Study and Application of Rock Drilling Resistance Characteristics in the Jiyang Depression Formation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Formation Drillability Test
2.1. Uniaxial Compressive Strength Test
2.2. Hardness and Plasticity Tests
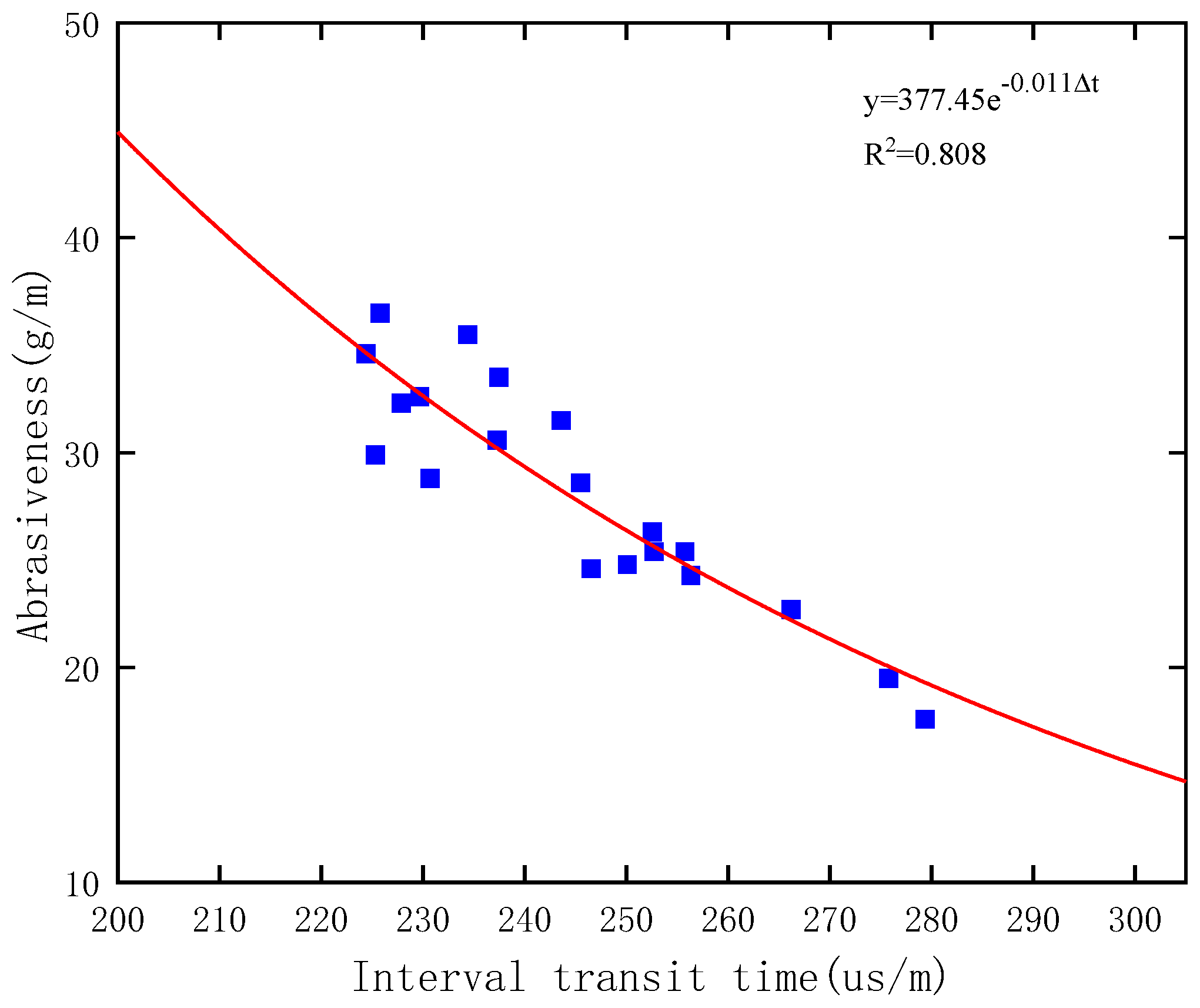
2.3. Abrasiveness Test
3. Geological Drillability Analysis
3.1. Modeling of Geological Drillability Parameters
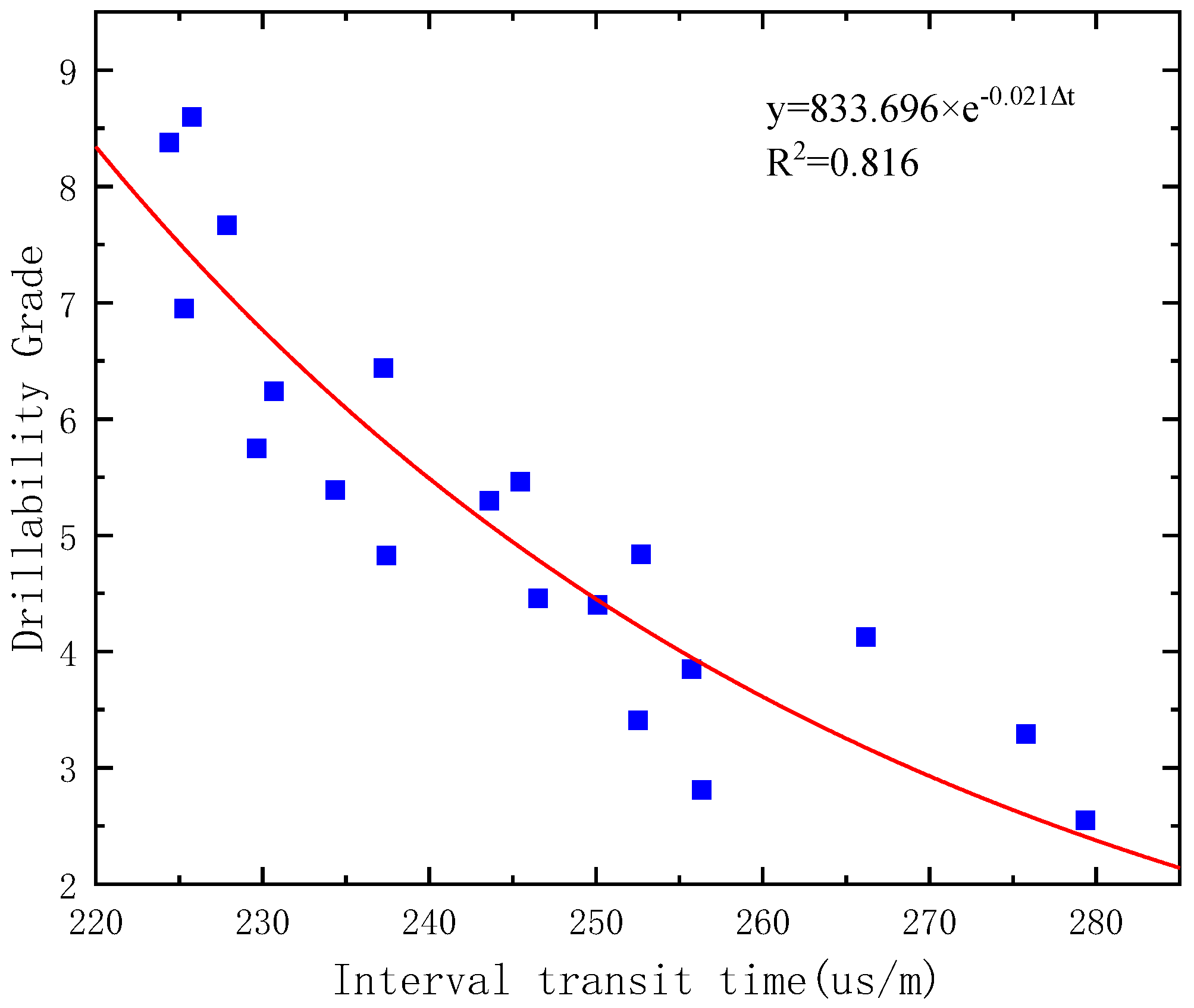
3.2. Profile of Rock Drillability Parameters
- (1)
- In the depth range of 3000–3500 m, there is a significant fluctuation in the rock drilling resistance characteristics parameters, indicating strong anisotropy of the rocks in this area, with greater variation in the lower layers compared to the upper layers. The abrupt change in drilling resistance parameters within this range may be attributed to variations in lithology or changes in horizontal stresses induced by bedding planes.
