Scale-Up and Control of the Acrylamide Polymerization Process in Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation
2.1. Kinetic Model
2.2. Energy Balances for Reactor and Jacket
2.3. Overall Heat-Transfer Coefficient
2.4. Temperature- and Monomer Concentration-Dependent Viscosity
3. Numerical Simulations
4. Results and Discussion
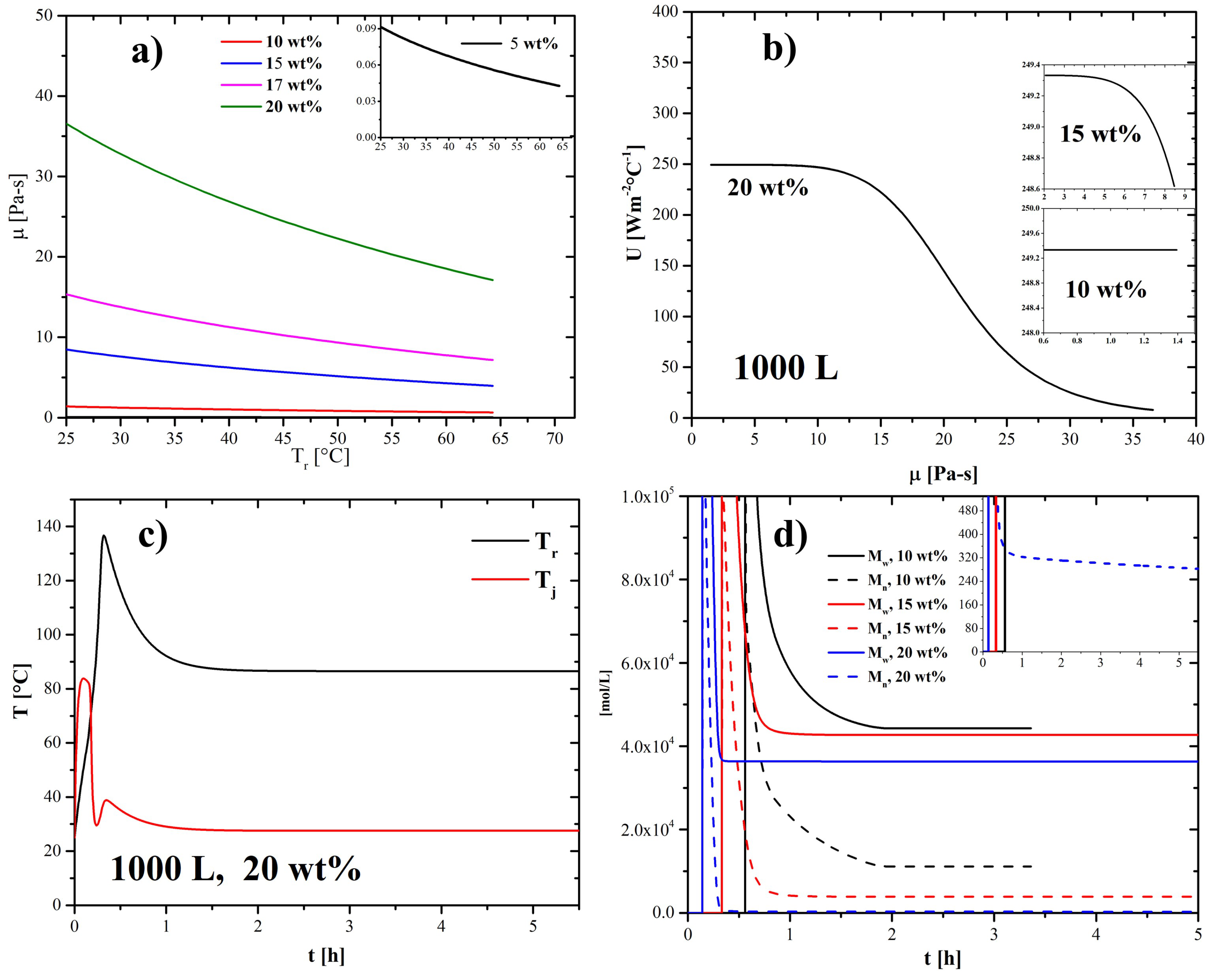
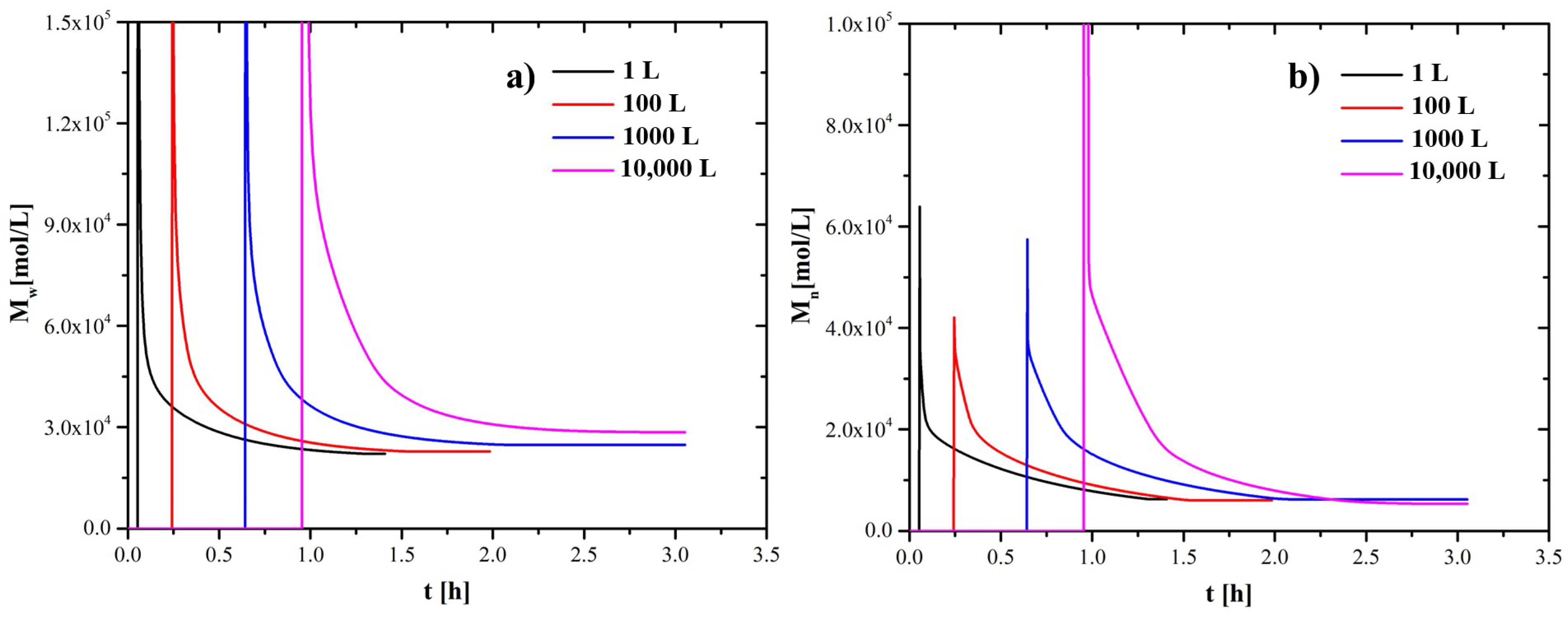
4.1. Scaling-Up Based on Similarity Principles
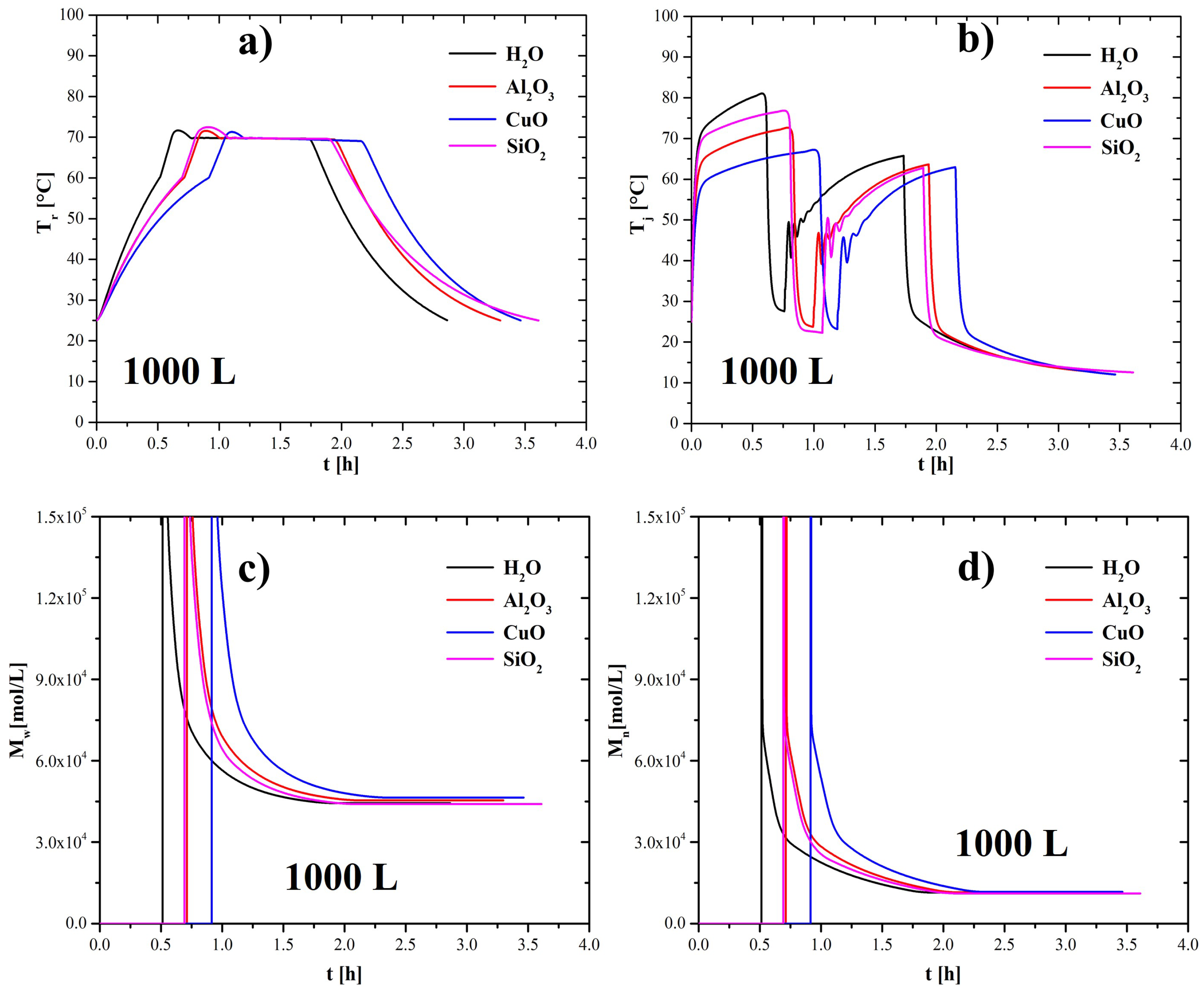
4.2. Effect of Nanoparticles in the Coolant
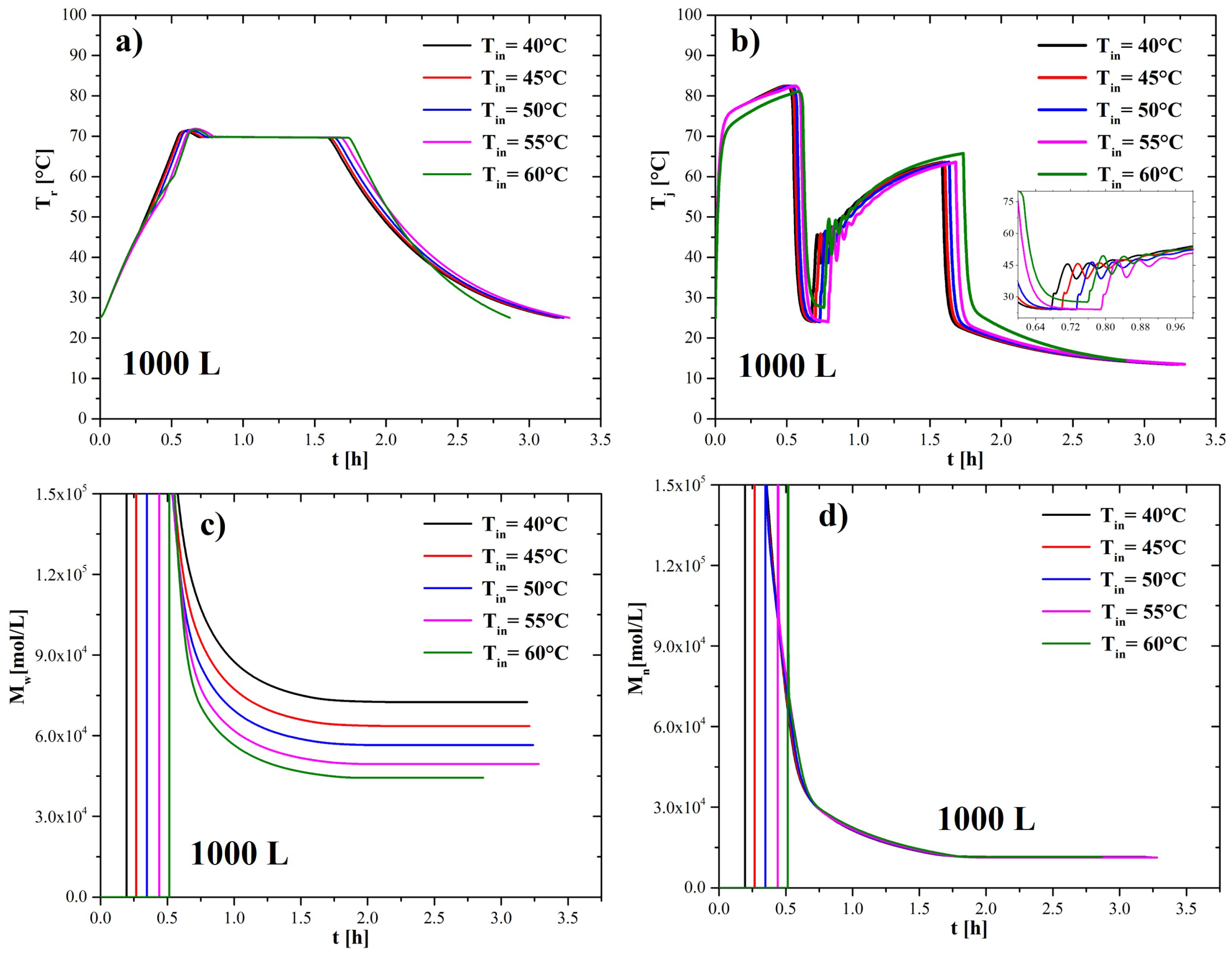
4.3. Effect of Adding Initiator at Different Temperatures
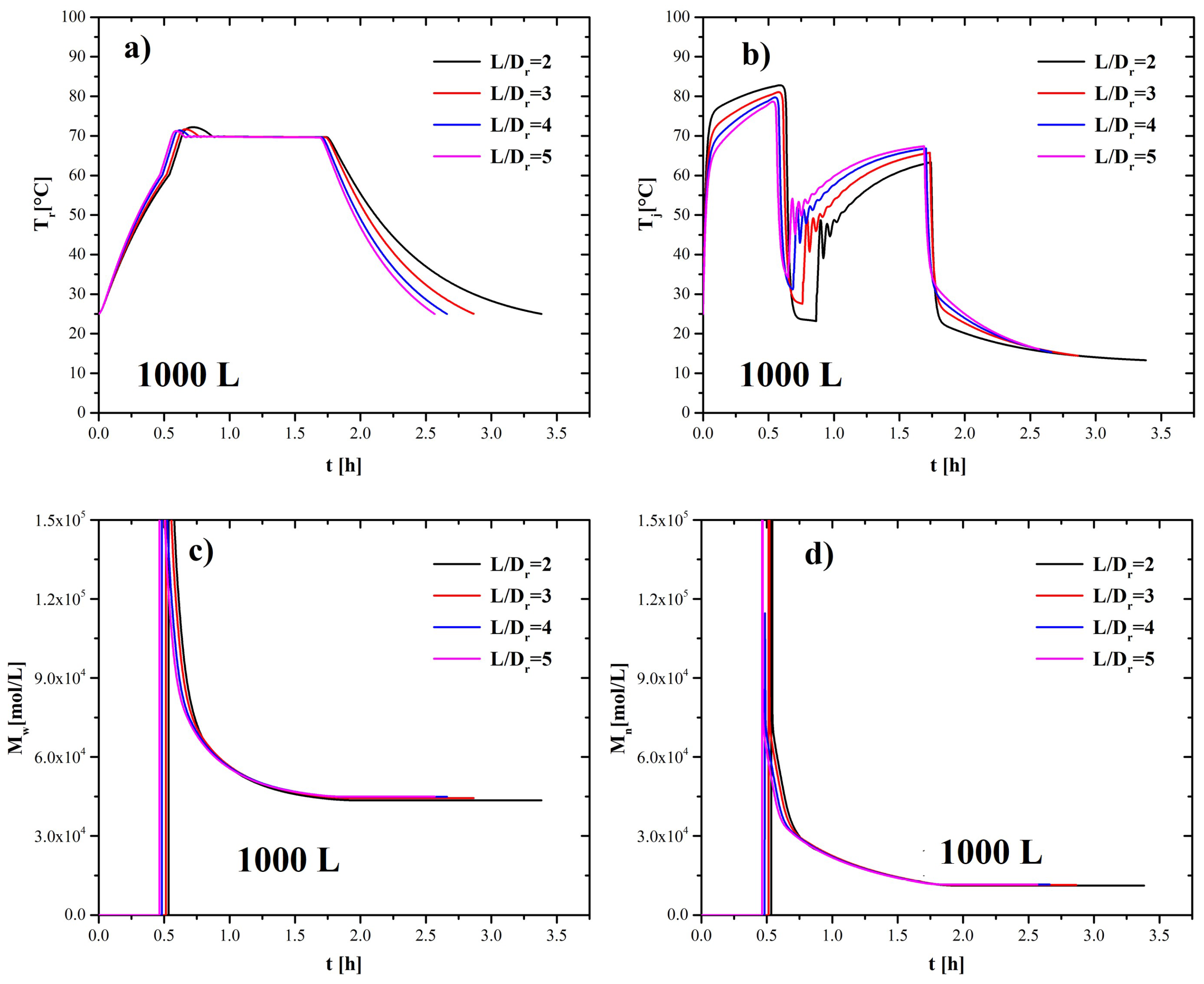
4.4. Non-Geometrical Similarity
4.5. Recommendations and Strategies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| A | heat-transfer area | m2 |
| specific heat capacity | J (kg K)−1 | |
| reactor diameter | m | |
| f | radical fraction | − |
| F | inlet flow rate | kg s−1 |
| I | initiator concentration | mol L−1 |
| rate constant initiation | mol L−1 | |
| rate constant disociation | s−1 | |
| rate constant termination | L mol−1s−1 | |
| L | reactor height | m |
| M | monomer concentration | mol L−1 |
| R | radical concentration | mol L−1s−1 |
| rate polymerization | mol L−1s−1 | |
| T | temperature | K |
