Unveiling the Superiority of Innovative Carbonated Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems in Improving the Stability of Acid-Labile Drugs: Atorvastatin as a Model Drug
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. UPLC Method for Drug Quantification
2.3. Preparation of SNEDDS Formulations
2.4. Preparation of Carbonated SNEDDS Formulation C-F6
2.5. Preparation of AT-Loaded SNEDDS Formulation
2.6. Miscibility Study
2.7. Emulsification Study
2.8. Particle Size, PDI, and Zeta Potential Measurement
2.9. AT Solubility
2.10. AT Content
2.11. In vitro Dissolution Study
2.12. Characterization of Solid SNEDDS Formulation
2.12.1. FTIR
2.12.2. DSC
2.12.3. PXRD
2.13. pH Measurement
2.14. Stability Study
2.15. Degradation Kinetic Study
3. Results and Discussion
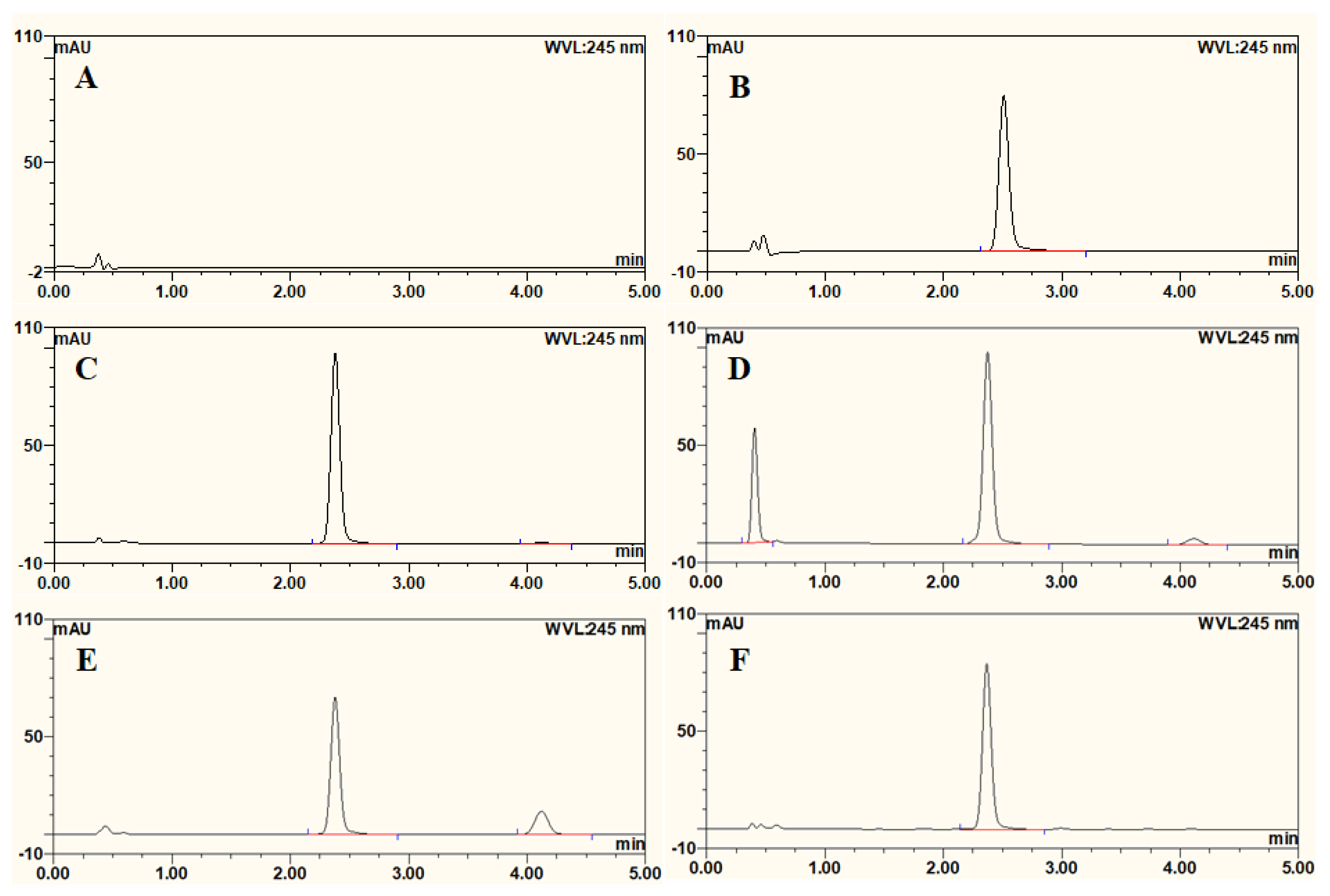
3.1. UPLC Method for Estimation of AT
3.2. Evaluation of SNEDDS Formulations
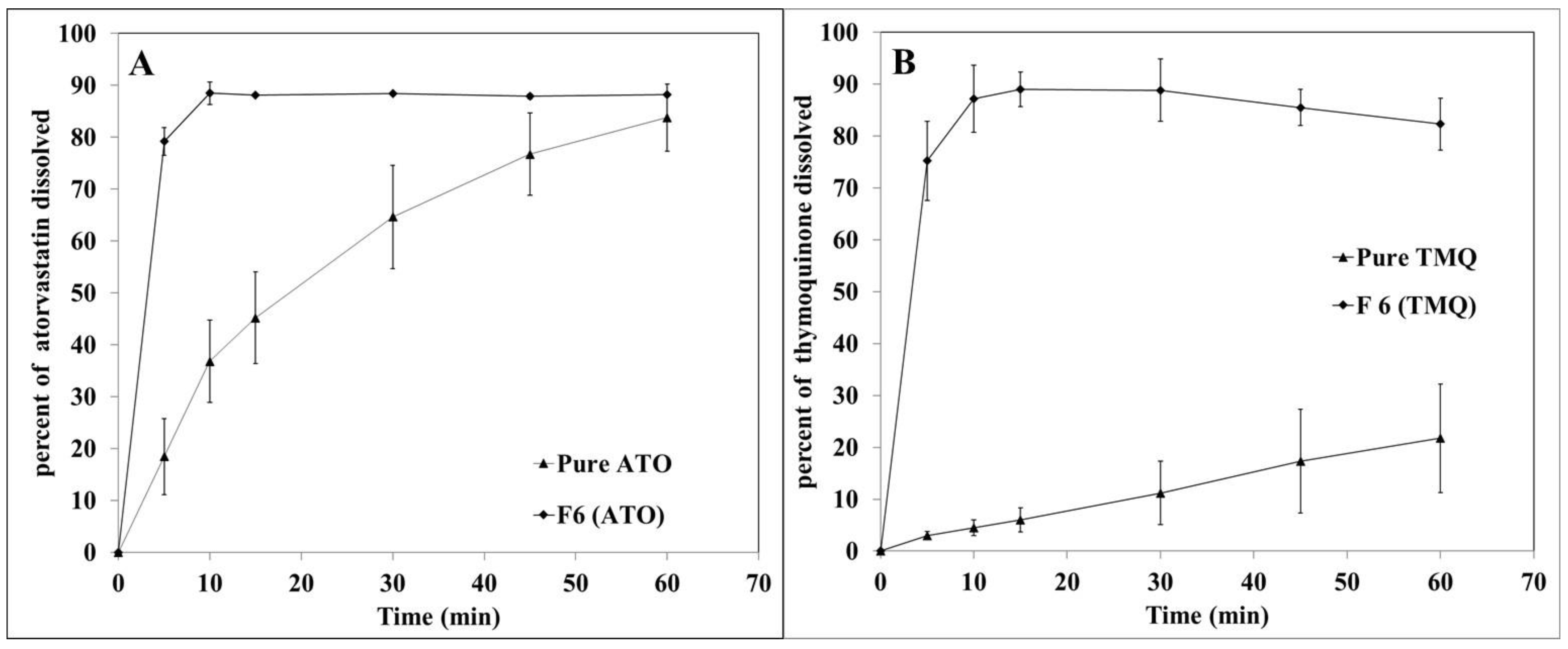
3.3. In vitro Dissolution Study
3.4. Evaluation of Solidified SNEDDS
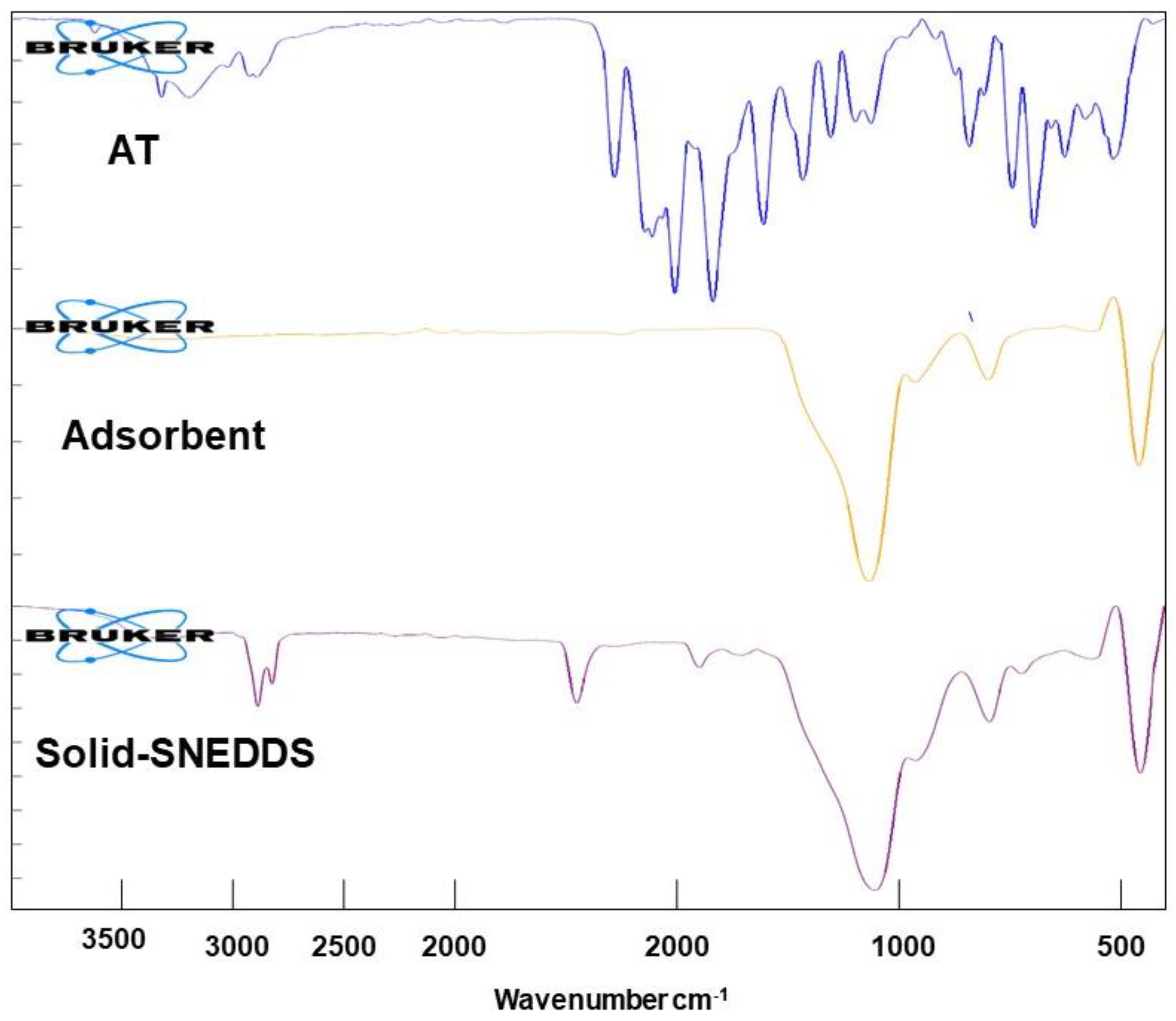
3.4.1. FTIR
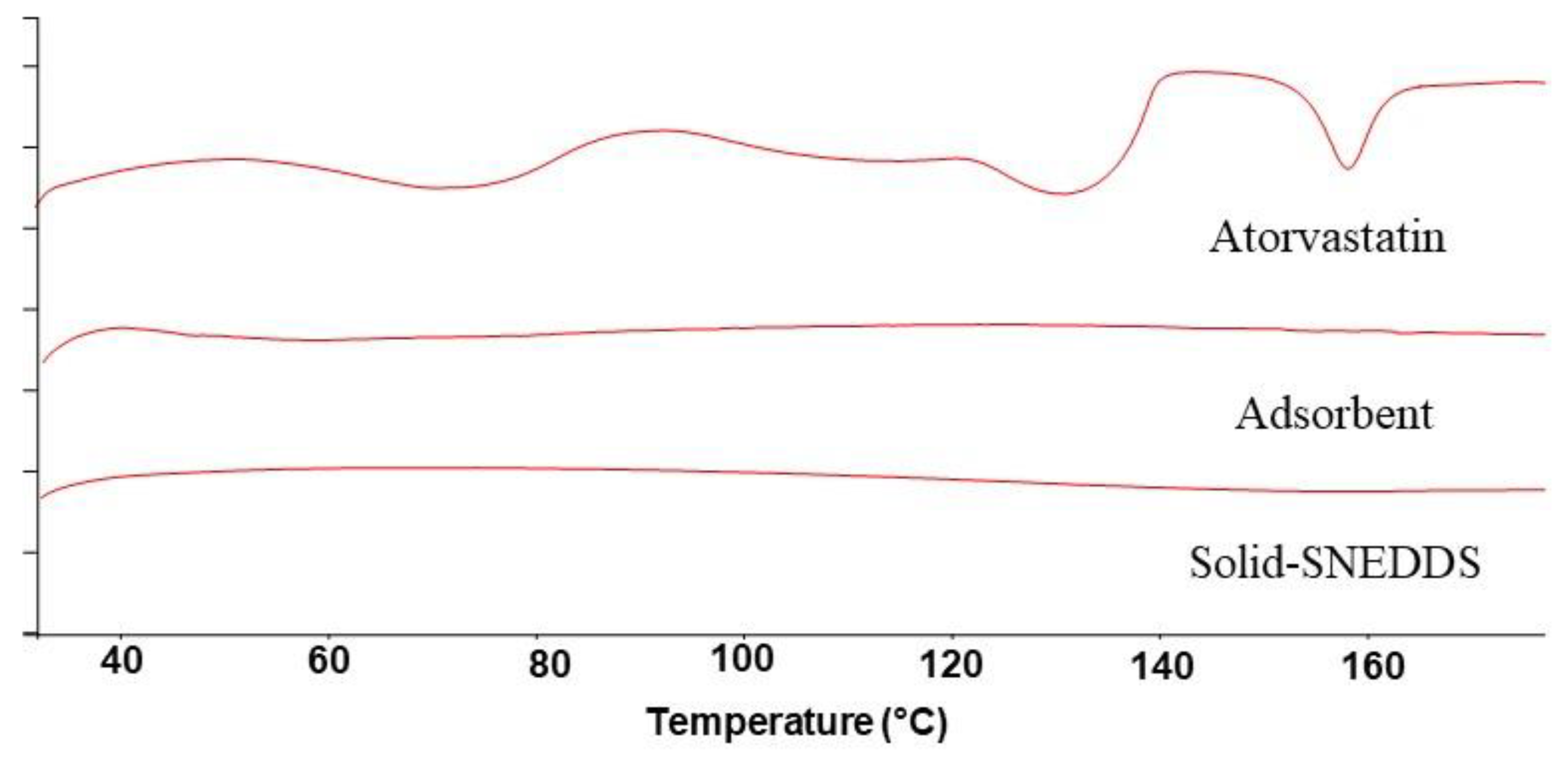
3.4.2. DSC
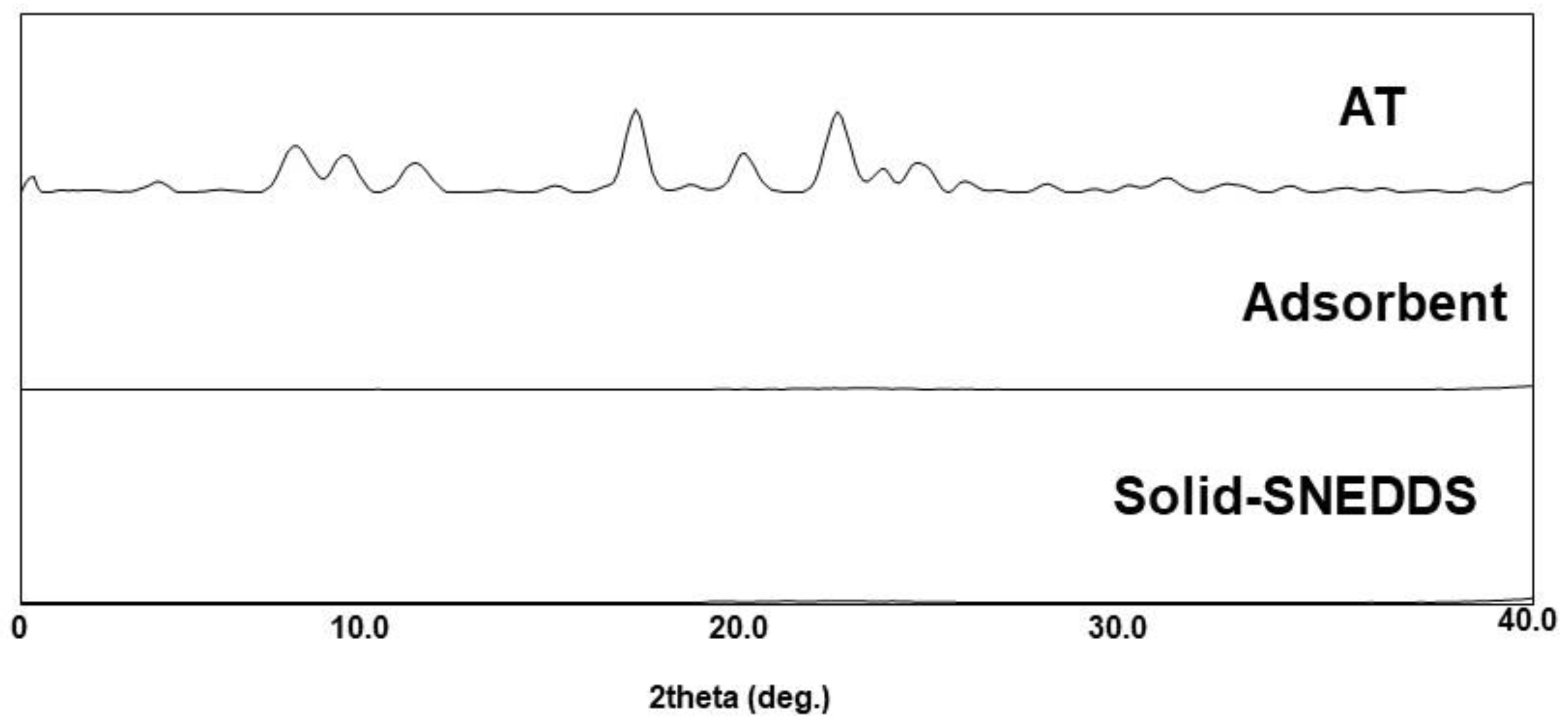
3.4.3. PXRD
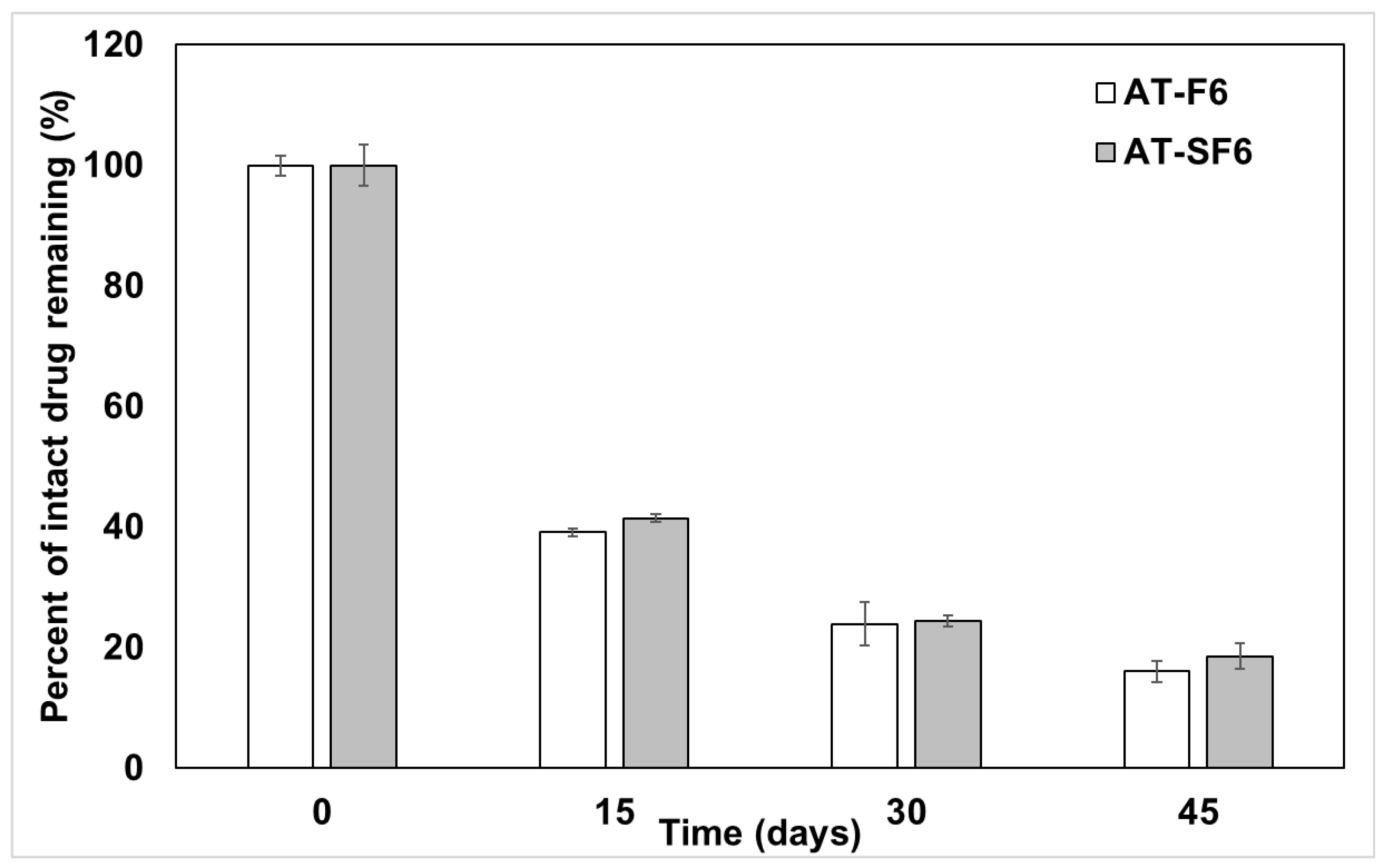
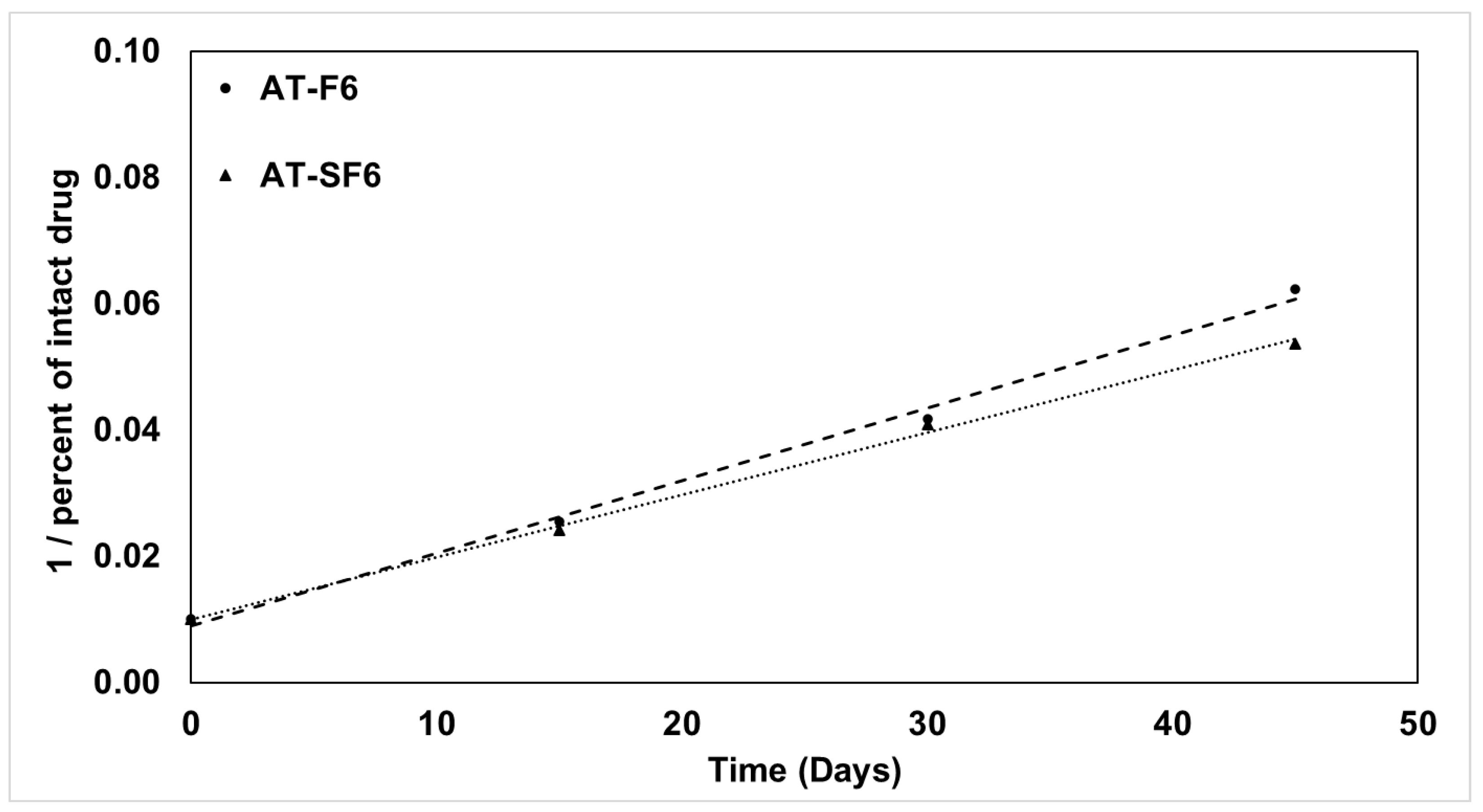
3.5. Kinetic Stability of AT in Liquid and Solid SNEDDS Formulation
3.6. Evaluation of Carbonated SNEDDS
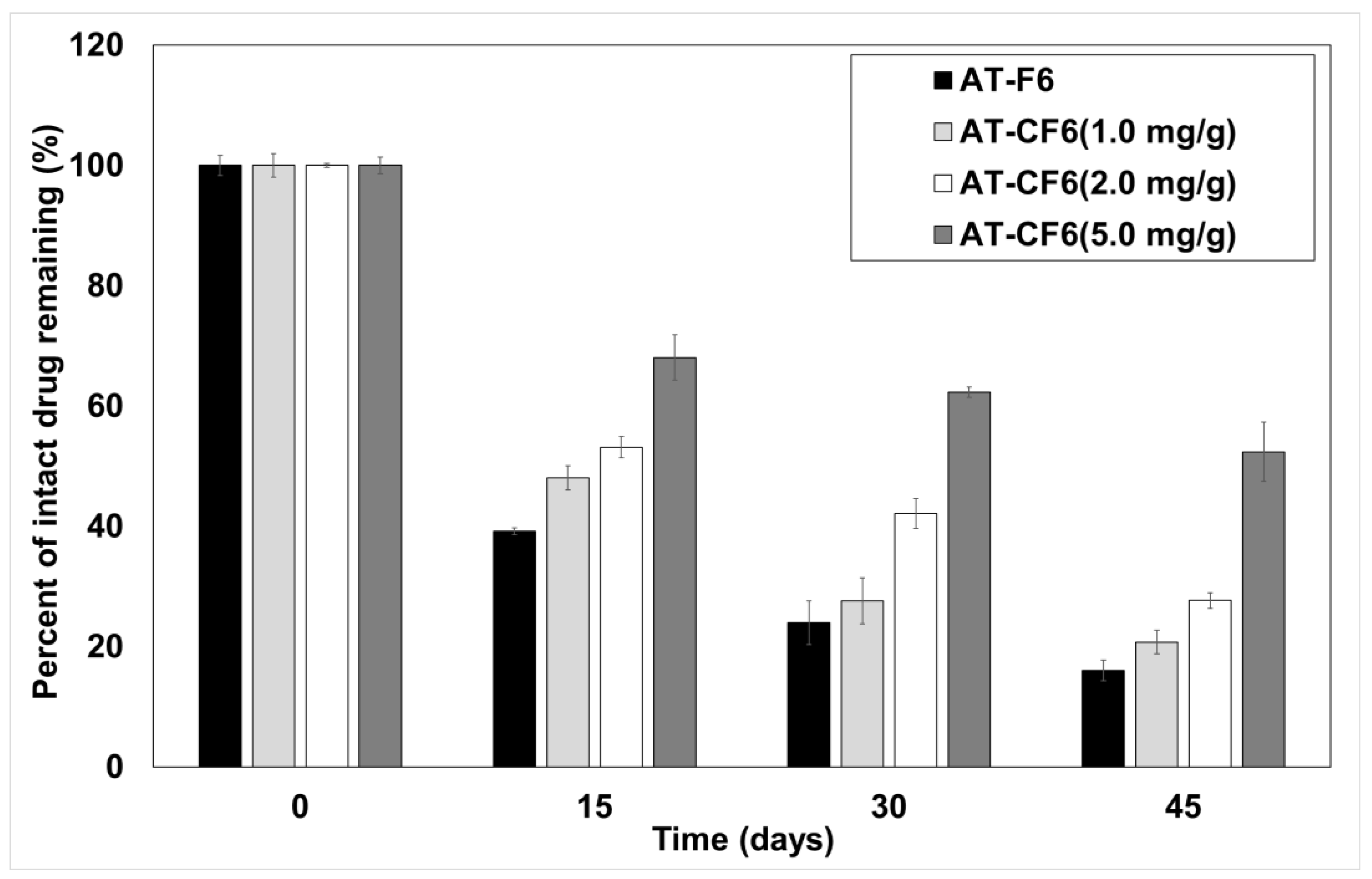
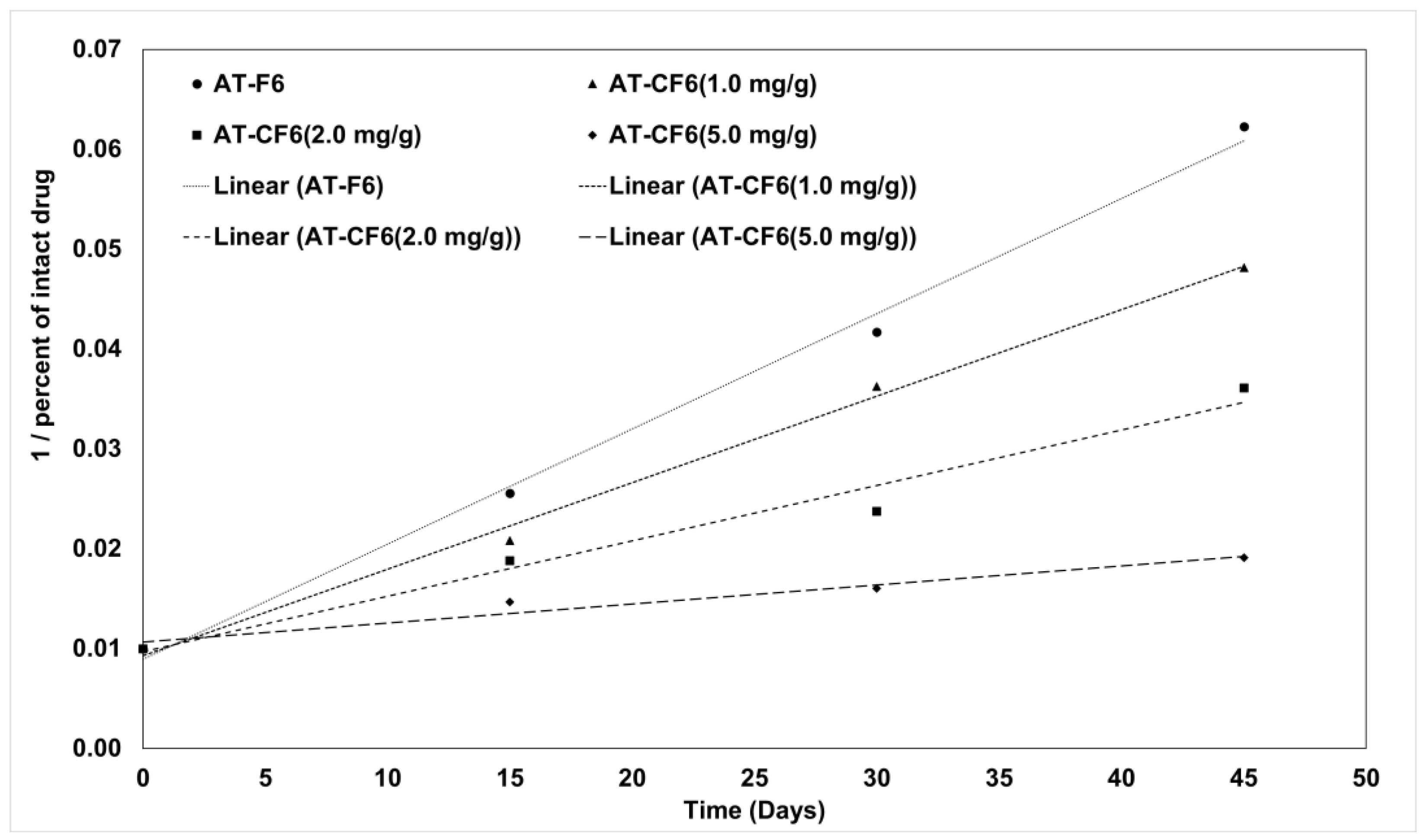
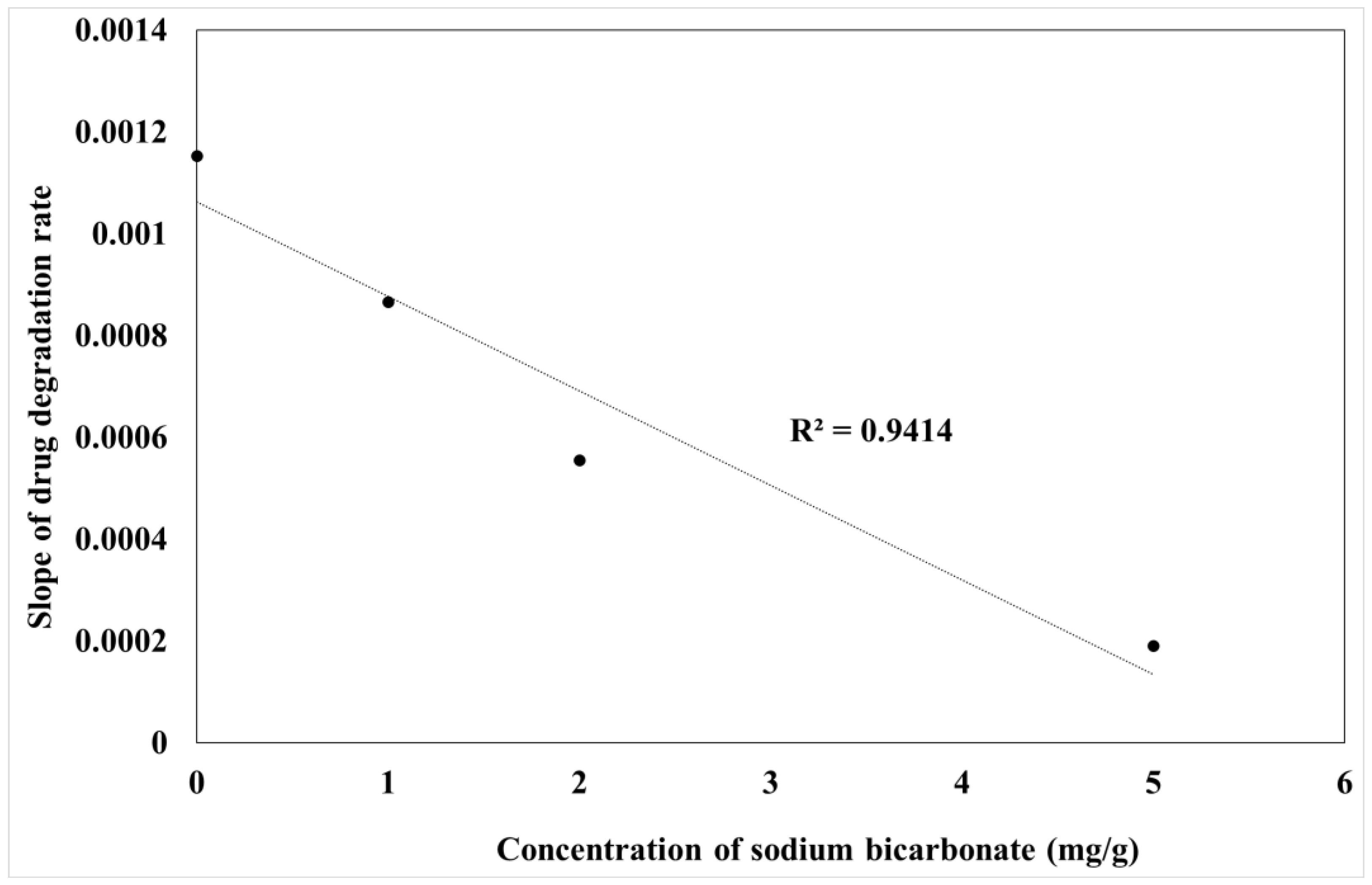
3.7. Kinetic Stability of AT in Liquid and Carbonated SNEDDS Formulation
3.8. Future Prospective
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Y.; Levons, J.; Narang, A.S.; Raghavan, K.; Rao, V.M. Reactive impurities in excipients: Profiling, identification and mitigation of drug–excipient incompatibility. Aaps Pharmscitech 2011, 12, 1248–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharate, S.S.; Bharate, S.B.; Bajaj, A.N. Interactions and incompatibilities of pharmaceutical excipients with active pharmaceutical ingredients: A comprehensive review. J. Excip. Food Chem. 2016, 1, 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthy, R.; Manning, M.C. The stability factor: Importance in formulation development. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2002, 3, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Koo, S.; Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Yaremenko, A.V.; et al. Oral drug delivery platforms for biomedical applications. Mater. Today 2023, 62, 296–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poovi, G.; Damodharan, N. Lipid nanoparticles: A challenging approach for oral delivery of BCS Class-II drugs. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 4, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Shrestha, N.; Préat, V.; Beloqui, A. Overcoming the intestinal barrier: A look into targeting approaches for improved oral drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2020, 322, 486–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Han, X.; Zhao, C.; Wang, S.; Tang, X. Recent advance in biological responsive nanomaterials for biosensing and molecular imaging application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Jiang, Z.; Akakuru, O.U.; Li, J.; Wu, A. Nanoscale covalent organic frameworks: From controlled synthesis to cancer therapy. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 12417–12435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, P.; Park, J.-S. Recent trends of self-emulsifying drug delivery system for enhancing the oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 439–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.L.J.; Billa, N. Improved bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs through gastrointestinal muco-adhesion of lipid nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beloqui, A.; del Pozo-Rodríguez, A.; Isla, A.; Rodríguez-Gascón, A.; Solinís, M.Á. Nanostructured lipid carriers as oral delivery systems for poorly soluble drugs. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 42, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daeihamed, M.; Dadashzadeh, S.; Haeri, A.; Faghih Akhlaghi, M. Potential of liposomes for enhancement of oral drug absorption. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umerska, A.; Gaucher, C.; Oyarzun-Ampuero, F.; Fries-Raeth, I.; Colin, F.; Villamizar-Sarmiento, M.G.; Maincent, P.; Sapin-Minet, A. Polymeric nanoparticles for increasing oral bioavailability of curcumin. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehanna, M.M.; Mneimneh, A.T. Formulation and applications of lipid-based nanovehicles: Spotlight on self-emulsifying systems. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsin, K.; Alamri, R.; Ahmad, A.; Raish, M.; Alanazi, F.K.; Hussain, M.D. Development of self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems for the enhancement of solubility and oral bioavailability of fenofibrate, a poorly water-soluble drug. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 2829–2838. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, F.U.; Shah, K.U.; Shah, S.U.; Khan, I.U.; Khan, G.M.; Khan, A. From nanoemulsions to self-nanoemulsions, with recent advances in self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS). Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 1325–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahba, A.A.-W.; Ahmed, A.R.; Alanazi, F.K.; Mohsin, K.; Abdel-Rahman, S.I. Multi-layer self-nanoemulsifying pellets: An innovative drug delivery system for the poorly water-soluble drug cinnarizine. Aaps Pharmscitech 2018, 19, 2087–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshadidi, A.; Shahba, A.A.