Preparation and Exploration of Spherical Fe-C Micro-Electrolysis Materials for the Removal of Crystal Violet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
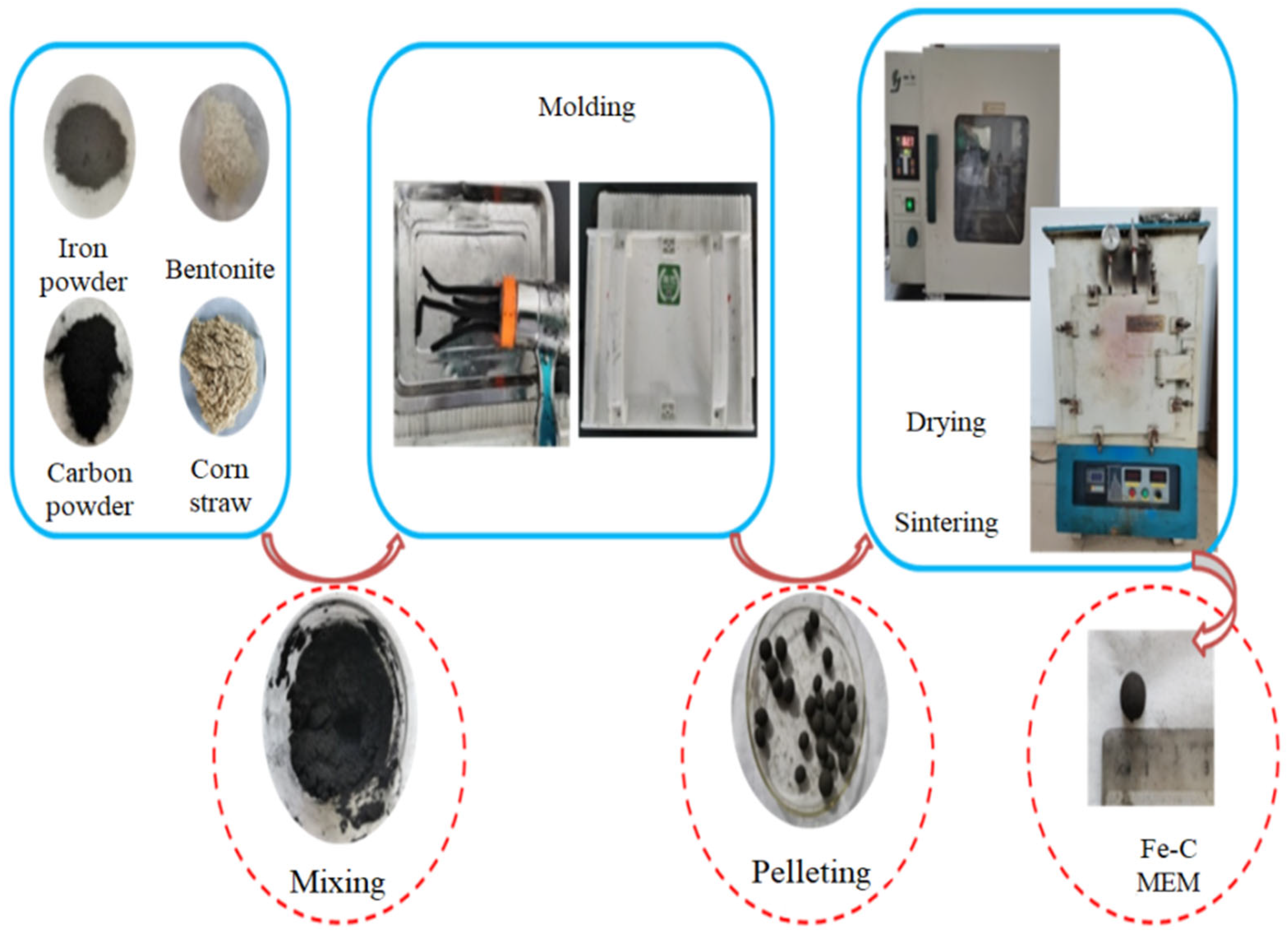
2.2. Preparation of Fe-C MEM
2.3. Optimization of Fe-C MEM
2.4. CV Removal by Fe-C MEM
2.5. Characterization
3. Results
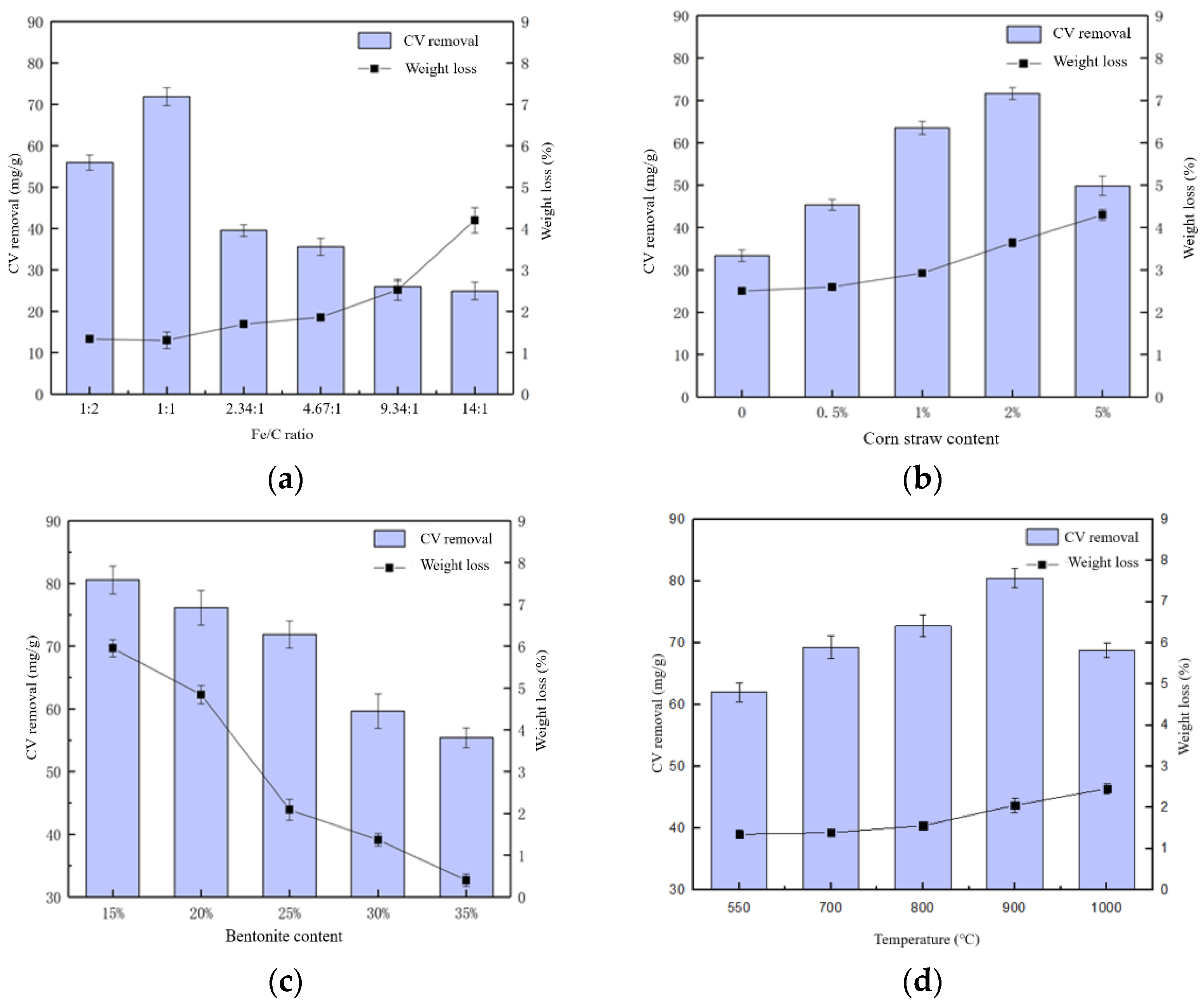
3.1. Optimization of Fe-C MEM Production
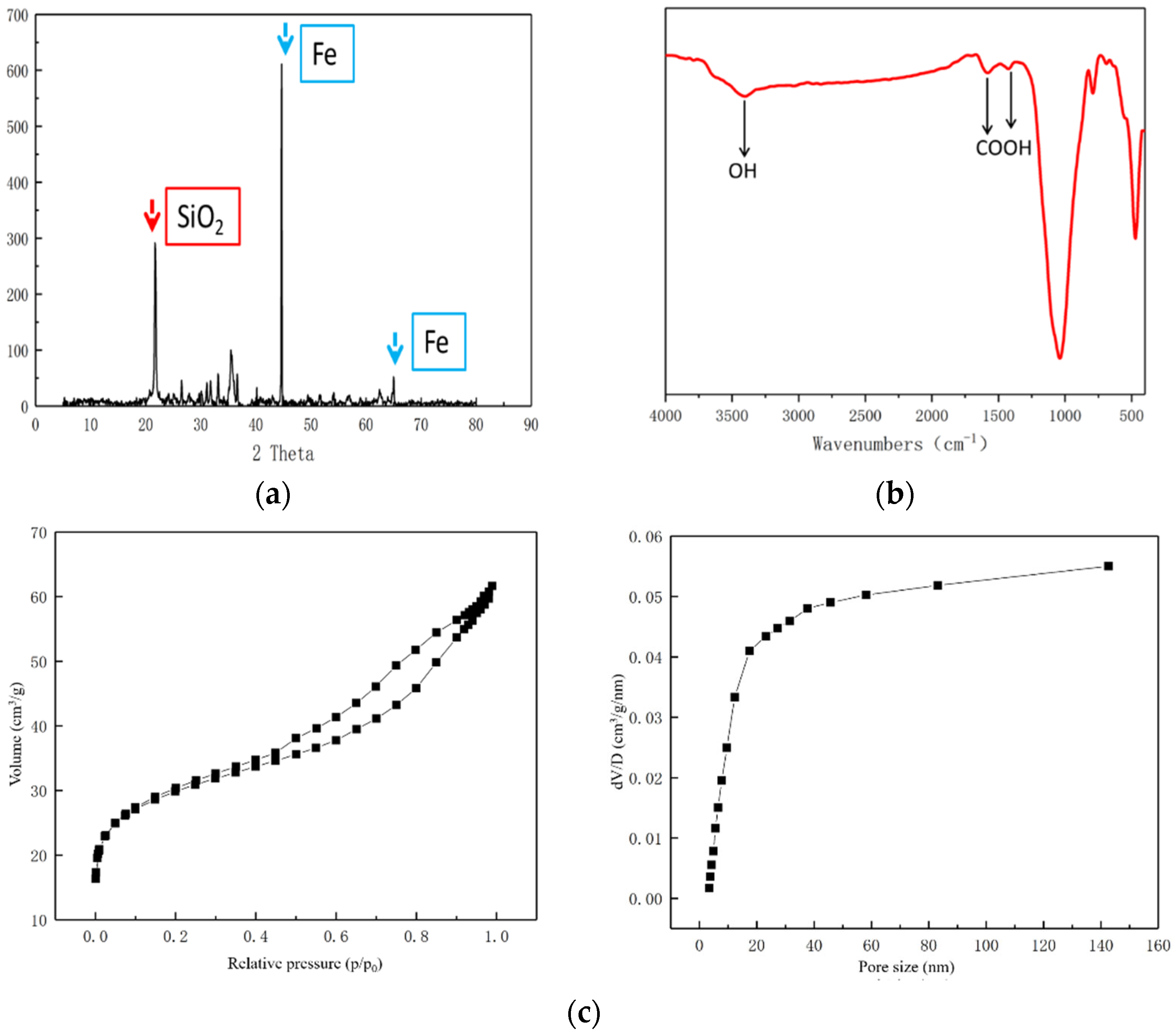
3.2. Characterization of Fe-C MEM
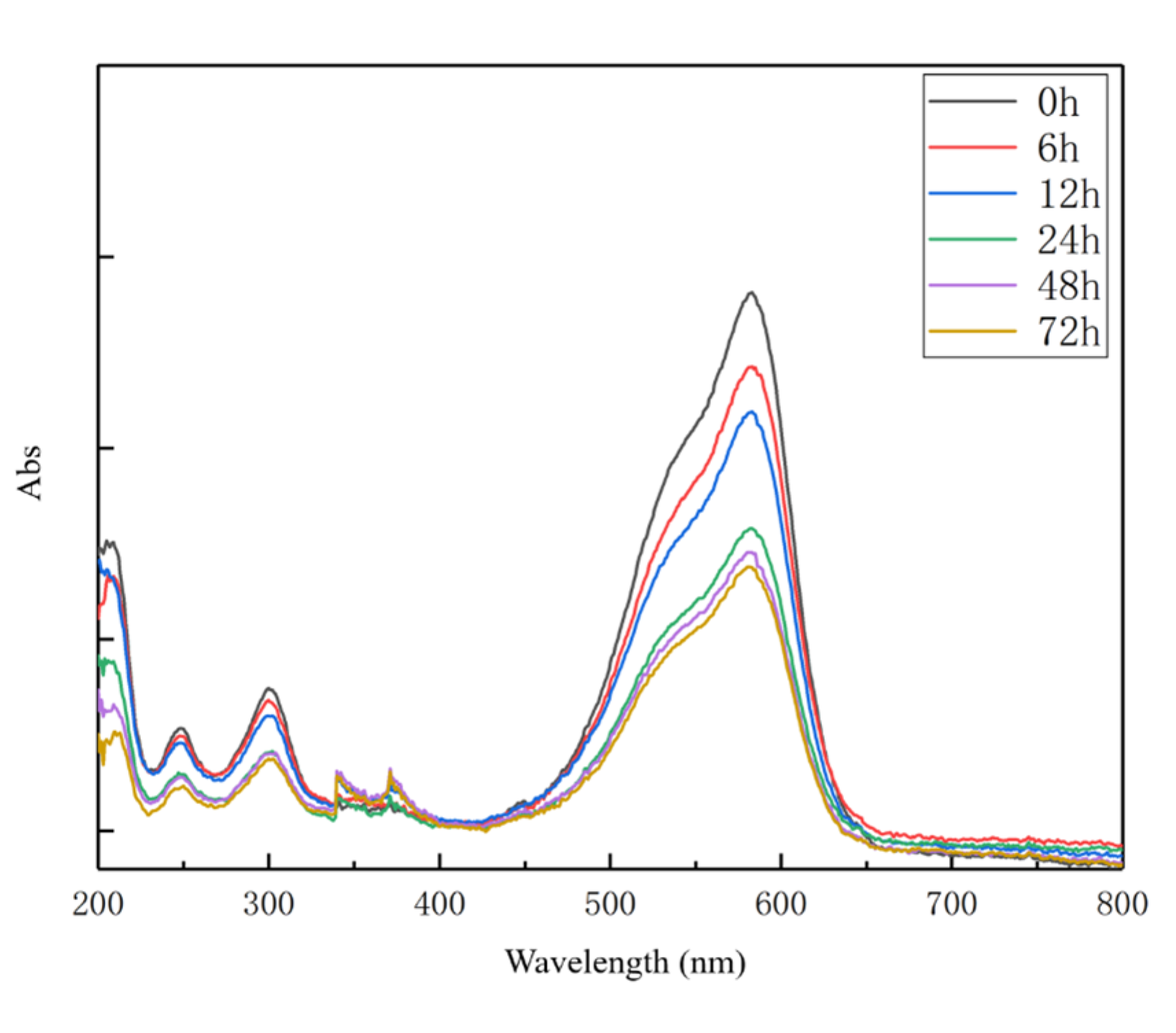
3.3. CV Removal by Fe-C MEM
3.4. Reuse of Fe-C MEM
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shabir, M.; Yasin, M.; Hussain, M.; Shafiq, I.; Akhter, P.; Nizami, A.S.; Jeon, B.H.; Park, Y.K. A review on recent advances in the treatment of dye-polluted wastewater. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 112, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyi, P.P.; Quansah, J.O.; Lee, C.G.; Moon, J.K.; Park, S.J. The removal of crystal violet from textile wastewater using palm kernel shell-derived biochar. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Peng, F.; Guo, H.J.; Wang, C.; Luo, M.T.; Zhao, C.; Xiong, L.; Chen, X.F.; Chen, X.D. Efficient COD degradation of turpentine processing wastewater by combination of Fe-C micro-electrolysis and Fenton treatment: Long-term study and scale up. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 351, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y.C.; Wang, J.; Gao, B.; Sato, S.; Feng, K.; Yin, W.; Igalavithana, A.D.; et al. Biochar-supported nZVI (nZVI/BC) for contaminant removal from soil and water: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 820–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Han, Y.; Xu, C.; Han, H.; Zhong, D.; Zhu, H.; Li, K. The mechanism of synergistic effect between iron-carbon microelectrolysis and biodegradation for strengthening phenols removal in coal gasification wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 271, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhang, M.; Ding, Y.; Sun, S.; He, S.; Yan, P. Enhanced nitrogen removal via iron carbon micro-electrolysis in surface flow constructed wetlands: Selecting activated carbon or biochar? