The Electrooxidation of Synthetic Bipyridyl Herbicide Wastewaters with Boron-Doped Diamond Electrodes: A Technical and Economic Study to Boost Their Application for Pollution Prevention in the Agricultural Sector
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Analytical Techniques
2.3. Experimental Setup
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Kinetic Experiments
2.6. Phytotoxicity Assays
3. Results and Discussion
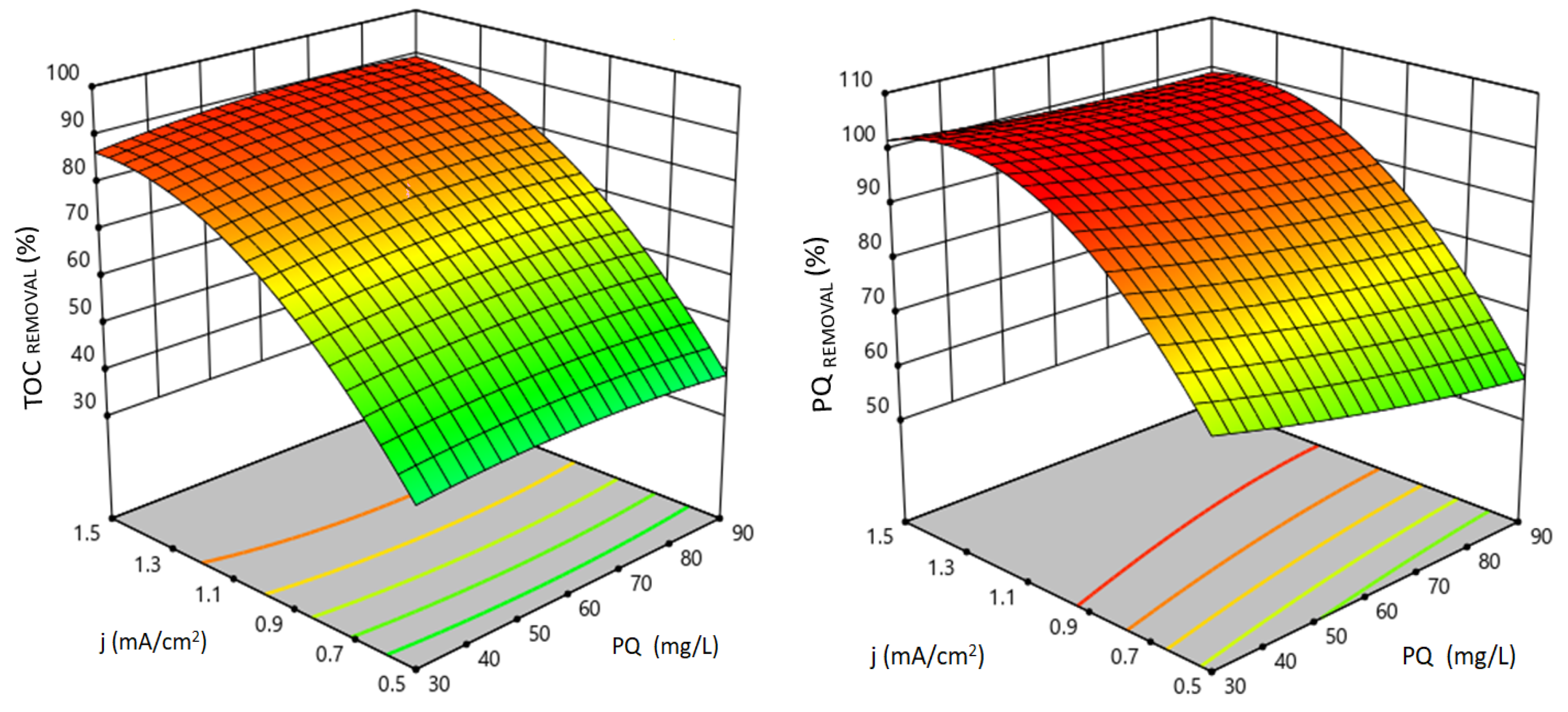
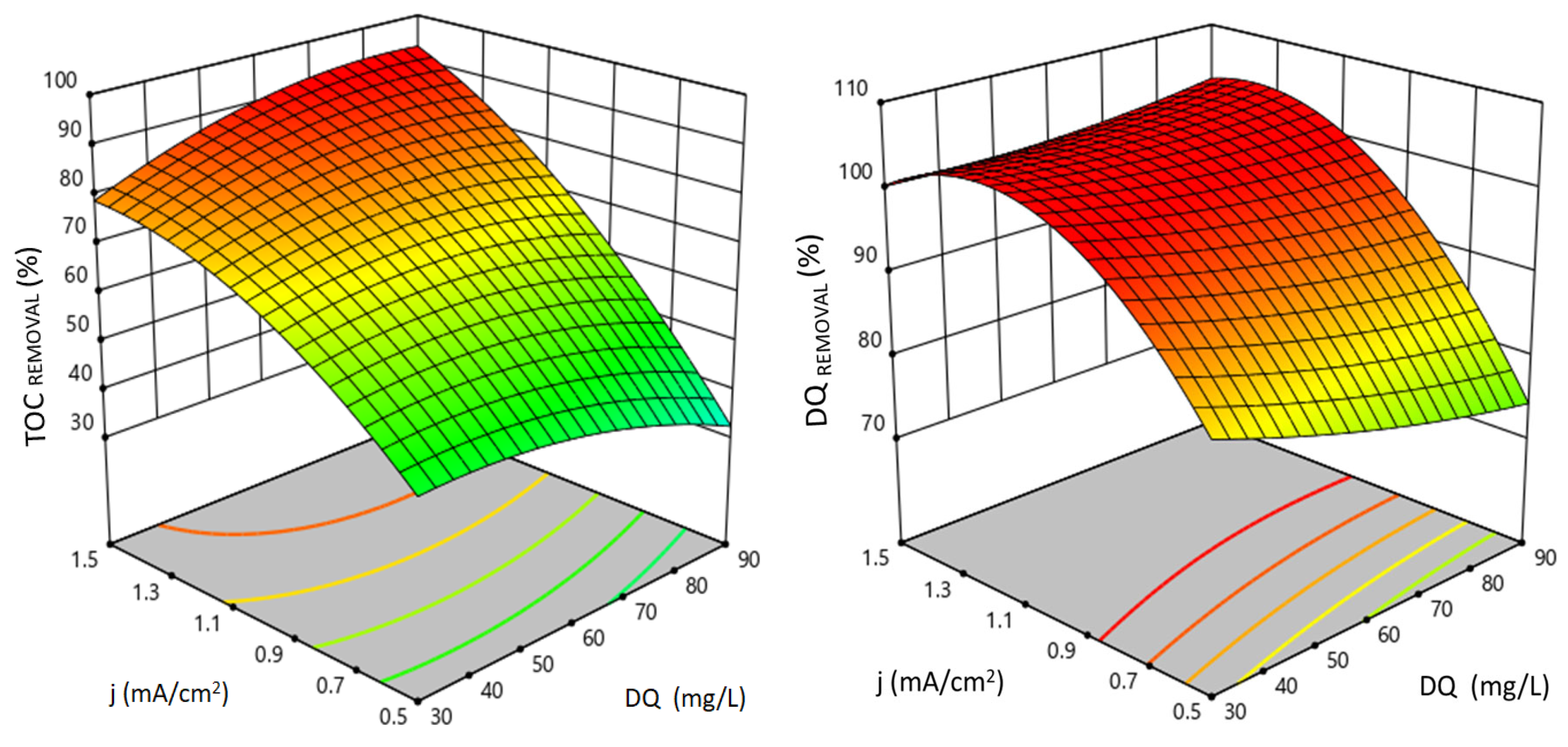
3.1. The Influence of Independent Experimental Variables on Electrochemical Processes
Validation of the Quadratic Models
3.2. Phytotoxicity Assay
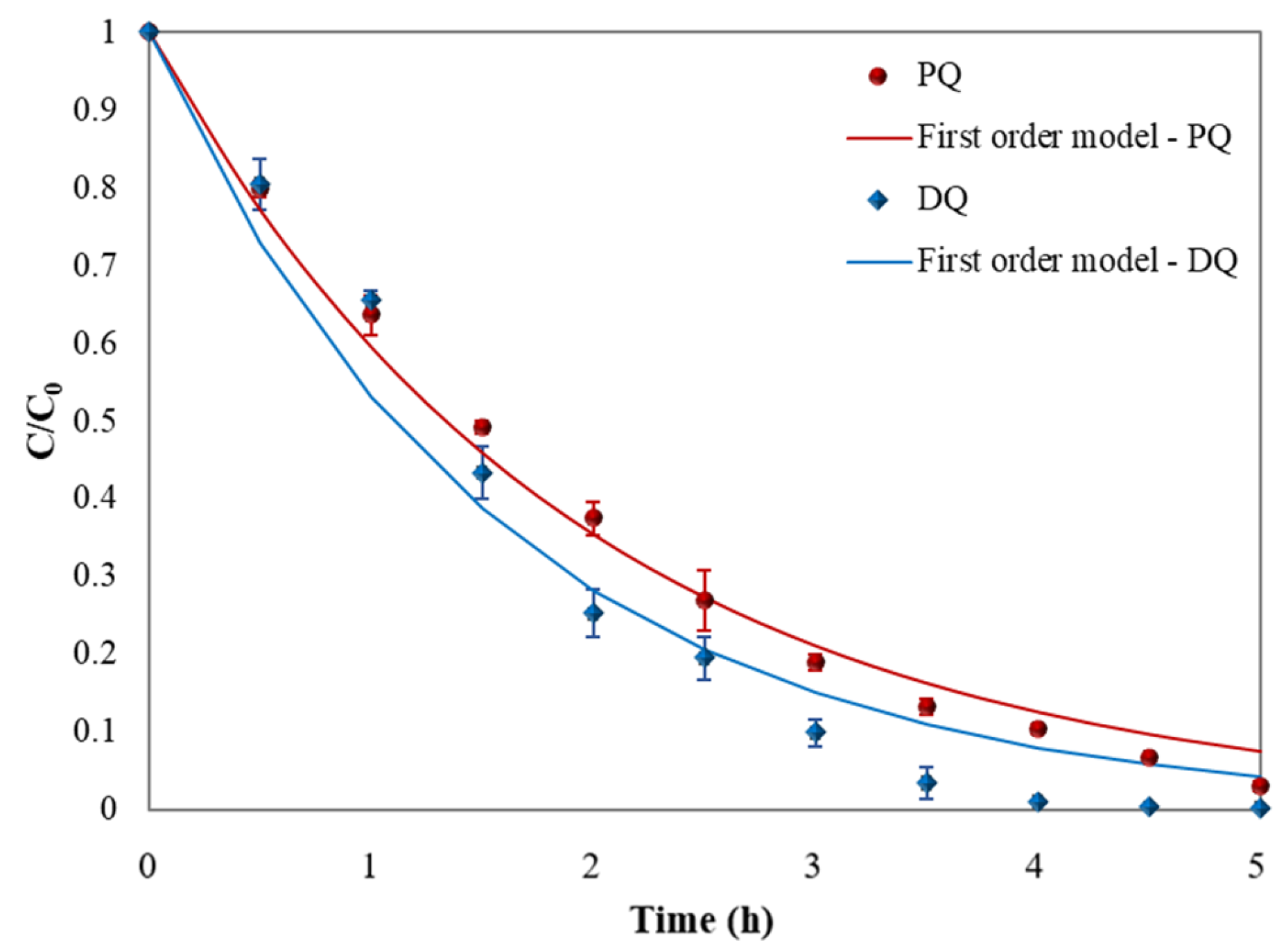
3.3. Kinetic Study
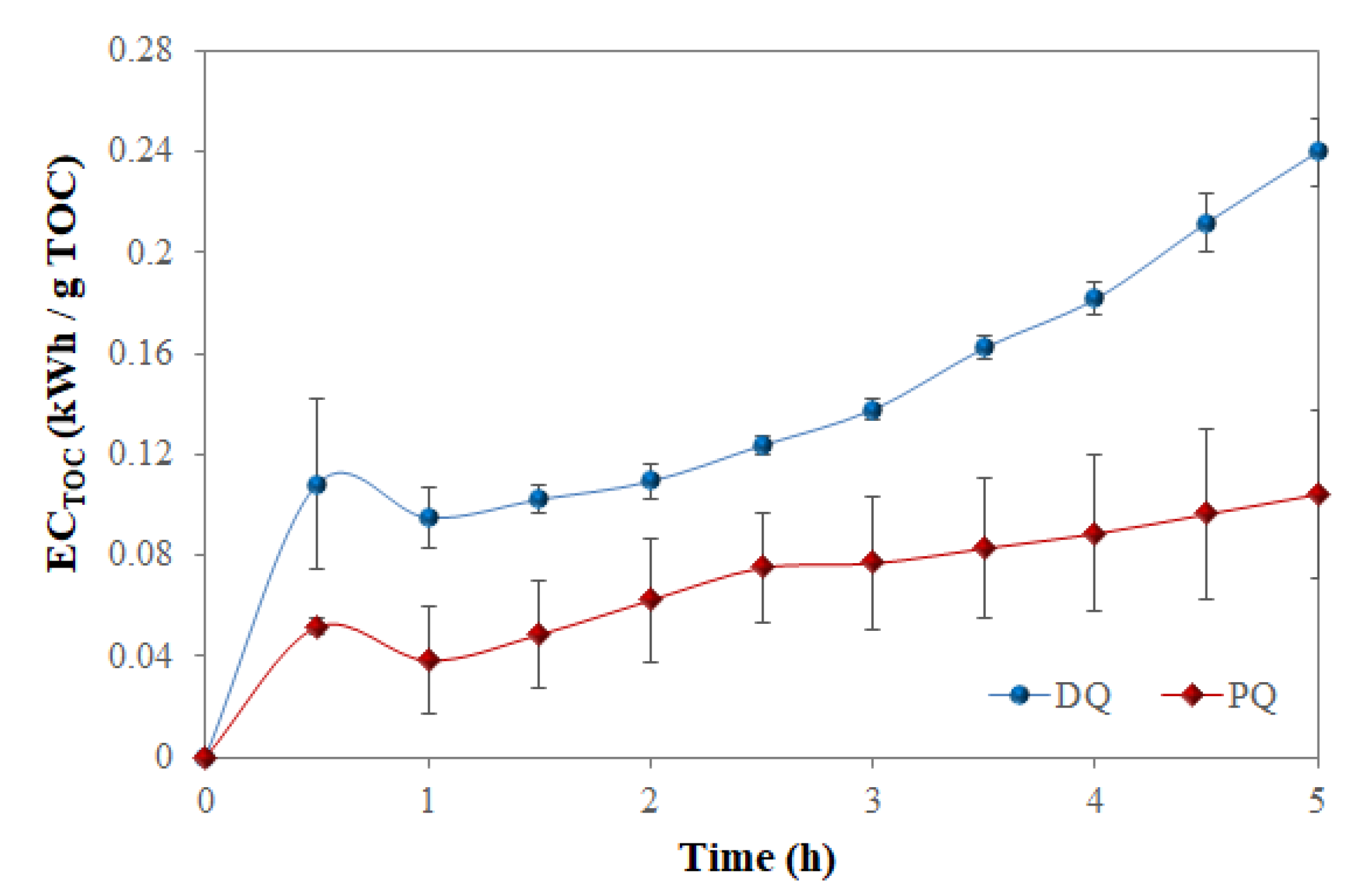
3.4. Parameters Analyzed
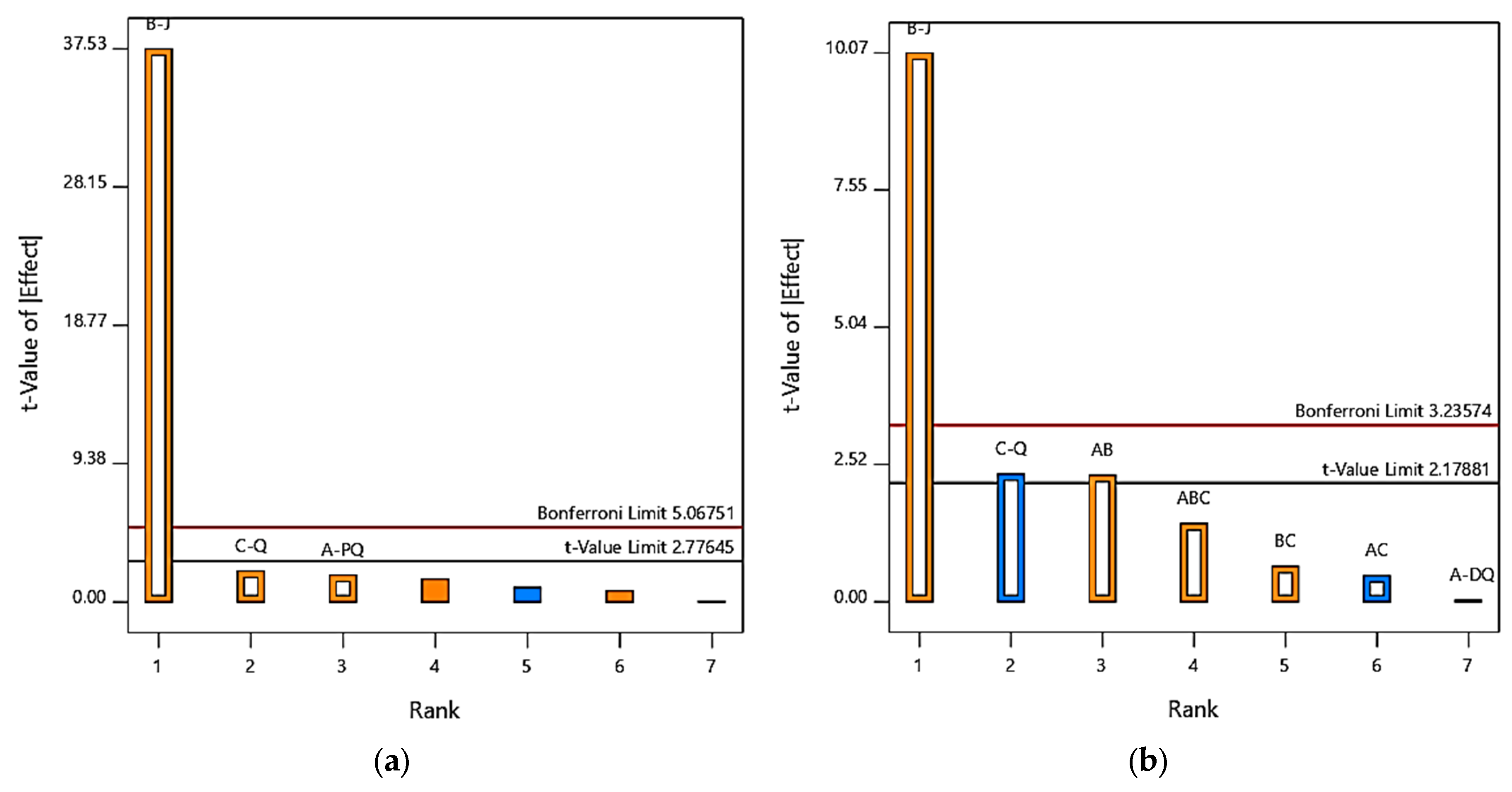
3.5. Factors Influencing PQ and DQ Electrochemical Degradation
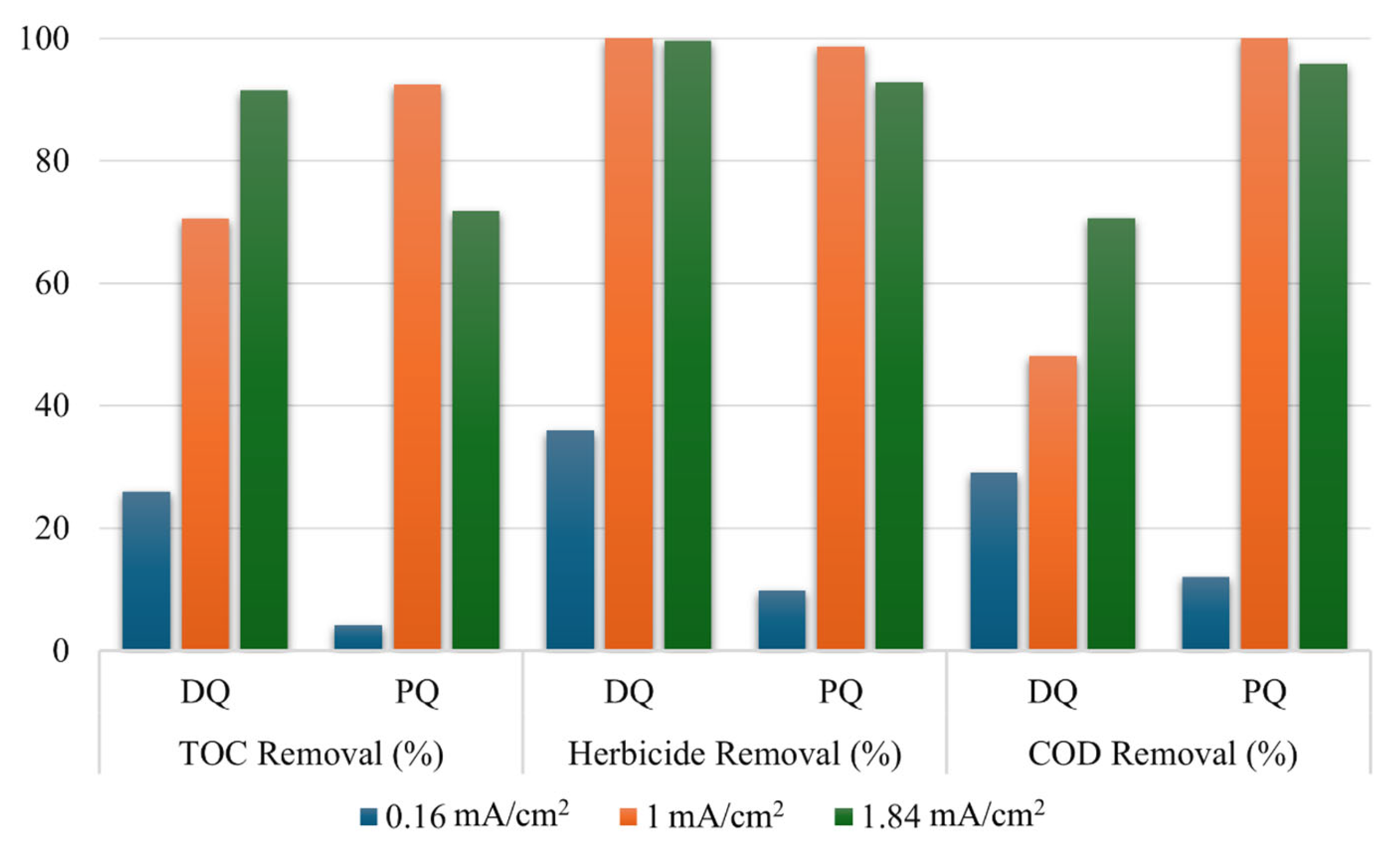
3.5.1. Effect of Current Density
3.5.2. Effect of Initial Concentration
3.6. Factors Influencing PQ and DQ Electrochemical Degradation: Concentration and Current Density
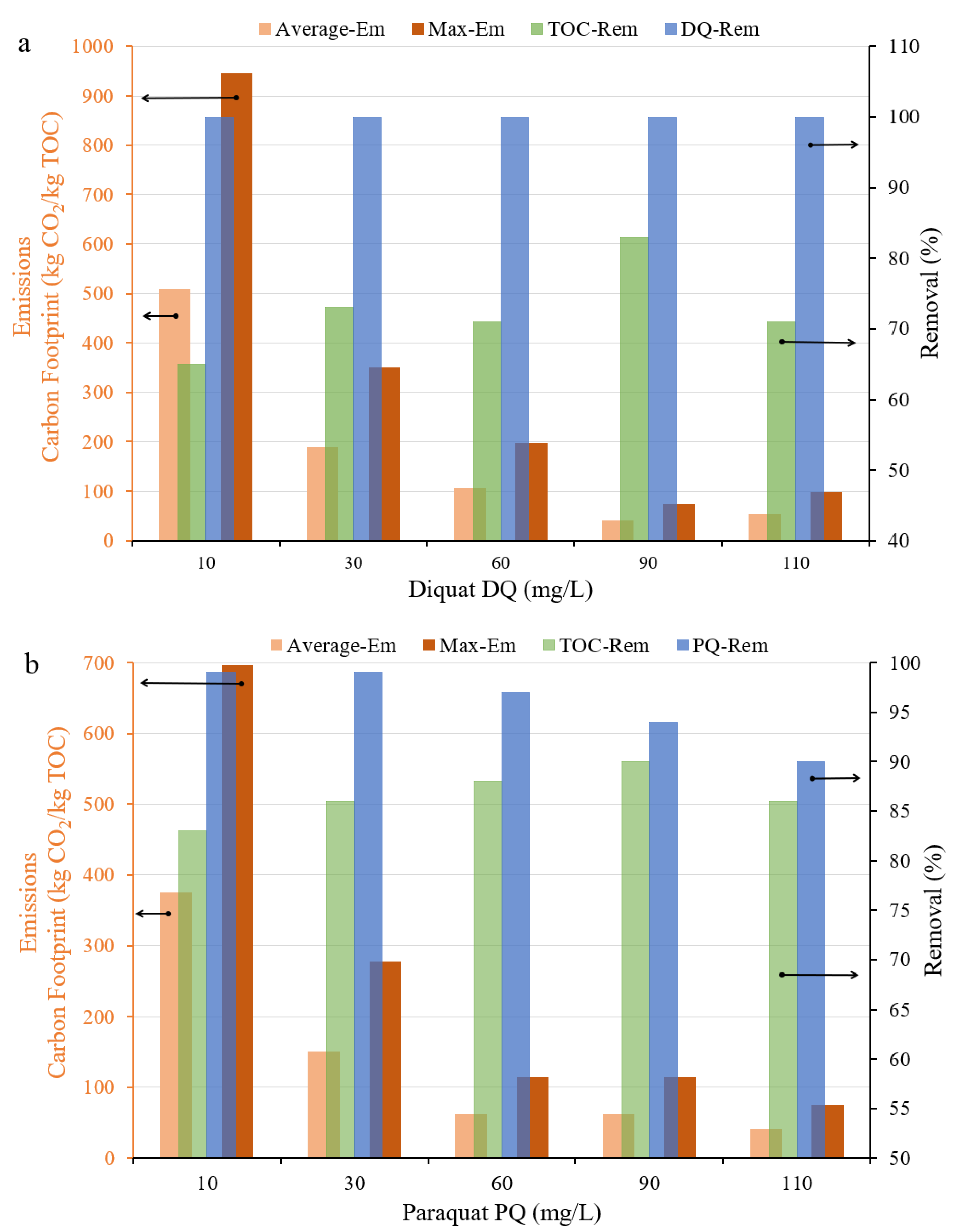
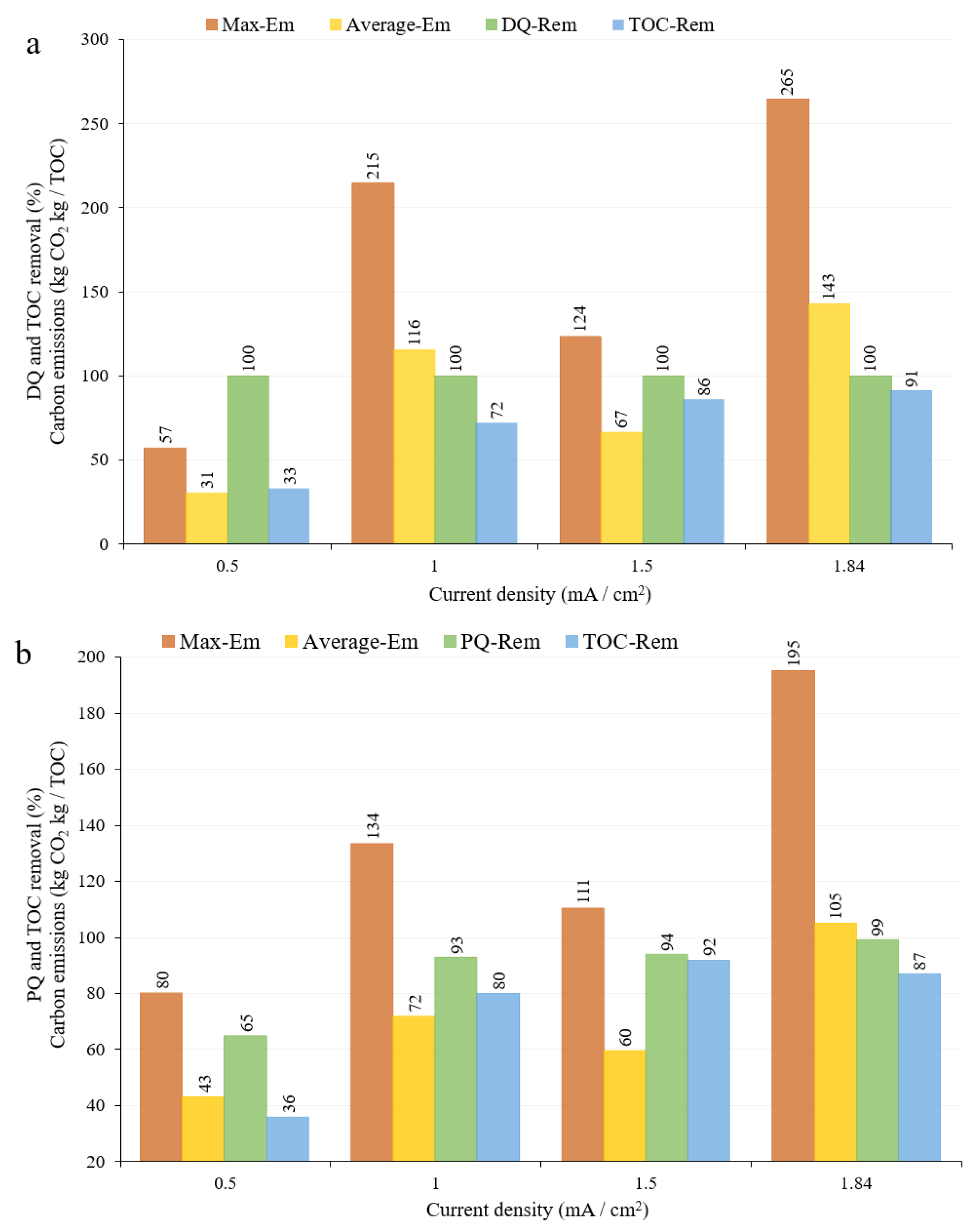
3.7. Environmental and Economic Performance of the Electrochemical Process
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumari, P.; Alka; Kumar, S.; Nisa, K.; Sharma, D.K. Efficient System for Encapsulation and Removal of Paraquat and Diquat from Aqueous Solution: 4-Sulfonatocalix[n]Arenes and Its Magnetite Modified Nanomaterials. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillas, E. Recent Development of Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation of Herbicides. A Review on Its Application to Wastewater Treatment and Soil Remediation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 290, 125841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongur, T.; Ayranci, E. Adsorption and Electrosorption of Paraquat, Diquat and Difenzoquat from Aqueous Solutions onto Activated Carbon Cloth as Monitored by in-Situ Uv-Visible Spectroscopy. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasca, E.; Siano, F.; Caruso, T. Fluorescence Detecting of Paraquat and Diquat Using Host–Guest Chemistry with a Fluorophore-Pendant Calix[6] Arene. Sensors 2023, 23, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, D.S.P.; Georgin, J.; Lima, E.C.; Silva, L.F.O. Advances Made in Removing Paraquat Herbicide by Adsorption Technology: A Review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 102988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, N.; Carvalho, F.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. Human and Experimental Toxicology of Diquat Poisoning: Toxicokinetics, Mechanisms of Toxicity, Clinical Features, and Treatment. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2018, 37, 1131–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzutti, I.R.; Vela, G.M.E.; De Kok, A.; Scholten, J.M.; Dias, J.V.; Cardoso, C.D.; Concenço, G.; Vivian, R. Determination of Paraquat and Diquat: LC-MS Method Optimization and Validation. Food Chem. 2016, 209, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaouadi, A.; Adhoum, N. Heterogeneous Catalytic Wet Peroxide Oxidation of Paraquat in the Presence of Modified Activated Carbon. Appl. Catal. B 2010, 97, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadayozzi, Y.S.; Santos, F.A.; dos Vicente, E.F.; Forti, J.C. Application of Oxidative Process to Degrade Paraquat Present in the Commercial Herbicide. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2021, 56, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, E.R.; Zapiola, M.L.; Avila, L.A.; De Garcia, M.A.; Plaza, G.; Gazziero, D.; Hoyos, V. Current Situation Regarding Herbicide Regulation and Public Perception in South America. In Weed Science; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020; Volume 68, pp. 