Effect of Nozzle Quantity on the Flow Field Characteristics and Grinding Efficiency in a Steam Jet Mill
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
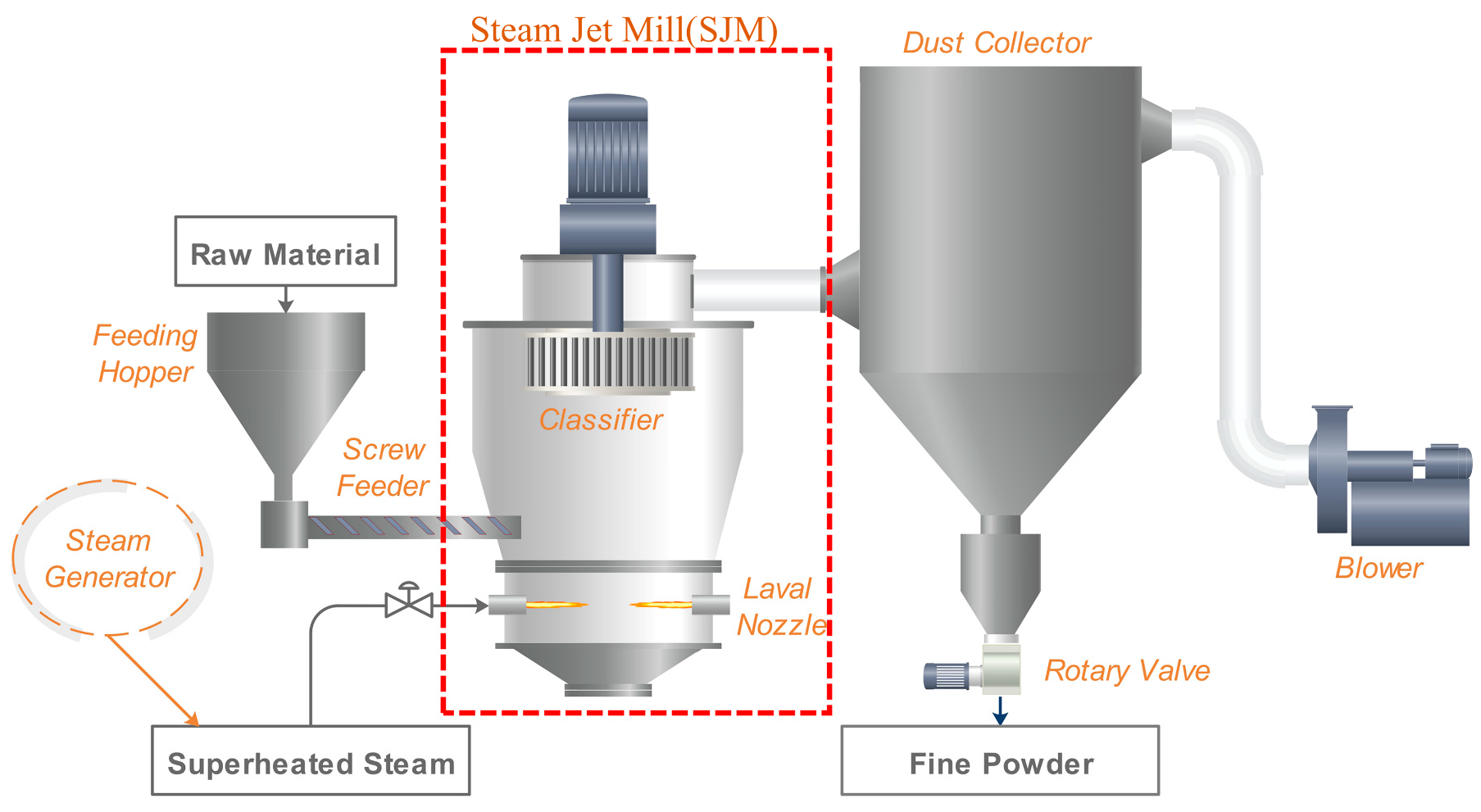
2.1. Fly Ash Grinding System
2.2. SJM
2.3. Experimental Conditions and Materials
2.4. Numerical Simulation
2.4.1. Fluid Governing Equations
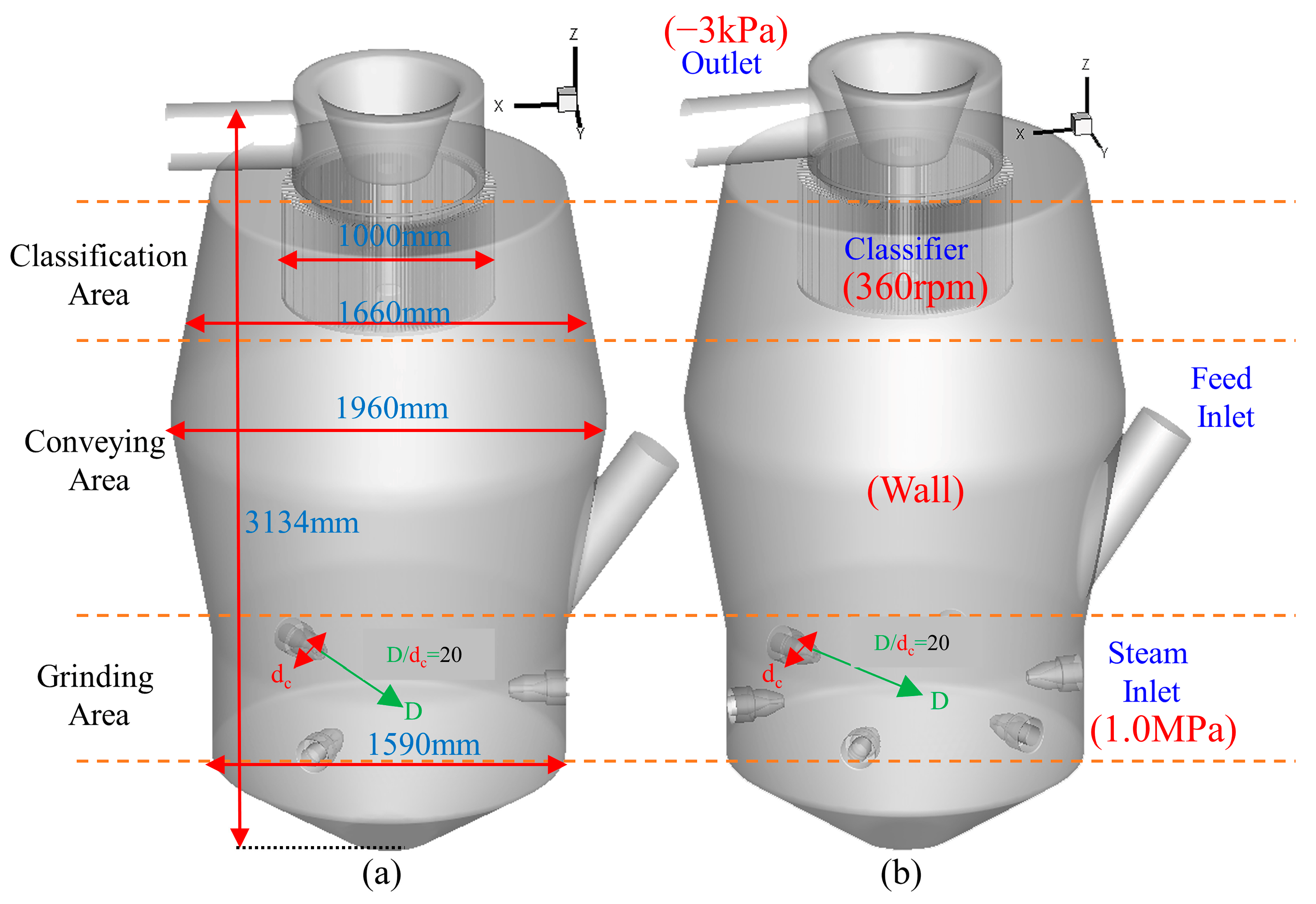
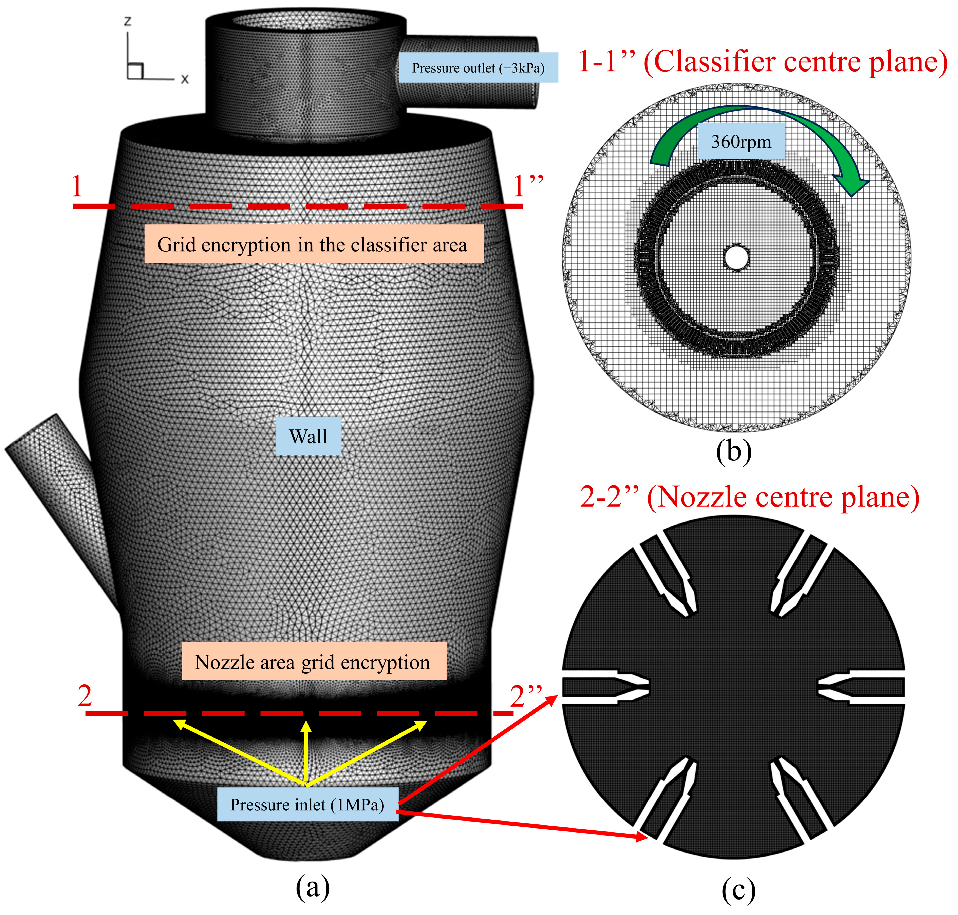
2.4.2. Mesh and Boundary Conditions
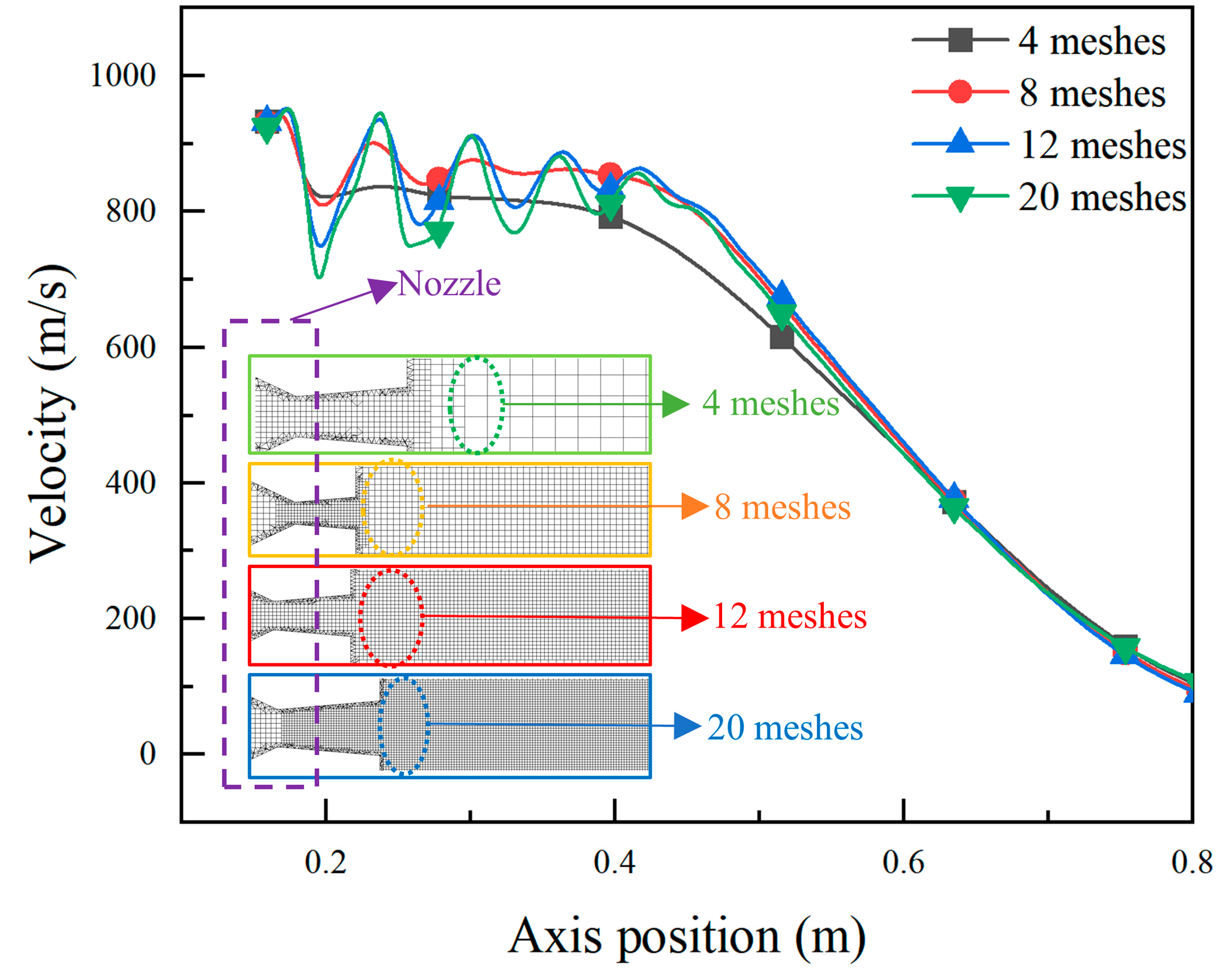
2.4.3. Mesh Independence Verification and Calculation Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Numerical Simulation Results
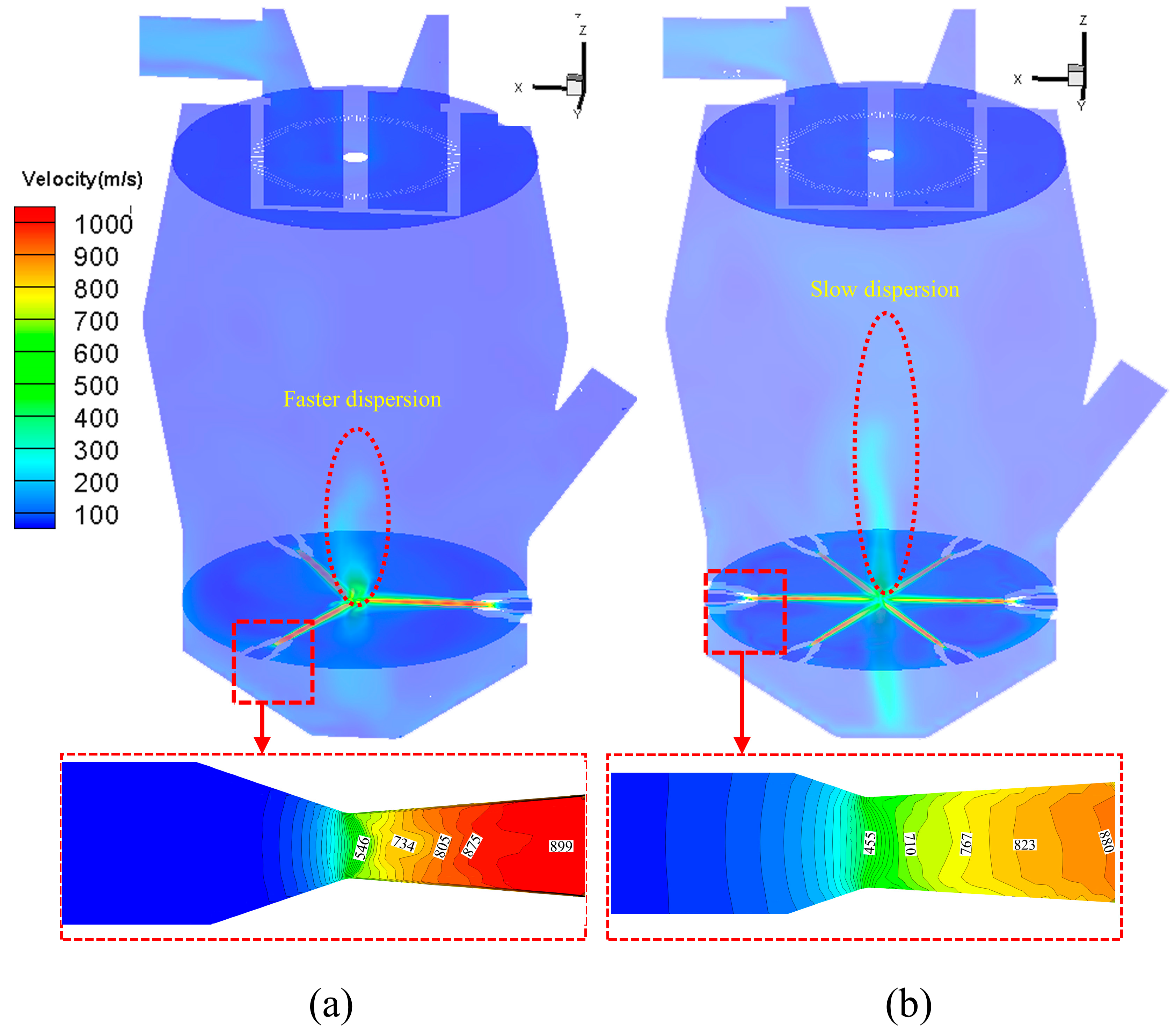
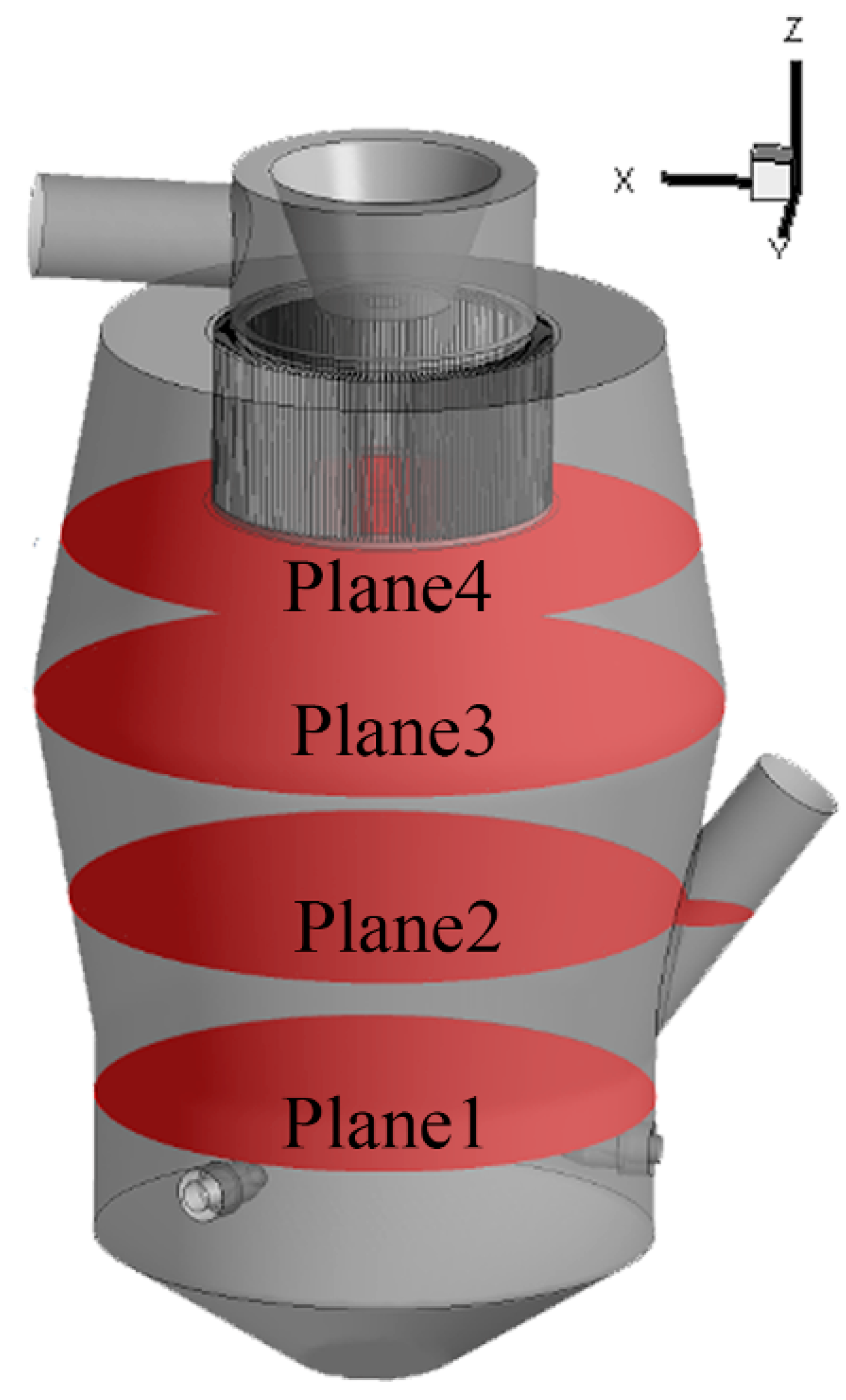
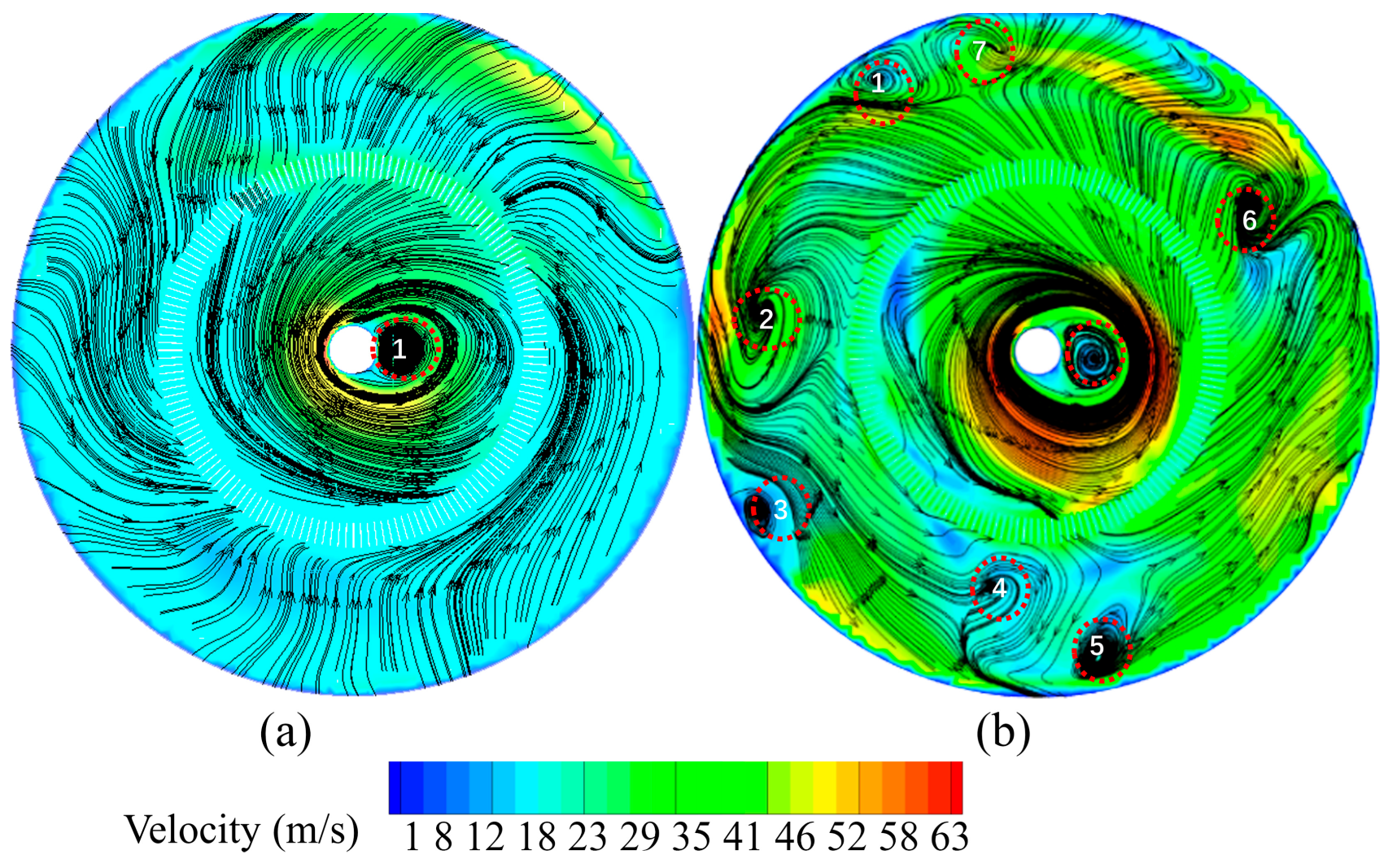
3.1.1. Flow Field Analysis of SJMs
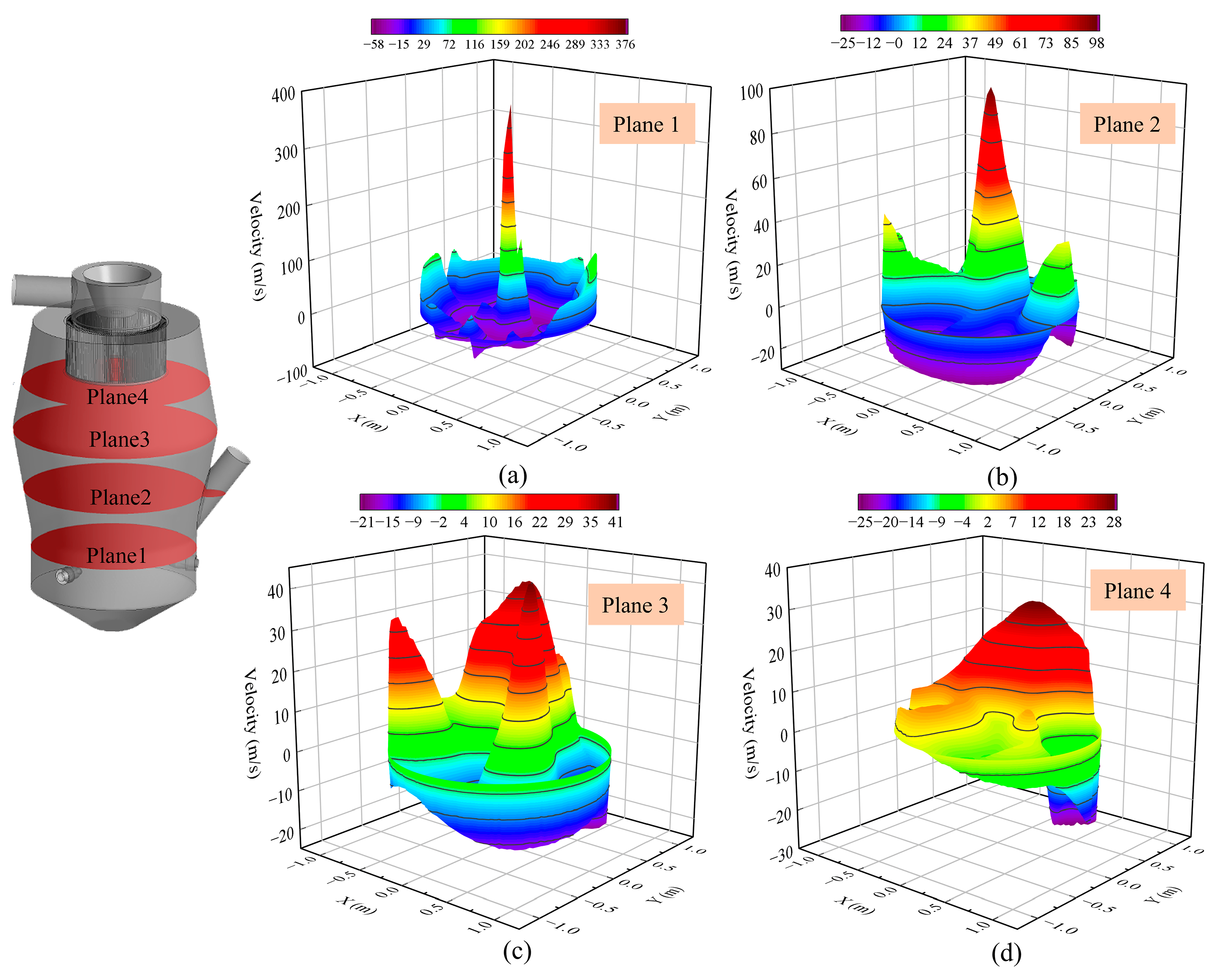
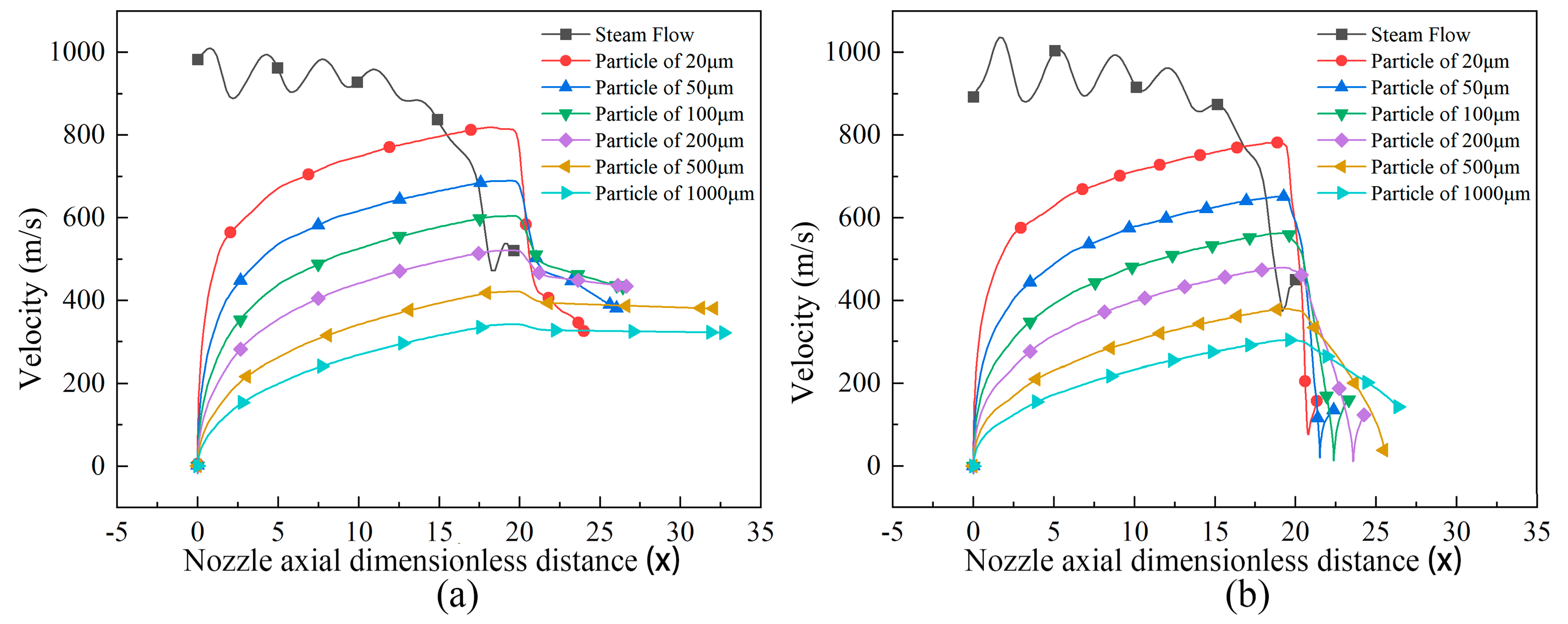
3.1.2. Effect of Nozzle Quantity on the Ascending Velocity in the Conveying Area
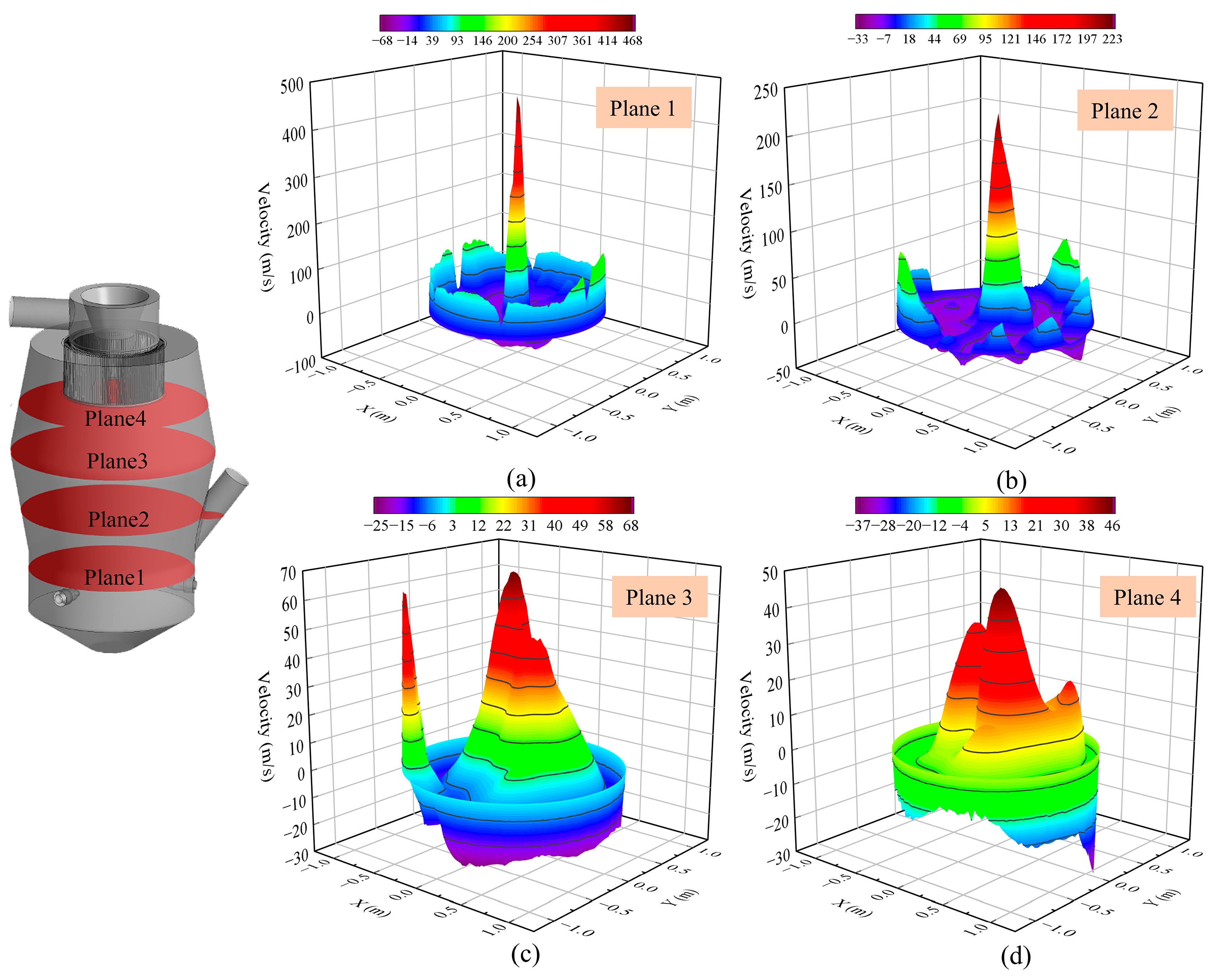
3.1.3. Effect of Nozzle Quantity on the Flow Field in the Grinding Area
3.1.4. Effect of Nozzle Quantity on the Flow Field in the Classification Area
3.2. Experimental Result
3.2.1. Effect of Nozzle Quantity on Fly Ash Grinding Production and Energy Consumption
