Assessing the Viability of Integrating Evaporation and Solvent Extraction Systems for Lithium Recovery from Low-Grade Brines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization of Brines (Samples)
2.2. Reagents and Solutions
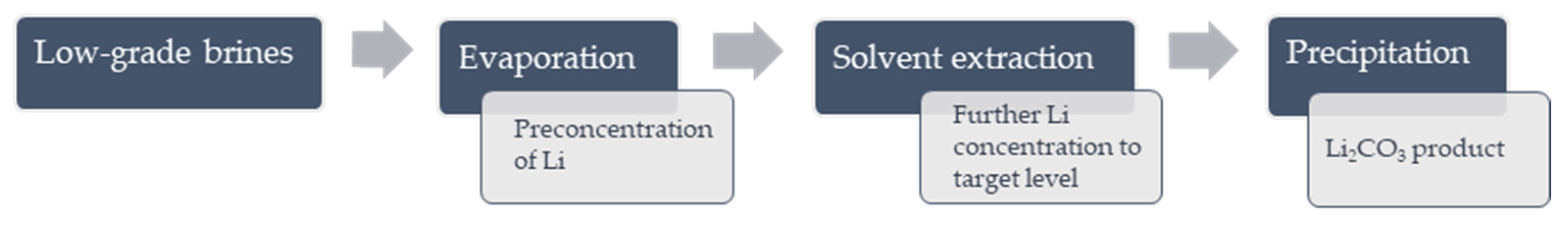
2.3. The Concept of Work and Experimental Procedures
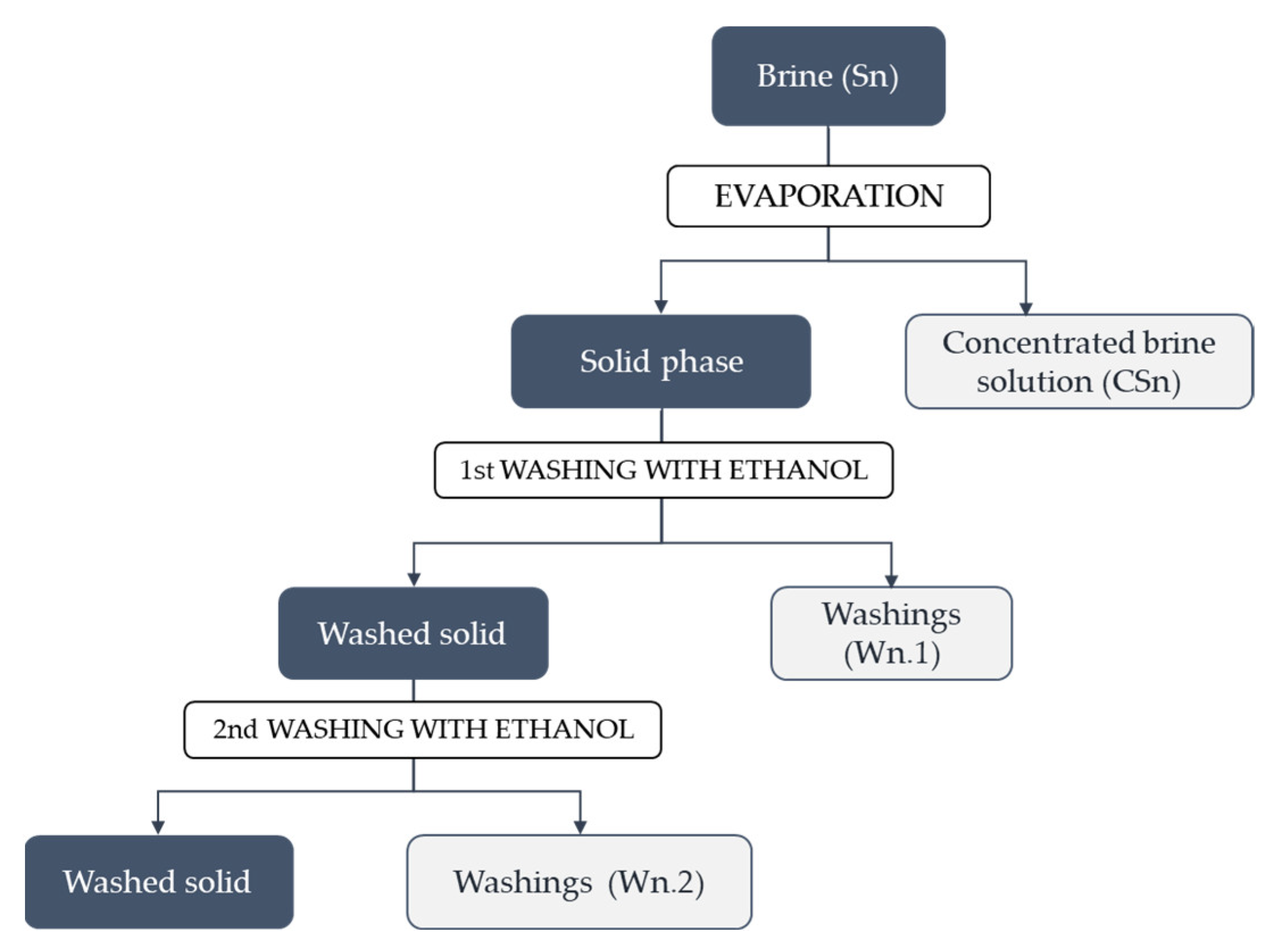
2.3.1. Evaporation
2.3.2. Solvent Extraction
2.4. Measurements of Li Concentrations
3. Results and Discussion
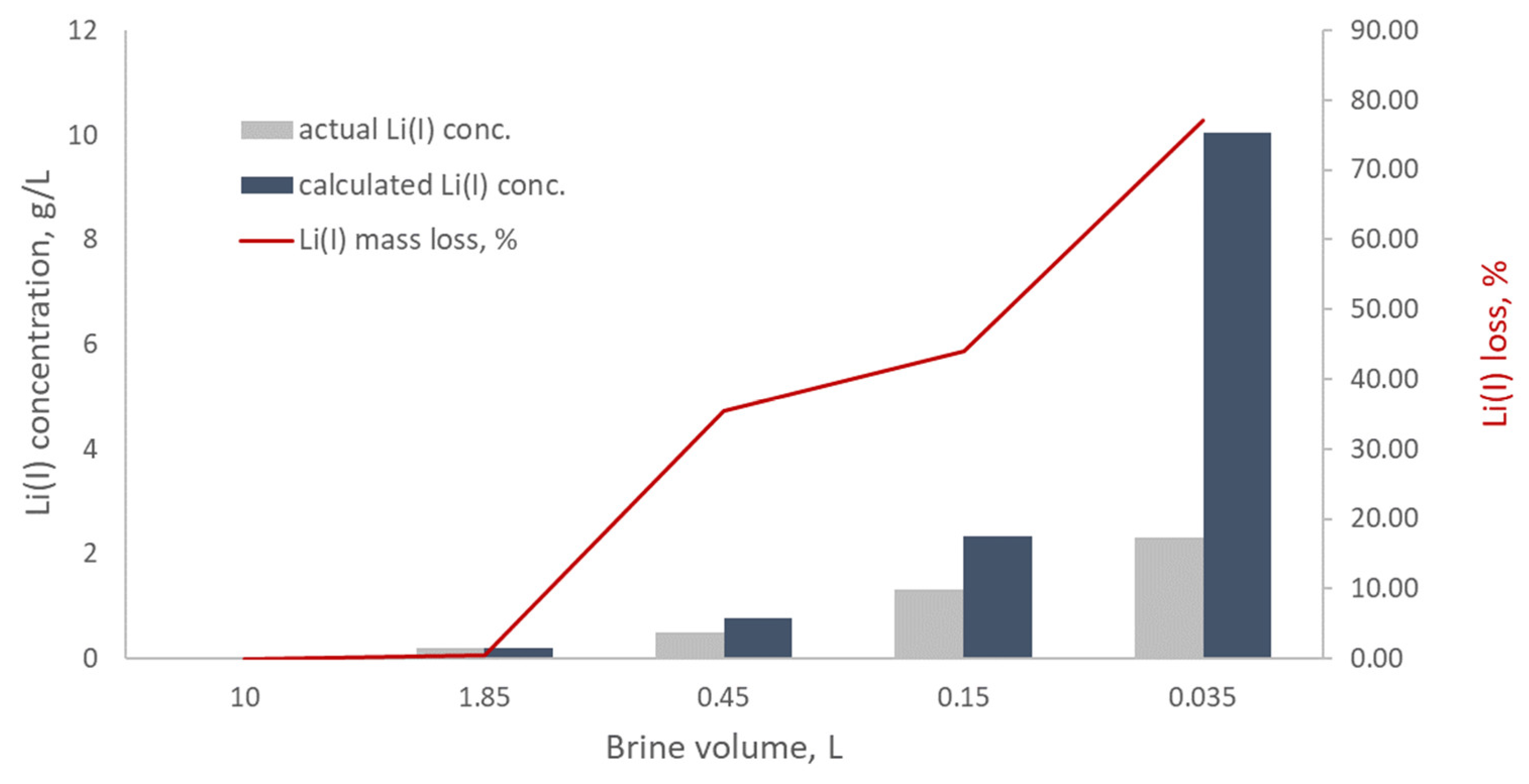
3.1. Evaporation Trials
3.2. Solvent Extraction Experiments
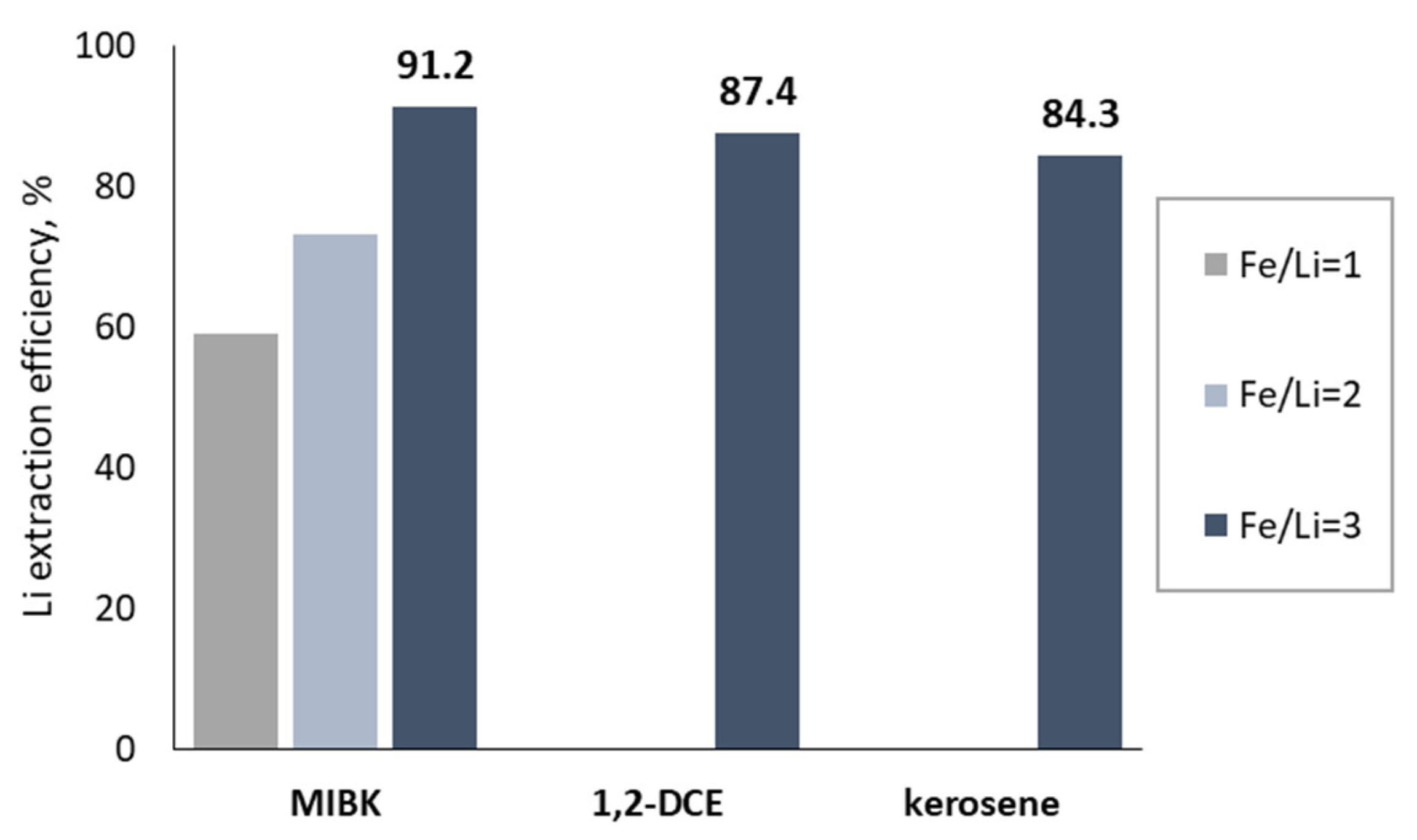
3.2.1. Lithium Extraction from Synthetic Solution
3.2.2. Lithium Extraction from Semi-Synthetic and Concentrated Real Brine
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Indicator | Unit | Brine | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GR | PR | ||
| pH-value (20.3 °C) | 5.5 | 6.7 | |
| Total hardness, calc. as mg CaCO3/L | mg/L | 59,600 | >500 |
| Temperature | °C | 20.3 | 21.8 |
| Total alkanity | mmol/L | 0.93 | 2.9 |
| Solid residue | mg/L | 379,000 | >250,000 |
| Residue on ignition (600 °C) | mg/L | 328,160 | 115,370 |
| Redox potential | mV | 82 | 98 |
| Dissolved solids | mg/L | 293,058 | >250,000 |
| Conductivity (20 °C) | μS/cm | 210,000 | 132,000 |
| TOC | mg/L | 8.24 | <1 |
| TIC | mg/L | 6.45 | 16.1 |
| Oxygen (electrom.) | mg/L | 3.9 | 9.8 |
| Chloride (Cl) | mg/L | 140,000 | 64,000 |
| Fluoride (F) | mg/L | <5.00 | <5.00 |
| Sulfate (SO4) | mg/L | 308 | 1200 |
| Nitrate (NO3) | mg/L | <25.0 | <10 |
| Nitrite (NO2) | mg/L | <20.0 | <5 |
| Phosphate (PO4) | mg/L | <5.00 | <10 |
| Bromide (Br) | mg/L | 989 | >20 |
| Hydrogen carbonate (HCO3) | mg/L | 55.8 | 175 |
| Carbonate (CO3) | mg/L | 56.9 | 172 |
| Sulfide (S), easily released | mg/L | <0.0400 | <0.04 |
| Hydrogen sulphide (H2S) calc. | mg/L | <0.041 | <0.028 |
| Ammonium (NH4) | mg/L | 130 | 24.9 |
| Borate (calc. as BO3) | mg/L | 132.783 | 53.93 |
| Calcium (Ca) | mg/L | 17,475 | 2451 |
| Potassium (K) | mg/L | 3176 | 266 |
| Lithium (Li) | mg/L | 65 | 1.17 |
| Magnesium (Mg) | mg/L | 871 | 913 |
| Sodium (Na) | mg/L | 96,972 | 63,556 |
| Strontium (Sr) | mg/L | 730.8 | 0.142 |
| Boron (B) | mg/L | 24.4 | 9.91 |
| Manganese (Mn) | mg/L | 13.2 | 1.85 |
| Zinc (Zn) | mg/L | 12.806 | <0.05 |
| Iron (Fe) | mg/L | 106 | 0.366 |
| Element | m/m% |
|---|---|
| Cl | 81.76 |
| Na | 11.76 |
| Al | 3.12 |
| Ca | 1.12 |
| Mg | 0.37 |
| K | 0.16 |
References