-W.; Sales, I.; Rashid, M.A.; Kazi, M. Combined curcumin and lansoprazole-loaded bioactive solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (Bio-SSNEDDS). Pharmaceutics 2021, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhasani, K.F.; Kazi, M.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Shahba, A.A.; Alanazi, F.K. Self-nanoemulsifying ramipril tablets: A novel delivery system for the enhancement of drug dissolution and stability. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5435–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandić, J.; Pobirk, A.Z.; Vrečer, F.; Gašperlin, M. Overview of solidification techniques for self-emulsifying drug delivery systems from industrial perspective. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 533, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahba, A.A.-W.; Alanazi, F.K.; Abdel-Rahman, S.I. Stabilization benefits of single and multi-layer self-nanoemulsifying pellets: A poorly-water soluble model drug with hydrolytic susceptibility. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.N.; Dehghan, M.H.G. Enhanced bioavailability and dissolution of atorvastatin calcium from floating microcapsules using minimum additives. Sci. Pharm. 2012, 80, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, M.A.; Elbadawy, H.M.; Shaker, M.A. Improved solubility, dissolution, and oral bioavailability for atorvastatin-Pluronic® solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 574, 118891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wei, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Qian, S. Co-amorphous systems for the delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs: Recent advances and an update. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 1411–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, A.M.; Ibrahim, H.M.; Samy, A.M. Development and optimisation of atorvastatin calcium loaded self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) for enhancing oral bioavailability: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Microencapsul. 2017, 34, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Mantri, S.; Pashikanti, S.; VRamana Murthy, K. Development and characterization of self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS) of atorvastatin calcium. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2012, 9, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, M.; Mallesh, K. Self-nano emulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) for oral delivery of atorvastatin-formulation and bioavailability studies. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2013, 3, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.S. Formulation and in vitro characterization of solid-self nanoemulsifying drug delivery system of atorvastatin calcium. Asian J. Pharm. (AJP) 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, K.S.; Arora, S.; Yasaswi, P.S.; Nirale, P.; Solanki, A.; Bhat, J. Self-nano-emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems of Atorvastatin Calcium Liquid Filled in Hard Shell Capsules for Improved Oral Bioavailability in Rabbits. Curr. Nanosci. 2024, 20, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, D.W.; Son, H.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.R.; Lee, S.G.; Song, S.H.; Chae, B.R.; Choi, Y.W. Development of a solidified self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (S-SMEDDS) for atorvastatin calcium with improved dissolution and bioavailability. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 506, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadu, P.J.; Kushare, S.S.; Thacker, D.D.; Gattani, S.G. Enhancement of oral bioavailability of atorvastatin calcium by self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS). Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2011, 16, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindarajan, R.; Landis, M.; Hancock, B.; Gatlin, L.A.; Suryanarayanan, R.; Shalaev, E.Y. Surface acidity and solid-state compatibility of excipients with an acid-sensitive API: Case study of atorvastatin calcium. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.A.; Yoshida, M.I.; Belinelo, V.J.; Valotto, R.S. Degradation kinetics of atorvastatin under stress conditions and chemical analysis by HPLC. Molecules 2013, 18, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameta, R.K.; Soni, K.; Bhattarai, A. Recent advances in improving the bioavailability of hydrophobic/lipophilic drugs and their delivery via self-emulsifying formulations. Colloids Interfaces 2023, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, A.Y.; Shahba, A.A.-W. Development of a Multifunctional Oral Dosage Form via Integration of Solid Dispersion Technology with a Black Seed Oil-Based Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahba, A.A.-W.; Sherif, A.Y.; Elzayat, E.M.; Kazi, M. Combined Ramipril and Black Seed Oil Dosage Forms Using Bioactive Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (BIO-SNEDDSs). Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazi, M.; Alhajri, A.; Alshehri, S.M.; Elzayat, E.M.; Al Meanazel, O.T.; Shakeel, F.; Noman, O.; Altamimi, M.A.; Alanazi, F.K. Enhancing oral bioavailability of apigenin using a bioactive self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (Bio-SNEDDS): In vitro, in vivo and stability evaluations. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshora, D.H.