Mercury Discharge Inventory Based on Sewage Treatment Process in China
Abstract
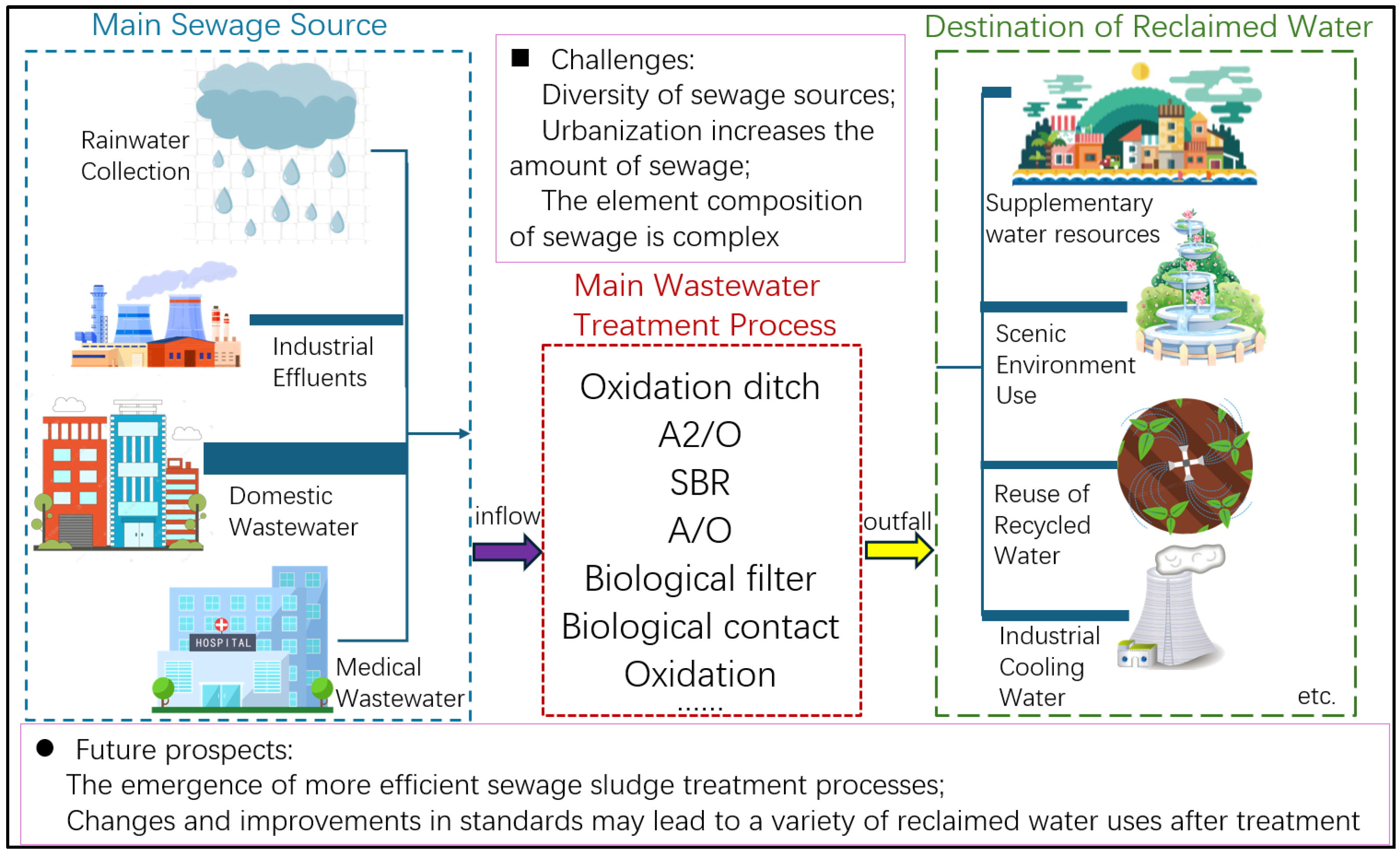
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area Characteristics
2.2. Data Sources and Processing Methods
2.2.1. Calculation of Mercury Emissions
2.2.2. Calculation of Dry Sludge Production Per Ton of Water in China
2.2.3. Estimation of Total Mercury in Sewage
2.2.4. Revised Calculation of Sludge Predicted Yield
3. Results
3.1. Relationship between Sewage Discharge and Total Mercury
3.1.1. Analysis of the Causes Affecting the Change of Sewage Discharge
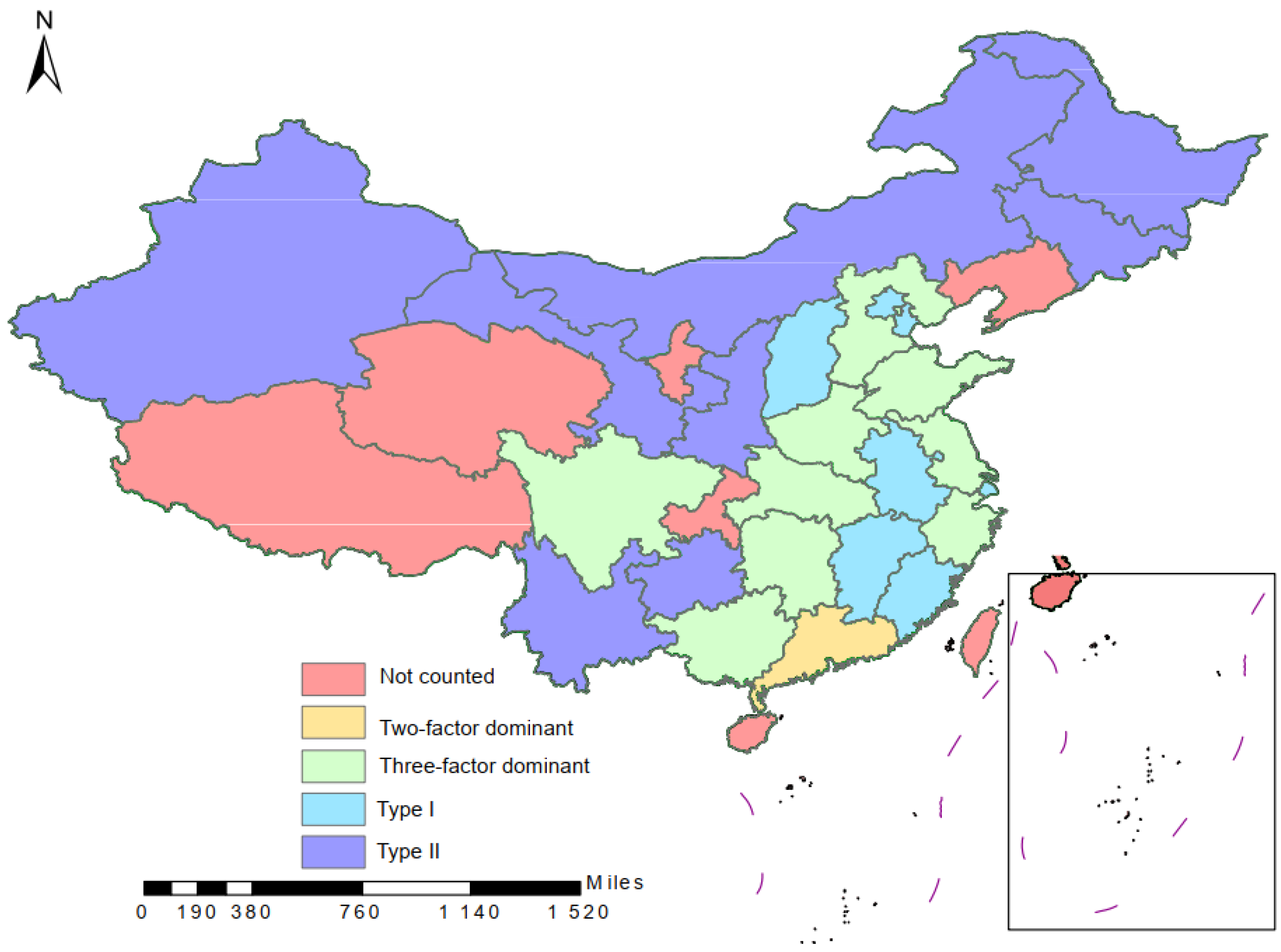
3.1.2. Difference Analysis of Domestic Sewage Discharge between Regions
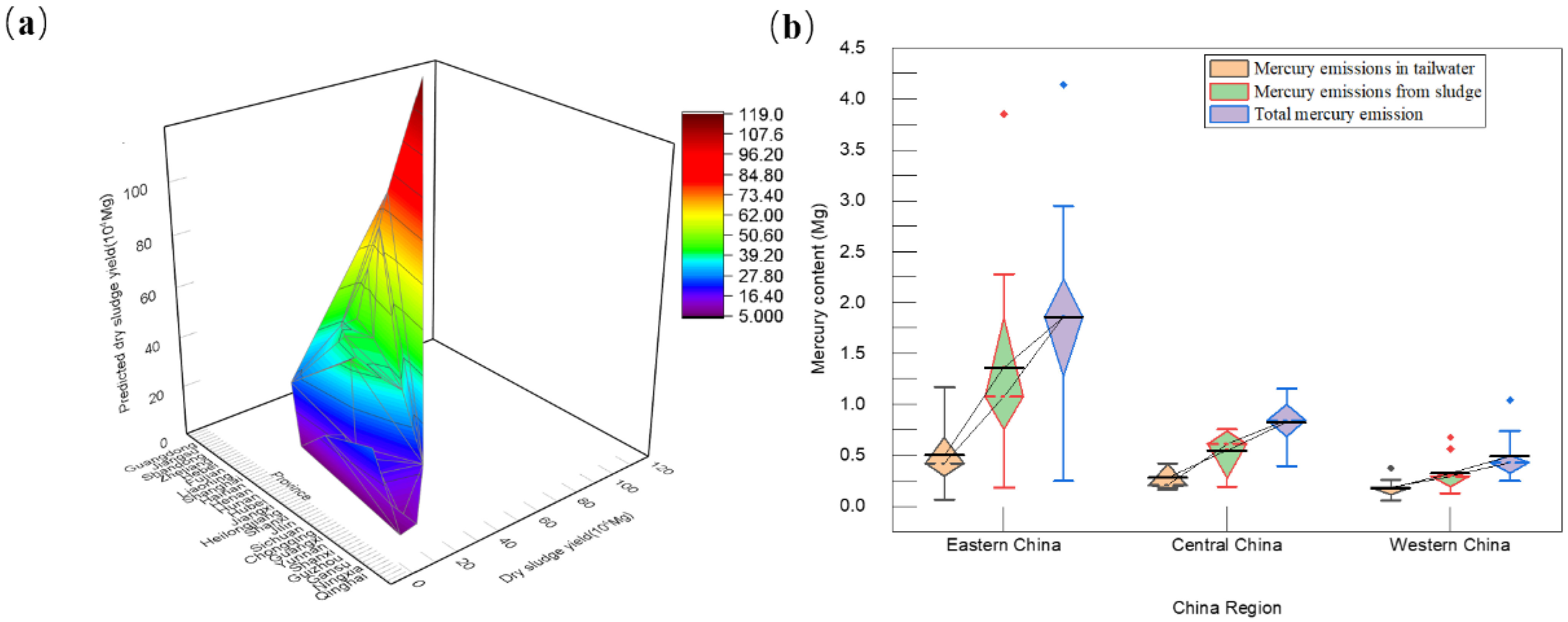
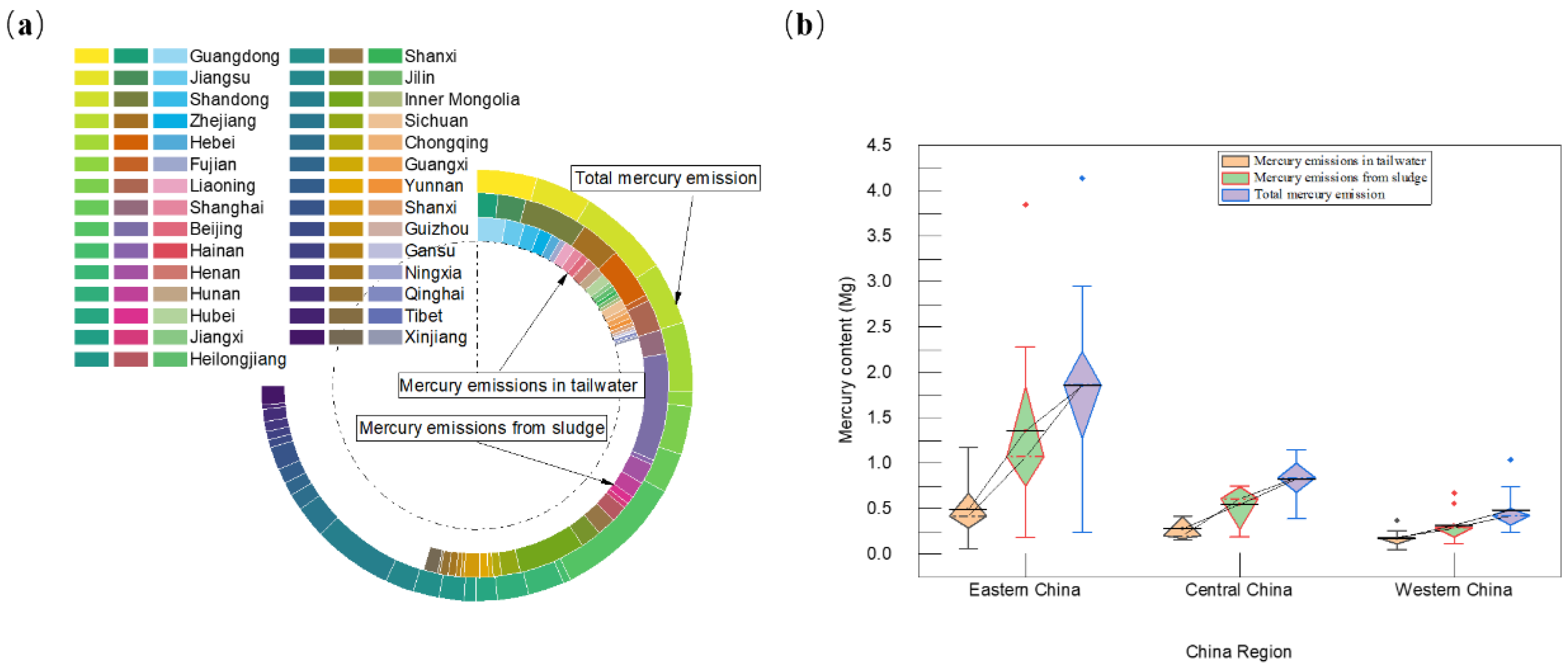
3.2. Mercury Discharge in Domestic Sewage
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Total Mercury in Sewage
4.1.1. Impact and Effectiveness of Environmental Policies
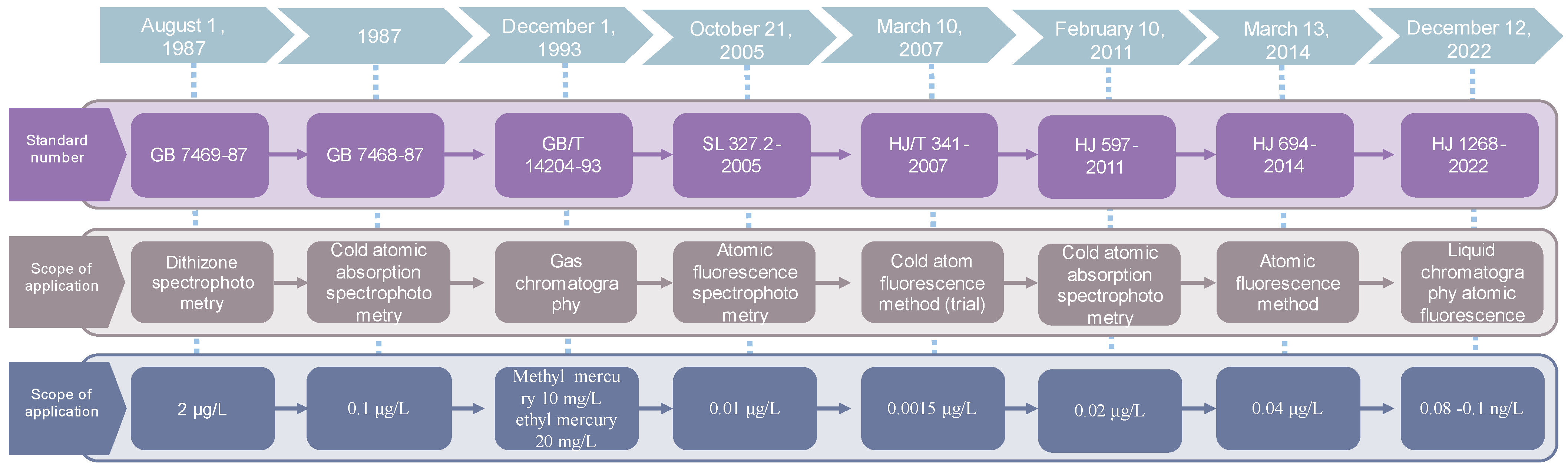
4.1.2. Measurement Methods and Their Development History
4.1.3. Influence of Residents’ Living Habits on Mercury Content in Sewage
4.1.4. Types of Industries Emitting Mercury
4.2. Changing Trend of Mercury in Sewage
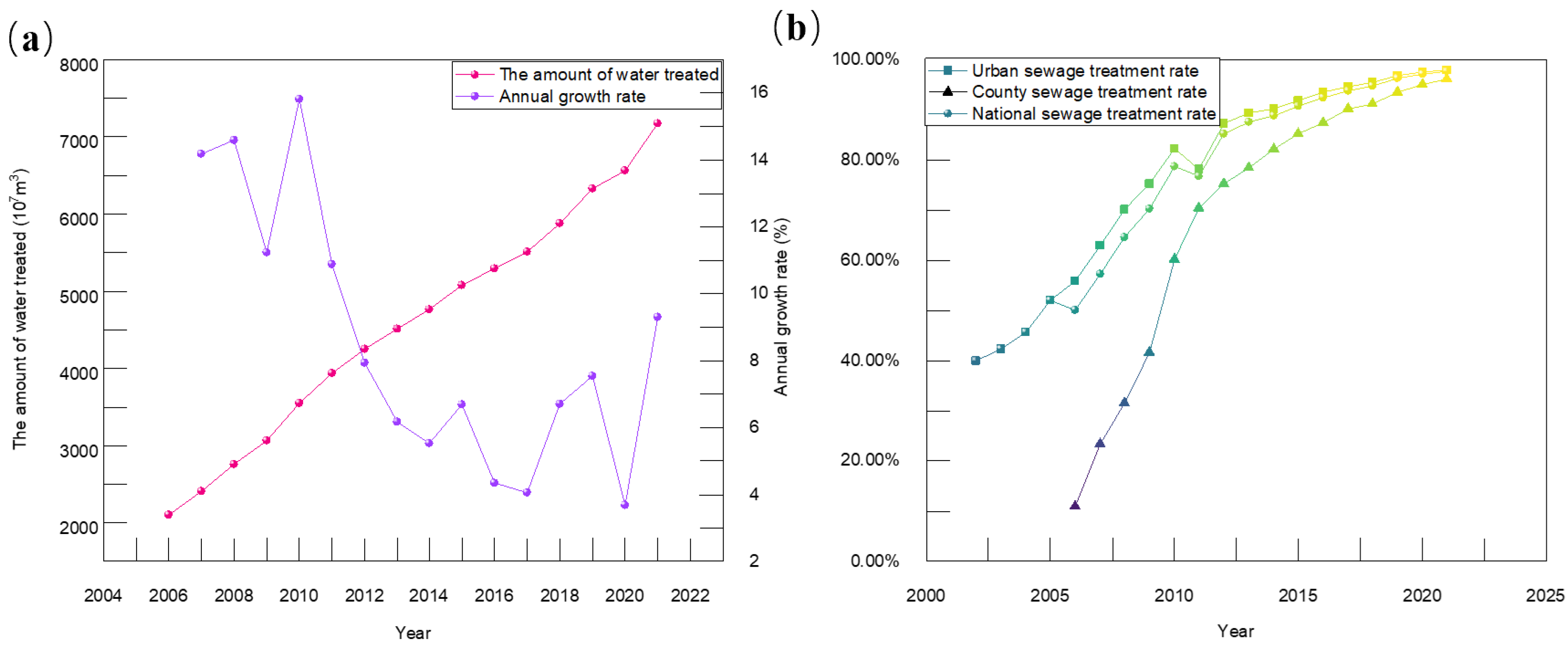
4.2.1. Changing Trend of Sewage Treatment Rate
4.2.2. Changing Trend of Mercury Content in Sewage
4.3. Removal and Transformation of Mercury in Sewage Treatment Process
