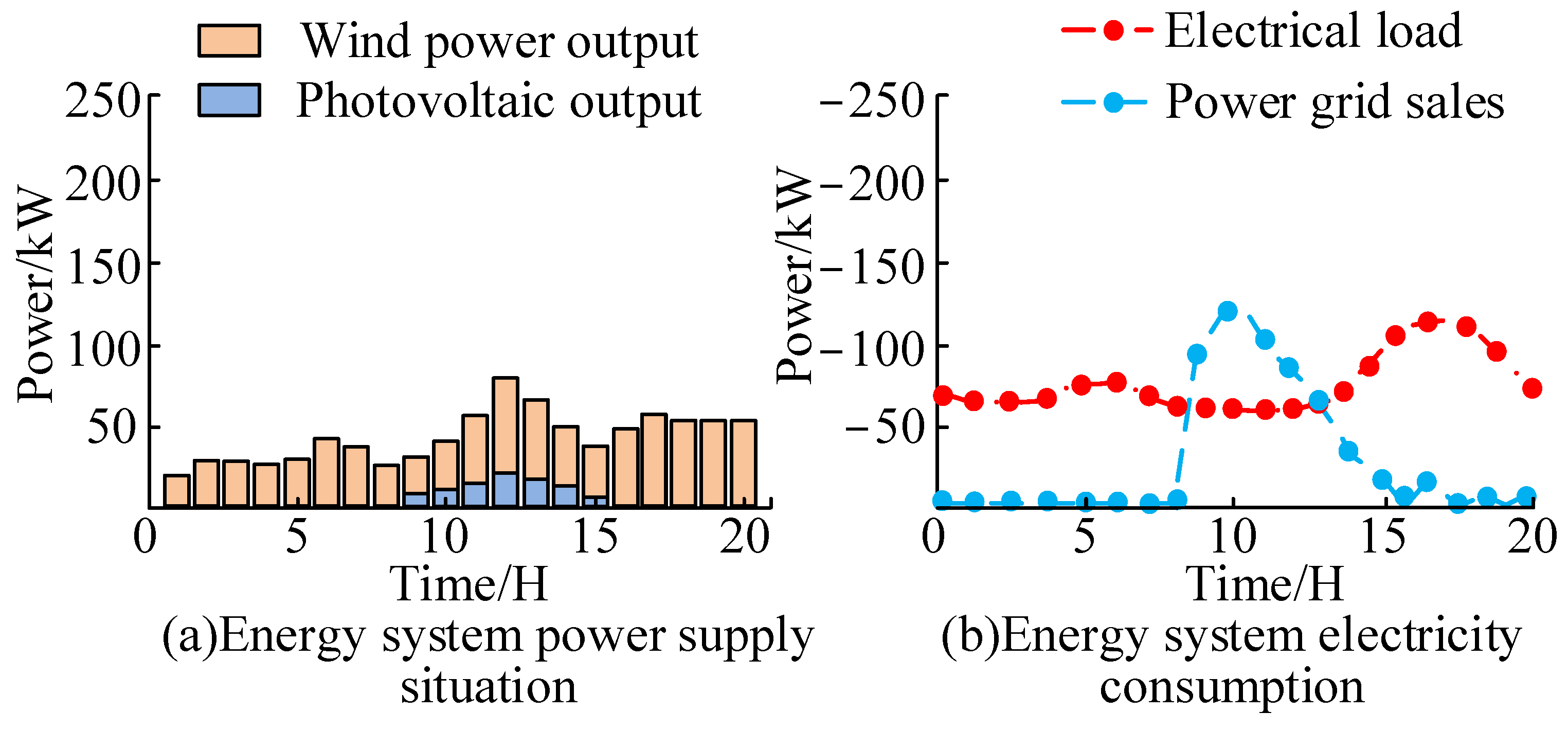
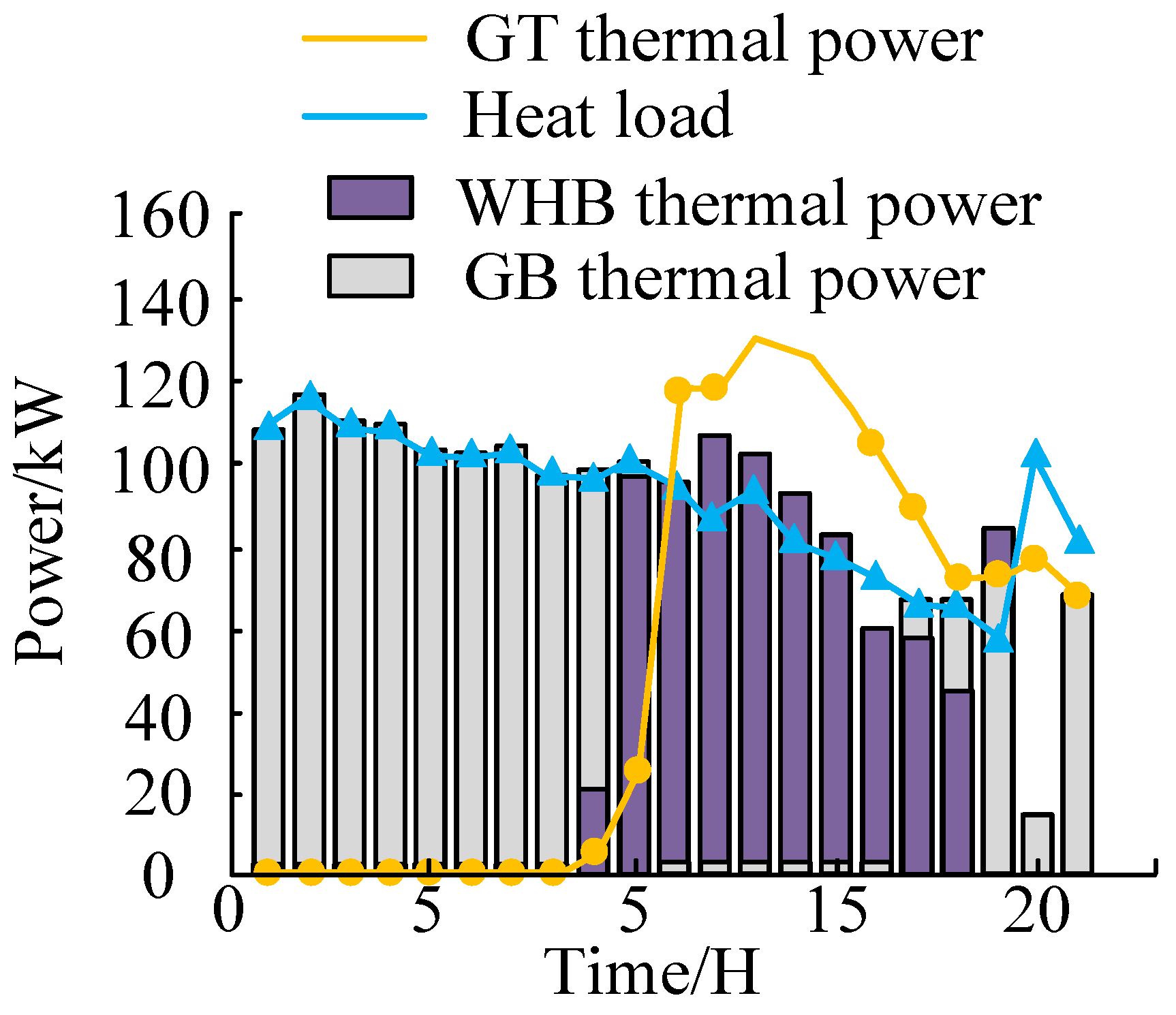
4.2. Application Effect Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, J.; Wei, Z.; Liu, K.; Quan, Z.; Li, Y. Battery-Involved Energy Management for Hybrid Electric Bus Based on Expert-Assistance Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 12786–12796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Wang, X.; Zheng, K.; Boudreau, G.; Bin Sediq, A.; Abou-Zeid, H. Intelligent Radio Access Network Slicing for Service Provisioning in 6G: A Hierarchical Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021, 69, 6063–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Dong, W.; Lv, Z.; Gu, Y.; Singh, S.; Kumar, P. Hybrid Microgrid Many-Objective Sizing Optimization with Fuzzy Decision. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 28, 2702–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Zhou, J.; Xu, G.; Wei, T.; Hu, S. Exploring Renewable-Adaptive Computation Offloading for Hierarchical QoS Optimization in Fog Computing. IEEE Trans. Comput. Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2019, 39, 2095–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgar-Dominguez, O.D.; Pourakbari-Kasmaei, M.; Mantovani, J.R.S. Adaptive Robust Short-Term Planning of Electrical Distribution Systems Considering Siting and Sizing of Renewable Energy Based DG Units. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2019, 10, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Mei, J.; Boudreau, G.; Abou-Zeid, H.; Bin Sediq, A. Situation-Aware Resource Allocation for Multi-Dimensional Intelligent Multiple Access: A Proactive Deep Learning Framework. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2020, 39, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.; Xu, H.; Qi, Z.; Song, B.; Shi, Y. Allocation method of communication interference resource based on deep reinforcement learning of maximum policy entropy. Xibei Gongye Daxue Xuebao/J. Northwestern Polytech. Univ. 2021, 39, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, T. A new adaptive controller based on distributed deep reinforcement learning for PEMFC air supply system. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 1267–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Al-Dhahir, N. Machine Learning for User Partitioning and Phase Shifters Design in RIS-Aided NOMA Networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021, 69, 7414–7428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, K.; Lipu, M.S.H.; Hannan, M.A.; Abdullah, M.A.; Jern, K.P.; Begum, R.A.; Mansur, M.; Muttaqi, K.M.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Dong, Z.Y. Intelligent Controllers and Optimization Algorithms for Building Energy Management Towards Achieving Sustainable Development: Challenges and Prospects. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 41577–41602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Luo, X.; Gao, M.; Abbas, A.; Xu, Y.