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Sherif, A.Y. Optimization and Validation of Sensitive UPLC-PDA Method for Simultaneous Determination of Thymoquinone and Glibenclamide in SNEDDs Formulations Using Response Surface Methodology. Separations 2023, 10, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inugala, S.; Eedara, B.B.; Sunkavalli, S.; Dhurke, R.; Kandadi, P.; Jukanti, R.; Bandari, S. Solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (S-SNEDDS) of darunavir for improved dissolution and oral bioavailability: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 74, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, N.A.; Shaban, S.A.; Ibrahim, F.A.; Mahmoud, A.S. Degradation of methyl orange using Fenton catalytic reaction. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgary, S.; Sahebkar, A.; Goli-Malekabadi, N. Ameliorative effects of Nigella sativa on dyslipidemia. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2015, 38, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majdalawieh, A.F.; Yousef, S.M.; Abu-Yousef, I.A. Thymoquinone, a major constituent in Nigella sativa seeds, is a potential preventative and treatment option for atherosclerosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 909, 174420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Oanzi, Z.H.; Alenazy, F.O.; Alhassan, H.H.; El-Aassar, M.R.; Alzarea, A.I.; Alzarea, S.I.; Abbas, A.M.; Alanazi, M.H.; Al-Enazi, M.M. Effects of Thymoquinone Alone or in Combination with Losartan on the Cardiotoxicity Caused by Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Hypercholesterolemia. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhu, L.; Liu, H.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, F.; Pei, Z. Thymoquinone reduces cardiac damage caused by hypercholesterolemia in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Yen, C.-C.; Hsu, M.-C.; Wu, Y.-T. Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems for enhancing solubility, permeability, and bioavailability of sesamin. Molecules 2020, 25, 3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, P.; Rastogi, V.; Verma, A. Application of Box–Behnken design and desirability function in the development and optimization of self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system for enhanced dissolution of ezetimibe. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, C.; Hemrajani, C.; Sharma, A.K.; Gupta, P.K.; Jha, N.K.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Gupta, G.; Singh, S.K.; Yang, J.-C.; Dwivedi, R.P.; et al. Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) mediated improved oral bioavailability of thymoquinone: Optimization, characterization, pharmacokinetic, and hepatotoxicity studies. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2023, 13, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardouh, A.R.; Nasef, A.M.; Mostafa, Y.; Gad, S. Design and evaluation of combined atorvastatin and ezetimibe optimized self-nano emulsifying drug delivery system. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 102093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kazemi, R.; Al-Basarah, Y.; Nada, A. Dissolution enhancement of atorvastatin calcium by cocrystallization. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqvi, A.; Ahmad, M.; Minhas, M.U.; Khan, K.U.; Batool, F.; Rizwan, A. Preparation and evaluation of pharmaceutical co-crystals for solubility enhancement of atorvastatin calcium. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 6191–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.Y.; Salwa Shirodkar, R.K.; Verma, R.; Kumar, L. Enhancement in dissolution rate of atorvastatin trihydrate calcium by formulating its porous tablet using sublimation technique. J. Pharm. Innov. 2020, 15, 498–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapourani, A.; Katopodis, K.; Valkanioti, V.; Chatzitheodoridou, M.; Cholevas, C.; Barmpalexis, P. Evaluation of suitable polymeric matrix/carriers during loading of poorly water soluble drugs onto mesoporous silica: Physical stability and in vitro supersaturation. Polymers 2024, 16, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, S.; An, J.; Park, C.; Kim, D.; Lee, J. Design and characterization of phosphatidylcholine-based solid dispersions of aprepitant for enhanced solubility and dissolution. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahraeini, S.S.; Akbari, J.; Saeedi, M.; Morteza-Semnani, K.; Abootorabi, S.; Dehghanpoor, M.; Rostamkalaei, S.S.; Nokhodchi, A. Atorvastatin solid lipid nanoparticles as a promising approach for dermal delivery and an anti-inflammatory agent. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shete, G.; Puri, V.; Kumar, L.; Bansal, A.K. Solid state characterization of commercial crystalline and amorphous atorvastatin calcium samples. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashish, A.Y.; Shahba, A.A.-W.; Alanazi, F.K.; Kazi, M. Adsorbent precoating by lyophilization: A novel green solvent technique to enhance cinnarizine release from solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (S-SNEDDS). Pharmaceutics 2022, 15, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-S.; Jin, S.-J.; Kim, J.-S.; Park, H.J.; Song, H.-S.; Neubert, R.H.; Hwang, S.-J. Preparation, characterization and in vivo evaluation of amorphous atorvastatin calcium nanoparticles using supercritical antisolvent (SAS) process. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhou, C.H.; Xu, Z.P. Self-nanoemulsifying drug-delivery system and solidified self-nanoemulsifying drug-delivery system. In Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 421–449. [Google Scholar]