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasaie, A.; Sabzehmeidani, M.M.; Ghaedi, M.; Ghane-Jahromi, M.; Sedaratian-Jahromi, A. Removal of Herbicide Paraquat from Aqueous Solutions by Bentonite Modified with Mesoporous Silica. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 262, 124296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, J.; Jian, T.; Shi, L.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Kan, B.; Jian, X. Case Series: Diquat Poisoning with Acute Kidney Failure, Myocardial Damage, and Rhabdomyolysis. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 991587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.S.F.; Alves, A.; Madeira, L.M. Paraquat Removal from Water by Oxidation with Fenton’s Reagent. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 175, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teutli-Sequeira, A.; Vasquez-Medrano, R.; Prato-Garcia, D.; Ibanez, J.G. Solar Photo-Assisted Degradation of Bipyridinium Herbicides at Circumneutral PH: A Life Cycle Assessment Approach. Processes 2020, 8, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Suárez, L.A.; Linares-Hernández, I.; Vasquez-Medrano, R.; Ibanez, J.G.; Santoyo-Tepole, F.; López-Rebollar, B.M.; Martínez-Miranda, V. Commercial Herbicide Degradation by Solar Corrosion Fenton Processes of Iron Filaments in a Continuous Flow Reactor and Its Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Simulation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2021, 412, 113249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares-Hernandez, I.; Castillo-Surez, L.A.; Ibanez, J.G.; Vasquez-Medrano, R.; Lopez-Rebollar, B.M.; Teutli-Sequeira, E.A. Degradation of Commercial Paraquat in a Solar-Fenton Pilot Lagoon Using Iron Oxalate as a Chelating Agent : Hydro-Thermal Analysis with CFD. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2022, 429, 113914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, Y.; Verma, A.; Toor, A.P. Abatement of Paraquat Contaminated Water Using Solar Assisted Heterogeneous Photo-Fenton like Treatment with Iron-Containing Industrial Wastes as Catalysts. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibin, O.M.; Yesodharan, S.; Yesodharan, E.P. Sunlight Induced Photocatalytic Degradation of Herbicide Diquat in Water in Presence of ZnO. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantavenera, M.J.; Catanzaro, I.; Loddo, V.; Palmisano, L.; Sciandrello, G. Photocatalytic Degradation of Paraquat and Genotoxicity of Its Intermediate Products. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2007, 185, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartaxo, M.A.M.; Borges, C.M.; Pereira, M.I.S.; Mendonça, M.H. Electrochemical Oxidation of Paraquat in Neutral Medium. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 176, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, F.C.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Brillas, E.; Vilar, V.J.P. Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation Processes: A Review on Their Application to Synthetic and Real Wastewaters. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 202, 217–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, A.L.; Vasquez-Medrano, R.; Ibanez, J.G.; Frontana-Uribe, B.A.; Prato-Garcia, D. Remediation of Diquat-Contaminated Water by Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation Processes Using Boron-Doped Diamond (BDD) Anodes. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2017, 228, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Javed, J.; Wu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liyang, H.; Yang, C.; Tsui, T.H.; Song, B.; Zhang, Q. Valorizing Waste Activated Sludge Incineration Ash to S-Doped Fe2+@Zeolite 4A Catalyst for the Treatment of Emerging Contaminants Exemplified by Sulfamethoxazole. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 369, 122382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oonnittan, A.; Sillanpaa, M.E. Water Treatment by Electro-Fenton Process. Curr. Org. Chem. 2012, 16, 2060–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshini, M.; Das, I.; Ghangrekar, M.M.; Blaney, L. Advanced Oxidation Processes: Performance, Advantages, and Scale-up of Emerging Technologies. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, S.A.; Ferreira, T.C.R.; Migliorini, F.L.; Baldan, M.R.; Ferreira, N.G.; Lanza, M.R.V. Electrochemical Degradation of the Insecticide Methyl Parathion Using a Boron-Doped Diamond Film Anode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2013, 702, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros-León, D.G.; Espinoza-Montero, P.J.; Bolaños-Mendez, D.; Alvarez-Paguay, J.; Fernández, L.; Saavedra-Alulema, P.F.; Lopez, K.; Astorga, D.; Piñeiros, J.L. Electrochemical Degradation of Surfactants in Domestic Wastewater Using a DiaClean® Cell Equipped with a Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 900670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurian, M. Advanced Oxidation Processes and Nanomaterials—A Review. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 2, 100090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosler, P.; Girão, A.V.; Silva, R.F.; Tedim, J.; Oliveira, F.J. Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation Processes Using Diamond Technology: A Critical Review. Environments 2023, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosler, P.; Girão, A.V.; Silva, R.F.; Tedim, J.; Oliveira, F.J. In-House vs. Commercial Boron-Doped Diamond Electrodes for Electrochemical Degradation of Water Pollutants: A Critical Review. Front. Mater. 2023, 10, 1020649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Coetsier, C.; Causserand, C.; Groenen Serrano, K. An Experimental and Modelling Study of the Electrochemical Oxidation of Pharmaceuticals Using a Boron-Doped Diamond Anode. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 333, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, F.C.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Brillas, E.; Vilar, V.J.P. Remediation of a Winery Wastewater Combining Aerobic Biological Oxidation and Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation Processes. Water Res. 2015, 75, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Li, W.; Liu, F.; Miao, D.; Ma, L.; Gao, X.; Wei, Q.; Zhou, K.; Yu, Z.; Yu, Y. Microstructure of Boron Doped Diamond Electrodes and Studies on Its Basic Electrochemical Characteristics and Applicability of Dye Degradation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchtová, G.; Hojová, L.; Staňová, A.V.; Marton, M.; Vrška, M.; Behúl, M.; Michniak, P.; Vojs, M.; Dušek, L. The Influence of Micro-/Macro-Structure of a Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode on the Degradation of Azo Dye Direct Red 80. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 464, 142924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, G.; Zhou, B.; Deng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, K.; Wei, Q. Periodic Porous 3D Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode for Enhanced Perfluorooctanoic Acid Degradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 297, 121556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Fu, L.; Lu, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, W.; Hu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, G. Electrochemical Oxidation Degradation of Rhodamine B Dye on Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode: Input Mode of Power Attenuation. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 401, 136794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbajal-Palacios, P.; Balderas-Hernández, P.; Ibanez, J.G.; Roa-Morales, G. Replacing Dichromate with Hydrogen Peroxide in the Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) Test. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Trovó, A.G.; Gomes, O.; Machado, A.E.H.; Neto, W.B.; Silva, J.O. Degradation of the Herbicide Paraquat by Photo-Fenton Process: Optimization by Experimental Design and Toxicity Assessment. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2013, 24, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargahi, A.; Vosoughi, M.; Ahmad Mokhtari, S.; Vaziri, Y.; Alighadri, M. Electrochemical Degradation of 2,4-Dinitrotoluene (DNT) from Aqueous Solutions Using Three-Dimensional Electrocatalytic Reactor (3DER): Degradation Pathway, Evaluation of Toxicity and Optimization Using RSM-CCD. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, H.; Majumdar, R.; Saha, S.K. Response Surface Methodology-Based Prediction Model for Working Fluid Temperature during Stand-Alone Operation of Vertical Cylindrical Thermal Energy Storage Tank. Renew. Energy 2022, 188, 619–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Seedling Emergence and Seedling Growth. In Ecological Effects Test Guidelines; EPA: Washington, WA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gerber, M.D.; Lucia, T.; Correa, L.; Neto, J.E.P.; Correa, É.K. Phytotoxicity of Effluents from Swine Slaughterhouses Using Lettuce and Cucumber Seeds as Bioindicators. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Wang, G.; Chen, W.; Yang, Y.; Ma, R.; Li, D.; Shen, Y.; Li, G.; Yuan, J. Phytotoxicity of Farm Livestock Manures in Facultative Heap Composting Using the Seed Germination Index as Indicator. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 247, 114251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelladurai, S.J.S.; Murugan, K.; Ray, A.P.; Upadhyaya, M.; Narasimharaj, V.; Gnanasekaran, S. Optimization of Process Parameters Using Response Surface Methodology: A Review. In Materials Today: Proceedings; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 37, pp. 1301–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghenymy, A.; Garcia-Segura, S.; Rodríguez, R.M.; Brillas, E.; El Begrani, M.S.; Abdelouahid, B.A. Optimization of the Electro-Fenton and Solar Photoelectro-Fenton Treatments of Sulfanilic Acid Solutions Using a Pre-Pilot Flow Plant by Response Surface Methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 221–222, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghavi, A.; Bagherian, G.; Rezaei-Vahidian, H. Degradation of Paraquat Herbicide Using Hybrid AOP Process: Statistical Optimization, Kinetic Study, and Estimation of Electrical Energy Consumption. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapałka, A.; Fóti, G.; Comninellis, C. Basic Principles of the Electrochemical Mineralization of Organic Pollutants ForWastewater Treatment. In Electrochemistry for the Environment; Comninellis, C., Chen, G., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orts, F.; del Río, A.I.; Molina, J.; Bonastre, J.; Cases, F. Electrochemical Treatment of Real Textile Wastewater: Trichromy Procion HEXL®. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 808, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valladares, N.; Vasquez-Medrano, R.; Prato-Garcia, D.; Ibanez, J.G. Electrochemical Oxidation of Bentazon at Boron-Doped Diamond Anodes: Implications of Operating Conditions in Energy Usage and Process Greenness. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2023, 67, 518–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera-Cevallos, J.V.; Prato-Garcia, D.; Espinoza-Montero, P.J.; Vasquez-Medrano, R. Electro-Oxidation of a Commercial Formulation of Glyphosate on Boron-Doped Diamond Electrodes in a Pre-Pilot-Scale Single-Compartment Cell. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2021, 232, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wei, F.; Zhao, Q.; Lv, S.; Yao, Y. Real Herbicide Wastewater Treatment by Combined Means of Electrocatalysis Application and Biological Treatment. Chem. Ecol. 2020, 36, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillas, E.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A. Decontamination of Wastewaters Containing Synthetic Organic Dyes by Electrochemical Methods. An Updated Review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 166–167, 603–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Cabrera, G.X.; Pliego-Cerdán, C.I.; Méndez, E.; Espinoza-Montero, P.J. Step-by-Step Guide for Electrochemical Generation of Highly Oxidizing Reactive Species on BDD for Beginners. Front. Chem. 2024, 11, 1298630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Bian, X.; Xia, Y.; Weng, M.; Zhou, W.; Dai, Q. Application of Response Surface Methodology in Electrochemical Degradation of Amoxicillin with Cu-PbO2 Electrode: Optimization and Mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 117109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Gao, S.; Lei, J.; Li, X.; Hu, X. Electrochemical Oxidation of Ceftazidime with Graphite/CNT-Ce/PbO2–Ce Anode: Parameter Optimization, Toxicity Analysis and Degradation Pathway. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Ge, S.; Xu, X.M.; Zhou, X. Application of the Synergistic Ti/SnO2-Sb-Cu Anode and Ti/ZnO/CuO Cathode in the Electrochemical Treatment of Wastewater. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process 2024, 172, 108097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajalifard, Z.; Mousazadeh, M.; Khademi, S.; Khademi, N.; Jamadi, M.H.; Sillanpää, M. The Efficacious of AOP-Based Processes in Concert with Electrocoagulation in Abatement of CECs from Water/Wastewater. NPJ Clean Water 2023, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marnasidis, S.; Stamatelatou, K.; Verikouki, E.; Kazantzis, K. Assessment of the Generation of Empty Pesticide Containers in Agricultural Areas. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). 7 Steps: Good Practice Guide for Empty Pesticide Containers; Environmental Protection Agency: Dublin, Ireland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, F.C.; Vilar, V.J.P.; Ferreira, A.C.C.; dos Santos, F.R.A.; Dezotti, M.; Sousa, M.A.; Gonçalves, C.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Alpendurada, M.F. Treatment of a Pesticide-Containing Wastewater Using Combined Biological and Solar-Driven AOPs at Pilot Scale. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 209, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malato, S.; Blanco, J.; Richter, C.; Maldonado, M.I. Optimization of Pre-Industrial Solar Photocatalytic Mineralization of Commercial Pesticides Application to Pesticide Container Recycling. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2000, 25, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, A.; Oller, I.; Sirtori, C.; Rodríguez, A.; Sánchez-Pérez, J.A.; López, A.; Mezcua, M.; Malato, S. Decontamination of Industrial Wastewater Containing Pesticides by Combining Large-Scale Homogeneous Solar Photocatalysis and Biological Treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 160, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán-Flores, E.; Sarrà, M.; Blánquez, P. A Review on the Management of Rinse Wastewater in the Agricultural Sector. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatello, J.J.; Oliveros, E.; MacKay, A. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Organic Contaminant Destruction Based on the Fenton Reaction and Related Chemistry. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 36, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florêncio, M.H.; Pires, E.; Castro, A.L.; Nunes, M.R.; Borges, C.; Costa, F.M. Photodegradation of Diquat and Paraquat in Aqueous Solutions by Titanium Dioxide: Evolution of Degradation Reactions and Characterisation of Intermediates. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganiyu, S.O.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Rodrigo, M.A. Renewable Energies Driven Electrochemical Wastewater/Soil Decontamination Technologies: A Critical Review of Fundamental Concepts and Applications. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 270, 118857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganiyu, S.O.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A. The Use of Renewable Energies Driving Electrochemical Technologies for Environmental Applications. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2020, 22, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Sirés, I.; Scialdone, O. Single and Coupled Electrochemical Processes and Reactors for the Abatement of Organic Water Pollutants: A Critical Review. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 13362–13407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabeyi, M.J.B.; Olanrewaju, O.A. The Levelized Cost of Energy and Modifications for Use in Electricity Generation Planning. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 495–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzisymeon, E.; Foteinis, S.; Mantzavinos, D.; Tsoutsos, T. Life Cycle Assessment of Advanced Oxidation Processes for Olive Mill Wastewater Treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 54, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisales, C.M.; Salazar, L.M.; Garcia, D.P. Treatment of Synthetic Dye Baths by Fenton Processes: Evaluation of Their Environmental Footprint through Life Cycle Assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 4300–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clímaco Cunha, I.L.; Machado, P.G.; de Oliveira Ribeiro, C.; Kulay, L. Bibliometric Analysis of Advanced Oxidation Processes Studies with a Focus on Life Cycle Assessment and Costs. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 22319–22338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisa, F.; Abdul Raman, A.A.; Wan Daud, W.M.A. Applicability of Fluidized Bed Reactor in Recalcitrant Compound Degradation through Advanced Oxidation Processes: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 260–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Lin, B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, T.; Zhan, Y.; Yu, Z.; Kuang, Y.; et al. Electrochemical Oxidation Processes Based on Renewable Energy towards Carbon Neutrality: Oxidation Fundamentals, Catalysts, Challenges and Prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 487, 150447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Panizza, M. Electrochemical Oxidation of Organic Pollutants for Wastewater Treatment. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2018, 11, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, F.L.; Lanza, M.R.V.; Llanos, J.; Sáez, C.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Cañizares, P. A Wind-Powered BDD Electrochemical Oxidation Process for the Removal of Herbicides. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 158, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Marchante, C.M.; Souza, F.L.; Millán, M.; Lobato, J.; Rodrigo, M.A. Improving Sustainability of Electrolytic Wastewater Treatment Processes by Green Powering. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, M.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Fernández-Marchante, C.M.; Canizares, P.; Lobato, J. Powering with Solar Energy the Anodic Oxidation of Wastewater Polluted with Pesticides. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 8303–8309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Name | Chemical Structure | λmax (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| Diquat C 12H12Br2N2, 6,7-dihydrodipyrido [1,2-a:2′,1′-c] pyrazinedium dibromide | 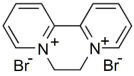 | 257 |
