A Mechanistic Model Based on Statistics for the Prediction of a Converter’s End-Point Molten Steel Temperature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Establishment of a Converter Temperature Prediction Model
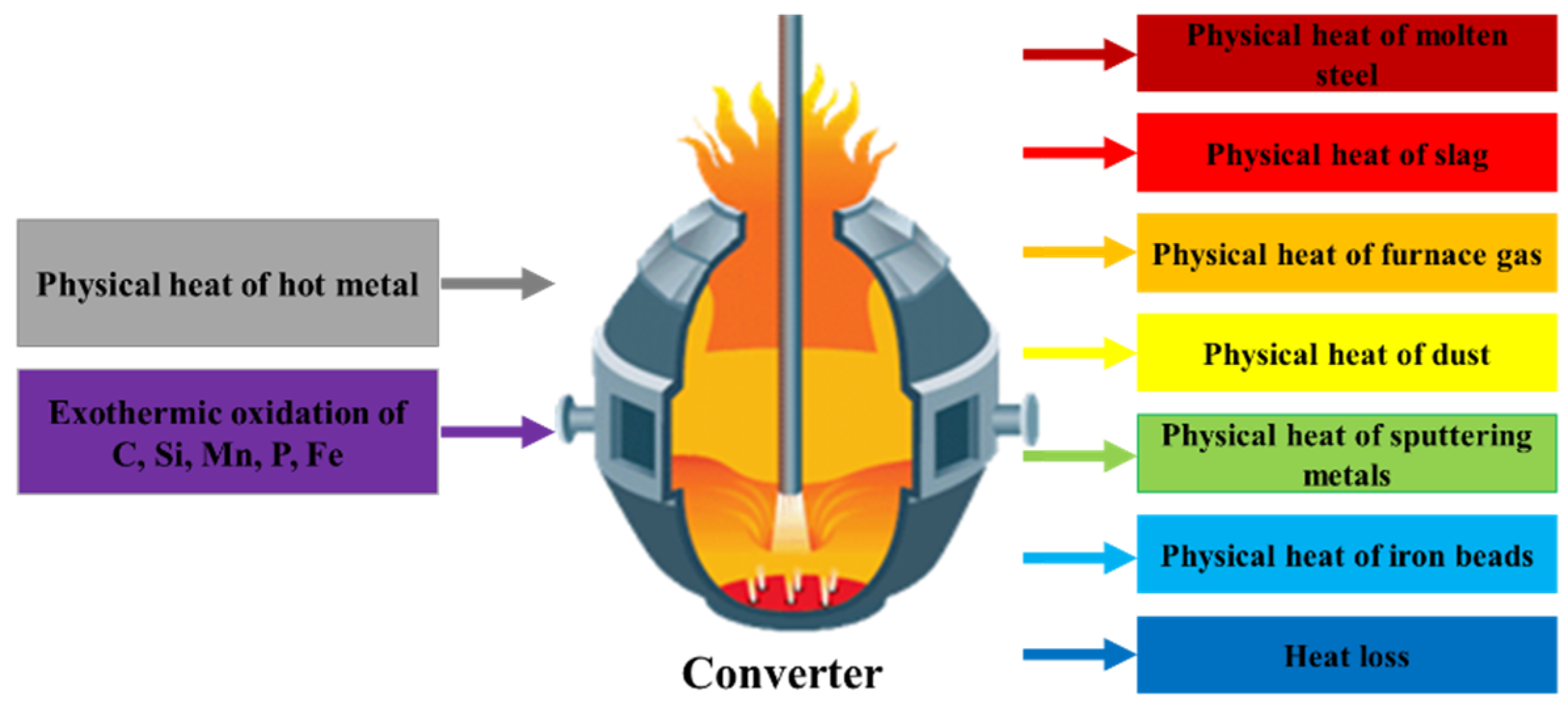
2.1. The Heat Balance of a Converter
- (1)
- Contents of carbon, silicon, manganese, and phosphorus in the molten steel in the melt pool;
- (2)
- Quantity of steel slag and molten steel;
- (3)
- Heat loss coefficient.
2.2. Calculation Model of Molten Steel Element Content in Molten Pool
2.3. Calculation of Steel Slag Quantity
- (1)
- Due to the infiltration of FeO in the slag to the interior of the lime, the lime gradually dissolves in the slag, thus increasing the CaO content at the interface;
- (2)
- SiO2 in the slag is enriched on the lime surface and reacts with CaO to form a 2CaO–SiO2 layer;
- (3)
- FeO continues to diffuse from the slag into the reaction interface;
- (4)
- The liquid-phase layer of CaO–FeO with a high FeO content is formed between the 2CaO–SiO2 layer and the lime;
- (5)
- The 2CaO–SiO2 layer peels off and dissolves in the slag under the action of the CaO–FeO liquid-phase layer with a high FeO content.