3.2.2. Influence of Feed Particle Size on Grinding Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, H.; Huang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Xiang, R.; Liu, Y. Release potential, neglected leakage and reduction countermeasures of COD and Ammonia in MSWLs. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Xiao, J.; Ye, S.; Liu, W.; Yang, M.; Yao, Z.; Zhong, Q. Closed-loop cleaning treatment system—Resource recovery of coal gangue, Energy Sources. Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2024, 46, 5236–5253. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Chen, C.; Chen, S.; Ren, Y.; Lu, J. Resource utilization of drinking water treatment aluminum sludge in green cementing materials: Hydration characteristics and hydration kinetics. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 144, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ma, S.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chu, P.K. Utilization of coal fly ash in China: A mini-review on challenges and future directions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 18727–18740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, L.; Li, X.; Cao, P.; Luo, J.; Jiang, H. Stepwise extraction and utilization of silica and alumina from coal fly ash by mild hydrothermal process. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 182, 918–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Cao, P.; Jiang, H.; Luo, J.; Jiang, T. Hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites-calcium silicate hydrate composite from coal fly ash with co-activation of Ca(OH)2-NaOH for aqueous heavy metals removal. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, S.K.; Edrisi, S.A. Developing sustainable measures to restore fly-ash contaminated lands: Current challenges and future prospects. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 4817–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Lang, L.; Liu, S.; Mu, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Han, L.; Duan, S.; Wang, P.; Li, J. Stabilization of iron ore tailing with low-carbon lime/carbide slag-activated ground granulated blast-furnace slag and coal fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 413, 134946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Song, R.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.C.; Lu, X. Preparation and Application of Slag-Based Catalyst for Steelmaking. Steel Res. Int. 2024, 95, 2300755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Yang, B.; Wu, D.; Gao, X.; Fei, X. Applications of crushing and grinding-based treatments for typical metal-containing solid wastes: Detoxification and resource recovery potentials. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Torres, I.; Tuzcu, E.T.; Reyes, I.A.; Rosales, G. A quantitative study between HPGR and cone crusher aided ball mill grinding: Mathematical modeling by evaluating the possible microfracture effect produced by HPGR technology and cone crusher. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2023, 60, 177620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, H. Steam jet mill—A prospective solution to industrial exhaust steam and solid waste. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 17842–17854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Hu, D.; An, R.; Lin, L.; Xiang, Y.; Han, L.; Yu, Y.; Ning, L.; Wu, J. Preparation of superfine and semi-hydrated flue gas desulfurization gypsum powder by a superheated steam powdered jet mill and its application to produce cement pastes. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Fu, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H. Effect of relative humidity on the desulfurization performance of calcium-based desulfurizer. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 138, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, D.; Zhang, X.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.; Tang, W.; Qiang, X. Improving the properties of metakaolin/fly ash composite geopolymers with ultrafine fly ash ground by steam-jet mill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 387, 131673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, H.; Lv, J.; Leng, H.; Xiao, J.; Wang, S. Effects of grinding and dehydration on kaolin in a steam jet mill. CLAY Miner. 2021, 56, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, L.; Yu, F.; Lihua, H.; Deliang, T.; Haiyan, C.; Belzile, N.; Yuwei, C. Preparation of a new high-performance calcium-based desulfurizer using a steam jet mill. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, Z.; Kou, F.; Wang, Q.; Lei, X.; Zhao, J.; Ming, J. Effect of superfine grinding chestnut powder on the structural and physicochemical properties of wheat dough. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.W.; Yuan, X.F.; Zhao, B. Jet milling improves the polyphenol dissolution profile and biological activities of the hemp seed shell. Food Biosci. 2024, 57, 103497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortun, A.; Bortun, M.; Brown, B.; Madynski, J. Effect of High-Energy Milling on Ceria-Zirconia’s Redox Properties. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, F. Parameter effects on dry fine pulverization of alumina particles in a fluidized bed opposed jet mill. Powder Technol. 2011, 214, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.A.D.; Baluni, S.; Bück, A. Eulerian Multiphase Simulation of the Particle Dynamics in a Fluidized Bed Opposed Gas Jet Mill. Processes 2020, 8, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeninger, B.; Spoetter, C.; Romeis, S.; Weber, A.P.; Wirth, K.E. Classifier performance during dynamic fine grinding in fluidized bed opposed jet mills. Adv. Powder Technol. 2019, 30, 1678–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otwinowski, H. Modeling the multi-stage classification in a fluidized bed jet mill. Part. Sci. Technol. 