| Paraquat C12H14Cl2N2, 1,1′-dimethyl-4,4′-bipyridylium dichloride |  | 309 |
| Herbicide | Experiment | Coded Value | Real Values | Observed Responses | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Herbicide mg/L | j mA/cm2 | Q cm3/min | % Removal | |||||||
| A | B | C | COT | Herbicide | DQO | |||||
| PQ | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 30 | 0.5 | 250 | 35.65 | 72.92 | 26.13 |
| 2 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 90 | 0.5 | 250 | 36.97 | 65.38 | 65.04 | |
| 3 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 30 | 1.5 | 250 | 81.60 | 98.77 | 97.84 | |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 90 | 1.5 | 250 | 84.87 | 94.06 | 94.69 | |
| 5 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 30 | 0.5 | 750 | 40.42 | 87.59 | 92.71 | |
| 6 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 90 | 0.5 | 750 | 39.75 | 65.69 | 65.71 | |
| 7 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 30 | 1.5 | 750 | 82.10 | 100 | 100 | |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 90 | 1.5 | 750 | 87.08 | 95.94 | 94.49 | |
| 9 | −1.68 | 0 | 0 | 9.55 | 1 | 500 | 76.32 | 100 | 100 | |
| 10 | 1.68 | 0 | 0 | 110.46 | 1 | 500 | 75.04 | 91.65 | 92.68 | |
| 11 | 0 | −1.68 | 0 | 60 | 0.16 | 500 | 4.17 | 9.90 | 11.99 | |
| 12 | 0 | 1.68 | 0 | 60 | 1.84 | 500 | 92.41 | 98.68 | 100 | |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | −1.68 | 60 | 1 | 79.55 | 82.07 | 94.18 | 91.91 | |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 1.68 | 60 | 1 | 920.45 | 81.32 | 98.92 | 97.01 | |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 1 | 500 | 71.75 | 92.90 | 95.93 | |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 1 | 500 | 80.45 | 97.13 | 95.39 | |
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 1 | 500 | 81.31 | 96.40 | 95.16 | |
| 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 1 | 500 | 76.10 | 95.02 | 95.66 | |
| 19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 1 | 500 | 77.99 | 95.30 | 91.49 | |
| 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 1 | 500 | 74.67 | 94.21 | 87.82 | |
| DQ | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 30 | 0.5 | 250 | 39.41 | 92.30 | 28.56 |
| 2 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 90 | 0.5 | 250 | 32.23 | 97.84 | 5.23 | |
| 3 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 30 | 1.5 | 250 | 82.44 | 100 | 53.28 | |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 90 | 1.5 | 250 | 86.02 | 100 | 47.09 | |
| 5 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 30 | 0.5 | 750 | 37.87 | 100 | 46.03 | |
| 6 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 90 | 0.5 | 750 | 7.43 | 66.69 | 17.89 | |
| 7 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 30 | 1.5 | 750 | 71.38 | 100 | 49.10 | |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 90 | 1.5 | 750 | 86.57 | 100 | 57.15 | |
| 9 | −1.68 | 0 | 0 | 9.55 | 1 | 500 | 60.84 | 100 | 29.08 | |
| 10 | 1.68 | 0 | 0 | 110.46 | 1 | 500 | 72.61 | 98.63 | 57.60 | |
| 11 | 0 | −1.68 | 0 | 60 | 0.16 | 500 | 25.98 | 35.90 | 29.08 | |
| 12 | 0 | 1.68 | 0 | 60 | 1.84 | 500 | 91.48 | 99.62 | 70.62 | |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | −1.68 | 60 | 1 | 79.55 | 80.24 | 100 | 58.81 | |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 1.68 | 60 | 1 | 920.45 | 57.91 | 100 | 57.90 | |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 1 | 500 | 70.50 | 100 | 48.06 | |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 1 | 500 | 70.61 | 100 | 92.94 | |
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 1 | 500 | 82.07 | 100 | 73.59 | |
| 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 1 | 500 | 75.59 | 100 | 70.28 | |
