Polysaccharide-Based Fat Replacers in the Functional Food Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
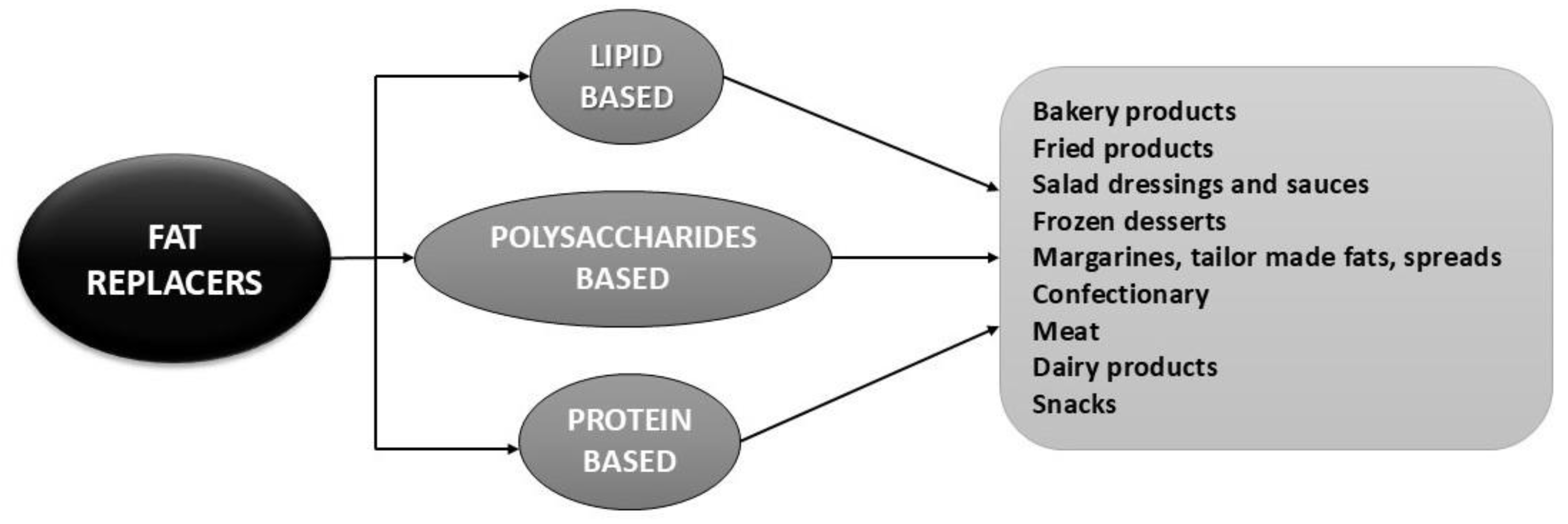
2. Fat Replacers
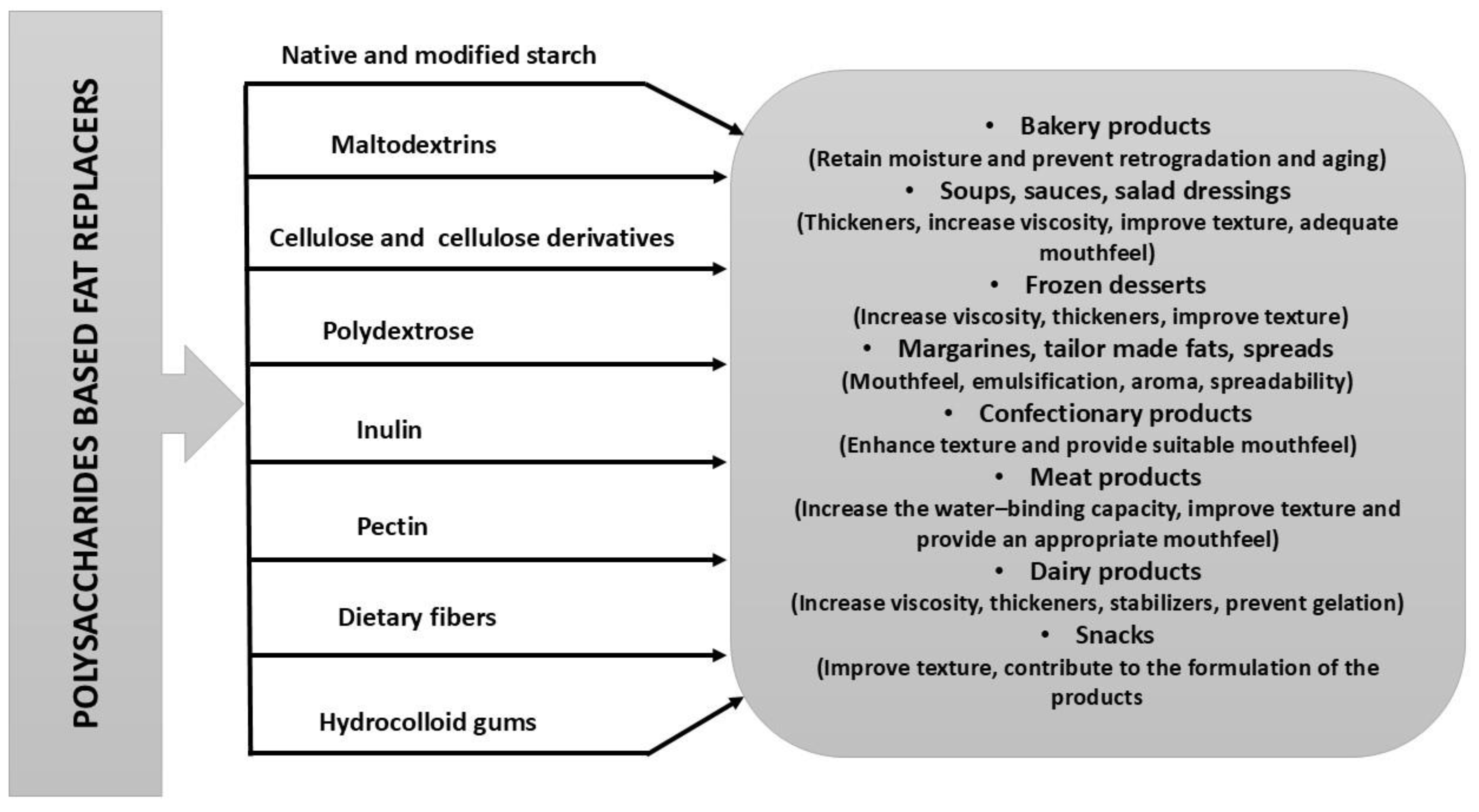
3. Polysaccharides-Based Fat Replacers
3.1. Technological Properties of Polysaccharide-Based Fat Replacers
3.2. Starch and Starch Derivatives as Fat Replacers
3.3. Cellulose and Cellulose Derivatives as Fat Replacers
3.4. Polydextrose
3.5. Inulin
3.6. Pectin
3.7. Other Fibers and Hydrocolloids Gums
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, J.; Charter, E. Functional Food Product Development; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Granato, D.; Barba, F.J.; Bursać Kovačević, D.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Cruz, A.G.; Putnik, P. Functional foods: Product development, technological trends, efficacy testing, and safety. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. T 2020, 11, 93–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topolska, K.; Florkiewicz, A.; Filipiak-Florkiewicz, A. Functional food—Consumer motivations and expectations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.P.; Jew, S. Functional food development: Concept to reality. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2007, 18, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palzer, S. Food structures for nutrition, health and wellness. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2009, 20, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee Mermel, V. Old paths new directions: The use of functional foods in the treatment of obesity. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2004, 15, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoh, C.C. Fat replacer. Food Technol. 1998, 52, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S.S.; Prosky, L. Application of complex carbohydrates to food products fat mimetics. In Complex Carbohydrates in Food; Cho, S.S., Prosky, L., Dreher, M.L., Eds.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 411–429. [Google Scholar]
- Ognen, C.F.; Darie, N.; Ognean, M. Fat Replacers. J. Agroaliment. Process Technol. 2006, 12, 433–442. [Google Scholar]
- Leilei, J.I.; Taihua, M.U.; Mengmei, M.A. Comparison of the Physicochemical Properties of Starch-based Fat Mimetics for Baking Prepared Using a Non-thermophysical Field-Assisted Enzymatic Method. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 38, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Nourmohammadi, N.; Austin, L.; Chen, D. Protein-based fat replacers: A focus on fabrication methods and fat-mimic mechanisms. Foods 2023, 12, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syan, V.; Kaur, J.; Sharma, K.; Patni, M.; Rasane, P.; Singh, J.; Bhadariya, V. An overview on the types, applications and health implications of fat replacers. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 61, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, R.D. Fats and Oils: Formulating and Processing for Applications; Chapter 4; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangoni, A.G.; Van Duynhoven, J.P.; Acevedo, N.C.; Nicholson, R.A.; Patel, A.R. Advances in our understanding of the structure and functionality of edible fats and fat mimetics. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omayma, E.S.; Youssef, M.M. Fat replacers and their applications in food products: A review. Alex. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 4, 29–44. [Google Scholar]