2014, 32, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luczak, B.; Müller, R.; Kessel, C.; Ulbricht, M.; Schultz, H.J. Visualization of flow conditions inside spiral jet mills with different nozzle numbers—Analysis of unloaded and loaded mills and correlation with grinding performance. Powder Technol. 2019, 342, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, L.; Borissova, A.; Burns, A.; Ghadiri, M. Effect of grinding nozzles pressure on particle and fluid flow patterns in a spiral jet mill. Powder Technol. 2021, 394, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhang, H. Effect of nozzle pressure ratios on the flow and distribution of abrasive particles in abrasive air jet machining. Powder Technol. 2022, 397, 117114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Lin, L.; Wang, J.; Huang, S.; Yan, C.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H. Particle size controllable jet milling technology for efficiently recycling titanium-bearing blast furnace slag: Numerical simulation and industrial test. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 247, 119144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Song, S.; Kim, H.T. Improvement of pulverization efficiency for micro-sized particles grinding by uncooled high-temperature air jet mill using a computational simulation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 207, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.Q.; Schurr, G. Effect of motive gases on fine grinding in a fluid energy mill. Powder Technol. 2002, 122, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Liang, L.; Liu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, G. CFD simulation and performance optimization of a new horizontal turbo air classifier. Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbronski, D. Analysis of the influence of selected parameters process on the performance of fluidized bed opposed jet mill. Part III. Comminution mechanism of grains. Gospod. Surowcami Miner. 2008, 24, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
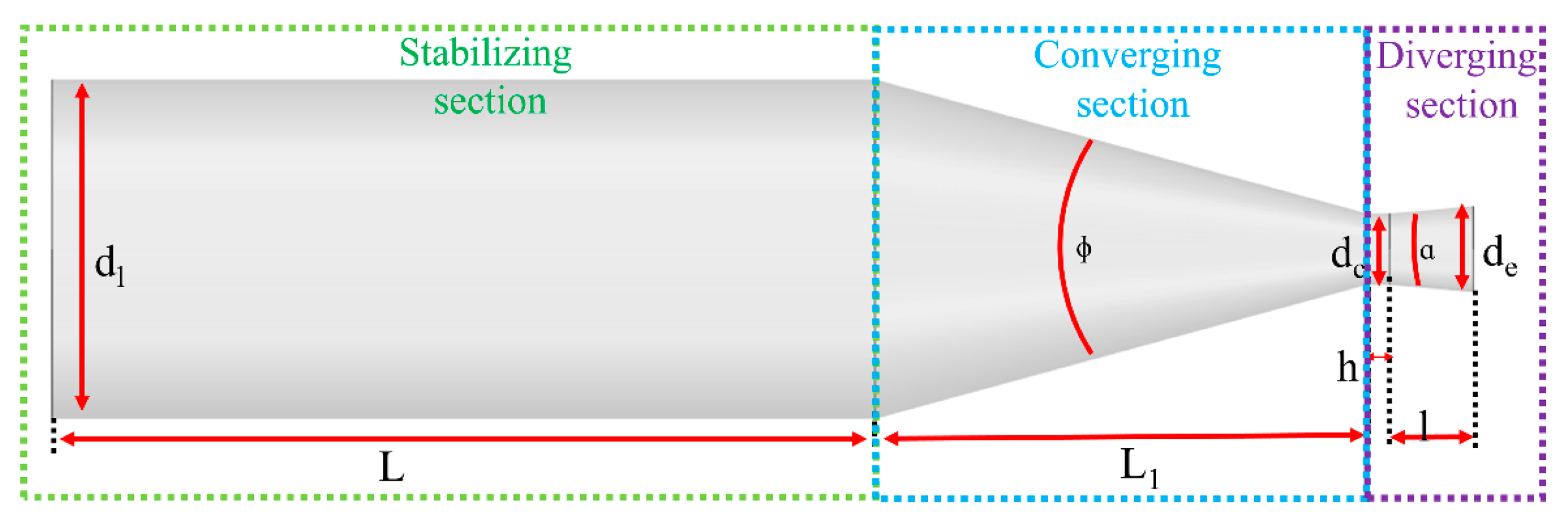



| Parameters for the Nozzles | Nozzle of N3 | Nozzle of N6 |
|---|---|---|
| dl (mm) | 90 | 90 |
| L (mm) | 241 | 241 |
| L1 (mm) | 92 | 103 |
| ɸ (·) | 37 | 37 |
| ɑ (·) | 9 | 7 |
| h (mm) | 2 | 2 |
| dc (mm) | 27.5 | 19.5 |
| de (mm) | 43.5 | 26 |
| Mass flow rate (kg/s) | 0.86 | 0.43 |
| Parameters for the SJMs | N3 | N6 |
|---|---|---|
| Steam pressure (MPa) | 1 | 1 |
| Nozzle throat diameter (mm) | 27.5 | 18 |
| Nozzle exit (mm) | 34 | 25 |
| Steam temperature (°C) | 260 | 260 |
| Outlet pressure (kPa) | −3 | −3 |
| Classifier velocity (rpm) | 360(760) | 360(760) |
| Steam mass flow rate (tons/h) | 10 | 10 |
| Parameters for the Steam | Model Description or Constant |
|---|---|
| Density (kg/m3) | Ideal gas Piecewise-polynomial Kinetic-theory Sutherland 18.01534 |
| Specific heat (J/(kg·K)) | |
| Thermal conductivity (w/(m·k)) | |
| Viscosity (kg/(m·s)) | |
| Molecular weight (kg/kmol) |