- Garrett, D.E. Handbook of Lithium and Natural Calcium Chloride; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Study on the EU’s List of Critical Raw Materials; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaci, H.; Young, P.; Snowdon, N.; Rai, A.; Chen, T.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Y.; Bailey, E.; Shi, R.; Zheng, N. Direct Lithium Extraction: A potential game changing technology. In Global Metals & Mining; Goldman Sachs Group Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wesselborg, T.; Virolainen, S.; Sainio, T. Recovery of lithium from leach solutions of battery waste using direct solvent extraction with TBP and FeCl3. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 202, 105593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.L.; Yu, X.P.; Guo, Y.F.; Wang, S.Q.; Liu, M.M.; Deng, T.L.; Chen, Y.W.; Belzile, N. Extraction of lithium from salt lake brine with triisobutyl phosphate in ionic liquid and kerosene. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2015, 31, 621–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, L.J.; Shi, D.; Peng, X.W.; Song, F.G.; Nie, F.; Han, W.S. Recovery of lithium from alkaline brine by solvent extraction with β-diketone. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 175, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Ge, T.; Xu, L.; Wang, L.; He, J.; Zhou, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, Z. A fundamental study on selective extraction of Li+ with dibenzo-14-crown-4 ether: Toward new technology development for lithium recovery from brines. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 310, 114705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pranolo, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Cheng, C.Y. Separation of lithium from sodium in chloride solutions using SSX systems with LIX 54 and Cyanex 923. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 154, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelebi, E.E.; Öncel, M.S.; Kobya, M.; Bayramoğlu, M. Extraction of lithium from wastewaters using a synergistic solvent extraction system consisting of Mextral EOL and Cyanex 923. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 185, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; He, J.; Pei, H.; Du, J.; Ma, X.; Li, J. A remarkable improved Li+/Mg2+ selectivity and Li+ recovery simultaneously by adding crown ether to tributyl phosphate-ionic liquid extraction system as co-extractant. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 335, 126162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Ma, L.; Bi, Q.; Xu, S. Extraction of lithium from magnesium-rich solution using a new ionic liquid extraction system. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 382, 121833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Zhang, L.; Peng, X.; Li, L.; Song, F.; Nie, F.; Ji, L.; Zhang, Y. Extraction of lithium from salt lake brine containing boron using multistage centrifuge extractors. Desalination 2018, 441, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Chen, H.; Yu, J. Investigation on the lithium extraction process with the TBP-FeCl3 solvent system using experimental and DFT methods. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 4672–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Qin, W.; Liang, S.; Tan, Y.; Fei, W. Recovery of Lithium Using Tributyl Phosphate in Methyl Isobutyl Ketone and FeCl3. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 12926–12932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Qin, W.; Liu, Y.; Fei, W. Extraction Equilibria of Lithium with Tributyl Phosphate in Kerosene and FeCl3. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2012, 57, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Nan, X.; Zhang, N.; Li, L.; Yu, X.; Guo, Y.; Deng, T. Solvent Extraction Process and Extraction Mechanism for Lithium Recovery from High Mg/Li-ratio Brine. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2019, 52, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Ciu, B.; Li, L.; Peng, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Lithium extraction from low-grade salt lake brine with ultrahigh Mg/Li ratio using TBP–kerosene–FeCl3 system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 211, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Wang, L.; Feng, M.; Fang, L.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, F. Ion-pair induced solvent extraction of lithium(I) from acidic chloride solutions with tributyl phosphate. Green Energy Environ. 2021, 6, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritcey, G.M. Solvent Extraction: Principles and Applications to Process Metallurgy, Revised Ed.; Elsevier Science Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.F.; Li, L.J.; Li, W.; Zhou, Y.Q. The key factors and mechanism study on lithium extraction by TBP-FeCl3 extraction system. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2020, 754, 137740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Chen, H.; Yu, J. Recovery of lithium from salt-lake brine by liquid–liquid extraction using TBP-FeCl3 based mixture solvent. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 101, 2139–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Tan, B.; Zhang, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Qi, T. Modelling of lithium extraction with TBP/P507–FeCl3 system from salt-lake brine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 282, 120110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Liang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Qin, W.; Fei, W. Lithium recovery from salt lake brine by counter-current extraction using tributyl phosphate/FeCl3 in methyl isobutyl ketone. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 171, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Ren, Z.; Zhou, Z. Selective extraction of lithium from high magnesium/lithium ratio brines with a TBP–FeCl3–P204–kerosene extraction system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 328, 125066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, W.; Chen, L.; Luo, G.; Sun, J.; Huang, Y.; Bizuneh, K.; Chao, Y.; Zhu, W. Temperature-responsive liquid-liquid extraction of Li+ from high Mg/Li ratio brine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 322, 124309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, L.; Li, W. Lithium Extraction from Salt Lake Brine with High Mass Ratio of Mg/Li Using TBP-DIBK Extraction System. Separations 2023, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.F.; Li, L.J.; Li, W. The extraction rules investigation of mental (Li, Na, K, Mg, Ca) ion in salt lake brine by TBP-FeCl3 extraction system. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2021, 763, 138249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Fan, J.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Wei, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, W.; Ren, Z. Recovery of lithium from salt-lake brines using solvent extraction with TBP as extractant and FeCl3 as co-extraction agent. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 191, 105244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, J. Selective separation of lithium from the high magnesium brine by the extraction system containing phosphate-based ionic liquids. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 274, 119051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Binnemans, K. Mechanism of Ferric Chloride Facilitating Efficient Lithium Extraction from Magnesium-Rich Brine with Tri-n-butyl Phosphate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 8538–8547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, L.; Peng, X.; Ji, L.; Li, W. Selective recovery of lithium from simulated brine using different organic synergist. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 27, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, L.; Qi, T. Combining selective extraction and easy stripping of lithium using a ternary synergistic solvent extraction system through regulation of Fe3+ coordination. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flexer, V.; Baspineiro, C.F.; Galli, C.I. Lithium recovery from brines: A vital raw material for green energies with a potential environment impact in its mining and processing. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 15, 1188–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidell, A.; Linke, W.F. Solubilities of Inorganic and Organic Compounds; Van Nostrand: New York, NY, USA, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, L.; Zhang, L.; Shi, D.; Peng, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, T.; Li, L. Mechanism and process for the extraction of lithium from the high magnesium brine with N,N-bis(2-ethylhexyl)-2-methoxyacetamide in kerosene and FeCl3. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 113, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, L.; Qi, T. Recovery of lithium from salt lake brine using a mixed ternary solvent extraction system consisting of TBP, FeCl3 and P507. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 197, 105487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wei, X.; Cai, Z.; Zhou, Z. Novel ionic liquid as co-extractant for selective extraction of lithium ions from salt lake brines with high Mg/Li ratio. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 277, 119471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Wei, X.; Li, R.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhuo, Z. Highly selective extraction of lithium ions from salt lake brines with sodium tetraphenylborate as co-extractant. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 269, 118756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide, D.R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 90th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes, W.M. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 97th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Valdez, S.K.; Flores, H.R.; Orce, A.M.; KwokLeung, H. Influence of The Evaporation Rate Over Lithium Recovery from Brines. World J. Res. Rev. 2016, 3, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- An, J.W.; Kang, D.J.; Tran, K.T.; Kim, M.J.; Lim, T. Recovery of lithium from Uyuni salar brine. Hydrometallurgy 2012, 117–118, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Gang, H.; Ma, Y.; Yang, S.; Mu, B. Behavior of Lithium during Brine Evaporation and KCl Production Plants in Qarhan Salt Lake. Minerals 2017, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, J. Metal Ions in Solution; Ellis Horwood Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Qin, W.; Fei, W. Extraction Equilibria of Lithium with Tributyl Phosphate in Three Diluents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 3518–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Liang, S.K.; Qin, W.; Fei, W.Y. Extraction equilibria of lithium with tributyl phosphate, diisobutyl ketone, acetophenone, methyl isobutyl ketone, and 2-heptanone in kerosene and FeCl. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 7912–7917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, A.M.; Zultanski, S.L.; Waldman, J.H.; Zhong, Y.L.; Shevlin, M.; Peng, F. General principles and strategies for salting-out informed by the Hofmeister series. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2017, 21, 1355–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacace, M.G.; Landau, E.M.; Ramsden, J. Biophysica. Quart. Rev. 1997, 30, 241–277. [Google Scholar]
- Marcus, Y. Effect of Ions on the Structure of Water: Structure Making and Breaking. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 1346–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdez, S.K.; Orce Schwarz, A.M.; Thames Cantolla, M.I. Empirical models to determine ions concentrations in lithium brines with high ionic strength. Results Eng. 2023, 18, 101145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; He, M.; Cao, M.; Zheng, X.; Gao, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z. Investigation of solution chemistry to enable efficient lithium recovery from low-concentration lithium-containing wastewater. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2020, 14, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.F. Calculation of Pitzer Parameters at High Ionic Strengths. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 4422–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Z.; Ahlberg, E. Activity Coefficients of Concentrated Salt Solutions: A Monte Carlo Investigation. J. Solut. Chem. 2019, 48, 1222–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, D.J.; Hemminger, J.C. Getting Specific About Specific Ion Effects. Science 2008, 319, 1197–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, K.P.; Elliott, G.R.; Robertson, H.; Kumar, A.; Wanless, E.J.; Webber, G.B.; Craig, V.S.; Andersson, G.G.; Page, A.J. Understanding specific ion effects and the Hofmeister series. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 12682–12718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Brine Source | Li | Na | Ca | Mg | K | Cl− (g/L) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/L | |||||||
| S1–S4 | 35–50 | 70,000 | 8.7 | ||||
| PR | 1.17 | 63,556 | 2451 | 913 | 266 | 64 | 8.7 |
| GR | 65 | 96,972 | 17,475 | 871 | 3176 | 140 | 5.5 |
| Solution | Volume (mL) | cLi (mg/L) | mLi (mg) | DLi (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S2 | 1000 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100 |
| CS2 | 140 | 201.5 | 28.2 | 56 |
| Washings W2.1 | 147 | 98.4 | 14.5 | 29 |
| Washings W2.2 | 73 | 20.9 | 1.53 | 3.0 |