- (2)
- Within the range of 3000–3500 m, the uniaxial compressive strength of rocks in this interval ranges from 40 to 65 MPa, the hardness ranges from 120 to 1400 MPa, the plasticity coefficient ranges from 1 to 2, the PDC drillability rating ranges from 3 to 8, and the abrasiveness index ranges from 15 to 36 g/m. According to the classification table, the rocks in this interval are classified as a soft to medium-hard level, with a medium to medium-high level of abrasiveness and, overall, exhibit low plasticity based on the plasticity coefficient.
- (3)
- Overall, with the change in well depth, the patterns of change in the compressive strength, rock hardness, drillability rating, and abrasiveness index of rocks are consistent, while the pattern of change in the plasticity coefficient is the opposite. As the well depth increases, the difficulty of drilling increases, and field drilling records show that the mechanical drilling speed in this interval is relatively low, especially near the bottom of the well at around 3350 m, where the mechanical drilling speed is as low as 1.13 m/h. This is due to the higher drillability rating and stronger abrasiveness of the rocks in this location.
4. Drill Bit Selection and Field Application
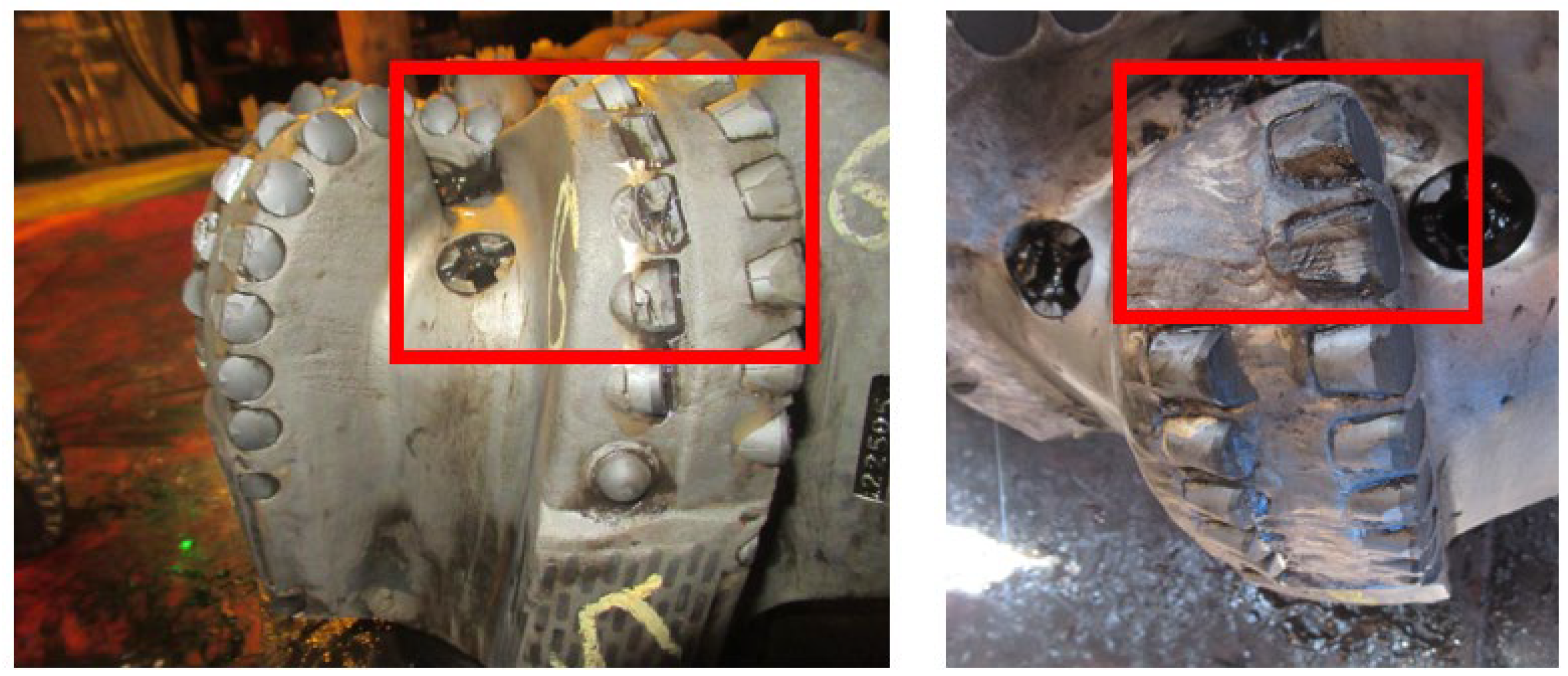
4.1. Drill Bit Failure Analysis and Selection
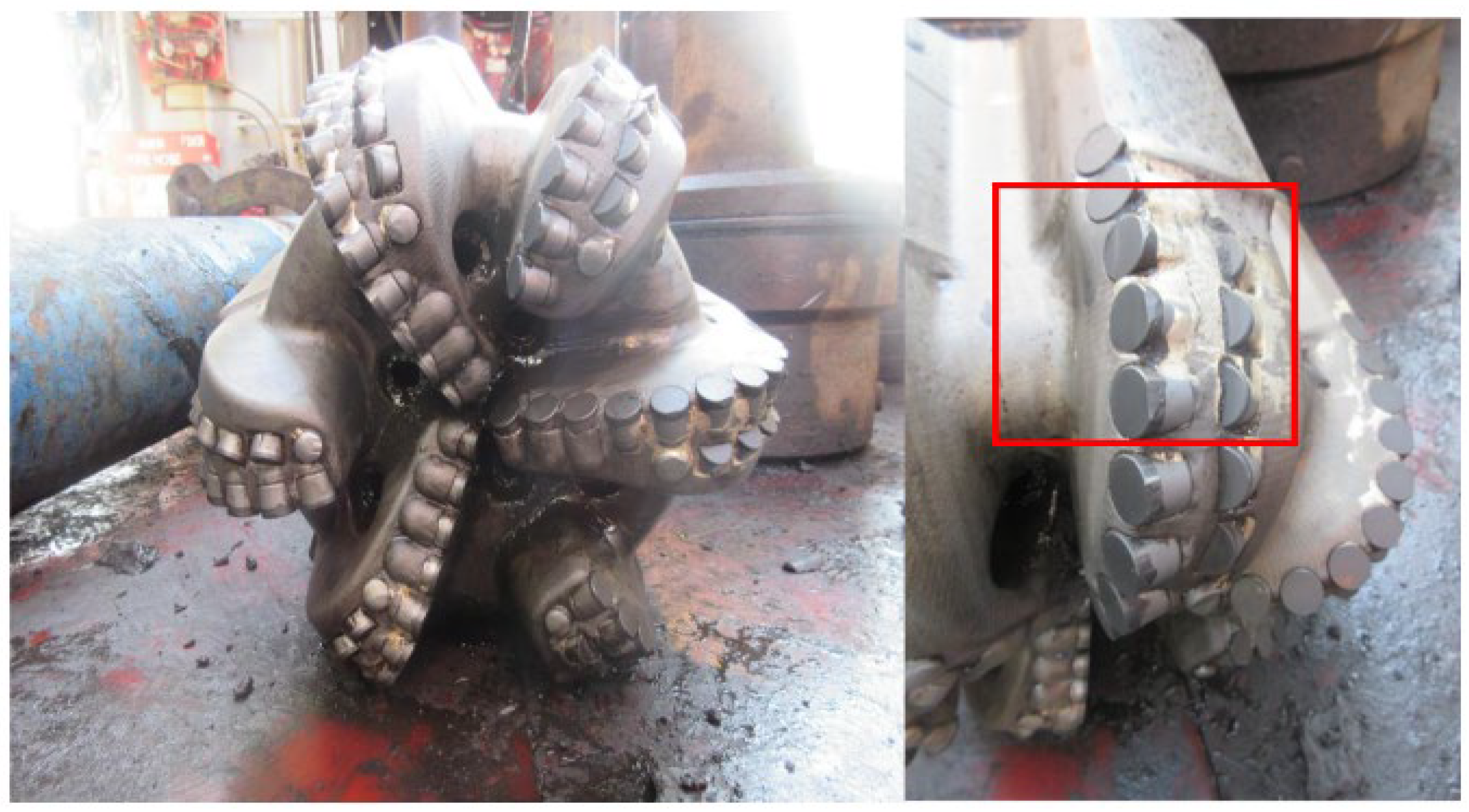
4.2. Field Application
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Based on logging data and laboratory experiments, a profile of rock drilling resistance parameters was established. The results indicate that within the Ji’yang sag formation, the uniaxial compressive strength ranges between 40 and 65 MPa, the hardness ranges between 120 and 1400 MPa, the plasticity coefficient ranges from 1 to 2, the PDC drillability index ranges between 3 and 8, and the abrasiveness index ranges between 15 and 36 g/m. The rocks within this interval are classified as a soft to medium-hard level, with a medium to medium-high level of abrasiveness, and overall exhibit low plasticity based on the plasticity coefficient.