| U | overall heat-transfer coefficient | W m−2 K−1 |
| Greek symbols | ||
| thermal diffusivity | m2s−1 | |
| enthalpy | J kg−1K−1 | |
| thermal conductivity | Wm−1 K−1 | |
| Subscripts | ||
| c | cold | |
| d | disotiation | |
| h | hot | |
| i | inner | |
| initiator | ||
| j | jacket | |
| m | master | |
| nanofluid | ||
| o | outer | |
| p | propagation | |
| r | reactor | |
| s | slave | |
| t | termination |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Moment Equation System
Appendix A.2. Kinetics Parameters
Appendix A.3. Nanoparticles
References
- Hoogendoorn, K.; Shaw, R. Control of polymerization processes. IFAC Proc. Vol. 1980, 13, 623–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Ramirez, J.; Puebla, H. On classical PI control of chemical reactors. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2001, 56, 2111–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coker, A.K. Modeling of Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Donati, G.; Paludetto, R. Scale up of chemical reactors. Catal. Today 1997, 34, 483–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüce, S.; Hasaltun, A.; Erdoğan, S.; Alpbaz, M. Temperature control of a batch polymerization reactor. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 1999, 77, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maly, M.; Schaper, S.; Kuwertz, R.; Hoffmann, M.; Heck, J.; Schläter, M. Scale-Up Strategies of Jet Loop Reactors for the Intensification of Mass Transfer Limited Reactions. Processes 2022, 10, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Sun, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J. Effect of the scale-up process on the reactor performance within the riser: Simulation using ozone decomposition. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 11479–11489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, S.; Alpbaz, M.; Karagöz, A.R. The effect of operational conditions on the performance of batch polymerization reactor control. Chem. Eng. J. 2002, 86, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, S.; Gesthuisen, R. Simultaneous estimation of the heat of reaction and the heat transfer coefficient by calorimetry: Estimation problems due to model simplification and high jacket flow rates—Theoretical development. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 4233–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieme, J.; De Roo, T.; Marin, G.B.; Heynderickx, G.J. Simulation of pilot- and industrial-scale vinyl chloride batch suspension polymerization reactors. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 1179–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubaker, A.; Mustafa, M. Mathematical modelling and simulation of an industrial propylene polymerization batch reactor. Int. J. Chem. Eng. Anal. Sci. 2016, 1, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Piccinno, F.; Hischier, R.; Seeger, S.; Som, C. From laboratory to industrial scale: A scale-up framework for chemical processes in life cycle assessment studies. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 135, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.; Al-Dirawi, K.H.; Bentham, E.; Mahmud, T.; Heggs, P.J. A non-adiabatic model for jacketed agitated batch reactors experiencing thermal losses. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 1316–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishige, T.; Hamielec, A.E. Solution polymerization of acrylamide to high conversion. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1973, 17, 1479–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, G.J.A. Puesta en Marcha de un Reactor Calorimetrico; Validación con una Reacción de Polimerización de Acrilamida en Solución. Bachelor’s Thesis, UNAM, Mexico City, Mexico, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Giz, A.; Catalgil-Giz, H.; Alb, A.; Brousseau, J.L.; Reed, W.F. Kinetics and mechanisms of acrylamide polymerization from absolute, online monitoring of polymerization reaction. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Thabit, N.Y. Thermochemistry of acrylamide polymerization: An illustration of auto-acceleration and gel effect. World J. Chem. Educ. 2017, 5, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajjha, R.S.; Das, D.K. Specific heat measurement of three nanofluids and development of new correlations. J. Heat Transf. Trans. ASME 2009, 131, 071601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajjha, R.S.; Das, D.K. A review and analysis on influence of temperature and concentration of nanofluids on thermophysical properties, heat transfer and pumping power. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 4063–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajjha, R.S.; Das, D.K.; Chukwu, G.K. An experimental determination of the viscosity of propylene glycol/water based nanofluids and development of new correlations. J. Fluids Eng. 2015, 137, 081201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, D.; Kumar, P.; Samantaray, S. A review of nanofluid preparation, stability, and thermo-physical properties. Heat Transf. Asian Res. 2017, 46, 1413–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Singh, V.; Kumar, R.; Said, Z. A review on thermophysical properties of nanofluids and