- Ariaeinia, M.; Rahimpour, E.; Mirzaeei, S.; Fathi Azarbayjani, A.; Jouyban, A. Thermodynamic analysis of atorvastatin calcium in solvent mixtures at several temperatures. Phys. Chem. Liq. 2023, 61, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Yang, M.; Fan, J.H.; Feng, C.X.; Zhang, S.J.; Wang, J.X.; Guan, P.P.; Wu, W. Influences of sodium carbonate on physicochemical properties of lansoprazole in designed multiple coating pellets. Aaps Pharmscitech 2010, 11, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsulays, B.B.; Kulkarni, V.; Alshehri, S.M.; Almutairy, B.K.; Ashour, E.A.; Morott, J.T.; Alshetaili, A.S.; Park, J.-B.; Tiwari, R.V.; Repka, M.A. Preparation and evaluation of enteric coated tablets of hot-melt extruded lansoprazole. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vukkum, P.; Babu, J.M.; Muralikrishna, R. Stress degradation behavior of atorvastatin calcium and development of a suitable stability-indicating LC method for the determination of atorvastatin, its related impurities, and its degradation products. Sci. Pharm. 2013, 81, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

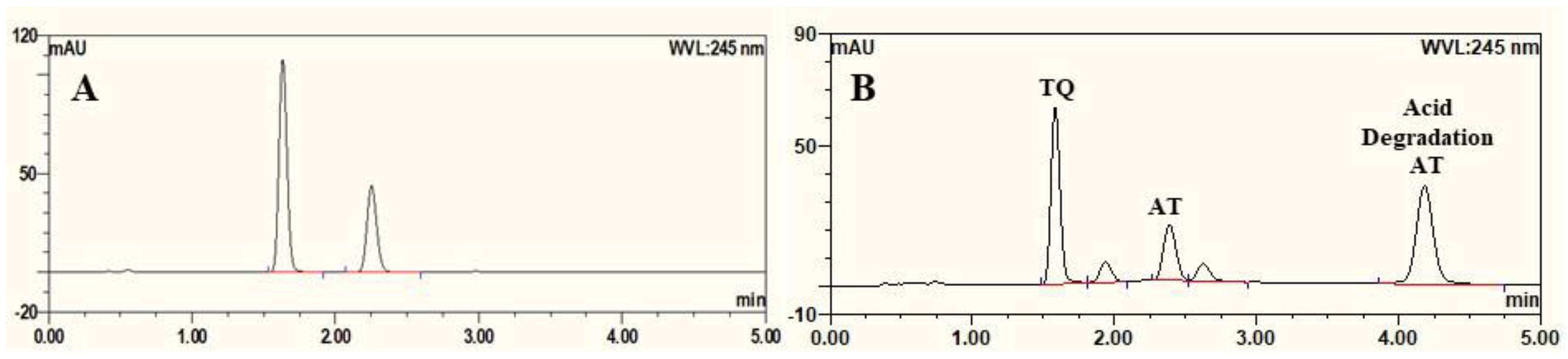
| Formulation Code | Surfactant (%) | Co-Surfactant (%) | Bioactive Oil (%) | ||||||
| T-85 | HCO-30 | LB | K-EL | PEG | I-308 | S-80 | LG | BSO | |
| F1 | 40 | 30 | 30 | ||||||
| F2 | 40 | 30 | |||||||
| F3 | 40 | 30 | |||||||
| F4 | 40 | 30 | |||||||
| F5 | 40 | 30 | |||||||
| F6 | 40 | 30 | |||||||
| F7 | 40 | 30 | |||||||
| F8 | 40 | 30 | |||||||
| F9 | 40 | 30 | |||||||
| F10 | 40 | 30 | |||||||
| F11 | 40 | 30 | |||||||
| F12 | 40 | 30 | |||||||
| F13 | 40 | 30 | |||||||
| F14 | 40 | 30 | |||||||
| F15 | 40 | 30 | |||||||
| F16 | 40 | 30 | |||||||
| Formulation Code | Miscibility | Physical Appearance | System Separation |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | Immiscible | ------ | ------ |
| F2 | Miscible | Turbid | Dispersible system with floating oil |
| F3 | Immiscible | ------ | ------ |
| F4 | Miscible | Turbid | Dispersible system with floating oil |
| F5 | Immiscible | ------ | ------ |
| F6 | Miscible | Clear solution | Uniform dispersion |
| F7 | Immiscible | ------ | ------ |
| F8 | Miscible | Suspended system | Indispensable system |
| F9 | Immiscible | ------ | ------ |
| F10 | Miscible | Semi-turbid solution | Dispersible system with floating oil |
| F11 | Miscible | Semi-turbid solution | Dispersible system with floating oil |
| F12 | Miscible | Semi-clear solution | Dispersible system with floating oil |
| F13 | Immiscible | ------ | ------ |
| F14 | Immiscible | ------ | ------ |
| F15 | Immiscible | ------ | ------ |