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, Z. Degradation of organic pollutants in near-neutral pH solution by Fe-C micro-electrolysis system. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 315, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, B.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, P.; Yang, J.; Wang, J. Degradation of 3, 3′-iminobis-propanenitrile in aqueous solution by Fe0/GAC micro-electrolysis system. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 1470–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yue, Q.; Yang, K.; Zhao, P.; Gao, B. Enhanced phosphorus and ciprofloxacin removal in a modified BAF system by configuring Fe-C micro electrolysis: Investigation on pollutants removal and degradation mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 342, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Rong, R.; Dai, M.; Bian, H.; Peng, C. Preparation of red mud-based zero-valent iron materials by biomass pyrolysis reduction: Reduction mechanism and application study. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 864, 160907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P. Effective reinforcement ozone oxidation degradation of N, N-dimethylformamide with cobalt doping micro electrolysis composite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 314, 123639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhang, X.; Mwamulima, T. Removal study of crystal violet and methylene blue from aqueous solution by activated carbon embedded zero-valent iron: Effect of reduction methods. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 799264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zou, W.; Ding, L.; Zhou, M. Enhanced removal of organic contaminants by novel iron–carbon and premagnetization: Performance and enhancement mechanism. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, N.; Takahashi, H.; Ishida, S.; Horiie, F.; Wakamatsu, M. Mechanistic study of solid-state reaction between kaolinite and ferrous oxide at high temperatures. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2000, 108, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiluweit, M.; Nico, P.S.; Johnson, M.G.; Kleber, M. Dynamic molecular structure of plant biomass-derived black carbon (biochar). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusmão, K.A.; Gurgel, L.V.; Melo, T.M.S.; Gil, L.F. Adsorption studies of methylene blue and gentian violet on sugarcane bagasse modified with EDTA dianhydride (EDTAD) in aqueous solutions: Kinetic and equilibrium aspects. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 118, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.H.; Salleh, N.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Selvasembian, R. Mesoporous Activated Carbon from Sunflower (Helianthus annuus) Seed Pericarp for Crystal Violet Dye Removal: Numerical Desirability Optimization and Mechanism Study. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Mines, P.D.; Huh, Y.S.; Andersen, H.R. Nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) synthesis in a Mg-aminoclay solution exhibits increased stability and reactivity for reductive decontamination. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 147, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Zhang, W.; Yan, J.; Han, L.; Chen, Y.; Ouyang, D.; Chen, M. Nanoscale zero-valent iron supported by biochars produced at different temperatures: Synthesis mechanism and effect on Cr(VI) removal. Environ. Pollution. 2017, 223, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyoti Saini, J.S.; Garg, V.K.; Gupta, R.K.; Navish Kataria, N.K. Removal of Orange G and Rhodamine B dyes from aqueous system using hydrothermally synthesized zinc oxide loaded activated carbon (ZnO-AC). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Ning, Q.