-P.; Pouramini, S. Minimization of energy consumption by building shape optimization using an improved Manta-Ray Foraging Optimization algorithm. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 1068–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, C.; Balachander, K. Design of power system stabilizer for multi- machine systems using modified swarm optimization algorithm with wind energy generation. J. Green Eng. 2021, 111, 156–178. [Google Scholar]
- Senthilkumar, G.; Chitra, M. An ensemble dynamic optimization based inverse adaptive heuristic critic in IaaS cloud computing for resource allocation. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 39, 7521–7535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheisarnejad, M.; Khooban, M.H. An Intelligent Non-Integer PID Controller-Based Deep Reinforcement Learning: Implementation and Experimental Results. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 3609–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Yuan, L.; Li, S.; Liu, C.H.; Cheng, X.; Wang, G. Active learning for domain adaptation: An energy-based approach. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2022, 36, 8708–8716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Cui, M.; Li, F.F.; Yin, S.; Wang, X. Model-Free Emergency Frequency Control Based on Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 17, 2336–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, C.; Pan, Y.; Dai, W.; Kawsar, I.; Li, Z.; Wang, G. Trajectory optimization of an electric vehicle with minimum energy consumption using inverse dynamics model and servo constraints. Mech. Mach. Theory 2023, 181, 105185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lu, J. Nonlinear Multivariable Control of a Dividing Wall Column Using a Different-Factor Full-Form Model-Free Adaptive Controller. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 1897–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, K.; Govindarajan, U. Optimal power flow control of hybrid renewable energy system with energy storage: A WOANN strategy. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2019, 11, 015501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z. Modeling and optimization of urban rail transit scheduling with adaptive fruit fly optimization algorithm. Open Phys. 2019, 17, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, A.; Geng, T.; Ng, S.X.; Liang, W. A Continuous Policy Learning Approach for Hybrid Offloading in Backscatter Communication. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 25, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barma, M.; Modibbo, U.M. Multiobjective mathematical optimization model for municipal solid waste management with economic analysis of reuse/recycling recovered waste materials. J. Comput. Cogn. Eng. 2022, 1, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Qiu, J. A Customized Voltage Control Strategy for Electric Vehicles in Distribution Networks with Reinforcement Learning Method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 6852–6863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Zou, Y.; Xu, J.; Hoang, D.T.; Lyu, B.; Niyato, D. Optimization-Driven Hierarchical Learning Framework for Wireless Powered Backscatter-Aided Relay Communications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 21, 1378–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarabaggio, P.; Carli, R.; Dotoli, M. Noncooperative Equilibrium-Seeking in Distributed Energy Systems Under AC Power Flow Nonlinear Constraints. IEEE Trans. Control. Netw. Syst. 2022, 9, 1731–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhuri, S.; Adeniye, S.; Sen, A. Distribution alignment using complement entropy objective and adaptive consensus-based label refinement for partial domain adaptation. Artif. Intell. Appl. 2023, 1, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirimtat, A.; Krejcar, O.; Ekici, B.; Tasgetiren, M.F. Multi-objective energy and daylight optimization of amorphous shading devices in buildings. Sol. Energy 2019, 185, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Numerical Value |
|---|---|
| Building thermal-equivalent resistance | N~(18, 0.5) |
| Building thermal-equivalent capacitance | N~(0.525, 0.1) |
| Overlay noise | N~(0.5, 0.2) |
| Explore factors | U~(0, 1) |
| Value network learning rate | 1.00 × 10−04 |
| Number of hidden layer neurons of the value network | [300,600,600,300] |
| Policy network learning rate | 1.00 × 10−04 |
| Number of hidden layer neurons in the policy network | [300, 600] |
| Target network update factor | 1.00 × 10−03 |
| Initial proportion of the superimposed noise | 1 |
| Superimposed noise decay factor | 0.997 |
| Superlay noise proportion minimum | 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Xue, Z. Adaptive Optimization Design of Building Energy System for Smart Elderly Care Community Based on Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient. Processes 2023, 11, 2155. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072155
Liu C, Xue Z. Adaptive Optimization Design of Building Energy System for Smart Elderly Care Community Based on Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient. Processes. 2023; 11(7):2155. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072155
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chunmei, and Zhe Xue. 2023. "Adaptive Optimization Design of Building Energy System for Smart Elderly Care Community Based on Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient" Processes 11, no. 7: 2155. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072155
APA StyleLiu, C., & Xue, Z. (2023). Adaptive Optimization Design of Building Energy System for Smart Elderly Care Community Based on Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient. Processes, 11(7), 2155. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072155