- BeMiller, J.N. Carbohydrate Chemistry for Food Scientists; AACC International: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2007; pp. 222–243. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, A.S. Physical, Chemical and Sensory Aspects of Fat Replacement. In Handbook of Fat Replacers; Chapter 1; Roller, S., Jones, S., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996; pp. 59–86. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Shang, M.; Li, X.; Sang, S.; McClements, D.J.; Chen, L.; Long, J.; Jiao, A.; Ji, H.; Jin, Z.; et al. Polysaccharide–based colloids as fat replacers in reduced–fat foods. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2023, 141, 104195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borderias, A.J.; Sanchez-Alonso, I.; Perez-Mateos, M. New Applications of Fibres in Foods: Addition to Fishery products. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2005, 16, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Yao, Y. Carbohydrates as fat replacers. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 331–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Ma, C.; Xu, Y.; Du, L.; Yang, X. Food Gels Based on Polysaccharide and Protein: Preparation, Formation Mechanisms, and Delivery of Bioactive Substances. Gels 2024, 10, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiljevic, T.; Varzakas, T. Bulking and fat-replacing agents. In Sweeteners: Nutritional Aspects, Applications and Production Technology; Varzakas, T., Labropoulos, A., Anestis, S., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 395–418. [Google Scholar]
- Lucca, P.A.; Tepper, B.J. Fat replacers and the functionality of fat in foods. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 1994, 5, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Jane, J.L. Gelatinization and rheological properties of starch. Starch-Stärke 2015, 67, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.; Sang, S.; Ji, H.; Jin, Z.; Qiu, C. Starch based fat replacers in food system: Modification, structured design, and application. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia Bangar, S.; Sunooj, K.V.; Navaf, M.; Phimolsiripol, Y.; Whiteside, W.S. Recent advancements in cross–linked starches for food applications-A review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2024, 27, 411–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, M.; Jekle, M.; Becker, T. Starch gelatinization and its complexity for analysis. Starch-Stärke 2015, 67, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C. Recent progress in understanding starch gelatinization—An important property determining food quality. Carbohyd Polym. 2022, 293, 119735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, S.; Mattea, C.; Denner, P.; Stapf, S. Effect of initial conformation on the starch biopolymer film formation studied by NMR. Molecules 2020, 25, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gałkowska, D.; Kapuśniak, K.; Juszczak, L. Chemically modified starches as food additives. Molecules 2023, 28, 7543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; She, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Gou, X. Use of starch-based fat replacers in foods as a strategy to reduce dietary intake of fat and risk of metabolic diseases. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werlang, S.; Bonfante, C.; Oro, T.; Biduski, B.; Bertolin, T.E.; Gutkoski, L.C. Native and annealed oat starches as a fat replacer in mayonnaise. J. Food Process Pres. 2021, 45, e15211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Olawuyi, I.F.; Lee, W.Y. Characteristics of low-fat mayonnaise using different modified arrowroot starches as fat replacer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subroto, E.; Indiarto, R.; Djali, M.; Rosyida, H.D. Production and application of crosslinking-modified starch as fat replacer: A review. Int. J. Eng. Trends Technol. 