| Solution | Volume (mL) | cLi (mg/L) | mLi (mg) | DLi (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S3 | 1000 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100 |
| CS3 | 93.0 | 248.5 | 23.1 | 46.2 |
| Washings W3.1 | 153 | 133.3 | 20.4 | 40.8 |
| Washings W3.2 | 82.0 | 32.6 | 2.7 | 5.4 |
| Solution | Volume Reduction Ratio | cLi (mg/L) | DLi (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CGR1 | 7 | 376.7 | 80/20 |
| CGR2 | 14 | 478.0 | 56/44 |
| CS4 Composition | SX Conditions | ELi (%) | PLi | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Phase | Aqueous Phase | |||
| Li: 917 mg/L Na: saturated | Org 1: 60% TBP + MIBK | CS4 & no additives | - | - |
| CS4 + FeCl3 (Fe/Li = 1) + 2 M AlCl3 | 59.0 | 1.197 | ||
| CS4 + FeCl3 (Fe/Li = 2) + 2 M AlCl3 | 73.0 | 2.437 | ||
| CS4 + FeCl3 (Fe/Li = 3) + 2 M AlCl3 | 91.2 | 10.395 | ||
| CS4 + FeCl3 (Fe/Li = 3) | 49.7 | 0.986 | ||
| Org 2: 60% TBP + kerosene | CS4 + FeCl3 (Fe/Li = 3) + 2 M AlCl3 | 84.3 | 5.927 | |
| Org 3: 60% TBP + 1,2-DCE | CS4 + FeCl3 (Fe/Li = 3) + 2 M AlCl3 | 87.4 | 7.168 | |
| Aq Phase Composition | cLi (mg/L) | SX Conditions | ELi (%) | PLi |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR-doped | 350 | Org 1 Aq + FeCl3 (Fe/Li = 3) + 2 M AlCl3 | 76.1 | 3.179 |
| CGR2 | 478 | Org 1 Aq: no additives | 1.0 | 0.010 |
| Org 1 Aq + FeCl3 (Fe/Li = 3) | 13.1 | 0.151 | ||
| Org 1 Aq + FeCl3 (Fe/Li = 3) + 2 M AlCl3 | 32.2 | 0.388 |
| Metal Ion | Me/Li | |
|---|---|---|
| PR-Doped | CGR2 | |
| Ca | 7.0 | 365 |
| K | 0.8 | 66 |
| Mg | 2.6 | 18 |
| Na | 181.6 | 296 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ochromowicz, K.; Zabłocka-Malicka, M.; Chojnacka, I.; Worsa-Kozak, M. Assessing the Viability of Integrating Evaporation and Solvent Extraction Systems for Lithium Recovery from Low-Grade Brines. Processes 2024, 12, 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071453
Ochromowicz K, Zabłocka-Malicka M, Chojnacka I, Worsa-Kozak M. Assessing the Viability of Integrating Evaporation and Solvent Extraction Systems for Lithium Recovery from Low-Grade Brines. Processes. 2024; 12(7):1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071453
Chicago/Turabian StyleOchromowicz, Katarzyna, Monika Zabłocka-Malicka, Ida Chojnacka, and Magdalena Worsa-Kozak. 2024. "Assessing the Viability of Integrating Evaporation and Solvent Extraction Systems for Lithium Recovery from Low-Grade Brines" Processes 12, no. 7: 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071453
APA StyleOchromowicz, K., Zabłocka-Malicka, M., Chojnacka, I., & Worsa-Kozak, M. (2024). Assessing the Viability of Integrating Evaporation and Solvent Extraction Systems for Lithium Recovery from Low-Grade Brines. Processes, 12(7), 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071453







