Controlled Micro–Nano-Scale Droplet Generation via Spin Dewetting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization
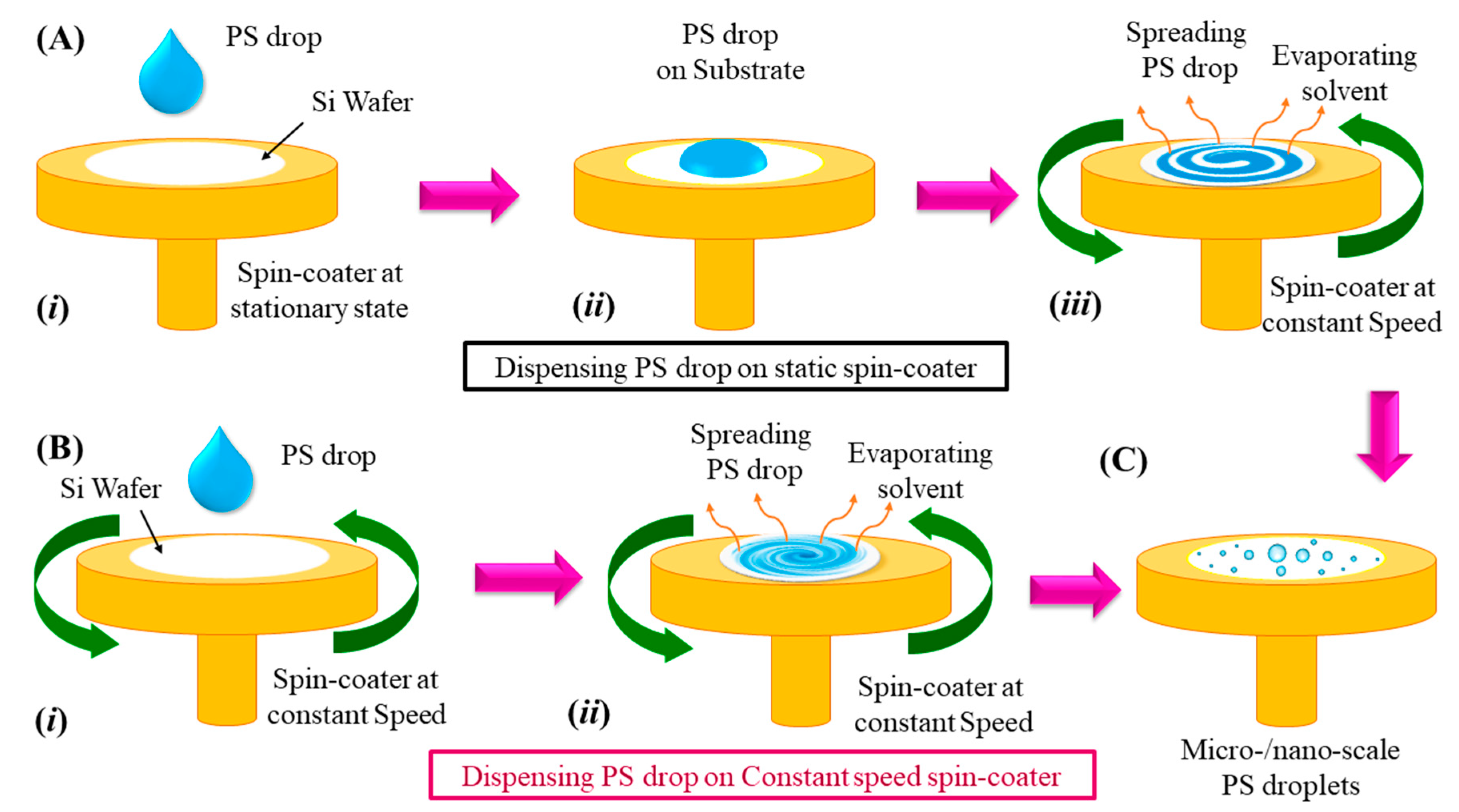
2.3. Methods
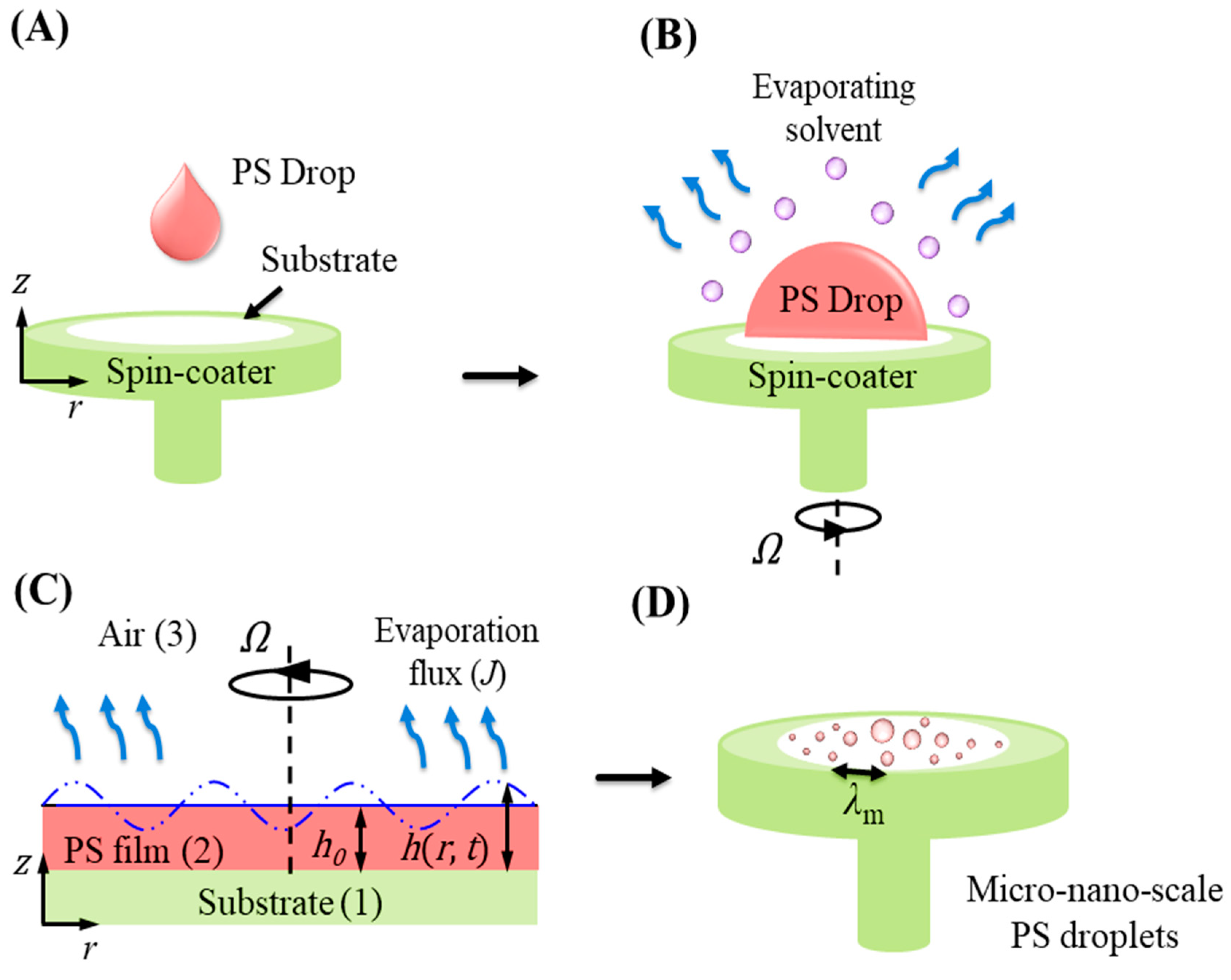
3. Theoretical Problem Formulation
Non-Dimensional Evolution Equation and Stability Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
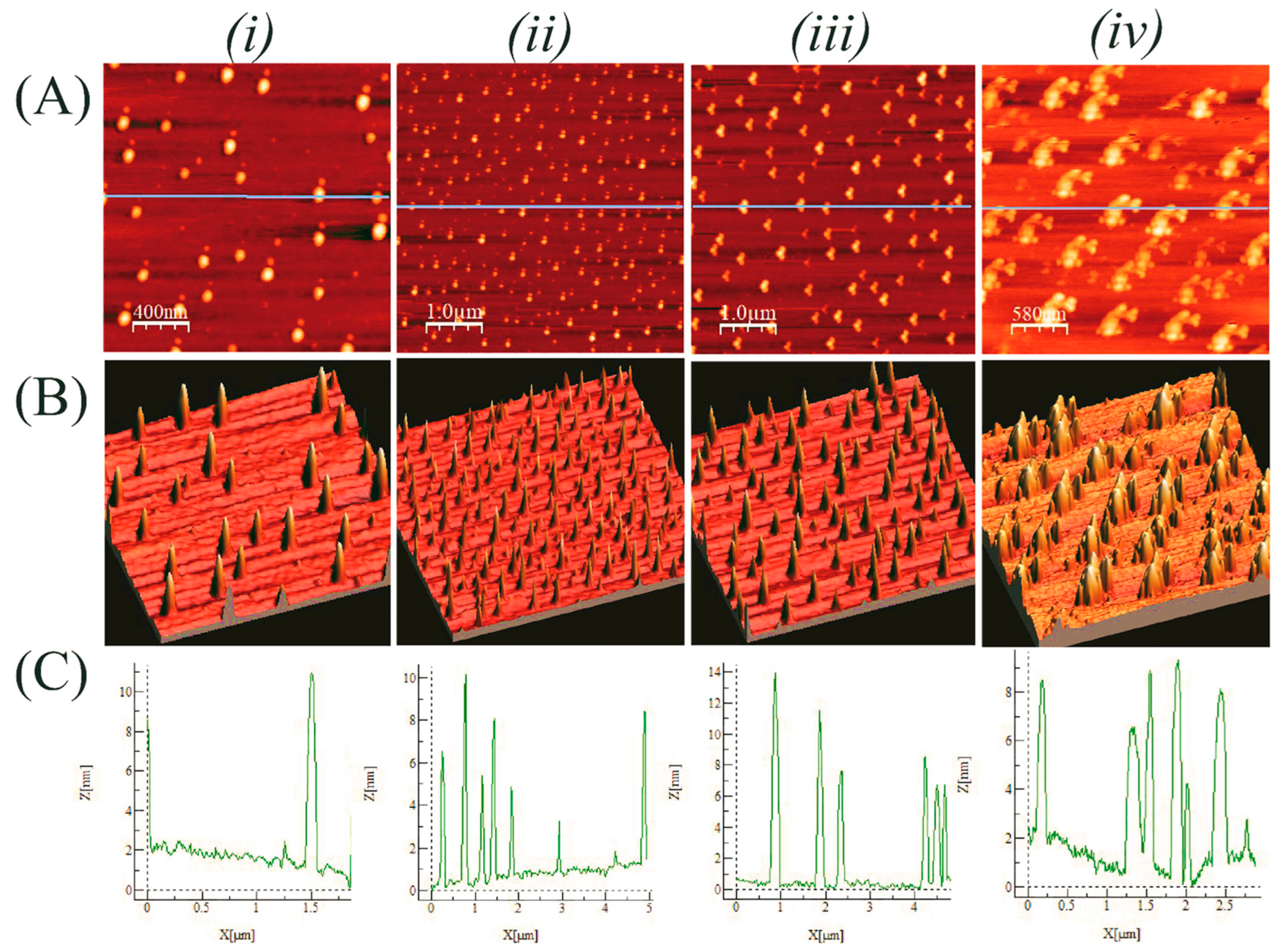
4.1. Experimental Understandings
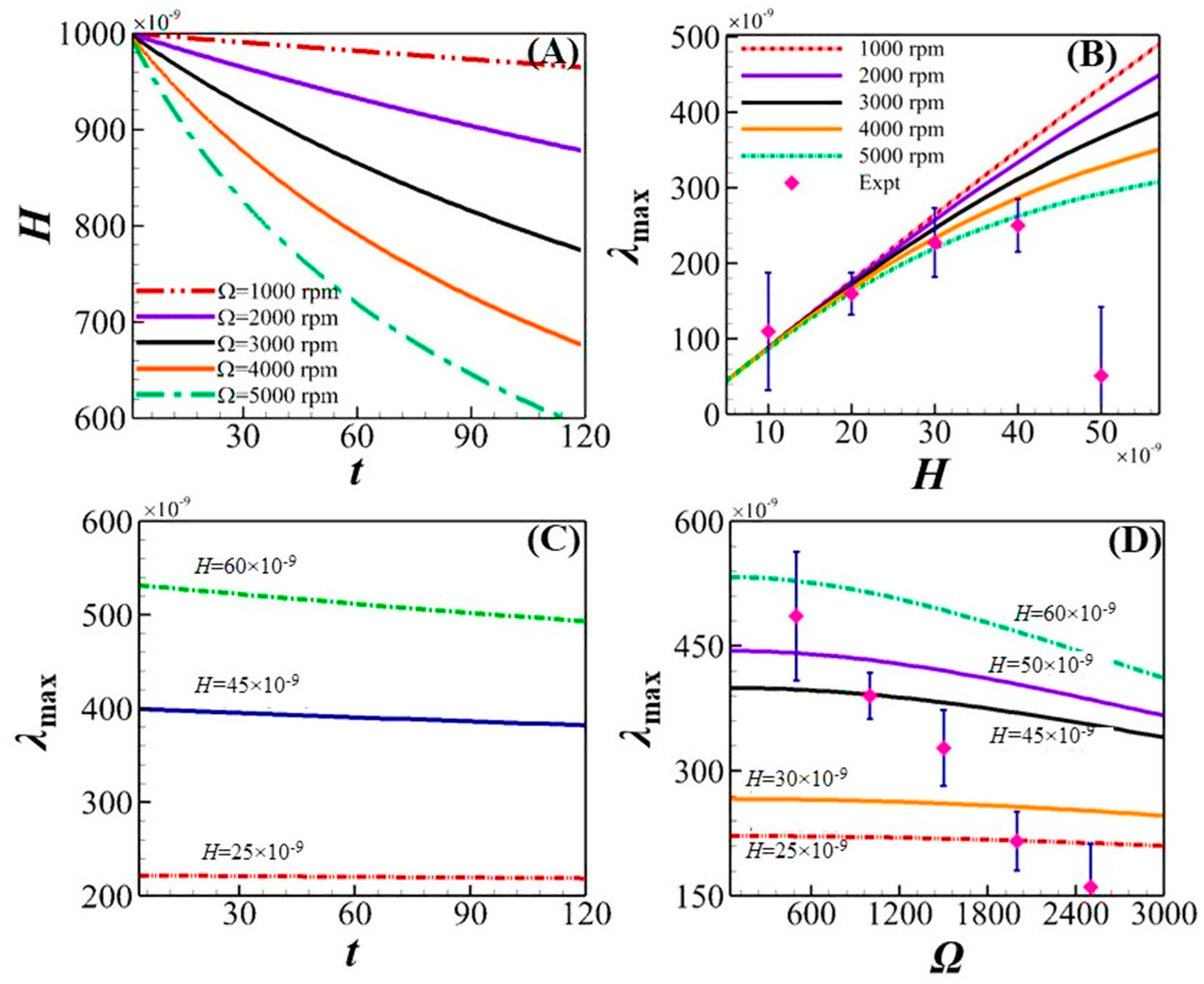
4.2. Essential Understandings from Theoretical Modeling
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lohse, D. Fundamental Fluid Dynamics Challenges in Inkjet Printing. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2022, 54, 349–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskell, S.J. Electrospray: Principles and Practice. J. Mass Spectrom. 1997, 32, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Wang, L. Passive and active droplet generation with microfluidics: A review. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 34–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Z.Z.; Tan, S.H.; Gañán-Calvo, A.M.; Tor, S.B.; Loh, N.H.; Nguyen, N.-T. Active droplet generation in microfluidics. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 35–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, Y. Emerging Droplet Microfluidics. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7964–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, F.; Demaree, B.; Ahmed, N.; Abate, A.R. Single-cell genome sequencing at ultra-high-throughput with microfluidic droplet barcoding. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhara, P.; Mukherjee, R. Influence of Substrate Surface Properties on Spin Dewetting, Texture, and Phase Transitions of 5CB Liquid-Crystal Thin Films. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhara, P.; Bhandaru, N.; Das, A.; Mukherjee, R. Transition from Spin Dewetting to continuous film in spin coating of Liquid Crystal 5CB. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speth, R.L.; Lauga, E. Capillary instability on a hydrophilic stripe. New J. Phys. 2009, 11, 075024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-K.; Lai, D.-Y. Weakly Nonlinear Stability Analysis of a Thin Magnetic Fluid during Spin Coating. Math. Probl. Eng. 2010, 2010, 987891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emslie, A.G.; Bonner, F.T.; Peck, L.G. Flow of a Viscous Liquid on a Rotating Disk. J. Appl. Phys. 1958, 29, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arscott, S. The limits of edge bead planarization and surface levelling in spin-coated liquid films. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2020, 30, 025003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraysse, N.; Homsy, G.M. An experimental study of rivulet instabilities in centrifugal spin coating of viscous Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids. Phys. Fluids 1994, 6, 1491–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, L.W.; Roy, R.V. Theoretical and numerical results for spin coating of viscous liquids. Phys. Fluids 2004, 16, 569–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Deng, W.; Xia, H. On axisymmetric dynamic spin coating with a single drop of ethanol. J. Fluid Mech. 2022, 951, A30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golany, Z.; Weisbord, I.; Abo-Jabal, M.; Manor, O.; Segal-Peretz, T. Polymer dewetting in solvent-non-solvent environment—New insights on dynamics and lithography-free patterning. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 596, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Dubey, N.; Verma, A. Controlling Lengthscales in Water-Solvent Induced Self-Organized Dewetting of Thin Polystyrene Films by Modulating the Surface Properties of the Substrate. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2022, 61, 914–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wen, G. Dewetting behavior of the spin-coated bilayer films of block copolymer and random copolymer induced by solvent vapor annealing. J. Polym. Res. 2023, 30, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wen, G.; Li, H. Dewetting Behavior of Random Copolymer Films Induced by Solvent Vapor Annealing. ChemPhysChem 2023, 24, e202200655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanarse, V.B.; Thakur, S.; Ghosh, A.; Parmar, P.R.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Coupled instability modes at a solvent/non-solvent interface to decorate cellulose acetate flowers. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 022115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Vanarse, V.B.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Electroosmotic Micromixing in Physicochemically Patterned Microchannels. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 5312–5325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Zheng, T.; Li, M.; Wu, J.; Ji, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, W.; Guo, J. Droplet-based microfluidics systems in biomedical applications. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 1580–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-T.; Wang, J.; Han, J.-J. Fabrication of Advanced Particles and Particle-Based Materials Assisted by Droplet-Based Microfluidics. Small 2011, 7, 1728–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrell, N.; Hansford, D. Fabrication of Micro- and Nanoscale Polymer Structures by Soft Lithography and Spin Dewetting. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2007, 28, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandaru, N.; Kaur, G.; Panjla, A.; Verma, S. Spin coating mediated morphology modulation in self assembly of peptides. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 8884–8892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Park, S.-Y. Light-driven 3D droplet manipulation on flexible optoelectrowetting devices fabricated by a simple spin-coating method. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1831–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamian, M.; Soltani-Kordshuli, F. Development of multiple-droplet drop-casting method for the fabrication of coatings and thin solid films. J. Coat Technol. Res. 2018, 15, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.; Lee, D.Y. Self-Organization via Dewetting in Polymeric Assemblies. Small, 2024; early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zheng, B.; Zhu, D.; Wu, Y.; Cardinaels, R.; Moldenaers, P.; Shen, Z.; Sheng, Y.; Zhu, H.; Yu, K.; et al. Regulation of dewetting and morphology evolution in spin-coated PS/PMMA blend films via graphene-based Janus nanosheets. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 630, 157393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, W.R. Cleaning Glass Surfaces. In Sol-Gel Technologies for Glass Producers and Users; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, W. The Evolution of Silicon Wafer Cleaning Technology. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1990, 137, 1887–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, G. Dewetting of thin polymer films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 68, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonberg, J.A.; DasGupta, S.; Wayner, P.C. An augmented Young-Laplace model of an evaporating meniscus in a microchannel with high heat flux. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 1995, 10, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DasGupta, S.; Schonberg, J.A.; Wayner, P.C. Investigation of an Evaporating Extended Meniscus Based on the Augmented Young–Laplace Equation. J. Heat Transfer 1993, 115, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargupta, K.; Konnur, R.; Sharma, A. Spontaneous Dewetting and Ordered Patterns in Evaporating Thin Liquid Films on Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Substrates. Langmuir 2001, 17, 1294–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münch, A.; Please, C.P.; Wagner, B. Spin coating of an