2020, 68, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Guo, R.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Zeng, L.; Wen, X.; Huang, Q. Effect of oil-modified crosslinked starch as a new fat replacer on gel properties, water distribution, and microstructures of pork meat batter. Food Chem. 2023, 409, 135337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, F.; Radi, M.; Amiri, S. Evaluating the function of cross–linked rice starch as a fat replacer in low fat cream. Int. J. Dairy. Technol. 2018, 71, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.F.E.; Mohamed, A.A.; Ahmed, I.A.M.; Alamri, M.S.; Al Juhaimi, F.Y.; Hussain, S.; Ibraheem, M.A.; Qasem, A.A. Acetylated corn starch as a fat replacer: Effect on physiochemical, textural, and sensory attributes of beef patties during frozen storage. Food Chem. 2022, 388, 132988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anggriawan, R.; Maksum, A.; Nurhayati, N. Production and Application of Octenyl Succinic-Modified Starch as Fat Replacer: A Review of Established and Recent Research. Preprints 2020, 2020050283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia, S.; Siroha, A.K.; Sandhu, K.S.; Kaur, M. Rheological and pasting behavior of OSA modified mungbean starches and its utilization in cake formulation as fat replacer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadnađev, T.D.; Hadnađev, M.; Pojić, M.; Rakita, S.; Krstonošić, V. Functionality of OSA starch stabilized emulsions as fat replacers in cookies. J. Food Eng. 2015, 167, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, S.A.; Dutta, H. Use of raw and physically modified rice starches as fat replacer in whipping cream. Curr. Res. Nut Food Sci. J. 2020, 8, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadnađev, M.; Hadnađev, T.D.; Dokić, L.J.; Pajin, B.; Torbica, A.; Šarić, L.; Ikonić, P. Physical and sensory aspects of maltodextrin gel addition used as fat replacers in confectionery filling systems. LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 59, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenana, M.E. Improving the quality of low-fat ice cream using some fat replacers. Ann. Agric. Sci. Moshtohor 2021, 59, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Khalesi, H.; He, J.; Fang, Y. Application of different hydrocolloids as fat replacer in low–fat dairy products: Ice cream, yogurt and cheese. Food Hydrocolloid 2023, 138, 108493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.P.; Rosario AI, L.; Silva, V.L.; Vieira, C.P.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Rheological, physical and sensory evaluation of low-fat cupuassu goat milk yogurts supplemented with fat replacer. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2022, 42, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El–Khair, A.; Abd–Alla, A.A.; Ateteallah, A.H.; Hassan, N.A. Physicochemical and Sensory Properties of Low–Fat Ice Cream Made with Inulin and Maltodextrin as Fat Replacers. J. Food Dairy. Sci. 2020, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazar, G.; Rosell, C.M. Fat replacers in baked products: Their impact on rheological properties and final product quality. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2023, 63, 7653–7676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Cui, L.; Meng, Z. Oleogels/emulsion gels as novel saturated fat replacers in meat products: A review. Food Hydrocolloid 2023, 137, 108313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, D.; Wang, L.J.; Wang, Y. Rheological properties and microstructure of a novel starch–based emulsion gel produced by one-step emulsion gelation: Effect of oil content. Carbohyd Polym. 2022, 281, 119061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.Y.; Li, D.; Wang, L.J.; Wang, Y. Development of corn starch-sodium alginate emulsion gels as animal fat substitute: Effect of oil concentration. Food Hydrocolloid 2024, 157, 110439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, D.; Cao, J.; Liu, X. Application of emulsion gels as fat substitutes in meat products. Foods 2022, 11, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves Barroso, L.; Grossi Bovi Karatay, G.; Dupas Hubinger, M. Effect of potato starch hydrogel: Glycerol monostearate oleogel ratio on the physico-rheological properties of bigels. Gels 2022, 8, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragán-Martínez, L.P.; Román-Guerrero, A.; Vernon-Carter, E.J.; Alvarez-Ramirez, J. Impact of fat replacement by a hybrid gel (canola oil/candelilla wax oleogel and gelatinized corn starch hydrogel) on dough viscoelasticity, color, texture, structure, and starch digestibility of sugar–snap cookies. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2022, 29, 100563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragán-Martínez, L.P.; Molina-Rodríguez, A.; Román-Guerrero, A.; Vernon-Carter, E.J.; Alvarez-Ramirez, J. Effect of starch gelatinization on the morphology, viscoelasticity, and water structure of candelilla wax–canola oil–starch hybrid gels. J. Food Process Pres. 2022, 46, e16520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabsangob, N. Plant-based cellulose nanomaterials for food products with lowered energy uptake and improved nutritional value-a review. NFS J. 2023, 31, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohrer, B.M.; Izadifar, M.; Barbut, S. Structural and functional properties of modified cellulose ingredients and their application in reduced-fat meat batters. Meat Sci. 2023, 195, 109011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsor-Atindana, J.; Chen, M.; Goff, H.D.; Zhong, F.; Sharif, H.R.; Li, Y. Functionality and nutritional aspects of microcrystalline cellulose in food. Carbohyd Polym. 2017, 172, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, T.; Quiles, A.; Salvador, A.; Hernando, I. Structural changes in biscuits made with cellulose emulsions as fat replacers. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2017, 23, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Zeng, X.; Wang, L.; Regenstein, J.M. Preparation of nanofibrillated cellulose from grapefruit peel and its application as fat substitute in ice cream. Carbohyd Polym. 2021, 254, 117415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Luo, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ma, L.; Chen, H.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Recent advances in protein-based emulsions: The key role of cellulose. Food Hydrocolloid 2023, 136, 108260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovich-Pinhas, M.; Barbut, S.; Marangoni, A.G. Edible applications of ethylcellulose oleogels. In Edible Oleogels; Marangoni, A.G., Garti, N., Eds.; AOCS Press: Champaign, IL, USA, 2018; pp. 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Zárate, M.; Macias-Rodriguez, B.A.; Toro-Vazquez, J.F.; Marangoni, A.G. Engineering rheological properties of edible oleogels with ethylcellulose and lecithin. Carbohyd Polym. 