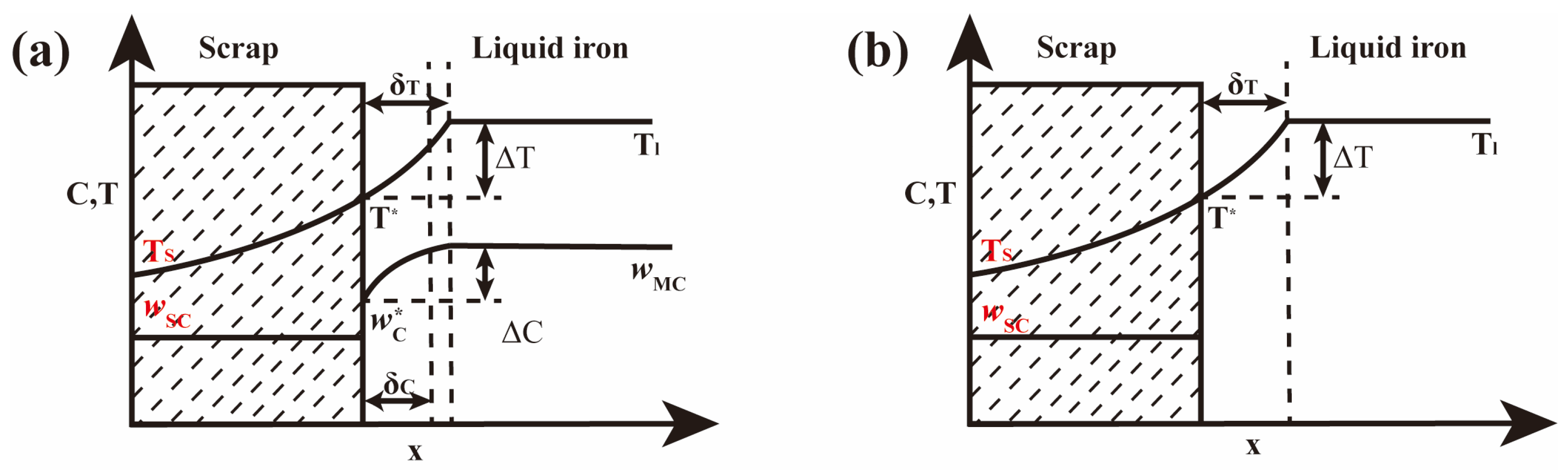
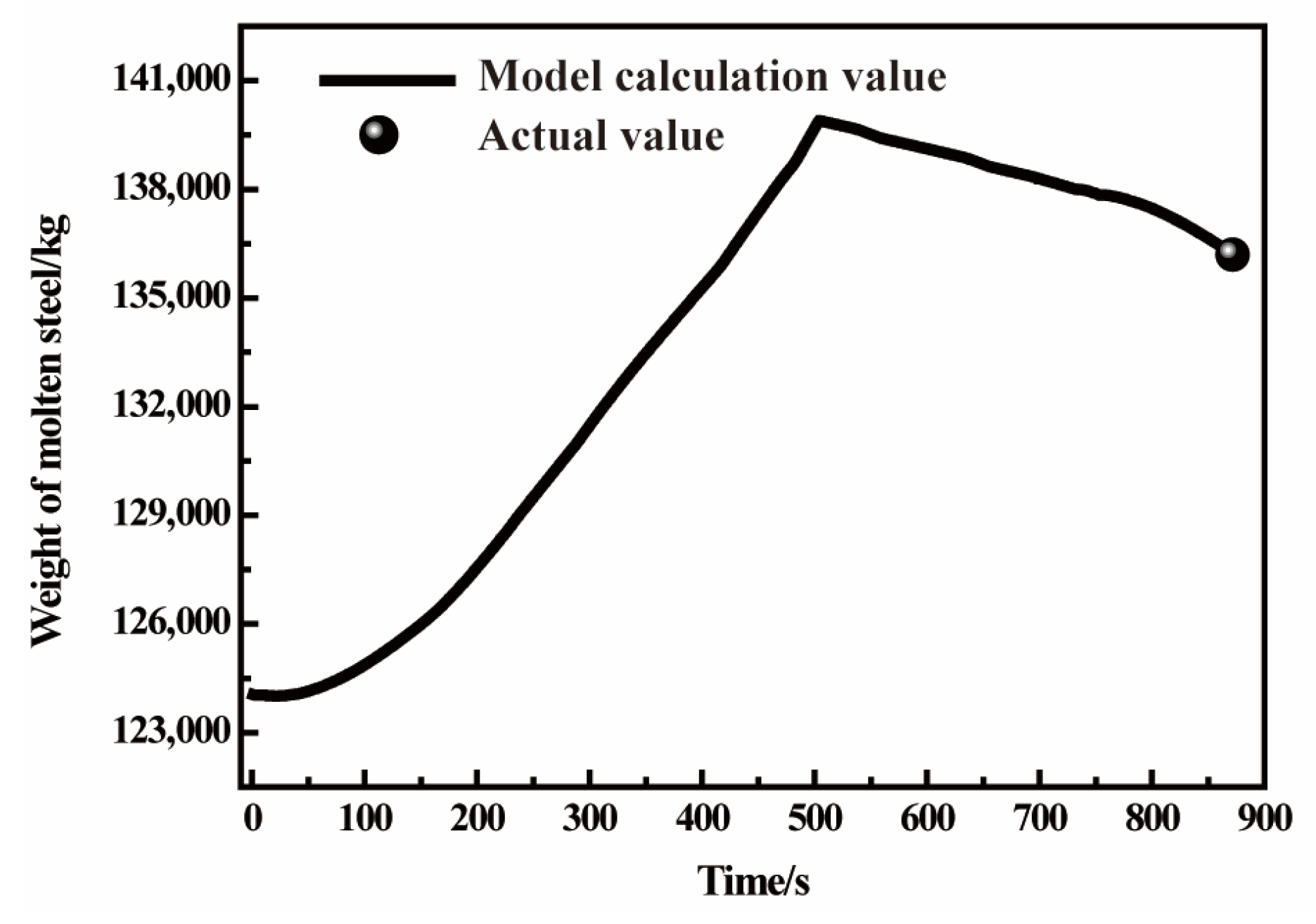
2.4. Calculation of Molten Steel Quantity in Molten Pool
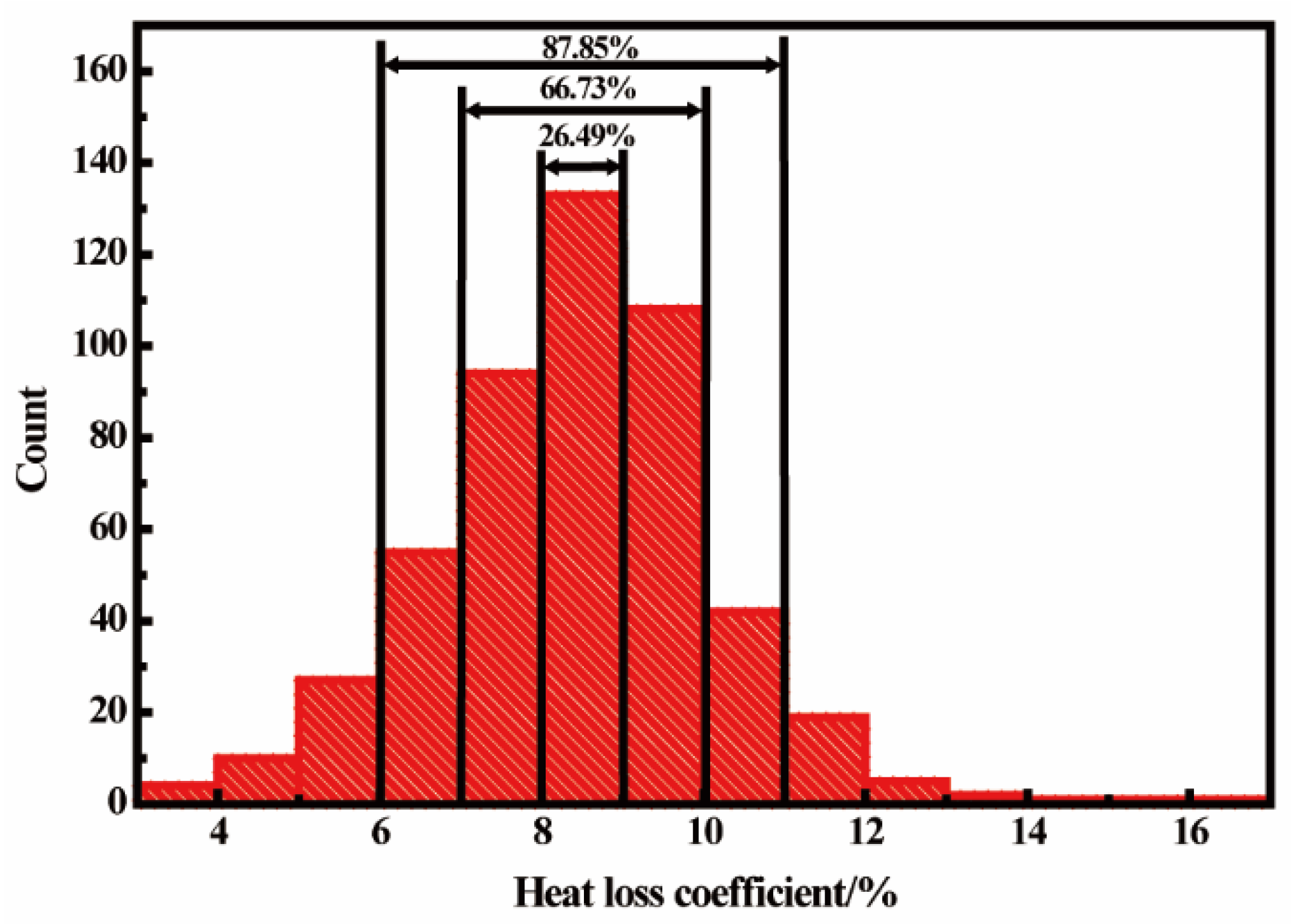
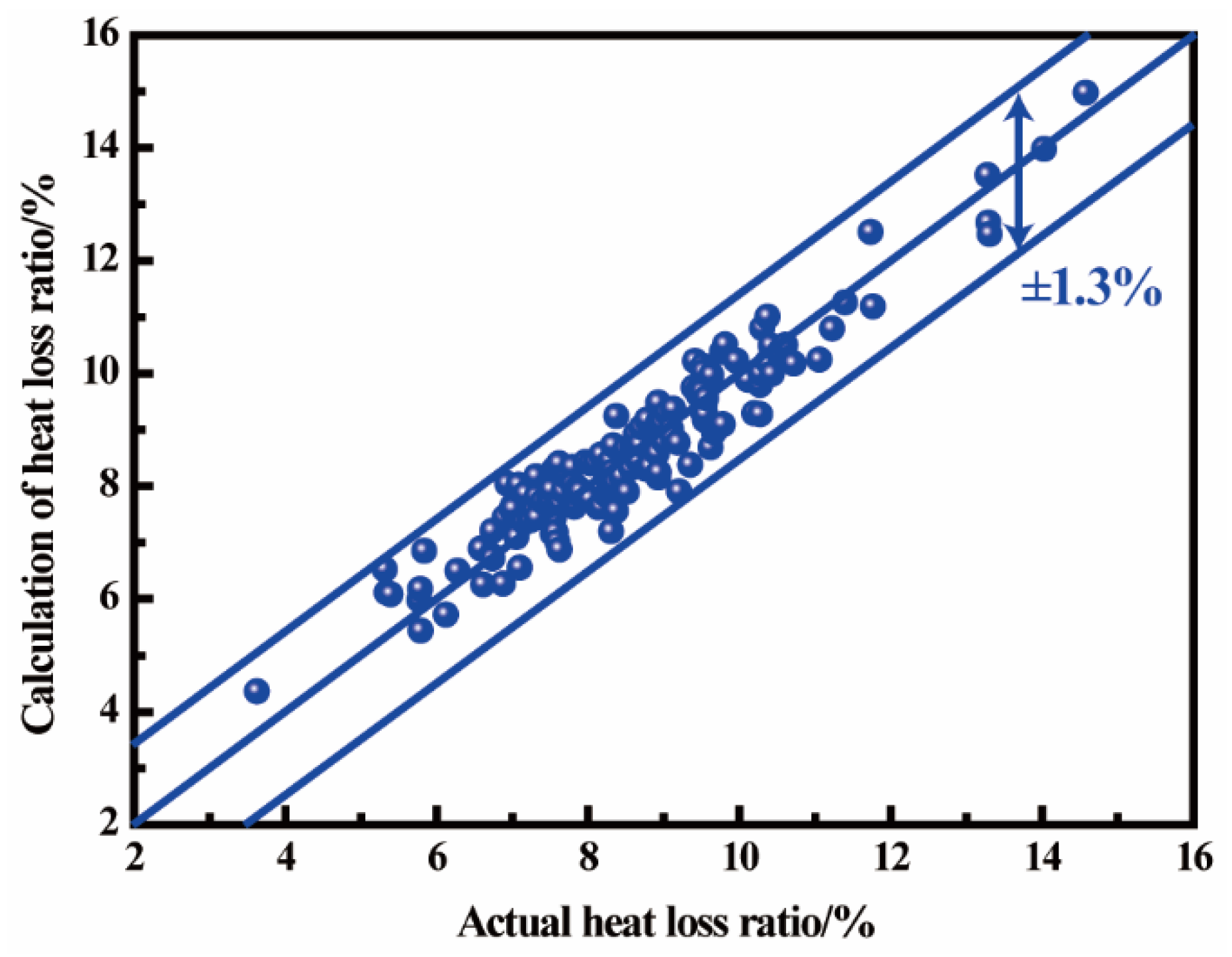
2.5. Calculation of Heat Loss Coefficient
3. Model Validation and Discussion
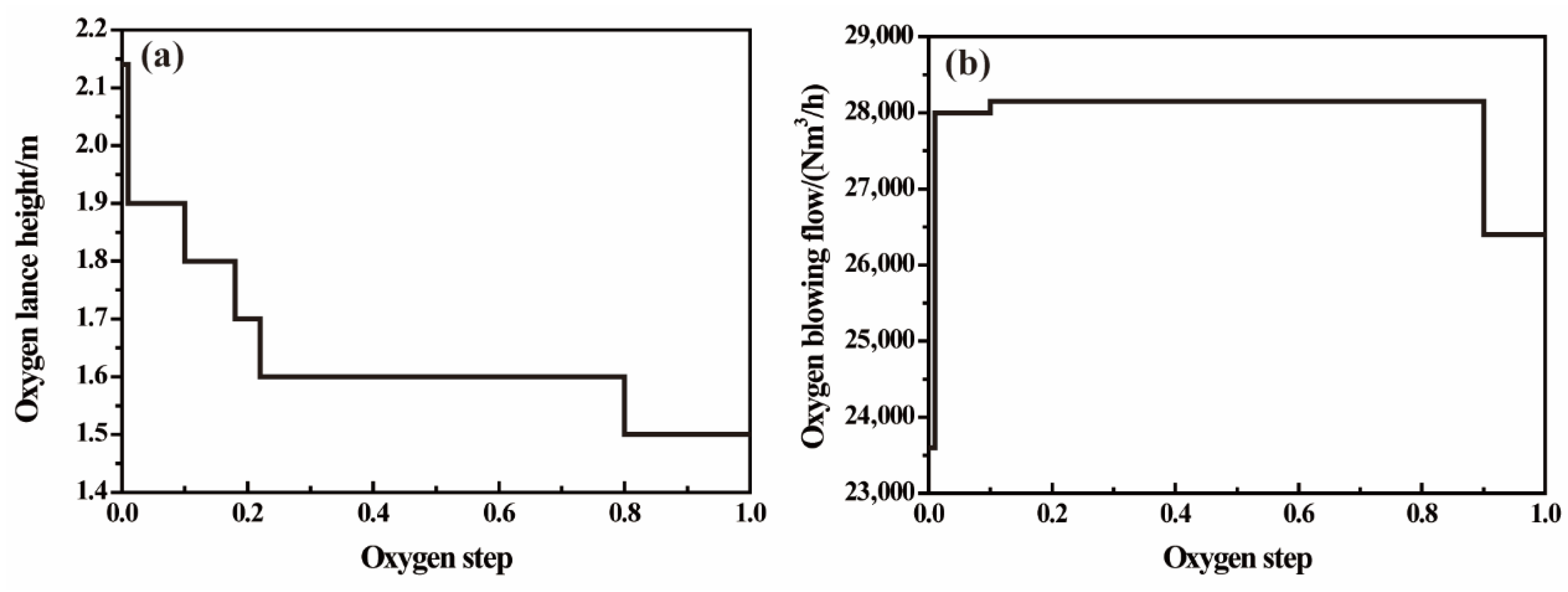
3.1. Implementation of the Model Using Finite Difference Method
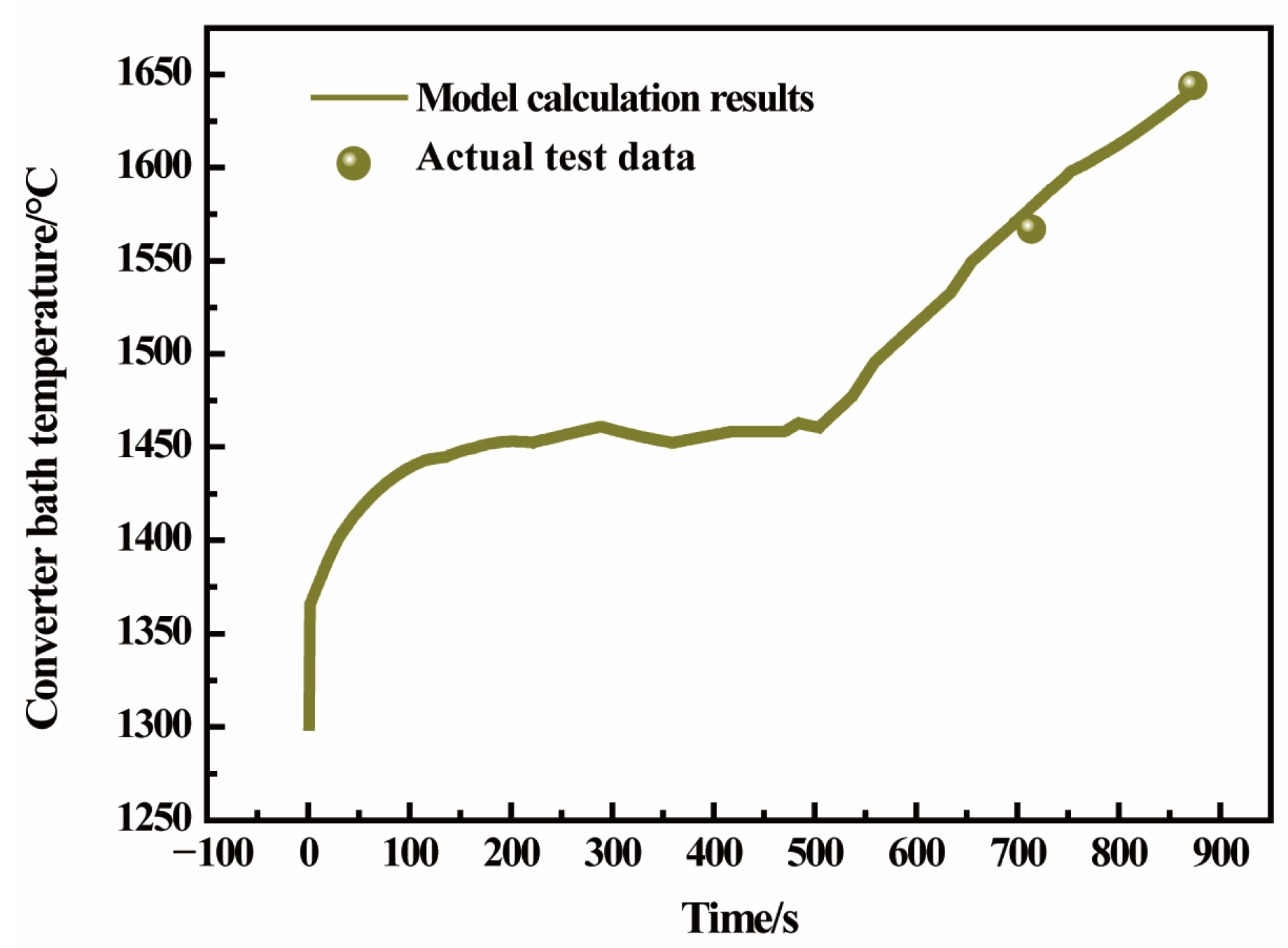
3.2. Composition and Temperature Verification in Converter-Blowing Process
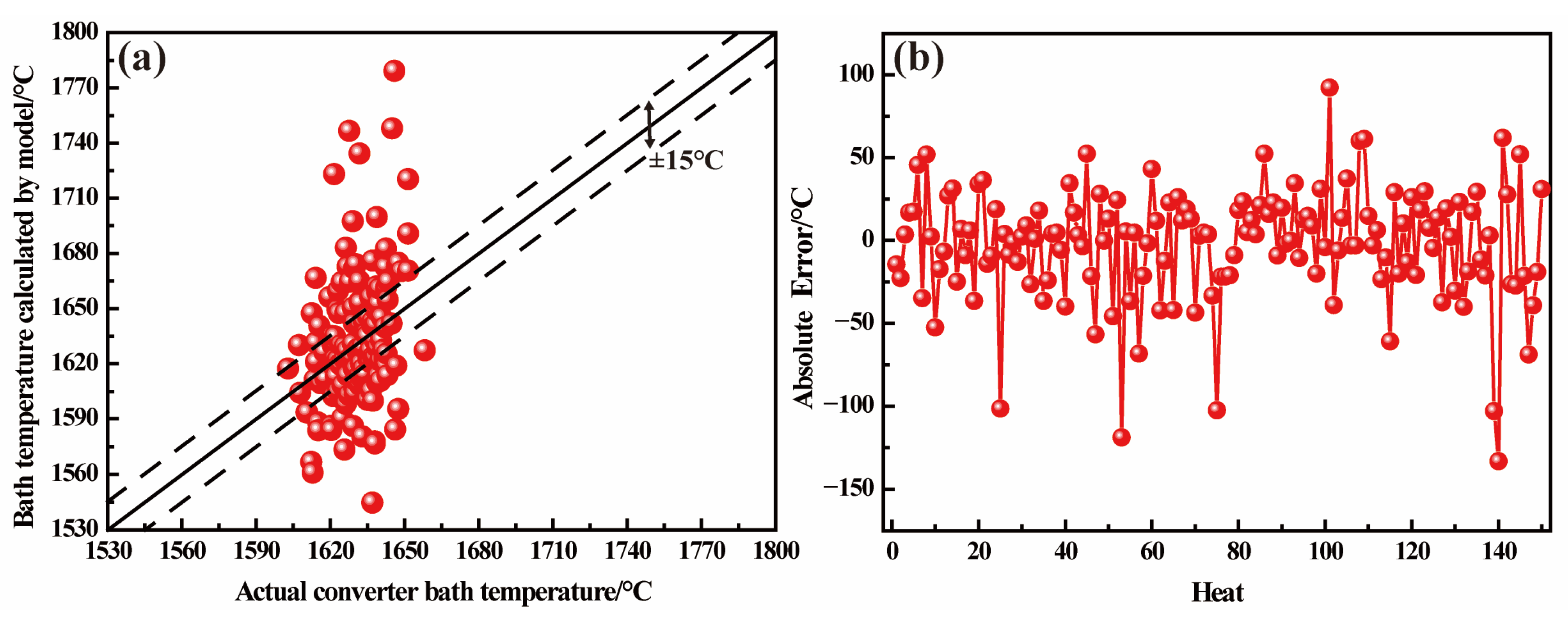
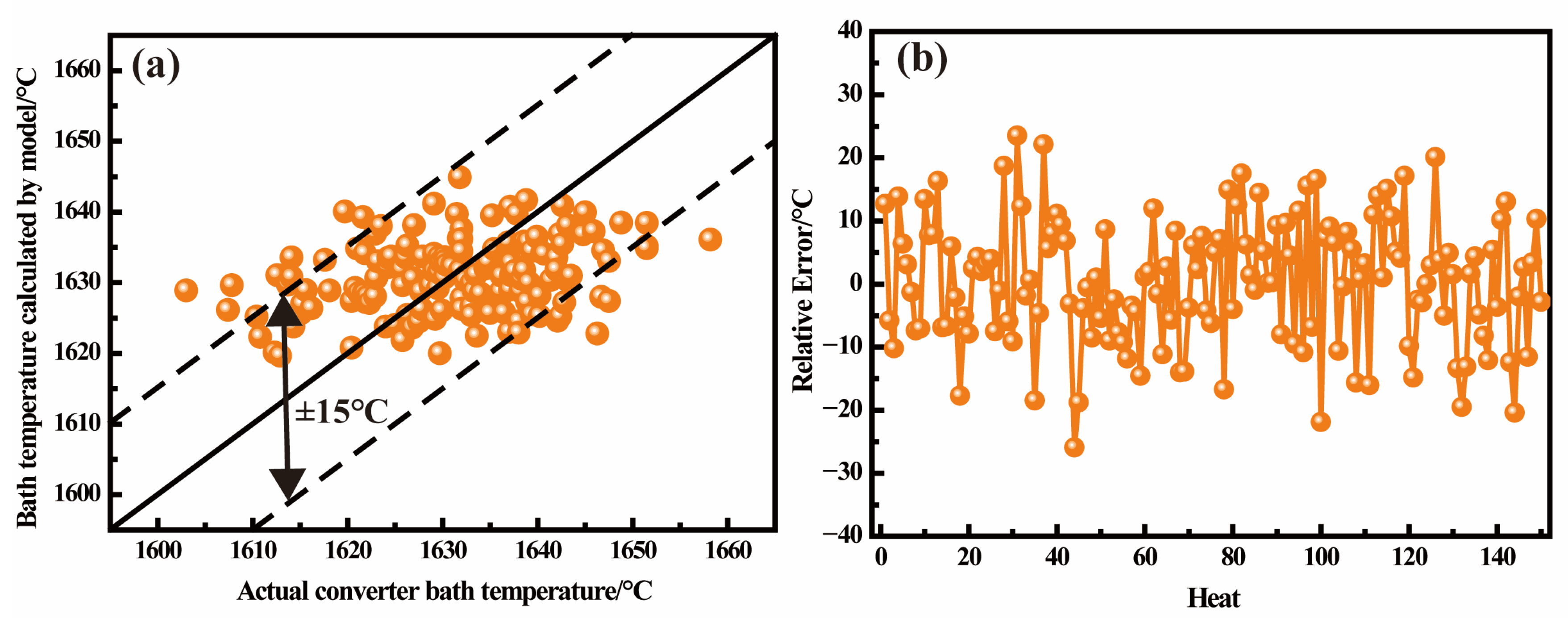
3.3. Endpoint Temperature Hit Rate Verification
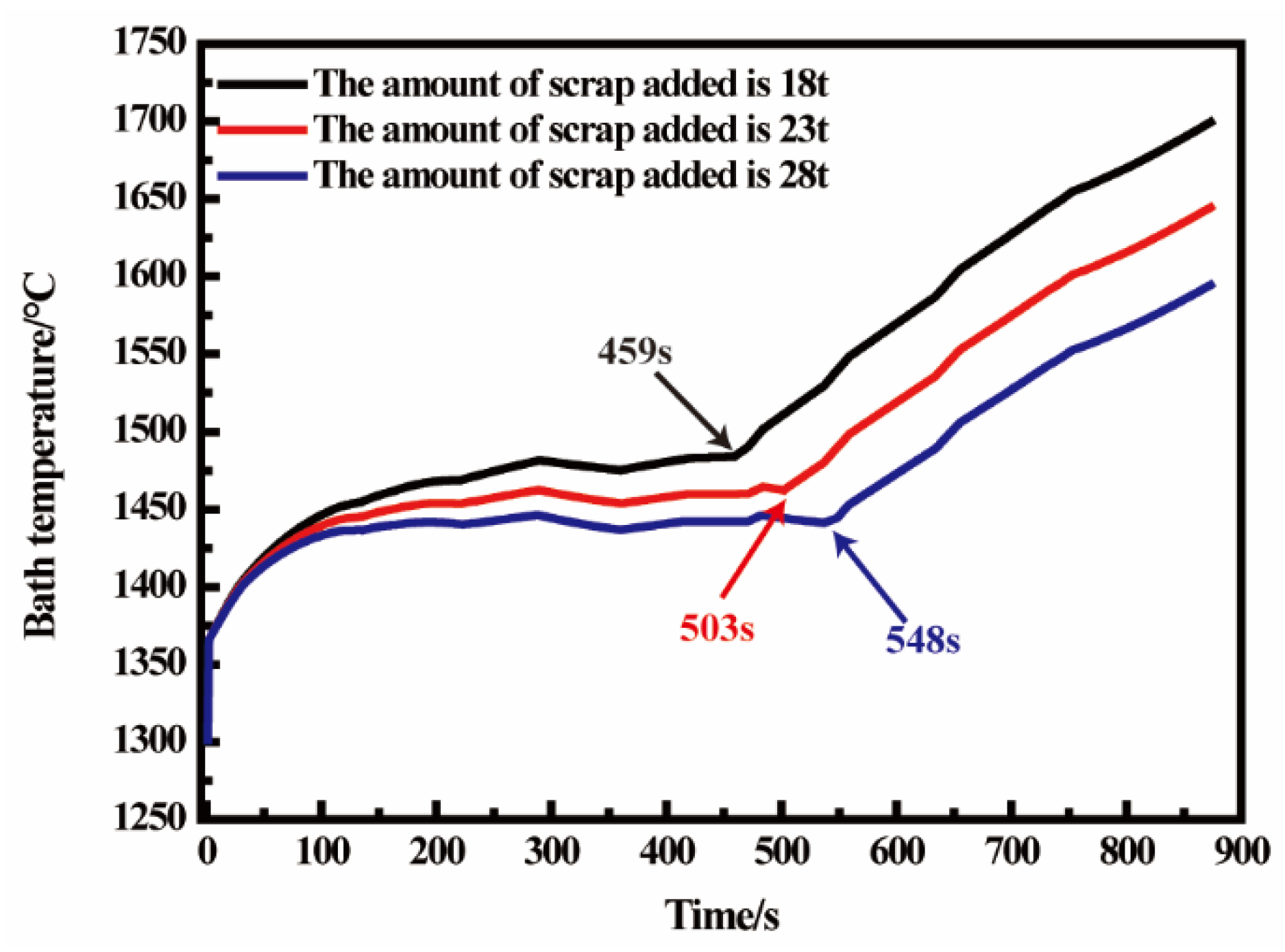
3.4. The Effect of Scrap Weight on Temperature of Molten Pool
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ocheri, C.; Ajani, O.O.; Daniel, A.; Agbo, N. The steel industry: A stimulus to national development. J. Powder Metall. Min. 2017, 6, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Mattom, J.; Herrick, P.; Agrawal, V.M. An Overview of Indian Steel Industry and Its Impact on Construction Sector. In Recent Trends in Civil Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, V. Effective Project Management in Steel Industry. Asian J. Manag. 2017, 8, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.C.; Fu, Z.X. Current situation of energy consumption and measures taken for energy saving in the iron and steel industry in China. Energy 2010, 35, 4356–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, C.J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.