evaporating polymer solution. Phys. Fluids 2011, 23, 102101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäumchen, O.; Marquant, L.; Blossey, R.; Münch, A.; Wagner, B.; Jacobs, K. Influence of slip on the Rayleigh-Plateau rim instability in dewetting viscous films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 14501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, B.; Bhattacharjee, M.; Ghosh, A.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Fabrication of pixelated liquid crystal nanostructures employing the contact line instabilities of droplets. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 1680–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, B.; Chakraborty, S.; Bhattacharjee, M.; Mitra, S.; Ghosh, A.; Gooh Pattader, P.S.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Pattern-Directed Ordering of Spin-Dewetted Liquid Crystal Micro- or Nanodroplets as Pixelated Light Reflectors and Locomotives. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 1066–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vanarse, V.; Ravi, B.; De, S.; Dubey, S.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Controlled Micro–Nano-Scale Droplet Generation via Spin Dewetting. Processes 2024, 12, 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12081562
Vanarse V, Ravi B, De S, Dubey S, Bandyopadhyay D. Controlled Micro–Nano-Scale Droplet Generation via Spin Dewetting. Processes. 2024; 12(8):1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12081562
Chicago/Turabian StyleVanarse, Vinod, Bolleddu Ravi, Srijita De, Saurabh Dubey, and Dipankar Bandyopadhyay. 2024. "Controlled Micro–Nano-Scale Droplet Generation via Spin Dewetting" Processes 12, no. 8: 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12081562
APA StyleVanarse, V., Ravi, B., De, S., Dubey, S., & Bandyopadhyay, D. (2024). Controlled Micro–Nano-Scale Droplet Generation via Spin Dewetting. Processes, 12(8), 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12081562