heat transfer applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 638–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gennes, P.G. Scaling Concepts in Polymer Physics; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H. When physics meets chemistry at the dynamic glass transition. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2024, 87, 032601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutuku, W.N. Ethylene glycol (EG)-based nanofluids as a coolant for automotive radiator. Asia Pac. J. Comput. Eng. 2016, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooque, Z.; Chauhan, N.R. Comparative study of Nano-fluids as Coolants in a Car Radiator. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1228, 012011. [Google Scholar]
- Jadeja, K.M.; Bumataria, R.; Chavda, N. Nanofluid as a coolant in internal combustion engine—A review. Int. J. Ambient. Energy 2023, 44, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefera, N.; Weickert, G.; Westerterp, K. Modeling of free radical polymerization up to high conversion. I. A method for the selection of models by simultaneous parameter estimation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 63, 1649–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, W.Y.; Carratt, G.M.; Soong, D.S. A computer model for the gel effect in free-radical polymerization. Macromolecules 1983, 16, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata-González, I.; Saldívar-Guerra, E. The method of moments used in polymerization reaction engineering for 70 years: An overview, tutorial, and minilibrary. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 101, 5324–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, A.; Mohammed, H.A.; Vanaki, S.M.; Osia, A.; Haghighi, M.R.G. Fluid flow and heat transfer of nanofluids in microchannel heat sink with V-type inlet/outlet arrangement. Alex. Eng. J. 2017, 56, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkman, H. The viscosity of concentrated suspensions and solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 1952, 20, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, J. A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism II; Oxford University Press: Cambridge MA, USA, 1904. [Google Scholar]
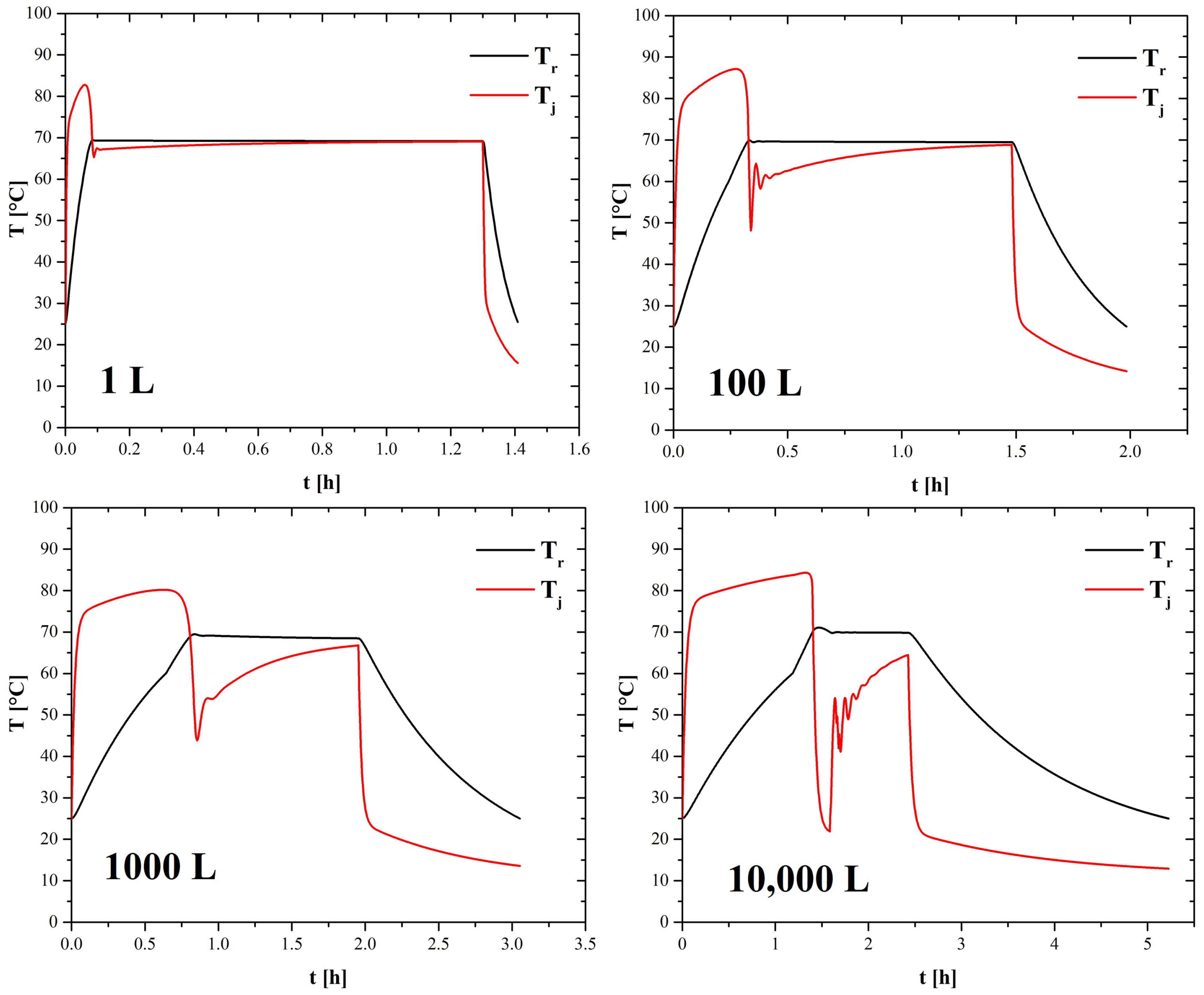
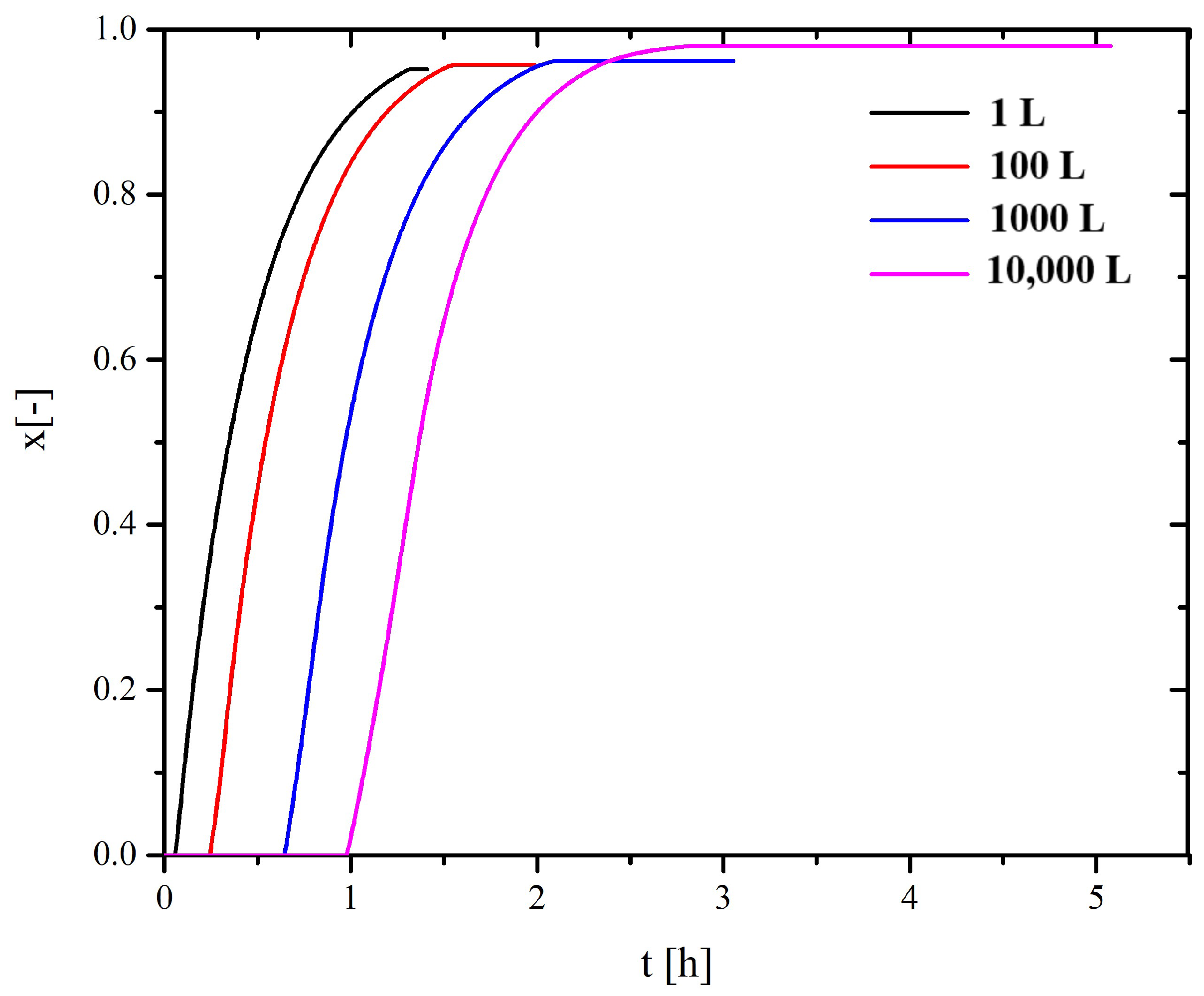
| 1 L | 100 L | 1000 L | 10,000 L | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (°C) | 70.24 | 69.52 | 70.74 | 69.6 |
| % error | 0.34% | 0.83% | 1.06% | 0.57% |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| (cP) | −0.02715446 |
| (°C) | 771.972464 |
| −415.658026 | |
| 103.326844 | |