| F16 | Miscible | Bluish solution | Uniform dispersion |
| Formulation Code | Particle Size (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) | AT Solubility (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| F6 | 46.62 ± 0.12 | −35.2 ± 3.6 | 58.21 ± 2.56 |
| F16 | 85.91 ± 1.11 | −21.2 ± 1.1 | 7.88 ± 0.19 |
| F6 | S-F6 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-order | Slope | −1.779926884 | −1.741588269 |
| r2 | 0.821546666 | 0.821816861 | |
| First order | Slope | −0.039844248 | −0.037165163 |
| r2 | 0.957916108 | 0.94371274 | |
| Second order | Slope | 0.001153033 | 0.000987203 |
| r2 | 0.995319989 | 0.997570124 |
| Formulation Code | pH | PS (nm) | ZP (mV) | AT Solubility (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F6 | 4.8 ± 0.02 | 46.62 ± 0.12 | −35.2 ± 3.6 | 58.21 ± 2.56 |
| CF6 (1.0 mg) | 5.9 ± 0.05 | 32.42 ± 0.20 | −19.7 ± 1.4 | 73.89 ± 1.55 |
| CF6 (2.0 mg) | 6.1 ± 0.01 | 30.64 ± 0.38 | −11.6 ± 2.7 | 87.01 ± 4.35 |
| CF6 (5.0 mg) | 6.9 ± 0.03 | 23.95 ± 0.11 | −20.2 ± 2.3 | 91.85 ± 4.79 |
| AT-F6 | AT-CF6 (1.0 mg/g) | AT-CF6 (2.0 mg/g) | AT-CF6 (5.0 mg/g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-order | Slope | −1.7799 | −1.7213 | −1.5198 | −0.9907 |
| r2 | 0.82155 | 0.86408 | 0.88434 | 0.86853 | |
| First order | Slope | −0.0398 | −0.0351 | −0.0272 | −0.0135 |
| r2 | 0.95792 | 0.96474 | 0.96702 | 0.91776 | |
| Second order | Slope | 0.00115 | 0.00087 | 0.00056 | 0.00019 |
| r2 | 0.99532 | 0.99565 | 0.97335 | 0.95475 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sherif, A.Y.; Ibrahim, M.A. Unveiling the Superiority of Innovative Carbonated Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems in Improving the Stability of Acid-Labile Drugs: Atorvastatin as a Model Drug. Processes 2024, 12, 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12061169
Sherif AY, Ibrahim MA. Unveiling the Superiority of Innovative Carbonated Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems in Improving the Stability of Acid-Labile Drugs: Atorvastatin as a Model Drug. Processes. 2024; 12(6):1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12061169
Chicago/Turabian StyleSherif, Abdelrahman Y., and Mohamed A. Ibrahim. 2024. "Unveiling the Superiority of Innovative Carbonated Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems in Improving the Stability of Acid-Labile Drugs: Atorvastatin as a Model Drug" Processes 12, no. 6: 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12061169
APA StyleSherif, A. Y., & Ibrahim, M. A. (2024). Unveiling the Superiority of Innovative Carbonated Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems in Improving the Stability of Acid-Labile Drugs: Atorvastatin as a Model Drug. Processes, 12(6), 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12061169