- (2)
- The predominant failure mode of PDC drill bits within this interval is the chipping of PDC teeth at the crown and the wear of gauge protection elements. This is attributed to the strong anisotropy within this interval, causing intense lateral vibrations of the drill bit. The frequent and uneven loading leads to chipping of the PDC teeth. Moreover, the elevated bottom-hole pressure and temperature, coupled with the abrasive nature of the rocks, exacerbate the wear of PDC teeth. Through the observation of rock cuttings after drilling, it was found that at the depth of 3350 m where the mechanical drilling speed of the drill bit was low, the rocks mainly consisted of sandstone and conglomerate. These types of rocks exhibit strong abrasiveness, low plasticity, high compressive strength, and poor drillability, which is consistent with the results obtained through the laboratory experiments. This confirms the credibility of the rock drilling resistance characteristics parameter profile calculated by combining laboratory experiments and logging data, providing guidance for the optimization of drill bits at this depth.
- (3)
- Based on the rock drilling resistance characteristics and the analysis of failed drill bits from previous field operations, selection criteria for PDC drill bits specific to this formation were proposed. Before optimization, the mechanical drilling speed of the drill bit was only 5.8 m/h. After optimization, the overall wear of the drill bit was minimal, with only slight wear at the crown nose, and the mechanical drilling speed reached 12.58 m/h. The performance of the selected PDC drill bits on-site was satisfactory, resulting in a noticeable increase in drilling speed.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bo, H.; Jiinjen, S.; Sreshta, H. Optimization and application of PDC bit in Jiyang deep depression formation. Pet. Drill. Tech. 2011, 39, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, M.; Wang, H.; He, S.; Zhao, C.; Xie, Y.; Wang, S. The principal factor—A three-dimensional golden-section drill bit optimizing menthod based on formation anti-drilling ability. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 231, 212378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, N.; Ma, T.; Zhu, G.; Su, Q. Anti-drilling ability of Ziliujing conglomerate formation in Western Sichuan Basin of China. Petroleum 2023, 9, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaofeng, X.; Wei, S.; Kuanliang, Z.; Changhao, W.; Yan, Z.; Yunfeng, L.; Shibin, L. PDC bit optimization scheme for tight oil reservoirs in the Jidong Oilfield based on rock anti-drilling characteristics. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2022, 12, 2869–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, M.-K.; Song, Z.; Miao, X.; Wang, S.; Gao, D.-L. Quantitative Prediction of Rock Drillability in Various Drilling Directions in Shale Formation. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Energy, Power and Environmental Engineering (ICEPEE2017), Shanghai, China, 23–24 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Y.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Q.; Luo, M.; Zhang, C.; Dai, X.; Wei, W.; Deng, X. A new model for evaluating rock drillability considering the rock plasticity and chip hold down effect caused by hydrostatic column pressure under high confining pressure. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 227, 211806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Yao, J.L.; Yang, B. Anti-drilling characteristics of Xujiahe formation of Shuangyushi structure in western Sichuan. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2022, 22, 7846–7852. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Yang, M.; Meng, Y.; Liu, H.; Han, L.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, H. The assessment of correlation between rock drillability and mechanical properties in the laboratory and in the field under different pressure conditions. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 30, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, U. Drillability of a Rock in Terms of Its Physico-Mechanical and Micro-Structural Properties//ARMA US Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium; ARMA-09-040; ARMA: Asheville, NC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- DZ/T 0276-2015; Testing Specifications for Rock Physical and Mechanical Properties. Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Moein, M.J.A.; Shaabani, E.; Rezaeian, M. Experimental evaluation of hardness models by drillability tests for carbonate rocks. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2014, 113, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z. Study on Rock Drillability Prediction and Drilling Parameter Optimization Based on Well Site Data of Nanhai A Block; Northeast Petroleum University: Daqing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, S.; Meng, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, G.; Yang, X.; Jiao, Y. Suggestions for improvement and optimization of rock drillability determination methods. Acta Pet. Sin. 2023, 44, 1562. [Google Scholar]
- SY/T 5426-2016; The Rock Drillability Testing and Grading Method for Oil and Gas Well Drilling Engineering. Nation Energy Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Yang, Y.X.; Gao, X.; Chen, H. A new method for measuring and grading of PDC bit rock drillability. Chin. J. Undergr. Space Eng. 2019, 15, 811–819. [Google Scholar]
- Etesami, D.; Shahbazi, K. Prediction of uniaxial compressive strength of underground formations from sonic log parameters. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2014, 32, 1641–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Meng, J.; Zhang, Z. Application of acoustic travel time logging in rock drillability prediction. Pet. Geol. Oil Field Dev. Daqing 2006, 25, 94–96. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Dang, W.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y. Individual Drilling Bit Design and Optimization in Mahu Area//MATEC Web of Conferences. EDP Sci. 2017, 128, 05017. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, X.; Guo, D.; Cao, D. Explanation method of coal and rock parameters based on conventional log information. Coal Min. Technol. 2014, 19, 13–16. [Google Scholar]


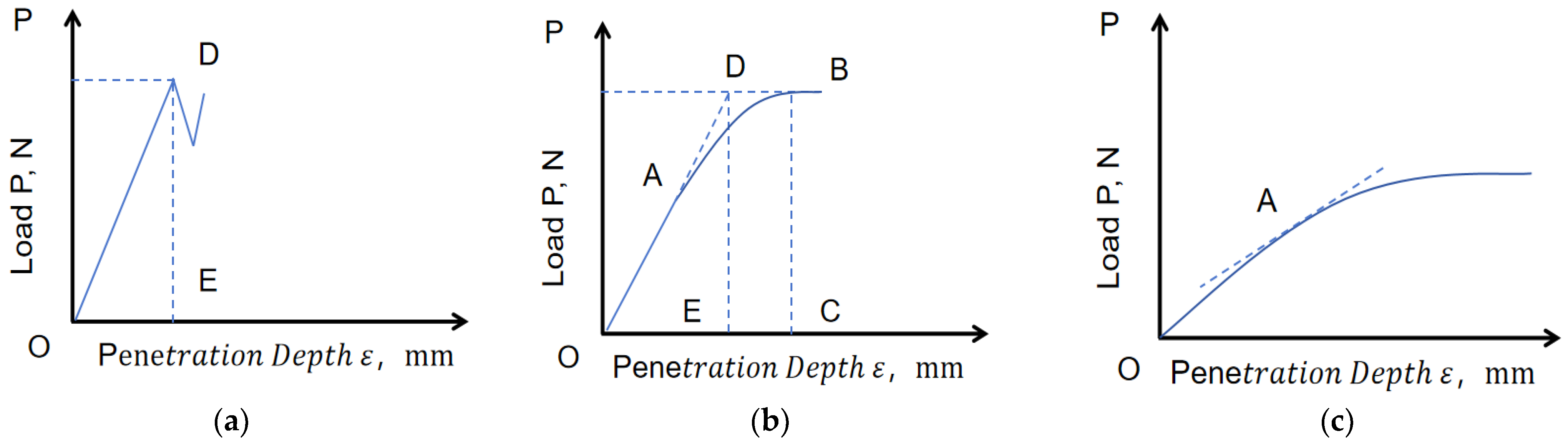







| Hardness, ×100 MPa | Grade | Category |
|---|---|---|
| ≤1 | 1 | Soft |
| 1~2.5 | 2 | |
| 2.5~5 | 3 | Medium-soft |
| 5~10 | 4 | |
| 10~15 | 5 | Medium-hard |
| 15~20 | 6 | |
| 20~30 | 7 | Hard |
| 30~40 | 8 | |
| 40~50 | 9 | Very hard |
| 50~60 | 10 | |
| 60~70 | 11 | Extremely hard |
| ≥70 | 12 |
| Category | Brittle | Brittle-Ductile Transition | Ductile | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Plasticity–High Plasticity | ||||||