| Type of SJM | Nozzle Quantity | Single-Nozzle Entrainment Rate (kg/s) | Total Entrainment Amount (kg/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| N3 | 3 | 0.663 | 1.899 |
| N6 | 6 | 0.367 | 2.204 |
| Type of SJM | d90 (μm) | Capacity (Tons/h) | Steam Consumption (ton) | Energy Consumption Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N6 | 45 | 25.55 | 325.58 | 0.59 |
| N3 | 29.96 | 226.12 | 0.36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, H. Effect of Nozzle Quantity on the Flow Field Characteristics and Grinding Efficiency in a Steam Jet Mill. Processes 2024, 12, 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071500
Huang S, Zhang Y, Yin X, Zhang M, Li H, Wang Z, Chen H, Wang H. Effect of Nozzle Quantity on the Flow Field Characteristics and Grinding Efficiency in a Steam Jet Mill. Processes. 2024; 12(7):1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071500
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Shenglong, Yulu Zhang, Xixi Yin, Mingxing Zhang, Hong Li, Zhe Wang, Haiyan Chen, and Huan Wang. 2024. "Effect of Nozzle Quantity on the Flow Field Characteristics and Grinding Efficiency in a Steam Jet Mill" Processes 12, no. 7: 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071500
APA StyleHuang, S., Zhang, Y., Yin, X., Zhang, M., Li, H., Wang, Z., Chen, H., & Wang, H. (2024). Effect of Nozzle Quantity on the Flow Field Characteristics and Grinding Efficiency in a Steam Jet Mill. Processes, 12(7), 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071500