-C. Industrial IoT for intelligent steelmaking with converter mouth flame spectrum information processed by deep learning. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 16, 2640–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H. Converter practice in China with respect to steelmaking and ferroalloys. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. 2019, 128, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Wei, G.; Zhu, R.; Wu, W.; Jiang, J.J.; Feng, C.; Dong, J.F.; Hu, S.Y.; Liu, R.Z. Utilization of carbon dioxide injection in BOF–RH steelmaking process. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 34, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, G. Energy saving technologies and productive efficiency in the Chinese iron and steel sector. Energy 2008, 33, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, K.; Zhu, L.; Han, Y. Research on terminal control model of intelligent mining of flame spectral information of converter mouth in late smelting stage. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2021, 48, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yang, N.; You, X.; Xing, K.; Hu, Y. A temperature prediction model of converters based on gas analysis. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2011, 2, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tang, L.; Liu, J. A stacked autoencoder with sparse Bayesian regression for end-point prediction problems in steelmaking process. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2019, 17, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branca, T.A.; Fornai, B.; Colla, V.; Murri, M.M.; Streppa, E.; Schröder, A.J. The Challenge of Digitalization in the Steel Sector. Metals 2020, 10, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.L.; Jacobs, M.; Dijkstra, J.; van Laar, H.; Cant, J.P.; Tulpan, D.; Ferguson, N. Synergy between mechanistic modelling and data-driven models for modern animal production systems in the era of big data. Animal 2020, 14, s223–s237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Zhang, L. Prediction model of end-point phosphorus content in BOF steelmaking process based on PCA and BP neural network. J. Process Control 2018, 66, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.-X.; Lin, W.-H.; Sun, J.-K.; Zhang, J.-S.; Zhang, D.-Z.; Feng, X.-M.; Liu, Q. Prediction model of end-point phosphorus content for BOF based on monotone-constrained BP neural network. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2022, 29, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chang, J.; Ju, Q.-P.; Xie, F.-M.; Wang, B.; Li, H.-W.; Wang, B.; Lu, X.-C.; Fu, G.-Q.; Liu, Q. Prediction model of end-point manganese content for BOF steelmaking process. ISIJ Int. 2012, 52, 1585–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Han, M.; Wang, J. Applying input variables selection technique on input weighted support vector machine modeling for BOF endpoint prediction. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2010, 23, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, W. Real time prediction for converter gas tank levels based on multi-output least square support vector regressor. Control Eng. Pract. 2012, 20, 1400–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Liu, H.; Xiong, Q.; Chen, Z. Just-in-time-learning based prediction model of BOF endpoint carbon content and temperature via vMF mixture model and weighted extreme learning machine. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2021, 154, 107488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, Q.M.; Wang, X.S.; Wang, H. Endpoint prediction of BOF steelmaking based on BP neural network combined with improved PSO. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2016, 51, 475–480. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, S.K.; Imam, R.; Ramanathan, K.; Pushpavanam, S. Sensitivity analysis and kinetic parameter estimation in a three way catalytic converter. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 3779–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltsakis, G.C.; Konstantinidis, P.A.; Stamatelos, A.M. Development and application range of mathematical models for 3-way catalytic converters. Metals 1997, 12, 161–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Gao, F.; Xing, L.; Chu, J.; Bao, Y. Continuous Prediction Model of Carbon Content in 120 t Converter Blowing Process. Metals 2022, 12, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, B.K.; Brooks, G.; Rhamdhani, M.A.; Li, Z.; Schrama, F.N.H.; Sun, J. Dynamic model of basic oxygen steelmaking process based on multi-zone reaction kinetics: Model derivation and validation. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2018, 49, 537–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, S. Dissolution behavior of lime into steelmaking slag. ISIJ Int. 2017, 57, 1670–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Xue, Z.; Zhu, R.; Mou, Q.; Zhu, H. Evolution of physicochemical properties of quick lime at converter-smelting temperature. High Temp. Mater. Process. 2021, 40, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, L.M.; de Oliveira, H.C.C.; Telles, V.B.; Junca, E.; Vieira, E.A.; de Oliveira, J.R. Influence of lime particle and slag properties on lime dissolution in BOF converter. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 14878–14886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Wang, N.; Chen, M.; Zhang, G. Dissolution behaviour of limestone in converter slag: Evolution of microstructure and reaction interface. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2020, 47, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penz, F.M.; Schenk, J. A Review of Steel Scrap Melting in Molten Iron-Carbon Melts. Steel Res. Int. 2019, 90, 1900124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Provatas, N. Kinetics of scrap melting in liquid steel: Multipiece scrap melting. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2008, 39, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskopf, A. A model for scrap melting in steel converter. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2015, 46, 1195–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Zhu, R.; Tang, T.; Dong, K. Study on the melting characteristics of steel scrap in molten steel. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2019, 46, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskopf, A.; Holappa, L. Scrap melting model for steel converter founded on interfacial solid/liquid phenomena. Metall. Res. Technol. 2018, 115, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Xu, A. Steel scrap melting model for a dephosphorisation basic oxygen furnace. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2020, 27, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Amount/t | T/℃ | C/% | Si/% | Mn/% | P/% | S/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hot metal | 124.05 | 1301 | 4.12 | 0.30 | 0.28 | 0.107 | 0.0025 |
| Scrap | 23.4 | 25 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Model Parameter | Value | Unit | Model Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.745 | KJ/(kg·°C) | qDust | 209.2 | KJ/kg | |
| 0.8368 | KJ/(kg·°C) | β | 0.98 | / | |
| qm | 217.568 | KJ/kg | α | 5.68 × 10−6 | / |
| 0.699 | KJ/(kg·°C) | k1 | 2.25 × 10−7 | / | |
| 0.8368 | KJ/(kg·°C) | k3 | 2.3845 × 10−4 | / | |
| qs | 271.96 | KJ/kg | k | 2.4773 × 10−5 | m/s |
| cSlag | 1.247 | KJ/(kg·°C) | αH | 39,000 | W/(m2·°C) |