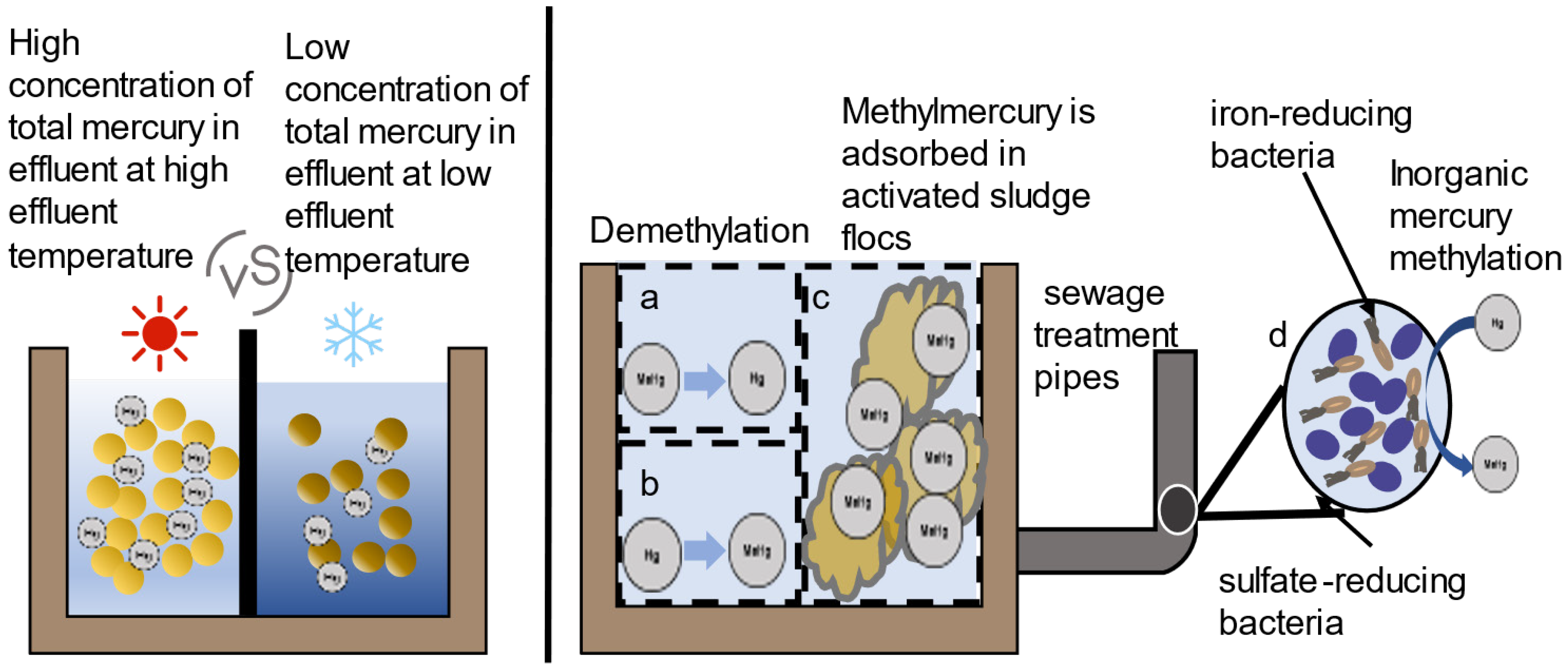
4.3.1. Removal of Total Mercury
4.3.2. Removal of Methylmercury
4.3.3. Mercury Removal in the Treatment Process of China’s Representative Sewage Treatment Plants
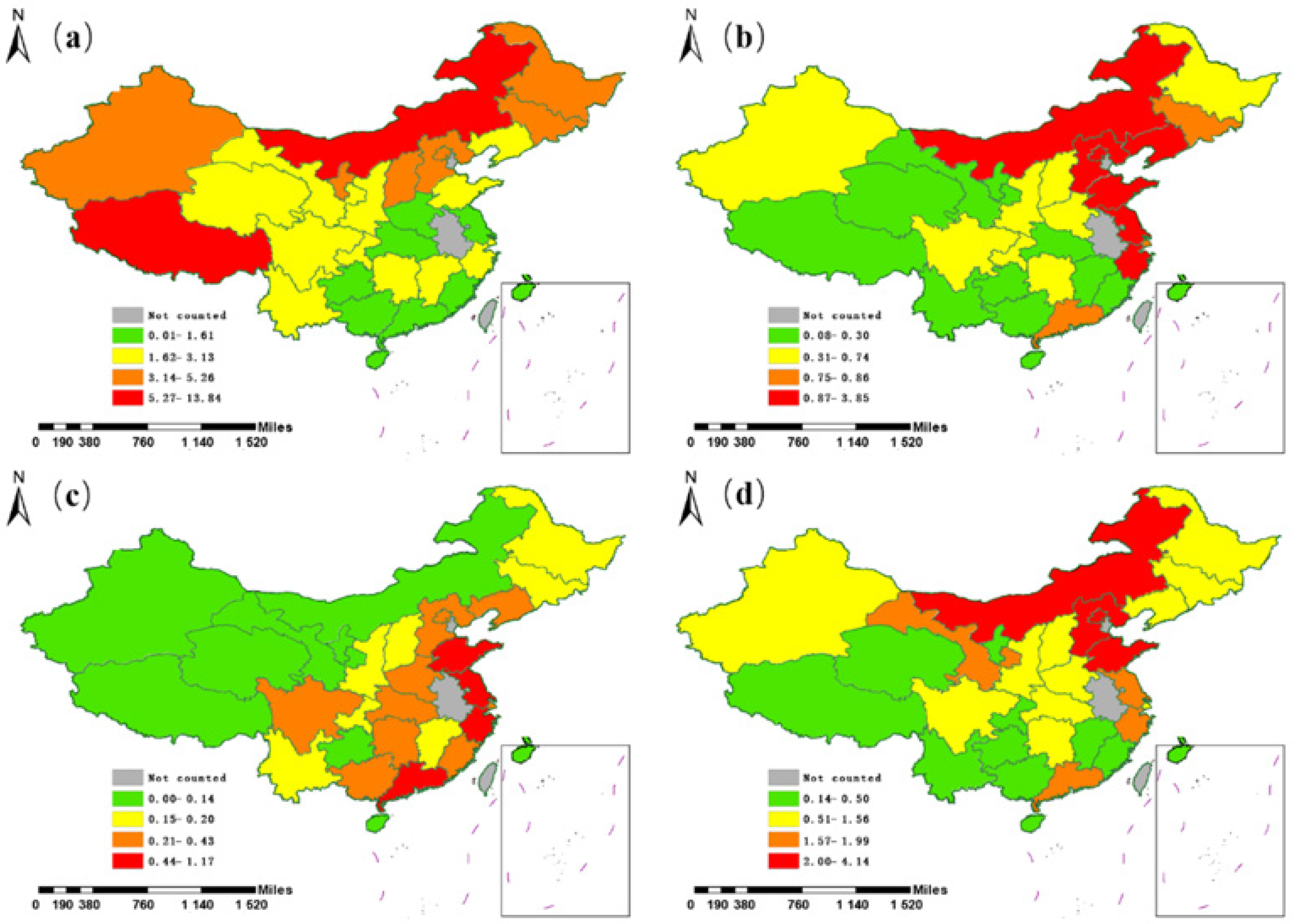
4.4. Changes and Regional Differences of Total Mercury Pollution in Sewage in the Future
4.4.1. Prediction and Evaluation of Total Mercury Pollution Based on Development Planning
4.4.2. Influencing Factors of Mercury Content in Sewage in the Future
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gonzalez-Raymat, H.; Liu, G.; Liriano, C.; Li, Y.; Yin, Y.; Shi, J.; Jiang, G.; Cai, Y. Elemental mercury: Its unique properties affect its behavior and fate in the environment. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Li, P.; Fu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Lin, C.-J. Mercury pollution in China: Implications on the implementation of the Minamata Convention. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2022, 24, 634–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Yang, C.; Xu, X.; Ao, M.; Xu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Qiu, G. Extremely Elevated Total Mercury and Methylmercury in Forage Plants in a Large-Scale Abandoned Hg Mining Site: A Potential Risk of Exposure to Grazing Animals. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 80, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Du, P.; Yu, C.; He, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Lin, H.; Luo, Y.; Xie, H.; Guo, J.; et al. Increases of Total Mercury and Methylmercury Releases from Municipal Sewage into Environment in China and Implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacyna, J.M. Recent advances in mercury research. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 73, 139955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Wu, Q.; Wang, S.; Ouyang, D.; Li, Z.; Ding, D.; Li, G.; Tang, Y.; Xiang, L.; Han, D.; et al. Highly Resolved Inventory of Mercury Release to Water from Anthropogenic Sources in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 13860–13868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, L.; Geng, Y.; Wang, N.; Mao, Y.; Cai, Y. Occurrence, speciation and fate of mercury in the sewage sludge of China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 186, 109787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoham-Frider, E.; Shelef, G.; Kress, N. Mercury speciation in sediments at a municipal sewage sludge marine disposal site. Mar. Environ. Res. 2007, 64, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pola, L.; Fernandez-Garcia, L.; Collado, S.; Oulego, P.; Diaz, M. Heavy metal solubilisation during the hydrothermal treatment of sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiest, L.; Gosset, A.; Fildier, A.; Libert, C.; Hervé, M.; Sibeud, E.; Giroud, B.; Vulliet, E.; Bastide, T.; Polomé, P.; et al. Occurrence and removal of emerging pollutants in urban sewage treatment plants using LC-QToF-MS suspect screening and quantification. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, M.T.; Myers, E.; Schober, D.; Thege, C.; Korzin, A.; Schuhen, K. Adaptable Process Design as a Key for Sustainability Upgrades in Wastewater Treatment: Comparative Study on the Removal of Micropollutants by Advanced Oxidation and Granular Activated Carbon Processing at a German Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Chen, X.; Jia, L.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X.; Han, D.; Cheng, J. Effluent concentration and removal efficiency of nine heavy metals in secondary treatment plants in Shanghai, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 17058–17065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Cai, L.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, B.; Zhao, W.; Cizdziel, J.V.; Chen, L. Total mercury and methylmercury migration and transformation in an A2/O wastewater treatment plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Cui, Y.; Li, H.; Mao, Y. A case study on the occurrence, transport, and fate of mercury species in a sewage treatment plant in Jiaozuo, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 21616–21622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suess, E.; Berg, M.; Bouchet, S.; Cayo, L.; Hug, S.J.; Kaegi, R.; Voegelin, A.; Winkel, L.H.E.; Tessier, E.; Amouroux, D.; et al. Mercury loads and fluxes from wastewater: A nationwide survey in Switzerland. Water Res. 2020, 17, 115708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R.; Shao, L.-B.; Liu, X.; Han, K.; Song, P. Variation of mercury fractionation and speciation in municipal sewage treatment plant: Effects of mercury on the atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 36475–36485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Cheng, L.; Ma, B.; Cai, Y. The fate of mercury in municipal wastewater treatment plants in China: Significance and implications for environmental cycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 306, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Lin, S.; Feng, L.; Huang, S.; Yuan, D. The distribution and sea–air transfer of volatile mercury in waste post-desulfurization seawater discharged from a coal-fired power plant. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 6191–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hargreaves, A.J.; Vale, P.; Whelan, J.; Constantino, C.; Dotro, G.; Cartmell, E. Mercury and antimony in wastewater: Fate and treatment. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, N.L.; Canario, J.; Serralheiro, M.L.; Carvalho, C. Optimization of microbial detoxification for an aquatic mercury-contaminated environment. J. Toxicol. Env. Health Part A 2017, 80, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, J.; Dash, H.R.; Das, S. 