2019, 205, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, G.O.; Williams, P.A. Handbook of Hydrocolloids, 2nd ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zetzl, A.K.; Marangoni, A.G.; Barbut, S. Mechanical properties of ethylcellulose oleogels and their potential for saturated fat reduction in frankfurters. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovich-Pinhas, M.; Gravelle, A.J.; Barbut, S.; Marangoni, A.G. Temperature effects on the gelation of ethylcellulose oleogels. Food Hydrocolloid 2015, 46, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravelle, A.J.; Marangoni, A.G. Ethylcellulose oleogels: Structure, functionality, and food applications. Adv. Food Nutri. Res. 2018, 84, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeli, M.H.; Milani, J.M.; Farmani, J.; Zargaraan, A. Development of innovative ethyl cellulose-hydroxypropyl methylcellulose biopolymer oleogels as low saturation fat replacers: Physical, rheological and microstructural characteristics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 792–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Lu, W.; Sun, C.; Khalesi, H.; Mata, A.; Andaleeb, R.; Fang, Y. Cellulose and cellulose derivatives: Different colloidal states and food-related applications. Carbohyd Polym. 2021, 255, 117334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, P.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, A.; Ahmadi, A.; Tabibiazar, M.; Mohammadifar, M. Development of ethyl cellulose-based formulations: A perspective on the novel technical methods. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 38, 685–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, P.; Tabibiazar, M.; Roufegarinejad, L.; Babazadeh, A. Development of behenic acid-ethyl cellulose oleogel stabilized Pickering emulsions as low calorie fat replacer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espert, M.; Wang, Q.; Sanz, T.; Salvador, A. Sunflower oil-based oleogel as fat replacer in croissants: Textural and sensory characterisation. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2023, 16, 1943–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasi, F.; Golmakani, M.T. Fabrication and characterization of a novel biphasic system based on starch and ethylcellulose as an alternative fat replacer in a model food system. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 2022, 78, 103028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakouri, S.; Arabshahi, S.; Madanchi, H.; Mohammadifar, M.A.; Abdolshahi, A. Effect of carboxymethyl cellulose incorporation to gelatin-sunflower oil bigel on the physicochemical and structural properties. Polym. Advan Technol. 2024, 35, e6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veena, N.; Nath, S.; Arora, S. Polydextrose as a functional ingredient and its food applications: A review. Indian J. Dairy. Sci. 2016, 69, 239–251. [Google Scholar]
- Chavan, R.S.; Khedkar, C.D.; Bhatt, S. Fat replacer. In The Encyclopedia of Food and Health; Caballero, B., Finglas, P., Toldrá, F., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2016; Volume 2, pp. 589–595. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Abdel-Hamid, M.; Romeih, E.; Zeng, Q.K.; Yang, P.; Walker, G.; Li, L. Textural and organoleptic properties of fat-free buffalo yogurt as affected by polydextrose. Int. J. Food Prop. 2020, 23, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, S.M.; Abdelmontaleb, H.S.; Mabrouk, A.M.; Abbas, K.A. Physicochemical, viability, microstructure, and sensory properties of whole and skimmed buffalo set-yogurts containing different levels of polydextrose during refrigerated storage. J. Food Process Pres. 2021, 45, e15643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.M.; Abd El-Gawad, M.A.; Kassem, J.M.; Salama, M. Application of fat replacers in dairy products: A review. Foods Raw Mater. 