| −0.77600662 | |
| 147.283398 |
| Parameter | |
|---|---|
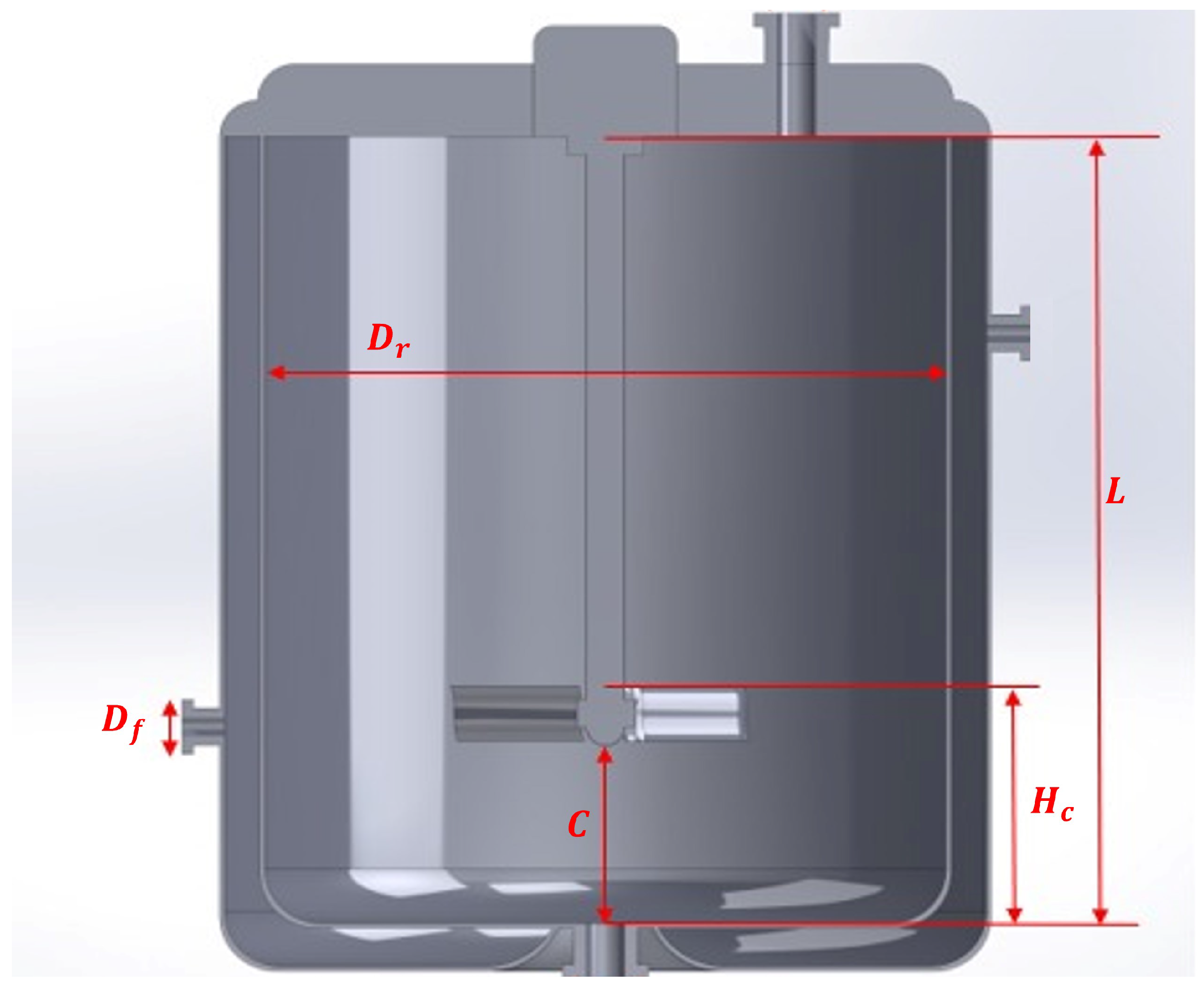
| Reactor height | |
| Nozzle diameter | |
| Clearance |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mil-Martínez, R.; Gómez-López, A.; Escandón, J.P.; Jimenez, E.M.; Martínez-Suástegui, L.; Vargas, R.O. Scale-Up and Control of the Acrylamide Polymerization Process in Solution. Processes 2024, 12, 1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12081624
Mil-Martínez R, Gómez-López A, Escandón JP, Jimenez EM, Martínez-Suástegui L, Vargas RO. Scale-Up and Control of the Acrylamide Polymerization Process in Solution. Processes. 2024; 12(8):1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12081624
Chicago/Turabian StyleMil-Martínez, Rubén, Aldo Gómez-López, Juan P. Escandón, Edson M. Jimenez, Lorenzo Martínez-Suástegui, and René O. Vargas. 2024. "Scale-Up and Control of the Acrylamide Polymerization Process in Solution" Processes 12, no. 8: 1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12081624
APA StyleMil-Martínez, R., Gómez-López, A., Escandón, J. P., Jimenez, E. M., Martínez-Suástegui, L., & Vargas, R. O. (2024). Scale-Up and Control of the Acrylamide Polymerization Process in Solution. Processes, 12(8), 1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12081624