6—Mercury Pollution and Bioremediation—A Case Study on Biosorption by a Mercury-Resistant Marine Bacterium. In Microbial Biodegradation and Bioremediation; Das, S., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 137–166. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.D.; Khanna, K.; Kour, J.; Dhiman, S.; Bhardwaj, T.; Devi, K.; Sharma, N.; Kumar, P.; Kapoor, N.; Sharma, P.; et al. Critical review on biogeochemical dynamics of mercury (Hg) and its abatement strategies. Chemosphere 2023, 319, 137917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, H.; Khaleefa Ali, S.; Basheer, M. Heavy metal ions removal using advanced oxidation (UV/H2O2) technique. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 870, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bao, Z.; Wang, C.; Wei, J.; Wei, Y.; Chen, M. Understanding of mercury and methylmercury transformation in sludge composting by metagenomic analysis. Water Res. 2022, 226, 119204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futsaeter, G.; Wilson, S. The UNEP Global Mercury Assessment: Sources, Emissions and Transport. E3S Web Conf. 2013, 1, 36001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zhu, F.; Li, Q.; Xue, C.; Xia, X.; Yu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, J.; Bai, S. Development, current state and future trends of sludge management in China: Based on exploratory data and CO2-equivaient emissions analysis. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 106093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, F.; Mei, Z.; Lv, L.; Chi, Y. Status and Development of Sludge Incineration in China. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 3541–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 18918-2002; Pollutant Discharge Standards for Urban Sewage Treatment Plants. National Bureau of Quality Inspection: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Zhang, Q.H.; Yang, W.N.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.S.; Jin, P.K.; Dzakpasu, M.; Yang, S.J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.C.; Ao, D. Current status of urban wastewater treatment plants in China. Env. Int 2016, 92–93, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, H.; Yang, G.; Zhang, H.; Chen, B. Spatial Variation of Domestic Water Consumption and Fate of Domestic Sewage in Rural Areas of Taihu Region, Jiangsu. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2015, 31, 158–165. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Huang, W. What influences the urban sewage discharge in China? The effect of diversified factors on the urban sewage discharge in different regions of China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 6099–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. The China Urban Construction Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2023.