2023, 12, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samakradhamrongthai, R.S.; Maneechot, S.; Wangpankhajorn, P.; Jannu, T.; Renaldi, G. Polydextrose and guar gum as a fat substitute in rice cookies and its physical, textural, and sensory properties. Food Chem. Advan 2022, 1, 100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengar, A.; Singh, A.P.; Khare, A.; Lal, A.B.; Singh, A. Effect of fat replacers on the multigrain biscuits. J. Healthc. Treat. Dev. (JHTD) 2022, 2, 19–30, ISSN 2799-1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola-Akinola, O.O.; Raji, T.J.; Olawoye, B. Lignocellulose, dietary fibre, inulin and their potential application in food. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illippangama, A.U.; Jayasena, D.D.; Jo, C.; Mudannayake, D.C. Inulin as a functional ingredient and their applications in meat products. Carbohyd Polym. 2022, 275, 118706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayarathna, G.N.; Jayasena, D.D.; Mudannayake, D.C. Garlic inulin as a fat replacer in vegetable fat incorporated low–fat chicken sausages. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2022, 42, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paglarini, C.D.S.; Vidal, V.A.S.; Ozaki, M.M.; Ribeiro, A.P.B.; Bernardinelli, O.D.; Câmara, A.K.F.I.; Herrero, A.M.; Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Sabadini, E.; Pollonio, M.A.R. Inulin gelled emulsion as a fat replacer and fiber carrier in healthier Bologna sausage. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2022, 28, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, G.F.; Ali, H.S.; Ragab, G.H.; Zaky, A.A. Evaluation of Inulin as a fat replacer in meat burger. Egypt J. Chem. 2024, 67, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Mohd Napi, N.N.; Mohamad, N.J. The Effect of Inulin Substitution as A Fat Replacer on Physicochemical and Sensory Properties of Muffins. Pertanika J. Trop. Agri. Sci. 2024, 47, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Song, K.Y.; Kim, Y. Physicochemical and retrogradation properties of low–fat muffins with inulin and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose as fat replacers. J. Food Process Pres. 2020, 44, e14816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciulli, M.; Littardi, P.; Carini, E.; Paradiso, V.M.; Castellino, M.; Chiavaro, E. Inulin–based emulsion filled gel as fat replacer in shortbread cookies: Effects during storage. LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 133, 109888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narala, V.R.; Orlovs, I.; Jugbarde, M.A.; Masin, M. Inulin as a fat replacer in pea protein vegan ice cream and its influence on textural properties and sensory attributes. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa–Ramírez, J.; Figueroa–Cárdenas, J.D.D.; Chuck–Hernández, C.; Garcia–Amezquita, L.E.; Dávila–Vega, J.P.; Casamayor, V.F.; Mariscal–Moreno, R.M. Agave inulin as a fat replacer in tamales: Physicochemical, nutritional, and sensory attributes. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 4472–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Cui, H.; Xu, X.; Li, J.; Lu, M.; Guan, X.; Zhu, D.; Liu, H. Effect of fat replacement by inulin on the physicochemical properties and sensory attributes of low-fat margarine. Food Hydrocolloid 2022, 133, 107868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, J.C. Development of Low-Fat Yogurt Using Fat Replacer (Inulin). Ph.D. Thesis, Chattogram Veterinary and Animal Sciences University, Chattogram, Bangladesh, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ishwarya, S.P.; Nisha, P. Advances and prospects in the food applications of pectin hydrogels. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2022, 62, 4393–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharefiabadi, E.; Serdaroğlu, M. Pectin: Properties and utilization in meat products. Food Health 2020, 7, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqash, F.; Masoodi, F.A.; Rather, S.A.; Wani, S.M.; Gani, A. Emerging concepts in the nutraceutical and functional properties of pectin—A Review. Carbohyd Polym. 2017, 168, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.; Ashraf, H.; Liaquat, A.; Nayik, G.A.; Ramniwas, S.; Alfarraj, S.; Ansari, M.J.; Gere, A. Exploring pectin from ripe and unripe Banana Peel: A novel functional fat replacer in muffins. Food Chem X 2024, 23, 101539101539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanitha, T.; Khan, M. Role of pectin in food processing and food packaging. In Pectins–Extraction, Purification, Characterization and Applications; Chapter 4; Masuelli, M.A., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Søndergaard, K.M.; Juul, A.G.; Nørbøge, L. Pectin Composition as Fat Replacer and Emulsifier; WO2000040098A1; WIPO (PCT): Algiers, Algeria, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Xu, X.M.; Guo, S.D. Rheological, texture and sensory properties of low-fat mayonnaise with different fat mimetics. LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Osama, K.; Gaur, V.K.; Farooqui, A.; Varjani, S.; Younis, K. Sustainable utilization of Citrus limetta peel for obtaining pectin and its application in cookies as a fat replacer. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 60, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frosi, I.; Balduzzi, A.; Moretto, G.; Colombo, R.; Papetti, A. Towards valorization of food–waste-derived pectin: Recent advances on their characterization and application. Molecules 2023, 28, 6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, N.A.; Abdul Manaf, M.; Harith, S.; Wan Ishak, W.R. Influence of avocado puree as a fat replacer on nutritional, fatty acid, and organoleptic properties of low–fat muffins. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2018, 37, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prihatin, A.; Shiguo, C.; Xingqian, Y. Pectin–enriched material from mandarin orange byproducts as a potential fat replacer in cookies. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2015, 5, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maneerat, N.; Tangsuphoom, N.; Nitithamyong, A. Effect of extraction condition on properties of pectin from banana peels and its function as fat replacer in salad cream. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongkaew, M.; Sommano, S.R.; Tangpao, T.; Rachtanapun, P.; Jantanasakulwong, K. Mango peel pectin by microwave-assisted extraction and its use as fat replacement in dried Chinese sausage. Foods 2020, 9, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasirpour-Tabrizi, P.; Azadmard-Damirchi, S.; Hesari, J.; Heshmati, M.K.; Savage, G.P. Rheological and physicochemical properties of novel low-fat emulgels containing flaxseed oil as a rich source of ω-3 fatty acids. LWT 2020, 133, 110107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadillah, U.; Dirpan, A.; Syarifuddin, A. Fat Replacers in Food System: A Focus on Ingredients, Fabrication Methods, and Applications in Food Products. Future Foods 2024, 10, 100490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, I.; Pajin, B.; Lončarević, I.; Šubarić, D.; Jozinović, A.; Lončarić, A.; Petrović, J.; Šereš, Z.; Dokić, L.; Šoronja-Simović, D. Technological Characteristics of Wheat-Fiber-Based Fat Mimetics in Combination with Food Additives. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, I.; Dokić, L.J.; Šereš, Z.; Šoronja-Simović, D.; Maravić, N.; Zahorec, J. Influence of additives on rheological and textural properties of cellulose based fat mimetic. Analecta Tech. Szeged. 2021, 15, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, I.; Petrović, J.; Pajin, B.; Lončarević, I.; Šubarić, D.; Ačkar, Đ.; Miličević, B.; Šereš, Z.; Dokić, L.; Šoronja-Simović, D.; et al. The Influence of Starch Sweeteners on Functional Properties of Cellulose Fat Mimetics: Rheological and Textural Aspects. Polymers 2023, 15, 2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Nie, S.P. The functional and nutritional aspects of hydrocolloids in foods. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 53, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemenicioğlu, A.; Farris, S.; Turkyilmaz, M.; Gulec, S. A review of current and future food applications of natural hydrocolloids. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 1389–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colla, K.; Costanzo, A.; Gamlath, S. Fat replacers in baked food products. Foods 2018, 7, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Luna, K.; Astiasarán, I.; Ansorena, D. Gels as fat replacers in bakery products: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 3768–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokusoglu, Ö.; Ünal, M.K. Fat replacers in meat products. Pak. J. Nutr. 2003, 2, 196–203. [Google Scholar]
- Caggia, C.; Palmeri, R.; Russo, N.; Timpone, R.; Randazzo, C.L.; Todaro, A.; Barbagallo, S. Employ of citrus by-product as fat replacer ingredient for bakery confectionery products. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.; Moin, A.; Ashraf, H.; Khan, A.; Giuffrè, A.M. Formulation and characterization of reduced fat muffins using a plant based fat replacer. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nikolić, I.; Šoronja-Simović, D.; Zahorec, J.; Dokić, L.; Lončarević, I.; Stožinić, M.; Petrović, J. Polysaccharide-Based Fat Replacers in the Functional Food Products. Processes 2024, 12, 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122701
Nikolić I, Šoronja-Simović D, Zahorec J, Dokić L, Lončarević I, Stožinić M, Petrović J. Polysaccharide-Based Fat Replacers in the Functional Food Products. Processes. 2024; 12(12):2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122701
Chicago/Turabian StyleNikolić, Ivana, Dragana Šoronja-Simović, Jana Zahorec, Ljubica Dokić, Ivana Lončarević, Milica Stožinić, and Jovana Petrović. 2024. "Polysaccharide-Based Fat Replacers in the Functional Food Products" Processes 12, no. 12: 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122701
APA StyleNikolić, I., Šoronja-Simović, D., Zahorec, J., Dokić, L., Lončarević, I., Stožinić, M., & Petrović, J. (2024). Polysaccharide-Based Fat Replacers in the Functional Food Products. Processes, 12(12), 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122701