| Level | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 1 | >1~2 | 2~3 | 3~4 | 4~6 | >6~∞ | |
| Number | Grade | Kd | Drilling Time t, s | Classification | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First | Second | Third | ||||
| 1 | I | Kd < 2 | t < 22 | I (Soft) | ||
| 2 | II | 2 ≤ Kd < 3 | 22 ≤ t < 23 | |||
| 3 | III | 3 ≤ Kd < 4 | 23 ≤ t < 24 | 22 ≤ t < 23 | ||
| 4 | IV | 4 ≤ Kd < 5 | 24 ≤ t < 25 | 23 ≤ t < 24 | ||
| 5 | V | 5 ≤ Kd < 6 | 25 ≤ t < 26 | 24 ≤ t < 25 | 22 ≤ t < 23 | II (Medium) |
| 6 | VI | 6 ≤ Kd < 7 | 26 ≤ t < 27 | 25 ≤ t < 26 | 23 ≤ t < 24 | |
| 7 | VII | 7 ≤ Kd < 8 | 26 ≤ t < 27 | 24 ≤ t < 25 | ||
| 8 | VIII | 8 ≤ Kd < 9 | 25 ≤ t < 26 | III (Hard) | ||
| 9 | IX | 9 ≤ Kd < 10 | 26 ≤ t < 27 | |||
| 10 | X | Kd ≥ 10 | ||||
| Number | Depth/m | Drilling Resistance Characteristics Parameters | Logging Data | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pucs (MPa) | Hy (MPa) | Kp | Kd | GWL (g/m) | AC (μs/m) | ||
| 1 | 3048.32 | 46.28 | 116.57 | 1.02 | 2.55 | 17.6 | 279.3495558 |
| 2 | 3052.43 | 48.90 | 262.78 | 1.10 | 2.81 | 24.3 | 256.3234251 |
| 3 | 3056.6 | 42.60 | 280.43 | 1.04 | 3.41 | 26.3 | 252.512415 |
| 4 | 3062.45 | 50.13 | 315.64 | 1.21 | 3.85 | 25.4 | 255.7313221 |
| 5 | 3113.9 | 49.60 | 470.28 | 1.13 | 4.40 | 24.8 | 250.0777333 |
| 6 | 3120.67 | 47.28 | 133.27 | 1.23 | 4.13 | 22.7 | 266.1806543 |
| 7 | 3140.69 | 53.80 | 156.32 | 1.03 | 3.29 | 19.5 | 275.7690876 |
| 8 | 3157.19 | 54.40 | 425.1217 | 1.12 | 4.84 | 25.4 | 252.7071961 |
| 9 | 3175.33 | 49.20 | 383.842 | 1.15 | 4.46 | 24.6 | 246.5077964 |
| 10 | 3186.47 | 52.10 | 640.39 | 1.13 | 5.46 | 28.6 | 245.4569892 |
| 11 | 3222.10 | 55.96 | 713.24 | 1.22 | 4.83 | 33.5 | 237.4300000 |
| 12 | 3256.54 | 57.70 | 752.61 | 1.26 | 5.39 | 35.5 | 234.3725875 |
| 13 | 3280.32 | 56.32 | 925.36 | 1.14 | 5.75 | 32.6 | 229.6540643 |
| 14 | 3300.67 | 62.10 | 764.32 | 1.15 | 5.30 | 31.5 | 243.5846692 |
| 15 | 3314.55 | 57.28 | 935.93 | 1.26 | 6.44 | 30.6 | 237.2523485 |
| 16 | 3350.46 | 60.78 | 1148.75 | 1.25 | 6.24 | 28.8 | 230.6710892 |
| 17 | 3380.70 | 67.28 | 1263.12 | 1.03 | 6.95 | 29.9 | 225.2970828 |
| 18 | 3392.60 | 63.96 | 1460.58 | 1.07 | 7.67 | 32.3 | 227.8445719 |
| 19 | 3410.78 | 66.32 | 1572.16 | 1.28 | 8.38 | 34.6 | 224.4036872 |
| 20 | 3460.30 | 70.50 | 1686.33 | 1.15 | 8.60 | 36.5 | 225.7457129 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Cheng, W.; Zhu, L. Study and Application of Rock Drilling Resistance Characteristics in the Jiyang Depression Formation. Processes 2024, 12, 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12050952
Ma X, Cheng W, Zhu L. Study and Application of Rock Drilling Resistance Characteristics in the Jiyang Depression Formation. Processes. 2024; 12(5):952. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12050952
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xiaoyong, Wei Cheng, and Liang Zhu. 2024. "Study and Application of Rock Drilling Resistance Characteristics in the Jiyang Depression Formation" Processes 12, no. 5: 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12050952
APA StyleMa, X., Cheng, W., & Zhu, L. (2024). Study and Application of Rock Drilling Resistance Characteristics in the Jiyang Depression Formation. Processes, 12(5), 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12050952