| cDus | 1.0 | KJ/(kg·°C) | ρs | 7200 | Kg/m3 |
| cGas | 1.136 | KJ/(kg·°C) | Cp(1) | 0.8368 | KJ/(kg·°C) |
| qSlag | 209.2 | KJ/kg |
| Oxygen Step | Lime | Lightly Burned Dolomite | Magnesium Ball |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.009 | 1514 | ||
| 0.014 | 2634 | 354 | |
| 0.129 | |||
| 0.326 | 949 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, F.; Wang, D.; Bao, Y.; Liu, X.; Xing, L.; Zhao, L. A Mechanistic Model Based on Statistics for the Prediction of a Converter’s End-Point Molten Steel Temperature. Processes 2023, 11, 2233. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11082233
Gao F, Wang D, Bao Y, Liu X, Xing L, Zhao L. A Mechanistic Model Based on Statistics for the Prediction of a Converter’s End-Point Molten Steel Temperature. Processes. 2023; 11(8):2233. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11082233
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Fang, Dazhi Wang, Yanping Bao, Xin Liu, Lidong Xing, and Lihua Zhao. 2023. "A Mechanistic Model Based on Statistics for the Prediction of a Converter’s End-Point Molten Steel Temperature" Processes 11, no. 8: 2233. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11082233
APA StyleGao, F., Wang, D., Bao, Y., Liu, X., Xing, L., & Zhao, L. (2023). A Mechanistic Model Based on Statistics for the Prediction of a Converter’s End-Point Molten Steel Temperature. Processes, 11(8), 2233. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11082233