| 19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 1 | 500 | 70.56 | 100 | 68.44 | |
| 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 1 | 500 | 77.43 | 100 | 82.29 | |
| Optimal Conditions | % Removal | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Herbicide | Herbicide mg/L | j mA/cm2 | Q mL/min | Herbicide | TOC | COD |
| PQ | 72.74 | 1.55 | 79.95 | 100 | 91 | 100 |
| DQ | 67.64 | 1.47 | 495.75 | 100 | 92 | 77 |
| Sum of Squares | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value Prob > F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PQ | ||||
| Model | 10,045.26 | 1116.14 | 40.52 | <0.0001 |
| A = [PQ] | 3.33 | 3.33 | 0.1210 | 0.7351 |
| B = j | 8035.09 | 8035.09 | 291.70 | <0.0001 |
| C = Q | 5.93 | 5.93 | 0.2153 | 0.6526 |
| A2 | 55.17 | 55.17 | 2.00 | 0.1874 |
| B2 | 1952.72 | 1952.72 | 70.89 | <0.0001 |
| C2 | 0.4166 | 0.4166 | 0.0151 | 0.9046 |
| Residual | 275.46 | 27.55 | ||
| Lack of Fit | 210.21 | 42.04 | 3.22 | 0.1125 |
| R2 = 0.9733 Adjusted R2 = 0.9493 Predicted R2 = 0.8367 | ||||
| DQ | ||||
| Model | 9449.62 | 1049.96 | 13.26 | 0.0002 |
| A = [DQ] | 0.0653 | 0.0653 | 0.0008 | 0.9776 |
| B = j | 7480.62 | 7480.62 | 94.47 | <0.0001 |
| C = Q | 405.37 | 405.37 | 5.12 | 0.0472 |
| A2 | 305.00 | 305.00 | 3.85 | 0.0781 |
| B2 | 794.95 | 794.95 | 10.04 | 0.0100 |
| C2 | 204.78 | 204.78 | 2.59 | 0.1389 |
| Residual | 791.88 | 79.19 | ||
| Lack of Fit | 678.16 | 135.63 | 5.96 | 0.0361 |
| R2 = 0.9227 Adjusted R2 = 0.8531 Predicted R2 = 0.4589 | ||||
| Treatment | Seed Germination, GS (%) | Root Length, RL (%) | Germination Index, GI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PARAQUAT | |||
| Control (distilled water) | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Raw effluent | 90 | 19.20 | 17.28 |
| Treated effluent | 100 | 92.82 | 92.82 |
| DIQUAT | |||
| Control (distilled water) | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Raw effluent | 90 | 14.97 | 13.47 |
| Treated effluent | 100 | 39.91 | 39.91 |
| Herbicide | Equation | Rate Constants | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PQ | C = e−0.0087t | 0.0087 min−1 | 0.9916 |
| DQ | C = e−0.0105t | 0.0105 min−1 | 0.9669 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teutli-Sequeira, E.A.; Vasquez-Medrano, R.; Prato-Garcia, D.; Ibanez, J.G. The Electrooxidation of Synthetic Bipyridyl Herbicide Wastewaters with Boron-Doped Diamond Electrodes: A Technical and Economic Study to Boost Their Application for Pollution Prevention in the Agricultural Sector. Processes 2024, 12, 2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112486
Teutli-Sequeira EA, Vasquez-Medrano R, Prato-Garcia D, Ibanez JG. The Electrooxidation of Synthetic Bipyridyl Herbicide Wastewaters with Boron-Doped Diamond Electrodes: A Technical and Economic Study to Boost Their Application for Pollution Prevention in the Agricultural Sector. Processes. 2024; 12(11):2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112486
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeutli-Sequeira, Elia Alejandra, Ruben Vasquez-Medrano, Dorian Prato-Garcia, and Jorge G. Ibanez. 2024. "The Electrooxidation of Synthetic Bipyridyl Herbicide Wastewaters with Boron-Doped Diamond Electrodes: A Technical and Economic Study to Boost Their Application for Pollution Prevention in the Agricultural Sector" Processes 12, no. 11: 2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112486
APA StyleTeutli-Sequeira, E. A., Vasquez-Medrano, R., Prato-Garcia, D., & Ibanez, J. G. (2024). The Electrooxidation of Synthetic Bipyridyl Herbicide Wastewaters with Boron-Doped Diamond Electrodes: A Technical and Economic Study to Boost Their Application for Pollution Prevention in the Agricultural Sector. Processes, 12(11), 2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112486