- Gui, Z.; Wen, J.; Fu, L.; Wang, S.; Zheng, B. Analysis on Mode and Benefit of Resource Utilization of Rural Sewage in a Typical Chinese City. Water 2023, 15, 2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, T.; Xie, Y.; Tan, Q. A simulation-assessment-optimization approach towards energy self-sufficiency and carbon reduction in regional-scale sewage systems. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 187, 106595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Ding, J.; Wu, T.; Zhao Yl Pang, J.W.; Jiang, J.P.; Jiang, J.Q.; Li, Y.; Ren, N.Q.; Yang, S.S. Bibliometric overview of research progress, challenges, and prospects of rural domestic sewage: Treatment techniques, resource recovery, and ecological risk. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 51, 103389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Action Plan for Prevention and Control of Water Pollution Printed and Distributed. Available online: https://english.mee.gov.cn/News_service/news_release/201504/t20150427_299595.shtml (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Chen, K.; Liu, X.; Ding, L.; Huang, G.; Li, Z. Spatial Characteristics and Driving Factors of Provincial Wastewater Discharge in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Wei, C.; Ke, X.; Pan, J.; Wei, G.; Chen, Y.; Wei, C.; Li, F.; Preis, S. Nationwide review of heavy metals in municipal sludge wastewater treatment plants in China: Sources, composition, accumulation and risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 437, 129267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Feng, Q. Risk Assessment and Potential Analysis of the Agricultural Use of Sewage Sludge in Central Shanxi Province. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Gong, H.; Shi, W.; Fang, N.; Tan, Y.; Zhou, W.; Huang, J.; Dai, L.; Dai, X.; Guo, Y. Insights into multisource sludge distributed in the Yangtze River basin, China: Characteristics, correlation, treatment and disposal. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 126, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, D.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Wen, G.; Wang, C. Distribution Characteristics of Typical Heavy Metals in Sludge from Wastewater Plants in Jiangsu Province (China) and Their Potential Risks. Water 2023, 15, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, C.; Jianfeng, Z.; Changshun, S. Characteristics and risk assessment of sewage sludge from urban wastewater treatment plants in Shaanxi Province, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, A.; Rockne, K.J.; Drummond, J.; Al-Hinai, M.; Ranjan, R. Geochemical influences and mercury methylation of a dental wastewater microbiome. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.-t.; Qi, W.-z.; Wang, S.; Song, X.-n.; Yang, D.-y.; Song, M.; Hang, T.-j. Toxicity and risk assessment of mercury exposures from cinnabar and Baizi Yangxin Pills based on pharmacokinetic and tissue distribution studies. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 250, 112489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, L.; Zhou, H.; Hu, Q.; Wang, L.; Cai, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Ji, S. Heavy Metals and Probabilistic Risk Assessment via Pheretima (a Traditional Chinese Medicine) Consumption in China. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 803592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Sha, Y.; Zhang, M.; Huang, K. Point discharge microplasma for the determination of mercury in Traditional Chinese Medicines by chemical vapor generation atomic emission spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2020, 155, 104695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.T.; Li, Y.L.; He, H.Z.; Jin, H.Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, L.; Gao, F.; Wang, Q.; Shen, Y.J.; Ma, S.C.; et al. Refined assessment of heavy metal-associated health risk due to the consumption of traditional animal medicines in humans. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Jia, P.; Zhao, F.; Kang, Y. Mercury Pollution, Treatment and Solutions in Spent Fluorescent Lamps in Mainland China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Luo, K. Household consumption of coal and related sulfur, arsenic, fluorine and mercury emissions in China. Energy Policy 2018, 112, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Huang, G.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Li, Y. A stepwise emission clustering analysis method for analyzing the effects of heavy metal emissions from multiple income groups. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 152472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, A.G.; Bouchet, S.; Guedron, S.; Amouroux, D.; Dominik, J.; Zopfi, J. High methylmercury production under ferruginous conditions in sediments impacted by sewage treatment plant discharges. Water Res. 2015, 80, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rule, K.L.; Comber, S.D.W.; Ross, D.; Thornton, A.; Makropoulos, C.K.; Rautiu, R. Diffuse sources of heavy metals entering an urban wastewater catchment. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name of the Process | Tons of Water Sludge Production (g) | Usage Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidation ditch | 201 | 21.00% |
| A2/O | 241 | 15.30% |
| SBR | 227 | 9.20% |
| A/O | 321 | 3.60% |
| Biological filter | 192 | 2.00% |
| Biological contact oxidation | 218 | 1.60% |
| Year | Arithmetic Mean of Mercury Content in Sludge | Geometric Mean of Mercury Content in Sludge |
|---|---|---|
| 2006 | 3.18 | 198.00% |
| 2013 | 2.8 | 140.00% |
| 2016 | 3.2 | 244.00% |
| 2019 | 1.91 | 128.00% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, C.; Guo, J.; Fan, R.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Huang, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, G. Mercury Discharge Inventory Based on Sewage Treatment Process in China. Processes 2024, 12, 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071534
Wei C, Guo J, Fan R, Zhang T, Wang X, Chen H, Huang S, Hu Y, Zhang G. Mercury Discharge Inventory Based on Sewage Treatment Process in China. Processes. 2024; 12(7):1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071534
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Chenglong, Jiaxu Guo, Rongyang Fan, Tingting Zhang, Xianbin Wang, Hao Chen, Song Huang, Yufei Hu, and Gang Zhang. 2024. "Mercury Discharge Inventory Based on Sewage Treatment Process in China" Processes 12, no. 7: 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071534
APA StyleWei, C., Guo, J., Fan, R., Zhang, T., Wang, X., Chen, H., Huang, S., Hu, Y., & Zhang, G. (2024). Mercury Discharge Inventory Based on Sewage Treatment Process in China. Processes, 12(7), 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071534