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L.; Tian, R.; Li, R.; Chen, J.; Xie, Q. A comparative study on the activation of persulfate by bare and surface-stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron for the removal of sulfamethazine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 230, 115869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption geloster stoffe. In Zeitschrift für Chemie und Industrie der Kolloide; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1898. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Kinetic models for the sorption of dye from aqueous solution by wood. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 1998, 76, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Über die adsorption in lösungen. Z. Für Phys. Chem. 1907, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumaran, C.; Sivakumar, V.M.; Thirumarimurugan, M. Adsorption isotherms and kinetic studies of crystal violet dye removal from aqueous solution using surfactant modified magnetic nanoadsorbent. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 63, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukoussa, B.; Hakiki, A.; Moulai, S.; Chikh, K.; Kherroub, D.E.; Bouhadjar, L.; Guedal, D.; Messaoudi, K.; Mokhtar, F.; Hamacha, R. Adsorption behaviors of cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solution on nanocomposite polypyrrole/SBA-15. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 7372–7386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponder, S.M.; Darab, J.G.; Mallouk, T.E. Remediation of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) Aqueous Solutions Using Supported, Nanoscale Zero-valent Iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 2564–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gao, H.; Yao, S.; Chen, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H. Degradation of Crystal Violet by catalytic ozonation using Fe/activated carbon catalyst. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 147, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, J.; Motamedi, E.; Naghavi, M.R.; Ghafoori, M. Removal of crystal violet from water using β-cyclodextrin functionalized biogenic zero-valent iron nanoadsorbents synthesized via aqueous root extracts of Ferula persica. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 367, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadnejad, M.; Nekoo, N.M.; Alizadeh, S.; Sadeghi, S.; Geranmayeh, S. Enhanced removal of organic dyes from aqueous solutions by new magnetic HKUST-1, Facile strategy for synthesis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.K.; Pandey, S.; Saha, S.; Singh, H.R.; Mishra, P.K.; Kumar, S.; Jha, S.K. Removal of crystal violet by Cu-chitosan nano-biocomposite particles using Box–Behnken design. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, M.; Raj, A.S.; Murugesan, A.; Kumar, P.S. Effective adsorption of crystal violet onto aromatic polyimides: Kinetics and isotherm studies. Chemosphere 2022, 304, 135332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkataraman, S.; Viswanathan, V.; Thangaiah, S.G.; Omine, K.; Mylsamy, P. Adsorptive exclusion of crystal violet dye using barium encapsulated alginate/carbon composites: Characterization and adsorption modeling studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 106718–106735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Li, S.; Zhou, S.; Li, F.; Li, T.; Li, H. Fe/sponge structure peanut shell carbon composite preparation for efficient Fenton oxidation crystal violet. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 105457–105473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| C0 (mg/L) | qe (mg/g) | Pseudo-First-Order Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (h−1) | R2 | k2 (h−1) | R2 | ||
| 300 | 46.99 | 0.127 | 0.938 | 0.0206 | 0.995 |
| 500 | 88.03 | 0.667 | 0.942 | 0.108 | 0.996 |
| 1000 | 105.48 | 0.846 | 0.9453 | 0.0091 | 0.997 |
| T (°C) | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | qm (mg/g) | b (L/mg) | RL | R2 | Kf | 1/n | ||
| 25 °C | 0.9978 | 105.47 | 0.008 | 0.05–0.27 | 0.988 | 23.68 | 0.4934 | |
| 35 °C | 0.9892 | 117.03 | 0.007 | 0.07–0.21 | 0.9833 | 29.74 | 0.3206 | |
| 45 °C | 0.9945 | 129.98 | 0.004 | 0.05–0.17 | 0.982 | 35.82 | 0.4428 | |
| T (K) | △H (KJ/mol) | △S (J/mol·K) | △G (KJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 °C | 24.12 | 124.13 | −15.69 |
| 35 °C | 24.12 | 124.13 | −17.24 |
| 45 °C | 24.12 | 124.13 | −19.26 |
| Adsorbents | Qm (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Palm Kernel Shell-Derived Biochar | 24.45 | [2] |
| Magnetic HKUST-1 MOF | 70.42 | [31] |
| Cu-chitosan nano-biocomposite particles | 84.75 | [32] |
| Aromatic polyamides (APIs)-1 APIs-2 | 285.71 303.03 | [33] |
| Barium encapsulated alginate/carbon composites | 50 | [34] |
| Fe/sponge structure peanut shell carbon composite | 143.25 (addition of H2O2) | [35] |
| Activated carbon embedded zero-valent iron | 95 | [12] |
| Fe-MEM | 105.48 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, M.; Wei, X.; Lin, C.; Xie, C.; Lai, Z.; Zhu, W.; Guo, J.; Peng, C. Preparation and Exploration of Spherical Fe-C Micro-Electrolysis Materials for the Removal of Crystal Violet. Processes 2024, 12, 2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112538
Dai M, Wei X, Lin C, Xie C, Lai Z, Zhu W, Guo J, Peng C. Preparation and Exploration of Spherical Fe-C Micro-Electrolysis Materials for the Removal of Crystal Violet. Processes. 2024; 12(11):2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112538
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Min, Xixi Wei, Chihpeng Lin, Chunsheng Xie, Zimin Lai, Wencan Zhu, Junhao Guo, and Changsheng Peng. 2024. "Preparation and Exploration of Spherical Fe-C Micro-Electrolysis Materials for the Removal of Crystal Violet" Processes 12, no. 11: 2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112538
APA StyleDai, M., Wei, X., Lin, C., Xie, C., Lai, Z., Zhu, W., Guo, J., & Peng, C. (2024). Preparation and Exploration of Spherical Fe-C Micro-Electrolysis Materials for the Removal of Crystal Violet. Processes, 12(11), 2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112538







